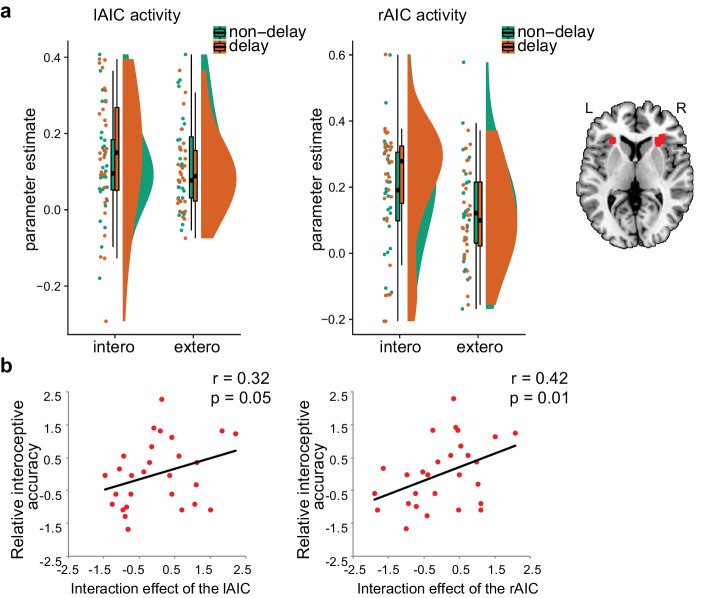
Figure 5. ROI results of the second fMRI sample.
(a) ROI analysis of the parameter estimates of the left and the right AIC under the four experimental conditions. Raincloud plots were used for visualization. (b) Correlation between the interaction effect of bilateral AIC and relative interoceptive accuracy. The values of the variable in b were normalized as z-scores.
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Raincloud plot visualization of respiratory volumes under the four experimental conditions from the second fMRI sample.