Abstract
Prevention and management of obesity through dietary modification is one of the top way to trim down its consequences. Development of adipose tissue requires the differentiation of less specialized cells, such as human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), into adipocytes. Since food constituents play a major role in the cell differentiation and proliferation, we sought to determine if various extracts of Cucurbita ficifolia (C. ficifolia), could affect the adipogenic differentiation of hMSCs. Flow cytometry analysis with quantitative and qualitative Nile red, and quantitative PCR methods were employed to evaluate the C. ficifolia effect on hMSCs adipogenesis. Results revealed that, chloroform extract exhibits significant adipogenic inhibition than that of hexane and methanol extracts. Chloroform extract treated cells display the down-regulation of ADIPOQ, FABP4, PPARGC1A, CEBPB & LPL and up-regulation of ACACB & CEBPA genes. Further, various phytoconstituents present in the chloroform extract of C. ficifolia were analyzed though LC-MS and GC-MS. Our results indicates that chloroform extract of C. ficifolia might be used as a food supplement to control obesity and its related consequences.
Keywords: Obesity, Cucurbita ficifolia, Adipogenesis, Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs)
1. Introduction
Contemporary lifestyles are often blamed for the existing obesity and associated chronic disease epidemics. Obesity represents a crucial health issue, because it is a risk factor for the development of metabolic disorders including, type 2 diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular diseases (CVD) (Bhupathiraju and Hu, 2016, Must et al., 1999, Rose et al., 2015). A dramatic increase in the prevalence of obesity has been noted since the 1970s with an increase of more than 100% by 2030 (Deitel, 2003, Finkelstein et al., 2012, Wang et al., 2007).
Adipose tissue is an endocrine organ, regulating metabolic processes by releasing hormones in response to changes in metabolic states (Ahima and Flier, 2000, Spiegelman and Flier, 2001). Adipose tissue secretes molecules such as, leptin, TNF-α, adiponectin, and resistin. Excess or lack of these molecules is associated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (Kahn and Flier, 2000, Rosen and Spiegelman, 2006, Saltiel, 2001). The differentiation process of adipocytes is a crucial stage in the growth of adipose tissue, during which adipocyte enlarge to accumulate triglycerides (Quanhong et al., 2005, Yang et al., 2014). Regulation of gene expression in adipogenesis can lead to a decrease in the accumulation of fat droplets in adipocytes (Darlington et al., 1998, Lefterova and Lazar, 2009). However, stimulation of adipogenic genes such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ or PPARG), CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α (CEBPA), and fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) leads to increase in adipocyte size, which increases insulin resistance (Fu et al., 2005, Skurk et al., 2007).
In various populations, traditional medicine uses plant extracts in the treatment of obesity or associated diseases. Natural plant sources have been used to treat diabetes and obesity since ancient times (Akhtar, 1982). Pumpkin (C. ficifolia) is a widely consumed vegetable, but only few studies have shown its effect against obesity. Previous reports have shown that pumpkin consumption has a positive effect on hypertension and lipid levels (al-Zuhair et al., 1997, Zuhair et al., 2000). Also, Cucurbita moschata has been shown to possess anti-obesity effects in a high fat diet-induced obesity in mouse model, the data revealed that water-soluble extract (PG105) from C. moschata has the potential to inhibit the lipid synthesis and accelerate the fatty acid breakdown (Choi et al., 2007).
Recent data demonstrated that C. ficifolia extract modulates systemic chronic inflammation in MSG-obese mice and enhances the adaptive immune system in obesity. Treatment with the extract decreased the body mass and reduced inflammation by suppressing the expression of TNF-α and IL-6. Furthermore, the extract also increased the protein levels of IL-10 in lean mice and IFN-γ in both lean and MSG-obese mice (Fortis-Barrera et al., 2016). These results suggest that, Cucurbitaceae family has anti-adipogenic property that could improve the conventional nature based anti-obese treatment. However, the differentiation of hMSCs into mature adipocytes is the key process in adipogenesis. Adipogenesis can be studied in murine-derived 3T3-L1 cell line and hMSCs. hMSCs is considered as the most suitable in vitro model to study the anti-adipogenesis because, differentiation of hMSCs into mature adipocytes occurs in two phases namely a determination phase and a differentiation phase. Further, hMSCs are multipotent cells that can differentiate into various lineages and particularly this cell line has been extensively characterized (Ali et al., 2017, Vishnubalaji et al., 2012a, Vishnubalaji et al., 2012b). To our knowledge, there is no report on the anti-adipogenic potential of C. ficifolia on hMSCs and other cells.
In our previous study, we used chloroform, hexane, and methanol solvents to extract the effective bioactive compounds from C. ficifolia. Further, we investigated the biocompatibility and cytotoxicity effects on hMSCs. Our previous results revealed that chloroform extract of C. ficifolia is biocompatible than that of methanol and hexane extracts (Aristatile and Alshammari, 2017). In the present study, we have investigated and compared the effects of three different extracts of C. ficifolia on the differentiation of hMSCs into adipocytes and on the expression of adipogenic genes.
Interestingly, overall our data revealed that the chloroform extract of C. ficifolia significantly down-regulated the genes responsible for adipogenesis. These results provide an evidence of the natural anti-adipogenic effects of C. ficifolia on human stem cells. Indeed, the active compounds found in the chloroform extract may be used as molecular tools for anti-adipogenesis and obesity treatment research.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Extraction
Extraction procedure was performed in accordance with our previously published protocols (Aristatile and Alshammari, 2017). Briefly, fresh C. ficifolia was purchased from Riyadh, Saudi Arabia and were identified by botany department, college of Science, King Saud University. From the whole pumpkin, the outer thin layer and seeds were removed. The inner pulp was washed with water, sliced into small pieces air-dried at 37 °C and were subsequently pulverized into powder. The powder (750 g) was immersed in hexane (1500 mL) in a 2500 mL glass flask for 24 hrs. This process was repeated thrice. The solvent was then filtered and evaporated by rotary evaporator under vacuum at 40 °C. This extraction procedure was repeated with new C. ficifolia using chloroform and methanol as solvents. The resultant dry extracts were kept at -80 °C until further analyses. Solvent-free extracts were reconstituted in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), the solubility of hexane, chloroform and methanol extracts were 3 mg/mL, 1 mg/mL and 3 mg/mL respectively.
2.2. Cell culture
hMSCs were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with D-glucose (4500 mg/L), L-glutamine (4 mM), sodium pyruvate (110 mg/L), 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1 × penicillin–streptomycin (Pen-strep), and non-essential amino acids (Procured from Gibco-Invitrogen, USA). hMSCs (hTERT – human bone marrow immortalized cell line) was kindly donated by stem cell unit, department of anatomy, college of medicine, King Saud University, Riyadh (Vishnubalaji et al., 2012b).
The hMSCs were cultured to reach 70–80% confluence. Each of the three extracts was diluted (1.1 μg/mL to 18 μg/mL), filter sterilized and then added to the hMSCs. The cells were cultured in basal medium containing DMSO as vehicle (control).
2.3. Adipocyte differentiation
hMSCs were differentiated as mentioned in the literature (Vishnubalaji et al., 2012b). Briefly, cells were seeded at a density of 0.5 × 106 cells/mL in 6 well plates for flow cytometry analysis & RNA isolation, and in 24 well plates for Nile Red imaging. At 70–80% confluence, cells were treated with respective extracts in different concentrations (1.1 μg/mL to 18 μg/mL) for 24 hrs. The medium was replaced in all test wells with adipogenic induction medium (AIM) supplemented with 10% FBS and AIM containing 10% Horse serum (Sigma), 1% penicillin–streptomycin, 100 nM dexamethasone, 0.45 mM isobutyl methyl xanthine [(IBMX) (Sigma)], 3 μg/mL insulin (Sigma), and 1 μM rosiglitazone [(BRL49653) (Novo Nordisk, Bagsvaerd, Denmark)]. The adipogenic medium was replaced every 3 days and experiments were terminated at day 10. Cells cultured in regular medium was used as the experimental control. The experiments were carried out at least in three times.
2.4. Adipocyte enumeration by flow cytometry
The flow cytometry-based adipocyte enumeration was performed as described previously (Vishnubalaji et al., 2012a). After the experimental period, cells were collected by trypsinization, washed once with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 min and Nile Red dye was added (100 ng/mL). The cells were then incubated on ice for 5 min, centrifuged, and washed once with PBS. Cells were subsequently re-suspended in an appropriate volume of PBS and kept on ice prior to flow cytometric analysis. The undifferentiated and differentiated hMSCs extract treated cells were analyzed by flow cytometry, (Beckman Coulter Navios, Indianapolis, USA). Nile Red staining was detected in FL1 fluorescence channel detector (FITC channel; 495 nm/519 nm), and the outcome data were analyzed by Kluza software. Mature adipocyte quantification was performed by dual dot plot analysis FL1 vs FL6 fluorescent channel since no compensation is needed between these detectors. The experiments were repeated three different times with triplicates.
2.5. RNA isolation and qRT-PCR gene expression analysis
RNA was isolated from control and different experimental adipocytes using the Total Tissue RNA purification kit (Norgen-Biotek Corp., Thorold, ON, Canada). RNA quantification was performed using NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA) and the quality and integrity of isolated RNA was confirmed using gel electrophoresis. 2 μg of total RNA was reverse transcribed using a high capacity cDNA reverse transcript kit [Part No: 4368814; Applied Biosystem (ABI)] according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The expression levels of adipogenic-related genes [ADIPOQ, FABP 4, PPARGC1A, ACACB, CEBPB, CEBPA, and LPL] were quantified using custom Taqman low density array cards (S1 Table), and ViiA 7 real-time PCR device (ABI). The 2−ΔΔCT value method was performed as previously described (Ali et al., 2017). The experiments were carried out at least in three times with triplicate.
2.6. GC-MS and LC-MS analysis
The chloroform extract was dissolved in HPLC grade methanol and pumped using helium (99.99%) gas at a constant flow rate of 1 mL/min in an Agilent GCMS unit (7890 A, MS5975system, USA), equipped with a J&W-5MS fused silica capillary column containing 5% diphenyl and 95% dimethylpolysiloxane (30 m × 0.25 mm), injected Dose (ID) × 1 μm (% ID/g), with an injection volume of 3 μL (split ratio of 10:1). The GC injector temperature and ion source temperature were set to 250 °C and 280 °C, respectively. The oven temperature was programmed initially at 50 °C for 4 min, then increased gradually to 300 °C. The ionization voltage was set to 70 eV with a scan interval of 0.5 s and fragments from 35 to 800 Da. Total GC run time was 35 min. Mass spectra and chromatograms were analyzed using Turbo Mass version 5.2. The results of mass spectra was compared and interpreted using the National Institute of Standard Technology (NIST-11) database library.
Subsequently, the qualitative analysis of chloroform extract was performed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) via SIM mode. 6120 quadrupole LC/MS system (M/s Agilent Technologies, USA) and the separated compounds were analyzed by ChemStation® software. Followed by C18 analytical column (ZORBAX Eclipse Plus; 4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm particle size) was employed to determine the compounds. Moreover, the desired compounds were eluted under the mobile phase (70% HPLC grade methanol; 30% ultra-pure water), column flow (1 mL min−1); injection volume 3 μL at 40 °C. The experiments were carried out thrice to reduce the percentage of error and the retention time was recorded at 2.386 min. The experiments were repeated thrice with different extract.
2.7. Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses and graphing were performed using Microsoft excel 2010 and GraphPad Prism 6.0 software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). P-values were calculated using the using the unpaired two-tailed t-test and ANOVA (RM one-way ANOVA, with Greenhouse-Geisser corrections).
3. Results
In the present study, we utilized hMSCs as an in vitro model to study the adipogenesis process. hMSCs were treated with various (1.1 μg/mL to 18 μg/mL) concentration of chloroform, hexane, and methanol extracts of C. ficifolia for 10 days. Visual monitoring was done in hMSCs differentiation over the period of ten days, using the standard differentiation protocol (Ali et al., 2017), and showed that the small lipid droplets developed in the hMSCs treated with chloroform-extract of C. ficifolia. In cell viability assay, we did not observe any statistical difference for concentrations upto 18 μg/mL in the viability of different extract treated cells when compared with control cells (Aristatile and Alshammari, 2017). On the other hand, we have observed morphological difference in different experimental cells treated with various extracts of C. ficifolia when compared to control cells.
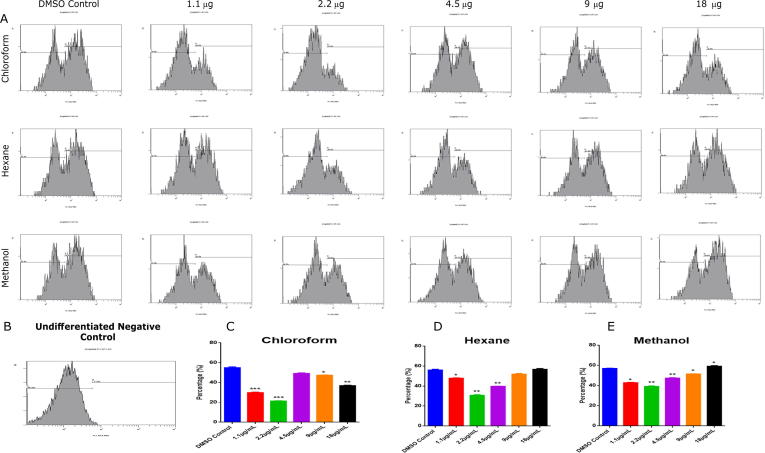
To identify the effects of different extracts on adipocyte differentiation we used flow cytometry with Nile red staining (Fig. 1). Adipocytes differentiated from hMSCs were analyzed by flow cytometry to visualize the mature adipocyte. Cells were treated with 1.1 μg/mL to 18 μg/mL of different extract of C. ficifolia. The chloroform (1.1 μg/mL - 29 ± 4% & 2.2 μg/mL – 21 ± 3%) extract showed more significant (P < 0.05) inhibitory role at 2.2 μg/mL, whereas hexane (1.1 μg/mL - 47 ± 6% & 2.2 μg/mL – 30 ± 4%) and methanol (1.1 μg/mL - 42 ± 5% & 2.2 ± 3 μg/mL – 39%) extracts showed comparatively less inhibition. Upon comparing all three extract treated groups, at 2.2 μg/mL, all three solvents showed maximum inhibition (Fig. 1). Further, when concentration is increased, anti-adipogenic effect is decreased, however we did not observe any cell death even at maximum concentration used in this study (18 μg/mL). This results shows that chloroform extract of C. ficifolia has maximum inhibitory effect in the adipogenesis of hMSCs.
Fig. 1.
Total differentiate adipocyte enumeration by flow cytometry. hMSCs treated with C. ficifolia extracts were differentiated and quantified by flow cytometry. Cells were with various concentrations (1.1 µg/mL to 18 µg/mL) of three different solvent-free extracts. (a) Differentiated DMSO control and undifferentiated negative control. (b) The histograms represent the differentiated cells that were stained with Nile red dye and analyzed in the FL1 channel, background normalized with undifferentiated control, quantitative comparison of each extracts with DMSO control, the data represent in percentage (%). The P-values were determined using ANOVA (RM one-way ANOVA, with the Greenhouse-Geisser corrections). Data are presented as mean ± S.E., n = 3. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
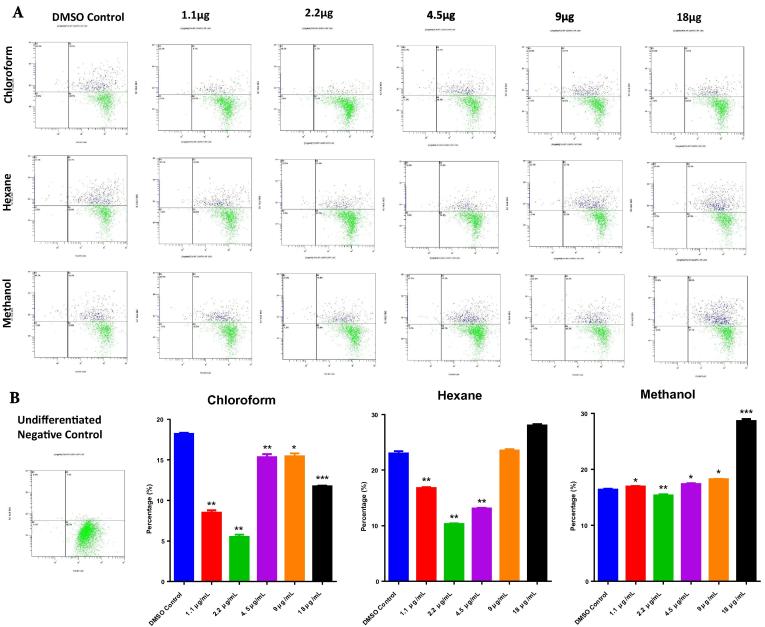
Further to confirm the anti-adipogenic effect of chloroform extract we have performed high intensity Nile red fluorescence. It is an sensitive technique used to observe the mature adipocytes because the stain is readily picked up by the large lipid droplets in the cytoplasm that characterizes these cells. The background was normalized with undifferentiated cells (Fig. 2). Concordant with the total adipocyte quantification, matured adipocyte analysis confirmed that hexane (1.1 μg/mL – 17 ± 2%; 2.2 μg/mL – 10 ± 2%) and methanol (1.1 μg/mL - 17 ± 2%; 2.2 μg/mL – 15 ± 2%) extracts almost had similar effects in both concentrations (Fig. 2), whereas chloroform (1.1 μg/mL – 9 ± 1%; 2.2 μg/mL – 6 ± 1%) extract inhibited the differentiation (Fig. 2). Interestingly, this study also confirms the previous findings that chloroform has maximum suppressive effect at 2.2 μg/mL when compared to hexane and methanol extract.
Fig. 2.
Matured adipocyte enumeration by flow cytometry. hMSCs treated with C. ficifolia extracts were differentiated into mature adipocytes and then quantified by flow cytometry. Cells were treated with various concentrations (1.1 µg/mL to 18 µg/mL) of three different solvent free extracts. (a) Differentiated DMSO control and undifferentiated negative control. (b) The dot plot with quadrant gates represents the differentiated cells stained with Nile red and analyzed in FL1 vs FL6 channel, upper right (R2) quadrant with blue color events represents the matured adipocytes, compared with DMSO control, and background normalized with undifferentiated control. The P-values were calculated using ANOVA (RM one-way ANOVA, with the Greenhouse-Geisser corrections). Data are presented as mean ± S.E., n = 3. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
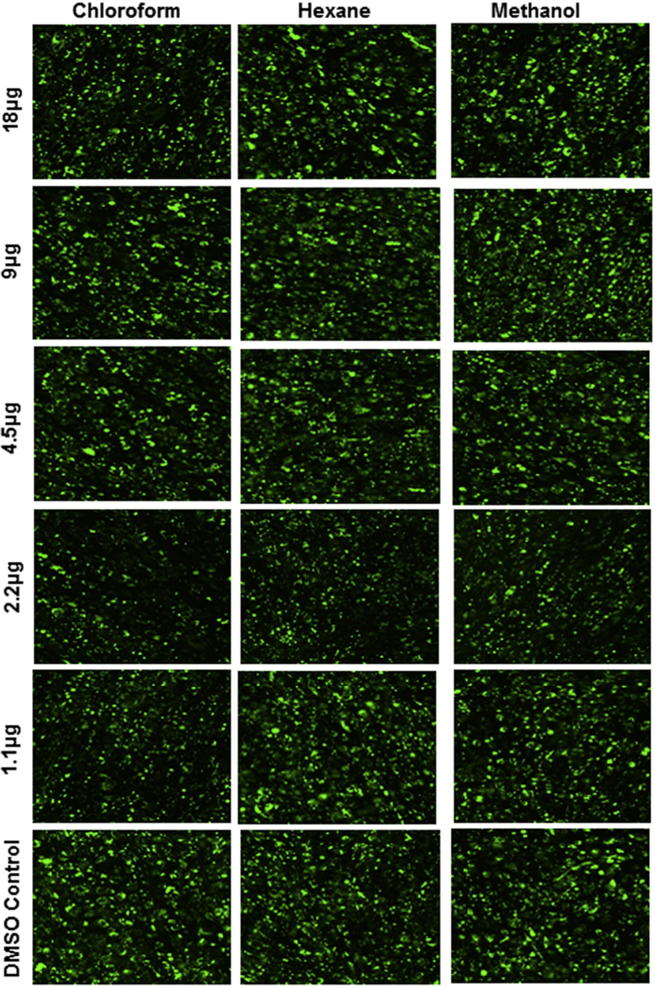
Qualitative Nile red imaging analysis was performed to support the quantitative total and matured adipocyte enumeration. We could observe obvious reductions of oil droplets at 2.2 μg/mL of chloroform extract; this reduction was also observed at 1.1 μg/mL of chloroform extract. Therefore, these images illustrate supporting evidence for the quantification analysis (Fig. 3). Previous studies strongly recommend Nile red staining for adipocyte cell quantification from the heterogeneous cell population (Vishnubalaji et al., 2012a). Furthermore, the percentage of differentiated adipocytes (Fig. 1) and the extent of lipid accumulation in mature adipocytes (Fig. 2) were confirmed by flow cytometric analysis with the lipophilic fluorescent dye Nile red. We observed a lesser number of adipocytes in chloroform extract-treated cells than in hexane extract treated cells. Furthermore, both were visually distinguishable by Nile Red stain at 1.1 μg/mL and 2.2 μg/mL of chloroform extract. As evident from mature adipocyte quantification, and qualitative image analysis all the extract showed maximum effect at 2.2 μg/mL, however chloroform extract showed maximum anti-adipogenic effect (chloroform > hexane > methanol).
Fig. 3.
Qualitative analysis of adipocyte differentiated hMSCs with Nile red stain. The hMSCs were treated with various concentrations of different solvent free C. ficifolia extracts (1.1 µg/mL to 18 µg/mL). The treated cells were stained with Nile red fluorescent dye. Images were acquired by fluorescence microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
Even though we did not observe any toxic effect between 4.5 μg/mL to 18 μg/mL, at the same time we did not observe statically significant anti-adipogenic effect. We subsequently sought to determine the mechanism by which chloroform, hexane, and methanol extracts inhibit hMSCs’ adipogenic lineage differentiation. Since 2.2 μg/mL of three different extracts showed maximum anti-adipogenic effect, we selected this concentration for further gene expression analysis.
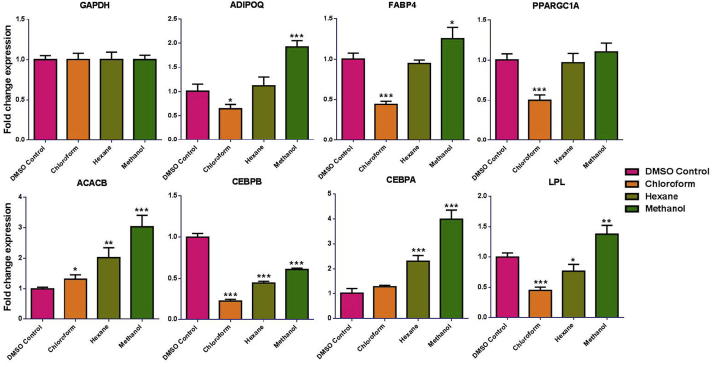
Gene expression analysis on adipocyte-associated genes, revealed significant down (P < 0.001) regulation when treated with chloroform extract of C. ficifolia as compared to hexane and methanol extracts. The chloroform extract showed the down regulation effect in all the observed genes (Except ACACB & CEBPA). Hexane extract also caused down regulation (Except CEBPA & LPL; No effect on PPARGC1A), but not as strongly as chloroform (Fig. 4). On the other hand, methanol extract showed up-regulation in gene expression as compared to the control (Except CEBPB). Data in this study show that exposure of hMSCs to chloroform extract down regulated PPARGC1A mRNA at the stage of differentiation and no such effect was observed upon treatment with hexane and methanol extracts (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
Identification of vital genes involced in adipogeneis of concentrol and different extract of C. ficifolia bona fide gene targets during adipogenic differentiation of hMSCs. Analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription with the polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of adipogenic-associated gene expression in induced and non-induced hMSCs. P values were calculated using the unpaired two-tailed t-test. Data are presented as mean ± S.E., n = 6. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
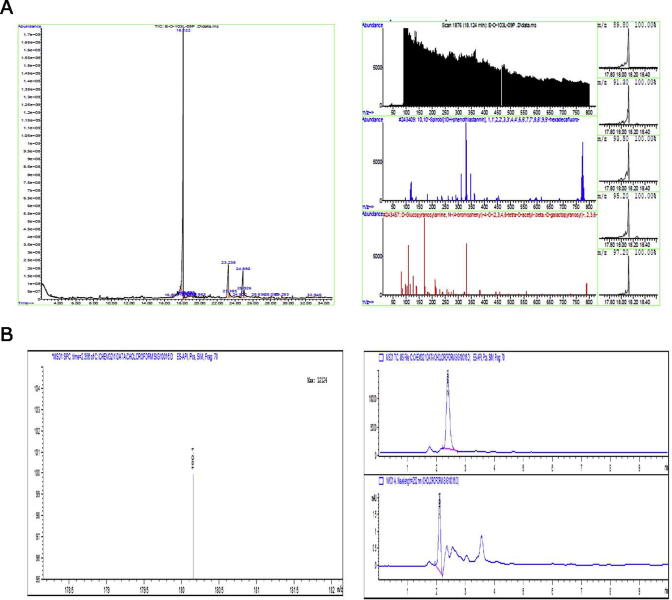
We intended to analyze major active compound responsible for anti-adipogenic effect. The GC-MS spectrum of the chloroform extracts of C. ficifolia established the existence of 18 constituents with three major phytochemical constituents in different retention times (RT). Further, these constituents were identified via mass spectrometry and compared with the NIST library. D-Glucopyranosylamine (67.8%), n-hexadecanoic acid (17.7%) and 1,4-cyclooctadiene (15.8%) were determined to be the major components (Fig. 5 (a)). Furthermore, our preliminary analysis with LC-MS revealed the existence of hexahydroxycyclohexane (cis-1, 2, 4-trans-3, 5, 6 –cyclohexanehexol) and cis-1, 2, 4-trans-3, 5, 6 –cyclohexanehexol (Glucopyranosylamine), however it needs further investigations to confirm the structure and properties of each active component (Fig. 5 (b)). From GC-MS and LCMS results, it could be concluded that chloroform extract of C. ficifolia contains majorly D-Glucopyranosylamine (67.8%), n-hexadecanoic acid (17.7%) and 1,4-cyclooctadiene (15.8%) in addition to various bioactive compounds that has anti-adipogenic properties.
Fig. 5.
GC-MS and LCMS analysis of C. ficifolia chloroform extracts (a) GC-MS chromatogram and peak abundance in different time points showing the details of phytocomponents. (b) LC-MS showing the peak of 1,2,4/3,5,6-Hexahydroxycyclohexane (cis-1, 2, 4-trans-3, 5, 6 –Cyclohexanehexol) in the retention time (RT) of 2.3 mints.
4. Discussion
Prolonged intake of a high-caloric diet is known to cause obesity, particularly as it is characterized by a disproportionate accumulation of fat mass in white adipose tissue, which occurs through an increase in adipocyte volume (hypertrophy), and number (hyperplasia), or a combination of both (hypertrophy–hyperplasia) (Bray and Popkin, 1998, Wang et al., 2014). Adipocyte commitment and differentiation are complex processes, which can be studied with various in vitro cell models and molecular biology techniques that allow for a better understanding of anti-adipogenesis (Ruiz-Ojeda et al., 2016). Adipocytes are derived from hMSCs, which differentiate into pre-adipocytes, undergo clonal expansion and subsequent terminal differentiation into mature adipocytes (Gregoire et al., 1998). In the present study we found that chloroform extract of C. ficifolia has anti-adipogeneic effect when compared to hexane and methanol extract.
Adipogenesis is a multi-step process with several stages, involving a cascade of transcription factors for key proteins that induce gene expression and lead to adipocyte development, among which PPARG and CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs) are considered the critical determinants of adipocyte fate (Lefterova and Lazar, 2009). Down regulating the expression of genes involved in fat accumulation may lead to the prevention or treatment of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (Fortis-Barrera et al., 2013, Lawrence and Burk, 1976, Torres-Leal et al., 2010). PPARGC1A expression was significantly down regulated in chloroform extract of C. ficifolia treated cells. PPARGC1A has been suggested to be a master regulator of adipogenesis (Gesta et al., 2007, Rosen and Spiegelman, 2001, Tomaru et al., 2009). Data in this study show that exposure of hMSCs to chloroform extract down regulated PPARGC1A mRNA at the stage of differentiation and no such effect was observed upon treatment with hexane and methanol extracts (Fig. 4).
Studies by (Park et al., 2014) shows that PPARG and C/EBPA pathways involves in adipogenic differentiation. Our present experimental result was exhibit that the chloroform extract highly down regulated C/EBPB mRNA expression but not C/EBPA mediated regulation. Based on our current findings, we conclude that, PPARG and C/EBPB mediated signaling cascades is the target of chloroform extracts. CEBPA also plays an important role in the adipogenesis processes and in PPARGC1A regulation (Gesta et al., 2007). All the extracts inhibited CEBPB, a protein that is involved in early adipogenic differentiation (Gregoire et al., 1998). Interestingly chloroform-extract treated cells showed down regulation of other adipogenic associated markers such as FABP4 and LPL (Fortis-Barrera et al., 2013, Torres-Leal et al., 2010). On the other hand, hexane extract did not cause any change in the FABP4, whereas LPL is down regulated. However, methanol extract up-regulated the both the gene expression. PPARGC1A and CEBPA act mutually to induce many adipogenic-associated genes, such as AdipoQ and FABP4, which sustain their expression via a positive feedback loop and result in mature adipocyte differentiation (Lawrence and Burk, 1976). Correspondingly, our RT-PCR gene profile demonstrated a marked decrease in all above-mentioned genes in chloroform extract-treated cell.
Previous studies have shown that the blood glucose levels in diabetic mice was significantly reduced by C. ficifolia (Jin et al., 2013). Earlier studies have shown that C. ficifolia contains phyto-constituents including flavonoids, alkaloids, palmitic, oleic and linoleic acids that possess numerous vital medicinal properties including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic and anti-carcinogenic properties (Yadav et al., 2010). Recent studies also have shown that the Cucurbita family has a wide range of novel biological applications including antihelminthics activity (Grzybek et al., 2016). Our previous study confirmed that chloroform extract is highly biocompatible, less toxic to the hBM-hMSCs and enhanced the cell proliferation (Aristatile and Alshammari, 2017). Our in vitro investigation provides evidence that chloroform extract of C. ficifolia has a significant inhibitory role in the adipogenic differentiation of hMSCs. Furthermore, we did not observe reductions in cell number of C. ficifolia extract treated cells. Thus, it is very interesting that extract of C. ficifolia can work as an anti-adipogenic agent without affecting the cell number, an important consideration in light of the physiological significance of adipose tissue.
5. Conclusion
Our data showed that chloroform extract of C. ficifolia inhibits adipocyte differentiation. Qualitative and quantitative Nile red analyses showed the C. ficifolia chloroform extract caused reduction of total and matured adipocytes. RT-PCR gene expression analysis revealed that the chloroform extract of C. ficifolia significantly inhibited vital adipogenic differentiation genes as compared to the hexane and methanol extracts. The presence of active components in the extracts were identified by GC-MS and LC-MS. Since pumpkin is used as food material, more consumption may be recommended in obese patient without further investigation. However further investigations are needed to elucidate active principle structure and mode of action.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through the Research Project No RI 7-03-63
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of King Saud University.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.10.002.
Appendix A. Supplementary material
The following are the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- Ahima R.S., Flier J.S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000;11:327–332. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(00)00301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar M.S. Trial of Momordica charantia Linn (Karela) powder in patients with maturity-onset diabetes. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 1982;32:106–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Zuhair H., Abd el-Fattah A.A., Abd el Latif H.A. Efficacy of simvastatin and pumpkin-seed oil in the management of dietary-induced hypercholesterolemia. Pharmacol. Res. 1997;35:403–408. doi: 10.1006/phrs.1997.0148. https://10.1006/phrs.1997.0148 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali D., Alshammari H., Vishnubalaji R., Chalisserry E.P., Hamam R., Alfayez M., Kassem M., Aldahmash A., Alajez N.M. CUDC-907 promotes bone marrow adipocytic differentiation through inhibition of histone deacetylase and regulation of cell cycle. Stem Cells Dev. 2017;26:353–362. doi: 10.1089/scd.2016.0183. https://10.1089/scd.2016.0183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aristatile B., Alshammari G.M. In vitro biocompatibility and proliferative effects of polar and non-polar extracts of cucurbita ficifolia on human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017;89:215–220. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.023. https://10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhupathiraju S.N., Hu F.B. Epidemiology of obesity and diabetes and their cardiovascular complications. Circ. Res. 2016;118:1723–1735. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306825. https://10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306825 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G.A., Popkin B.M. Dietary fat intake does affect obesity! Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998;68:1157–1173. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/68.6.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi H., Eo H., Park K., Jin M., Park E.-J., Kim S.-H., Park J.E., Kim S. A water-soluble extract from Cucurbita moschata shows anti-obesity effects by controlling lipid metabolism in a high fat diet-induced obesity mouse model. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2007;359:419–425. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G.J., Ross S.E., MacDougald O.A. The role of C/EBP genes in adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:30057–30060. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.46.30057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitel M. Overweight and obesity worldwide now estimated to involve 1.7 billion people. Obes. Surg. 2003;13:329–330. doi: 10.1381/096089203765887598. https://10.1381/096089203765887598 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein E.A., Khavjou O.A., Thompson H., Trogdon J.G., Pan L., Sherry B., Dietz W. Obesity and severe obesity forecasts through 2030. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2012;42:563–570. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2011.10.026. https://10.1016/j.amepre.2011.10.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortis-Barrera A., Alarcon-Aguilar F.J., Banderas-Dorantes T., Diaz-Flores M., Roman-Ramos R., Cruz M., Garcia-Macedo R. Cucurbita ficifolia Bouche (Cucurbitaceae) and D-chiro-inositol modulate the redox state and inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013;65:1563–1576. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12119. https://10.1111/jphp.12119 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortis-Barrera Á., García-Macedo R., Almanza-Perez J.C., Blancas-Flores G., Zamilpa-Alvarez A., Flores-Sáenz J.L., Cruz M., Román-Ramos R., Alarcón-Aguilar F.J. Cucurbita ficifolia (Cucurbitaceae) modulates inflammatory cytokines and IFN-γ in obese mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016;95:170–177. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2015-0475. https://10.1139/cjpp-2015-0475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y., Luo N., Klein R.L., Garvey W.T. Adiponectin promotes adipocyte differentiation, insulin sensitivity, and lipid accumulation. J. Lipid Res. 2005;46:1369–1379. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M400373-JLR200. https://10.1194/jlr.M400373-JLR200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesta S., Tseng Y.-H., Kahn C.R. Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell. 2007;131:242–256. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.004. https://10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoire F.M., Smas C.M., Sul H.S. Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physiol. Rev. 1998;78:783–809. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1998.78.3.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzybek M., Kukula-Koch W., Strachecka A., Jaworska A., Phiri A.M., Paleolog J., Tomczuk K. Evaluation of anthelmintic activity and composition of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) seed extractsin vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016;17 doi: 10.3390/ijms17091456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin H., Zhang Y.J., Jiang J.X., Zhu L.Y., Chen P., Li J., Yao H.Y. Studies on the extraction of pumpkin components and their biological effects on blood glucose of diabetic mice. J. Food Drug Anal. 2013;21:184–189. https://10.1016/j.jfda.2013.05.009 [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B.B., Flier J.S. Obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 2000;106:473–481. doi: 10.1172/JCI10842. https://10.1172/JCI10842 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R.A., Burk R.F. Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1976;71:952–958. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90747-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefterova M.I., Lazar M.A. New developments in adipogenesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009;20:107–114. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2008.11.005. https://10.1016/j.tem.2008.11.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Must A., Spadano J., Coakley E.H., Field A.E., Colditz G., Dietz W.H. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA. 1999;282:1523–1529. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.16.1523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park A., Kim W.K., Bae K.H. Distinction of white, beige and brown adipocytes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. World J. Stem Cells. 2014;6:33–42. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i1.33. https://10.4252/wjsc.v6.i1.33 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quanhong L., Caili F., Yukui R., Guanghui H., Tongyi C. Effects of protein-bound polysaccharide isolated from pumpkin on insulin in diabetic rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2005;60:13–16. doi: 10.1007/s11130-005-2536-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D.P., Gracheck P.J., Vona-Davis L. The interactions of obesity, inflammation and insulin resistance in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2015;7:2147–2168. doi: 10.3390/cancers7040883. https://10.3390/cancers7040883 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E.D., Spiegelman B.M. PPAR gamma: a nuclear regulator of metabolism, differentiation, and cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:37731–37734. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100034200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E.D., Spiegelman B.M. Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature. 2006;444:847–853. doi: 10.1038/nature05483. https://10.1038/nature05483 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Ojeda F.J., Ruperez A.I., Gomez-Llorente C., Gil A., Aguilera C.M. Cell models and their application for studying adipogenic differentiation in relation to obesity: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016;17 doi: 10.3390/ijms17071040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A.R. You are what you secrete. Nat. Med. 2001;7:887–888. doi: 10.1038/90911. https://10.1038/90911 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurk T., Alberti-Huber C., Herder C., Hauner H. Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007;92:1023–1033. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1055. https://10.1210/jc.2006-1055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B.M., Flier J.S. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell. 2001;104:531–543. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaru T., Steger D.J., Lefterova M.I., Schupp M., Lazar M.A. Adipocyte-specific expression of murine resistin is mediated by synergism between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:6116–6125. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808407200. [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Leal F.L., Fonseca-Alaniz M.H., Rogero M.M., Tirapegui J. The role of inflamed adipose tissue in the insulin resistance. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2010;28:623–631. doi: 10.1002/cbf.1706. https://10.1002/cbf.1706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishnubalaji R., Al-Nbaheen M., Kadalmani B., Aldahmash A., Ramesh T. Comparative investigation of the differentiation capability of bone-marrow- and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by qualitative and quantitative analysis. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;347:419–427. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1306-3. https://10.1007/s00441-011-1306-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishnubalaji R., Manikandan M., Al-Nbaheen M., Kadalmani B., Aldahmash A., Alajez N.M. In vitro differentiation of human skin-derived multipotent stromal cells into putative endothelial-like cells. BMC Dev. Biol. 2012;12 doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-12-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q.A., Scherer P.E., Gupta R.K. Improved methodologies for the study of adipose biology: insights gained and opportunities ahead. J. Lipid Res. 2014;55:605–624. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R046441. https://10.1194/jlr.R046441 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y.C., Colditz G.A., Kuntz K.M. Forecasting the obesity epidemic in the aging US population. Obesity. 2007;15:2855–2865. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.339. https://10.1038/oby.2007.339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav M., Jain S., Tomar R., Prasad G., Yadav H. Medicinal and biological potential of pumpkin: an updated review. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010;23:184–190. doi: 10.1017/S0954422410000107. https://10.1017/s0954422410000107 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S.J., Park N.Y., Lim Y. Anti-adipogenic effect of mulberry leaf ethanol extract in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2014;8:613–617. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2014.8.6.613. https://10.4162/nrp.2014.8.6.613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuhair H.A., Abd El-Fattah A.A., El-Sayed M.I. Pumpkin-seed oil modulates the effect of felodipine and captopril in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2000;41:555–563. doi: 10.1006/phrs.1999.0622. https://10.1006/phrs.1999.0622 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.