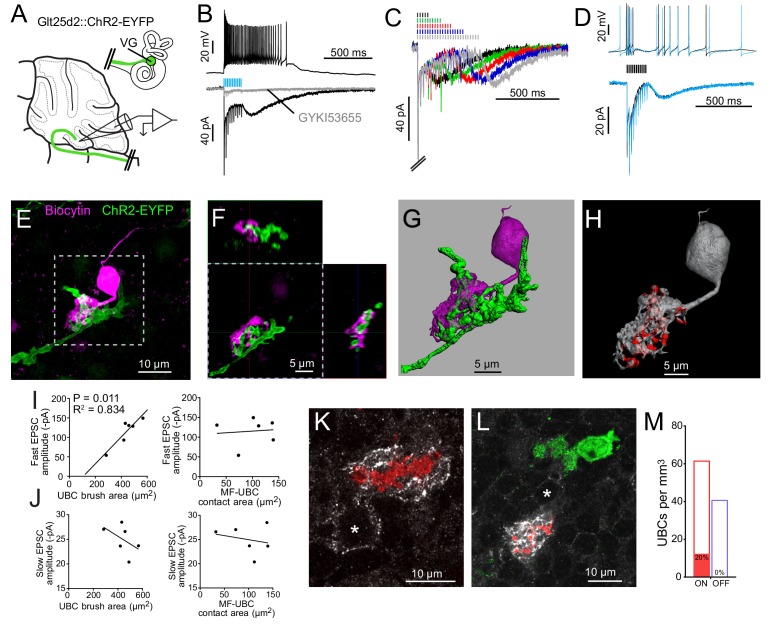
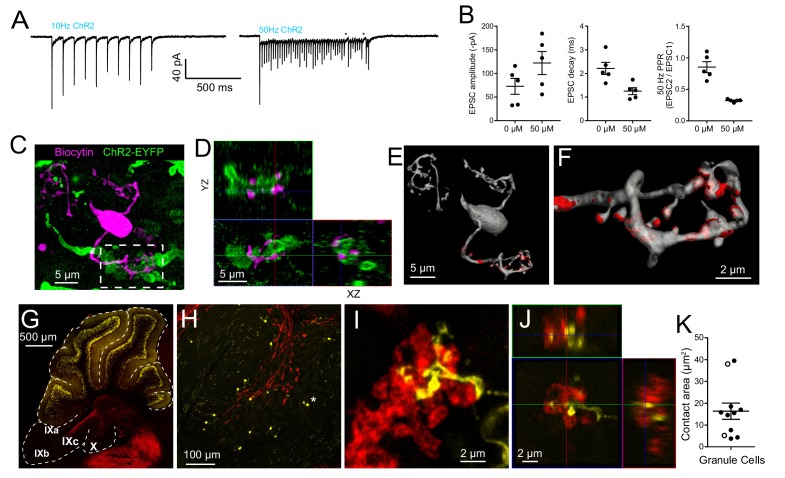
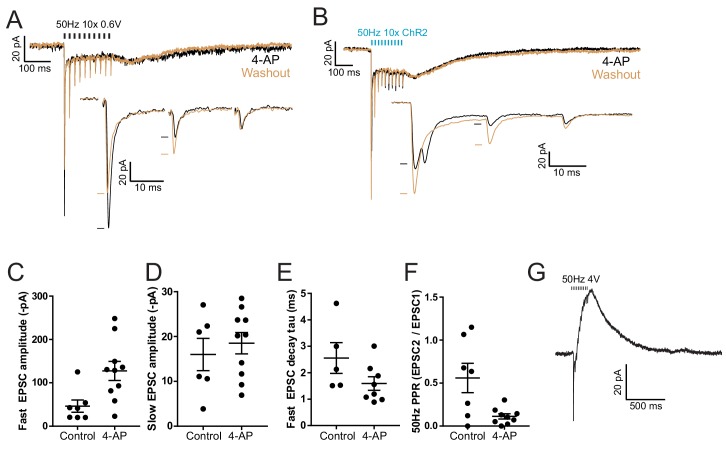
Figure 3. Primary vestibular afferents project to ON UBCs in lobe X.
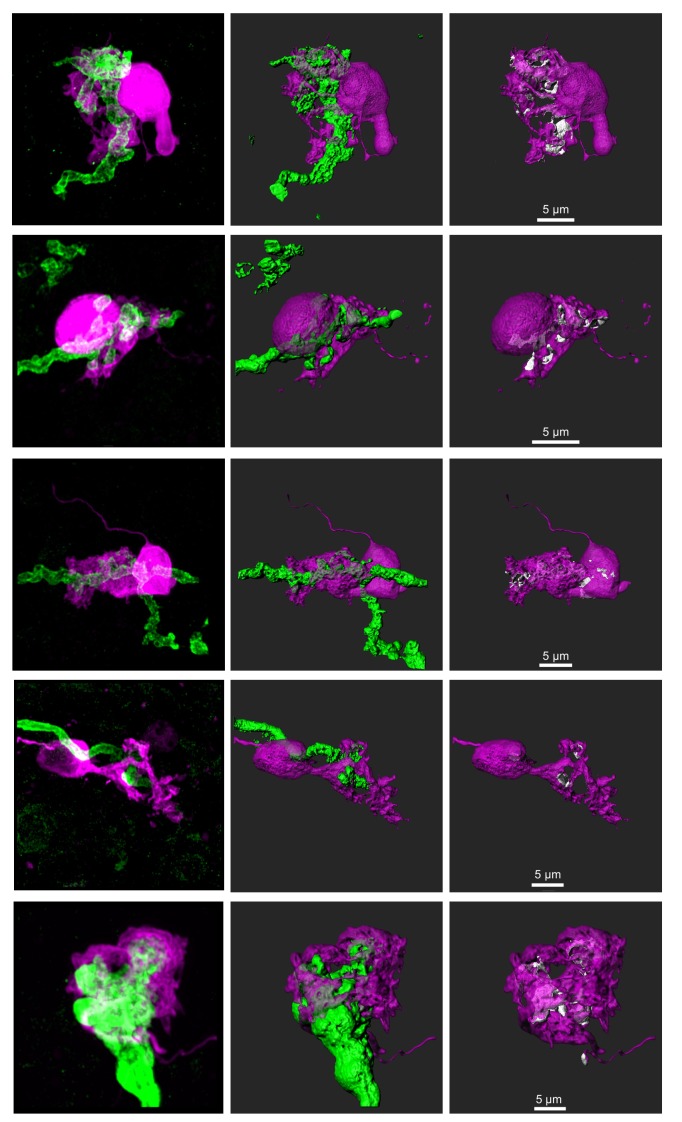
(A) In the Glt25d2::ChR2-EYFP cross, primary afferents from the vestibular ganglion (VG) expressed ChR2 and were activated by blue light during whole-cell recordings of UBCs in an acute slice preparation. (B) Mossy fibers were activated by LED light pulses (50 Hz 0.25 ms) that evoked spiking responses in postsynaptic UBC that outlasted mossy fiber activation. In the same cell in voltage clamp (below) light pulses evoked fast EPSCs that depressed, followed by a slow inward current. 50 μM GYKI53655 blocked the majority of the inward current. This slow AMPAR-mediated current after the offset of stimulation is diagnostic of an ON UBC. This case was without 4-AP in the bath. All UBCs that had light evoked PSCs were ON UBCs (n = 13). (C) 50 Hz light stimulation of various train durations illustrated as lines above the traces. The slow AMPAR-mediated current begins at the offset of stimulation, consistent with re-activation of AMPARs as they recover from desensitization while glutamate gradually leaves the synapse. (D) Spiking response (top) and EPSCs (bottom) evoked by electrical stimulation (3.8 V, 50 Hz, 0.25 ms, black) were similar to those evoked by ChR2 stimulation (50 Hz 0.25 ms, blue) in the same cell. (E) UBCs were filled with biocytin and recovered in 6/13 cases. This UBC received input from ChR2-EYFP expressing primary vestibular afferent. Maximum intensity projection. (F) Orthogonal view of the boxed region in B, showing UBC brush wrapping around mossy fiber. (G) Surfaces were created on the fluorescence to characterize the structure of the mossy fiber-UBC synapse. (H) A one voxel thick contact layer between the UBC and mossy fiber surfaces was made to calculate the apposition area between the two surfaces (shown in red). The calculated apposition area of this mossy fiber to UBC contact was 137.66 μm2. (I) The postsynaptic EPSC correlated with the area of the UBC brush (left), but did not correlate with the contact area between the mossy fiber and brush (right). Currents are in the presence of 4-AP. (J) The slow EPSC did not correlate with the UBC brush area (left) or contact area between the mossy fiber and brush (right), suggesting that this current is due to the action of glutamate at distant receptors. Currents are in the presence of 4-AP. (K–L) In Glt25d2::tdTomato cross, tdTomato+ primary afferents were seen innervating the brushes of mGluR1+ UBCs (white), but not calretinin+ UBCs (green). Soma of mGluR1+ UBCs identified with *. Single image planes. (M) 20% of counted mGluR1+ UBCs were contacted by tdTomato+ primary afferents. No counted calretinin+ UBCs were contacted by these primary afferents. See also Figure 3—figure supplements 1–5.