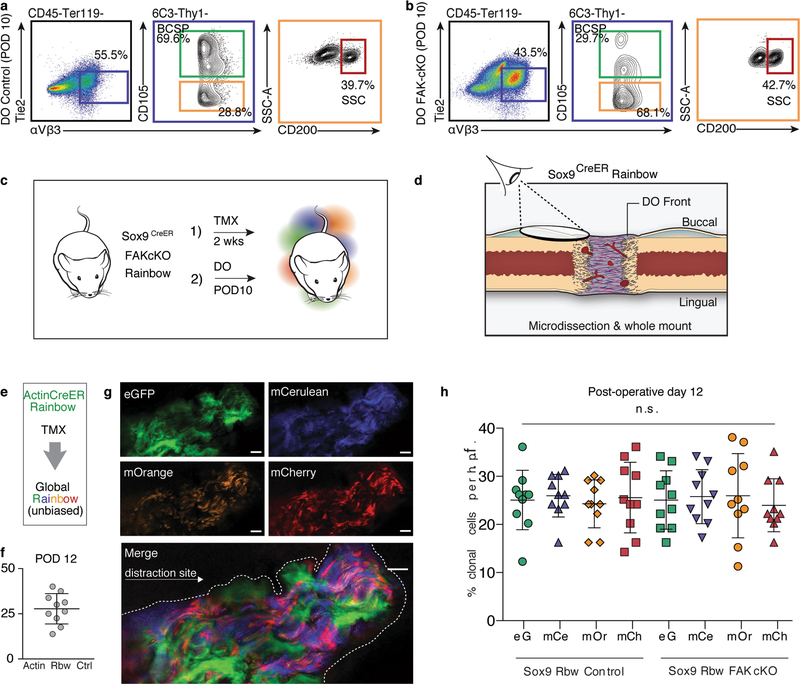
Extended Data Fig. 7 |. Cellular dynamics during distraction osteogenesis in FAK(cKO) mice.
a, b, FACS isolation of cells from control mice (a, Sox9creERT2;Ptk2fl/fl, no TMX) and FAK(cKO) mice (b, Sox9creERT2;Ptk2fl/fl, TMX treatment) shows that the SSC hierarchy (first column, black gate) is disrupted similarly in FAK(cKO) mice and in FAKi (Extended Data Fig. 6h). In the FAK(cKO) mice, the proportion of downstream multipotent BCSPs (green gate) compared with SSCs (orange and red gates) is lower than in controls. Representative of three independent replicates. c, Experimental strategy for clonal analysis of FAK(cKO) Rainbow contribution to regeneration in response to distraction, using whole-mount specimens from callus microdissection of mandibles in Sox9creERT2;R26Rainbow mice. d, Vantage point for the acquisition of the confocal images of whole-mount specimens shown in Fig. 3g, h. e, Experimental strategy for clonal analysis in ActincreERT2;R26Rainbow mice. f, Quantification of average clone size at POD12 during distraction osteogenesis in ActincreERT2;R26Rainbow mice (n = 10; mean ± s.d.). g, Whole-mount imaging at the site of distraction at POD12 in ActincreERT2;R26Rainbow mice. The view is a lateral-to-medial view of callus overlying the distraction site (indicated by the white dotted outline overlying the distraction gap). The distraction gap contains large clones with a migratory spreading phenotype (n = 4 for each of three independent replicates). h, Quantification of clones (whole-mount imaging) that are positive for each fluorophore per h.p.f. (×40 magnification) two weeks after tamoxifen induction (one injection per day, five days total) plus distraction until POD12, using Sox9creERT2;R26Rainbow mice (left) and FAK(cKO)Rainbow mice (right) (n = 10; mean ± s.d.). n refers to the number of animals in each independent experiment.