Abstract
Background
Endometriosis is a common gynaecological condition that affects women and can lead to painful symptoms and infertility. It greatly affects women's quality of life, impacting their careers, everyday activities, sexual and nonsexual relationships and fertility. Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are most commonly used as first‐line treatment for women with pain associated with endometriosis.
Objectives
To assess effects of NSAIDs used for management of pain in women with endometriosis compared with placebo, other NSAIDs, other pain management drugs or no treatment.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Gynaecology and Fertility Group Specialised Register of Controlled Trials (October 2016), published in the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in the Cochrane Library, as well as MEDLINE (January 2008 to October 2016), Embase (date limited from 1 January 2016 to 19 October 2016, as all earlier references are included in CENTRAL output as a result of the Embase project), registers of ongoing trials and the reference lists of relevant publications. We identified no new randomised controlled trials. Unless we identify new evidence in the future, we will not update this review.
Selection criteria
We included all randomised controlled trials (RCTs) describing use of NSAIDs for management of pain associated with endometriosis in women of all ages.
Data collection and analysis
In the 2009 update of this review, two review authors (CA and SH) independently read and extracted data from each of the included studies. We analysed cross‐over trials using the inverse variance method of RevMan to calculate odds ratios for binary outcomes.
Main results
We identified no new trials for the 2016 update. This review includes two trials, but we included only one trial, with 24 women, in the analyses.
The overall risk of bias was unclear owing to lack of methodological detail. Using the GRADE method, we judged the quality of the evidence to be very low. We downgraded evidence for risk of bias and for imprecision (wide confidence intervals and evidence based on a single small trial).
Comparison of NSAIDs (naproxen) versus placebo revealed no evidence of a positive effect on pain relief (odds ratio (OR) 3.27, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.61 to 17.69; one trial, 24 women; very low‐quality evidence) in women with endometriosis. Evidence indicating whether women taking NSAIDs (naproxen) were less likely to require additional analgesia (OR 0.12, 95% CI 0.01 to 1.29; one trial, 24 women; very low‐quality evidence) or to experience side effects (OR 0.46, 95% CI 0.09 to 2.47; one trial, 24 women; very low‐quality evidence) when compared with placebo was inconclusive.
Studies provided no data on quality of life, effects on daily activities, absence from work or school, need for more invasive treatment or participant satisfaction with treatment.
Authors' conclusions
Owing to lack of high‐quality evidence and lack of reporting of outcomes of interest for this review, we can make no judgement as to whether NSAIDs (naproxen) are effective in managing pain caused by endometriosis. There is no evidence that one NSAID is more effective than another. As shown in other Cochrane reviews, women taking NSAIDs must be aware that these drugs may cause unintended effects.
Plain language summary
Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs for management of pain in women with endometriosis
What is the issue?
Endometriosis is a gynaecological condition that commonly affects women of childbearing age. It can lead to painful symptoms, including painful periods, pain during or after sexual intercourse, pelvic and lower abdominal pain and infertility. It can greatly affect women's quality of life by impacting their careers, everyday activities, sexual and nonsexual relationships and fertility. Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are most commonly used as first‐line treatment for women with endometriosis because they have few side effects, and many are available over the counter.
Why is this important?
Endometriosis is very common, but the condition can be difficult to diagnose. In 2015, 1.8 billion women (aged 15 to 49 years) in the world had received a diagnosis of endometriosis. It is estimated that up to 60% of women with painful periods have endometriosis. Endometriosis greatly affects women's quality of life, impacting their careers, everyday activities, sexual and nonsexual relationships and fertility. An unpublished survey conducted by a patient support organisation in the United Kingdom ‐ Endometriosis UK (www.endometriosis‐uk.org/) ‐ found that 65% of women with endometriosis reported that their condition had negatively affected their employment. Ten per cent of women had to reduce their hours of work, and 30% had not been able to continue in the same employment. As many as 16% of women were unable to continue in any employment, and 6% needed to claim state benefits; thus, in addition to their feelings of loss as contributors to society, they became dependent upon others. This increased their feelings of low self‐esteem. Endometriosis is seen as a significant public health issue because a large number of women are affected and illnesses associated with this disease are significant.
Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs are readily available without prescription for pain relief. They work by preventing or slowing down the production of prostaglandins, which helps to relieve the painful cramps associated with endometriosis. However, a Cochrane review on the use of NSAIDs for painful periods found greater risk of stomach upset (e.g. nausea, diarrhoea) or other side effects (e.g. headache, drowsiness, dizziness, dryness of the mouth). We conducted the present review to compare all NSAIDs used to treat women with painful symptoms caused by endometriosis versus placebo, other pain management drugs or no treatment, to evaluate their effectiveness and safety.
What evidence did we find?
We searched for new evidence in October 2016 and identified no new randomised controlled trials.
From previous updates, this review found limited evidence on the effectiveness of NSAIDs (specifically naproxen) for management of pain caused by endometriosis. This review is also limited in that it includes only one study with data suitable for analysis, and this study involved only 20 women. Available evidence is of very low quality, mainly owing to poor reporting of methods, lack of precision in findings for overall pain relief, unintended side effects of treatment and the need for extra pain relief. The included trial did not report on quality of life, effects on daily activities, absence from work or school or participant satisfaction with treatment.
What does this mean?
Available evidence does not allow us to conclude whether NSAIDs are effective for managing pain caused by endometriosis, or whether any individual NSAID is more effective than another. As has been shown in other Cochrane reviews, women who use NSAIDs must be aware that NSAIDs may cause adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, headache and drowsiness. Unless we identify new evidence in the future, we will not update this review again.
Quality of evidence
Evidence was of very low quality owing to risk of bias and imprecision (findings were based on a single small trial).
Summary of findings
Summary of findings for the main comparison. NSAID compared with placebo for pain in women with endometriosis.
| NSAID compared with placebo for pain in women with endometriosis | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with endometriosis Setting: Finland Intervention: nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Comparison: placebo | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | Number of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Risk with placebo | Risk with NSAID | |||||
| Pain relief assessed with: overall pain relief score follow‐up: median 2 months | 50 per 100 | 77 per 100 (38 to 95) | OR 3.27 (0.61 to 17.69) | 24 (1 RCT) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b | |
| Unintended effects from treatment follow‐up: median 2 months | 58 per 100 | 39 per 100 (11 to 78) | OR 0.46 (0.09 to 2.47) | 24 (1 RCT) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b | |
| Quality of life: not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Effects on daily activities: not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Absence from work or school: not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Number of women requiring more invasive treatment: not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Requirements for additional medication follow‐up: median 2 months | 83 per 100 | 38 per 100 (5 to 87) | OR 0.12 (0.01 to 1.29) | 24 (1 RCT) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b | |
| Participant satisfaction with treatment: not reported | ||||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; OR: odds ratio. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. High quality: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of effect but may be substantially different. Low quality: Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of effect. Very low quality: We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect. | ||||||
aDowngraded one level owing to overall unclear risk of bias for included trial.
bDowngraded two levels for imprecision because confidence interval is wide, consistent with benefit and harm and evidence based on a single small trial.
Background
Description of the condition
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue (stromal and glandular) outside the normal uterine cavity (Barbieri 1990). Endometriosis is a common gynaecological condition that can lead to painful symptoms and infertility. Symptoms may include dysmenorrhoea (painful periods), dyspareunia (pain during or after sexual intercourse) and pelvic or lower abdominal pain. A less common symptom is cyclical pain at other sites related to endometriosis (Prentice 2003). Endometriosis can be divided into four stages of severity (stage I: minimal disease; stage IV: severe disease), as defined by the classification system of the American Fertility Society (Canavan 2000). Staging does not correlate with degree or severity of symptoms but quantifies the extent of disease visible at laparoscopy. The link between the pain experienced by women and the extent of endometriosis observed is not well understood, and the severity of the pain experienced does not always directly correlate with the severity of endometriosis (Kauppila 1985). Even when endometriosis is diagnosed, it may not be the cause of a woman's symptoms, as the mechanism by which pain is caused is not fully understood.
Endometriosis greatly affects women's quality of life, impacting their careers, everyday activities, sexual and nonsexual relationships and fertility (Davies 2003; Jones 2002). In an unpublished survey conducted by a patient support organisation in the United Kingdom ‐ Endometriosis UK (www.endometriosis‐uk.org/) ‐ 65% of women with endometriosis reported that their condition had adversely affected their employment. Ten per cent of women had to reduce their hours of work, and 30% had not been able to continue in the same employment. As many as 16% of women were unable to continue in any employment, and 6% needed to claim state benefits; thus, in addition to their feelings of loss as contributors to society, they became dependent upon others, which increased their feelings of low self‐esteem.
Prevalence
The exact prevalence of endometriosis is unknown. However, endometriosis is a significant problem for a great number of women and incurs high socioeconomic costs (Prentice 2003). Endometriosis primarily affects women of reproductive age (i.e. women who are menstruating). In women who experience no symptoms, the prevalence of endometriosis has been estimated to range from 2% to 22%, depending on the diagnostic criteria used and the populations studied. In women with painful periods, the prevalence of endometriosis ranges from 40% to 60%, and in women with subfertility, from 20% to 30%. The severity of symptoms and the probability of diagnosis increase with age, peaking at about 40 years of age (Berube 1998; Vessy 1992). In the year 2000, 1.5 billion women aged 15 to 49 years were living in the world. Prevalence of 1% means, therefore, that 15 million women worldwide could have endometriosis, assuming that 20% prevalence would indicate that 300 million women would have endometriosis. The actual figure must lie somewhere between these but is unknown, as the epidemiology of endometriosis is difficult to understand (Kennedy 2003).
Diagnosis
Laparoscopy is considered the 'gold standard' for diagnosis of endometriosis (Canavan 2000; rAFS 1985). However, endometriosis may also be diagnosed (or presumed) on the basis of a description of symptoms provided by a woman (and that may be suspected by the practitioner on the basis of history, pelvic examination and other tests such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and the CA‐125 blood test). However, examination results, test findings and the presence or absence of a classic history and symptoms cannot confirm or rule out endometriosis.
Description of the intervention
The practitioner can treat symptoms of endometriosis in many ways, but treating the underlying disease often requires repeated medical or surgical interventions. Management of endometriosis is varied. Medical treatments for endometriosis include oral contraceptives, progestogens, testosterone derivatives and gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists (Rice 2002). Surgical treatments include ablative techniques (destroying the endometriosis with energy such as laser or electricity) and excision (using scissors, electricity or laser). The latter surgical approach aims to relieve symptoms whilst conserving reproductive function. Practitioners may also perform more radical surgery in the form of hysterectomy, removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy) or both. Conventional medical and surgical treatments for endometriosis aim to remove or decrease deposits of ectopic endometrium (tissue like that lining the uterus but found outside the uterus) (Barbieri 1990). Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used most commonly as simple first‐line treatment for women with endometriosis because they have few side effects, and many are available over the counter. They do not remove or decrease deposits of ectopic endometrium. NSAIDs may act on local cytokines within actual endometriotic deposits and may act as analgesics.
How the intervention might work
Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) work by decreasing pain severity. NSAIDs (including cyclo‐oxygenase (COX)‐2 inhibitors) inhibit prostaglandin production. Prostaglandins are locally produced chemicals that are believed to be responsible for causing the pain of endometriosis. NSAIDs purchased over the counter may be taken in doses that are insufficient to relieve pain. However, NSAIDs taken in high doses have the potential to cause side effects. A Cochrane review of 31 studies that compared NSAIDs versus placebo for primary dysmenorrhoea found a statistically significantly increased risk of adverse effects in the gastrointestinal (e.g. nausea, diarrhoea) and nervous (e.g. headache, drowsiness, dizziness, dryness of the mouth) systems (Marjoribanks 2015). NSAIDs are analgesics that inhibit COX enzymes, thereby also inhibiting production of prostaglandins and alleviating cramps (Dawood 1986; Marjoribanks 2015). The first drug with this mode of action was aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), which was introduced in 1899. However, the term 'NSAID' was not used until the 1950s, when phenylbutazone was developed. Since that time, NSAIDs have become more widely used (Hart 1984; Marjoribanks 2015).
Why it is important to do this review
Endometriosis is seen as a significant public health issue because a large number of women are affected and illnesses associated with this disease are significant (Murphy 2002). NSAIDs are widely used drugs that are readily available (both over the counter and by prescription). We conducted this review to compare all NSAIDs used to treat women with painful symptoms caused by endometriosis versus placebo, other pain management drugs or no treatment, to evaluate their effectiveness and safety.
Objectives
To assess effects of NSAIDs used for management of pain in women with endometriosis compared with placebo, other NSAIDs, other pain management drugs or no treatment.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We included all randomised controlled trials (RCTs) describing use of NSAIDs to treat women of all ages with endometriosis. We included cross‐over trials, as the cross‐over is a valid design in this context.
Types of participants
We included women with endometriosis of any stage or severity. We diagnosed endometriosis by visualisation (e.g. laparoscopy, laparotomy), or we suspected the diagnosis on the basis of history and pelvic examination and other tests such as ultrasonography, MRI and the CA‐125 blood test. We excluded women with chronic pelvic pain that was known to be due to causes other than endometriosis.
Types of interventions
We included all RCTs involving NSAIDs as pain treatment for women with endometriosis versus placebo, other NSAIDs, other drug pain management approaches or no treatment. We considered RCTs describing NSAIDs of any type and administered at any dose, frequency or duration, or by any route of administration.
Types of outcome measures
We recorded data on each of the following outcomes as reported by included trials, when available.
Primary outcomes
Pain relief (measured by visual analogue scale (VAS) or another validated scale, or as a dichotomous outcome, e.g. improved, not improved)
Unintended effects of treatment (incidence and duration of total side effects and types of side effects)
Secondary outcomes
Quality of life (measured on a validated scale, e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36)
Effects on daily activities (measured as proportion of women who reported activity restriction)
Absence from work or school (measured as proportion of women reporting absences from work or school, and also as hours or days of absence as a more selective measure)
Number of women requiring more invasive treatment (e.g. laparoscopic surgery) and length of follow‐up
Requirements for additional medication (measured as proportion of women requiring analgesics (not NSAIDs) in addition to assigned treatment)
Participant satisfaction with treatment (measured as proportion of women who reported improvement and satisfaction with treatment)
Search methods for identification of studies
We searched for all published and unpublished RCTs on use of NSAIDs for management of pain in women with endometriosis, while applying no language restriction and working in consultation with the Cochrane Gynaecology and Fertility Group (CGF) Information Specialist.
Electronic searches
We searched the Cochrane Gynaecology and Fertility Group (CGF) Specialised Register of Controlled Trials (October 2016), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, and CINAHL to identify all publications which described, or might describe, randomised trials of any NSAID in the treatment of endometriosis. Search strategies are outlined in the appendices (Appendix 1; Appendix 2; Appendix 3; Appendix 4; Appendix 5; Appendix 6).
No new randomised controlled trials were identified in 2016.
Searching other resources
We also searched the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (http://www.who.int/ictrp/network/en/index.html) and the US National Institutes of Health trial register (Clinicaltrials.gov; http://www.clinicaltrials.gov) for ongoing studies using the terms 'endometriosis' AND 'non steroidal anti inflammatory', OR 'NSAIDs'. We identified no ongoing trials that were relevant to this review. We checked references in relevant reports to identify additional studies.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
In 2016, support staff from the Cochrane Gynaecology and Fertility Group screened the titles and abstracts of all retrieved records to identify trials for possible inclusion in the review. We obtained full copies of reports for each of the records not rejected and identified no new studies for inclusion.
Data extraction and management
In previous updates, two review authors (CA and SH) independently extracted data using a prespecified data extraction form and resolved disagreements by discussion. Information extracted from each included trial consisted of the following.
Characteristics of trial participants (including age, stage and severity of disease and method of diagnosis) and inclusion and exclusion criteria of the trial.
Type of intervention (including type, dose, duration and frequency of NSAID vs placebo; type, dose, duration and frequency of another NSAID; another pain management drug; or no treatment).
Type of outcome measure (including level of pain reduction, improvement in quality of life score (based on a validated scale), effects on daily activities, absence from work or school, length of follow‐up, unintended effects of treatment, number of women requiring more invasive treatment and length of follow‐up).
When data for a trial were insufficient or missing, we sought information from the named contact author of the trial. We attempted to contact Dr Kauppila but have been unable to elicit a response.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
For previous updates, two review authors used the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool (Higgins 2011) to independently assess included studies for the following risks of bias.
Selection (random sequence generation and allocation concealment).
Perfomance (blinding of participants and personnel).
Detection (blinding of outcome assessors).
Attrition (incomplete outcome data).
Reporting (selective reporting).
Other bias.
We assigned judgements as recommended in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Section 8.5 (Higgins 2011), and resolved disagreements by discussion. We described all judgements and presented all conclusions in the 'Risk of bias' table.
Measures of treatment effect
Both of the trials identified for inclusion in this review were cross‐over trials. Only one trial (Kauppila 1985) provided sufficient information for inclusion in a meta‐analysis. We analysed this trial using the method described by Elbourne and colleagues (Elbourne 2002), that is, by analysing information from both parts of the two‐period, two‐treatment cross‐over trial. For each binary outcome, we calculated the log odds ratio as a measure of different effects of the two treatments, along with its corresponding standard error. We then applied this information in the meta‐analysis using the inverse variance method available in RevMan.
Unit of analysis issues
We utilised the method described above to facilitate appropriate inclusion of cross‐over data in the meta‐analysis.
Dealing with missing data
We analysed the data on an intention‐to‐treat basis as far as possible (i.e. by including all randomised participants in the analysis, in the groups to which they were randomised). We attempted to obtain missing data from the original trialists but could not obtain them.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We intended to consider whether clinical and methodological characteristics of the included studies were sufficiently similar for meta‐analysis to provide a clinically meaningful summary. We intended to assess statistical heterogeneity by using the measure of I2, with I2 greater than 50% taken to indicate substantial heterogeneity (Higgins 2011).
Assessment of reporting biases
In view of the difficulty of detecting and correcting for publication bias and other reporting biases, we aimed to minimise their potential impact by ensuring a comprehensive search for eligible studies and by staying alert for duplication of data. If we had included 10 or more studies in the analysis, we would have used a funnel plot to explore the possibility of small study effects (i.e. tendency for estimates of the intervention effect to be more beneficial in smaller studies).
Data synthesis
We carried out statistical analyses using Review Manager software (RevMan 2014) and a fixed‐effect model.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
We did not conduct subgroup analyses by analysing women with endometriosis and type of NSAID or type of diagnosis (by direct visualisation or just presumed), as data were insufficient. The decision about whether to combine the results of individual trials was dependent on assessment of heterogeneity. In the first instance, we assessed trials for clinical and methodological homogeneity. We had decided that when we judged trials to be sufficiently homogeneous, we would carry out a meta‐analysis of these trials and would investigate statistical heterogeneity in the event that we did not carry out the meta‐analysis.
Sensitivity analysis
We intended to conduct sensitivity analyses for the primary outcomes to determine whether conclusions were robust to arbitrary decisions made regarding eligibility and analysis, with regard to statistical model (fixed‐effect vs random‐effects) and choice of effect estimate (odds ratio vs risk ratio). However, data were insufficient for performance of such sensitivity analyses.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
In earlier updates of this review, searches identified 53 citations. Of these, we obtained full papers for eight possibly relevant trials. We identified only two trials that met the inclusion criteria for this review. We found one trial that was potentially relevant but decided to exclude it from the review. The other five possibly relevant trials investigated use of naproxen specifically for dysmenorrhoea, not for endometriosis. We identified no ongoing trials.
Included studies
The first trial (Kauppila 1979) was a two‐period, four‐treatment cross‐over trial that compared indomethacin (25 mg, three times per day), acetylsalicylic acid (500 mg, three times per day), tolfenamic acid (200 mg, three times per day) and placebo (three times per day) in 24 women with symptomatic endometriosis (stage and severity not described). Each woman received each of the four drugs for two menstrual cycles, but how the women were randomised was unclear. Diagnosis of endometriosis was based on laparoscopic results or pelvic examination findings.
The second trial (Kauppila 1985) was a two‐period, two‐treatment cross‐over trial that compared naproxen sodium (275 mg, four times per day) with placebo (four times per day) in 24 women with endometriosis as classified by the American Fertility Society (mild endometriosis, n = 7; moderate endometriosis, n = 8; severe endometriosis, n = 6). Diagnosis was based on pelvic examination, history of menstrual distress or direct visualisation of pelvic regions at laparoscopy or laparotomy. Each woman received naproxen sodium for two menstrual cycles followed by placebo for two menstrual cycles, or placebo for two menstrual cycles followed by naproxen sodium for two menstrual cycles.
Excluded studies
Review authors excluded a trial (Cobellis 2004) that assessed use of a COX‐2‐specific inhibitor (rofecoxib) for management of pain related to endometriosis. However, this drug was withdrawn from the marketplace in November 2004 on the grounds of safety; therefore, it is inappropriate to assess the efficacy of the product in this review. If the drug is re‐launched, we will review this decision at the time the review would be updated.
Risk of bias in included studies
We summarised information on potential risk of bias for each of the included studies in a 'Risk of bias' table and in an overall summary presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
1.
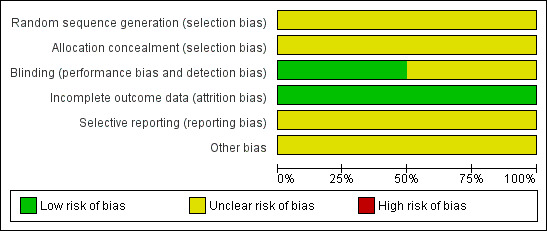
Methodological quality graph: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item presented as percentages across all included studies.
2.
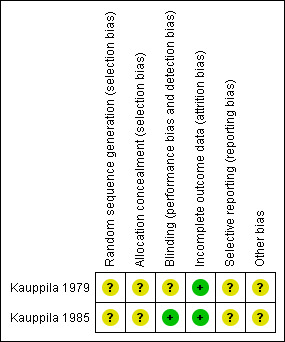
Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study.
Allocation
Neither of the included trials (Kauppila 1979; Kauppila 1985) provided information on the method of randomisation or concealment of allocation sequence. One trial (Kauppila 1985) described how each woman received naproxen sodium for two menstrual cycles followed by placebo for two menstrual cycles, or placebo for two menstrual cycles followed by naproxen sodium for two menstrual cycles. In Kauppila 1979, each woman received each of four drugs (indomethacin, acetylsalicylic acid, tolfenamic acid and placebo) for two menstrual cycles, but how the women were randomised remains unclear. We rated both studies as having unclear risk of selection bias.
Blinding
Investigators described both of the trials (Kauppila 1979; Kauppila 1985) as double‐blind and specifically mentioned that drugs were dispensed in identical capsules in one trial (Kauppila 1985). Researchers in both trials provided no information on blinding of outcome assessors or data analysers. We considered Kauppila 1985 to be at low risk for this bias, and Kauppila 1979 to be at unclear risk.
Incomplete outcome data
In Kauppila 1979, researchers randomised 24 women but included only 18 in the analysis. Trialists did not provide reasons for loss to follow‐up. In Kauppila 1985, investigators randomised 24 women and included only 20 in the analysis. Reasons given for loss to follow‐up included pregnancy (n = 1), psychiatric problems (n = 1) and unknown reasons (n = 2).
Kauppila 1979 presented data graphically for each menstrual cycle (144 cycles), not per woman included in the trial. Therefore, it was not possible to link each of the menstrual cycles from one treatment with the corresponding menstrual cycle from an alternative treatment. It also was not possible to link the two menstrual cycles for each woman with each treatment. It appears as though the study authors, in carrying out their analysis, did not account for pairing within each treatment group. For these reasons, we did not include this trial in the overall analysis.
We rated both studies as having low risk of attrition bias.
Selective reporting
We judged both included trials (Kauppila 1979; Kauppila 1985) as having unclear risk of bias because neither trial clearly prespecified primary and secondary outcomes.
Other potential sources of bias
We judged both included trials as having unclear risk of bias owing to insufficient information to enable a judgement of low risk of bias.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1
Comparison of naproxen sodium versus placebo
Primary outcomes
Overall pain relief
One trial reported data on overall pain relief (Kauppila 1985). Whether results showed a difference between naproxen sodium (275 mg, four times a day) and placebo in producing excellent to moderate relief of pain caused by endometriosis was not clear (odds ratio (OR) 3.27, 95% CI 0.61 to 17.69; one RCT, 24 women; very low‐quality evidence).
Unintended effects of treatment
One trial reported data on unintended effects of treatment (Kauppila 1985). Whether results showed a difference between women taking naproxen sodium and experiencing unintended effects of treatment and those taking placebo and experiencing unintended effects of treatment is unclear (OR 0.46, 95% CI 0.09 to 2.47; one RCT, 24 women; very low‐quality evidence). Unintended effects of treatment reported with naproxen sodium (n = 4) included fatigue, light‐headedness, eye lid swelling and chest pain. Unintended effects of treatment reported with placebo (n = 7) included hypomenorrhoea (loss of a small amount of menstrual blood with still regular menstrual cycles), diarrhoea, increased diuresis, headache, epigastric pain, nausea and vomiting, tremor and dizziness.
Secondary outcomes
Requirement for additional medication
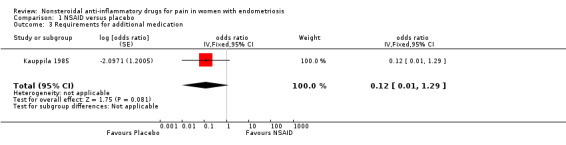
One trial (Kauppila 1985) provided data on the need for supplementary analgesia. Whether results showed a difference between women taking naproxen sodium and requiring supplementary analgesia and those taking placebo and requiring supplementary analgesia (OR 0.12, 95% CI 0.01 to 1.29; one RCT, 24 women) for pain caused by endometriosis is unclear.
The included trial did not report on the other secondary outcomes of this review (quality of life, effects on daily activities, absence from work or school, number of women requiring more invasive treatment, participant satisfaction with treatment).
Discussion
Summary of main results
Despite rigorous searches, we identified only two randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) versus placebo for treatment of women with pain associated with endometriosis. Whether results showed a difference between NSAIDs and placebo for overall pain relief, unintended effects of treatment or requirement for additional medication remains unclear (Table 1). Investigators provided no data on the other secondary outcomes of this review (quality of life, effects on daily activities, absence from work or school, number of women requiring more invasive treatment, participant satisfaction with treatment). The evidence is surprising, given that NSAIDs are widely prescribed and are bought over the counter for management of pain caused by endometriosis. In comparison, much of the literature suggests that NSAIDs can be used as treatment for women with primary dysmenorrhoea. It is likely that prostaglandins are involved in causing pain in both groups of patients. A recent Cochrane review (Marjoribanks 2015) presented evidence indicating that NSAIDs provide effective treatment for women with pain caused by primary dysmenorrhoea, although women taking NSAIDs must be aware of the risk of unintended effects of treatment.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
Owing to the lack of RCTs undertaken to explore the use of NSAIDs as treatment for women with pain associated with endometriosis, we are unable to comment on many of the outcomes that are important to women who have endometriosis, such as quality of life, effects on daily activities and absence from school or work. We assessed only four NSAIDs (naproxen sodium, indomethacin, acetylsalicylic acid and tolfenamic acid) for the management of pain associated with endometriosis (Kauppila 1985; Kauppila 1979). One trial (Kauppila 1979) analysed three of these NSAIDs (indomethacin, acetylsalicylic acid and tolfenamic acid), but we did not analyse study findings in this review, as the study had serious methodological flaws. However, many other prescribed and over‐the‐counter NSAIDs are available. We found no evidence to support use of these to control pain caused by endometriosis.
The only remaining trial (Kauppila 1985) included and analysed in this review provided no evidence of an effect when comparing NSAIDs (naproxen sodium) versus placebo for the management of pain caused by endometriosis. Evidence was inconclusive to show whether women taking NSAIDs were less likely to take supplementary analgesia than those taking placebo. We believe that this most likely occurred because the trial was very small (randomising only 24 women); therefore, we would recommend caution when these results are applied to a larger population.
Evidence was also inconclusive to show whether women taking NSAIDs were more likely to experience unintended effects of treatment compared with women taking placebo. Four women experienced unintended effects of treatment while taking naproxen sodium compared with seven women who experienced these effects while taking placebo. Unintended effects reported when women were randomised to placebo may have been related to the pain caused by endometriosis, rather than to the placebo itself. However, drawing firm conclusions is difficult because this trial included a small number of women.
Quality of the evidence
We judged the risk of bias to be unclear owing to lack of methodological detail. We used the GRADE method and judged that the overall quality of the evidence was very low owing to unclear risk of bias, imprecision with wide confidence intervals and evidence derived from a single small study (Table 1).
Potential biases in the review process
The review authors believe that we have minimised potential biases in the review process by searching published and unpublished literature with no restrictions on date of publication or language. We were unable to judge the potential effect of publication bias, as we identified fewer than 10 trials.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
Despite the findings reported in this review, we believe it is important to highlight the findings of another Cochrane review on NSAIDs for management of pain caused by primary dysmenorrhoea (Marjoribanks 2015), which showed that NSAIDs appear to provide very effective treatment for women with dysmenorrhoea, but evidence is insufficient to show which (if any) individual NSAID is most safe and effective.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Evidence is inconclusive to show whether nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (naproxen sodium) are effective for management of pain caused by endometriosis. No evidence suggests whether any individual NSAID is more effective than another. As reported in other Cochrane reviews, women using NSAIDs must be aware that these drugs may cause unintended effects.
Implications for research.
Investigators conducted the two included studies in the late 1970s and the mid 1980s, and randomised small numbers of women. A systematic search of the literature revealed no randomised controlled trials comparing NSAIDs versus other treatments. One trial compared different types of NSAIDs; however, this trial had methodological limitations. Researchers must conduct additional trials with larger numbers of women to ensure that they are of a robust design, and to assess and report outcomes that are important to women with endometriosis (e.g. quality of life, effects on daily activities, absence from school or work, need for more invasive treatment).
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 4 May 2017 | Review declared as stable | Authors did not identify any new or ongoing studies relevant to this review and more studies are unlikely. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 2, 2004 Review first published: Issue 4, 2005
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 15 November 2016 | New citation required but conclusions have not changed | The searches identified no new studies for inclusion. Unless new evidence emerges, we will no longer update this review. |
| 1 November 2016 | New search has been performed | We updated this review in October 2016. |
| 20 September 2010 | Amended | We updated contact details. |
| 11 February 2009 | New citation required but conclusions have not changed | We updated the review in Apirl 2008. |
| 31 August 2008 | New search has been performed | We updated searches on 21 April 2008. We found no new studies. We amended the review. We added risk of bias tables and 2 new figures. We moved search strategies to appendices. |
| 29 April 2008 | Amended | We converted the review to new review format. |
| 23 August 2005 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | We made substantive amendments. |
Acknowledgements
2016: we acknowledge the support of the Cochrane Gynaecology and Fertility Group in assisting with electronic searching of databases (Marian Showell), and of Julie Brown and Tineke Crawford in searching for potential studies, amending the structure of the review and adding the 'Summary of findings' table.
Previous versions: we should like to thank Ruth Buist for searching MEDLINE and Embase; Anne Eisinga for assisting with citations and proofreading; Jini Hetherington for proofreading; Stephen Kennedy for providing additional papers and giving advice; Jane Marjoribanks for providing help and encouragement during writing of the review; Sarah Moore for ordering copies of studies; Michelle Proctor for providing help and encouragement during writing of the review and peer refereeing; Andy Vail for providing statistical advice and expertise; and the UK Cochrane Centre training team for providing appropriate training.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Cochrane Gynaecology and Fertility Group search strategy
From inception to 19 October 2016:
Procite platform
Keywords CONTAINS "endometriosis" or "endometriosis scores" or "pelvic pain" or "dyschezia" or "dyspareunia" or Title CONTAINS "endometriosis" or "endometriosis scores" or "pelvic pain" or "dyschezia" or "dyspareunia"
AND
Keywords CONTAINS "nonsteroidal" or "NSAID" or "NSAIDs" or "mefenamic acid" or "Naprosyn" or "naproxen" or "Ibuprofen" or "Flurbiprofen " or "Meclofenamic Acid" or "Meclofenamate" or "diclofenac" or "acetylsalicylic" or "Aspirin" or "indomeixin" or "indometacin" or "indomethacin"or "Ketoprofen" or "Piroxicam" or "Flufenamic Acid" or "nimesulide"or "COX‐2 inhibitors" or "cyclooxygenase" or Title CONTAINS "nonsteroidal" or "NSAID" or "NSAIDs" or "mefenamic acid" or "Naprosyn" or "naproxen" or "Ibuprofen" or "Flurbiprofen " or "Meclofenamic Acid" or "Meclofenamate" or "diclofenac" or "acetylsalicylic" or "Aspirin" or "indomeixin" or "indometacin" or "indomethacin"or "Ketoprofen" or "Piroxicam" or "Flufenamic Acid" or "nimesulide"or "COX‐2 inhibitors" or "cyclooxygenase" (31 hits)
Appendix 2. CENTRAL CRSO search strategy
From inception to 19 October 2016:
CRSO web platform
#1 MESH DESCRIPTOR Endometriosis EXPLODE ALL TREES 509
#2 Endometriosis:TI,AB,KY 1127
#3 dyspareunia*:TI,AB,KY 483
#4 dyschezia:TI,AB,KY 18
#5 (pelvic adj2 pain):TI,AB,KY 840
#6 #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 2111
#7 MESH DESCRIPTOR Anti‐Inflammatory Agents, Non‐Steroidal EXPLODE ALL TREES 14868
#8 MESH DESCRIPTOR Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors EXPLODE ALL TREES 887
#9 (nonsteroidal* or non steroidal*):TI,AB,KY 8816
#10 nsaid*:TI,AB,KY 2886
#11 (COX 2 or COX‐2 or COX2):TI,AB,KY 896
#12 (diclofenac or flurbiprofen or ibuprofen or meclofenamic acid or mefenamic acid or naproxen or aspirin):TI,AB,KY 16304
#13 (etoricoxib* or lumiracoxib* or parecoxib*):TI,AB,KY 542
#14 (rofecoxib* or valdecoxib*):TI,AB,KY 509
#15 (acemetacin or celecoxib or dexibuprofen or dexketoprofen or indometacin or ketoprofen):TI,AB,KY 2744
#16 (ponstan or voltaren):TI,AB,KY 223
#17 (cyclooxygenase inhibitor* or cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor*):TI,AB,KY 1665
#18 (sulphonanilide* or flufenamic or nimesulide):TI,AB,KY 386
#19 (salicylate* or sulindac or acetylsalicylic):TI,AB,KY 6178
#20 piroxicam:TI,AB,KY 1051
#21 #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20 30354
#22 #6 AND #21 89
Appendix 3. MEDLINE search strategy
From 1946 to 19 October 2016:
Ovid platform
1 exp Endometriosis/ (18905) 2 Endometriosis.tw. (18913) 3 dyspareuni$.tw. (3086) 4 (pelvic adj2 pain).tw. (7661) 5 dyschezia.tw. (220) 6 or/1‐5 (31643) 7 exp anti‐inflammatory agents, non‐steroidal/ or exp aspirin/ or exp diclofenac/ or exp flurbiprofen/ or exp ibuprofen/ or exp indomethacin/ or exp ketoprofen/ or exp meclofenamic acid/ or exp mefenamic acid/ or exp naproxen/ or exp piroxicam/ or exp cyclooxygenase inhibitors/ or exp cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors/ (177771) 8 nonsteroidal$.tw. (20990) 9 non‐steroidal$.tw. (16588) 10 nsaid$.tw. (21016) 11 (COX 2 or COX‐2 or COX2).tw. (27740) 12 (diclofenac or flurbiprofen or ibuprofen or meclofenamic acid or mefenamic acid or naproxen or aspirin).tw. (65356) 13 (etoricoxib$ or lumiracoxib$ or parecoxib$).tw. (1135) 14 (rofecoxib$ or valdecoxib$).tw. (2313) 15 (acemetacin or celecoxib or dexibuprofen or dexketoprofen or indometacin or ketoprofen).tw. (9277) 16 (ponstan or voltaren).tw. (406) 17 (cyclooxygenase inhibitor$ or cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor$).tw. (6591) 18 (sulphonanilide$ or flufenamic or nimesulide).tw. (2422) 19 (salicylate$ or sulindac or acetylsalicylic).tw. (19959) 20 piroxicam.tw. (2765) 21 or/7‐20 (242543) 22 6 and 21 (515) 23 randomized controlled trial.pt. (432907) 24 controlled clinical trial.pt. (91818) 25 randomized.ab. (373304) 26 placebo.tw. (185009) 27 clinical trials as topic.sh. (180215) 28 randomly.ab. (265279) 29 trial.ti. (163329) 30 (crossover or cross‐over or cross over).tw. (71501) 31 or/23‐30 (1098911) 32 exp animals/ not humans.sh. (4325953) 33 31 not 32 (1011983) 34 22 and 33 (86)
Appendix 4. Embase search strategy
From 1974 to 19 October 2016:
Ovid Platform
1 exp ENDOMETRIOSIS/ (30469) 2 endometriosis.tw. (25587) 3 (pelv$ adj2 pain).tw. (11770) 4 dyschezia.tw. (417) 5 dyspareunia.tw. (5383) 6 or/1‐5 (44542) 7 exp nonsteroid antiinflammatory agent/ (507110) 8 exp acetylsalicylic acid/ (183969) 9 exp CELECOXIB/ (18678) 10 exp DICLOFENAC/ (34108) 11 exp ETORICOXIB/ (2430) 12 exp FLURBIPROFEN/ (7048) 13 exp ibuprofen/ or exp ketoprofen/ or exp ketorolac/ or exp mefenamic acid/ or exp naproxen/ or exp piroxicam/ or exp rofecoxib/ or exp salicylic acid/ or exp valdecoxib/ (100090) 14 nonsteroidal$.tw. (24626) 15 non‐steroidal$.tw. (22681) 16 nsaid$.tw. (33773) 17 exp prostaglandin synthase inhibitor/ or exp cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor/ (474499) 18 (COX 2 or COX‐2 or COX2).tw. (36253) 19 (acetylsalicylic acid or celecoxib or diclofenac or etoricoxib).tw. (31334) 20 (flurbiprofen or ibuprofen or ketoprofen or ketorolac).tw. (24017) 21 (mefenamic acid or naproxen or piroxicam or rofecoxib or salicylic or valdecoxib).tw. (25457) 22 (sulphonanilide$ or flufenamic or nimesulide).tw. (3217) 23 (ponstan or voltaren).tw. (2942) 24 (acemetacin or dexibuprofen or dexketoprofen or indometacin).tw. (1861) 25 (cyclooxygenase inhibitor$ or cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor$).tw. (7200) 26 or/7‐25 (574498) 27 6 and 26 (1737) 28 Clinical Trial/ (978910) 29 Randomized Controlled Trial/ (454730) 30 exp randomization/ (83085) 31 Single Blind Procedure/ (26186) 32 Double Blind Procedure/ (135680) 33 Crossover Procedure/ (53307) 34 Placebo/ (319417) 35 Randomi?ed controlled trial$.tw. (146931) 36 Rct.tw. (21980) 37 random allocation.tw. (1611) 38 randomly allocated.tw. (26329) 39 allocated randomly.tw. (2198) 40 (allocated adj2 random).tw. (842) 41 Single blind$.tw. (18462) 42 Double blind$.tw. (171618) 43 ((treble or triple) adj blind$).tw. (626) 44 placebo$.tw. (245414) 45 prospective study/ (380568) 46 or/28‐45 (1749996) 47 case study/ (91637) 48 case report.tw. (320145) 49 abstract report/ or letter/ (980824) 50 or/47‐49 (1383573) 51 46 not 50 (1700346) 52 27 and 51 (481)
Appendix 5. PsycINFO search strategy
From 1806 to 19 October 2016:
Ovid Platform
1 exp Gynecological Disorders/ (1613) 2 endometriosis.tw. (206) 3 (pelv$ adj2 pain).tw. (517) 4 dyspareunia.tw. (527) 5 or/1‐4 (2611) 6 exp Aspirin/ (438) 7 exp Analgesic Drugs/ (17453) 8 (non?steroidal adj5 anti?inflammatory).tw. (86) 9 (non‐steroidal$ adj5 anti‐inflammatory).tw. (460) 10 nsaid$.tw. (799) 11 (COX 2 or COX‐2).tw. (733) 12 (acetylsalicylic acid or celecoxib or diclofenac or etoricoxib).tw. (594) 13 (flurbiprofen or ibuprofen or ketoprofen or ketorolac).tw. (627) 14 (mefenamic acid or naproxen or piroxicam or rofecoxib or salicylic acid or valdecoxib).tw. (341) 15 aspirin.tw. (1033) 16 or/6‐15 (20157) 17 5 and 16 (31)
Appendix 6. CINAHL search strategy
From 1982 to 19 October 2016:
Ebsco platform
| # | Query | Results |
| S42 | S29 AND S41 | 40 |
| S41 | S30 OR S31 OR S32 OR S33 OR S34 OR S35 OR S36 OR S37 OR S38 OR S39 OR S40 | 1,081,306 |
| S40 | TX allocat* random* | 5,281 |
| S39 | (MH "Quantitative Studies") | 14,919 |
| S38 | (MH "Placebos") | 9,827 |
| S37 | TX placebo* | 39,650 |
| S36 | TX random* allocat* | 5,281 |
| S35 | (MH "Random Assignment") | 41,699 |
| S34 | TX randomi* control* trial* | 110,746 |
| S33 | TX ( (singl* n1 blind*) or (singl* n1 mask*) ) or TX ( (doubl* n1 blind*) or (doubl* n1 mask*) ) or TX ( (tripl* n1 blind*) or (tripl* n1 mask*) ) or TX ( (trebl* n1 blind*) or (trebl* n1 mask*) ) | 857,082 |
| S32 | TX clinic* n1 trial* | 190,012 |
| S31 | PT Clinical trial | 79,719 |
| S30 | (MH "Clinical Trials+") | 203,397 |
| S29 | S6 AND S28 | 104 |
| S28 | S7 OR S8 OR S9 OR S10 OR S11 OR S12 OR S13 OR S14 OR S15 OR S16 OR S17 OR S18 OR S19 OR S20 OR S21 OR S22 OR S23 OR S24 OR S25 OR S26 OR S27 | 30,886 |
| S27 | TX piroxicam | 209 |
| S26 | TX(salicylate* or sulindac or acetylsalicylic) | 1,237 |
| S25 | TX(sulphonanilide* or flufenamic or nimesulide) | 100 |
| S24 | TX(cyclooxygenase inhibitor* or cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor*) | 801 |
| S23 | TX(ponstan or voltaren) | 28 |
| S22 | TX(acemetacin or celecoxib or dexibuprofen or dexketoprofen or indometacin or ketoprofen) | 1,030 |
| S21 | TX(rofecoxib* or valdecoxib*) | 520 |
| S20 | TX(etoricoxib* or lumiracoxib* or parecoxib*) | 316 |
| S19 | TX(diclofenac or flurbiprofen or ibuprofen or meclofenamic acid or mefenamic acid or naproxen or aspirin) | 14,883 |
| S18 | TX (COX 2 or COX‐2 or COX2) | 5,065 |
| S17 | TX nsaid* | 3,651 |
| S16 | TX nonsteroidal* or TX non steroidal* | 12,754 |
| S15 | (MM "Cox‐2 Inhibitors") | 1,857 |
| S14 | (MM "Piroxicam") | 104 |
| S13 | (MM "Naproxen") | 269 |
| S12 | (MM "Ketorolac") | 273 |
| S11 | (MM "Indomethacin") | 450 |
| S10 | (MM "Ibuprofen") | 798 |
| S9 | (MM "Diclofenac") | 566 |
| S8 | (MM "Aspirin") | 4,207 |
| S7 | (MM "Antiinflammatory Agents, Non‐Steroidal+") | 12,096 |
| S6 | S1 OR S2 OR S3 OR S4 OR S5 | 5,662 |
| S5 | TX (pelvic N2 pain) | 2,557 |
| S4 | TX dyschezia | 19 |
| S3 | TX dyspareuni* | 916 |
| S2 | TX Endometriosis | 2,764 |
| S1 | (MM "Endometriosis") | 1,702 |
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. NSAID versus placebo.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Overall pain relief | 1 | odds ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.27 [0.61, 17.69] | |
| 2 Unintended effects of treatment | 1 | odds ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.46 [0.09, 2.47] | |
| 3 Requirements for additional medication | 1 | odds ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.12 [0.01, 1.29] |
1.1. Analysis.
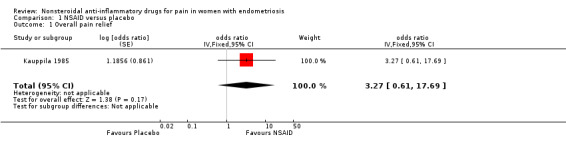
Comparison 1 NSAID versus placebo, Outcome 1 Overall pain relief.
1.2. Analysis.
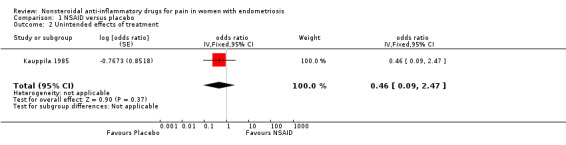
Comparison 1 NSAID versus placebo, Outcome 2 Unintended effects of treatment.
1.3. Analysis.
Comparison 1 NSAID versus placebo, Outcome 3 Requirements for additional medication.
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Kauppila 1979.
| Methods | Trial design: 2‐period, 4‐treatment cross‐over trial | |
| Participants | 24 women randomised; 18 analysed Mean age: 33 (22‐43) years Inclusion criteria: women with symptomatic endometriosis (stage and severity not described). Endometriosis was diagnosed by laparoscopy (n = 13) and by pelvic examination (n = 5). Exclusion criteria: not clear Setting: Finland Timing: unclear |
|
| Interventions | Group 1: indomethacin 25 mg given 3 × daily for 2 menstrual cycles, then cross‐over to acetylsalicylic acid, tolfenamic acid and placebo for 2 menstrual cycles each (n = 6) Group 2: acetylsalicylic acid 500 mg given 3 × daily for 2 menstrual cycles, then cross‐over to tolfenamic acid, placebo and indomethacin for 2 menstrual cycles each (n = 6) Group 3: tolfenamic acid 200 mg given 3 × daily for 2 menstrual cycles, then cross‐over to placebo, indomethacin and acetylsalicylic acid for 2 menstrual cycles each (n = 6) Group 4: placebo given 3 × daily for 2 menstrual cycles, then cross‐over to indomethacin, acetylsalicylic acid and tolfenamic acid for 2 menstrual cycles each (n = 6) |
|
| Outcomes | These were self‐reported by questionnaire, which was completed by the participant immediately after each menstrual cycle. Pain relief: pelvic pain, lower back pain, pain in walking, dyspareunia, pain on defecation, headache; number not reported but described as more common with placebo and indomethacin Quality of life: not reported Effect on daily activities: not reported Absence from work or school: not reported Unintended effects of treatment: gastrointestinal complaints (nausea and vomiting), number not reported but described as more common with indomethacin; psychic complaints (insomnia and nervousness), number not reported but described as more common with indomethacin Number of women requiring more invasive treatment: not reported Requirements for additional medication: not reported Participant satisfaction with treatment: not reported |
|
| Notes | Drugs for use in the trial were provided by Medica Ltd, Helsinki, Finland. "The authors wish to thank Medica Ltd, Helsinki, Finland, for the drugs." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | "placebo‐controlled double‐blind trial" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | "Twenty‐four patients...volunteered for this study. Eighteen women completed the trial; the remaining six terminated treatment for a variety of personal reasons." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Prespecified primary and secondary outcomes were not clearly defined. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information was provided to enable a judgement of low risk of bias. |
Kauppila 1985.
| Methods | Trial design: 2‐period, 2‐treatment cross‐over trial | |
| Participants | 24 women randomised; 20 analysed Mean age: group 1, 32 years; group 2, 35 years Inclusion criteria: women with endometriosis classified by the American Fertility Society (mild endometriosis, n = 7; moderate endometriosis, n = 8; severe endometriosis, n = 6). Endometriosis was diagnosed by pelvic examination, history of menstrual distress and direct visualisation of pelvic regions at laparoscopy or laparotomy. Exclusion criteria: not clear Setting: Finland Timing: unclear |
|
| Interventions | Group 1: naproxen sodium (nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drug (NSAID)) 275 mg (102 tablets) 4 × daily for 2 menstrual cycles, then cross‐over to placebo for 2 menstrual cycles (n = 12)
Additional interventions: Additional analgesia was allowed if no relief was noted after the first 2 doses of NSAID. Group 2: placebo given for 2 menstrual cycles, then cross‐over to naproxen sodium (NSAID) for 2 menstrual cycles (n = 12) Additional interventions: Additional analgesia was allowed if no relief was noted after first 2 doses. |
|
| Outcomes | All were self‐reported by questionnaire, which was completed by the participant immediately after each menstrual cycle. Pain relief: measured after each menstrual cycle (score 3 to ‐1) Quality of life: not reported Effects on daily activities: activity of participant (score 4 to 0) Absence from work or school: not reported Unintended effects of treatment: fatigue, light‐headedness, eye lid oedema and chest pain (n = 4 while taking naproxen sodium); hypomenorrhoea, diarrhoea, increased diuresis, headache, epigastric pain, nausea and vomiting, tremor and dizziness (n = 7 while taking placebo) Number of women requiring more invasive treatment: not reported Requirements for additional medication: Supplemental analgesia was more common in the placebo group (14) than in the NSAID group (2). Participant satisfaction with treatment: not reported |
|
| Notes | Drugs used in the trial were supplied by Syntex Research, Maidenhead, England. "The study drugs were kindly supplied by Syntex Research, Maidenhead, England." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | "The study was conducted according to a randomized, double‐blind, four‐period crossover design." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | "Twenty‐four patients...entered the present study...One patient became pregnant before the first treatment, one patient had psychiatric problems that rendered her responses unreliable, and two patients were lost to follow‐up for unknown reasons during the trial." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Prespecified primary and secondary outcomes were not clearly defined. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Information provided was insufficient to enable a judgement of low risk of bias. |
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Cobellis 2004 | This trial assessed use of the cyclo‐oxygenase (COX)‐2‐specific inhibitor (rofecoxib) for management of pain related to endometriosis. However, this drug was withdrawn from the marketplace in November 2004 on safety grounds; therefore, it is inappropriate to assess the efficacy of the product in this review. If the drug is re‐launched, we will review this decision at the time the review would be updated. |
Differences between protocol and review
The original review included six primary outcomes. In 2016, we reduced these to two.
Pain relief (measured by visual analogue scale (VAS) or another validated scale, or as a dichotomous outcome, e.g. improved, not improved).
Unintended effects of treatment (incidence and duration of total side effects, types of side effects).
The remaining primary outcomes became secondary outcomes.
Contributions of authors
2016: JB and TC searched for potential studies, amended the structure of the review and added the summary of findings table. CA, SH and AP commented on and approved the draft.
Previous updates: CA, SH and AP were involved in all aspects of the review. CA and SH were responsible for the first draft. AP gave feedback on three subsequent drafts. CA, SH and AP considered and addressed referees' comments. CA, DG, SH and AP were involved in updating the review.
Sources of support
Internal sources
Cochrane Collaboration Secretariat, UK.
UK Cochrane Centre, NHS R & D Programme, UK.
University of Cambridge, UK.
External sources
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
One review author (CA) has endometriosis and is a member of Endometriosis UK. Another review author (AP) was Chairman of Endometriosis UK at the time the review was originally written. JB, TC and SH have no interests to declare.
Stable (no update expected for reasons given in 'What's new')
References
References to studies included in this review
Kauppila 1979 {published data only}
- Kauppila A, Puolakka J, Ylikorkala O. Prostaglandin biosynthesis inhibitors and endometriosis. Prostaglandins 1979;18(4):655‐61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylikorkala O, Viinikka L. Postaglandins and endometriosis. Acta Obstetrica et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1983;113 Suppl:105‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kauppila 1985 {published data only}
- Kauppila A, Ronnberg L. Naproxen sodium in dysmenorrhoea secondary to endometriosis. Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1985;65(3):379‐83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Cobellis 2004 {published data only}
- Cobellis L, Razzi S, Simone S, Sartini A, Fave A, Danero S, et al. The treatment with a COX‐2 specific inhibitor is effective in the management of pain related to endometriosis. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology 2004;116:100‐2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Barbieri 1990
- Barbieri RL. Endometriosis 1990 ‐ current treatment approaches. Drugs 1990;39(4):502‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Berube 1998
- Berube S, Marcoux S, Maheux R, Graves G, Wrixon W, O'Keane J, et al. Characteristics related to the prevalence of minimal or mild endometriosis in infertile women. Epidemiology 1998;9(5):504‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Canavan 2000
- Canavan TP, Radosh L. Managing endometriosis. Strategies to minimize pain and damage. Postgraduate Medicine 2000;107(3):213‐6, 222‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Davies 2003
- Davies B. The best practice in treatment. Living with Endometriosis ‐ The Way Forward (oral presentation, London, UK) 2003; Vol. April 30.
Dawood 1986
- Dawood MY. Current concepts in the etiology and treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1986;138 Suppl:7‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Elbourne 2002
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtin F, Worthington HV. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31:140‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hart 1984
- Hart FD, Huskisson EC. Non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs. Current status and rational therapeutic use. Drugs 1984;27(3):232‐55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org. [Google Scholar]
Jones 2002
- Jones GL, Kennedy SH, Jenkinson C. Health‐related quality of life measurement in women with common benign gynecologic conditions: a systematic review. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2002;187(2):501‐11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kennedy 2003
- Kennedy S. International links. Living with Endometriosis ‐ The Way Forward (oral presentation, London, UK) 2003; Vol. April 30.
Marjoribanks 2015
- Marjoribanks J, Ayeleke RO, Farquhar C, Proctor M. Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs for dysmenorrhoea. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 7. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001751.pub3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Murphy 2002
- Murphy AA. Clinical aspects of endometriosis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2002;955:1‐10, Discussion 34‐6, 396‐406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Prentice 2003
- Prentice A, Deary AJ, Bland E. Progestogens and anti‐progestogens for pain associated with endometriosis (Cochrane Review). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002122] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
rAFS 1985
- Revised American Fertility Society classification of endometriosis. Revised American Fertility Society classification of endometriosis. Fertility and Sterility 1985;43:351‐2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rice 2002
- Rice VM. Conventional medical therapies for endometriosis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2002;955:343‐52, Discussion 389‐93, 396‐406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vessy 1992
- Vessey MP, Villard‐Mackintosh L, Painter R. Epidemiology of endometriosis in women attending family planning clinics. BMJ 1992;306(6871):182‐4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Allen 2004
- Allen C, Hopewell S, Prentice A. Non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs for pain in women with endometriosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004753] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Allen 2005
- Allen C, Hopewell S, Prentice A, Gregory D. Non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs for pain in women with endometriosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004753.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Allen 2009
- Allen C, Hopewell S, Prentice A, Gregory D. Nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs for pain in women with endometriosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004753.pub3] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


