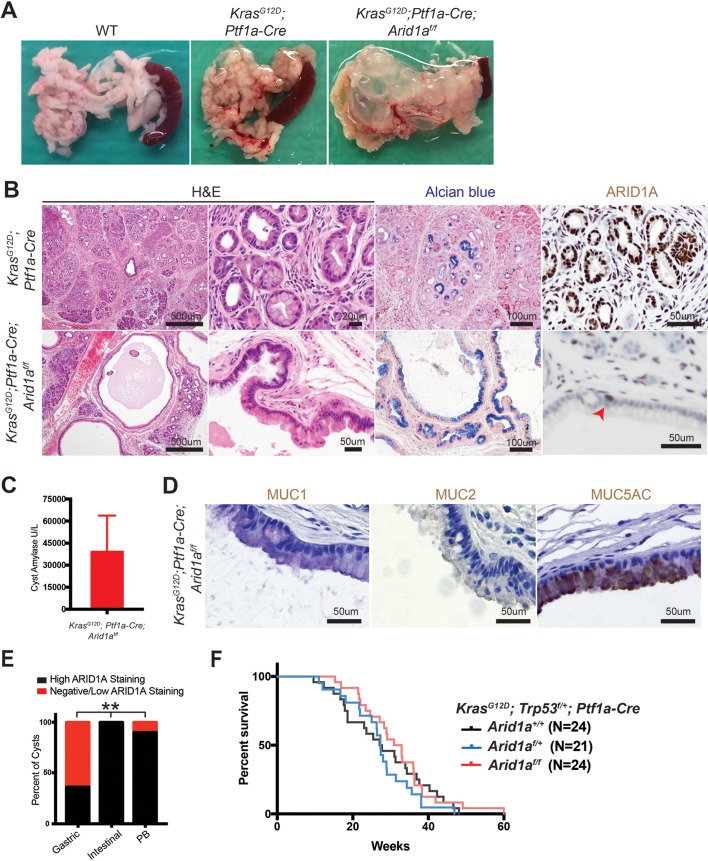
Figure 2.
Kras activation synergises with Arid1a loss in the pancreas to induce intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs). (A) KrasG12D; Ptf1a-Cre (KC) mice had oedema, while KrasG12D; Ptf1a-Cre; Arid1af/f (KCA) mice formed large pancreatic cysts. (B) KC mice showed significant inflammation and numerous pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. KCA mice formed large mucinous cysts with papillary projections that were mosaic for ARID1A (arrowhead points to ARID1A-positive cells). (C) KCA cyst fluid was amylase rich (normal serum amylase <10 U/L), suggesting a direct connection to the pancreatic ductal system, consistent with IPMN. n=4, error bars represent SEM. (D) KCA cysts with mucin expression patterns consistent with human gastric subtype IPMN. (E) Human gastric subtype (n=28) and pancreaticobiliary subtype (PB, n=10) IPMN showed areas with negative or low ARID1A staining, as compared with intestinal subtype (n=6). **P<0.01. (F) Kaplan-Meier curve estimating survival of KrasG12D; Trp53f/+; Ptf1a-Cre mice that were Arid1a+/+, Arid1af/+ or Arid1af/f.