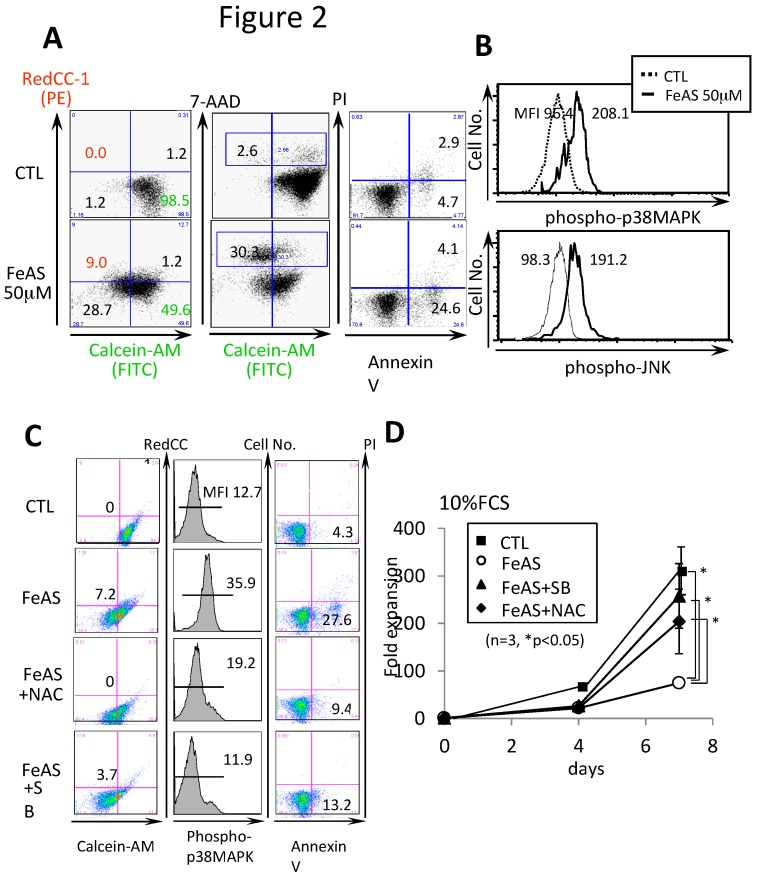
Figure 2.
FeAS induces growth inhibition and cell death through reactive oxygen species (ROS)-activated p38MAPK. (A) After 72 h of culture with or without FeAS, LSK cells were stained with Calcein-AM and Red CC-1 and subjected to flow cytometry analyses. Intracellular labile iron and total ROS were detected with Calcein-AM and Red CC-1, respectively. FeAS-induced cell death was assessed as Calcein-AM low/negative and 7-AAD positive staining. The percentage of 7-AAD positive dead cells is indicated by the number in the quadrant. (B) After 72 h of culture with or without FeAS, cells were stained with specific antibodies, and threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation of p38MAPK and JNK/SAPK was examined by FACS. (C) Effects of the anti-oxidant (N-Acetyl-l-cysteine, NAC) and p38MAPK inhibitor (SB203580, SB) on ROS-accumulation (left panel), phosphorylation of p38MAPK (middle panel), and the type and stage of cell death (right panel) was examined by FACS. LSK cells were cultured with 50 μM of FeAS in combination with either 100 μM NAC or 10 μM SB203580 for 72 h. The percentage of Calcein-AM low/RedCC1+ fraction, mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of phosphor-p38MAPK, and annexinV+/PI- apoptotic fraction are indicated, respectively. (D) Effects of NAC and SB on FeAS-induced growth inhibition of LSKs were evaluated. Data is shown as the means ± SD of summarized data obtained from three independent experiments (* p < 0.05).