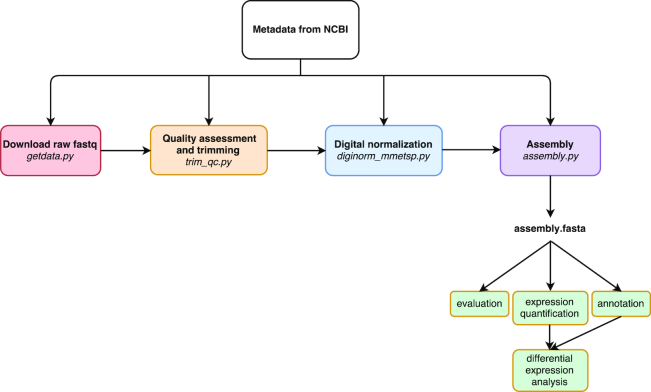
Figure 1:
A programmatically automated de novo transcriptome assembly pipeline was developed for this study. Metadata in the SraRunInfo.csv file downloaded from the National Center for Biotechnology Information was used as input for each step of the pipeline to indicate which samples were processed. The steps of the pipeline are as follows: download raw fastq data with the fastq-dump script in the SRA Toolkit, perform quality assessment with FastQC and trim residual Illumina adapters and low-quality bases (Q<2) with Trimmomatic, do digital normalization with khmer version 2.0, and perform de novo transcriptome assembly with Trinity. If a process was terminated, the automated nature of this pipeline allowed for the last process to be run again without starting the pipeline over. In the future, if a new sample is added, the pipeline can be run from beginning to end with just new samples, without having to repeat the processing of all samples in the dataset as one batch. If a new tool becomes available, e.g., a new assembler, it can be substituted in lieu of the original tool used by this pipeline.