Abstract
Increasing consumer awareness of potentially harmful pesticides used in conventional agriculture has prompted organic farming to become notably more prevalent in recent decades. Central European countries are some of the most important producers of blueberries, raspberries and strawberries in the world and organic cultivation methods for these fruits have a significant market share. Fungal pathogens are considered to be the most significant threat to organic crops of berries, causing serious economic losses and reducing yields. In order to ameliorate the harmful effects of pathogenic fungi on cultivations, the application of rapid and effective identification methods is essential. At present, various molecular methods are applied for fungal species recognition, such as PCR, qPCR, LAMP and NGS.
Keywords: Colletotrichum acutatum, Verticillium spp., Phytophthora spp., Botrytis cinerea, PCR, qPCR, molecular identification, phytopathogenic fungi, strawberry, organic agriculture
1. Introduction
Organic fruit production has been increasing constantly in recent decades and has also increased its market share in the production of food worldwide. Strawberry, blueberry and raspberry fruits are important products of Central Europe and increasing consumer demand to introduce organic methods of fruit cultivation is a major reason to seek alternative ways to reduce losses. The main concerns of food producers are diseases caused by fungi, these pathogens attack plants and fruits from the early stages of sowing to the moment of market sale, thereby causing the unpredictable spoilage of products. The crucial plant pathogens discussed in this review are those from the genera Verticillium and Phytophthora as well as species such as Colletotrichum acutatum and Botrytis cinerea.
For many years, morphological methods of identification have been applied for the purposes of recognizing the causal agents of soil-borne diseases. However, these traditional methods are time consuming, error-prone and occasionally inaccurate. Because of these disadvantages, more efficient methods, such as adopting analytical techniques which function at the molecular level are being used more frequently. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based methods allow for the multiplication of targeted fragments of DNA over a short periods of time in order to obtain enough genetic material for further research. The purpose of this review is to gather together the most important information concerning the molecular methods of identifying important berry pathogens.
2. Organic Plantations and Fungal Pathogens
The area of land under organic cultivation worldwide has increased fivefold since 1999. Since then, this area has increased from 11 to nearly 58 billion hectares in 2016, and the area has increased in every continent. As of 2016, Central Europe had more than a billion hectares increase in organic arable land area in comparison to 2007 which is [1]. Almost one-quarter of the organic lands on the globe [1]. Europe has nearly half of the worlds harvesting area of strawberry, blueberry and raspberry fruit [2] and Central European countries produce big share of those fruits with 335,000, 113,500 and 30,000 tones berries produced in 2017, respectively. What is more, this region holds quarter of the world’s raspberry harvesting area [2]. Europe noted 320% increase in production of strawberries, blueberries and raspberries from 2007 to 2016 [2]. Eleven percent of worlds strawberry farmlands in 2016 was organic and what is more, in European Union, nearly 20% of berries were grown in organic agricultures [3]. In addition to an increase in the land area of organic farming activity in Europe, the sales market for organic farm produce is also growing significantly. The enlargement of the market in the years 2000–2015 was more than 300% in both areas. The main reason for the higher sales indicator from 2005 to 2014, was the constant increase in the consumption of ecological foods [4]. Poland and Hungary, as two Central European countries, have relatively small markets. Yet, they produce a large share of the organic crops in the free trade area and that makes them important exporters of ecological products [5]. Poland alone was the 3rd biggest exporter of prepared fruits in the world with 429,600 tonnes of fruits exported in 2015. Strawberries and fruit juices are also important export products with 16,500 and 79,000 tonnes, respectively, being exported in 2015. In 2016, Poland was also the 3rd biggest fruit exporter in the world [2].
Fields cultivated using organic methods are particularly exposed to pathogens due to the exclusion of chemical spraying for the purposes of disease management. Central Europe countries have a relatively warm and humid climate [6], which are ideal conditions for the development of fungal diseases. Berries are especially vulnerable to the harmful effects of fungal pathogens due to their thin cell walls, growth close to the wet soil surface and exposure to rainfall. Fungal diseases can lower the yields even down to 50%, even with application of appropriate chemical sprayings [7,8]. The optimal treatment is even more difficult due to the fact that diseases can remain dormant even for many years, waiting for optimal conditions to attack theirs hosts [9,10,11,12]. The pathogens which repeatedly attack cultivations of soft fruits, as well the fruit harvest in cold storage, are typically various species of fungi. The most common and threatening fungi in Central Europe are those of the Verticillium and Phytophthora genera, as well as Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum acutatum that are involved in yield and quality losses of soft berry fruits. The abandonment of conventional fungicides creates the need for early and effective detection methods of causal agents of plant diseases to prevent the spread of disease to the entire crop during current and future growing seasons.
3. Fungal Pathogens—Characteristics, Occurrence, Properties and Threats to Organic Farming
3.1. Verticillium spp.
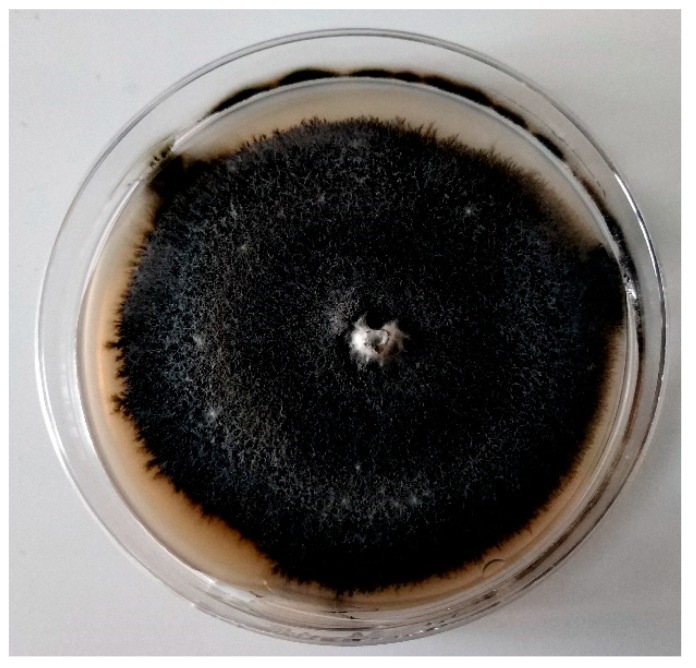
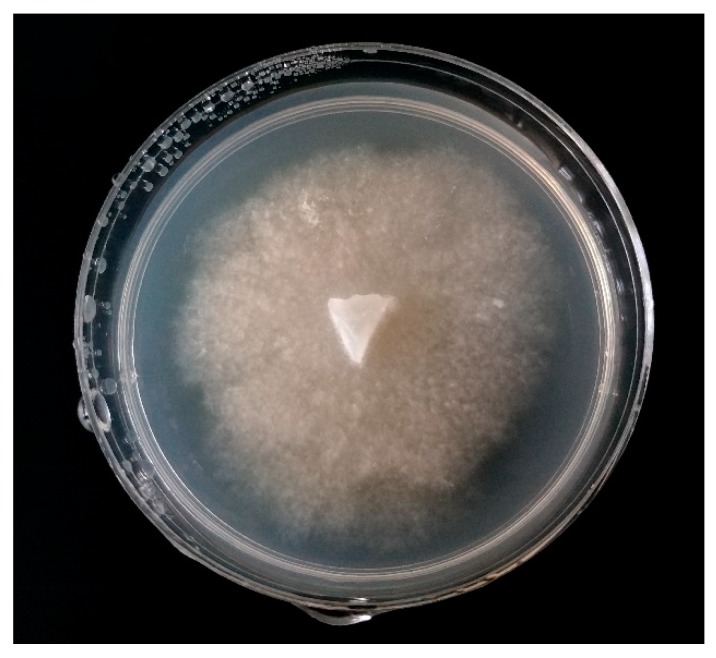
Fungi belonging to Verticillium spp. attack various species of fruits, vegetables, flowers and forest trees, including many species of soft fruits. Theirs host range includes: strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duchesne), red raspberry (Rubus idaeus), black raspberry (Rubus occidentalis), thimbleberry (Rubus parviflorus) and some cultivars of blackberry (Rubus ursinus). Only 5 families of plants, such as: Cactaceae, Gramineae, Gymnospermae, Monocotyledoneae and Polypodiaceae; are reported to be resistant or immune to soil-borne disease called Verticillium wilt [13,14,15]. V. dahliae and V. albo-atrum are two species with the most significant pathogenicity amongst the 10 which have been distinguished recently: V. albo-atrum, V. alfalfa, V. dahliae, V. isaacii, V. klebahnii, V. longisporum, V. nonalfalfae, V. nubilum, V. tricorpus and V. zaregamsianum [16]. Most of Verticillium species are not host-specific, and symptoms of infection vary between carriers, thus there are no universal signs of the disease on the plant. Some of the species of the genus may easily be distinguished by the shape of their microsclerotia and the length of the conidia they form on hosts and potato dextrose agar (PDA) [16]. Hyaline colonies formed on agar plates are whitish, turning darker with time (Figure 1), and they produce bountiful conidia [17,18,19,20]. The fungus degrades the cell walls of the host with several enzymes, which causes necrosis and other symptoms [21]. One of these enzymes is polygalacturonase [22] and its production level is related to the degree of fungus pathogenicity [23]. Moreover, Verticillium wilts are easily spread via contaminated plant material, soil and equipment. The conidia-producing specimen—V. albo-atrum is spread via air currents. When the wilt is securely situated in soil, it can survive for more than 25 years [9,15]. As a result of infection, the probability of the infected plant producing fruit is vastly reduced [15]. The plant often becomes infected through wounds in the roots [24]. The most effective way to control the disease is through the elimination of contaminated plants from the field [21], thus the rapid and efficient identification of the pathogen is obligatory.
Figure 1.
Verticillium sp. isolated on PDA medium from ecological strawberry plantation after 10 days of incubation in 22 °C.
3.2. Phytophthora spp.
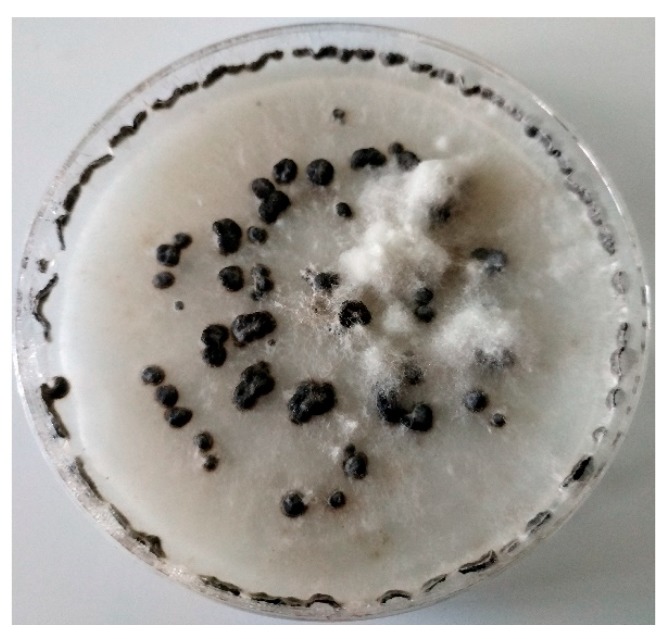
The Phytophthora genus includes at least 124 described species [25]. The pathogen infects a wide variety of plants worldwide, and its introduction to a new continent can damage the whole ecosystem. In Victoria, Australia, Phytophthora cinnamomi, as well as 13 other species in the taxa is a leading pathogen which has been discovered in the soil. The fungus is an important threat to native plants on the continent and can harm fruit plantations [26]. European and American strawberry and raspberry plantations are also attacked by Phytophthora, causing crown and leather rot, resulting in the dieback of plants and severe harvest reduction. Fungi occurring in the soil, belonging to the Phytophthora spp., are not host specific, and are a threat for both, strawberry and red raspberry. Disease manifestations on fruits are similar to those caused by Colletotrichum acutatum or Verticillium dahliae and are often misdiagnosed. In a study from 2018, Wilcox’s team proved that the main raspberry pathogen present in soil was Phytophthora rubi and that it was the main causative late-summer symptom of disease [27,28,29,30]. The selective media utilized for Phytophthora sp. isolation are V8 juice agar (V8) and cornmeal agar (CMA) with the addition of various antibiotics. Antibiotics and specific antifungal agents are added to inhibit the development of bacteria and other than Phytophthora sp. fungi competing for resources. The morphological identification of colonies may be difficult because random mutations and the different growth conditions present in nature may lead to a variability in the phenotype of the species. An overlap of morphological features of the genus also impedes accurate identification. Nevertheless, the size of the sporangium and papilla, as well as the appearance of sporangia are commonly considered for the classification of the fungus (Figure 2) [31].
Figure 2.
Phytophthora sp. isolated on PDA medium from ecological strawberry plantation after 10 days of incubation in 22 °C.
3.3. Botrytis cinerea
Botrytis cinerea, which causes gray mold, is an important necrotrophic fungus infecting more than five hundred species of plants [32,33,34,35], including strawberry and raspberry [10,34,36,37]. When considering the impact of fungus on fruit production, it took second place in the list of top ten fungal pathogens of molecular plant biology in 2012 [38]. The susceptibility of strawberry plants to the fungus is known to severely decrease harvests, even down to 50% [36]. The presence of the pathogen may remain hidden. In that case necrotrophic disease may be triggered by outside conditions, such as rainfall, a relative humidity higher than 80% for at least 4 hours, and an appropriate ambient temperature of 2–28 °C [10,11,35,39]. The pathogen can propagate on harvested strawberry, raspberry, blueberry and blackberry fruits at temperatures above freezing, which is a significant problem for the cold storage of soft fruits [40]. The disease may occur on fruits at any time from seedling to sale, what makes it difficult to predict and effectively counteract [38,41]. However, it is known that ripe fruits are most susceptible to infection [42]. In order to infect the host, spores are produced and spread, mainly conidia distributed by wind, rain and insects [43,44]. Fungus germ tubes and appresorias may produce an extracellular matrix, which helps them to attach to the cell walls of hosts and degrades them with enzymes [45]. In some cases, pathogens may penetrate the cuticle without the secretion of enzymes [46]. Invasions through wounds and blossoms are also often detected [40,47]. Pollinating insects such as honey bees have the potential to disperse disease in a similar fashion [48]. B. cinerea colonies grown for 7 days at room temperature on a PDA medium produces abundant whitish mycelium, which becomes darker with time (Figure 3). However, some of the isolates may have diminutive mycelium and produce a yellow pigment on PDA, which is undeveloped on other commonly used medias [49,50]. Conidia, ovoid or ellipsoid and one-celled, are on average 8–13 µm in length and 4–7 µm in width and are dispersed by the air [50].
Figure 3.
Botrytis cinerea isolated on PDA medium from ecological strawberry plantation after 10 days of incubation in 22 °C.
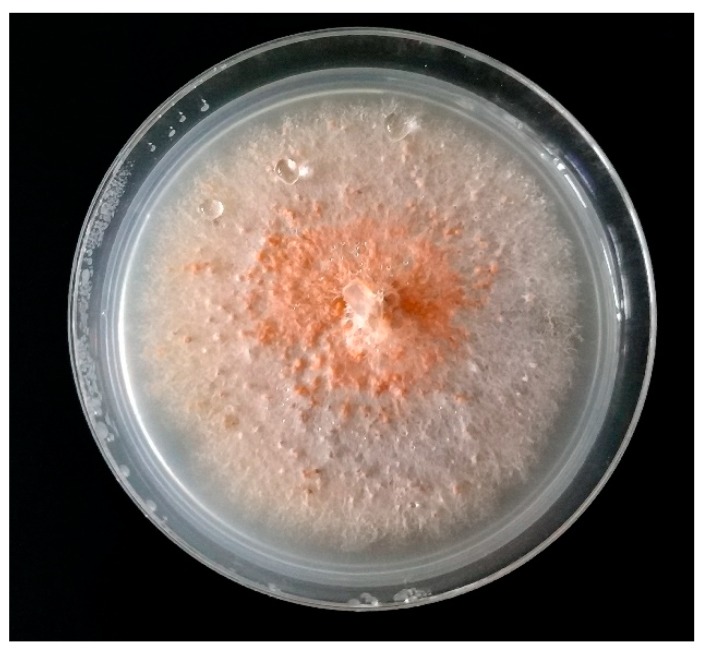
3.4. Colletotrichum acutatum
Anthracnose is a disease caused by Colletotrichum acutatum. The fungus attacks a wide range of plant species around the world [51] and is known mainly as a pathogen of strawberries. Colletotrichum spp. have been evaluated as the 8th most important fungal pathogen in plant biology [38]. Infection may remain dormant until the fruit is stored, and then cause losses of up to 100% [37]. The fungus is necrotrophic lifestyle, and causes black spots to form on strawberry fruits, additionally attacking roots, crowns and leaves [52,53,54,55]. The colonies of the pathogen isolated on PDA are whitish at first, becoming gray with time and the reverse of the Petri dish is pink or pale orange (Figure 4). Conidia, observed under a light microscope, are 8–16 × 2.5–4 µm in size, one-celled, straight, but pointed at the end (fusiform). Conidial appresoria are grey and globular in shape [54,56]. The fungus is mainly dispersed by rain, and can enter the host via any plant tissue. Dispersal of conidia can reach as far as 1.75 m through splashing and the infection of one plant in the field by the pathogen proceeds to the whole cultivation [57]. Most frequently C. acutatum infects strawberries through the crown, as there is a humid microclimate [58]. The fungus is capable of wintering in the soil for at least two winters with temperatures falling below 0 °C, this causes anthracnose to develop in subsequent years [12,59]. This is the reason why optimal treatment for the disease is necessary not only for the harvest in the current year, but also for consecutive seasons.
Figure 4.
Colletotrichum acutatum isolated on PDA medium from ecological strawberry plantation after 10 days of incubation in 22 °C.
4. Detection Methods of Plant Pathogenic Fungal Species
4.1. Traditional Methods
Traditional methods of fungal pathogen identification include experienced scientists studying their morphological attributes such as colony appearance and the production of asexual structures on microbiological media or on the host. Samples isolated on adequate agar media may be observed using a light microscope to track the presence of the slightest structures. This method is time consuming and only mature colonies may be evaluated. Occasionally colonies have to meet certain conditions to produce conidia and this may cause inconvenience in laboratory work-flow [60,61,62]. Selective medias have been proposed and used for identification, for example Botrytis Selective Media (BSM) for Botrytis cinerea [63]. The recognition of external infection symptoms induced by fungi on theirs hosts can also be used to verify the pathogen, although most species are not host specific and plants may be inhabited by many fungi. The lack of carrier specificity and symptom differences between plant populations at different latitudes makes an accurate identification based only on the morphology of the colonies very difficult or even impossible. Furthermore, interpretations of the pathogen’s morphology are subjective and highly reliant on one’s experience. The human factor may lead to an incorrect identification of the pathogen, causing misguided plant protection activities.
4.2. Molecular Methods
In recent years, molecular methods are being more and more willingly used by researches in many fields. They are also widely applied in order to identify fungal diseases or for recognition of new fungal species and the description of pathogen populations. The identification of fungi is in fact more accurate when molecular markers are applied, compared with assignment to the species based only on morphology [64,65] and the technique may be used by personnel without specific taxonomic expertise [66].
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) process includes the in-vitro amplification of targeted genes from previously isolated DNA [67]. After the reaction, an electrophoresis is performed on the agarose gel of the fragments produced which are stained with EtBr (Ethidium bromide) or SYBR Green. The occurrence of a fragment of specific length confirms the presence of a pathogen. Further sequencing of the products may also be performed to ensure the specificity of the obtained amplicon.
The modification of the method, allowing the observation of the amplification results in real-time and the quantification of the genetic material in the sample is quantitative PCR (qPCR) [68,69]. An assay has many advantages in comparison with PCR. The reaction does not require further electrophoresis, as the analytical techniques used in the reaction allows for the observation of the size of the fluorescent signal which is proportional to the amount of amplified DNA. The qPCR technique also allows for the analysis of from 96 to 386 samples simultaneously as it is performed on plates [66]. A comparison of PCR with qPCR by Garrido’s team demonstrated that the qPCR reaction is 100 times more sensitive compared with PCR when it is applied to the identification of plant pathogenic fungi on strawberry fruit [70].
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) is another method utilizing DNA polymerase, with the distinction of a constant temperature throughout the whole reaction and the utilization of two or three sets of primers. The assay is highly specific due to the presence of a larger number of primers in comparison with PCR. For the same reason, the reaction is insensitive to contamination with non-specific DNA [71]. LAMP can be verified directly through the examination of a color change in the samples or by electrophoresis [66]. What is more, Bst polymerase which are often used in the reaction are less susceptible to inhibitors compared with Taq polymerase. Therefore, LAMP does not always require DNA isolation and may be performed directly from the environmental sample [72]. Also, due to the constant temperature character of the reaction LAMP doesn’t require specialist equipment such as a thermocycler [73].
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) belongs to the methods that were developed after automated Sanger assays—‘first generation’ for sequencing genetic material. The most important advantage of NGS is the ability to sequence billions of nucleotides during one run, thus sequencing whole genomes has become available for academic uses [74,75]. Table 1 presents the data concerning genome assemblies of fungal pathogens described in this paper. Although most of the genomes have already been deposited in the international bioinformatics database, the information is not sufficient to describe all features and functions of these organisms and still there are a lot of work to get to know them well.
Table 1.
Sequenced genomes of fungal pathogens from NCBI genome database.
| Targeted Organism | Number of Genome Assemblies | Median Total Length (Mb) | Median Protein Count | Median GC% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verticillium dahliae | 11 | 33.2952 | 10393 | 55.6 |
| Verticillium alfalfae | 2 | 32.7521 | 10237 | 55.4 |
| Verticillium tricorpus | 2 | 35.5915 | nd | 57.4 |
| Verticillium nonalfalfae | 2 | 32.9671 | 9431 | 54.8 |
| Verticillium albo-atrum | 1 | 36.4685 | nd | 56.5 |
| Verticillium longisporum | 2 | 99.8546 | 20932 | 53.05 |
| Verticillium isaacii | 1 | 35.6909 | nd | 57.5 |
| Verticillium zaregamsianum | 1 | 37.1319 | nd | 57.5 |
| Verticillium klebahnii | 1 | 36.0824 | nd | 57.6 |
| Verticillium nubilum | 1 | 37.9116 | nd | 53.7 |
| Phytophthora infestans | 2 | 190.329 | 17797 | 36.9 |
| Phytophthora capsici | 7 | 56.0343 | nd | 49.9 |
| Phytophthora ramorum | 23 | 40.7668 | nd | 54 |
| Phytophthora nicotianae | 3 | 71.414 | 13910 | 50.2 |
| Phytophthora cactorum | 2 | 63.5331 | 24172 | 49.65 |
| Phytophthora rubi | 2 | 76.9186 | nd | 53.15 |
| Phytophthora fragariae | 2 | 76.4756 | nd | 53.2 |
| Phytophthora cinnamomi | 4 | 58.3834 | nd | 54 |
| Phytophthora parasitica | 9 | 54.2899 | 27003 | 49.6 |
| Phytophthora kernoviae | 11 | 38.1112 | 9990 | 50.3 |
| Phytophtora lateralis | 5 | 49.0253 | nd | 53.3 |
| Phytophthora palmivora | 1 | 107.773 | 24271 | 48.7 |
| Phytophthora sojae | 1 | 82.5976 | 26489 | 54.4 |
| Phytophthora litchii | 1 | 38.2009 | nd | 49.2 |
| Phytophthora colocasiae | 1 | 56.5926 | nd | nd |
| Phytophthora agathidicida | 2 | 37.2895 | nd | 52.6 |
| Phytophthora pluvialis | 2 | 53.178 | nd | 54.2 |
| Phytophthora multivora | 2 | 40.1961 | nd | 51.9 |
| Phytophthora pinifolia | 1 | 94.6173 | nd | 54.9 |
| Phytophthora cryptogea | 1 | 63.8393 | nd | 51.9 |
| Phytophthora cambivora | 1 | 230.616 | nd | 52.9 |
| Phytophthora plurivora | 1 | 40.4412 | nd | 51.7 |
| Phytophthora megakarya | 1 | 101.505 | 34804 | 48.7 |
| Phytophthora x alni | 1 | 236 | nd | 51.3 |
| Phytophthora pisi | 1 | 58.8567 | nd | 54.6 |
| Botrytis cinerea | 4 | 41.8726 | 13703 | 42.26 |
| Colletotrichum acutatum | 2 | 48.5246 | nd | 50.8 |
nd.—no data present.
It is known that inter- and intra-specific variability are likely widespread in fungi. This fact has implications for research on fungal taxonomy, phylogenetics, evolution, and population genetics. However, described methods can be successfully used to portray intra- and inter-specific variability of microorganisms occurring in the environment, in particular pathogenic fungi, but also the other fungi. More specific approaches have been already developed, such as: Restriction Fragments Length Polymorphism (RFLP), Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD), Terminal Restriction Fragments Length Polymorphism (tRFLP) and Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP). When planning the experiment, it is important to remember to take into account native strains of fungi that are present in the habitat, as intra-specific variability can affect the analysis [76,77,78]. It is also important to highlight that detection limits of the fungi reported in this work can only be treated as guidelines and not certainty, as those limits are dependent on numerous factors, including the type of medium, age of the culture or isolation methods.
4.2.1. Verticillium spp.
Many studies have utilized a comparison with the ITS region in the phylogenic analysis of Verticillium spp. [19,79]. Some of protein-coding genes were also used for distinguishing species, such as: cytochrome c oxidase III (COX3), NADH dehydrogenase subunit I (NAD1), actin (ACT), elongation factor 1-α (EF), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD) and tryptophan synthase (TS) [16,19]. The detection of V. dahliae, V. tricorpus and V. albo-atrum in strawberry fields was performed using five simplex loci, including ACT, EF, GPD, TS genes and ITS region. The discrimination between the species was performed using multiplex PCR with listed markers with an irrefutable outcome [79]. The ITS region sequencing was again successfully used for the confirmation of V. dahliae as an olive tree pathogen [20]. However, Yu’s team was not able to distinguish between V. dahliae and V. longisporum based only on the analysis of the ITS1-5.8S marker, thus COX3 and NAD1 genes were also included in the study to make the analysis more specific [19].
Lievens’ team developed a real-time PCR assay for the identification and quantification of 3 species linked to Verticillium wilt on tomato plants. The targeted marker was the ITS1 region. Primers were specific to all three targeted species, those being V. albo-atrum, V. dahliae and V. tricorpus, and the amplification did not occur with any of the additionally tested fungi [80]. The marker gene was also used in a similar study to estimate the number of strawberry pathogens in the soil samples, including Verticillium spp. The method was able to detect 17.7 pg of the V. dahliae DNA [81]. The ITS marker was also applied in the quantification of V. dahliae in affected strawberry roots and soil. The detection limit for the fungus genetic material was 0.93/µL pg and the lowest amount of V. dahliae detected in soil equaled 10.48 pg/µL [82]. A different study, demonstrating differentiation between V. dahliae and V. longisporum and the identification of V. tricorpus by qPCR was published in 2011. The amplification of the ITS region of V. tricorpus was performed with specific primers and was able to detect 0.1 microsclerotia/g of soil. V. dahliae and V. longisporum were distinguished based on the sequence of the β-tubulin gene, and the assay was able to track as little as 0.5 fungus microsclerotia/g of soil [83,84]. An analysis of the abovementioned β-tubulin primers, with the addition of an ITS marker, were also used for the identification of V. longisporum oilseed rape in qPCR. The β-tubulin primers were specific for the targeted specimen, however they did not detect 3 of the isolates. This may confirm that the new taxonomy of fungi proposed by Inderbitzin is correct [16]. The ITS marker was also highly specific to the genus, and detected 0.56 fg of fungal DNA. Despite that, the marker was not able to distinguish V. longisporum from other species in the Verticillium genus used in the study. Another disadvantage of the ITS primers was that they were also specific for B. cinerea and a few Alternaria isolates [85]. The quantification of V. dahliae in lettuce leaves was successfully performed by Klosterman. The assay amplified the β-tubulin targeted gene and was able to detect 2.5 fg of fungal DNA 21 days after the inoculation of the pathogen on the plant [86]. Another marker successfully used in qPCR was an intergenic spacer of genomic DNA (IGS). The reaction was performed to identify V. dahliae and V. tricorpus pathogens on various plants, including strawberry. Two pairs of created primers were specific only to V. dahliae and V. tricorpus, and none of the non-targeted species were amplified. Bilodeau’s team succeeded in detecting as little as 3 fg of fungus DNA with the assay. Also, they estimated the number of copies of IGS in the pathogen genome, comparing the amplification of the aforenamed region with the single-copy genes such as: endochitinase, β-tubulin and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (G3PD). They averaged the number of the IGS region in different isolates to 46 copies in the haploid genome with the qPCR assay. In the study, an additional specific primer pair of IGS for V. albo-atrum was designed, however, in an initial examination only V. dahliae was apparent in the samples. This is why only the first pair of primers was used in further stages of research [87]. Another gene targeted for the detection of V. dahliae in potato crops was an extracellular trypsin protease (VTP1). The PCR technique detected 25 pg of fungal DNA, but primers were also specific for V. longisporum. The qPCR technique was 10 times more sensitive than the PCR technique with the same primers. Also, the duplex qPCR technique additionally targeting the potato actin gene was developed and was able to detect as little as 0.25 pg of V. dahliae DNA [88]. The multiplex approach was further investigated with the VTP1 gene of V. dahliae and the internal control actin gene (ACT) of Solanum tuberosum. The assay was performed in field conditions with remarkable reliability [89]. The quantification of soil-borne diseases on strawberry fruit was performed with the application of ITS1 primers as described previously by Lieven’s team [80,81]. In agreement with their discoveries, in the Ozyilmaz study, the marker was specific for at least 5 of the Verticillium species. The reaction detected 0.6 pg of pathogen DNA [81]. The identification of Verticillium species in soil was also performed by the Tzelepis’ team using a qPCR assay with newly designed primers for V. dahliae, V. longisporum, V. tricorpus and V. albo-atrum. The detection level equaled 5 and 6 fg DNA/g of soil for V. longisporum and V. dahliae, respectively, and the last two fungi were not detected in the soil samples [90]. The most important information described above are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
Selected primers designed for molecular analysis of Verticillium spp.
| Targeted Organism (Number of Strains Analyzed) | Assay | Marker | Primers Sequences 5′-3′ | Primers Authors | Primers Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
V. albo-atrum (5) V. tricorpus (7) |
multi-plex PCR | ITS 1 | CCGGTCCATCAGTCTCTCTG CTGTTGCCGCTTCACTCG |
[79] | [79] |
| V. longisporum (42) | EF 2 | AAGTGGAGCCCCGTATCTTGAAT CAACTGGCAACAGGGCTTGAAT |
|||
| V. isaacii (14) | CGATGTCGCGATGACCTCG CGGCAGCCTCCTAAACATGG |
||||
| V. klebahnii (7) | ACATCCTGAGGCTGCTTGAGA CGGCAGCCTCCTAAACATGG |
||||
| V. zaregam- sianum (10) | GPD 3 | GGTTTCCTCCCCTCACACG CCACCCTTGATGTGGGCGGA |
|||
| V. longisporum (42) | CCCCGGCCTTGGTCTGAT TGCCGGCATCGACCTTGG |
||||
| V. alfalfae (7) | TCATGCCCCCTTTGTTCATCGAT TGCCGGCATCGACCTTGG |
||||
| V. albo-atrum (5) | ACT | GGCCTCGATAGCATCGCC CTGGATGGAGACGTAGAAGGC |
|||
| V. tricorpus (5) | CGTGCTGTCTTCCGTAAGTTTG CTGGATGGAGACGTAGAAGGC |
||||
| V. nonalfalfae (9) | TS 5 | CCTCGAAAAATCCACCAGCTCTA GTGGTTGAGATCCTCACGCTTC |
|||
| V. nubilum (4) | GGTCCCCCTCGTTCATGCAATC GTGGTTGAGATCCTCACGCTTC |
||||
| V. dahliae (10) V. longisporum (10) | PCR | ITS 1 | GGA AGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC |
[91] | [19] |
| COX3 6 | TGATTTAGAGATST AATATCAGAAG CCGTGGAAACCTGTSCCAAAATA |
[19] | |||
| NAD1 7 | ATGGCSAGTATGCAAAGAAGA GCATGTTC TGTCATAAASCCACTAAC |
[92] | |||
| Verticillium spp. (7) | qPCR | ITS 1 | CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA AAAGTTTTAATGGTTCGCTAAGA |
[80] | [80] |
| V. tricorpus (4) | qPCR | ITS 1 | CCGGTGTTGGGGATCTACT GTAGGGGGTTTAGAGGCTG |
[91] | [83] |
| V. dahliae (9) + V. longisporum | β-tubulin | GGCCAGTGCGTAAGTTATTCT ATCTGGTTACCCTGTTCATCC |
[84] | ||
| V. longisporum (11) | β-tubulin | GCAAAACCCTACCGGGTTATG AGATATCCATCGGACTGTTCGTA |
|||
| V. dahliae (1) + V. longisporum (1) | qPCR | ITS 1 | CAGCGAAACGCGATATGTAG GGCTTGTAGGGGGTTTAGA |
[93] | [93] |
| V. dahliae (44) | qPCR | IGS 8 | CGTTTCCCGTTACTCTTCT GGATTTCGGCCCAGAAACT |
[87] | [87] |
| V. tricorpus (13) | endochitinase | TAGTAGAATACTAGATARCTAG AGCCTAGGTCTTTATAGCTAG |
|||
| V. dahliae | CTCGGAGGTGCCATGTACTG ACTGCCTGGCCCAGGTTC |
||||
| V. dahliae | β-tubulin | GCGACCTTAACCACCTCGTT CGCGGCTGGTCAGAGGA |
|||
| G3PD 9 | CACGGCGTCTTCAAGGGT CAGTGGACTCGACGACGTAC |
||||
| VTP1 10 | GCGGTGGCTGGTTCCTATCAAC CAACGACTTCGCCATCTGGAAG |
||||
| V. albo-atrum group 1 (isolation from soil) | qPCR | actin | GCCCTCTTCCAGCCCTCCGTTCTC TCGGCGTGGTTTTGTGGTGAG |
[87] | [94] |
| V. albo-atrum group 2 (isolation from soil) | qPCR | IGS 8 | CGTGTTTAGTGTATTTCACCCTTG TCGCAGAGTAGTACGATTTCTC |
[94] | |
| V. longisporum (isolation from soil) | CGAGGAGTGAAAAGAAAACGGTTA CGCGCCGAGGCTAGTCAC |
||||
| V. dahliae (5) | qPCR | not explained in the study | TCCTAGGCAGGCGAGCAG TAGGGCTGTCTGTCGGTGA |
[90] | [90] |
| V. albo-atrum (4) | TTTCACGACCGATGAAAGCG CACATCGGCGAGGATCTGTC |
||||
| V. tricopus (4) | CACCCTCGGGCACACCAATA TCCGTGGAGGTTGAGCGCTAT |
||||
| V. longisporum (4) | CGAGGAGTGAAAAGAAAACGGTTA CGCGCCGAGGCTAGTCAC |
1 internal transcribed spacer, 2 elongation factor 1-α, 3 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, 4 actine, 5 tryptophan synthase, 6 cytochrome oxidase subunit III, 7 NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1, 8 intergenic spacer of genomic DNA, 9 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, 10 extracellular trypsin protease.
A LAMP assay with newly designed primers for the selection of previously established random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) makers was performed by Moradi’s team. The reaction was able to detect as little as 50 fg DNA from V. dahliae isolates, which was 10,000 times more sensitive than that conducted by the team nested-PCR. What is more, none of non-targeted species were amplified in the reaction, including other soil-borne pathogens and other Verticillium species [95].
The phylogenic analysis of Verticillium dahliae with the application of NGS was completed in 2013. The team also acquired a draft genome sequence of the fungus [96]. As a continuation of the study, Faino’s team assembled a complete and gapless genome of the pathogen [75,97]. Further genome sequencing of V. dahliae genetic material obtained from strawberry pathogenic strands resulted from c. 33 Mb assembly with 44–80-fold coverage [98]. With the de novo genome sequencing of V. nonalfalfae, Jelen’s team additionally identified the mitochondrial genome of the fungus. The size of the acquired mitochondrial sequence averaged 27% GC content and close to 26 kb of nucleotides [99]. The complete V. longisporum genome assembly acquired in 2018 was estimated at 70 Mb, and the mitochondrial genome equaled c. 27 kb [100].
4.2.2. Phytophthora spp.
In order to identify species in the Phytophthora genus, ITS1 and ITS2 were amplified using PCR and sequenced. The variability of ITS2 was less significant in comparison with ITS1, but both of the markers were useful in species identification within the genus [101]. Ristaino’s team developed an assay for rapid identification within the genus. They amplified the ITS region, and for species recognition, employed restrictions enzymes. Additionally, they developed a specific primer for P. capsici (PCAP) [102]. Cooke’s team analyzed the ITS marker of various Phytophthora species, containing red raspberry and strawberry pathogens for phylogenic purposes [103]. Also, they designed genus-specific primers for the Phytophthora spp. with the application of the cytochrome oxidase I (COX1) gene with high specificity. In order to establish a greater distinction between P. ramorum, P. nemorosa, and P. pseudosyringae, they used nested PCR with species-specific primers. The primers amplified targeted species sufficiently and did not produce a sequence with any of the non-targeted species added in the study [104]. The ITS marker was also used for the identification of the Phytophthora pathogen causing rot of cranberry [105]. Further, the multilocus approach for the phylogenic analysis of the genus was developed by Blair’s team. In the study, 27 loci were targeted, and 7 loci were successfully amplified: 28S ribosomal DNA, 60S ribosomal protein L10, β-tubulin, elongation factor 1 α, enolase, heat shock protein 90 and the TigA gene fusion protein. The first two markers were both amplified within the genus, but the second one was not long enough (496 bp) to deliver sufficient phylogenetic information. β-tubulin, enolase and TigA loci provided satisfactory phylogenetic information among the Phytophthora genus. Next, heat shock protein 90 and elongation factor 1 α produced a moderate level of information among most clades [106]. In a continuation of the cited study, Martin’s team provided an additional analysis of 4 mitochondrial loci within the genus. The markers used in the report: cytochrome c oxidase subunit II (COX2), NADH dehydrogenase subunit IX (NAD9), 40S ribosomal protein S10 (RPS10) and protein translocase subunit SecY (SECY) loci, and the phylogenic tree was comparable with the one constructed in the former study [25,106]. In a paper published in 2014, an analysis of the ITS marker was once more applied to the identification of Phytophthora spp. obtained from nursery plants, irrigation water, and potting media. Sixteen species within the genus were identified, then isolates from P. citricola complex were additionally sequenced with β-tubulin primers to ensure the specificity of the obtained products [107].
The first employment of the qPCR assay for monitoring Phytophthora spp. in different host tissues showed that the method may in fact be successfully used for this purpose. The assay contained the design of new primers for P. infestans and P. citricola: specific GC rich nuclear satellite DNA with unknown function, and ITS1, respectively. The reaction was able to detect 1 µg of P. infestans and 10 ng of P. citricola through template DNA in the sample [108]. The detection of Phytophthora spp., as well as the species-specific identification of P. ramorum was also further performed. Both pairs of primers were targeted for the ITS gene. Also, primers for the detection of false-negatives were used with the implementation of the COX gene. The genus-specific primers amplified all of the Phytophthora species in the study, however, non-targeted isolates of Pythium were also amplified [109]. P. cactorum was one of the targeted species in the qPCR assay used for the identification of strawberry pathogens in the soil. The fungus was successfully detected in the amount of 8.6 fg/μL through the amplification of the ITS region with specific primers [81]. The ITS marker was also used for the identification of strawberry soil-borne pathogens. The qPCR assay detected 1 pg of P. cactorum’s DNA per 1 g of soil [110]. The identification of the pathogen causing late-summer disease symptoms on raspberry fruit was performed by Weiland’s team with the application of qPCR. Even though the disease was first connected to the presence of Verticillium dahliae, diagnostic tests produced conflicting results. Ultimately, qPCR indicated that the main cause of the late-summer symptoms of disease was Phytophthora rubi [29]. The multilocus approach was performed for the identification of P. colocasiae with the application of 3 markers: RAS-related protein (YPT1), G protein alpha-subunit (GPA1) and phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase (TRP1) genes. All of the amplifications were successful, thus the best sensitivity was demonstrated by YPT1, with the detection of 12.5 fg of fungal DNA. The pathogen was amplified using a qPCR assay 15 hours after the artificial infection of the plant; 3 hours earlier than in PCR [111]. The simultaneous detection of two pathogens, P. nicotianae and P. cactorum from strawberry tissues in the qPCR assay was also performed. The primers designed for the ITS region and the YPT1 gene were utilized with sufficient results. The assay was able to detect 10 fg and 1 pg of targeted DNA from P. nicotianae and P. cactorum, respectively [112]. The triple approach of detecting Malus Miller pathogens using qPCR was also verified in a recent study. Three pairs of primers for enolase (ENOL), ras-like protein YPT1 and HSP90 gene sequences were designed for P. hibernalis, P. cambivora and P. syringae. The primers were capable of simultaneously detecting 20 pg of the two first species and 0.2 pg of the third fungus genomic DNA [113]. Table 3 summarizes selected facts containing the primer sequences used in the above-described papers.
Table 3.
Selected primers designed for molecular analysis of Phytophthora spp.
| Targeted Organism (No. of Strains Analyzed) | Assay | Marker | Primers Sequences 5′-3′ | Primer Authors | Primers Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phytophthora spp. (15 in [101]; 14 in [102]) | PCR | ITS 1 | GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC |
[91] | [101,102] |
| Phytophthora spp. (51) | PCR | COX1 2 | GCGTGGACCTGGAATGACTA AGGTTGTATTAAAGTTTCGATCG |
[114] | [114] |
| COX2 3 | AAAAGAGAAGGTGTTTTTTATGGA GCAAAAGCACTAAAAATTAAATATAA |
||||
| P. ramorum | nested PCR | Spacer sequences between the COX 2 and COX1 gene | GTATTTAAAATCATAGGTGTAATTTG TGGTTTTTTTAATTTATATTATCAATG |
||
| P. nemorosa | AATAAAATTAATTTTAATATATAATTAG TATGTTTAATATCTGTAAATAATAG |
||||
| P. pseudo- syringae | CAGTTTCATTAGAAGATTATTTAC AAAATTGTTTGATTTTATTAAGTATC |
||||
| Phytophthora spp. (82) | PCR | 60S ribosomal protein L10 | GCTAAGTGTTACCGTTTCCAG ACTTCTTGGAGCCCAGCAC |
[106] | [106] |
| β-tubulin | GCCAAGTTCTGGGARGTSAT GCCAAGTTCTGGGARGTSAT |
||||
| Enolase | CTTTGACTCGCGTGGCAAC CCTCCTCAATACGMAGAAGC |
||||
| Heat shock protein 90 | GCTGGACACGGACAAGAACC CGTGTCGTACAGCAGCCAGA |
||||
| tigA gene fusion | TTCGTGGGCGGYAACTGG TCGTGGGCGGYAAYTGGAA GCCTACATCACGGAGCARA TCGCYATCAACGGMTTCGG CCGAAKCCGTTGATRGCGA GCCCCACTCRTTGTCRTACCAC |
||||
| EF 4 | GGTCACCTGATCTACAAGTGC CCTTCTTGTTCACCGACTTG |
||||
| P. infestans (1) | qPCR | GC-rich nuclear satellite DNA with unknown function | GCCAT CAAGACGTGCGAGA GCAGGGATTCGGGCATA |
[108] | [108] |
| P. citricola (1) | ITS 1 | TCAACCCTTTTAGTTGGGGGTC TTTAAAACAAAAAGCTACTAGCCCAGAC |
|||
| Phytophthora spp. (71) | qPCR | ITS 1 | TGCGGAAAGGATCATTACCACACC GCGAGCCTAGACATCCACTG |
[109] | [109] |
| P. colocasiae (49) | qPCR | YPT1 5 | GGTGTGGACTTTGTGAGTTTCAG AAGGGAGTTGGCACAACCATT |
[111] | [111] |
| TRP1 6 | AGCGCCTTAACGCTCCCT GAGCCCTTGAACCACTTGGG |
||||
| GPA1 7 | TTGGTGGCGTGTAGTCTGTG AGCTTCCGGTTGATGGTAGC |
||||
| Phytophthora spp. (15) | qPCR | YPT1 4 | ATGAACCCCGAATAGTRCGTGC TGTTSACGTTCTCRCAGGCG |
[115] | [115] |
| TRP1 6 | GAGGAGATCGCGGCGCAGCG GCGCACATRCCGAGVTTGTG |
||||
| GPA1 7 | GGACTCTGTGCGTCCCAGATG ATAATTGGTGTGCAGTGCCGC |
||||
| P. nicotianae (7) | qPCR | ITS 1 | CCTATCAAAAAAAAGGCGAACG TACACGGAAGGAAGAAAGTCAAG |
[112] | [112] |
| P. cactorum (7) | YPT1 5 | CATGGCATTATCGTGGTGTA GCTCTTTTCCGTCGGC |
1 internal transcribed spacer, 2 cytochrome oxidase subunit I, 3 cytochrome oxidase subunit II, 4 Elongation factor 1-α, 5 RAS-related protein, 6 phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase, 7 G protein α-subunit.
The ITS marker in the LAMP assay was used for the detection of P. ramorum in plants. Despite the lower sensitivity of LAMP compared to qPCR with the same marker, the reaction was successfully used to detect small amounts of the pathogen’s DNA in the sample [116]. The YPT1 gene was used in order to compare it to the effectiveness of the nested PCR and LAMP assays to identify P. melonis. Consequently, both assays were c. 1 000 times more specific than PCR. The LAMP reaction was able to detect 10 fg of fungal DNA, thus it may be utilized in the early stages of infection [117]. Si Ammour’s team confirmed this thesis, as they detected P. infestans with LAMP 24 hours after the artificial inoculation of potato plants [118]. The efficiency of the marker in LAMP for P. infestans identification was reinforced by Khan’s team study. The team compared PCR with nested PCR, qPCR and LAMP with the application of the YPT1 gene marker. LAMP was in fact the most sensitive reaction, being 10 times more sensitive than nested PCR and 100 times more sensitive than qPCR. What is more, the team detected the pathogen as soon as one hour after inoculation on the plant [119]. Taking under account the above mentioned results the detection limits of Phytophthora sp. was ranged from 1µg to 10 fg depending on selected method and tested species.
Whole genome sequencing of a few Phytophthora species has already been performed. In 2006, a draft of the genome sequences of P. sojae and P. ramorum were obtained. The genetic material of the fungi had a 9-fold coverage of the 95 Mb and a 7-fold coverage of the 65 Mb of P. sojae and P. ramorum genomes, respectively. The identification of a number of SNPs for both species was also achieved [120]. P. infestans whole-genome sequencing was also achieved with a 9-fold coverage assembly spanning 229 Mb of the pathogen’s genome [121]. Both of the abovementioned studies utilized a shot-gun approach, and the application of the Illumina platform was utilized for P. rubi and P. fragariae. The pathogen genetic material sequencing resulted in a 76-fold coverage of 5.88 Mb for P. fragariae and a 92-fold coverage of 6.96 Mb for P. rubi [122].
4.2.3. Botrytis Cinerea
Rigotti’s team proposed specific primers for a RAPD assay in PCR for the detection of 13 strains of Botrytis cinerea in fields of symptomless strawberry plants. They proved that the presence of 0.2 pg of fungal DNA in the sample is enough for pathogen detection with this method [123]. The application of the SCAR assay was applied for the development of a specific marker for the detection of B. cinerea, B. fabae, and B. fabiopsis. The proposed primers were capable of distinguishing species from each other, as well as detecting 400 pg of B. cinerea in the reaction [124]. The markers mentioned above with the addition of the ITS region, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (G3PDH), heat-shock protein 60 gene (HSP60) and DNA-dependent RNA polymerase subunit II gene (RPB2) markers were used for the identification of the strawberry pathogen. An analysis of the sequenced fragments showed that the disease was caused by B. cinerea [125]. In 2016, Kim’s team proposed ITS region amplification for the identification of pathogens causing grey mould on red raspberry. The reaction identified the pathogen as B. cinerea. However, for further investigation the sequencing of G3PDH, HSP60, and RPB2 was performed. Those three protein-coding markers were also 100% identical with those of B. cinerea, confirming the identification of the fungus [126]. The ITS marker was also applied for the identification of the pathogen causing gray mould on economically important crops, including strawberry fruit. The analysis was also executed in connection with morphology identification and BIOLOG application. As a result, all of the methods confirmed that the pathogen was in fact B. cinerea [127]. Furthermore, the ITS region was also used for the identification of the strawberry postharvest pathogen in Pakistan. The method identified the fungus as B. cinerea [128]. Also, the amplification of the marker with PCR confirmed the presence of the fungus on H. bracteatum [129]. Another study published in 2018 included a phylogenic analysis of B. cinerea isolates obtained from strawberry cultivations. The sequences used in the study were 4 microsatellite markers and they contained enough phylogenic information for the analysis [35].
The application of β-tubulin and actin gene-specific markers were utilized for the quantification of B. cinerea on the Arabidopsis thaliana plant via a qPCR assay. Ten ng of fungal DNA was detectable for both of the markers [130]. Also, a different protein-coding gene marker—cutinase A gene was useful for the detection and quantification of B. cinerea from infected plants. The assay was capable of successfully detecting 16.7 ng of the genomic DNA of the pathogen [131]. Furthermore, Suarez’s team designed primers for IGS, the β-tubulin gene and the species-specific sequence-characterized amplified region (SCAR) genes of the fungus. Those regions were analyzed before and after the manifestation of the disease in order to detect and quantify the pathogen on strawberry plants. The application of the IGS and SCAR primers resulted in a high degree of specificity. What is more, the amplification of the IGS gene was the most sensitive method, detecting 20 fg of fungal DNA [132]. Furthermore, Reich’s team proved IGS primers to be useful in multiplex qPCR reactions for discrimination between B. cinerea and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [133]. Multiplex qPCR for the simultaneous detection of the resistance of B. cinerea to benzimidazoles, dicarboximides, SDHIs, and SBIs was utilized in a recent study. The assay included the design of 4 specific pairs of primers for SNPs in genes responsible for the fungicide resistance, which are β-tubulin, succinate dehydrogenase iron-sulfur subunit (SdhB), putative osmosensor histidine kinase (BcOS1) and 3-ketoreductase (erg27) genes. The assay was capable to simultaneously detect all of the alleles when the concentration of genomic DNA was higher than 0.1 ng [134]. Primer sequences as well as the information of authors and targeted markers are described below in Table 4.
Table 4.
Selected primers designed for molecular analysis of Botrytis spp.
| Targeted species (No. of Strains Analyzed) | Assay | Marker | Primers Sequences 5′-3′ | Primer Authors | Primers Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Botrytis spp. (1) | PCR | ITS 1 | GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC |
[91] | [125] |
| B. cinerea (13) | PCR | ITS 1 | ACCCGCACCTAATTCGTCAAC GGGTCTTCGATACGGGAGAA |
[123] | [123] |
| B. cinerea (29) | PCR | RAPD 2 marker | CAGGAAACACTTTTGGGGATA GAGGGACAAGAAAATCGACTAA |
[124] | [124] |
| B. fabae (8) | NEP1 3 | TCACGGTTTCTTGTCCATCC TCGGGCGTTGTACTCTTCAT |
|||
| B. fabiopsis (8) | RAPD2 marker | TCCTTTCTATCCTCGCTGCC CTGGTGGTTTGTAAAGCTGC |
|||
| Botrytis spp. (52) | PCR | RPB2 4 | GATGATCGTGATCATTTCGG CCCATAGCTTGCTTACCCAT |
[135] | [135] |
| G3PDH 5 | ATTGACATCGTCGCTGTCAACGA ACCCCACTCGTTGTCGTACCA |
||||
| HSP60 6 | CAACAATTGAGATTTGCCCACAAG GATGGATCCAGTGGTACCGAGCAT |
||||
| B. cinerea (39 in [49]; 273 in [35]) | PCR | microsatellite marker | ACCCGCACCTAATTCGTCAAC GGGTCTTCGATACGGGAGAA |
[49] | [35] |
| B. cinerea (117 in [136]) | PCR | microsatellite marker | AAGCCCTTCGATGTCTTGGA ACGGATTCCGAACTAAGTAA |
[136] | [35] |
| B. cinerea (75 in [137]) | PCR | microsatellite marker | AGGGAGGGTATGAGTGTGTA TTGAGGAGGTGGAAGTTGTA |
[137] | [35] |
| microsatellite marker | CATACACGTATTTCTTCCAA TTTACGAGTGTTTTTGTTAG |
||||
| microsatellite marker | GGATGAATCAGTTGTTTGTG CACCTAGGTATTTCCTGGTA |
||||
| microsatellite marker | CATCTTCTGGGAACGCACAT ATCCACCCCCAAACGATTGT |
||||
| microsatellite marker | CGTTTTCCAGCATTTCAAGT CATCTCATATTCGTTCCTCA |
||||
| microsatellite marker | ACTAGATTCGAGATTCAGTT AAGGTGGTATGAGCGGTTTA |
||||
| microsatellite marker | CCAGTTTCGAGGAGGTCCAC GCCTTAGCGGATGTGAGGTA |
||||
| microsatellite marker | CTCGTCATAACCACGCAGAT GCAAGGTCTCGATGTCGATC |
||||
| microsatellite marker | TCCTCTTCCCTCCCATCAAC GGATCTGCGTGGTTATGACG |
||||
| B. cinerea (1) | qPCR | β-tubulin | CCGTCATGTCCGGTGTTACCAC CGACCGTTACGGAAATCGGAAG |
[130] | [130] |
| actin | TGGAGATGAAGCGCAATCCAA AAGCGTAAAGGGAGAGGACGG |
||||
| B. cinerea (1) | qPCR | cutinase A | AGCCTTATGTCCCTTCCCTTGCG GAAGAGAAATGGAAAATGGTGAG |
[131] | [131] |
| B. cinerea (24) | qPCR | β-tubulin | GTTACTTGACATGCTCTGCCATT CACGGCTACAGAAAGTTAGTTTCTACAA |
[132] | [132] |
| IGS 7 | FGCTGTAATTTCAATGTGCAGAATCC GGAGCAACAATTAATCGCATTTC |
||||
| SCAR8 marker | TTCGTGATTATCACCTGGGTTG GCTCCTAGAACGTACGACCACA |
[123] | |||
| B. cinerea (11) | multi-plex qPCR | β-tubulin | GTCGTCCCATCGCCAAAGGT ACGGTGACAGCACGGAAAGA |
[134] | [134] |
| SdhB 9 | ACACCGACCCAGCACCAGA TTAGCAATAACCGCCCAAA |
||||
| BcOS1 10 | AGGTCACCCGCGTAGCAAGA TGCTTGATTTCACCCTTACA |
||||
| erg27 11 | GCGTGGAGAACTCTAAATCGG AGTGTAAGGCTTGATGGTATGC |
1 internal transcribed spacer, 2 random amplification of polymorphic DNA, 3 necrosis-and ethylene-inducing protein 1, 4 DNA-dependent RNA polymerase subunit II gene, 5 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, 6 heat-shock protein 60 gene, 7 intergenic spacer of genomic DNA, 8 sequence characterized amplified region, 9 succinate dehydrogenase iron–sulfur subunit, 10 putative osmosensor histidine kinase, 11 3-ketoreductase.
In 2010, the first LAMP reaction with IGS primers for B. cinerea detection was designed, and it resulted in a high level of efficiency. The assay was capable of detecting 65 pg of pathogen DNA in the sample, but for some of the reactions even an amount 10 times smaller was sufficient to detect the pathogen. The reaction also amplified only the closest related specimen, Botrytis pelargonii. What is more, detection was possible only 15 minutes after the start of the reaction [138]. Duan’s team proved the usefulness of the mitogen-activated protein kinase gene (Bcos5) which is an analysis designed to discriminate between B. cinerea on strawberry and tomato and 8 other plant pathogens in LAMP [139]. Also, LAMP assays for the detection of fungicide-resistant B. cinerea mutants have been developed [140,141,142]. Based on the presented above results concerning the detection limits of B. cinerea it was observed that depending on selected method and tested isolates the detection was within the limits between 17 ng and 20 fg.
The first genome sequencing of B. cinerea was obtained using Sanger technology, with the result of low coverage [143], which was a reason to search for more cost-effective and thorough methods. In 2012, Staats and van Kan employed Illumina technology to build an assembly with a size of c. 41 Mb, and a GC content of 42.5% [144]. Furthermore, a complete pathogen genome was accomplished with the final length of 43.5 Mb [145].
4.2.4. Colletotrichum acutatum
Colletotrichum acutatum on berries has been identified with the application of a wide range of markers used in PCR reactions. In a study from 2009, cranberry fruit pathogens were detected with the application of the ITS region, which contained ITS1, 5.8S ribosomal RNA gene and ITS2. Also, an analysis of the partial sequence of the 28S ribosomal RNA gene—LSU was utilized. An analysis of the second marker resulted in an improved phylogeny for the species [146]. However, with strawberry pathogens the sequencing of the ITS region produced sufficient results for the differentiation of the fungus from C. gleosporide [52]. Additionally, the identification of strawberry pathogens in Belgium with the aforementioned marker was sufficient to distinguish between C. acutatum, C. gloeosporioides and C. coccodes [147]. Also, an analysis of a different marker—the IGS region, for 31 isolates of strawberry pathogens, as well the utilization of species-specific primers in PCR for C. acutatum was carried by Xie’s team. In agreement with the conclusions of Garrido and van Hemelrijck, the method was capable of identifying three species from the Colletotrichum genus, including C. acutatum [148]. A different approach, utilizing a restriction fragments length polymorphism (RFLP) protocol with glutamine synthetase (GS) introne marker also prevailed for the purpose of differentiating between both species [149]. The ITS region with the addition of the β-tubulin gene was also considered for the identification of the fungus isolated from different hosts. The β-tubulin based phylogeny tree had a higher resolution compared to that constructed with ITS, but both [150]. An extended number of markers were utilized for the identification of the causes of strawberry anthracnose in China. The application of primers directed for fragments of actin (ACT), β-tubulin, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH), and chitin synthase (CHS-1) were satisfactory for distinguishing between C. acutatum and C. gleosporide [151]. The cytochrome b (cytb) gene was also utilized to reveal the fungicide resistance of the strawberry attacking pathogens [152].
The first application of ITS region and β-tubulin gene in a qPCR assay for the detection of Colletotrichum acutatum proved the specificity of the method. In the fungus genome the β-tubulin region exists only in one copy, in contrast with the multiple copies of the ITS region. Therefore, the method based on ITS marker was c. 66 times more sensitive and detected 50 fg of genomic DNA [153]. Furthermore, a duplex qPCR assay for the simultaneous detection of C. godetiae and C. acutatum was developed by Schena’s team. The method included the design of 2 pairs of specific primers, based on 2 markers: β-tubulin and histone H3 genes. The presence of 10 pg of genomic DNA in the sample was enough to detect both species [154]. A summary of the most important information containing markers, primers sequences and authors of the assays is given in Table 5.
Table 5.
Selected primers designed for molecular analysis of Colletotrichum spp.
| Targeted species (No. of Strains Analyzed) | Assay | Marker | Primers Sequences 5′-3′ | Primer Authors | Primers Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. acutatum (16 in [146]) | PCR | ITS 1 | GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC |
[91] | [146] |
| C. acutatum (16 in [146]) | PCR | LSU 2 | ATCCTGAGGGAAACTTC AGATCTTGGTGGTAGTA |
[155] | [146] |
| Colletotrichum spp. (29) | PCR | ITS 1 | AACCCTTTGTGAACRTACCTA TTACTACGCAAAGGAGGCT |
[156] | [156] |
| Colletotrichum spp. (100 in [151] | PCR | GPDH 3 | TCCCATCAAGGTCGGCATCA ACCTTGCCGACAGCCTTGG |
[157] | [151] |
| CHS-1 4 | GATGCCTGGAAGAAGATTGTCGT GTCTCGCCAGTAGCGGACTTGAC |
||||
| CAL 5 | GAATTCAAGGAGGCCTTCTC CTTCTGCATCATGAGCTGGAC |
||||
| C. acutatum (181) | PCR | Cytb 6 | GAAGAGGTATGTACTACGGTTCATATAG TAGCAGCTGGAGTTTGCATAG |
[152] | [152] |
| C. acutatum (23 in [70]) | qPCR | ITS 1 | CGGAGGAAACCAAACTCTATTTACA CCAGAACCAAGAGATCCGTTG |
[91] | [70] |
| C. acutatum (6) | qPCR | ITS 1 | GGATCATTACTGAGTTACCGC GCCCACGAGAGGCTTC |
[153] | [153] |
| β-tubulin | CGTCTACTTCAACGAAGTTTGTTATCC GAGGCCTGGTTGGGTGAG |
||||
| C. acutatum (15) | qPCR | histone H3 | TCCAGCGTCTGGTAAGTTGAGAA AGAAGTGTTAGCCGATGCGATT |
[154] | [154] |
1 internal transcribed spacer, 2 partial sequence of the 28S ribosomal RNA gene, 3 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, 3 chitin synthase, 4 calmoduline, 5 cytochrome b.
The LAMP reaction was also used for the rapid identification of pathogens from different hosts, including strawberry and raspberry plants. Zhang’s team utilized previously designed primers for the ITS region and β-tubulin 2 gene, with a greater specificity of the second marker. Nevertheless, the ITS marker was more sensitive, but it amplified the fragment for C. acutatum, C. gloeosporioides and C. fragariae [158].
The whole-genome sequence for C. acutatum has already been attained in 2016 by Han’s team. The team utilized NGS technology, and the final assembly was longer than 52 Mb, with a GC content of c. 51.5% [159].
5. Summary and Future Challenges
Soil-borne diseases are a serious threat to organic berry plantations, severely reducing crop yields. Until recently, the most effective way to prevent the spread of pathogenic fungi in the field was to immediately remove infected plants from the cultivation. Thus, fast and correct pathogen identification is essential for the eradication of the disease in time [12,21,160]. The accurate identification of pathogens can be problematic, as fungi attacking berries from the Phytophthora and Verticillium genera, as well Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum acutatum species cause similar symptoms on different plants and fruits. Identification based only on the morphology of the colonies is time-consuming and prone to misinterpretations, as it is based on human experience. These circumstances have led to the intense development of molecular techniques which allow for pathogen recognition and quantification [161]. Despite the fact that various molecular methods to detect fungi described in this review have already been established, they all have some disadvantages. These methods are only sensitive for a given region, also the majority of the assays are designed for pure strains. Those pure strains of fungi are more suitable for DNA isolation and recognition because the samples do not contain other closely related nor competitive microorganisms and their secretions, which often inhibit reactions. Therefore it is necessary to develop molecular methods that are more sensitive, specific and work under different soil and climatic conditions. Additionally, most of the pathogens causing agricultural losses cannot be grown in artificial cultures due to their specific environmental requirements, thus identification methods that do not necessitate the cultivation of pure cultures also have to be established.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization M.F., J.P., and D.M.; Literature review, D.M., J.P. and M.F.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, D.M., J.P. and M.F.; Figures, J.P. and D.M.; Tables, D.M.; Writing-Review & Editing, D.M., J.P. and M.F.; Revisions & Final editing, D.M., J.P. and M.F.
Funding
This paper was financed by The National Centre for Research and Development in frame of the project BIOSTRATEG, contract number BIOSTRATEG3/344433/16/NCBR/2018.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Willer H., Lernoud J., Kemper L. The World of Organic Agriculture. Statistics and Emerging Trends 2018. FiBL; Frick, Switzerland: 2018. The world of organic agriculture 2018: Summary; pp. 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- 2.FAOSTAT. [(accessed on 7 November 2018)]; Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC.
- 3.Lenroud J., Willer H. The World of Organic Agriculture. Statistics and Emerging Trends 2018. FiBL; Frick, Switzerland: 2018. Current statistics on organic agriculture worldwide: Area, operators and market; pp. 34–125. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brągiel E., Ślusarczyk B. Tendencje na europejskim rynku żywności ekologicznej. Zesz. Nauk. Szk. Głównej Gospod. Wiej. Warszawie, Probl. Rol. Światowego. 2017;17:29–38. doi: 10.22630/PRS.2017.17.3.50. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sahota A. The World of Organic Agriculture. Statistics and Emerging Trends 2018. FiBL; Frick, Switzerland: 2018. The global market for organic food and drink; pp. 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Palter J.B. The role of the gulf stream in European climate. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015;7:113–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-015656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mertely J.C., Chandler C.K., Xiao C.L., Legard D.E. Comparison of Sanitation and Fungicides for Management of Botrytis Fruit Rot of Strawberry. Plant Dis. 2007;84:1197–1202. doi: 10.1094/PDIS.2000.84.11.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Prokkola S., Kivijärvi P. Effect of biological sprays on the incidence of grey mould, fruit yield and fruit quality in organic strawberry production. Agric. Food Sci. 2007;16:25–33. doi: 10.2137/145960607781635886. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Spitzer T., Matušinsky P. Detecting pathogens of Verticillium wilt in winter oilseed rape using ELISA and PCR-Comparison of the two methods and with visual stand evaluation. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendelianae Brun. 2017;65:205–210. doi: 10.11118/actaun201765010205. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Boff P., Kastelein P., de Kraker J., Gerlagh M., Kohl J. Epidemiology of grey mould in annual waiting-bed production of strawberry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2001;107:615–624. doi: 10.1023/A:1017932927503. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wilcox W.F., Seem R.C. Relationship between strawberry gray mold incidence, environmental variables, and fungicide apllications during different periods of the fruiting season. Phytopathology. 1994;84:264–270. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-84-264. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lilja A.T., Parikka P., Pääskynkivi E.A., Hantula J.I., Vainio E.J., Vartiamäki H.A., Lemmetty A.H., Vestberg M.V. Phytophthora cactorum and Colletotrichum acutatum: Survival and detection. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2006;71:121–128. [Google Scholar]
- 13.McCain A.H., Raabe R.D., Wilhelm S. Plants Resistant or Susceptible to Verticillium Wilt. University of California; Oakland, CA, USA: 1981. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bhat R.G., Subbarao K.V. Host range specificity in Verticillium dahliae. Phytopathology. 1999;89:1218–1225. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.1999.89.12.1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Osbourn A.E. Verticillium wilt of strawberry. PNAS. 2001;98:14187–14188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261573598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Inderbitzin P., Bostock R.M., Davis R.M., Usami T., Platt H.W., Subbarao K.V. Phylogenetics and taxonomy of the fungal vascular wilt pathogen Verticillium, with the descriptions of five new species. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e28341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Goud J.K.C., Termorshuizen A.J., Gams W. Morphology of Verticillium dahliae and V. tricorpus on semi-selective media used for the detection of V. dahliae in soil. Mycol. Res. 2003;107:822–830. doi: 10.1017/S0953756203008050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goud J.K.C., Termorshuizen A.J. Quality of methods to quantify microsclerotia of Verticillium dahliae in soil. Erupean J. Plant Pathol. 2003;109:523–534. doi: 10.1023/A:1024745006876. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yu J.M., Cafarov I.H., Babadoost M. Morphology, molecular identity, and pathogenicity of Verticillium dahliae and V. longisporum sssociated with internally discolored horseradish roots. Plant Dis. 2016;100:749–757. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-15-0846-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Özer G., Bayraktar H. First report of Verticillium dahliae causing verticillium wilt on Goji berry in Turkey. J. Plant Pathol. 2016;98:682. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fradin E.F., Thomma B.P.H.J. Physiology and molecular aspects of Verticillium wilt diseases caused by V. dahliae and V. albo-atrum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006;7:71–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2006.00323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huang L., Mahoney R.R. Purification and characterization of an endo- polygalacturonase from Verticillium albo-atrum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999;86:145–156. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00645.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Carder J.H., Hignett R.C., Swinburne T.R. Relationship between the virulence of hop isolates of Verticillium albo-atrum and their in vitro secretion of cell-wall degrading enzymes. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1987;31:441–452. doi: 10.1016/0885-5765(87)90056-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Barnes E.H. Atlas and Manual of Plant Pathology. Plenum Press; New York, NY, USA: 1979. Verticillium wilt; pp. 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Martin F.N., Blair J.E., Coffey M.D. A combined mitochondrial and nuclear multilocus phylogeny of the genus Phytophthora. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014;66:19–32. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2014.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dunstan W.A., Howard K., Stj Hardy G.E., Burgess T.I. An overview of Australia’s Phytophthora species assemblage in natural ecosystems recovered from a survey in Victoria. IMA Fungus. 2016;7:47–58. doi: 10.5598/imafungus.2016.07.01.04. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Meszka B., Michalecka M. Identification of Phytophthora spp. isolated from plants and soil samples on strawberry plantations in Poland. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2016;123:29–36. doi: 10.1007/s41348-016-0007-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wilcox W.F., Scott P.H., Hamm P.B., Kennedy D.M., Duncan J.M., Brasier C.M., Hansen E.M. Identity of a Phytophthora species attacking raspberry in Europe and North America. Mycol. Res. 1993;97:817–831. doi: 10.1016/S0953-7562(09)81157-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Weiland J.E., Benedict C., Zasada I.A., Scagel C.R., Beck B.R., Davis A., Graham K., Peetz A., Martin R.R., Dung J.K.S., et al. Late-summer disease symptoms in western washington red raspberry fields associated with co-occurrence of Phytophthora rubi, Verticillium dahliae and Pratylenchus penetrans, but not raspberry bushy dwarf virus. Plant Dis. 2018;102:938–947. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-17-1293-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gigot J., Walters T.W., Zasada I.A. Impact and Occurrence of Phytophthora rubi and Pratylenchus penetrans in commercial red raspberry (Rubus ideaus) fields in Northwestern Washington. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2013;13:357–372. doi: 10.1080/15538362.2013.748373. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Martin F.N., Abad Z.G., Balci Y., Ivors K. Identification and detection of Phytophthora: Reviewing our progress, identifying our needs. Plant Dis. 2012;96:1080–1103. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-12-11-1036-FE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dewey (Molly) F.M., Yohalem D. Botrytis: Biology, Pathology and Control. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2007. Detection, quantification and immunolocalisation of Bortytis species; pp. 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Elad Y., Williamson B., Tudzynski P., Delent N. Botrytis: Biology, Pathology and Control. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2007. Botrytis spp. and diseases they cause in agricultural systems—An introduction; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Choquer M., Fournier E., Kunz C., Levis C., Pradier J.-M., Simon A., Viaud M. Botrytis cinerea virulence factors: New insights into a necrotrophic and polyphageous pathogen. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007;277:1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rasiukevičiūtė N., Rugienius R., Šikšnianienė J.B. Genetic diversity of Botrytis cinerea from strawberry in Lithuania. Zemdirbyste-Agric. 2018;105:265–270. doi: 10.13080/z-a.2018.105.034. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Blanco C., De Los Santos B., Romero F. Relationship between concentrations of Botrytis cinerea conidia in air, environmental conditions, and the incidence of grey mould in strawberry flowers and fruits. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2006;114:415–425. doi: 10.1007/s10658-006-0007-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Prusky D. Pathogen quiescence in postharvest diseases. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1996;34:413–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.34.1.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Dean R., Van Kan J.A.L., Pretorius Z.A., Hammond-Kosack K.E., Di Pietro A., Spanu P.D., Rudd J.J., Dickman M., Kahmann R., Ellis J., et al. The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012;13:414–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Elad Y. Responses of plants to infection by botrytis cinerea and novel means involved in reducing their susceptibility to infection. Biol. Rev. 1997;72:381–422. doi: 10.1017/S0006323197005057. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Droby S., Lichter A. Botrytis: Biology, Pathology and Control. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2007. Post-harvest Botrytis infection: Etiology, development and managment; pp. 349–368. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kozhar O., Peever T.L. How does Botrytis cinerea infect red raspberry? Phytopathology. 2018;108:1287–1298. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-01-18-0016-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Xu X., Wedgwood E., Berrie A.M., Allen J., O’Neill T.M. Management of raspberry and strawberry grey mould in open field and under protection. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012;32:531–543. doi: 10.1007/s13593-011-0032-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fitt B.D.L., Creighton N.F., Bainbridge A. Role of wind and rain in dispersal of Botrytis fabae conidia. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1985;85:307–312. doi: 10.1016/S0007-1536(85)80193-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Louis C., Girard M., Kuhl G., Lopez-Ferber M. Persistence of Botrytis cinerea in its vector Drosophila melanogaster. Phytopathology. 1996;86:934–939. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-86-934. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Doss R.P. Composition and enzymatic activity of the extracellular matrix secreted by germlings of Botrytis cinerea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999;65:404–408. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.2.404-408.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nelson K.E. Effect of humidity on infection of table grapes by Botrytis cinerea. Phytopathology. 1951;41:859–864. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Holz G., Coertze S., Williamson B. Botrytis: Biology, Pathology and Control. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2007. The ecology of Botrytis on plant surfaces; pp. 9–28. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Elmer P.A.G., Michailides T.J. Botrytis: Biology, Pathology and Control. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2007. Epidemiology of Botrytis cinerea in orchard and vine crops. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rigotti S., Viret O., Gindro K. Two new primers highly specific for the detection of Botrytis cinerea Pers.: Fr. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2006;45:253–260. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Khazaeli P., Zamanizadeh H., Morid B., Bayat H. Morphological and molecular identification of Botrytis cinerea causal agent of gray mold in rose greenhouses in centeral regions of Iran. Int. J. Agric. Sci. Res. 2010;1:20–24. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Whitelaw-Weckert M.A., Curtin S.J., Huang R., Steel C.C., Blanchard C.L., Roffey P.E. Phylogenetic relationships and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum acutatum isolates from grape in subtropical Australia. Plant Pathol. 2007;56:448–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2007.01569.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Garrido C., Carbú M., Fernández-Acero F.J., Vallejo I., Manuel Cantoral J. Phylogenetic relationships and genome organisation of Colletotrichum acutatum causing anthracnose in strawberry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2009;125:397–411. doi: 10.1007/s10658-009-9489-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Freeman S., Katan T. Identification of Colletotrichum species responsible for anthracnose and root necrosis of strawberry in Israel. Phytopathology. 1997;87:516–521. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.1997.87.5.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sonavane P., Venkataravanappa V., Reddy M.K. First report of Collectotrichum acutatum associated with anthracnose disease in malayan apple from India. Plant Dis. 2017;5:465–472. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wagner K., Springer B., Pires V.P., Keller P.M. Molecular detection of fungal pathogens in clinical specimens by 18S rDNA high-throughput screening in comparison to ITS PCR and culture. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:6964. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25129-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Liu F., Tang G., Zheng X., Li Y., Sun X., Qi X., Zhou Y., Xu J., Chen H., Chang X., et al. Molecular and phenotypic characterization of Colletotrichum species associated with anthracnose disease in peppers from Sichuan Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:1–17. doi: 10.1038/srep32761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Debode J., van Hemelrijck W., Xu X.M., Maes M., Creemers P., Heungens K. Latent entry and spread of Colletotrichum acutatum (species complex) in strawberry fields. Plant Pathol. 2015;64:385–395. doi: 10.1111/ppa.12247. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Madden L.V., Yang X., Wilson L.L. Effects of rain intensity on splash dispersal of Colletoreichum acutatum. Phytopathology. 1996;86:864–874. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-86-864. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Eastburn D.M., Gubler W.D. Strawberry anthracnose: Detection and survival of Colletotrichum acutatum in soil. Plant Dis. 1990;74:161–163. doi: 10.1094/PD-74-0161. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Narayanasamy P. Microbial Plant Pathogens—Detection and Disease Diagnosis: Fungal Pathogens. Volume 1. Springer Science + Business Media B.V.; Berlin, Germany: 2011. Detection of fungal pathogens in plants; pp. 5–199. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Larkin R.P., Ristaino J.B., Campbell L.C. Detection and quantification of Phytophthora capsici in soil. Am. Phytopathol. Soc. 1995;85:1057–1063. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-85-1057. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Frąc M., Jezierska-Tys S., Yaguchi T. Occurrence, detection, and molecular and metabolic characterization of heat-resistant fungi in soils and plants and their risk to human health. Adv. Agron. 2015;132:161–204. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Edwards S.G., Seddon B. Selective media for thw specific isolatiotion and enumeration of Botrytis cinerea conidia. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001;32:63–66. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765x.2001.00857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Arbefeville S., Harris A., Ferrieri P. Comparison of sequencing the D2 region of the large subunit ribosomal RNA gene (MicroSEQ®) versus the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions using two public databases for identification of common and uncommon clinically relevant fungal species. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2017;140:40–46. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2017.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Panek J., Frąc M. Development of a qPCR assay for the detection of heat-resistant Talaromyces flavus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018;270:44–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Capote N., Pastrana M.A., Aguado A., Sanchez-Torres P. Plant pathology. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2012. Molecular tools for detection of plant pathogenic fungi and fungicide resistance. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Saiki R.K., Stoffel S., Scharf S.J., Higuchi R., Horn G.T., Mullis K.B., Erlich H.A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988;239:487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.239.4839.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Higuchi R., Dollinger G., Walsh S.P., Griffith R. Simultaneous amplification and detection of specific DNA sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 1992;10:413–417. doi: 10.1038/nbt0492-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Higuchi R., Fockler C., Dollinger G., Watson R. Kinectic PCR analysis: Real-time monitoring of DNA amplification reactions. Nat. Biotechnol. 1993;11:1026–1030. doi: 10.1038/nbt0993-1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Garrido C., Carbú M., Fernández-Acero F.J., Boonham N., Colyer A., Cantoral J.M., Budge G. Development of protocols for detection of Colletotrichum acutatum and monitoring of strawberry anthracnose using real-time PCR. Plant Pathol. 2009;58:43–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2008.01933.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Notomi T., Okayama H., Masubuchi H., Yonekawa T., Watanabe K., Amino N., Hase T. Loop mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:e63. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.12.e63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Francois P., Tangomo M., Hibbs J., Bonetti E.J., Boehme C.C., Notomi T., Perkins M.D., Schrenzel J. Robustness of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction for diagnostic applications. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011;62:41–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2011.00785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Niessen L. Current state and future perspectives of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)-based diagnosis of filamentous fungi and yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014;99:553–574. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Metzker M.L. Sequencing technologies the next generation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:31–46. doi: 10.1038/nrg2626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Faino L., Thomma B.P.H.J. Get your high-quality low-cost genome sequence. Trends Plant Sci. 2014;19:288–291. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Panek J., Frąc M., Bilińska-Wielgus N. Comparison of chemical sensitivity of fresh and long-stored heat resistant Neosartorya fischeri environmental isolates using Biolog Phenotype MicroArray system. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0147605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Diguta C.F., Vincent B., Guilloux-Benatier M., Alexandre H., Rousseaux S. PCR ITS-RFLP: A useful method for identifying filamentous fungi isolates on grapes. Food Microbiol. 2011;28:1145–1154. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2011.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Krupa P. Identification by PCR-RFLP of a fungus isolated from mycorrhizal roots of a distinguishable birch growing in areas disturbed by industry. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 1999;8:161–163. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Inderbitzin P., Davis R.M., Bostock R.M., Subbarao K.V. Identification and differentiation of Verticillium species and V. longisporum lineages by simplex and multiplex PCR assays. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e65990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lievens B., Brouwer M., Vanachter A.C.R.C., Cammue B.P.A., Thomma B.P.H.J. Real-time PCR for detection and quantification of fungal and oomycete tomato pathogens in plant and soil samples. Plant Sci. 2006;171:155–165. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.03.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ozyilmaz U., Benlioglu K., Yildiz A., Benlioglu H.S. Effects of soil amendments combined with solarization on the soil microbial community in strawberry cultivation using quantitative real-time PCR. Phytoparasitica. 2016;44:661–680. doi: 10.1007/s12600-016-0552-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Mirmajlessi S.M., Larena I., Mänd M., Loit E. A rapid diagnostic assay for detection and quantification of the causal agent of strawberry wilt from field samples. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B — Soil Plant Sci. 2016;66:619–629. doi: 10.1080/09064710.2016.1205656. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Debode J., van Poucke K., França S.C., Maes M., Höfte M., Heungens K. Detection of multiple Verticillium species in soil using density flotation and real-time polymerase chain reaction. Plant Dis. 2011;95:1571–1580. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-04-11-0267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.O’Donnell K., Cigelnik E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997;7:103–116. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1996.0376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Knüfer J., Lopisso D.T., Koopmann B., Karlovsky P., von Tiedemann A. Assessment of latent infection with Verticillium longisporum in field-grown oilseed rape by qPCR. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017;147:819–831. doi: 10.1007/s10658-016-1045-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Klosterman S.J. Real-Time PCR for the Quantification of Fungi in Planta. Volume 835. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2012. pp. 121–132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Bilodeau G.J., Koike S.T., Uribe P., Martin F.N. Development of an assay for rapid detection and quantification of Verticillium dahliae in soil. Phytopathology. 2012;102:331–343. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-05-11-0130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Pasche J.S., Mallik I., Anderson N.R., Gudmestad N.C. Development and validation of a real-time PCR assay for the quantification of Verticillium dahliae in potato. Plant Dis. 2013;97:608–618. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-06-12-0554-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Pasche J.S., Thompson A.L., Gudmestad N.C. Quantification of field resistance to Verticillium dahliae in eight russet-skinned potato cultivars using real-time PCR. Am. J. Potato Res. 2013;90:158–170. doi: 10.1007/s12230-012-9280-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Tzelepis G., Bejai S., Sattar M.N., Schwelm A., Ilbäck J., Fogelqvist J., Dixelius C. Detection of Verticillium species in Swedish soils using real-time PCR. Arch. Microbiol. 2017;199:1383–1389. doi: 10.1007/s00203-017-1412-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.White T.J., Bruns T., Lee S., Taylor J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protoc. A Guid. to Methods Appl. 1990;18:315–322. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Pantou M.P., Mavridou A., Typas M.A. IGS sequence variation, group-I introns and the complete nuclear ribosomal DNA of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium: Excellent tools for isolate detection and phylogenetic analysis. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2003;38:159–174. doi: 10.1016/S1087-1845(02)00536-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Eynck C., Koopmann B., Grunewaldt-Stoecker G., Karlovsky P., von Tiedemann A. Differential interactions of Verticillium longisporum and V. dahliae with Brassica napus detected with molecular and histological techniques. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007;118:259–274. doi: 10.1007/s10658-007-9144-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Borza T., Beaton B., Govindarajan A., Gao X., Liu Y., Ganga Z., Wang-Pruski G. Incidence and abundance of Verticillium dahliae in soil from various agricultural fields in Prince Edward Island, Canada. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018;151:825–830. doi: 10.1007/s10658-017-1408-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Moradi A., Almasi M.A., Jafary H., Mercado-Blanco J. A novel and rapid loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the specific detection of Verticillium dahliae. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014;116:942–954. doi: 10.1111/jam.12407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.De Jonge R., Bolton M.D., Kombrink A., van Den Berg G.C.M., Yadeta K.A., Thomma B.P.H.J. Extensive chromosomal reshuffling drives evolution of virulence in an asexual pathogen. Genome Res. 2013;23:1271–1282. doi: 10.1101/gr.152660.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Faino L., Seidl M.F., Datema E., van den Berg G.C.M., Janssen A., Wittenberg A.H.J., Thomma B.P.H.J. Single-molecule real-time sequencing combined with optical mapping yields completely finished fungal genome. MBio. 2015;6:e00936-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00936-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Fan R., Cockerton H.M., Armitage A.D., Bates H., Cascant-Lopez E., Antanaviciute L., Xu X., Hu X., Harrison R.J. Vegetative compatibility groups partition variation in the virulence of Verticillium dahliae on strawberry. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:1–21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Jelen V., De Jonge R., van De Peer Y., Javornik B., Jakše J. Complete mitochondrial genome of the Verticillium wilt causing plant pathogen Verticillium nonalfalfae. PLoS ONE. 2016;11 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Fogelqvist J., Tzelepis G., Bejai S., Ilbäck J., Schwelm A., Dixelius C. Analysis of the hybrid genomes of two field isolates of the soil-borne fungal species Verticillium longisporum. BMC Genom. 2018;19:1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4407-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Cooke D.E.L., Duncan J.M. Phylogenetic analysis of Phytophthora species based on ITS1 and ITS2 sequences of the ribosomal RNA gene repeat. Mycol. Res. 1997;101:667–677. doi: 10.1017/S0953756296003218. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Ristaino J.B., Madritch M., Trout C., Parra G. PCR amplification of ribosomal DNA for species identification of Phytophthora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998;64:948–954. doi: 10.1128/aem.64.3.948-954.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Cooke D.E.L., Drenth A., Duncan J.M., Wagels G., Brasier C.M. A molecular phylogeny of phytophthora and related oomycetes. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2000;30:17–32. doi: 10.1006/fgbi.2000.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Martin F.N., Tooley P.W., Blomquist C. Molecular detection of Phytophthora ramorum, the causal agent of sudden oak death in California, and two additional species commonly recovered from diseased plant material. Phytopathology. 2004;94:621–631. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.6.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Polashock J.J., Vaiciunas J., Oudemans P.V. Identification of a new Phytophthora species causing root and runner rot of cranberry in New Jersey. Phytopathology. 2005;95:1237–1243. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-95-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Blair J.E., Coffey M.D., Park S.-Y., Geiser D.M., Kang S. A multi-locus phylogeny for Phytophthora utilizing markers derived from complete genome sequences. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008;45:266–277. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2007.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Bienapfl J.C., Balci Y. Movement of Phytophthora spp. in Maryland’s Nursery Trade. Plant Dis. 2014;98:134–144. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-06-13-0662-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Böhm J., Hahn A., Schubert R., Bahnweg G., Adler N., Nechwatal J., Oehlmann R., Oßwald W.F. Real-time quantitative PCR: DNA determination in isolated spores of the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae and monitoring of Phytophthora infestans and Phytophthora citricola in their respective host plants. Phytopathology. 1999;147:409–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0434.1999.tb03842.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kox L.F.F., Van Brouwershaven I.R., Van De Vossenberg B.T.L.H., Van den Beld H.E., Bonants P.J.M., de Gruyter J. Diagnostic values and utility of immunological, morphological, and molecular methods for in planta detection of Phytophthora ramorum. Phytopathology. 2007;97:1119–1129. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-97-9-1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Pastrana A.M., Basallote-Ureba M.J., Aguado A., Capote N. Potential inoculum sources and incidence of strawberry soilborne pathogens in Spain. Plant Dis. 2017;101:751–760. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-16-1177-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Nath V.S., Hegde V.M., Jeeva M.L., Misra R.S., Veena S.S., Raj M., Unnikrishnan S.K., Darveekaran S.S. Rapid and sensitive detection of Phytophthora colocasiae responsible for the taro leaf blight using conventional and real-time PCR assay. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014;352:174–183. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Li M., Inada M., Watanabe H., Suga H., Kageyama K. Simultaneous detection and quantification of Phytophthora nicotianae and P. cactorum, and distribution analyses in strawberry greenhouses by duplex real-time PCR. Microbes Environ. 2013;28:195–203. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME12177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Liao F., Zhang Y., Zhu L.-H., Cao B., Lv D., Luo J.-F., Li G.-R. Triplex real-time PCR detection of three quarantine Phytophthora pathogens infecting Malus Miller. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2018;125:325–330. doi: 10.1007/s41348-017-0144-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Martin F.N., Tooley P.W. Phylogenetic relationships among Phytophthora species inferred from sequence analysis of mitochondrially encoded cytochrome oxidase I and II genes. Mycologia. 2003;95:269–284. doi: 10.1080/15572536.2004.11833112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Ioos R., Andrieux A., Marçais B., Frey P. Genetic characterization of the natural hybrid species Phytophthora alni as inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA analyses. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2006;43:511–529. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2006.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Tomlinson J.A., Barker I., Boonham N. Faster, simpler, more-specific methods for improved molecular detection of Phytophthora ramorum in the field. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007;73:4040–4047. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00161-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Chen Q., Li B., Liu P., Lan C., Zhan Z., Weng Q. Development and evaluation of specific PCR and LAMP assays for the rapid detection of Phytophthora melonis. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013;137:597–607. doi: 10.1007/s10658-013-0273-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Si Ammour M., Bilodeau G.J., Tremblay D.M., van der Heyden H., Yaseen T., Varvaro L., Carisse O. Development of real-time isothermal amplification assays for on-site detection of Phytophthora infestans in potato leaves. Plant Dis. 2017;101:1269–1277. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-12-16-1780-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Khan M., Li B., Jiang Y., Weng Q., Chen Q. Evaluation of different PCR-based assays and LAMP method for rapid detection of Phytophthora infestans by targeting the Ypt1 gene. Front. Microbiol. 2017;8:1–11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Tyler B.M., Tripathy S., Zhang X., Dehal P., Jiang R.H.Y., Aerts A., Arredondo F.D., Baxter L., Bensasson D., Beynon J.L., et al. Phytophthora genome sequences uncover evolutionary origins and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 2006;313:1261–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.1128796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Haas B.J., Kamoun S., Zody M.C., Jiang R.H.Y., Handsaker R.E., Cano L.M., Grabherr M., Kodira C.D., Raffaele S., Torto-Alalibo T., et al. Genome sequence and analysis of the Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Nature. 2009;461:393–398. doi: 10.1038/nature08358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Tabima J.F., Kronmiller B.A., Press C.M., Tyler B.M., Zasada I.A., Grünwald N.J. Whole genome sequences of the raspberry and strawberry pathogens Phytophthora rubi and P. fragariae. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2017;30:767–769. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-04-17-0081-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Rigotti S., Gindro K., Richter H., Viret O. Characterization of molecular markers for specific and sensitive detection of Botrytis cinerea Pers.: Fr. In strawberry (Fragaria×ananassa Duch.) using PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002;209:169–174. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(02)00491-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Fan X., Zhang J.Z., Yang L., Wu M., Chen W., Li G. Development of PCR-based assays for detecting and differentiating three species of Botrytis infecting broad bean. Plant Dis. 2015;99:691–698. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-07-14-0701-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kamaruzzaman M., Hao F., Wu M., Li G. Gray mold of strawberry (Fragaria ananassa) caused by a rare pink-colored isolate of Botrytis cinerea in China. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2018;47:587–589. doi: 10.1007/s13313-018-0593-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Kim J.Y., Aktaruzzaman M., Afroz T., Kim B.S., Shin H.D. First report of gray mold caused by Botrytis cinerea on red raspberry (Rubus idaeus) in Korea. Plant Dis. 2016;100:533. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-15-0869-PDN. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Wang H.C., Li L.C., Cai B., Cai L.T., Chen X.J., Yu Z.H., Zhang C.Q. Metabolic phenotype characterization of Botrytis cinerea, the causal agent of gray mold. Front. Microbiol. 2018;9:1–9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Alam M.W., Gleason M.L., Malik A.U., Amin M., Fiaz M., Ali S., Rosli H., Rehman A. First report of Botrytis spp. as a postharvest pathogen of strawberry in Pakistan. J. Plant Pathol. 2017;99:287–304. [Google Scholar]
- 129.Garibaldi A., Bertetti D., Ortega S.F., Pensa P., Gullino M.L. First report of Botrytis blight caused by Botrytis cinerea on Helichrysum bracteatum in Italy. J. Plant Pathol. 2018;99:287–304. [Google Scholar]
- 130.Brouwer M., Lievens B., van Hemelrijck W., van Den Ackerveken G., Cammue B.P.A., Thomma B.P.H.J. Quantification of disease progression of several microbial pathogens on Arabidopsis thaliana using real-time fluorescence PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003;228:241–248. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00759-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Gachon C., Saindrenan P. Real-time PCR monitoring of fungal development in Arabidopsis thaliana infected by Alternaria brassicicola and Botrytis cinerea. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004;42:367–371. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2004.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Suarez M.B., Walsh K., Boonham N., O’Neill T.M., Pearson S., Barker I. Development of real-time PCR (TaqMan®) assays for the detection and quantification of Botrytis cinerea in planta. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005;43:890–899. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2005.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Reich J.D., Alexander T.W., Chatterton S. A multiplex PCR assay for the detection and quantification of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016;62:379–385. doi: 10.1111/lam.12566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Zhang X., Xie F., Lv B., Zhao P., Ma X. Suspension array for multiplex detection of eight fungicide-resistance related alleles in Botrytis cinerea. Front. Microbiol. 2016;7:1–10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Staats M., van Baarlen P., van Kan J.A.L. Molecular phylogeny of the plant pathogenic genus Botrytis and the evolution of host specificity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005;22:333–346. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msi020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Fournier E., Levis C., Fortini D., Leroux P., Giraud T., Brygoo Y. Characterization of Bc-hch, the Botrytis cinerea homolog of the Neurospora crassa het-c vegetative incompatibility locus, and its use as a population marker. Mycologia. 2003;95:251–261. doi: 10.1080/15572536.2004.11833110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Fournier E., Giraud T., Loiseau A., Vautrin D., Estoup A., Solignac M., Cornuet J.M., Brygoo Y. Characterization of nine polymorphic microsatellite loci in the fungus Botrytis cinerea (Ascomycota) Mol. Ecol. Notes. 2002;2:253–255. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-8286.2002.00207.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Tomlinson J.A., Dickinson M.J., Boonham N. Detection of Botrytis cinerea by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010;51:650–657. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.02949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Duan Y.B., Ge C.Y., Zhang X.K., Wang J.X., Zhou M.G. Development and evaluation of a novel and rapid detection assay for Botrytis cinerea based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification. PLoS ONE. 2014;9 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Duan Y.B., Yang Y., Li M.X., Li T., Fraaije B.A., Zhou M.G. Development and application of a simple, rapid and sensitive method for detecting moderately carbendazim-resistant isolates in Botrytis cinerea. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2018;172:355–365. doi: 10.1111/aab.12426. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Duan Y.B., Yang Y., Wang J.X., Chen C.J., Steinberg G., Fraaije B.A., Zhou M.G. Simultaneous detection of multiple benzimidazole-resistant β-tubulin variants of Botrytis cinerea using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Plant Dis. 2018;102:2016–2024. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-03-18-0542-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Hu X.R., Dai D.J., Wang H.D., Zhang C.Q. Rapid on-site evaluation of the development of resistance to quinone outside inhibitors in Botrytis cinerea. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:1–9. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13317-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Amselem J., Cuomo C.A., van Kan J.A.L., Viaud M., Benito E.P., Couloux A., Coutinho P.M., de Vries R.P., Dyer P.S., Fillinger S., et al. Genomic analysis of the necrotrophic fungal pathogens sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Staats M., van Kan J.A.L. Genome update of Botrytis cinerea strains B05.10 and T4. Eukaryot. Cell. 2012;11:1413–1414. doi: 10.1128/EC.00164-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.van Kan J.A.L., Stassen J.H.M., Mosbach A., van Der Lee T.A.J., Faino L., Farmer A.D., Papasotiriou D.G., Zhou S., Seidl M.F., Cottam E., et al. A gapless genome sequence of the fungus Botrytis cinerea. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017;18:75–89. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Polashock J.J., Caruso F.L., Oudemans P.V., McManus P.S., Crouch J.A. The North American cranberry fruit rot fungal community: A systematic overview using morphological and phylogenetic affinities. Plant Pathol. 2009;58:1116–1127. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2009.02120.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 147.van Hemelrijck W., Debode J., Heungens K., Maes M., Creemers P. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of Colletotrichum isolates from Belgian strawberry fields. Plant Pathol. 2010;59:853–861. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02324.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Xie L., Zhang J.Z., Wan Y., Hu D. Identification of Colletotrichum spp. isolated from strawberry in Zhejiang Province and Shanghai City, China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 2010;11:61–70. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B0900174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Liu B., Louws F.J., Sutton T.B., Correll J.C. A rapid qualitative molecular method for the identification of Colletotrichum acutatum and C. gloeosporioides. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012;132:593–607. doi: 10.1007/s10658-011-9904-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Shivas R.G., Tan Y.P. A taxonomic re-assesment of Colletotrichum acutatum, introducing C. fioriniae comb. at stat. nov. and C. simmondsii sp. nov. Fungal Divers. 2009:111–122. [Google Scholar]
- 151.Han Y.C., Zeng X.G., Xiang F.Y., Chen F.Y., Gu Y.C. Distribution and characteristics of Colletotrichum spp. associated with anthracnose of strawberry in Hubei, China. Plant Dis. 2016;100:996–1006. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-15-1016-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Forcelini B.B., Seijo T.E., Amiri A., Peres N.A. Resistance in strawberry isolates of Colletotrichum acutatum from Florida to quinone-outside inhibitor fungicides. Plant Dis. 2016;100:2050–2056. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-01-16-0118-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Debode J., van Hemelrijck W., Baeyen S., Creemers P., Heungens K., Maes M. Quantitative detection and monitoring of Colletotrichum acutatum in strawberry leaves using real-time PCR. Plant Pathol. 2009;58:504–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2008.01987.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Schena L., Abdelfattah A., Mosca S., Li Destri Nicosia M.G., Agosteo G.E., Cacciola S.O. Quantitative detection of Colletotrichum godetiae and C. acutatum sensu stricto in the phyllosphere and carposphere of olive during four phenological phases. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017;149:337–347. doi: 10.1007/s10658-017-1185-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Vilgalys R., Hester M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of anzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990;172:4238–4246. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4238-4246.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Martinez-Culebras P.V., Querol A., Suarez-Fernandez M.B., Garcia-Lopez M.D., Barrio E. Phylogenetic relationships among Colletotrichum pathogens of strawberry and design of PCR primers for their identification. J. Phytopathol. 2003;151:135–143. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0434.2003.00694.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Weir B.S., Johnston P.R., Damm U. The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex. Stud. Mycol. 2012;73:115–180. doi: 10.3114/sim0011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Zhang X., Harrington T.C., Batzer J.C., Kubota R., Peres N.A., Gleason M.L. Detection of Colletotrichum acutatum sensu lato on strawberry by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Plant Dis. 2016;100:1804–1812. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-15-1013-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Han J.H., Chon J.K., Ahn J.H., Choi I.Y., Lee Y.H., Kim K.S. Whole genome sequence and genome annotation of Colletotrichum acutatum, causal agent of anthracnose in pepper plants in South Korea. Genomics Data. 2016;8:45–46. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2016.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Frąc M., Hannula S.E., Belka M., Jȩdryczka M. Fungal biodiversity and their role in soil health. Front. Microbiol. 2018;9:1–9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Mirmajlessi S.M., Destefanis M., Gottsberger R.A., Mänd M., Loit E. PCR-based specific techniques used for detecting the most important pathogens on strawberry: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2015;4:9. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-4-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]