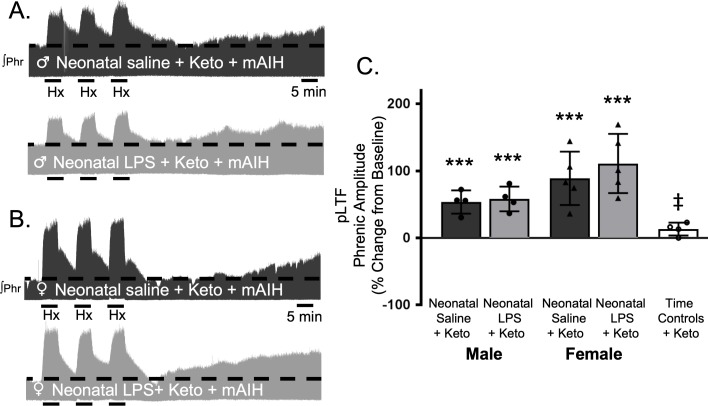
Figure 3. Acute, adult anti-inflammatory (ketoprofen, Keto) restores Q-pathway-evoked pLTF after neonatal systemic inflammation in adult male and female rats.
Representative integrated phrenic neurograms for adult male (A) and female (B) rats after neonatal (P4) saline (top traces, black) or LPS (1 mg/kg, i.p.; bottom traces, grey) and acute, adult ketoprofen (12.5 mg/kg, i.p., 3 hr). Q-pathway-evoked pLTF is evident as the progressive increase in phrenic nerve amplitude from baseline (black dashed line) over 60 min following moderate acute intermittent hypoxia (mAIH, 3 × 5 min episodes, PaO235–45 mmHg). Group data (C) demonstrate adult ketoprofen restores Q-pathway-evoked pLTF 60 min after mAIH in adults after neonatal LPS in both males (circles) and females (triangles) and no change in phrenic amplitude in time controls (***p < 0.001 from baseline, ‡ p < 0.05 from all other groups).