Abstract
Objective
While maternal folate deficiency has been linked to poor pregnancy outcomes such as neural tube defects, anaemia and low birth weight, the relationship between folate and preterm birth (PTB) in the context of the US post-folic acid fortification era is inconclusive. We sought to explore the relationship between maternal folate status and PTB and its subtypes, i.e. spontaneous and medically indicated PTB.
Design
Observational study.
Setting
Boston Birth Cohort, a predominantly urban, low-income, race/ethnic minority population at a high risk for PTB.
Participants
Mother–infant dyads (n 7675) enrolled in the Boston Birth Cohort. A sub-sample (n 2313) of these dyads had maternal plasma folate samples collected 24–72 h after delivery.
Results
Unadjusted and adjusted logistic regressions revealed an inverse relationship between the frequency of multivitamin supplement intake and PTB. Compared with less frequent use, multivitamin supplement intake 3–5 times/week (adjusted OR (aOR) = 0·78; 95 % CI 0·64, 0·96) or >5 times/week (aOR = 0·77; 95 % CI 0·64, 0·93) throughout pregnancy was associated with reduced risk of PTB. Consistently, higher plasma folate levels (highest v. lowest quartile) were associated with lower risk of PTB (aOR = 0·74; 95 % CI 0·56, 0·97). The above associations were similar among spontaneous and medically indicated PTB.
Conclusions
If confirmed by future studies, our findings raise the possibility that optimizing maternal folate levels across pregnancy may help to reduce the risk of PTB among the most vulnerable US population in the post-folic acid fortification era.
Keywords: Folate status, Preterm birth, Multivitamin supplementation
Preterm birth (PTB; birth before 37 completed weeks of gestation) has been recognized as one of the most pressing challenges to maternal and child health in the USA and worldwide(1). The role of maternal nutrition remains a promising but understudied area of investigation in the identification of important and modifiable risk factors for PTB.
Folates are a group of naturally occurring water-soluble B vitamins involved in biological reactions needed for fetal and placental growth such as DNA synthesis, repair and methylation(2). Maternal folate deficiency is a modifiable nutritional status that has been linked with adverse pregnancy outcomes such as neural tube defects, congenital anomalies, low birth weight, maternal megaloblastic anaemia and pre-eclampsia(3–5). Folic acid is a synthetic form of folate that is used in multivitamin supplements and grain product fortification. Despite the establishment of national folate intake recommendations and mandatory folic acid fortification programmes in the USA since 1998(6,7), folate consumption is still of public health significance as data suggest that 25 % of women of reproductive age have insufficient folate levels(8).
To date, much attention has been paid to the role of periconception folate intake to prevent neural tube defects in offspring (a first-trimester event)(9–12). However, considerable knowledge gaps remain regarding the role of folate in PTB (a third-trimester event). A population-based analysis demonstrated reduced PTB risk after the implementation of mandatory folic acid fortification in the USA(13). Some US studies have found an association between lower folate status and PTB(14–18), while other studies found no association(19,20). These mixed results may be due to variations across studies in terms of sociodemographic characteristics of the study population, whether the studies were conducted prior to or after the mandatory folic acid fortification programme, differences in definitions and measurement of folate status (self-reported intake v. biomarkers) and/or timing of folic acid administration (preconception v. specific trimesters). The optimal timing of folic acid intake in relation to PTB remains unclear; i.e. whether there is a critical window of folic acid intake such as the periconception period (as has been demonstrated in the folate–neural tube defects relationship) v. during a specific trimester of gestation, given PTB is a later event. To date, most relevant studies were based on self-report of folic acid supplementation, which is known to be imprecise and associated with large variation in plasma folate levels, a biomarker of folate nutritional status(21). There is a need for contemporary post-folic acid fortification studies that examine the associations between folic acid intake as well as folate biomarkers and PTB and how the association between folate status and PTB varies by PTB subtypes, i.e. spontaneous v. medically indicated (induced) PTB, in high-risk US populations.
Our study sought to address the aforementioned gaps in understanding of the association between maternal folate status and PTB in a large, predominantly urban low-income minority birth cohort in the USA. Specifically, we examined the relationship between PTB and self-reported preconception (6 months prior to pregnancy) and pregnancy multivitamin supplementation (during each trimester), as well as biomarker measures of maternal plasma folate at delivery. We also explored whether the associations differed for spontaneous v. medically indicated PTB.
Participants and methods
Study population
We analysed data from the Boston Birth Cohort study which commenced in 1998 and is ongoing to date(22,23). Our data set included 8494 mother–infant dyads enrolled in the study from 1998 to 2014. The Boston Birth Cohort is registered at https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03228875. The initial and continuation of the study protocol were approved by the institutional review boards of Boston University Medical Center and Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Mothers who delivered at the Boston Medical Center, which serves a predominantly low-income, minority, inner-city patient population, were recruited 24–72 h after delivery while still hospitalized. Of note, the length of stay in hospitals after childbirth in the USA is 2 d for vaginal delivery and 4 d for caesarean section(24,25). Cases were defined as mother–infant dyads with singleton, live, low-birth-weight (<2500 g) or preterm infants (<37 weeks of gestation) regardless of birth weight. Controls were defined as mother–infant dyads with singleton, live, term infants with birth weight of 2500 g or more. Of note, the present paper specifically examines PTB v. term birth, regardless of birth weight.
Data collection
After informed consent was obtained, the study staff collected the epidemiological data, clinical data and maternal venous blood and placental samples. Epidemiological data were collected within 24–72 h postpartum via an in-person maternal questionnaire interview. Clinical data were abstracted from medical records using a standardized form. Plasma folate levels were measured in a sub-sample of the maternal blood samples obtained within 24–72 h postpartum from mothers who continued to receive care at Boston Medical Center.
Definition of key variables
PTB was defined as delivery before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Gestational age was determined using an algorithm based on the first day of the last menstrual period and the results of early ultrasound (<20 weeks of gestation), as previously published(23).
Multivitamin supplement intake was determined during the maternal interview based on responses to the following questions: ‘Did you take prenatal vitamins prescribed by your doctor?’ and ‘Did you take any over-the-counter multivitamins?’ during pre-pregnancy (6 months prior to conception), first trimester (day 1 to day 90 of pregnancy), second trimester (day 91 to day 180 of pregnancy), third trimester (day 181 of pregnancy to birth)? Response categories included: none, 1 time per week, 2 times per week, 3–5 times per week and almost daily. Based on responses to these two questions, preconception multivitamin intake was dichotomized (none v. any). Intake for each trimester as well as across all trimesters was divided into the following categories: none, 1–2 times/week, 3–5 times/week and almost daily. In the USA, prenatal or over-the-counter multivitamins typically contain 800 or 400 µg of folic acid, respectively, and are to be taken daily; however, a majority of mothers enrolled in the cohort received prenatal care and were advised to take prenatal vitamins which contain 800 µg of folic acid(26). A continuous measure of overall multivitamin supplement intake across all trimesters (henceforth referred to as the ‘multivitamin supplement intake index’) was developed by adding multivitamin intake across the three trimesters to create a composite index of multivitamin supplement intake across pregnancy. For each trimester, frequency of intake was coded as none = 0, 1–2 times/week = 1, 3–5 times/week = 3 and almost daily = 4. Thus, the composite index ranged from 0 to 12.
Plasma folate concentrations were measured using chemiluminescent immunoassay with diagnostic kits (Shenzhen New Industries Biomedical Engineering Co., Ltd, Shenzhen, China) using a Beckman Coulter ACCESS Immunoassay System (Beckman-Coulter Canada, Mississauga, Canada)(27). Plasma folate levels were assessed as: (i) a continuous variable in nmol/l; (ii) quartiles of plasma folate levels; and (iii) categorizations as per the WHO guidelines (folate deficiency/insufficiency, <13·5 nmol/l; normal, 13·5–45·3 nmol/l; elevated, >45·3 nmol/l)(28).
Other covariates included sociodemographic factors, such as: maternal age at delivery (<20, 20–34, ≥35 years); maternal education (≤elementary, high school, ≥college); race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic White, Hispanic, Other); marital status (unmarried v. married); parity (nulliparous v. multiparous); receipt of public assistance including WIC (Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children), food stamps, AFDC (Aid to Families with Dependent Children, now known as TANF (Temporary Aid to Needy Families)), housing assistance or fuel assistance (yes v. no); and maternal nativity (US born v. foreign born). Behavioural risk factors included: alcohol use (never v. any); smoking status (never used, ever used, used in pregnancy); and stress (an indicator for mother’s report of life or pregnancy as being ‘very’ stressful). Biomedical factors from abstracted records included: pre-eclampsia disorders (pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, gestational hypertension, HELLP (haemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets) syndrome); maternal diabetes (presence of either gestational or pre-gestational diabetes); intra-uterine infection/inflammation (presence of maternal fever or placenta pathology findings of villitis, deciduitis, chorioamnionitis, chorionitis, subchorionitis, funisitis, free membranitis); and pre-pregnancy BMI (calculated from self-reported height and weight) grouped into four categories (underweight, <18·5 kg/m2; normal weight, 18·5–24·9 kg/m2; overweight, 25·0–29·9 kg/m2; obesity, ≥30·0 kg/m2).
Statistical analyses
All analyses were conducted using the statistical software package Stata version 14. Preliminary data analysis was performed in the full sample (n 7576) of all enrolled women with multivitamin supplement intake data and the plasma folate sub-sample (n 2313) of these women who received follow-up paediatric care at Boston Medical Center. The χ2 test for categorical variables and t test for continuous variables were used to compare maternal characteristics by PTB status. Cronbach’s α was used to ensure the reliability of the scale ‘multivitamin supplement intake index’ (Cronbach’s α = 0·87). Unadjusted and adjusted logit regressions were used to graph the probability of PTB by plasma folate level. Crude and adjusted logistic regressions were used to explore the relationship between PTB and self-reported multivitamin supplement intake and plasma folate level. Supplemental analyses were conducted for the PTB subgroups of spontaneous and medically indicated PTB. All P values in the analyses were two-sided and the Type I error rate was set at 0·05.
Results
The present study was based on a full sample of 7576 women with complete multivitamin supplement intake information from 6 months before conception to the third trimester of pregnancy and a sub-sample (n 2313) with plasma folate samples collected at delivery. Those included in the full sample and those who had plasma folate data had similar baseline characteristics, except for a higher proportion of non-Hispanic Black mothers and PTB in the sub-sample.
Table 1 displays the maternal characteristics for the total study population and plasma folate sub-sample (maternal characteristics by PTB subtype are presented in the online supplementary material, Supplemental Table 1). In the full sample, 27 % of women had a preterm delivery. Compared with women with term births, women with PTB were more likely to be non-Hispanic Black, older, US-born, unmarried, cigarette smokers, alcohol consumers and report a very stressful life or pregnancy. These women were also likely to have had pre-eclampsia disorders, intra-uterine infection/inflammation, diabetes mellitus and be obese/overweight.
Table 1.
Maternal characteristics of the study population: predominantly urban, low-income, minority mother–infant dyads (n 7576) enrolled in the Boston Birth Cohort, USA, from 1998 to 2014
| Maternal characteristics | Multivitamin supplement sample | Plasma folate sub-sample | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Term (n 5507; 73 %) | PTB (n 2069; 27 %) | Term (n 1593; 69 %) | PTB (n 720; 31 %) | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Race/ethnicity | ||||||||
| Non-Hispanic Black* | 2764 | 50·2 | 1083 | 52·3 | 1133 | 71·1 | 555 | 77·1 |
| Non-Hispanic White | 645 | 11·7 | 275 | 13·3 | 65 | 4·1 | 27 | 3·8 |
| Hispanic | 1614 | 29·3 | 536 | 25·9 | 323 | 20·3 | 115 | 16·0 |
| Other | 451 | 8·2 | 163 | 7·9 | 72 | 4·5 | 23 | 3·2 |
| Missing | 33 | 0·6 | 12 | 0·6 | 0 | 0·0 | 0 | 0·0 |
| Age (years) | ||||||||
| <20 | 608 | 11·0 | 195 | 9·4 | 159 | 10·0 | 67 | 9·3 |
| 20–34 | 4053 | 73·6 | 1446 | 69·9 | 1171 | 73·5 | 494 | 68·6 |
| ≥35 | 813 | 14·8 | 416 | 20·1 | 263 | 16·5 | 159 | 22·1 |
| Missing | 33 | 0·6 | 12 | 0·6 | 0 | 0·0 | 0 | 0·0 |
| Nativity | ||||||||
| Foreign born | 3403 | 61·8 | 1118 | 54·0 | 970 | 60·9 | 377 | 52·4 |
| US born | 2029 | 36·8 | 935 | 45·2 | 596 | 37·4 | 338 | 46·9 |
| Missing | 75 | 1·4 | 16 | 0·8 | 27 | 1·7 | 5 | 0·7 |
| Education | ||||||||
| Less than high school | 1680 | 30·5 | 623 | 30·1 | 434 | 27·2 | 204 | 28·3 |
| High school/GED | 1800 | 32·7 | 741 | 35·8 | 575 | 36·1 | 279 | 38·8 |
| Some/beyond college | 1970 | 35·8 | 684 | 33·1 | 578 | 36·3 | 234 | 32·5 |
| Missing | 57 | 1·0 | 21 | 1·0 | 6 | 0·4 | 3 | 0·4 |
| Marital status | ||||||||
| Married | 2038 | 37·0 | 698 | 33·7 | 564 | 35·4 | 225 | 31·3 |
| Unmarried | 3339 | 60·6 | 1339 | 64·7 | 1019 | 64·0 | 488 | 67·8 |
| Missing | 130 | 2·4 | 32 | 1·5 | 10 | 0·6 | 7 | 1·0 |
| Receipt of public assistance† | ||||||||
| No | 856 | 15·5 | 354 | 17·1 | 208 | 13·1 | 112 | 15·6 |
| Yes | 4651 | 84·5 | 1715 | 82·9 | 1385 | 86·9 | 608 | 84·4 |
| Parity | ||||||||
| Multiparous | 3119 | 56·6 | 1180 | 57·0 | 933 | 58·6 | 425 | 59·0 |
| Nulliparous | 2374 | 43·1 | 885 | 42·8 | 657 | 41·2 | 294 | 40·8 |
| Missing | 14 | 0·3 | 4 | 0·2 | 3 | 0·2 | 1 | 0·1 |
| Cigarette smoking | ||||||||
| Never | 4449 | 80·8 | 1534 | 74·1 | 1321 | 82·9 | 545 | 75·7 |
| Ever | 376 | 6·8 | 175 | 8·5 | 114 | 7·2 | 73 | 10·1 |
| Continued in pregnancy | 611 | 11·1 | 336 | 16·2 | 145 | 9·1 | 99 | 13·8 |
| Missing | 17 | 1·3 | 24 | 1·2 | 13 | 0·8 | 3 | 0·4 |
| Alcohol consumption | ||||||||
| No | 4858 | 88·2 | 1782 | 86·1 | 1431 | 89·8 | 644 | 89·4 |
| Yes | 474 | 8·6 | 218 | 10·5 | 124 | 7·8 | 67 | 9·3 |
| Missing | 175 | 3·2 | 69 | 3·3 | 38 | 2·4 | 9 | 1·3 |
| Stress‡ | ||||||||
| No | 4404 | 80·0 | 1544 | 74·6 | 1270 | 79·7 | 535 | 74·3 |
| Yes | 1078 | 19·6 | 516 | 24·9 | 317 | 19·9 | 183 | 25·4 |
| Missing | 25 | 0·5 | 9 | 0·4 | 6 | 0·4 | 2 | 0·3 |
| BMI category§ | ||||||||
| Underweight | 227 | 4·1 | 97 | 4·7 | 62 | 3·9 | 27 | 3·8 |
| Normal | 2494 | 45·3 | 859 | 41·5 | 701 | 44·0 | 269 | 37·4 |
| Overweight/obese | 2367 | 43·0 | 973 | 47·0 | 745 | 46·8 | 386 | 53·6 |
| Missing | 419 | 7·6 | 140 | 6·8 | 85 | 5·3 | 38 | 5·3 |
| Pre-eclampsia disorders║ | ||||||||
| No | 5047 | 91·6 | 1582 | 76·5 | 1483 | 93·1 | 534 | 74·2 |
| Yes | 460 | 8·4 | 487 | 23·5 | 110 | 6·9 | 186 | 25·8 |
| Intra-uterine infection/inflammation¶ | ||||||||
| No | 4371 | 79·4 | 1557 | 75·3 | 1361 | 85·4 | 560 | 77·8 |
| Yes | 690 | 12·5 | 432 | 20·9 | 169 | 10·6 | 151 | 21·0 |
| Missing | 446 | 8·1 | 80 | 3·9 | 63 | 4·0 | 9 | 1·3 |
| Diabetes mellitus | ||||||||
| None | 5162 | 93·7 | 1850 | 89·4 | 1498 | 94·0 | 632 | 87·8 |
| Gestational | 220 | 4·0 | 124 | 6·0 | 53 | 3·3 | 49 | 6·8 |
| Pre-gestational | 75 | 1·4 | 79 | 3·8 | 31 | 1·9 | 34 | 4·7 |
| Missing | 50 | 0·9 | 16 | 0·8 | 11 | 0·7 | 5 | 0·7 |
| Multivitamin supplement intake preconception | ||||||||
| None | 5137 | 93·3 | 1940 | 93·8 | 1504 | 94·4 | 671 | 93·2 |
| Any | 370 | 6·7 | 129 | 6·2 | 89 | 5·6 | 49 | 6·8 |
PTB, preterm birth; GED, General Equivalency Diploma.
Non-Hispanic Black includes Black, African American, Haitian, Cape Verdian.
Public assistance is defined as receipt of any of the following: WIC (Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children), food stamps, AFDC (Aid to Families with Dependent Children, now known as TANF (Temporary Aid to Needy Families)), housing assistance or fuel assistance.
Mother’s self-report of life or pregnancy being very stressful.
Underweight, BMI <18·5 kg/m2; normal weight, BMI = 18·5–24·9 kg/m2; overweight/obesity, BMI≥25·0 kg/m2.
Pre-eclampsia disorders are defined as the presence of pre-eclampsia, gestational hypertension and HELLP (haemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets) syndrome.
Intra-uterine infection/inflammation is defined as the presence of maternal fever or placenta pathology findings of villitis, deciduitis, chorioamnionitis, chorionitis, subchorionitis, funisitis and free membranitis.
Within the plasma folate sub-sample, 31 % of women experienced PTB. The mean and median plasma folate concentration at delivery was 32·3 (sd 20·0) and 28·5 nmol/l, respectively, for PTB; significantly lower than 36·3 (sd 24·7) and 31·5 nmol/l, respectively, for term births. Significant associations between maternal characteristics and PTB that were seen in the total supplement intake sample persisted in the plasma folate sub-sample. Plasma folate was mildly correlated with multivitamin supplement intake in the third trimester (ρ = 0·10, P <0·001). The relationship between plasma folate concentrations and gestational age is presented graphically in the online supplementary material, Supplemental Fig. 1. Every unit increase in plasma folate concentration was associated with a 0·01-week increase in gestational age (95 % CI 0·004, 0·016).
Table 2 displays the association between self-reported multivitamin supplement intake and PTB (analysis by PTB subtypes is presented in the online supplementary material, Supplemental Table 2). The overall multivitamin supplement intake across pregnancy was significantly associated with PTB. Specifically, each unit increase in the multivitamin supplement intake index reduced the odds of PTB (adjusted OR (aOR) = 0·98; 95 % CI 0·97, 0·99). As a categorical variable, consistent multivitamin supplement intake (3–5 times/week or >5 times/week) reduced the odds of PTB compared with no intake across pregnancy (aOR = 0·78; 95 % CI 0·64, 0·96 and aOR = 0·77; 95 % CI 0·64, 0·93, respectively). The relationship between multivitamin supplement intake across different time points and PTB showed that intake during the preconception period did not reduce PTB odds. Intake during the first trimester (>5 times/week) was associated with a reduction in PTB odds (aOR = 0·85; 95 % CI 0·73, 0·98). During the third trimester, intake of 3–5 times/week and >5 times/week were associated with lower odds of PTB (aOR = 0·75; 95 % CI 0·63, 0·85 and aOR = 0·74; 95 % CI 0·64, 0·87, respectively). There was no significant difference in the odds of PTB among women with consistent multivitamin supplement intake of 1–2 times/week throughout pregnancy compared with no intake throughout pregnancy. Sensitivity analysis presented in Supplemental Table 3 showed a consistent pattern of a relationship of multivitamin supplement intake at all time points with PTB among non-Hispanic Blacks only.
Table 2.
Relationship between multivitamin supplement intake and preterm birth (PTB) among predominantly urban, low-income, minority mother–infant dyads (n 7576) enrolled in the Boston Birth Cohort, USA, from 1998 to 2014
| Period | Term (n 5507) | PTB (n 2069) | Unadjusted | Adjusted OR* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ncases | % | ncases | % | OR | 95 % CI | OR | 95 % CI | |
| Multivitamin supplement intake in pregnancy (first to third trimester) | ||||||||
| Continuous (index)† | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0·97 | 0·96, 0·98 | 0·98 | 0·97, 0·99 |
| Categorical | ||||||||
| None (ref.) | 436 | 7·9 | 219 | 10·6 | 1·00 | n/a | 1·00 | n/a |
| 1–2 times/week | 933 | 16·9 | 406 | 19·6 | 0·87 | 0·71, 1·06 | 0·91 | 0·74, 1·12 |
| 3–5 times/week | 1373 | 24·9 | 476 | 23·0 | 0·69 | 0·57, 0·84 | 0·78 | 0·64, 0·96 |
| >5 times/week | 2765 | 50·2 | 968 | 46·8 | 0·70 | 0·58, 0·83 | 0·77 | 0·64, 0·93 |
| Multivitamin supplement intake in specific time periods | ||||||||
| Preconception | ||||||||
| None (ref.) | 5137 | 93·3 | 1940 | 93·8 | 1·00 | n/a | 1·00 | n/a |
| Any | 370 | 6·7 | 129 | 6·2 | 0·92 | 0·75, 1·14 | 0·90 | 0·72, 1·12 |
| First trimester | ||||||||
| None (ref.) | 914 | 16·6 | 402 | 19·4 | 1·00 | n/a | 1·00 | n/a |
| 1–2 times/week | 204 | 3·7 | 97 | 4·7 | 1·08 | 0·83, 1·41 | 1·08 | 0·82, 1·43 |
| 3–5 times/week | 1582 | 26·9 | 539 | 26·1 | 0·83 | 0·71, 0·96 | 0·90 | 0·76, 1·06 |
| >5 times/week | 2907 | 52·8 | 1031 | 49·8 | 0·81 | 0·70, 0·92 | 0·85 | 0·73, 0·98 |
| Second trimester | ||||||||
| None (ref.) | 642 | 11·7 | 290 | 14·0 | 1·00 | n/a | 1·00 | n/a |
| 1–2 times/week | 220 | 4·0 | 108 | 5·2 | 1·09 | 0·83, 1·42 | 1·19 | 0·90, 1·57 |
| 3–5 times/week | 1558 | 28·3 | 570 | 27·6 | 0·81 | 0·68, 0·96 | 0·92 | 0·77, 1·10 |
| >5 times/week | 3087 | 56·1 | 1101 | 53·2 | 0·79 | 0·68, 0·92 | 0·86 | 0·73, 1·02 |
| Third trimester | ||||||||
| None (ref.) | 655 | 11·9 | 345 | 16·8 | 1·00 | n/a | 1·00 | n/a |
| 1–2 times/week | 255 | 4·6 | 99 | 4·8 | 0·74 | 0·56, 0·96 | 0·80 | 0·61, 1·06 |
| 3–5 times/week | 1558 | 28·3 | 543 | 26·2 | 0·66 | 0·56, 0·78 | 0·75 | 0·63, 0·90 |
| >5 times/week | 3039 | 55·2 | 1082 | 52·3 | 0·68 | 0·58, 0·78 | 0·75 | 0·64, 0·87 |
ref., reference category; n/a, not applicable.
Adjusted for maternal race, age, nativity, education, marital status, receipt of public assistance, parity, cigarette use, alcohol use, stress, pre-eclampsia disorders, intra-uterine infection/inflammation and diabetes mellitus.
Composite measure of supplement intake from first to third trimester.
Table 3 displays the unadjusted and adjusted odds of PTB by plasma folate concentration. Each unit and interquartile increase in plasma folate concentration reduced the odds of PTB (aOR = 0·99; 95 % CI 0·99, 1·00 and aOR = 0·88; 95 % CI 0·79, 0·97, respectively). This association persisted when plasma folate concentration was categorized. Compared with the lowest quartile (<19·4 nmol/l), the highest quartile of plasma folate concentration (>43·8 nmol/l) was associated with a reduction in PTB odds of over 25 % (aOR = 0·74; 95 % CI 0·56, 0·79) Similarly, excess plasma folate concentration (>45·3 nmol/l) was associated with reduced odds of PTB (aOR = 0·70; 95 % CI 0·55, 0·98) compared with normal plasma concentration (13·5–45·3 nmol/l).
Table 3.
Relationship between maternal plasma folate levels and preterm birth (PTB) among predominantly urban, low-income, minority mother–infant dyads (n 2313) enrolled in the Boston Birth Cohort, USA, from 1998 to 2014
| Plasma folate level | Term (n 1593) | PTB (n 720) | Unadjusted | Adjusted OR* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ncases | % | ncases | % | OR | 95 % CI | OR | 95 % CI | |
| Continuous plasma folate concentration (nmol/l) | ||||||||
| Each unit increase† | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0·991 | 0·986, 0·995 | 0·994 | 0·990, 0·999 |
| Each interquartile increase in folate level‡ | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0·81 | 0·73, 0·90 | 0·88 | 0·79, 0·97 |
| Quartiles of plasma folate concentration (nmol/l) | ||||||||
| Lowest quartile: 6·6–19·4 (ref.) | 378 | 23·7 | 201 | 27·9 | 1·00 | n/a | 1·00 | n/a |
| Second quartile: 19·4–30·0 | 386 | 24·2 | 192 | 26·7 | 0·94 | 0·73, 1·19 | 1·02 | 0·79, 1·33 |
| Third quartile: 30·0–43·8 | 393 | 24·7 | 185 | 25·7 | 0·89 | 0·69, 1·13 | 1·09 | 0·83, 1·42 |
| Highest quartile: 43·8–185·5 | 436 | 27·4 | 142 | 19·7 | 0·61 | 0·47, 0·79 | 0·74 | 0·56, 0·97 |
| WHO classification (nmol/l) | ||||||||
| Insufficiency/deficiency: <13·5 | 155 | 9·7 | 82 | 11·4 | 1·07 | 0·80, 1·43 | 0·86 | 0·63, 1·18 |
| Normal: 13·5–45·3 (ref.) | 1030 | 64·7 | 508 | 70·6 | 1·00 | n/a | 1·00 | n/a |
| Excess: >45·3 | 408 | 25·6 | 130 | 18·1 | 0·65 | 0·52, 0·81 | 0·70 | 0·55, 0·89 |
ref., reference category; n/a, not applicable.
Adjusted for maternal race, age, nativity, education, marital status, receipt of public assistance, parity, tobacco use, alcohol use, stress, BMI, pre-eclampsia disorders, intra-uterine infection/inflammation, and diabetes.
Mean (sd) for term birth and PTB: 36·6 (24·7) and 32·3 (20·0) nmol/l, respectively.
Median (interquartile range) for term birth and PTB: 31·5 (20·8–45·6) and 28·5 (19·0–38·5) nmol/l, respectively.
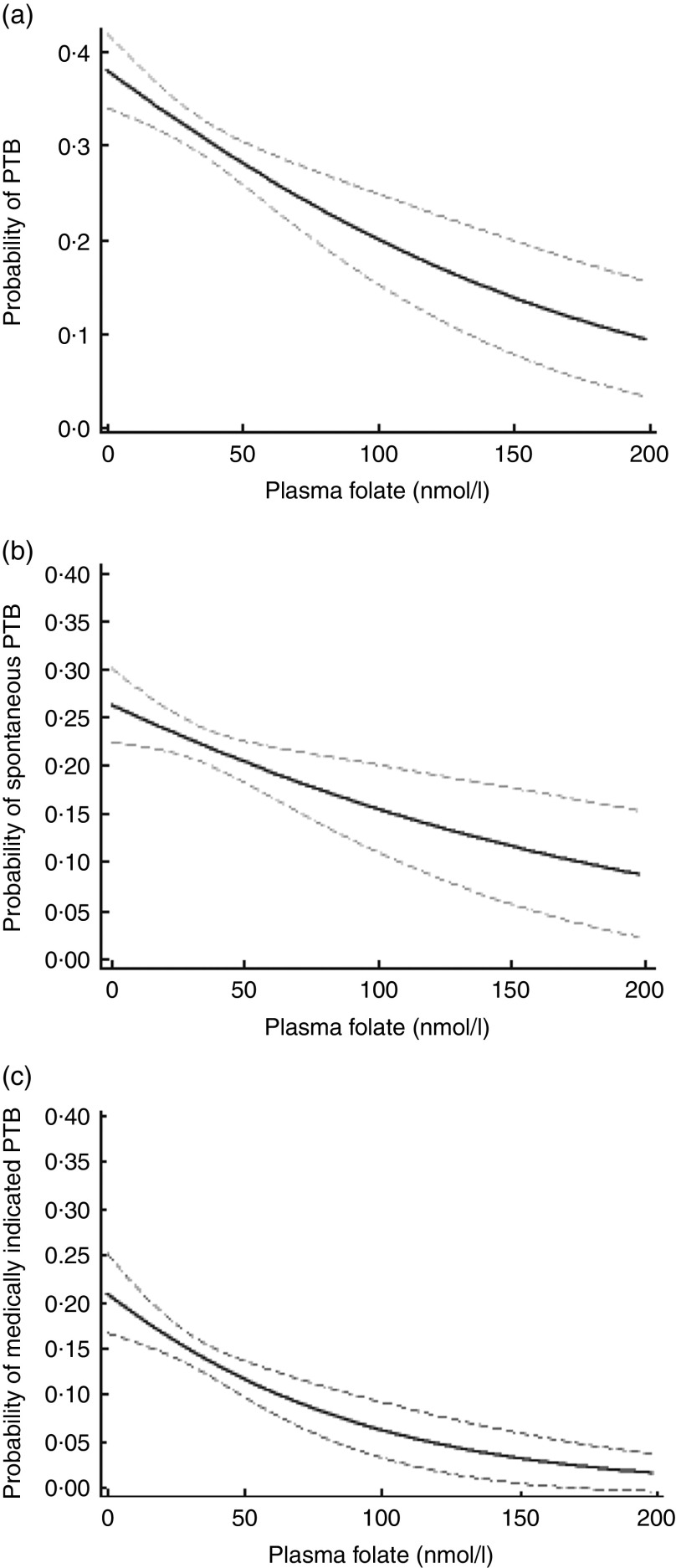
Figure 1 displays the association between plasma folate concentration at delivery and probability of PTB, stratified by subtypes. Plasma folate concentration demonstrated a mild curvilinear relationship with overall PTB, a linear relationship with spontaneous PTB and a curvilinear relationship with medically indicated PTB, where higher concentrations of plasma folate were associated with a reduced probability of PTB or its subtypes.
Fig. 1.
Probability (solid line) and 95% confidence interval (dashed lines) of (a) overall, (b) spontaneous and (c) medically indicated preterm birth (PTB) by plasma folate concentration among predominantly urban, low-income, minority mother–infant dyads (n 2313) enrolled in the Boston Birth Cohort, USA, from 1998 to 2014
In Table 4, the relationship between plasma folate concentration and spontaneous v. medically indicted PTB is presented. The final regression model for medically indicated PTB did not include biomedical risk factors to avoid the introduction of factors potentially in the causal pathway. Each unit increase in plasma folate concentration was associated with reduced odds of spontaneous (aOR = 0·99; 95 % CI 0·99, 1·00) as well as medically indicated (aOR = 0·98; 95 % CI 0·98, 0·99) PTB. Among medically indicated PTB, plasma folate concentration in the highest quartile was associated with a reduction in the odds of PTB; this relationship did not reach statistical significance for spontaneous PTB. Plasma folate concentrations in excess of 45·3 nmol/l were associated with a 30 % reduction in the odds of spontaneous (aOR = 0·72; 95 % CI 0·55, 0·95) and medically indicated PTB (aOR = 0·58; 95 % CI 0·40, 0·82).
Table 4.
Plasma folate levels and unadjusted and adjusted odds of preterm birth (PTB) subtypes among predominantly urban, low-income, minority mother–infant dyads (n 2313) enrolled in the Boston Birth Cohort, USA, from 1998 to 2014
| Plasma folate level | Spontaneous PTB | Medically indicated PTB | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ncases | % | aOR* | 95 % CI | ncases | % | aOR† | 95 % CI | |
| Continuous plasma folate concentration (nmol/l) | ||||||||
| Each unit increase | n/a | n/a | 0·995 | 0·990, 1·000 | n/a | n/a | 0·99 | 0·98, 0·99 |
| Each interquartile increase in folate level | n/a | n/a | 0·90 | 0·80, 1·01 | n/a | n/a | 0·73 | 0·62, 0·87 |
| Quartiles of plasma folate concentration (nmol/l) | ||||||||
| Lowest quartile: 6·6–19·4 (ref.) | 114 | 23·2 | 1·00 | n/a | 87 | 18·7 | 1·00 | n/a |
| Second quartile: 19·4–30·0 | 119 | 23·6 | 1·12 | 0·82, 1·53 | 73 | 15·9 | 0·85 | 0·60, 1·21 |
| Third quartile: 30·0–43·8 | 124 | 24·0 | 1·27 | 0·93, 1·73 | 61 | 13·4 | 0·68 | 0·47, 0·99 |
| Highest quartile: 43·8–185·5 | 96 | 18·1 | 0·86 | 0·62, 1·18 | 46 | 9·5 | 0·46 | 0·31, 0·69 |
| WHO classification (nmol/l) | ||||||||
| Insufficiency/deficiency: <13·5 | 45 | 22·5 | 0·77 | 0·53, 1·12 | 37 | 19·3 | 1·25 | 0·83, 1·86 |
| Normal: 13·5–45·3 (ref.) | 321 | 23·8 | 1·00 | n/a | 187 | 15·4 | 1·00 | n/a |
| Excess: ≥45·3 | 87 | 17·6 | 0·72 | 0·55, 0·95 | 43 | 9·5 | 0·58 | 0·40, 0·82 |
aOR, adjusted odds ratio; ref., reference category; n/a, not applicable.
Adjusted for maternal race, age, nativity, education, marital status, receipt of public assistance, parity, tobacco use, alcohol use, stress, BMI, pre-eclampsia disorders, intra-uterine infection/inflammation and diabetes.
Adjusted for maternal race, age, nativity, education, marital status, receipt of public assistance, parity, tobacco use, alcohol use and stress.
Discussion
In our full sample, multivitamin supplement intake and plasma folate concentrations were generally adequate or high, as expected in this era of mandatory folic acid fortification of the food supply. Still, about a quarter of women had a relatively low plasma folate concentration (<19·4 nmol/l), which was associated with an increased risk of PTB. While there are no national data, an association between folate fortification and reduced PTB rates was observed in California among live births that occurred from January 1990 through December 2000(13). After adjusting for maternal age, parity, race/ethnicity, education, year of birth and fortification period, fortification was shown to reduce PTB risk (relative risk ratio = 0·96; 95 % CI 0·94, 0·97).
After controlling for confounding factors, our analysis shows that multivitamin supplement intake of at least 3 times/week throughout pregnancy was significantly associated with a reduction in the odds of PTB, consistent with other US-based prospective studies that have assessed dietary folate intake(14,16). A study in a low-income minority population showed that low (≤240 µg/d) and intermediate (241–400 µg/d) dietary folate intake were associated with an increased risk of PTB, respectively, as compared with women who had a folate intake >400 µg/d(14). In another study, dietary folate intake ≤500 µg/d was associated with an almost two times greater risk of preterm delivery(16).
We note that there was no significant association between preconceptional supplement intake and PTB, contrary to the findings of Bukowski et al., which demonstrated a 50–70 % related reduction in the incidence of early spontaneous PTB(18). However, in our study, preconception supplement intake was very low (7·1 %) and may have resulted in reduced statistical power to detect significant associations. Multivitamin supplementation in the first and third trimester were both significantly associated with reduced PTB odds, with use during the third trimester associated with a greater reduction in PTB odds than use during the first trimester. It is unclear why second-trimester multivitamin supplement intake is not associated with PTB. While the association observed in the third trimester may be a reflection of intake in other trimesters given the high correlation across trimesters, these findings suggest that the third trimester may be a critical time window in the folate–PTB relationship. While folate is needed for maternal tissue and fetal and placental growth throughout pregnancy, the rapid fetal development occurring during the third trimester is associated with maximum folate catabolism and thus increased requirements during this critical period(29,30). Studies show that women who stopped multivitamin or folate supplementation after the first trimester had lower concentrations of maternal serum and red-blood-cell folate(29–31). The association between multivitamin supplement intake and PTB was corroborated using plasma folate concentration at delivery. Increasing plasma folate concentrations significantly reduced the odds of PTB. Our findings are consistent with other US-based studies with folate measurements during pregnancy, wherein each 1 nmol/l increase in serum folate concentration at 28 weeks of gestation was also associated with reduced risk of PTB(14) and serum folate concentration less than 36·9 nmol/l in the second trimester (24–29 weeks of gestation) led to a nearly twofold increased risk of PTB(16). These findings demonstrating the relationship between maternal folate status and PTB are particularly important given that the national PTB rates have remained high, 10·4 % in 2007 and 9·8 % in 2016, despite research and intervention efforts(32). Our research on a predominantly minority population is also appropriate given that the national PTB rate was highest among non-Hispanic Black births (13·8 %)(32). The patient population from which we derived the Boston Birth Cohort has a high rate of PTB (15–17 %) and the higher rates of PTB seen in the study sample are because the study oversampled PTB at enrolment. Among this population at a particular high risk of PTB and inadequate folate intake, we have shown that, in such a setting, the lower levels of plasma folate with preterm delivery may be a reflection of the duration of folic acid supplementation and that maternal adequate folate status can reduce the risk of PTB(33).
Maternal factors well demonstrated in the literature to be associated with, but not necessarily in the causal pathway of PTB include demographic, obstetric, medical and psychosocial risk factors(34). However, the underlying mechanisms for the link between folate and PTB are not well understood but appear to be biologically plausible. For example, variations in key genes involved in folate metabolism, such as those encoding dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) and serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT1), appear to increase the risk for spontaneous PTB(35). Other mechanistic pathways that may explain the folate–PTB relationship include hyperhomocysteinaemia, placental implantation and intra-uterine infection and inflammation(36,37). Low folate status is associated with hyperhomocysteinaemia, which has been linked with increased arterial stiffness, insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction. Folate may also affect placental implantation and vascular remodelling through its role as a superoxide scavenger in antioxidant defences(36). Folate deficiency is also associated with abnormal inflammatory responses, which could conceivably trigger premature parturition in the context of intra-uterine infection(38,39).
Strengths of our study include the use of complementary measures of folate status, from maternal self-report (capturing pattern of long-term use) and more objective biomarkers, providing multi-measure consistent evidence to support the folate–PTB relationship. The study is the largest investigation with recent birth cohort data on plasma folate and PTB published to date and is the first one that performed PTB subtype analyses. While maternal folate status has been linked with spontaneous PTB(18), its relationship with medically indicated PTB has been demonstrated only in animal studies(40). Again, such research is particularly relevant among high-risk populations such as non-Hispanic Blacks who have lower folate levels compared with other race/ethnic groups(8) and a higher proportion of medically indicated PTB(41).
Our study contributes new knowledge to the field by exploring specific patterns of multivitamin supplementation during the preconception period and across trimesters. This facilitates identifying the critical period over the course of pregnancy to reinforce adequate folate intake in order to reduce PTB. Finally, our study focuses on the high-risk non-Hispanic Black US populations in need for interventions to address both PTB and lower folate status.
However, we acknowledge some limitations of the present study. While plasma or serum folate is a common inexpensive measurement used in clinical and research settings, it reflects only short-term folate status within the past few days in contrast to red-cell-folate concentrations which measure long-term folate status. Thus, plasma folate concentration at delivery can be used as a proxy only for third-trimester folate concentration(42). As shown in a previous publication(21), maternal self-reported multivitamin intake during the third trimester was positively associated with maternal plasma folate levels. While folate measurements during early pregnancy would be more ideal, plasma folate concentration at delivery can be used as a proxy for third-trimester folate concentration. In addition, multivitamin supplement intake was based on self-report, which is subject to recall bias as well as the fact that there was no information on the actual dosage of folic acid consumed. Also, the determination of folate status based on the frequency of supplement intake may be incomplete, since folate status may also be influenced by dietary intake of folate-rich/fortified foods and other factors affecting folate metabolism. Due to the high correlations between multivitamin supplement intake across all trimesters (ρ = 0·58–0·85, P <0·001), further adjustments for intake during other trimesters were not conducted when we explored the associations in each trimester. This was an observational study enriched by PTB, and by its nature cannot enable causal inference(43) as unobserved or uncontrolled confounding remains a threat to validity. Additional detail on some of the confounding variables, such as the level of cigarette and alcohol consumption in each trimester, would have been helpful. While no randomized controlled trial has been conducted in the USA and is unlikely given the advantageous role of folate on pregnancy outcomes, study findings need to be confirmed in other nationally representative prospective longitudinal studies. This is a US urban low-income population in a post-folate fortification context and caution is needed in generalizing study findings to other populations with different characteristics. We also acknowledge that ours is a high-risk (low-income, minority, urban) US population in a post-folate fortification context and that our findings may be reproducible in other populations in other countries.
There are important implications to be gleaned from the present study. The association between folate and PTB among this predominantly minority, urban low-income population is important, because studies have shown that women who were non-White (non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic women), aged 18–24 years, and had less than a high-school education or had an annual household income of <$US 25 000 are the least likely to report daily consumption of a supplement containing folic acid(44). In addition, minority populations are less likely to have heard about folic acid, to know it can prevent birth defects, and to consume foods fortified with folic acid or take vitamins containing folic acid(45,46).
Lastly, our study supports the importance of consistent folate intake throughout pregnancy to mitigate adverse pregnancy outcomes, including PTB(9,29,47). Our study demonstrated minimal difference in PTB mitigation related to multivitamin supplement intake of 3–5 times/week v. >5 times/week, suggesting a possible threshold dosing schedule of 3 times/week. If corroborated by other studies, this finding may impact the recommendations for frequency of multivitamin supplement intake before and during pregnancy. Specifically, this finding suggests that the same protective benefit can be derived from a three times weekly dose compared with a daily dose. Finally, folate has a broad biological function and there is increasing recognition that folate supplementation during pregnancy may affect both short-term and long-term health of the offspring. For example, in the same cohort, we demonstrated beneficial effects of adequate maternal plasma folate levels on offspring obesity(48,49). Furthermore, our recent study(21) along with that of others(50) raised concern about the potential risk of extremely high levels of folate on autism. Therefore, more work remains to be done to determine the optimal range of maternal folate levels throughout pregnancy for major organs and systems in the offspring. Ultimately, we need to define an optimal range of folate levels (neither too low nor too high), preconception and during pregnancy, which can maximize its health benefits and minimize its risk. This may require careful consideration of a woman’s health conditions, dietary intake and folic acid supplementation, and measurement of plasma folate levels as needed.
Acknowledgements
Financial support: The Boston Birth Cohort (the parent study) was supported in part by the March of Dimes Perinatal Epidemiological Research Initiative (grant numbers 20-FY02-56, 21-FY07-605); the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (grant numbers R21ES011666, R01HD041702, R21HD066471, U01AI090727, R21AI079872 and R01HD086013); and the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) of the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) (grant numbers R40MC27443 and UJ2MC31074). The authors are also grateful for general support from the Hopkins Population Center (grant number NICHD R24HD042854). This information or content and conclusions are those of the authors and should not be construed as the official position or policy of, nor should any endorsements be inferred by, any funding agencies. The funding agencies had no role in the design, analysis or writing of this article. Conflict of interest: None of the authors reported a conflict of interest related to the study. Authorship: B.O., A.Sa. and X.W. designed the research; B.O., R.R. and Y.J. performed statistical analyses; G.W., X.H. and Y.J. performed lab assays; B.O. wrote the paper; and all other co-authors participated in data interpretation and presentation, critical review and revision of the manuscript. X.W. is the Principal Investigator of the Boston Birth Cohort and had primary responsibility for final content. All authors approved the final manuscript for submission. Ethics of human subject participation: This study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki and all procedures involving human subjects were approved by Institutional Review Boards of Boston University Medical Center and the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Supplementary material
For supplementary material accompanying this paper visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980018003221.
click here to view supplementary material
References
- 1. Frey HA & Klebanoff MA (2016) The epidemiology, etiology, and costs of preterm birth. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 21, 68–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Bailey LB & Gregory JF 3rd (1999) Folate metabolism and requirements. J Nutr 129, 779–782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Smits LJ & Essed GG (2001) Short interpregnancy intervals and unfavourable pregnancy outcome: role of folate depletion. Lancet 358, 2074–2077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Zhu BP (2005) Effect of interpregnancy interval on birth outcomes: findings from three recent US studies. Int J Gynecol Obstet 89, Suppl. 1, S25–S33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Moussa HN, Hosseini Nasab S, Haidar ZA et al. (2016) Folic acid supplementation: what is new? Fetal, obstetric, long-term benefits and risks. Future Sci OA 2, FSO116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Pfeiffer CM, Johnson CL, Jain RB et al. (2007) Trends in blood folate and vitamin B-12 concentrations in the United States, 1988 2004. Am J Clin Nutr 86, 718–727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Crider KS, Bailey LB & Berry RJ (2011) Folic acid food fortification – its history, effect, concerns, and future directions. Nutrients 3, 370–384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Tinker SC, Hamner HC, Qi YP et al. (2015) US women of childbearing age who are at possible increased risk of a neural tube defect-affected pregnancy due to suboptimal red blood cell folate concentrations, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007 to 2012. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 103, 517–526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Czeizel AE, Dudas I, Vereczkey A et al. (2013) Folate deficiency and folic acid supplementation: the prevention of neural-tube defects and congenital heart defects. Nutrients 5, 4760–4775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Blom HJ (2009) Folic acid, methylation and neural tube closure in humans. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 85, 295–302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Smithells RW, Sheppard S, Schorah CJ et al. (1980) Possible prevention of neural-tube defects by periconceptional vitamin supplementation. Lancet 1, 339–340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Curry SJ et al. (2017) Folic acid supplementation for the prevention of neural tube defects: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 317, 183–189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Shaw GM, Carmichael SL, Nelson V et al. (2004) Occurrence of low birthweight and preterm delivery among California infants before and after compulsory food fortification with folic acid. Public Health Rep 119, 170–173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Scholl TO, Hediger ML, Schall JI et al. (1996) Dietary and serum folate: their influence on the outcome of pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 63, 520–525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Scholl TO & Johnson WG (2000) Folic acid: influence on the outcome of pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 71, 5 Suppl., 1295S–1303S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Siega-Riz AM, Savitz DA, Zeisel SH et al. (2004) Second trimester folate status and preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 191, 1851–1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Bodnar LM, Himes KP, Venkataramanan R et al. (2010) Maternal serum folate species in early pregnancy and risk of preterm birth. Am J Clin Nutr 92, 864–871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Bukowski R, Malone FD, Porter FT et al. (2009) Preconceptional folate supplementation and the risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a cohort study. PLoS Med 6, e1000061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Dunlop AL, Taylor RN, Tangpricha V et al. (2012) Maternal micronutrient status and preterm versus term birth for black and white US women. Reprod Sci 19, 939–948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Shaw GM, Carmichael SL, Yang W et al. (2011) Periconceptional intake of folic acid and food folate and risks of preterm delivery. Am J Perinatol 28, 747–752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Raghavan R, Riley AW, Volk H et al. (2017) Maternal multivitamin intake, plasma folate and vitamin B12 levels and autism spectrum disorder risk in offspring. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 32, 100–111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Surkan PJ, Dong L, Ji Y et al. (2017) Paternal involvement and support and risk of preterm birth: findings from the Boston Birth Cohort. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. Published online: 16 November 2017. doi: 10.1080/0167482X.2017.1398725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23. Wang X, Zuckerman B, Pearson C et al. (2002) Maternal cigarette smoking, metabolic gene polymorphism, and infant birth weight. JAMA 287, 195–202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Blumenfeld YJ, El-Sayed YY, Lyell DJ et al. (2015) Risk factors for prolonged postpartum length of stay following cesarean delivery. Am J Perinatol 32, 825–832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (2014) Average Length of Stay: Childbirth 2014/1. Paris: OECD Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- 26. Greenberg JA & Bell SJ (2011) Multivitamin supplementation during pregnancy: emphasis on folic acid and l-methylfolate. Rev Obstet Gynecol 4, 126–127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Huo Y, Li J, Qin X et al. (2015) Efficacy of folic acid therapy in primary prevention of stroke among adults with hypertension in China: the CSPPT randomized clinical trial. JAMA 313, 1325–1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. World Health Organization (2015) Serum and Red Blood Cell Folate Concentrations for Assessing Folate Status in Populations. Geneva: WHO. [Google Scholar]
- 29. Wang S, Ge X, Zhu B et al. (2016) Maternal continuing folic acid supplementation after the first trimester of pregnancy increased the risk of large-for-gestational-age birth: a population-based birth cohort study. Nutrients 8, 493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Chanarin I, Rothman D, Ward A et al. (1968) Folate status and requirement in pregnancy. Br Med J 2, 390–394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. McNulty B, McNulty H, Marshall B et al. (2013) Impact of continuing folic acid after the first trimester of pregnancy: findings of a randomized trial of folic acid supplementation in the second and third trimesters. Am J Clin Nutr 98, 92–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Osterman MJ et al. (2017) Births: Provisional Data for 2016. Vital Statistics Rapid Release Report no. 2. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Cheng TL, Mistry KB, Wang G et al. (2018) Folate nutrition status in mothers of the Boston Birth Cohort, sample of a US urban low-income population. Am J Public Health 108, 799–807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Behrman RE & Butler AS (editors) (2007) Preterm Birth: Causes, Consequences, and Prevention. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Johnson WG, Scholl TO, Spychala JR et al. (2005) Common dihydrofolate reductase 19-base pair deletion allele: a novel risk factor for preterm delivery. Am J Clin Nutr 81, 664–668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Chen LW, Lim AL, Colega M et al. (2015) Maternal folate status, but not that of vitamins B-12 or B-6, is associated with gestational age and preterm birth risk in a multiethnic Asian population. J Nutr 145, 113–120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Bergen N, Jaddoe V, Timmermans S et al. (2012) Homocysteine and folate concentrations in early pregnancy and the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes: the Generation R Study. BJOG 119, 739–751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Cunningham F, Leveno K, Bloom S et al. (2004) Williams Obstetrics, 24th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education/Medical. [Google Scholar]
- 39. Courtemanche C, Elson-Schwab I, Mashiyama ST et al. (2004) Folate deficiency inhibits the proliferation of primary human CD8+T lymphocytes in vitro. J Immunol 173, 3186–3192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Zhao M, Chen YH, Dong XT et al. (2013) Folic acid protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm delivery and intrauterine growth restriction through its anti-inflammatory effect in mice. PLoS One 8, e82713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Ananth CV & Vintzileos AM (2006) Epidemiology of preterm birth and its clinical subtypes. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 19, 773–782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Farrell C-JL, Kirsch SH & Herrmann M (2013) Red cell or serum folate: what to do in clinical practice? Clin Chem Lab Med 51, 555–569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Szklo M & Nieto FJ (2014) Epidemiology: Beyond the Basics. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- 44. Saccone G, Sarno L, Roman A et al. (2016) 5-Methyl-tetrahydrofolate in prevention of recurrent preeclampsia. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 29, 916–920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Yang QH, Carter HK, Mulinare J et al. (2007) Race-ethnicity differences in folic acid intake in women of childbearing age in the United States after folic acid fortification: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2001–2002. Am J Clin Nutr 85, 1409–1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Ahluwalia IB & Daniel KL (2001) Are women with recent live births aware of the benefits of folic acid? MMWR Recomm Rep 50, 3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Higgins JR, Quinlivan EP, McPartlin J et al. (2000) The relationship between increased folate catabolism and the increased requirement for folate in pregnancy. BJOG 107, 1149–1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Wang G, Hu FB, Mistry KB et al. (2016) Association between maternal prepregnancy body mass index and plasma folate concentrations with child metabolic health. JAMA Pediatr 170, e160845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Wang H, Mueller NT, Li J et al. (2017) Association of maternal plasma folate and cardiometabolic risk factors in pregnancy with elevated blood pressure of offspring in childhood. Am J Hypertens 30, 532–540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Wiens D & DeSoto M (2017) Is high folic acid intake a risk factor for autism? – A review. Brain Sci 7, 149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
For supplementary material accompanying this paper visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980018003221.
click here to view supplementary material