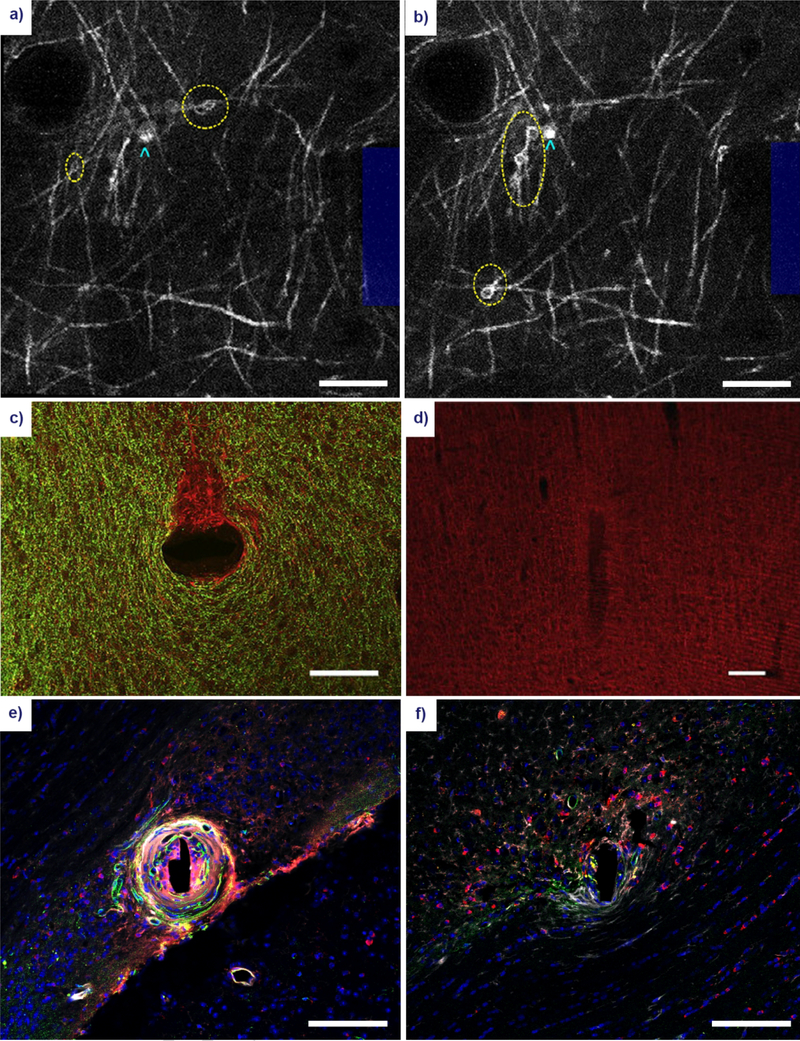
Figure 4. Gross morphological changes to oligodendrocyte and myelin structure following microelectrode implantation.
Acute myelin damage in the form of myelinosomes (yellow ellipses) can be observed within the vicinity of the electrode (blue outline) at 1 hour (a) and 6 hours (b) post-insertion using in vivo two-photon microscopy of CNP-eGFP mice. Oligodendrocyte cell bodies can be identified as adjacent somas (cyan arrowheads). Reproduced with permission from IOP Publishing [145]. Scale bar = 100 μm. Large scale damage to the myelin architecture has been observed at 12 weeks post-insertion of an electrode in the rat cortex. (c) A stain for myelin basic protein (green) shows demyelination in a discrete area of unmyelinated axons (red) in a horizontal section. Reprinted from [11], with permission from Elsevier. Scale bar = 100 μm. (d) A coronal section of the implanted electrode shows a similar characteristic reduction in myelin around the insertion site. Reprinted from [209], with permission from Elsevier. Scale bar = 100 μm. (e) A stain for APC/CC1 oligodendrocytes (red), platelet-derived growth factor β pericytes (PDGFβ, green), immunoglobulin IgG (white), and cell nuclei (blue) in white matter region CA1 of the adult mouse brain. Scale bar = 100 μm. (f) Similar stain, implant duration, and implant region as in (e) in an apoptosis-resistant Caspase-1 knockout mouse. Scale bar = 100 μm. Reprinted from [26], with permission from Elsevier.