Abstract
Background
Traditionally, radical prostatectomy and radiotherapy with or without androgen deprivation therapy have been the main treatment options to attempt to cure men with localised or locally advanced prostate cancer. Cryotherapy is an alternative option for treatment of prostate cancer that involves freezing of the whole prostate (whole gland therapy) or only the cancer (focal therapy), but it is unclear how effective this is in comparison to other treatments.
Objectives
To assess the effects of cryotherapy (whole gland or focal) compared with other interventions for primary treatment of clinically localised (cT1‐T2) or locally‐advanced (cT3) non‐metastatic prostate cancer.
Search methods
We updated a previously published Cochrane Review by performing a comprehensive search of multiple databases (CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE), clinical trial registries (ClinicalTrials.gov, World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform) and a grey literature repository (Grey Literature Report) up to 6 March 2018. We also searched the reference lists of other relevant publications and conference proceedings. We applied no language restrictions.
Selection criteria
We included randomised or quasi‐randomised trials comparing cryotherapy to other interventions for the primary treatment of prostate cancer.
Data collection and analysis
Two independent reviewers screened the literature, extracted data, and assessed risk of bias. We performed statistical analyses using a random‐effects model and interpreted them according to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. We rated the quality of evidence (QoE) according to the GRADE approach.
Main results
We included only one comparison of whole gland cryotherapy versus external beam radiotherapy, which was informed by two trials with a total of 307 randomised participants. The median age of the included studies was around 70 years. The median follow‐up of included studies ranged from 100 to 105 months.
Primary outcomes: we are uncertain about the effect of whole gland cryotherapy compared to radiation therapy on time to death from prostate cancer; hazard ratio (HR) of 1.00 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.11 to 9.45; 2 trials, 293 participants; very low QoE); this would correspond to zero fewer death from prostate cancer per 1000 men (95% CI 85 fewer to 520 more). We are equally uncertain about the effect of quality of life‐related urinary function and bowel function (QoL) at 36 months using the UCLA‐Prostate Cancer Index score for which higher values (range: 0 to 100) reflect better quality of life using minimal clinically important differences (MCID) of 8 and 7 points, respectively; mean difference (MD) of 4.4 (95% CI −6.5 to 15.3) and 4.0 (95% CI −73.96 to 81.96), respectively (1 trial, 195 participants; very low QoE). We are also uncertain about sexual function‐related QoL using a MCID of 8 points; MD of −20.7 (95% CI −36.29 to −5.11; 1 trial, 195 participants; very low QoE). Lastly, we are uncertain of the risk for major adverse events; risk ratio (RR): 0.91 (95% CI 0.47 to 1.78; 2 trials, 293 participants; very low QoE); this corresponds to 10 fewer major adverse events per 1000 men (95% CI 58 fewer to 86 more).
Secondary outcomes: we are very uncertain about the effects of cryotherapy on time to death from any cause (HR 0.99, 95% CI 0.05 to 18.79; 2 trials, 293 participants; very low QoE), and time to biochemical failure (HR 2.15, 95% CI 0.07 to 62.12; 2 trials, 293 participants; very low QoE). Rates of secondary interventions for treatment failure and minor adverse events were either not reported in the trials, or the data could not be used for analyses.
We found no trials that compared whole gland cryotherapy or focal cryotherapy to other treatment forms such as radical surgery, active surveillance, watchful waiting or other forms of radiotherapy.
Authors' conclusions
Based on very low quality evidence, primary whole gland cryotherapy has uncertain effects on oncologic outcomes, QoL, and major adverse events compared to external beam radiotherapy. Reasons for downgrading the QoE included serious study limitations, indirectness due to the use of lower doses of radiation in the comparison group than currently recommended, and serious or very serious imprecision.
Plain language summary
Primary cryotherapy for localised or locally advanced prostate cancer
Review question
How does freezing of the prostate gland (cryotherapy) compare to other treatments in men with prostate cancer who have not been treated before?
Background
Prostate cancer is commonly treated with surgery or radiation if it has not yet spread to other organs. These treatments can have serious side‐effects. Freezing of the prostate is another way to treat prostate cancer. This can be done by freezing the whole prostate (whole gland cryotherapy) or only the part of the prostate where the main cancer is (focal cryotherapy). We do not understand well how freezing of the prostate compares to other treatments.
Study characteristics
We searched the medical literature for evidence from trials up to 6 March 2018. We found two randomised trials that compared freezing of the whole prostate to radiation treatment. These included 307 randomised men with prostate cancer (cryotherapy 154 men, radiation 153 men). Their average age was around 70 years. These studies followed men for eight to nine years after treatment. We did not find any studies that compared freezing the prostate to surgery. Also, we did not find randomised trials that compared freezing of parts of the prostate (focal cryotherapy) to radiation, surgery or no treatment.
Key results
We are uncertain of the effects of freezing of the whole prostate compared to radiation treatment on the time to death from prostate cancer, quality of life for urinary, bowel, and sexual function and serious unwanted treatment reactions.
Quality of the evidence
The quality of evidence was very low for all outcomes meaning that the real effect of whole gland cryotherapy may differ a lot from the findings in this review. Further research is very likely to change these findings.
Summary of findings
Summary of findings for the main comparison. Whole gland primary cryotherapy compared to external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) for localised or locally advanced prostate cancer (long‐term outcomes).
| Participants: men with localised or locally advanced prostate cancer Setting: single institution in Canada Intervention: whole gland cryotherapy Comparator: external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) | |||||
| Outcomes | № of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Relative effect (95% CI) | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | |
| Risk with EBRT | Risk difference with cryotherapy | ||||
| Time to death from prostate cancer (absolute effects: disease‐specific mortality)1 Follow‐up: range 5 years to 8 years | 293 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOW 2 3 4 | HR 1.00 (0.11 to 9.45) | Study population | |
| 97 per 1000 | 0 fewer per 1000 (85 fewer to 520 more) | ||||
| Quality of life ‐ urinary function
assessed with: UCLA‐PCI 5
Range 0 ‐ 100; higher values reflect better quality of life Follow‐up: mean 36 months |
195 (1 RCT) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOW 2 3 6 | ‐ | The mean quality of life ‐ urinary function was 88.6 | MD 4.4 higher (6.5 lower to 15.3 higher) |
| Quality of life ‐ bowel function
assessed with: UCLA‐PCI 5
Range 0 ‐ 100; higher values reflect better quality of life Follow‐up: mean 36 months |
195 (1 RCT) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOW 2 3 6 | ‐ | The mean quality of life ‐ bowel function was 84.1 | MD 4 higher (73.96 lower to 81.96 higher) |
| Quality of life ‐ sexual function
assessed with: UCLA‐PCI 5
Range 0 ‐ 100; higher values reflect better quality of life Follow‐up: mean 36 months |
195 (1 RCT) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOW 2 3 6 | ‐ | The mean quality of life ‐ sexual function was 36.7 | MD 20.7 lower (36.29 lower to 5.11 lower) |
| Major adverse events Follow‐up: median range 100 months to 105 months | 293 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOW 2 3 6 | RR 0.91 (0.47 to 1.78) | Study population | |
| 110 per 1000 | 10 fewer per 1000 (58 fewer to 86 more) | ||||
| Time to death from any cause (absolute effects: overall mortality)1 Follow‐up: range 5 years to 8 years | 293 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOW 2 3 4 | HR 0.99 (0.05 to 18.79) | Study population | |
| 166 per 1000 | 2 fewer per 1000 (157 fewer to 801 more) | ||||
| Secondary interventions for treatment failure ‐ not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; EBRT: external beam radiotherapy; HR: hazard ratio; MD: mean difference; RCT: randomised controlled trial; RR: risk ratio; UCLA‐PCI: UCLA‐Prostate Cancer Index | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High quality: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect Moderate quality: We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different Low quality: Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect Very low quality: We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect | |||||
1 Mortality instead of survival to estimate anticipated absolute effect is reported for methodological reason.
2 Downgraded by one level for study limitations: unclear or high risk of bias in half of domains in included studies.
3 Downgraded by one level for indirectness (differences in intervention): prescribed dose of radiotherapy in the included studies was lower than 74 Gy as recommended by current guidelines (EAU 2017). Also, radiotherapy should be given in combination with long‐term androgen deprivation therapy (two to three years) in patients with high risk prostate cancer.
4 Downgraded by two levels for imprecision: wide confidence interval cross assumed threshold of clinically important differences.
5 UCLA‐Prostate Cancer Index contains six domains (urinary function (4 items), urinary bother (1 item), sexual function (5 items), sexual bother (1 item), bowel function (3 items), bowel bother (1 item)) which are scored separately (low score = worst, high score = better) (Litwin 1998).
6 Downgraded by one level for imprecision: confidence interval crosses assumed threshold of clinically important difference.
Background
Description of the condition
Prostate cancer represents one of the most important medical problems affecting the male population. It is the most common neoplasm (cancer) in men in Europe and the USA, where approximately 417,000 and 209,000 new cases, respectively, are diagnosed annually (USCS Group 2014). Worldwide, prostate cancer accounts for 14% (˜903,500) of all new cancer cases and 6% of cancer‐related deaths (Jemal 2011).
Determination of the stage of prostate cancer includes digital rectal examination, measurement of prostate‐specific antigen (PSA) level and the Gleason score (the Gleason grading system is specific for prostate cancer) (D'Amico 2003) determined by a prostate biopsy. Clinical tumour stage (T‐stage) is often classified as localised (organ‐confined, cT1/T2) or locally advanced (extraprostatic, i.e. outside the prostate, T3/T4). Prostate cancer stage is commonly expressed using a risk group classification system (D'Amico 2003). Men are often classified as being at low‐risk (PSA < 10, Gleason < 7, and cT1‐cT2a), intermediate‐risk (any of the following: PSA 10 to 20, Gleason 7, or cT2b), or high‐risk (PSA > 20, Gleason > 7; localised‐cT2c or locally‐advanced‐cT3‐T4) (EAU 2017). Risk stratification models are used to predict cancer‐specific mortality and to guide treatment decisions (Babaian 2008; D'Amico 2003). In patients with low risk prostate cancer, active surveillance or watchful waiting are now the preferred management approach. Even men with intermediate risk and high risk prostate cancer have a comparatively favorable prognosis compared to other cancers. Depending on the underlying Gleason score, many men are at higher risk of dying from other causes than prostate cancer (Albertsen 1995).
Radical prostatectomy (RP), external beam radiotherapy (EBRT), and interstitial brachytherapy are the most commonly used interventions for treatment of localised or locally advanced prostate cancer. Patient‐specific factors and increased awareness of treatment‐related factors, adverse events, and health‐related quality of life (HRQoL) have led to the development of alternative treatment approaches for prostate cancer (Beerlage 2003). Cryotherapy is a minimally invasive procedure that has been recognised as an alternative option for prostate cancer treatment (AUA 2017; EAU 2017; Thompson 2007).
Description of the intervention
Advancements in cryotherapy for prostate cancer over the past 50 years have focused on maximising destruction of prostate tissue while minimising injury to adjacent tissues (Cooper 2001). Early studies used whole gland cryotherapy as a method for treating prostate cancer, but recent improvements in imaging and diagnostic methods, such as multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and three‐dimensional mapping biopsy, have led to a greater emphasis on focal treatment of localised prostate cancer (Barqawi 2014).
The modern procedure uses pressurised argon gas to achieve cooling, and helium for warming. Under the guidance of transrectal ultrasonography, small probes, or cryoneedles, are placed into the prostate through a perineal incision. Thermocoupling needles are also used to monitor temperatures within the gland. These instruments are integrated into computer software to generate geometric and thermal mapping throughout the procedure. Urethral warming catheters and saline injections posterior to the prostate are used to minimise injury to the urethra and anterior rectal wall, respectively (Baust 2005; Cohen 2004; Donnelly 2002b; Rees 2004).
General principles for preparation include targeting the cooling to prostate or seminal vesicles, or both, while sparing the urethra, rectum, and the neurovascular bundles in patients with an interest in preservation of sexual function. Real‐time ultrasound permits visualisation of the so‐called "ice‐ball" (the visible formation of an area of frozen tissue within the prostate), and thermosensors provide measurements from various points in and around the prostate. A target temperature of −40 ℃ is desired to achieve maximal lethal effect of prostate tissue (Gage 1998). Additional tissue destruction can be enhanced by increasing the freeze rate, allowing a slow thaw, and performing a double freeze‐thaw cycle (Baust 2005).
Cryotherapy can target either the entire prostate (whole gland cryotherapy) or parts of the prostate only (focal therapy). In the latter case, prior imaging or biopsy findings, or both, will seek to determine the 'index lesion', that is, the one that is likely to determine the particular patient's cancer natural history. Limiting freezing to the index lesion is thought to reduce the frequency and severity of treatment‐related adverse effects. Given its conceptual appeal, focal therapy has increased in use, whereas the use of whole gland therapy has decreased (Barqawi 2014).
Comparative treatments include surgery and radiotherapy. Surgical treatment of prostate cancer with RP involves the physical removal of the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, with or without draining lymph nodes, followed by reconstruction of the continuity of the bladder with the membranous urethra. Radiotherapy involves the use of ionising radiation to cause DNA damage, and subsequent cell death (Koukourakis 2009). Ionising radiation can be delivered from an external source, as in EBRT, in which high energy photons are generated and directed at the prostate, or internally via brachytherapy, in which a radioactive source is implanted directly into the prostate.
Adverse effects of the intervention
Adverse events known to be associated with cryotherapy include urinary retention, urinary tract infections, perineal pain, and pain or swelling in the penis or scrotum. Other, longer‐term side‐effects include persistent adverse events include erectile dysfunction, urinary incontinence, recto‐urethral fistula, urethral stricture, urethral sloughing, and penile/scrotal pain (AUA 2017; EAU 2017; Rees 2004).
How the intervention might work
The rationale for the effectiveness of cryotherapy dates back to the 19th century, when James Arnott used cold to destroy breast and cervical cancers (Arnott 1851). Liquid nitrogen gained popularity in the mid 20th century for treatment of various skin conditions and in 1963 became available via the Cooper device for treatment of deeper tissues. By definition, cryotherapy is a type of thermal treatment in which tissues are cooled to extremely low temperatures to promote targeted destruction (Cooper 2001). Physiologically, freezing results in a series of cellular responses that cause tissue necrosis.
The mechanism by which cell death is produced involves three main phases. Initially, cooling leads to the formation of ice in the extracellular space; this creates a hyperosmotic gradient that causes cell shrinkage and damage to intracellular proteins. Continuation damages endothelial cells and causes thrombosis and tissue hypoxia. Finally, ice forms and expands in the intracellular space and disruption of the cell membranes ensues and activates cellular apoptosis (Baust 2004).
Why it is important to do this review
Treatment decisions for prostate cancer involve an assessment of tumour characteristics and risk classification, as well as patient life expectancy and overall health status. For men who elect to have treatment for prostate cancer, the choice of intervention involves patient preferences, other health conditions, treatment‐related factors, and complications. While RP and radiation remain the standard choices, alternative options have emerged for patients poorly suited to these interventions (AUA 2017; EAU 2017).
Cryotherapy is a minimally invasive treatment option that can be performed in an outpatient setting at a lower cost than comparative treatments (Robinson 2002). Potential candidates include men who are poor candidates for surgical prostatectomy (due to medical comorbidities, obesity with narrow pelvis), or have contra‐indications to radiotherapy (prior pelvic radiation, inflammatory bowel disorders, rectal disease). The American Urologic Association has recognised cryotherapy as an 'option' for organ‐confined disease of any grade and negative metastatic evaluation (AUA 2017; Babaian 2008). The European Urological Association has recognised cryotherapy as an alternative option for prostate cancer that is organ‐confined, or with minimal tumour extension outside the prostate, with low‐to‐intermediate risk classification (EAU 2017). The evidence cited to support these recommendations is based on observational studies and one randomised clinical trial. The purpose of this review is to evaluate the evidence comparing cryotherapy to standard treatment options for primary treatment of localised or locally advanced prostate cancer. This is an update of a review published in 2007 (Shelley 2007), with inclusion of two randomised controlled trials published since that time and application of the GRADE approach to rating the quality of evidence (QoE).
Objectives
To assess the effects of cryotherapy (whole gland or focal) compared with other interventions for primary treatment of clinically localised (cT1‐T2) or locally‐advanced (cT3) non‐metastatic prostate cancer.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We included parallel‐group randomised or quasi‐randomised trials (e.g. alternate allocation bases on date of birth or case record number) comparing cryotherapy to other interventions for the primary treatment of prostate cancer.
Types of participants
Men with clinical stage T1‐T3, node‐negative (N0), non‐metastatic (M0) prostate cancer who have not received prior therapy.
Types of interventions
We planned to investigate the following comparisons of experimental intervention versus comparator intervention. Concomitant interventions had to be the same in the experimental and comparator groups to establish fair comparison.
Experimental interventions
Cryotherapy (whole gland or focal)
We chose to include only cryoablation procedures that utilised a urethral warming catheter and real‐time imaging of cryo‐probe(s) placement and freeze‐thaw cycles. We included studies in which androgen deprivation therapy was administered prior to or following cryotherapy, or both, if an identical regimen was used in the comparator group. Since many cryotherapy protocols allow a second cryoablation procedure within the treatment phase, we included studies using such protocols.
Comparator interventions
No intervention (watchful‐waiting or sham cryotherapy)
Active surveillance
Brachytherapy
External beam radiation (EBRT)
Radical prostatectomy
Types of outcome measures
We did not use the measurement of the outcomes assessed in this review as an eligibility criterion.
Primary outcomes
Time to death from prostate cancer
QoL
Major adverse events
Secondary outcomes
Time to death from any cause
Secondary interventions for treatment failure
Time to biochemical failure
Minor adverse events
Method and timing of outcome measurement
Time to death from prostate cancer: measured as the date of randomisation to the date of death due to prostate cancer (Mariotto 2014).
QoL: mean change assessed with validated questionnaire such as UCLA‐Prostate Cancer Index (UCLA‐PCI; Litwin 1998), and European Organisation for Research and Treatment core QoL questionnaire (EORTC QLQ C‐30; Aaronson 1993).
Major adverse events: graded as the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE): Grade 3 = severe; Grade 4 = life‐threatening or disabling; Grade 5 = death‐related; we also considered the definition used in each clinical trial (National Cancer Institute). If the study authors of eligible studies did not use the CTCAE system, we judged the severity of the adverse events using the available information described in the studies.
Time to death from any cause: measured as the date from randomisation to the date of death due to any cause (Mariotto 2014).
Secondary interventions for treatment failure: events requiring other treatment modalities (e.g. salvage cryotherapy, or radiation therapy) after intervention.
Time to biochemical failure: measured as the date of randomisation to the date of biochemical failure using the American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) definition (Roach 2006).
Minor adverse events: graded as the CTCAE: Grade 1 = mild; Grade 2 = moderate. If the authors did not use CTCAE system, we graded the adverse events as described above.
We used clinically important difference for the review outcomes to rate the QoE for imprecision in Table 1 (Johnston 2010). We did not find any published information about a clinically important difference for time to death from prostate cancer, any cause, or biochemical failure, so we considered the clinically important difference as a relative risk reduction of at least 25% for these outcomes (Guyatt 2011a). Using the UCLA‐PCI, we considered other minimal clinically important differences (MCIDs) to be as follows: for urinary function, 8 points; bowel function, 7 points; sexual function, 8 points; urinary bother, 9 points; bowel bother, 8 points; and sexual bother, 11 points (Jayadevappa 2012). If available, we considered MCIDs of EORTC QLQ C‐30 based on the previous literature (Bedard 2014). While no threshold was established for the major and minor adverse events, we also considered the clinically important difference as relative risk reduction of at least 25% (Guyatt 2011a).
Search methods for identification of studies
We performed a comprehensive search with no restrictions for the language of publication or publication status.
Electronic searches
We updated the published Cochrane Review by searching the following sources between 2006 and 9 June 2015 thereby overlapping with the original search by Shelley 2007 (from 1996 to 2006). We re‐ran the searches in all relevant databases on 6 March 2018, and incorporated any identified relevant studies into the review. See Appendix 1 for the search strategy.
-
Cochrane Library (via Wiley; for the search strategy)
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR)
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL)
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE)
Health Technology Assessment Database (HTA)
MEDLINE (via Ovid)
EMBASE (via Ovid)
LILACS (Latin American and the Caribbean Health Sciences Literature; www.bireme.br/)
Scopus
Web of Science
We also searched the following trials registers on 9 June 2015 and again on 6 March 2018.
ClinicalTrials.gov (https://clinicaltrials.gov/)
World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform search portal (http://apps.who.int/trialsearch/)
Grey Literature Report (http://www.greylit.org/)
When we detected additional relevant key words during any of the electronic or other searches, we modified the electronic search strategies to incorporate these terms and documented the changes.
Searching other resources
We tried to identify other potentially eligible trials or ancillary publications by searching the reference lists of included trials, reviews, meta‐analyses and health technology assessment reports. We also contacted study authors of included trials to identify any further studies that we might have missed. We contacted drug/device manufacturers for ongoing or unpublished trials. We searched for unpublished studies by handsearching the abstract proceedings of the annual meetings of American Urological Association, European Association of Urology, and the American Society of Clinical Oncology from 2012 to 2017.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
We used EndNote reference management software to identify and remove potential duplicate records. Two review authors (JHJ, BR or RG) independently scanned the abstract, title, or both, of remaining records retrieved, to determine which studies should be assessed further through Covidence. Two review authors (JHJ, BR or RG) investigated all potentially relevant records as full text, mapped records to studies, and classified studies as included studies, excluded studies, studies awaiting classification, or ongoing studies in accordance with the criteria for each provided in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011a). We resolved any discrepancies through consensus or recourse to a third review author (PD). We documented reasons for exclusion of studies that may have reasonably been expected to be included in the review in a Characteristics of excluded studies table. In Figure 1, we present an adapted PRISMA flow diagram showing the process of study selection (Liberati 2009).
1.
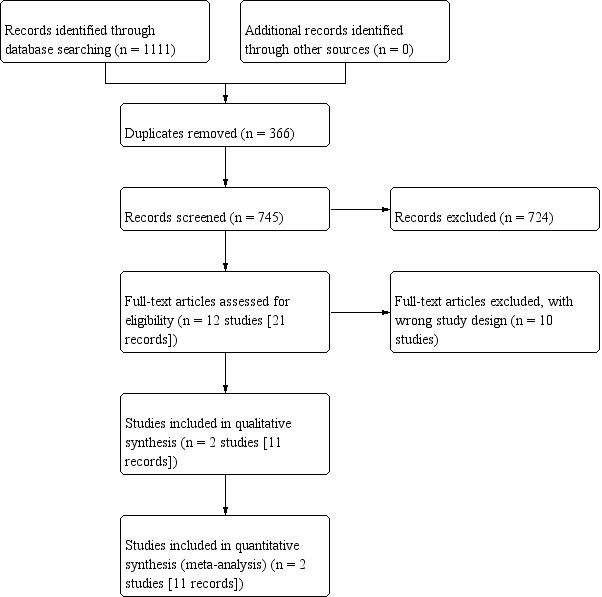
Flow diagram.
Data extraction and management
We developed a dedicated data abstraction form that we pilot tested ahead of time.
For studies that fulfilled inclusion criteria, two review authors (JHJ, BR or RG) independently abstracted the following information, which we provide in the Characteristics of included studies table. For all eligible studies we abstracted the following information:
Study design;
Study dates (we reported if dates were not available);
Study settings and country;
Participant inclusion and exclusion criteria;
Participant details, baseline demographics;
Number of participants by study and by study arm;
Details of relevant experimental and comparator interventions;
Definitions of relevant outcomes, and methods and timings of outcome measurements, as well as any relevant subgroups;
Sources of study funding;
Declarations of interest by primary investigators.
We extracted outcome data relevant to this review for calculation of summary statistics and measurement of variance. For dichotomous outcomes, we obtained numbers of events and totals for population of a 2 x 2 table, as well as summary statistics with corresponding measures of variance. For continuous outcomes, we obtained means and standard deviations, or the data necessary to calculate this information. For time‐to‐event outcomes, we obtained hazard ratios (HRs) with corresponding measures of variance, or the data necessary to calculate this information.
We resolved the few, minor disagreement by discussion, or, if required, by consultation with a third review author (PD).
We provided information, including trial identifier, about potentially relevant ongoing studies in the table Characteristics of ongoing studies.
We contacted authors of included studies to obtain key missing data as needed.
Dealing with duplicate and companion publications
In the event of duplicate publications, companion documents or multiple reports of a primary study, we maximised yield of information by mapping all publications to unique studies and collating all available data, and used the most complete data‐set aggregated across all known publications. Where there was doubt, we gave priority to the publication reporting the longest follow‐up associated with our primary or secondary outcomes.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors (JHJ, BR) assessed the risk of bias of each included study independently. We resolved disagreements by consensus, or by consultation with a third review author (PD).
We assessed risk of bias using the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool (Higgins 2011b). We assessed the following domains:
Random sequence generation (selection bias);
Allocation concealment (selection bias);
Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias);
Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias);
Incomplete outcome data (omission bias)
Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias);
Selective reporting (reporting bias);
Other sources of bias.
We judged risk of bias domains as being at 'low risk', 'high risk' or 'unclear risk', and evaluated individual bias items as described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011b).
For selection bias (random sequence generation and allocation concealment), we evaluated risk of bias at a trial level.
For performance bias (blinding of participants and personnel), we considered all outcomes similarly susceptible to performance bias therefore underscoring the importance of blinding participants and personnel.
For detection bias (blinding of outcome assessment), we grouped outcomes as susceptible to detection bias (subjective outcomes) or not susceptible to detection bias (objective outcomes).
We defined the following endpoints as subjective outcomes:
Time to death from prostate cancer;
QoL;
Major adverse events;
Time to biochemical failure;
Minor adverse events.
We defined the following endpoints as objective outcomes:
Time to death from any cause;
Secondary interventions for treatment failure.
We also assessed attrition bias (incomplete outcome data) on an outcome‐specific basis, but sought to create groups of outcomes based on similar reporting characteristics.
For reporting bias (selective reporting), we evaluated risk of bias at a trial level.
We further summarised the risk of bias across domains for each outcome in each included study, as well as across studies and domains for each outcome, in accordance with the approach for summary assessments of the risk of bias presented in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011b).
Measures of treatment effect
We expressed dichotomous data as risk ratios (RRs < 1: favoring intervention arm) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). We expressed continuous data as mean differences (MD > 0: favoring intervention arm) with 95% CI. We expressed time‐to‐event data as HRs (HR < 1: favoring intervention arm) with 95% CI.
Unit of analysis issues
The unit of analysis was the individual participant. If we had identified cross‐over trials, cluster‐randomised trials, or trials with more than two intervention groups for inclusion in the review, we would have handled these in accordance with guidance provided in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011c).
Dealing with missing data
We sought to obtain missing data from the investigators and performed intention‐to‐treat analyses if data were available; otherwise, we performed available case analyses. We investigated attrition rates, e.g. dropouts, losses to follow‐up and withdrawals, and appraised instances where data were missing critically. We did not impute missing data.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We identified heterogeneity (inconsistency) through visual inspection of the forest plots to assess the amount of overlap of CIs, and the I2 statistic, which quantifies inconsistency across studies and permits assessment of the impact of heterogeneity on the meta‐analysis (Higgins 2002; Higgins 2003). We interpreted I2 as follows (Deeks 2011):
0% to 40%: may not be important;
30% to 60%: may indicate moderate heterogeneity;
50% to 90%: may indicate substantial heterogeneity;
75% to 100%: indicates considerable heterogeneity.
When we identified heterogeneity, we determined possible reasons for it by examining individual study and subgroup characteristics.
Assessment of reporting biases
We attempted to obtain study protocols to assess for selective outcome reporting. We did not perform funnel plots to assess small study effects due to paucity of included studies.
Data synthesis
We summarised data using a random‐effects model and interpreted these with due consideration of the whole distribution of effects. In addition, we performed meta analyses according to the statistical guidelines contained in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011a). For dichotomous outcomes, we used the Mantel‐Haenszel method; for continuous outcomes, we used the inverse variance method; and for time‐to‐event outcomes, we used the generic inverse variance method. We used Review Manager 5 software to perform statistical analyses (Review Manager 2014).
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
We expected the following characteristics to introduce clinical heterogeneity, and planned to carry out a subgroup analysis with investigation of interactions limited to the primary outcomes.
-
D'Amico risk classification:
low versus intermediate versus high
We planned these subgroup analyses because a higher local tumour stage prompts a different surgical approach (D’Amico 2008; EAU 2017) and cryotherapy may have different effectiveness based on this risk classification.
Sensitivity analysis
We planned to perform a sensitivity analysis limited to the primary outcomes in order to explore the influence on the estimated effect size of restricting the analysis by taking risk of bias into account (when applicable).
'Summary of findings' table
We presented the overall QoE for each outcome according to the GRADE approach, which takes into account five criteria that relate to internal validity (risk of bias, inconsistency, imprecision, publication bias) and also to external validity such as directness of results (Guyatt 2008). For each comparison, two review authors (JHJ, BR) independently rated the QoE for each outcome as 'high', 'moderate', 'low', or 'very low' using GRADEproGDT; we resolved discrepancies by consensus, or, if necessary, by arbitration of a third review author (PD). For each comparison, we presented a summary of the evidence for the main outcomes in a 'Summary of findings' table, which provides key information about the best estimate of the magnitude of the effect, in relative terms and absolute differences for each relevant comparison of alternative management strategies; numbers of participants and studies addressing each important outcome; and the rating of the overall confidence in effect estimates for each outcome (Guyatt 2011b; Schünemann 2011).
We included the following outcomes in our SoF table according to priority (Table 1).
Time to death from prostate cancer
QoL
Major adverse event
Time to death from any cause
Secondary interventions for treatment failure
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
We identified 1111 records through an electronic database search. We did not find additional records through handsearching other sources. After removal of 366 duplicates, we screened the titles and abstracts of 745 records, and excluded 724 records. We screened 21 full‐text articles, and excluded 10 studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria or were not relevant to the question under trial. We included a total of two studies (11 records) in the review. We did not identify studies awaiting classification and ongoing trials. The flow of literature through the assessment process is shown in the PRISMA flowchart (Figure 1).
Included studies
Details of included studies are presented in the Characteristics of included studies, Table 2, and Table 3.
1. Baseline characteristics of included studies.
| Study name | Trial period | Setting/ country | Participants | Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Age (median, years) | No of men with clinical tumour stage (T2a; 2b; 2c; 3a; 3b) | Biopsy Gleason score (<7; 7; >7) | PSA (median, ng/mL) | Median follow‐up (months) |
| Chin 2008 | 1999 to 2002 | Single institution in Canada | Histologically proven prostate cancer, clinically staged as T2c, T3a or T3b with no evidence of lymph node or distant metastasis and serum PSA < 25 ng/mL | Whole gland cryotherapy | 70.4 | ‐; ‐; 12; 17; 2 | 2; 24; 5 | 11.1 | 105 |
| EBRT | 70.5 | ‐; ‐; 8; 15; 8 | 1; 24; 6 | 8.6 | |||||
| Donnelly 2010 | 1997 to 2003 | Single institution in Canada | Histologically proven adenocarcinoma of the prostate, a biopsy tumour classification of T2 or T3, no evidence of lymph node or distant metastases, a pretreatment PSA level < 20 ng/mL, and a gland volume < 60 cm3 | Whole gland cryotherapy | 69.4 | 22; 28; 49; 17; 6 | 42; 69; 11 | 8.1 | 100 |
| EBRT | 68.6 | 20; 23; 57; 18; 4 | 44; 65; 13 | 9.0 |
EBRT: external beam radiotherapy; PSA: prostate specific antigen
2. Participants randomized and analyzed in included studies.
| Study name | Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Screened/ eligible | Randomised | Treatment completed | Treatment analysed |
| Chin 2008 | Whole gland cryotherapy | NR/140 | 32 | NR | 31 (96.8%) |
| EBRT | 31 | 31 (100.0%) | |||
| Total | 63 | NR | 62 (98.4%) | ||
| Donnelly 2010 | Whole gland cryotherapy | NR/764 | 122 | NR | 117 (95.9%) |
| EBRT | 122 | 114 (93.4%) | |||
| Total | 244 | NR | 231 (94.6%) | ||
| Grand total | 307 | NR | 293 (95.4%) | ||
EBRT: external beam radiotherapy; NR: not reported
Source of data
We identified two published full text studies through our electronic database search (Chin 2008; Donnelly 2010). Both trials were published in English. We attempted to contact both corresponding authors of included trials to obtain additional information on study methodology and results but did not obtain any meaningful additional results that were not found in the published reports (Appendix 2).
Study design and settings
Both trials were parallel randomised controlled trials that compared whole gland cryotherapy to EBRT. One study was reported as 'open label' in the protocol (Donnelly 2010), but the other included no information regarding blinding (Chin 2008). Both studies were conducted at single institutions in Canada. The studies were performed between 1997 and 2003.
Participants
We included 307 randomised participants (cryotherapy 154, EBRT 153), of whom 293 were included in the analyses of the intervention and control groups (cryotherapy 148, EBRT 145). The median age of the included studies was around 70 years. Median prostate volume was 35.6 mL in Chin 2008 while Donnelly 2010 did not specify the prostate volume. The median PSA ranged from 8 to 10 ng/mL (Chin 2008: 9.9, Donnelly 2010: 8.1 to 9.0).
The trials included men with histologically proven localised or locally advanced prostate cancer, clinically staged as T2 or T3 (using the American Joint Committee on Cancer nomenclature, with no evidence of lymph node or distant metastases, and a serum PSA less than 25 ng/ml (Chin 2008; Donnelly 2010). Chin 2008 included more men with T3 disease (42/62 (67.7%)) compared to Donnelly 2010 (45/244 (18.4%)) (Table 2).The most common biopsy Gleason score was 7. Major exclusion criteria included a history of prior pelvic radiotherapy or hormone therapy, node‐positive disease or distant metastases, or both. Chin 2008 excluded men with an enlarged prostate that exceeded 75 mL or American Society of Anesthesiology Risk Class > 3. Donnelly 2010 excluded men who had undergone transurethral resection of the prostate within three months of screening.
Intervention(s) and comparator(s)
Both included trials used third‐generation cryotherapy. Cryotherapy was performed under general or spinal anaesthesia. It was administered using transrectal ultrasound guidance, a urethral warming device, thermosensor monitoring, and two freeze‐thaw cycles. A suprapubic catheter was placed in all participants and removed around two or three weeks postoperatively. A repeat cryotherapy procedure was offered to men who had a subsequent positive biopsy (Chin 2008), or early PSA failure (Donnelly 2010), at three or six months.
EBRT was administered using a 4‐field box technique with a prescribed dose of 66 Gy (Chin 2008), or 68 Gy (Donnelly 2010), received as 2 Gy daily, five days per week (Chin 2008: 6.5 weeks, Donnelly 2010: from 6.8 to 7.4 weeks). In one study the total dose was increased to 70 Gy in 2000 and to 73.5 Gy in 2002 (Donnelly 2010). The target included the prostate gland and seminal vesicles.
All participants received androgen deprivation therapy with luteinising hormone‐releasing hormone for six months. Cryotherapy or EBRT was performed 90 to 210 days after the first injection in Chin 2008, and 180 to 210 days after the first injection in Donnelly 2010, However, only three months of hormonal therapy was administered before local treatment in the early stage of Donnelly 2010. In 2001, the investigators amended the protocol to include six months of hormonal treatment (Donnelly 2010).
The median follow‐up of the included studies was 105 months in Chin 2008, and 100 months in Donnelly 2010.
Comparisons
Both studies compared whole gland cryotherapy to EBRT; we identified none that compared whole gland cryotherapy to no intervention, active surveillance, brachytherapy, or RP. We did not find any randomised controlled trials that used focal cryotherapy.
Outcomes
Chin 2008 reported oncologic outcomes, namely time to death from prostate cancer, any cause, and biochemical failure at four years and eight years for each intervention. Donnelly 2010 reported time to death from prostate cancer and any cause at five years. Time to biochemical failure was stated at 36, 60, and 84 months post‐randomisation. Both studies only described the Kaplan Meier survival curves for the time to biochemical failure. All trials reported biochemical failure using both the ASTRO definition of three consecutive increases in serum PSA following nadir (ASTRO Consensus Panel 1997), and Phoenix criteria (second Radiation Treatment Oncology Group ‐ ASTRO Consensus Conference) of serum PSA reaching 2 ng/mL above the nadir (Roach 2006).
QoL was assessed with the UCLA‐PCI and EORTC QLQ C‐30, and was reported at three and 36 months post‐randomisation in one study (Donnelly 2010). Given that EORTC QLQ C‐30 was reported only in a figure, we used UCLA‐PCI data only for the meta‐analysis in this review. The UCLA‐PCI was developed to evaluate the QoL of men treated for early‐stage prostate cancer. It consists of 20 items related to urinary function (5 items), urinary bother (1 item), sexual function (8 items), sexual bother (1 item), bowel function (4 items), and bowel bother (1 item) which are scored by 3‐ to 6‐point Likert scales (low score is worse, high score is better) (Litwin 1998).
Both studies reported adverse events. Donnelly 2010 categorised adverse events according to the codes of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Common Toxicity Criteria (National Cancer Institute; version 2.0). However, we were not able to extract the data for minor adverse events due to a unit of analysis error.
Neither of the studies reported on secondary interventions for treatment failure.
Funding sources and conflicts of interests
Chin 2008 and Donnelly 2010 were supported by research grants from Astra‐Zeneca and the National Cancer Institute of Canada and the Alberta Cancer Board, respectively. The first author in Chin 2008 and one of the co‐authors in Donnelly 2010 disclosed relevant conflicts of interest.
Excluded studies
There were a total of 10 studies that we reviewed fully and excluded because they were the wrong study design; eight were single‐armed studies and two were non‐RCTs (Aus 2002; Bahn 2002; Cohen 1996; Coogan 1995; Donnelly 2002a; Gould 1999; Liu 2016; Long 1998; Prepelica 2005; Wong 1997). Details of the excluded studies are presented in Characteristics of excluded studies.
Risk of bias in included studies
Summaries of 'Risk of bias' judgements for the included studies are presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3).
2.
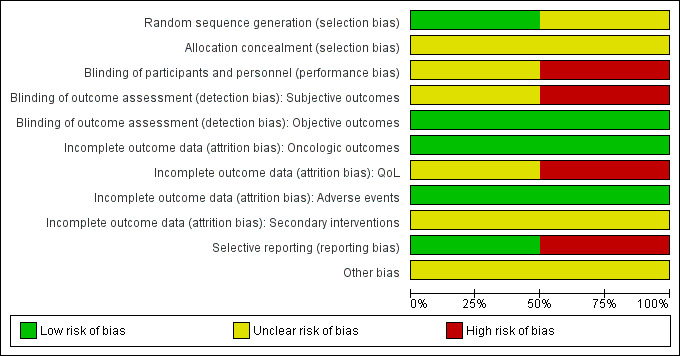
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
3.
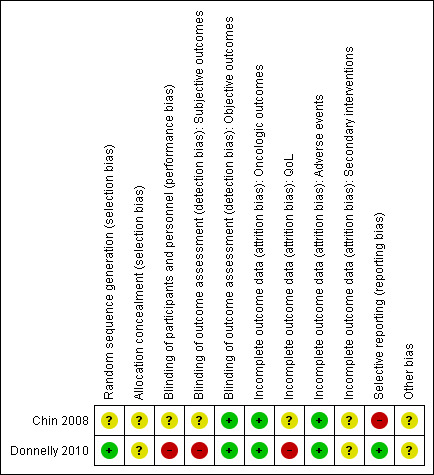
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
Allocation
Random sequence generation
We rated Donnelly 2010 as having low risk of bias as describing an appropriate method of sequence generation, but Chin 2008 as having unclear risk of bias due to a lack of information about random sequence generation.
Allocation concealment
We rated both studies as being at unclear risk of bias due to a lack of information about implementation of allocation.
Blinding
Blinding of participants and personnel
We rated Chin 2008 as being at unclear risk of bias due to lack of information as to whether participants and personnel were masked. We judged Donnelly 2010 as being at high risk of bias due to its open label study design.
Blinding of outcome assessment
For the subjective outcomes (i.e. time to death from prostate cancer, QoL, major adverse events, time to biochemical failure, and minor adverse events), we rated Chin 2008 as being at unclear risk of bias due to lack of information as to whether outcome assessors were masked and Donnelly 2010 as being at high risk of bias due to its open label study design.
For objective outcomes (i.e. time to death from any cause and secondary interventions for treatment failure), we rated both studies as being at a low risk of bias as these objective outcomes were unlikely to be affected by lack of blinding.
Incomplete outcome data
For time to death from prostate cancer, any cause, and biochemical failure, we rated both studies as being at low risk of bias.
For QoL, we rated Chin 2008 as having an unclear risk of bias due to attrition rates between 10% and 19% for at least one treatment arm, and Donnelly 2010 as having a high risk of bias due to attrition rates of 20% or greater for at least one trial arm.
For adverse events, we rated both studies as being at low risk of bias due to attrition rates of less than 10%.
For secondary interventions for treatment failure, we judged both studies as being at unclear risk of bias as the outcome was not measured.
Selective reporting
We judged Donnelly 2010 as having a low risk of bias given that the reported analyses and outcomes corresponded to the description in the study protocol. As Chin 2008 did not report our prespecified secondary outcome (treatment failure), we rated this trial as having a high risk of bias in this domain.
Other potential sources of bias
We rated both studies as being at unclear risk of bias due to imbalances of important baseline characteristics or violation of inclusion criteria.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1
A summary of our results is provided in Table 1.
Whole gland cryotherapy versus EBRT
We included data from two studies for the outcomes of time to death from prostate cancer, major adverse events, time to death from any cause, and time to biochemical failure (293 men; cryotherapy 148, EBRT 145). For QoL, we included only one study with 194 men (cryotherapy 106, EBRT 88) at 3 months follow‐up and 195 men (cryotherapy 98, EBRT 97) at 36 months follow‐up (Donnelly 2010) .
Time to death from prostate cancer
We are uncertain about the effect of whole gland cryotherapy on time to death from prostate cancer (HR 1.00, 95% CI 0.11 to 9.45; Analysis 1.1). This corresponds to zero fewer death (85 fewer to 520 more) from prostate cancer per 1000 men. We rated the QoE as very low, downgrading for study limitations, indirectness, and very serious imprecision.
1.1. Analysis.
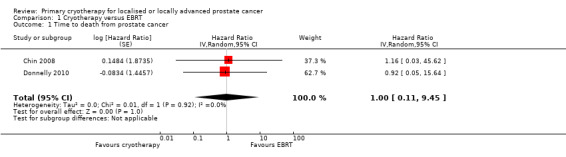
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 1 Time to death from prostate cancer.
QoL
At 3 months follow‐up
We are uncertain about the effects of whole gland cryotherapy on urinary (MD −21.30, 95% CI −37.35 to −5.25), bowel (MD 2.30, 95% CI −2.67 to 7.27), and sexual function (MD −25.70, 95% CI −45.06 to −6.34) (Analysis 1.2). We rated the QoE as very low, downgrading for study limitations, indirectness, and imprecision.
1.2. Analysis.
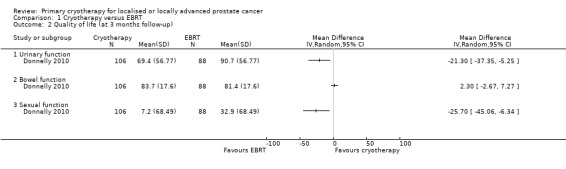
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 2 Quality of life (at 3 months follow‐up).
At 36 months follow‐up
We are uncertain about the effects of whole gland cryotherapy on urinary (MD 4.40, 95% CI −6.50 to 15.30), bowel (MD 4.00, 95% CI −73.96 to 81.96), and sexual function (MD −20.70, 95% CI −36.29 to −5.11) (Analysis 1.3). We rated the QoE as very low, downgrading for study limitations, indirectness, and imprecision.
1.3. Analysis.
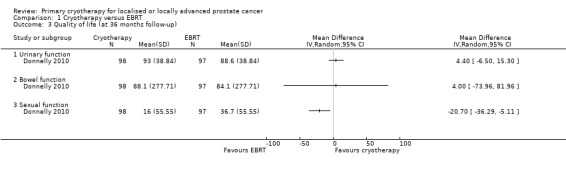
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 3 Quality of life (at 36 months follow‐up).
Major adverse events
We are uncertain about the effect of whole gland cryotherapy on major adverse events (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.47 to 1.78; Analysis 1.4). This corresponds to 10 fewer major adverse events (58 fewer to 86 more) per 1000 men. We rated the QoE as very low, downgrading for study limitations, indirectness, and imprecision.
1.4. Analysis.
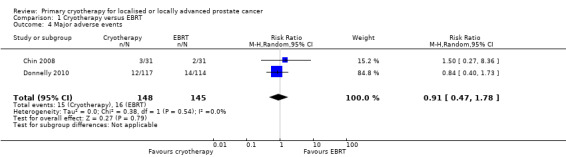
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 4 Major adverse events.
Time to death from any cause
We are uncertain about the effect of whole gland cryotherapy on time to death from any cause (HR 0.99, 95% CI 0.05 to 18.79; Analysis 1.5). This corresponds to 2 fewer deaths from any cause (157 fewer to 801 more) per 1000 men. We rated the QoE as very low, downgrading for study limitations, indirectness, and imprecision.
1.5. Analysis.
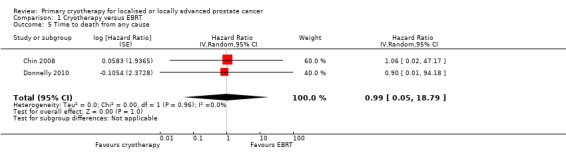
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 5 Time to death from any cause.
Secondary interventions for treatment failure
We did not find data related to secondary interventions for treatment failure.
Time to biochemical failure
We used Phoenix criteria to define time to biochemical failure in the meta‐analyses. We are uncertain about the effect of whole gland cryotherapy on time to biochemical failure (HR 2.15, 95% CI 0.07 to 62.12; Analysis 1.6). This corresponds to 237 more biochemical failures (278 fewer to 697 more) per 1000 participants. We rated the QoE as very low, downgrading for study limitations, indirectness, and very serious imprecision.
1.6. Analysis.
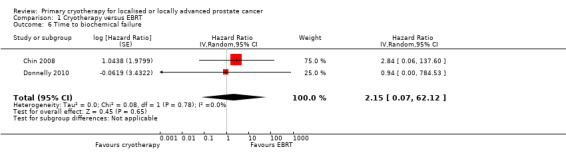
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 6 Time to biochemical failure.
Minor adverse events
We did not find data related to adverse events categorised as minor.
Subgroup and sensitivity analysis
We were not able to perform our predefined subgroup or sensitivity analyses due to an absence of available data, and the low number of included studies, respectively.
Discussion
Summary of main results
We included two studies, with a total of 307 randomised men, that compared whole gland cryotherapy to EBRT. The male participants were clinically staged as T2 and T3, did not have locoregional or distant metastases and had a PSA of up to 25 ng/mL.
Based on the available evidence, we are uncertain of the effects of whole gland cryotherapy compared to EBRT on both the primary outcomes (i.e. time to death from prostate cancer, QoL and major adverse events) and secondary outcomes of this review. The quality of evidence for all outcomes was very low. We found no data for rates of re‐treatment or minor adverse events.
We were unable to perform any of our predefined secondary analyses.
We found no eligible trials that compared whole gland or focal gland cryotherapy to alternative treatments such as surgery, active surveillance, or watchful waiting.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
While we believe that the two included trials represent the only two existing trials of primary cryotherapy for localised or locally advanced prostate cancer, this body of evidence has important limitations with regard to applicability to contemporary practice.
Both trials represent single institution experiences from Canada, which may not be representative of the type of patients and clinical practice in other parts of the world. Multi‐institutional trials from other countries would have been informative.
The trials included men with clinical T3 disease who are at high risk of local and distant failure and would currently have been categorised as high risk. In addition, there was an imbalance in the proportions of participants with T3 disease between the included studies (Chin 2008: 67.7%; Donnelly 2010: 18.4%). We were unable to analyse the outcomes of low‐ and intermediate‐risk men separately, which would have been desirable.
The two trials reported additional outcomes such prostate volume and disease progression. Both were not considered as directly patient important as those we had planned to include in this update and therefore omitted.
Both trials consistently used neoadjuvant or adjuvant hormone therapy plus interventions (both cryotherapy and radiotherapy) for the participants with intermediate risk as well as high risk. Although recent guidelines recommend the use of androgen deprivation therapy with radiotherapy as a standard treatment option for men with intermediate‐risk localised prostate cancer (AUA 2017), it remains controversial whether these results should be applied to men with intermediate risk localised prostate cancer (EAU 2017). Meanwhile, the value of concomitant hormone therapy is less clear in men undergoing cryotherapy (AUA 2017).
Although both trials used the most recent generation cryotherapy (third‐generation), they were performed between 1997 and 2003 when the third‐generation was first introduced. Therefore, their results may not reflect the contemporary status of prostate cryoablation accurately.
Although there has been a recent shift of interest from whole gland to focal cryotherapy, we failed to identify any eligible trials.
Quality of the evidence
We consistently downgraded the quality of evidence to very low for all outcomes. Issues that lowered our confidence in the estimates of effect included study limitations, specifically selection bias (unclear allocation), performance and detection bias (the lack of blinding), and other bias (baseline imbalance, violation of inclusion criteria, early stopping of the trial). We also downgraded for indirectness and imprecision due to difference in intervention (prescribed dose of radiotherapy and duration of androgen deprivation therapy) and wide confidence intervals, respectively.
Potential biases in the review process
Although we searched multiple databases and other sources with a comprehensive search strategy identical to the Cochrane standard, we found only two RCTs. The small number of studies included in this review were insufficient to generate funnel plots; therefore, the risk of publication bias may have been underestimated. Since the included studies did not report HR or the number of surviving participants in their oncologic outcomes, we calculated HRs for the time to death from prostate cancer and any cause based on percent of survival at the specific time point (Chin 2008: 8 years, Donnelly 2010: 5 years) after intervention using the method published in Parmar 1998. In addition, we estimated HRs for the biochemical disease‐free survival based on the Kaplan Meier curve from each study (Parmar 1998). We also calculated standard deviations from MDs and P values in the included studies with regards to QoL (Higgins 2011d). While we received additional information from both study authors, we received no suitable data to perform additional meta‐analyses (Appendix 2). This may represent a source of bias.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
A recent systematic review and meta‐analysis revealed no significant differences in comparisons of whole gland cryotherapy versus radiotherapy and whole gland cryotherapy versus RP for time to death from prostate cancer and any cause (Gao 2016). A network meta‐analysis published in 2014 showed that whole gland cryotherapy also did not improve survival compared to observational management, RP, conventional radiotherapy, and conformal radiotherapy (Xiong 2014). While Gao 2016 revealed no significant difference between whole gland cryotherapy and radiotherapy in urinary and sexual bother at 12 months or longer, Xiong 2014 reported that whole gland cryotherapy resulted in fewer adverse gastrointestinal events than radiotherapy. There was no evidence that whole gland cryotherapy has less adverse effects than other treatment forms.
In this review, whole gland cryotherapy was associated with similar oncologic outcomes to EBRT, which is consistent with the findings from other recent reviews. While Gao 2016 reported no differences in QoL using non RCTs, we found that whole gland cryotherapy was inferior to EBRT in terms of sexual QOL at 36 months follow‐up. We found no difference in major adverse events between whole gland cryotherapy and EBRT. However, we are uncertain of the effects of whole gland cryotherapy on all review outcomes based on GRADE approach.
While there is an increasing number of prospective registered trials for focal gland cryotherapy, most studies are retrospective cohort studies with variable standards of reporting (Tay 2016; Valerio 2014). We also found no eligible randomised controlled trials comparing focal gland cryotherapy to other treatments.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
When this cryotherapy review was published in 2007 (Shelley 2007), the authors could identify no clinical trials to inform the comparative effectiveness of cryotherapy. In this update, we found two trials that investigated the comparison of primary whole gland cryotherapy to EBRT but we rated the QoE, consistently, as very low. We found no trials for other whole gland treatment comparisons and no eligible trials investigating focal therapy.
Patients, healthcare providers and healthcare policymakers considering the use of primary cryotherapy should recognise that our understanding of its oncological outcomes, QoL outcomes, and risk of major adverse events compared to radiotherapy is based on very low quality evidence. While we found few differences in outcomes between cryotherapy and EBRT except for decreased sexual function related QoL, we are very uncertain of these findings. It should be noted that the body of evidence informing the comparative effectiveness of radiation therapy (for example compared to radical surgery) as well as prognostic information on expected outcomes is considerably larger than it is for cryotherapy, which should find consideration in treatment decisions.
There are to date no trials comparing primary cryotherapy to other interventions such as surgery nor are there trials of focal cryotherapy.
Implications for research.
There is a critical need for higher quality studies to assess the comparative effectiveness of whole gland and focal cryotherapy. The existing paucity of randomised controlled trials is in part explained by the lower evidentiary standards for the approval of device‐related procedures versus drugs. The IDEAL Collaboration has previously developed a framework for surgical innovation that includes devices (McCulloch 2009). The inherent challenges of trials in surgery and prostate cancer notwithstanding, there is a critical need to assess cryotherapy (and other innovative treatment approaches to clinically localised prostate cancer in a rigorous manner. Critical aspects include a head‐to‐head comparison with the most applicable standard of care, which may include active surveillance, watchful waiting and brachytherapy, a focus on patient‐important outcomes and sufficiently long follow‐up. These trials should be multi‐institutional, both to enhance generalisability and improve accrual. The recent ProTecT trial has provided has shown how involving an impartial research nurse can improve prostate cancer patients' willingness to participate in a randomized trial (Hamdy 2016). Also, the reporting of a single‐armed trial of focal therapy with transrectal high intensity ultrasound as a prospective development study according to IDEAL provides hope that higher quality trials may be conducted in the future (Dickinson 2013; Ganzer 2017).
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 25 May 2018 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | This updated review now includes two randomized controlled trials. Its title was changed to reflect its focus on primary treatment. It was furthermore thoroughly revised to reflect current methodological standards that include a focus on patient‐important outcomes and the use of GRADE. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 4, 2004 Review first published: Issue 3, 2007
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 January 2012 | Amended | Added grant information |
| 24 April 2008 | Amended | Converted to new review format |
| 1 March 2007 | Amended | Substantive Amendment |
Notes
We have based parts of the Methods section of this protocol on a standard template developed by the Cochrane Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders Group, which has been modified and adapted for use by Cochrane Urology.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Francisco Donis, Julio Pow‐Sang, and Timothy McClure for having served as peer reviewers. We would like to thank Cochrane Urology and our editors Mari Imamura and Alea Miller for supporting this review.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Search strategies
| Cochrane Library (Wiley) |
| #1 MeSH descriptor: [Prostatic Neoplasms] explode all trees #2 MeSH descriptor: [Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia] explode all trees #3 (prostat*):ti,ab,kw near/3 (cancer* or carcinoma* or malignan* or tumor* or tumour* or neoplas* or intraepithelial or adeno*):ti,ab,kw #4 (#1 or #2 or #3) #5 MeSH descriptor: [Cryotherapy] explode all trees #6 MeSH descriptor: [Cryosurgery] explode all trees #7 MeSH descriptor: [Hypothermia, Induced] explode all trees #8 (cryo* or hypotherm* or freez*):ti,ab,kw near/3 (prostat*):ti,ab,kw (cryo* or hypotherm* or freez*):ti,ab,kw near/3 (prostat*):ti,ab,kw #9 (#5 or #6 or #7 or #8) #10 (#4 and #9) |
| MEDLINE (Ovid) |
| 1 Cryotherapy/ 2 Cryosurgery/ 3 Hypothermia, Induced/ 4 ((cryo* or hypotherm* or freez*) adj3 prostat*).tw. 5 cryoablat*.tw. 6 or/1‐5 7 exp Prostatic Neoplasms/ 8 prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia/ 9 (prostat* adj3 (cancer* or carcinoma* or malignan* or tumo?r* or neoplas* or intraepithelial or adeno*)).tw. 10 or/7‐9 11 6 and 10 12 randomized controlled trial.pt. 13 controlled clinical trial.pt. 14 randomized.ab. 15 placebo.ab. 16 drug therapy.fs. 17 randomly.ab. 18 trial.ab. 19 groups.ab. 20 or/12‐19 21 exp animals/ not humans.sh. 22 20 not 21 23 11 and 22 24 limit 23 to yr="2006 ‐Current" |
| EMBASE (Ovid) |
| 1. exp prostate cancer/ 2. exp prostate carcinoma/ 3. exp prostate adenocarcinoma/ 4. exp Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia/ 5. exp prostate tumor/ 6. exp prostate adenoma/ 7. (prostat* adj3 (cancer* or carcinoma* or neoplas* or tumo?r* or malignan*)).tw. 8. or/1‐7 9. cryotherapy/ 10. cryosurgery/ 11. induced hypothermia/ 12. ((cryo* or hypotherm* or freez*) adj3 prostat*).tw. 13. cryoablat*.tw. 14. cryoablation/ 15. or/9‐14 16. Crossover Procedure/ 17. double‐blind procedure/ 18. randomized controlled trial/ 19. single‐blind procedure/ 20. (random* or factorial* or crossover* or cross over* or placebo* or assign* or allocat* or volunteer*).mp. 21. ((doubl* or singl*) adj blind*).mp. 22. or/16‐21 23. 8 and 15 and 22 24. limit 23 to yr="2006 ‐Current" |
| ISI Web of Science (Thompson Reuters) |
| # 1 TS= clinical trial* OR TS=research design OR TS=comparative stud* OR TS=evaluation stud* OR TS=controlled trial* OR TS=follow‐up stud* OR TS=prospective stud* OR TS=random* OR TS=placebo* OR TS=(single blind*) OR TS=(double blind*) # 2 TS=(cryo* or hypotherm* or freez*) # 3 TS=(prostat* SAME (cancer* or carcinoma* or tumor* or tumour* or neoplas* or malignan*)) # 4 #3 AND #2 AND #1 |
| LILACS |
| (mh:(prostatic neoplasms)) OR (mh:(prostatic neoplasms, castration resistant)) OR (tw:(prostat*)) AND (mh:(cryotherapy)) OR (mh:(hypothermia, induced)) OR (tw:(cryo* or hypotherm* or freez* crioterapia or criocirugia or hipotermia or congel*)) |
| Scopus |
| TITLE‐ABS‐KEY(cryo* or hypotherm* or freez*) AND TITLE‐ABS‐KEY (prostat*) AND TITLE‐ABS‐KEY (cancer* OR carcinoma* OR tumor* OR tumour* OR neoplas* OR malignan*) AND TITLE‐ABS‐KEY (rct OR random*) |
| PUBMED |
| #1 ((prostatic neoplasms[MeSH Terms] OR prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia[MeSH Terms])) #2 ((prostat*) AND (cancer* OR carcinoma* OR malignan* OR tumor* OR tumour* OR neoplas* OR intraepithelial OR adeno*)) #3 (#1 or #2) #4 ((cryotherapy[MeSH Terms] OR cryosurgery[MeSH Terms] OR hypothermia, induced[MeSH Terms] OR cryo* OR hypotherm* OR freez*) #5 ((randomized controlled trial[pt] OR controlled clinical trial[pt] OR randomized[tiab] OR placebo[tiab] OR clinical trials[MeSH Terms] OR randomly[tiab] OR trial[ti])) #6 (#3 and #4 and #5) #7 MEDLINE[sb] #8 (#6 NOT #7) |
| OpenGrey |
| ‘Cryotherapy’ ‐ records scanned for relevance. |
| WHO ICTRP |
| 1. Prostate and cryotherapy 2. Prostate and cryosurgery 3. Prostate and cryoablation |
| Clinicaltrials.gov |
| 1. Prostate and cryotherapy 2. Prostate and cryosurgery 3. Prostate and cryoablation |
Appendix 2. Survey of trial investigators providing information on included trials
| Study | Date trial author contacted (first) | Date trial author provided data (latest) |
Data trial author provided (short summary) |
| Chin 2008 | 16 July 2015 | 17 August 2017 | Method: randomization sequence/ Data: the number of participants who died due to any cause and underwent repeated cryotherapy within 6 months after initial cryotherapy. |
| Donnelly 2010 | 16 July 2015 | 17 August 2017 | Available data were not provided. |
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Cryotherapy versus EBRT.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Time to death from prostate cancer | 2 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.11, 9.45] | |
| 2 Quality of life (at 3 months follow‐up) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 Urinary function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 Bowel function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.3 Sexual function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Quality of life (at 36 months follow‐up) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 Urinary function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 Bowel function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.3 Sexual function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Major adverse events | 2 | 293 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.47, 1.78] |
| 5 Time to death from any cause | 2 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.05, 18.79] | |
| 6 Time to biochemical failure | 2 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 2.15 [0.07, 62.12] |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Chin 2008.
| Methods |
Study design: parallel randomised controlled trial Study conducted: 1999 to 2002 Setting: single institution Geographic location: Canada |
|
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: men with histologically proven prostate cancer, clinically staged as T2c, T3a or T3b based on digital rectal examination or transrectal ultrasound findings, or both, negative computerised tomography of the abdomen and pelvis, negative bone scan and serum PSA < 25 ng/mL Exclusion criteria: men with node‐positive disease and distant metastases, prior pelvic radiotherapy or hormone therapy, prostate volume > 75 mL or American Society of Anesthesiology Risk Class > 3 Total number randomly assigned: 63 Group A (whole gland cryotherapy)
Group B (EBRT)
|
|
| Interventions |
Group A (whole gland cryotherapy): Cryocare System (Endocare Inc, Irvine, CA, USA) was used under general or spinal anaesthesia using transrectal ultrasound‐guided probe placement. In most cases, 5 cryoprobes (range 2–8) were used and 2 freeze–thaw cycles were administered with the urethra protected by a urethra‐warming device (Cook Urologic Inc, Spencer, IN, USA). 3 thermocouple probes at the respective neurovascular bundles and in the midline apex were placed for monitoring purposes and to ensure that the required temperature of < −40 °C was reached. A trocar suprapubic catheter was inserted intraoperatively and kept open for 3 weeks. Group B (EBRT): 66 Gy in 33 fractions, administered at 2 Gy per day, 5 days a week for 6.5 weeks, directed at the prostate, seminal vesicles, and peri‐prostatic region. Co‐interventions: 6 months of hormonal therapy with LHRH agonists (goserelin) was administered starting 3 months before the date of cryosurgery or start of the radiotherapy sessions Follow‐up period (median): 105 months |
|
| Outcomes |
Primary outcomes: overall survival or disease specific survival
Secondary outcomes: biochemical disease‐free survival or clinical progression
Adverse events
|
|
| Funding sources | Research grant from Astra‐Zeneca, Canada | |
| Declarations of interest | Primary author: financial interest or relationship with US HIFU, or both | |
| Notes |
Publication status: full text publication Language of publication: English |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comments: not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comments: not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Comments: not described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Comments: not described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | Comments: objective outcomes were probably not affected by lack of blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Oncologic outcomes | Low risk | Comments: 31/32 (96.8%) and 31/31 (100.0%) men randomised to cryotherapy and EBRT were included in analysis |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) QoL | Unclear risk | Comments: the outcome was not measured. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Adverse events | Low risk | Comments: 31/32 (96.8%) and 31/31 (100.0%) of men randomised to cryotherapy and EBRT were included in analysis |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Secondary interventions | Unclear risk | Comments: the outcome was not measured. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comments: protocol was not published and treatment failure (secondary outcome of study) data were not reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comments: only 64 out of the planned 150 participants who planned to be randomised were accrued. Lower average prostate volumes likely favor the cryotherapy group. |
Donnelly 2010.
| Methods |
Study design: parallel randomised controlled trial Study conducted: December 1997 to February 2003 Setting: single institution Geographic location: Canada |
|
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: men with histologically proven adenocarcinoma of the prostate, a biopsy tumour classification of T2 or T3, no evidence of lymph node or distant metastases, a pretreatment PSA level < 20 ng/mL, and a gland volume < 60 cm3 Exclusion criteria: men were ineligible if they had: clinically bulky T3 tumour; received prior pelvic radiation; received previous androgen‐deprivation therapy (ADT) at any time; or had undergone transurethral resection of prostate within the previous 3 months Total number randomly assigned: 244 Group A (whole gland cryotherapy)
Group B (EBRT)
|
|
| Interventions |
Group A (whole gland cryotherapy): transrectal ultrasound guidance with argon/helium third‐generation equipment was used in all participants. The investigators routinely applied thermosensor monitoring, urethral warming, and saline injections to separate the anterior rectal wall from the posterior prostate. 2 freeze‐thaw cycles were used in all men. Group B (EBRT): 4‐field box technique, received 2 Gy daily (5 days per week) using high‐energy mega‐voltage X‐rays (> 10 MV), prescribed dose was 68 Gy initially then increased to 70 Gy in 2000 and 73.5 Gy in 2002 based on standard practice. Clinical target volume included prostate gland and seminal vesicle base (if biopsy tumour classification < T3c) or entirety (if biopsy tumour classification T3c). Co‐interventions: all participants received ADT using LHRH agonist therapy. A single 3‐month depot of LHRH agonist was given followed by local treatment between 90 days and 120 days after the injection. In 2001, the local standard care changed to include 6 months of ADT before EBRT using 2 consecutive 3‐month depots of LHRH, and the protocol was amended accordingly to reflect this change with local treatment commencing between 180 days and 210 days after the first injection. Follow‐up period (median, range): 100 months (53‐128) |
|
| Outcomes |
Primary outcomes: treatment failure
Secondary outcomes: overall survival or disease‐specific survival or prevalence of positive biopsies
QoL
Adverse events
|
|
| Funding sources | Grant from the National Cancer Institute of Canada and the Calgary Health Region | |
| Declarations of interest | Supported by the National Cancer Institute of Canada, and the Alberta Cancer Board. One of coauthor (Dr Rewcastle) was research director for Endocare, Inc |
|
| Notes |
Publication status: full text publication Language of publication: English |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The study biostatistician (P.M.A.B.) randomly assigned eligible patients to receive 1 of 2 treatments, with stratification according to biopsy tumor classification (bT2 vs bT3), Gleason score (2‐4 vs 5‐7 vs 8‐10), and PSA (7.5 ng/mL vs >7.5 ng/mL) with use of dynamic randomization with a biased coin". |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comments: not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Quote: Study reported as "Open Label" in protocol |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | High risk | Quote: Study reported as "Open Label" in protocol; outcome assessment not explicitly reported but judged to have been unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | Comments: objective outcomes were not likely to be affected by lack of blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Oncologic outcomes | Low risk | Comments: 117/122 (95.9%) and 114/122 (93.4%) men randomised to cryotherapy and EBRT were included in analysis |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) QoL | High risk | Comments: Short term: 106/122 (86.8%) and 88/122 (72.1%) men randomised to cryotherapy and EBRT were included in analysis Long term: 98/122 (80.3%) and 97/122 (79.5%) men randomised to cryotherapy and EBRT were included in analysis |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Adverse events | Low risk | Comments: 117/122 (95.9%) and 114/122 (93.4%) men randomised to cryotherapy and EBRT were included in analysis |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Secondary interventions | Unclear risk | Comments: the outcome was not measured. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Protocol (NCT00489060) was published and all review outcomes were well described |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Quote: "Trial was closed prematurely because of diminishing patient accrual, and not because of adverse events", "One interim analysis was planned"; some participants with PSA > 20 ng/mL were included in EBRT group. |
ADT: androgen deprivation therapy; EBRT: external beam radiotherapy; LHRH: luteinising hormone‐releasing hormone; PSA: prostate specific antigen; QoL: quality of life
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Aus 2002 | Ineligible study design (single arm) |
| Bahn 2002 | Ineligible study design (single arm) |
| Cohen 1996 | Ineligible study design (single arm) |
| Coogan 1995 | Ineligible study design (single arm) |
| Donnelly 2002a | Ineligible study design (single arm) |
| Gould 1999 | Ineligible study design (retrospective study) |
| Liu 2016 | Ineligible study design (non‐randomized study) |
| Long 1998 | Ineligible study design (single arm) |
| Prepelica 2005 | Ineligible study design (single arm) |
| Wong 1997 | Ineligible study design (single arm) |
Differences between protocol and review
The protocol for this review was published in 2008. Therefore, considerable changes were necessary to align this update with Cochrane's current methodological standards, including more specific definitions of primary and secondary outcomes, their measurement, planned secondary analyses, the details of the search and the use of GRADE on a per outcome basis to assess the quality of evidence. Specific issues are highlighted below:
Title: as cryotherapy also is used in the salvage situation, we added the word ”Primary” to the title.
Type of outcome measures: we have revised the outcomes included in the review. In the prior version of the review, outcomes were listed as: "The main outcome measures of interest included biochemical disease‐free survival, disease‐free survival and treatment‐induced complications. Secondary outcomes included disease specific survival, overall survival, QoL outcome measures and economic impact measures." These were now prioritized based on perceived patient‐importance.
Type of outcome measures: we have renamed the oncologic outcomes to time to death from prostate cancer, any cause, or biochemical failure to reflect them representing time‐to‐event outcomes.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies: we have described the method to assess risk of bias in detail. In addition, we grouped all outcomes that have a similarly susceptibility to performance bias in one group.
Subgroup and sensitivity analysis: we have limited these analyses to the primary outcomes.
Contributions of authors
Jae Hung Jung (JHJ): acquired trial reports, performed trial selection, data extraction, data analysis, data interpretation, and drafted the review.
Michael C Risk (MCR): provided clinical and methodological advice on the review, and final approval.
Robert Goldfarb (RG): drafted the protocol, developed the search strategy, acquired trial reports, and performed trial selection.
Balaji Reddy (BR): performed trial selection, data extraction, data analysis, data interpretation, and drafted the review.
Bernadette Coles (BC): developed the search strategy and acquired trial reports.
Philipp Dahm (PD): responsible for conception and study design, provided clinical and methodological advice on the review, and final approval.
Sources of support
Internal sources
Department of Urology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Korea, South.
Minneapolis VA Health Care System, USA.
Department of Urology, University of Minnesota, USA.
External sources
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
JHJ: none known.
MCR: none known.
RG: none known.
BR: none known.
BC: none known.
PD: none known.
Edited (conclusions changed)
References
References to studies included in this review
Chin 2008 {published data only}
- Al‐Zahrani A, Yutkin V, Autran A, Izawa J, Chin J. Long‐term outcome of randomized trial between cryoablation and external beam therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer (T2c‐T3b). Urology 2012;80(3):S271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al‐Zahrani AA, Autran AM, Williams A, Bauman G, Chin JL. Long‐term outcome of randomized trial between cryoablation and external beam therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer (T2c‐T3b). European Urology Supplements 2011;10(2):52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al‐zahrani A, Autran AM, Williams A, Bauman G, Izawa J, Chin J. Long‐term outcome of randomized trial between cryoablation and external beam therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer (T2c‐T3b). Journal of Urology 2011;185 (4 Suppl):e258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al‐zahrani AA, Autran Gomez A, Williams A, Bauman G, Izawa J, Chin J. Long‐term outcome of randomized trial between cryoablation and external beam therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer (T2C‐T3B). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011;29(7 Suppl 1):78. [Google Scholar]
- Chin JL, Al‐Zahrani AA, Autran‐Gomez AM, Williams AK, Bauman G. Extended follow up oncologic outcome of randomized trial between cryoablation and external beam therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer (T2c‐T3b). Journal of Urology 2012;188(4):1170‐5. [DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.06.014] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin JL, Ng CK, Abdelhady M, Downey D, Baumna G, Pus N, et al. Results of a controlled randomised trial of primary cryoablation versus external beam radiotherapy for locally advanced prostate cancer. Journal of Urology 2006;175(4):1130. [Google Scholar]
- Chin JL, Ng CK, Touma NJ, Pus NJ, Hardie R, Abdelhady M, et al. Randomized trial comparing cryoablation and external beam radiotherapy for T2C‐T3B prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases 2008;11(1):40‐5. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.pcan.4500988] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Donnelly 2010 {published data only}
- Donnelly BJ, Saliken JC, Brasher P, Ernst S, Lau H, Trypkov K. A randomised controlled trial comparing external beam radiation and cryoablation in localised prostate cancer. Journal of Urology 2007;177(4):376‐7. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly BJ, Saliken JC, Brasher PM, Ernst SD, Rewcastle JC, Lau H, et al. A randomized trial of external beam radiotherapy versus cryoablation in patients with localized prostate cancer. Cancer 2010;116(2):323‐30. [DOI: 10.1002/cncr.24779] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly BJ, Saliken JC, Brasher PM, Ernst SD, Rewcastle JC, Lau H, et al. A randomized trial of external beam radiotherapy versus cryoablation in patients with localized prostate cancer. Journal of Endourology 2010;24(8):1217‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson JW, Donnelly BJ, Siever JE, Saliken JC, Ernst SD, Rewcastle JC, et al. A randomized trial of external beam radiotherapy versus cryoablation in patients with localized prostate cancer: quality of life outcomes. Cancer 2009;115(20):4695‐704. [DOI: 10.1002/cncr.24523] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Aus 2002 {published data only}
- Aus G, Pileblad E, Hugosson J. Cryosurgical ablation of the prostate: 5‐year follow‐up of a prospective study. European Urology 2002;42(2):133‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bahn 2002 {published data only}
- Bahn DK, Lee F, Badalament R, Kumar A, Greski J, Chernick M. Targeted cryoablation of the prostate: 7‐year outcomes in the primary treatment of prostate cancer. Urology 2002;60(2 Suppl 1):3‐11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cohen 1996 {published data only}
- Cohen JK, Miller RJ, Rooker GM, Shuman BA. Cryosurgical ablation of the prostate: two‐year prostate‐specific antigen and biopsy results. Urology 1996;47(3):395‐401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Coogan 1995 {published data only}
- Coogan CL, McKiel CF. Percutaneous cryoablation of the prostate: preliminary results after 95 procedures. Journal of Urology 1995;154(5):1813‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Donnelly 2002a {published data only}
- Donnelly BJ, Saliken JC, Ernst DS, Ali‐Ridha N, Brasher PM, Robinson JW, et al. Prospective trial of cryosurgical ablation of the prostate: five‐year results. Urology 2002;60:645‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gould 1999 {published data only}
- Gould RS. Total cryosurgery of the prostate versus standard cryosurgery versus radical prostatectomy: comparison of early results and the role of transurethral resection in cryosurgery. Journal of Urology 1999;162(5):1653‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Liu 2016 {published data only}
- Liu YY, Chiang PH. Comparisons of oncological and functional outcomes between primary whole‐gland cryoablation and high‐intensity focused ultrasound for localized prostate cancer. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2016;23:328‐34. [DOI: 10.1245/s10434-015-4686-x] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Long 1998 {published data only}
- Long JP, Fallick ML, LaRock DR, Rand W. Preliminary outcomes following cryosurgical ablation of the prostate in patients with clinically localized prostate carcinoma. Journal of Urology 1998;159(2):477‐84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Prepelica 2005 {published data only}
- Prepelica KL, Okeke Z, Murphy A, Katz AE. Cryosurgical ablation of the prostate: high risk patient outcomes. Cancer 2005;103(8):1625‐30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wong 1997 {published data only}
- Wong WS, Chinn DO, Chinn M, Chinn J, Tom WL. Cryosurgery as a treatment for prostate carcinoma: results and complications. Cancer 1997;79(5):963‐74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Aaronson 1993
- Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ‐C30: a quality‐of‐life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 1993;85(5):365‐76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Albertsen 1995
- Albertsen P C, Fryback D G, Storer B E, Kolon T F, Fine J. Long‐term survival among men with conservatively treated localized prostate cancer. JAMA 1995;274(8):626‐31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Arnott 1851
- Arnott J. On the Treatment of Cancer by the Regulated Application of an Anaesthetic Temperature. London (UK): Churchill, 1851:32‐54. [Google Scholar]
ASTRO Consensus Panel 1997
- ASTRO Consensus Panel. Consensus statement: guidelines for PSA following radiation therapy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 1997;35:1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
AUA 2017
- American Urological Association. Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO/SUO Guideline. www.auanet.org/guidelines/clinically‐localized‐prostate‐cancer‐new‐(aua/astro/suo‐guideline‐2017) (accessed 20 August 2017).
Babaian 2008
- Babaian RJ, Donnelly B, Bahn D, Baust JG, Dineen M, Ellis D, et al. Best practice statement on cryosurgery for the treatment of localized prostate cancer. Journal of Urology 2008;180:1993‐2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barqawi 2014
- Barqawi AB, Stoimenova D, Krughoff K, Eid K, O'Donnell C, Phillips JM, et al. Targeted focal therapy for the management of organ confined prostate cancer. Journal of Urology 2014;192(3):749‐53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Baust 2004
- Baust JG, Gage AA, Clarke D, Baust JM, Buskirk R. Cryosurgery‐‐a putative approach to molecular‐based optimization. Cryobiology 2004;48:190‐204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Baust 2005
- Baust JG, Gage AA. The molecular basis of cryosurgery. BJU International 2005;95:1187‐91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bedard 2014
- Bedard G, Zeng L, Zhang L, Lauzon N, Holden L, Tsao M, et al. Minimal important differences in the EORTC QLQ‐C30 in patients with advanced cancer. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014;10(2):109‐17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Beerlage 2003
- Beerlage HP. Alternative therapies for localized prostate cancer. Current Urology Reports 2003;4:216‐20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cohen 2004
- Cohen JK. Cryosurgery of the prostate: techniques and indications. Reviews in Urology 2004;6 Suppl 4:S20‐6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cooper 2001
- Cooper SM, Dawber RP. The history of cryosurgery. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 2001;94:196‐201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Covidence [Computer program]
- Veritas Health Innovation. Covidence. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation, (accessed 14 March 2018).
D'Amico 2003
- D'Amico AV, Moul J, Carroll PR, Sun L, Lubeck D, Chen MH. Cancer‐specific mortality after surgery or radiation for patients with clinically localized prostate cancer managed during the prostate‐specific antigen era. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2003;21:2163‐72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Deeks 2011
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG, editor(s). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Dickinson 2013
- Dickinson L, Ahmed HU, Kirkham AP, Allen C, Freeman A, Barber J, et al. A multi‐centre prospective development study evaluating focal therapy using high intensity focused ultrasound for localised prostate cancer: The INDEX study. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2013;36(1):68‐80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Donnelly 2002b
- Donnelly BJ, Saliken JC. Salvage cryosurgery ‐ how I do it. Reviews in Urology 2002;4 Suppl 2:S24‐9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
D’Amico 2008
- D’Amico AV, Chen MH, Renshaw AA, Loffredo M, Kantoff PW. Androgen suppression and radiation vs radiation alone for prostate cancer. JAMA 2008;299(3):289–295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
EAU 2017
- European Association of Urology. Prostate cancer (EAU guideline). uroweb.org/guideline/prostate‐cancer (accessed 20 August 2017).
EndNote [Computer program]
- Clarivate Analytics. EndNote. Version 7.5. Clarivate Analytics, 2016.
Gage 1998
- Gage AA. History of cryosurgery. Seminars in Surgical Oncology 1998;14:99‐109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ganzer 2017
Gao 2016
- Gao L, Yang L, Qian S, Tang Z, Qin F, Wei Q, et al. Cryosurgery would be an effective option for clinically localized prostate cancer: a meta‐analysis and systematic review. Scientific Reports 2016;6:27490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
GRADEproGDT [Computer program]
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEproGDT. Version accessed 20 August 2017. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Guyatt 2008
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck‐Ytter Y, Schünemann HJ, et al. GRADE: what is "quality of evidence" and why is it important to clinicians?. BMJ 2008;336(7651):995‐8. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39490.551019.BE] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Guyatt 2011a
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso‐Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence‐‐imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1283‐93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Guyatt 2011b
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hamdy 2016
- Hamdy FC, Donovan JL, Lane JA, Mason M, Metcalfe C, Holding P, et al. 10‐year outcomes after monitoring, surgery, or radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2016;375(15):1415‐24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2002
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. [DOI: 10.1002/sim.1186] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2003
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta‐analyses. BMJ 2003;327(7414):557‐60. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011a
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011b
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA, editor(s). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011c
- Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Altman DG, editor(s). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011d
- Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, editor(s). Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Jayadevappa 2012
- Jayadevappa R, Malkowicz SB, Wittink M, Wein AJ, Chhatre S. Comparison of distribution‐ and anchor‐based approaches to infer changes in health‐related quality of life of prostate cancer survivors. Health Services Research 2012;47(5):1902‐25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jemal 2011
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2011;61:69‐90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Johnston 2010
- Johnston BC, Thorlund K, Schunemann HJ, Xie F, Murad MH, Montori VM, et al. Improving the interpretation of quality of life evidence in meta‐analyses: the application of minimal important difference units. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2010;8:116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Koukourakis 2009
- Koukourakis G, Kelekis N, Armonis V, Kouloulias V. Brachytherapy for prostate cancer: a systematic review. Advances in Urology 2009. [DOI: 10.1155/2009/327945; Article ID: 327945] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Liberati 2009
- Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta‐analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLOS Medicine 2009;6(7):e1000100. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Litwin 1998
- Litwin MS, Hays RD, Fink A, Ganz PA, Leake B, Brook RH. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Index: development, reliability, and validity of a health‐related quality of life measure. Medical Care 1998;36(7):1002‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mariotto 2014
- Mariotto AB, Noone AM, Howlader N, Cho H, Keel GE, Garshell J, et al. Cancer survival: an overview of measures, uses, and interpretation. Journal of the National Cancer Institute Monographs 2014;49:145‐86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McCulloch 2009
- McCulloch P, Altman DG, Campbell WB, Flum DR, Glasziou P, Marshall JC, et al. No surgical innovation without evaluation: the IDEAL recommendations. Lancet 2009;374(9695):1105‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
National Cancer Institute
- National Cancer Institute. Common Toxicity Criteria. ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm (accessed 23 August 2017).
Parmar 1998
- Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta‐analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Statistics in Medicine 1998;17(24):2815‐34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rees 2004
- Rees J, Patel B, MacDonagh R, Persad R. Cryosurgery for prostate cancer. BJU International 2004;93:710‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roach 2006
- Roach M 3rd, Hanks G, Thames H Jr, Schellhammer P, Shipley WU, Sokol GH, et al. Defining biochemical failure following radiotherapy with or without hormonal therapy in men with clinically localized prostate cancer: recommendations of the RTOG‐ASTRO Phoenix Consensus Conference. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 2006;65(4):965‐74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Robinson 2002
- Robinson JW, Donnelly BJ, Saliken JC, Weber BA, Ernst S, Rewcastle JC. Quality of life and sexuality of men with prostate cancer 3 years after cryosurgery. Urology 2002;60:12‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schünemann 2011
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and ‘Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Shelley 2007
- Shelley M, Wilt TJ, Coles B, Mason MD. Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007, Issue 18. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005010.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tay 2016
- Tay KJ, Polascik TJ. Focal cryotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Archivos Españoles de Urología 2016;69(6):317‐26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thompson 2007
- Thompson I, Thrasher JB, Aus G, Burnett AL, Canby‐Hagino ED, Cookson MS, et al. Guideline for the management of clinically localized prostate cancer: 2007 update. Journal of Urology 2007;177:2106‐31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
USCS Group 2014
- US Cancer Statistics Working Group. United States Cancer Statistics: 1999 ‐ 2011 Incidence and Mortality Web‐based Report. nccd.cdc.gov/uscs. Altanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Cancer Institute, (accessed 28 September 2017).
Valerio 2014
- Valerio M, Ahmed HU, Emberton M, Lawrentschuk N, Lazzeri M, Montironi R, et al. The role of focal therapy in the management of localised prostate cancer: a systematic review. European Urology 2014;66(4):732‐51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Xiong 2014
- Xiong T, Turner RM, Wei Y, Neal DE, Lyratzopoulos G, Higgins JP. Comparative efficacy and safety of treatments for localised prostate cancer: an application of network meta‐analysis. BMJ Open 2014;4(5):e004285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


