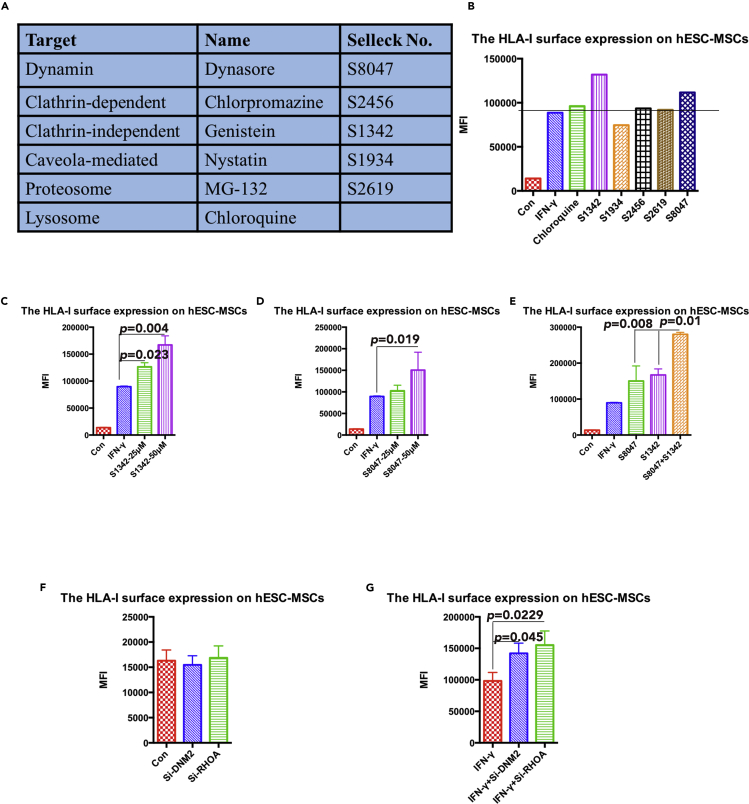
Figure 4.
The Identification of the Selected Endocytosis Pathway for HLA-I in hESC-MSCs
(A) Summary of the selected inhibitors for different endocytosis pathways.
(B) The mean fluorescence index of HLA-I surface expression on hESC-MSCs with different inhibitor treatment was compared by flow cytometry analysis. The black dashed line indicates the compared hESC-MSCs group with only IFN-γ treatment. Data are shown as mean fluorescence index.
(C) The mean fluorescence index of HLA-I surface expression on IFN-γ-treated hESC-MSCs with different dosage of S1342 treatment was compared by flow cytometry analysis. Data are shown as means ± SEM.
(D) The mean fluorescence index of HLA-I surface expression on IFN-γ-treated hESC-MSCs with different dosage of S8047 treatment was compared by flow cytometry analysis. Data are shown as means ± SEM.
(E) The mean fluorescence index of HLA-I surface expression on IFN-γ-treated hESC-MSCs with the combination of S1342 and S8047 treatment was compared by flow cytometry analysis. Data are shown as means ± SEM.
(F) The mean fluorescence index of HLA-I surface expression on hESC-MSCs with different small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection was compared by flow cytometry analysis. Data are shown as means ± SEM.
(G) The mean fluorescence index of HLA-I surface expression on IFN- γ-treated hESC-MSCs with different siRNA transfection was compared by flow cytometry analysis. Data are shown as means ± SEM.