Mohandas A, Kumar PT S, Raja B, et al. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10(Suppl 1):53–66.
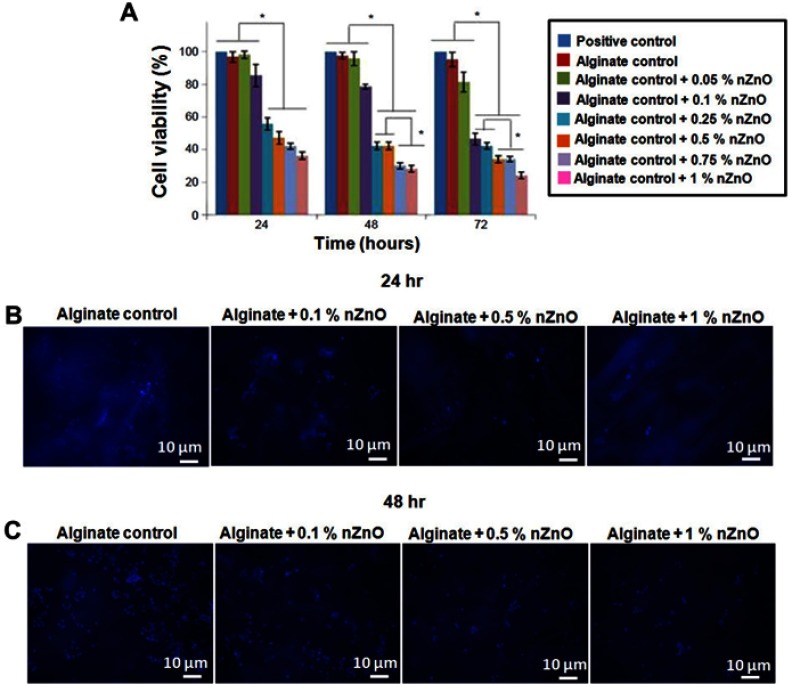
The authors have advised that Figure 8B and C (page 62) were incorrect in the original manuscript, as the Alginate control group is inadvertently repeated in the Alginate +0.1% nZnO group. Due to this mistake they have repeated the entire cell attachment studies using DAPI. The authors have confirmed that this does not in any way affect the conclusions from Figure 8B and C, and that it is not going to affect the overall conclusion of this published paper. They apologize for any inconvenience. The correct version of Figure 8 is presented below.
Figure 8.
Evaluation of cytocompatability of alginate hydrogel/nZnO composite bandages. (A) Cell viability evaluation of HDF cells using Alamar blue assay. Student’s t-test was performed and P-values <0.05 were considered significant. (B and C) DAPI stained fluorescence microscopic images of HDF cells attached onto the composite bandages. *Indicates significant difference compared the control. Scale bar denotes 10 μm.
Abbreviations: HDF, human dermal fibroblast; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; nZnO, zinc oxide nanoparticles; hr, hours.