Significance
Organ formation is an essential process in plants and animals, driven by cell division and cell identity establishment. Root branching where lateral roots form along the primary root axis increases the root system and aids the capture of water and nutrients. We have discovered that tight control of the cell width is necessary to coordinate asymmetric cell divisions in cells that give rise to a new lateral root organ. Although biomechanical processes have been shown to play a role in plant organogenesis, including lateral root formation, our data give mechanistic insights into cell size control during lateral root initiation.
Keywords: lateral root development, cell wall remodeling, EXPANSIN A1, radial cell expansion, Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
In plants, postembryonic formation of new organs helps shape the adult organism. This requires the tight regulation of when and where a new organ is formed and a coordination of the underlying cell divisions. To build a root system, new lateral roots are continuously developing, and this process requires the tight coordination of asymmetric cell division in adjacent pericycle cells. We identified EXPANSIN A1 (EXPA1) as a cell wall modifying enzyme controlling the divisions marking lateral root initiation. Loss of EXPA1 leads to defects in the first asymmetric pericycle cell divisions and the radial swelling of the pericycle during auxin-driven lateral root formation. We conclude that a localized radial expansion of adjacent pericycle cells is required to position the asymmetric cell divisions and generate a core of small daughter cells, which is a prerequisite for lateral root organogenesis.
In plants, organogenesis requires a well-defined sequence of (asymmetric) cell divisions (1). The formation of a new lateral root organ is a self-organizing process during which founder cells invariably undergo a first asymmetric anticlinal division. In the resulting lateral root initiation site (stage I lateral root primordium), small daughter cells are positioned next to each other in the center and are flanked by larger ones. Additional features, such as auxin response oscillation in the basal meristem, migration of nuclei in adjacent pericycle cells toward the common cell wall, radial expansion of these cells, and auxin response in the endodermis, mark lateral root initiation (2–10). The correct execution of these steps is essential to set the founder cells on the right developmental path required for proper lateral root primordium morphogenesis. At later stages, however, flexibility with respect to the number, order, and orientation of cell divisions in the growing lateral root primordium is allowed (11, 12). The whole process of lateral root formation is regulated by several plant hormones with auxin being the dominant signal (13–15).
Previously, it was shown that radial expansion of the pericycle founder cells and spatial accommodation by the overlying endodermis are essential for the formation of a lateral root and the first asymmetric cell divisions to occur (9). In addition, ablation experiments demonstrated that removal of the endodermis triggers radial expansion of pericycle cells and unusual periclinal pericycle cell divisions and that auxin in the pericycle is required for correct anticlinal orientation of these divisions (7). Taken together, our current view of lateral root formation suggests a link between radial expansion of pericycle cells and the correct execution of the first founder cell division. However, we still largely lack knowledge on how this integrates the necessary regulation of the cell wall, which is an active structure that plays a key role in cell expansion and is involved in several important physiological events.
Cell wall polysaccharides, such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin form the major component of the primary cell wall in Arabidopsis (16, 17). Several models have been proposed for the architecture of the primary cell wall and its implications on wall extensibility (16, 18–21). The most recent “hotspot” hypothesis proposes the presence of limited points of contact between the cellulose microfibrils mediated by xyloglucans that work as load-bearing sites and as targets of cell wall loosening (22, 23). There is also increasing evidence for the importance of pectin in control of wall extensibility, with the formation of Ca2+-pectate cross-links considered to play a major load-bearing role in the absence of the cellulose–xyloglucan network in the cell wall (24–30). Although there is good understanding of the major components of the cell wall, the interactions between these components in an active cell wall and in response to developmental cues are not yet well understood. Alterations to the structure of the cell wall in response to growth are thought to be brought about by several cell wall remodeling agents that belong to different families and act upon different components of the cell wall (18, 31–34). Classic cell wall remodeling agents are expansins, which are known to alter the mechanical properties of the cell wall through nonenzymatic reversible disruption of noncovalent bonds in cell wall polymers thereby creating local mechanical alterations in the cell wall (31, 35). Detailed characterization of the binding site of expansin in Arabidopsis cell walls highlighted the remarkable similarities in the expansin binding site to the “biomechanical hotspots” described in the cell wall, suggesting these sites to be the target sites of expansin action (22, 23, 36). However, the precise mechanism by which this occurs remains unclear.
Here, we identify EXPA1 as an early marker of pericycle founder cell radial expansion. Based on detailed analyses of expansin a1 mutants, we show that EXPA1 is required for the proper radial expansion which licenses the correct positioning of first anticlinal divisions. This suggests that a specific pericycle width is necessary to trigger asymmetric pericycle cell divisions during lateral root initiation.
Results and Discussion
Transcriptomics Identifies EXPA1 as a Putative Regulator of Pericycle Cell Wall Remodeling.
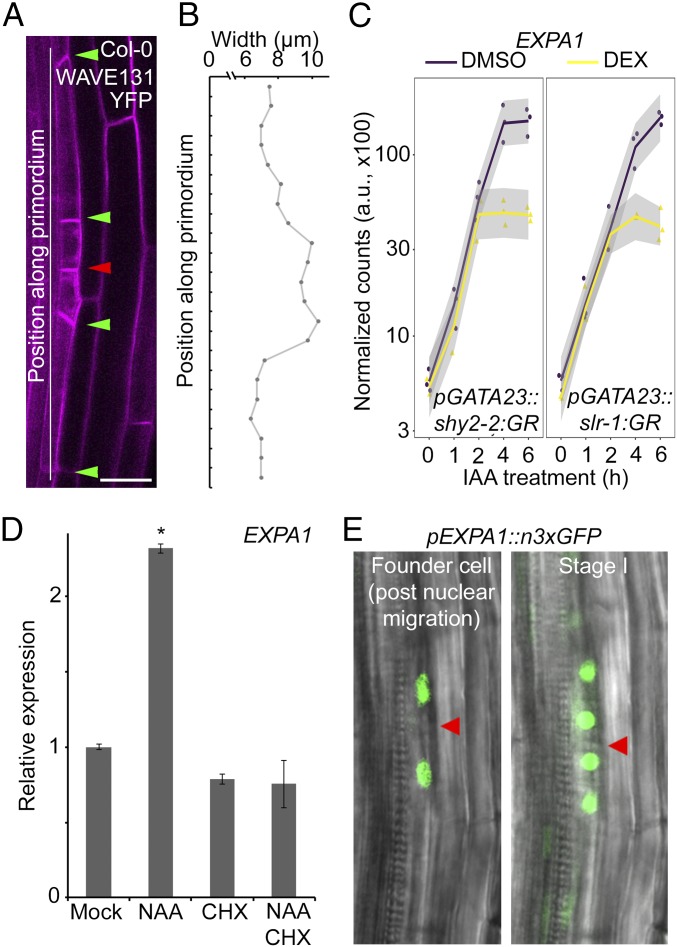
During the early stages of auxin-triggered lateral root initiation, localized radial swelling of the lateral root founder pericycle cells takes place concomitant with the migration of the nuclei to the common wall (2, 9). Consequently, stage I primordia showed a distinct bulging at the position of the small daughter cells (Fig. 1 A and B). Mechanistically, this likely involves (local) cell wall remodeling. To identify genes involved in the early phases of lateral root initiation, we used a previously described lateral root inducible system to synchronously induce lateral root initiation (4, 37–39) and profiled the transcriptomes of roots after 0, 1, 2, 4, and 6 h of auxin treatment in conditions where IAA14- or IAA3-dependent auxin signaling is blocked. For this, we used seedlings expressing nondegradable versions of the AUX/IAAs IAA14 (slr-1) or IAA3 (shy2-2) fused to the glucocorticoid receptor domain (slr-1:GR or shy2-2:GR) under the control of the pericycle and founder cell specific GATA23 promoter. Treatment with dexamethasone induces, specifically in pericycle cells, the nuclear translocation of the nondegradable AUX/IAA that acts as a dominant repressor of auxin signaling resulting in a complete block of lateral root formation and strongly reduced radial swelling of the founder cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S1). Transcriptome analysis identified 398 differentially expressed genes of which the expression was modulated by auxin and dependent on IAA14 and IAA3 (SI Appendix, Fig. S2 and Dataset S1). Among a cluster of 37 genes highly up-regulated by auxin in IAA14- and IAA3-dependent ways, EXPA1 (AT1G69530) appeared as one of the most differentially expressed auxin-responsive genes (Fig. 1C and SI Appendix, Fig. S2). EXPA1 expression increased in response to auxin, and this auxin-mediated induction can be blocked by IAA14 or IAA3 after 4 h of treatment, suggesting it could play a role in pericycle cell wall remodeling associated with lateral root initiation. In addition, EXPA1 was previously already identified as an important lateral root initiation gene involved in asymmetric cell division (4), making this a strong candidate to function in pericycle cell wall modification accompanying the lateral root initiation process.
Fig. 1.
Transcriptomics identifies EXPA1 as a potential regulator of lateral root initiation. (A) Representative image of a stage I lateral root primordium in Col-0. Cell outline visualized through the plasma membrane marker WAVE131YFP. Red and green arrowheads indicate the junction between adjacent pericycle cells that have divided asymmetrically and resulting daughter cells, respectively. (Scale bar, 20 µm.) (B) Representative pericycle cell width profile of a stage I lateral root primordium in Col-0. (C) EXPA1 expression following auxin (IAA) treatment and dexamethasone (DEX)-mediated induction of pGATA23::shy2-2:GR or pGATA23::slr-1:GR (profile based on transcriptome data, see Materials and Methods for the statistical model). a.u., arbitrary unit. (D) EXPA1 expression in Col-0 seedlings 3 d after germination transferred on mock, 10 μM NAA, 10 μM CHX, or 10 μM NAA + 10 μM CHX plates for 6 h. Average of three biological replicates (with each ∼15 roots) ± SE. Statistical significance (Student’s t test) compared with mock is indicated: *P value < 0.01. (E) Representative images of in vivo expression analysis of pEXPA1::n3xGFP in the pericycle during lateral root initiation in lateral root founder cells post nuclei migration (Left) and a stage I lateral root primordium (Right). The red arrowhead indicates the junction between adjacent pericycle cells that undergo asymmetric cell division.
Since auxin has a dominant role in lateral root initiation (14), we confirmed that exogenous auxin treatment leads to an increase in EXPA1 expression in the root (Fig. 1D) and that its expression is dependent on functional IAA14- or IAA3-dependent signaling (SI Appendix, Fig. S3). To assess if this effect was direct, we used the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX) in combination with auxin as auxin-mediated degradation of labile AUX/IAA repressors results in AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR (ARF)-regulated gene expression without de novo protein synthesis (40, 41). This revealed that, although EXPA1 expression is dependent on IAA14 and IAA3, it is regulated indirectly by auxin (Fig. 1D).
To assess if EXPA1 is specifically expressed in the root during lateral root initiation and to more directly connect EXPA1 activity with this process, we mapped the EXPA1 expression pattern during the early stages of lateral root development. For this, we performed an in vivo expression analysis of pEXPA1::n3xGFP using a previously described bending assay (42). This revealed that EXPA1 is expressed in the pericycle following nuclear migration preceding lateral root initiation and then remained expressed in the small daughter cells (Fig. 1E and Movies S1 and S2). Apart from this, EXPA1 expression was also observed in the cortical but not in the endodermal cells overlying the lateral root primordium from stage II onward (SI Appendix, Fig. S4). In addition, seedling roots subjected to a previously described lateral root inducible system (4, 37–39) (SI Appendix, Fig. S5) displayed only very weak pEXPA1::n3xGFP expression in some vascular cells on the auxin transport inhibitor 1-N-naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA), but expression increased and was apparent in pericycle cells and developing lateral primordia and in the cortex overlaying the primordia after transfer to naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) for 6 h (SI Appendix, Fig. S4). Taken together, the cell wall remodeling agent EXPA1 acts downstream of auxin-triggered lateral root initiation.
EXPA1 Controls Patterned Anticlinal Asymmetric Pericycle Cell Divisions.
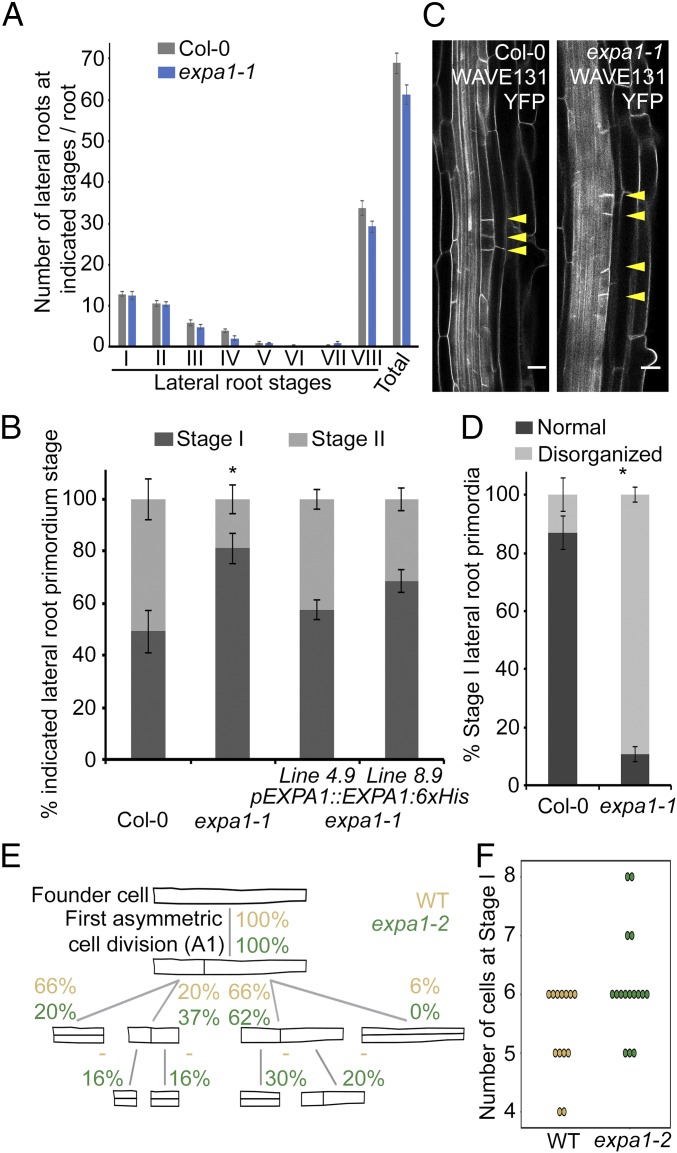
To evaluate if EXPA1 mediates lateral root initiation and/or emergence, we used an expa1 T-DNA insertion line with very low EXPA1 levels (about 5% of the control), named expa1-1 (43), and we obtained a second mutant, named expa1-2, using the CRISPR system (SI Appendix, Fig. S6). In the latter allele, a cytosine at position 767 is deleted resulting in a frameshift after amino acid 121 and a premature stop at position 145 (SI Appendix, Fig. S6). This premature stop results in reduced EXPA1 expression levels, partial retention of the first intron, and likely produces a protein half the size of the wild-type (WT) protein lacking the C-terminal cellulose binding domain (SI Appendix, Fig. S6). Together this suggests that expa1-2 is a hypomorphic allele. In our conditions, the primary root lengths of expa1-1 and expa1-2 were not dramatically different compared with the control, and a detailed lateral root staging analysis also did not reveal an obvious difference in any of the stages in the expa1-1 and expa1-2 mutants compared with the control (Fig. 2A and SI Appendix, Fig. S7). We then analyzed the progression through the stages of lateral root development using the bending assay (42). Examination of the root bends at 18 h post a gravitropic stimulus revealed a delay in the progression of the lateral root primordia from stage I to stage II in expa1-1 compared with the WT (Fig. 2B). To confirm that the observed lateral root initiation phenotype in expa1-1 is due to the loss of EXPA1 activity, we performed complementation experiments. Indeed, expression of an EXPA1 construct (pEXPA1::EXPA1:6xHis) in expa1-1 could largely restore the lateral root stage I to stage II progression defect in two independent lines (Fig. 2B). A similar defect was observed with the expa1-2 allele (SI Appendix, Fig. S7). Together these results indicate that expa1 mutants show defects in the transition from stage I to stage II.
Fig. 2.
Lateral root initiation defects in expa1-1. (A) Lateral root staging of Col-0 and expa1-1 roots at 10 d after germination for different stages of lateral root primordia. The graph shows the average of two biological replicates (with approximately six to eight roots each) ± SE. No statistical difference (using Student’s t test at P value < 0.01) was found compared with Col-0. VIII, all emerged lateral roots. Total, all lateral root stages combined. (B) Progression through lateral root development using the bending assay at 18 h post bend in Col-0, expa1-1, and two independent expa1-1 lines expressing pEXPA1::EXPA1-6xHis. Average of combined results from two to four biological replicates each with 11–21 individual seedlings. stage II, when at least one periclinal cell division was observed. Statistical significance (Student’s t test) compared with Col-0 is indicated: *P value < 0.05. (C) Normal and disorganized stage I primordia in Col-0 and expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP, respectively. Cell outline visualized through the plasma membrane marker WAVE131YFP. (Scale bar, 20 µm.) (D) Quantification of frequency of occurrence of normal and disorganized primordia (with displaced or supernumerary anticlinal cell divisions) in Col-0 and expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP at 10 d after germination. Average of two biological replicates ± SE, with a total of 90 and 102 primordia from different Col-0 (7) and expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP roots (8), respectively. Statistical significance (Z test calculator for two population proportions, P < 0.05) compared with Col-0 (*) is indicated. (E) Pattern of founder cell divisions and their frequency in expa1-2 and the cosegregating WT. The frequency of occurrence of each type of division for the WT and expa1-2 until the first periclinal cell division was determined in time-lapse confocal series and are indicated as percentages. In both genotypes, 100% of cells undergo a first anticlinal division (A1). A “—“ indicates that the divisions were not scored. Some 13 WT and 16 expa1-2 lateral root primordia were analyzed. (F) Number of cells in stage 1 primordium when the first periclinal division occurs in expa1-2 and WT.
To analyze in more detail the transition from stage I to stage II, we performed live imaging to explore if expa1 mutants displayed alterations in the pericycle cell division pattern during lateral root initiation. We introduced the plasma membrane marker line pUBQ10::EYFP:NPSN12 (referred to as WAVE131YFP) (44) in expa1-1 (then referred to as expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP) and took advantage of the presence of reporters for the nuclei of founder cells (pGATA23::H2B:3xGFP) and cell contours (pUB10::PIP1;4:3xmCHERRY) in the background used to generate the expa1-2 allele and performed a detailed in vivo analysis of the early stages of lateral root primordium development. In the loss of function expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP mutant, about 75% of what resembled stage I primordia (which were included as stage I in Fig. 2A) showed small daughter cells not positioned next to each other, resulting in a loss of organized pattern (Fig. 2 C and D). In the hypomorphic expa1-2 mutant, more subtle defects were observed. Whereas WT stage I primordia typically have four to six cells resulting from one to three anticlinal divisions, the expa1-2 stage I had up to eight cells resulting from more anticlinal divisions before the first periclinal division (Fig. 2 E and F and SI Appendix, Fig. S8, and Movie S1). We measured the length ratio of the daughter cells resulting from the first anticlinal in WT and expa1-2 and observed that in the mutant this first division is less asymmetric than in WT (SI Appendix, Fig. S8). In both alleles, the stage I defect is transitory, and the aberrant pattern of anticlinal divisions is later compensated by subsequent divisions that restore a more or less organized stage II lateral root primordium that continues to develop normally thereafter (SI Appendix, Fig. S8 and Movie S1). However, these subtle defects impact auxin-induced lateral root formation as observed in the number of emerged lateral roots when subjecting expa1-1 and expa1-1 pEXPA1::EXPA1:6xHis lines to a low concentration of auxin (SI Appendix, Fig. S9). Taken together, the loss of EXPA1 activity affects the position of the first asymmetric and anticlinal cell divisions during lateral root initiation, resulting in the disruption of a typical stage I pattern.
EXPA1 Is Involved in Pericycle Cell Expansion During Lateral Root Initiation.
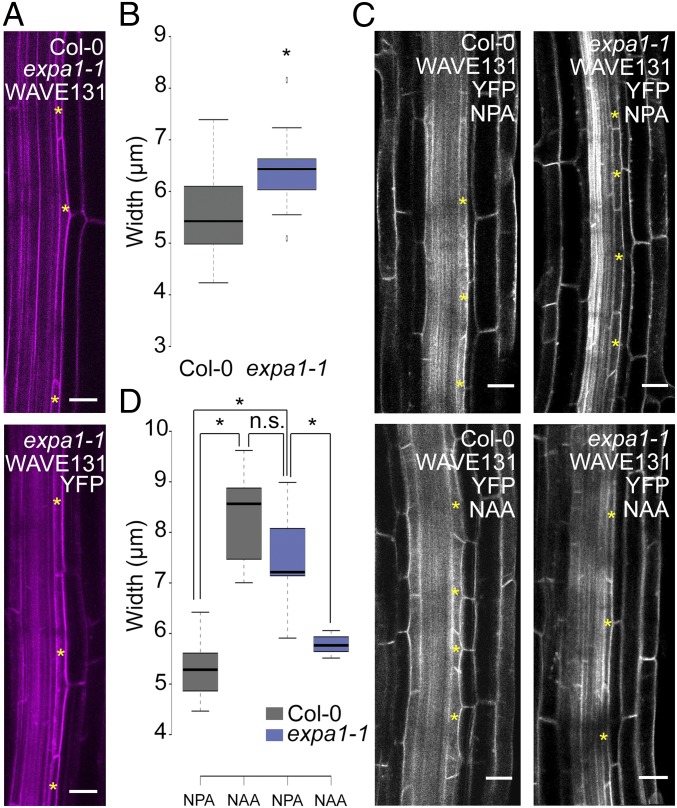
Given that the loss of EXPA1 specifically affects stage I, we analyzed if there were any observable differences in the radial expansion of the xylem pole pericycle cells, which is a hallmark of lateral root initiation (9, 45) (Fig. 1 A and B). Therefore, we measured the width of naive pericycle cells of WT, expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP, and expa1-2. This revealed marginally significant differences between WT and expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP and no difference with expa1-2 (Fig. 3 A and B and SI Appendix, Fig. S10). However, in expa1-2, we observed a slightly reduced pericycle thickness in stage I primordia, just before the transition to stage II (SI Appendix, Fig. S10). Since only a limited number of pericycle cells are primed at any time to form a lateral root, pericycle cell width during lateral root initiation is not straightforward to capture and measure under regular growth conditions. Given the more subtle phenotype affecting stage I in the hypomorphic expa1-2, we subjected the roots of WAVE131YFP and of the loss of function expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP to the above-mentioned lateral root inducible system that provides a uniform and synchronized population of pericycle cells undergoing lateral root initiation. Measurement of pericycle cell width of NPA-grown WAVE131YFP and expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP roots, which represent a synchronously primed pericycle cell population that is not dividing, revealed that the pericycle cells of expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP were significantly wider than WAVE131YFP (Fig. 3 C and D and SI Appendix, Fig. S5). This is in agreement with the control conditions where we observed a subtle difference in pericycle cell width (Fig. 3 A and B). Upon auxin treatment, which induces lateral root initiation, the pericycle cells of WAVE131YFP increase in width (Fig. 3 C and D). Strikingly, the auxin-induced pericycle cell width of WT pericycle cells corresponds to that of NPA-grown expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP pericycle cells (Fig. 3 C and D), suggesting that expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP pericycle cells are at an advanced stage compared with WT. Furthermore, expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP pericycle cells did not increase further in width upon auxin treatment and actually seem to reduce in width (Fig. 3 C and D), possibly explaining why there is no extensive division in these cells at this time point. In contrast, the widths of the endodermis and cortex cells seemed largely unaffected in expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP, compared with the control (SI Appendix, Fig. S10). In conclusion, the loss of EXPA1 activity impacts pericycle cell width (Fig. 3 A–D), which appears to be essential for correct positioning of the anticlinal pericycle cell division (Fig. 2 C and D) and, subsequently, for the transition from stage I to stage II (periclinal cell divisions) (Fig. 2 E and F).
Fig. 3.
Pericycle cell width in expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP. (A) Representative images of Col-0 and expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP illustrating pericycle width in control growth conditions. The yellow asterisks mark pericycle cells. Cell outline visualized through the plasma membrane marker WAVE131YFP. (Scale bar, 20 µm.) (B) Boxplot of pericycle cell width in Col-0 and expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP in control growth conditions at 5 d after germination. At least 15 cells from eight different roots were analyzed per genotype. Statistical significance (Student’s t test) compared with Col-0 is indicated: *P value < 0.01. (C) Representative confocal images of Col-0 and expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP roots at 3 d after germination on 10 μM NPA or after transfer from NPA to 10 μM NAA for 6 h. Cell outline visualized through the plasma membrane marker WAVE131YFP. The yellow asterisk indicates representative pericycle cells used for cell width measurements. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (D) Boxplot of pericycle cell width in Col-0 and expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP at 3 d after germination on 10 μM NPA or after transfer from NPA to 10 μM NAA for 6 h. At least 12 roots were analyzed per genotype and per treatment with a total of, at least, 15 cells. Statistical significance (Student’s t test) compared with Col-0 is indicated: *P value < 0.01.
Pericycle Cell Wall Composition During Auxin-Induced Lateral Root Initiation Is Affected in expa1-1.
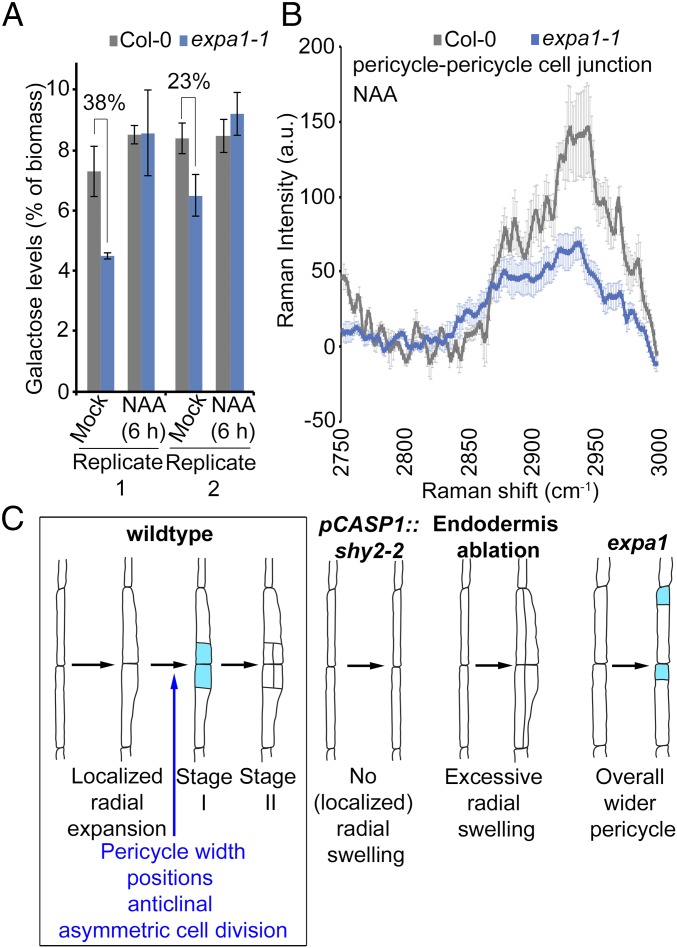
Given the impact of EXPA1 loss of function on pericycle cell width and the role of expansins in cell wall loosening through altering interactions between the cell wall polymers (27, 31, 36), we investigated if the loss of EXPA1 activity leads to changes in cell wall composition. First, we profiled key sugar monomers, namely, glucose, galactose, arabinose, and xylose, using high-performance anion exchange chromatography coupled with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAEC-PAD) on hydrolyzed whole roots of Col-0 and the loss of function expa1-1. These sugar monomers are breakdown products of key cell wall polymers, such as cellulose, xyloglucan, and pectin polymers. HPAEC-PAD analysis revealed that expa1-1 had reproducibly reduced galactose levels compared with Col-0 with no significant differences in other sugar monomers (Fig. 4A and SI Appendix, Figs. S11 and S12). Auxin has long been known to induce changes in the cell wall largely through acidification of the apoplastic space and triggering the activity of several cell wall remodeling agents, such as expansins (35, 46, 47). To evaluate if auxin-driven alterations in the cell wall require EXPA1, whole roots were treated with 10 µM NAA for 6 h and analyzed through HPAEC-PAD. Upon auxin treatment, no striking reproducible differences between WT and expa1-1 were observed; however, the galactose levels in expa1-1 were restored to WT levels (Fig. 4A and SI Appendix, Fig. S12).
Fig. 4.
Cell wall composition of expa1-1. (A) Monosaccharide sugar analysis on hydrolyzed Col-0 and expa1-1 roots at 7 d after germination with and without 6-h 10 µM NAA treatment using HPAEC-PAD. Two independent biological replicates are shown with averages of technical replicates (2 or 3 for replicate 1 or 2, respectively) ± SE. The percentage reduction is indicated. There is no statistical difference (Student’s t test) compared with Col-0 at P value < 0.05, but both biological replicates show similar trends. (B) Confocal Raman microscopy analysis of pericycle cell wall junction. Chemical spectra in the C–H stretching region 2,750–3,000 cm−1 depicting an average of four to six measurements ± SE of pericycle cell junctions on cross sections of NAA-treated Col-0 and expa1-1 roots. a.u., arbitrary unit. Statistical significance (Student’s t test) is listed in Dataset S2: *P value < 0.05. (C) Model summarizing the role of EXPA1 in lateral root initiation.
Although the spatial resolution of the above-used techniques is poor due to whole root level analysis, we noted that the expa1-1 roots exhibited altered cell wall polymers associated with galactose-containing polysaccharides in their side chains (17, 48). Galactose-containing side chains of xyloglucan, for instance, are a major contributor of the load-bearing capacity of the wall (23, 49, 50), and galactosylation of xyloglucans affects the tensile strength of the cell wall through altered accessibility of xyloglucans to cell wall remodeling enzymes (50–52). To investigate more subtle alterations in the biochemical composition of the pericycle cell wall at higher spatial resolution, we performed confocal Raman microscopy analyses on the xylem pole pericycle cell wall junctions during lateral root initiation. To probe the chemical structure of specific points of interest at high spatial resolution without the need to label or stain the sample, we used transverse sections of Col-0 and expa1-1 of roots subjected to the above-mentioned lateral root inducible system (SI Appendix, Fig. S5) and evaluated these for differences in their biochemical spectral profile. We chose to focus on the C–H stretching region (2,750–3,000 cm−1) as this region contains only vibrational modes associated with C–H stretching in aliphatic carbohydrate-based polymers, unobscured by the vibrational modes of H2O, D2O, and HOD which would otherwise complicate analysis. The spectra collected from the cell wall junctions appeared to represent an approximate superposition of the spectra of the principal aliphatic biopolymers—cellulose, xyloglucan, and pectin (SI Appendix, Fig. S13). We observed subtle changes in the spectral profile of the pericycle−pericycle cell junctions in NPA-grown versus auxin-treated Col-0 seedlings (SI Appendix, Fig. S14) and in the spectra comparing NPA-grown Col-0 and expa1-1 (SI Appendix, Fig. S14). Most importantly, we observed that the intensities of all Raman bands in the C–H stretching region at pericycle−pericycle cell junctions in auxin-treated Col-0 roots were less pronounced in auxin-treated expa1-1 (Fig. 4B). Interestingly, we did not observe the same changes for the pericycle−endodermis cell junction and the endodermis−endodermis cell junction (SI Appendix, Fig. S14), suggesting that EXPA1 locally affects the cell wall to accommodate radial expansion. As the spectra collection has been normalized to acquisition time and extent of focus, this would indicate a change in the concentration of the biopolymers in response to auxin in addition to more subtle changes in the biochemical properties of the pericycle cell wall during lateral root initiation in expa1-1 initiated either directly or indirectly. Regardless of the specific origin, our data suggest that EXPA1 is involved in pericycle cell wall remodeling upon auxin-induced lateral root initiation and appears to specifically target the expansion at the pericycle−pericycle cell junction of the xylem pole pericycle cells (Fig. 4C).
Conclusion
Several stages and checkpoints in early lateral root development have been described, and auxin is central to this process (2–6, 8–10, 14). Here, through detailed characterization of the EXPA1 expression pattern and expa1 mutant developmental and biochemical phenotypes in the pericycle, we established a link among cell wall properties, cell geometry, cell expansion, and (asymmetric) cell division. We showed that EXPA1 is required for proper radial pericycle cell expansion during lateral root initiation that licenses the correct positioning of the first anticlinal divisions (Fig. 4C). In WT, pericycle cell swelling is asymmetric, resulting in the typical localized bulging of these cells and in coordinately positioned anticlinal asymmetric cell divisions (Figs. 1A and 4C). If the pericycle width is too low as observed in the pCASP1::shy2-2 line, no lateral root initiation takes place (Fig. 4C) (9). If the pericycle width is too high, and no auxin-mediated correction occurs, periclinal cell divisions take place (Fig. 4C) (7). In the expa1 mutant, the pericycle swells across the whole cell length resulting in a loss of coordination of the position of the anticlinal asymmetric pericycle cell divisions (Fig. 4C). Although this defect is transient and the lateral root primordia manage to resume lateral root development, this highlights the importance of a tight control of pericycle swelling for the onset of lateral root formation. By modifying the properties of the cell wall, expansins may modify the mechanics of the tissue at the site of initiation, in turn, influencing the positioning of the cell division plane (53). This role of expansins is reminiscent of leaf organogenesis where expansins are shown to alter the physical stress pattern in the meristem so that tissue bulging occurs and organ formation is triggered (54, 55).
It was recently reported that cell wall remodeling due to acidification (AHA1/2-driven) and EXPA‐dependent loosening (EXPA1 driven) brings about a change in cell shape important for the differentiation of cells leaving the primary root meristem (43). Other EXPAs, such as EXPA10, EXPA14, and EXPA15, act redundantly in the primary root (43), but of those EXPAs, only EXPA15 was differentially expressed in our lateral root initiation-focused transcriptomes (Dataset S1) (4). In addition, the auxin-inducible LDB18 targets EXPA14 and EXPA17 play a role in lateral root emergence (56, 57). Taken together, this suggests both overlapping and developmentally specific roles of EXPAs.
In conclusion, altered EXPA1 activity impacts—directly or indirectly—on cell wall composition, which, in turn, controls pericycle cell width. At present, we cannot explain the counterintuitive phenotype in the expa1-1 x WAVE131YFP line with respect to cell wall composition and pericycle cell expansion. Whether the observed differences are a direct effect of the loss of EXPA1 activity or a secondary effect resulting in an altered overall cell wall composition remains to be investigated. It will be interesting to understand how local (polarity) cues drive action of EXPA1, coordinate with auxin, instruct the positioning of the nucleus and cell division plane, and how this is coupled to the spatial accommodation by the overlaying endodermis.
Materials and Methods
Detailed description of plant materials, plant growth conditions, plasmids, and methods for root and cell measurements, microscopy, transcriptome analysis, and monosaccharide analysis, can be found in SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Joop Vermeer for critical reading of the paper. This work was supported by a BBSRC David Phillips Fellowship (BB_BB/H022457/1) and a Marie Curie European Reintegration Grant (PERG06-GA-2009–256354) (to I.D.S.). P.R. acknowledges financial support from the University of Nottingham Vice-Chancellor’s Scholarship for Research Excellence. Work in the A.M. laboratory was supported by the DFG Grant FOR2581 (MA5293/6-1) and the Boehringer Ingelheim Foundation. L.D.V. is a recipient of the VIB International PhD Scholarship in Life Sciences. The Confocal Raman microscopy work was supported by a University of Nottingham Interdisciplinary Centre for Analytical Science (UNICAS) award.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1820882116/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.De Smet I, Beeckman T. Asymmetric cell division in land plants and algae: The driving force for differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:177–188. doi: 10.1038/nrm3064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.De Rybel B, et al. A novel aux/IAA28 signaling cascade activates GATA23-dependent specification of lateral root founder cell identity. Curr Biol. 2010;20:1697–1706. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.De Smet I, et al. Auxin-dependent regulation of lateral root positioning in the basal meristem of Arabidopsis. Development. 2007;134:681–690. doi: 10.1242/dev.02753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.De Smet I, et al. Receptor-like kinase ACR4 restricts formative cell divisions in the Arabidopsis root. Science. 2008;322:594–597. doi: 10.1126/science.1160158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goh T, Joi S, Mimura T, Fukaki H. The establishment of asymmetry in Arabidopsis lateral root founder cells is regulated by LBD16/ASL18 and related LBD/ASL proteins. Development. 2012;139:883–893. doi: 10.1242/dev.071928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Laskowski M, Ten Tusscher KH. Periodic lateral root priming: What makes it tick? Plant Cell. 2017;29:432–444. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Marhavý P, et al. Targeted cell elimination reveals an auxin-guided biphasic mode of lateral root initiation. Genes Dev. 2016;30:471–483. doi: 10.1101/gad.276964.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Moreno-Risueno MA, et al. Oscillating gene expression determines competence for periodic Arabidopsis root branching. Science. 2010;329:1306–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.1191937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vermeer JE, et al. A spatial accommodation by neighboring cells is required for organ initiation in Arabidopsis. Science. 2014;343:178–183. doi: 10.1126/science.1245871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xuan W, et al. Root cap-derived auxin pre-patterns the longitudinal axis of the Arabidopsis root. Curr Biol. 2015;25:1381–1388. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.03.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lucas M, et al. Lateral root morphogenesis is dependent on the mechanical properties of the overlaying tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:5229–5234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210807110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.von Wangenheim D, et al. Rules and self-organizing properties of post-embryonic plant organ cell division patterns. Curr Biol. 2016;26:439–449. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.12.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fukaki H, Tasaka M. Hormone interactions during lateral root formation. Plant Mol Biol. 2009;69:437–449. doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lavenus J, et al. Lateral root development in Arabidopsis: Fifty shades of auxin. Trends Plant Sci. 2013;18:450–458. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2013.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Overvoorde P, Fukaki H, Beeckman T. Auxin control of root development. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2:a001537. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a001537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Carpita NC, Gibeaut DM. Structural models of primary cell walls in flowering plants: Consistency of molecular structure with the physical properties of the walls during growth. Plant J. 1993;3:1–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.1993.tb00007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rose JKC. The Plant Cell Wall. Blackwell Publishing Ltd; Oxford: 2003. p. 381. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fry SC, et al. Xyloglucan endotransglycosylase, a new wall-loosening enzyme activity from plants. Biochem J. 1992;282:821–828. doi: 10.1042/bj2820821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pauly M, Albersheim P, Darvill A, York WS. Molecular domains of the cellulose/xyloglucan network in the cell walls of higher plants. Plant J. 1999;20:629–639. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1999.00630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cosgrove DJ. Growth of the plant cell wall. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:850–861. doi: 10.1038/nrm1746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Keegstra K, Talmadge KW, Bauer WD, Albersheim P. The structure of plant cell walls: III. A model of the walls of suspension-cultured sycamore cells based on the interconnections of the macromolecular components. Plant Physiol. 1973;51:188–197. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Park YB, Cosgrove DJ. A revised architecture of primary cell walls based on biomechanical changes induced by substrate-specific endoglucanases. Plant Physiol. 2012;158:1933–1943. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.192880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Park YB, Cosgrove DJ. Xyloglucan and its interactions with other components of the growing cell wall. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015;56:180–194. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zykwinska A, Thibault J-F, Ralet M-C. Competitive binding of pectin and xyloglucan with primary cell wall cellulose. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;74:957–961. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang T, Park YB, Cosgrove DJ, Hong M. Cellulose-pectin spatial contacts are inherent to never-dried Arabidopsis primary cell walls: Evidence from solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. Plant Physiol. 2015;168:871–884. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vincken JP, de Keizer A, Beldman G, Voragen AG. Fractionation of xyloglucan fragments and their interaction with cellulose. Plant Physiol. 1995;108:1579–1585. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.4.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Park YB, Cosgrove DJ. Changes in cell wall biomechanical properties in the xyloglucan-deficient xxt1/xxt2 mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012;158:465–475. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.189779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Peaucelle A, et al. Arabidopsis phyllotaxis is controlled by the methyl-esterification status of cell-wall pectins. Curr Biol. 2008;18:1943–1948. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.10.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Peaucelle A, et al. Pectin-induced changes in cell wall mechanics underlie organ initiation in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol. 2011;21:1720–1726. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.08.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Popper ZA, Fry SC. Xyloglucan-pectin linkages are formed intra-protoplasmically, contribute to wall-assembly, and remain stable in the cell wall. Planta. 2008;227:781–794. doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0656-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.McQueen-Mason S, Durachko DM, Cosgrove DJ. Two endogenous proteins that induce cell wall extension in plants. Plant Cell. 1992;4:1425–1433. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.11.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Eklöf JM, Brumer H. The XTH gene family: An update on enzyme structure, function, and phylogeny in xyloglucan remodeling. Plant Physiol. 2010;153:456–466. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.156844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wolf S, Greiner S. Growth control by cell wall pectins. Protoplasma. 2012;249:S169–S175. doi: 10.1007/s00709-011-0371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Peaucelle A, Braybrook S, Höfte H. Cell wall mechanics and growth control in plants: The role of pectins revisited. Front Plant Sci. 2012;3:121. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McQueen-Mason SJ, Cosgrove DJ. Expansin mode of action on cell walls. Analysis of wall hydrolysis, stress relaxation, and binding. Plant Physiol. 1995;107:87–100. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang T, et al. Sensitivity-enhanced solid-state NMR detection of expansin’s target in plant cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:16444–16449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1316290110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vanneste S, et al. Cell cycle progression in the pericycle is not sufficient for SOLITARY ROOT/IAA14-mediated lateral root initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 2005;17:3035–3050. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.035493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Himanen K, et al. Auxin-mediated cell cycle activation during early lateral root initiation. Plant Cell. 2002;14:2339–2351. doi: 10.1105/tpc.004960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Himanen K, et al. Transcript profiling of early lateral root initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:5146–5151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308702101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Abel S, Oeller PW, Theologis A. Early auxin-induced genes encode short-lived nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:326–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Worley CK, et al. Degradation of Aux/IAA proteins is essential for normal auxin signalling. Plant J. 2000;21:553–562. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Péret B, et al. Auxin regulates aquaporin function to facilitate lateral root emergence. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:991–998. doi: 10.1038/ncb2573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pacifici E, Di Mambro R, Dello Ioio R, Costantino P, Sabatini S. Acidic cell elongation drives cell differentiation in the Arabidopsis root. EMBO J. 2018;37:e99134. doi: 10.15252/embj.201899134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Geldner N, et al. Rapid, combinatorial analysis of membrane compartments in intact plants with a multicolor marker set. Plant J. 2009;59:169–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.De Smet I, Vanneste S, Inzé D, Beeckman T. Lateral root initiation or the birth of a new meristem. Plant Mol Biol. 2006;60:871–887. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-4547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cosgrove DJ. Plant cell enlargement and the action of expansins. BioEssays. 1996;18:533–540. doi: 10.1002/bies.950180704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Valent BS, Albersheim P. The structure of plant cell walls: V. On the binding of xyloglucan to cellulose fibers. Plant Physiol. 1974;54:105–108. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Moller IE, et al. 2012. Glycan profiling of plant cell wall polymers using microarrays. J Vis Exp, e4238.
- 49.Ryden P, et al. Tensile properties of Arabidopsis cell walls depend on both a xyloglucan cross-linked microfibrillar network and rhamnogalacturonan II-borate complexes. Plant Physiol. 2003;132:1033–1040. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.021873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Peña MJ, Ryden P, Madson M, Smith AC, Carpita NC. The galactose residues of xyloglucan are essential to maintain mechanical strength of the primary cell walls in Arabidopsis during growth. Plant Physiol. 2004;134:443–451. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.027508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Thompson JE, Fry SC. Restructuring of wall-bound xyloglucan by transglycosylation in living plant cells. Plant J. 2001;26:23–34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nishitani K. Construction and restructuring of the cellulose-xyloglucan framework in the apoplast as mediated by the xyloglucan-related protein family—A hypothetical scheme. J Plant Res. 1998;111:159–166. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Louveaux M, Julien J-D, Mirabet V, Boudaoud A, Hamant O. Cell division plane orientation based on tensile stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E4294–E4303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600677113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Pien S, Wyrzykowska J, McQueen-Mason S, Smart C, Fleming A. Local expression of expansin induces the entire process of leaf development and modifies leaf shape. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:11812–11817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191380498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fleming AJ, McQueen-Mason S, Mandel T, Kuhlemeier C. Induction of leaf primordia by the cell wall protein expansin. Science. 1997;276:1415–1418. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lee HW, Kim J. EXPANSINA17 up-regulated by LBD18/ASL20 promotes lateral root formation during the auxin response. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013;54:1600–1611. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lee HW, Kim MJ, Kim NY, Lee SH, Kim J. LBD18 acts as a transcriptional activator that directly binds to the EXPANSIN14 promoter in promoting lateral root emergence of Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2013;73:212–224. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.