Abstract
Measurement of drug concentrations in hair provides a non-invasive approach to assess drug adherence. Here, we report on the development and validation of a method for the quantification of the antiretroviral dolutegravir (DTG) extracted from human hair. DTG is extracted from hair samples by sonication and incubation in 50:50 methanol:acetonitrile with 2% formic acid overnight at 40°C. Following extraction, samples are analyzed by reverse phase chromatography on a Waters Atlantis T3 (50×2.1mm, 3μm particle size) column with subsequent detection by electrospray ionization in positive ion mode on an AB Sciex API-5000 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer. The stable, isotopically labeled 13C,d5-DTG is used as an internal standard in the assay. The calibration range is 5-10,000pg DTG/mL of extraction solvent with the ability to extract between 1-10mg of hair/mL of extraction solvent. The assay was linear, accurate (inter-assay % bias within ± 6.5%) and precise (inter-assay % CV ≤ 10.3%). The assay was successfully used to analyze clinical samples from subjects on DTG regimens. Analysis of clinical samples suggested the potential presence of a degradation product, which was subsequently confirmed to occur with exposure to sunlight. The degradation of DTG could complicate absolute interpretation of clinical results, but the presence of this degradation product is easily evaluated with this assay to aid in data interpretation.
Keywords: Hair, Validation, Dolutegravir, Antiretroviral, Adherence
Introduction
Over the last 20 years, antiretrovirals have advanced to once daily single tablet regimens that can suppress viral replication for many years. Yet, less than perfect adherence to these treatment regimens has been associated with suboptimal HIV treatment outcomes and can lead to eventual acquisition of drug resistance and treatment failure [1]. While HIV viral load provides a biological measure of adherence, by the time waning adherence is identified by increasing plasma HIV RNA, viral drug resistance may have already developed. Since class resistance is common among low genetic barrier agents like non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) and integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs), failure of a single regimen can severely limit future treatment options [2].
Measuring antiretroviral concentrations by plasma or dried blood spots (DBS) provides an alternative biological measure of adherence that can identify waning adherence early and facilitate clinical response before treatment failure [2, 3]. However, interpreting plasma concentrations of antiretrovirals with short plasma half-lives such as raltegravir and lopinavir only provides information about recent dosing and is subject to white coat adherence (where a clinical event such as a doctor or clinical study visit prompts drug administration) [4]. Additionally, collecting plasma requires specialized instrumentation and freezer storage capacity that limits its utility in resource limited settings. DBS address some of these limitations by allowing for the quantification of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTIs) active metabolites that have relatively long half-lives (ranging from 16-112 hours) [5]. While sample processing is minimal, DBS still require freezer storage to prevent degradation [6] and have not been explored for NRTI sparing regimens [3].
In light of current limitations in pharmacologic assessment of adherence, hair has been explored as an adherence record that can span months, requires minimal sample processing and allows for room temperature storage. High concentrations of protease inhibitors (atazanavir and lopinavir) and NNRTIs (nevirapine) in hair have been shown to correlate with virologic suppression [7-9]. Over the past 2-3 years, dolutegravir (DTG) has become one of the most prescribed drugs for HIV infection, due to potency, limited side effects, and co-formulation with other antiretrovirals. This drug is being used in combination with other antiretrovirals for the treatment of HIV, typically as a 50mg once daily. Herein we report the first LC-MS/MS method to measure the INSTI dolutegravir in hair as a novel measure of long-term exposure.
Materials and Methods
Materials
DTG was purchased from MedChemExpress (Monmouth Junction, NJ, USA) and the stable isotopically labeled internal standard 13C, d5-DTG (DTG-IS) was synthesized by ALSACHIM (Illkirch Graffenstaden, France). Acetonitrile (HPLC grade), methanol (HPLC grade), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; Certified grade), and formic acid (Certified ACS, 88%) were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA). Water was purified by a Hydro Picosystem® UV Plus (Durham, NC, USA). Drug-free human hair was acquired from BioreclamationIVT (Westbury, NY, USA). Clinical hair samples from three de-identified subjects on DTG-containing regimens were used for method development. These hair samples were obtained from participants in the Women’s Interagency HIV Study (WIHS), which is the largest and longest ongoing multi-ethnic cohort of HIV-infected women in the U.S. (NCT00000797) [10].
Extraction from hair
Hair samples were cut into small pieces (1-2mm) using scissors and transferred into 8mL Class A borosilicate glass vials (Fisher Scientific, Fair Lawn, NJ, USA). The hair was weighed on a Mettler Toledo XS-205DU balance (Columbus, OH, USA) to allow for unit conversion to ng/mg hair. Extraction solvent (50:50 methanol:acetonitrile with 2% formic acid) was added to each vial. The volume of solvent added varied from 1-5mL depending on the mass of hair extracted as follows: 1-2mg hair (1mL of solvent), 2-3mg hair (2mL of solvent), 3-4mg of hair (3 ml of solvent), 4-5mg of hair (4mL of solvent), and samples >5mg of hair (5mL of solvent). The samples were then sonicated for 1 hour, and incubated overnight(approximately 19 hours) in a Thermo Scientific Precision SWB15 reciprocal shaking bath (Waltham, MA, USA) at 40°C and a speed of 80 RPM.
Following incubation, 250μL of the sample was mixed with 50μL of internal standard solution (DTG-IS at 5ng/mL in 50:50 methanol:water). The samples were vortexed for approximately 5 minutes on a Vortex Genie 2 (Scientific Industries, Bohemia, NY, USA) and centrifuged at room temperature for 5 minutes at 13.2 rcf (Eppendorf 5415R, Hauppauge, NY, USA). The resulting supernatant was evaporated to dryness under a gentle stream of nitrogen at 50°C for 50 minutes using a Biotage TurboVap LV (Charlotte, NC, USA). The dried extracts were reconstituted with 100 μL of 70:30 water:methanol prior to LC-MS/MS analysis.
LC-MS/MS conditions
A Shimadzu Prominence HPLC system including pumps (LC-20AD), degasser (DGU-20A), and controller (CBM-20A) were supplied from Shimadzu (Columbia, MD, USA). A Waters Atlantis T3 (50×2.1mm, 3μm particle size) column was used under reverse phase conditions with 0.1% formic acid in water (mobile phase A) and 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile (mobile phase B) with a flow rate of 0.450mL/min. The column heater (CTO-20A) was set at 40 °C, and the autosampler (SIL-20AC/HT) was maintained at 15 °C. The injection volume was 5μL. The LC gradient was maintained at 35% B for 0.25 minutes and increased to 95% B at 2.25 minutes and held until 2.75 minutes. The gradient reverted back to the starting condition of 35% B at 2.80 minutes and held for a total run time of 4.00 minutes.
An API-5000 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (SCIEX, Foster City, CA, USA) operated in positive ion TurboIonspray mode was used to acquire data. Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) was used to detect the analyte [precursor/product] transitions (m/z) as follows: DTG [420/277] and DTG-IS [426/277]. The source temperature was 450 °C and the ion spray voltage (ISV) was 5500V. The declustering potential (DP) was 120V with a collision energy (CE) of 37V for the method analyte and internal standard.
Linear regression of concentration (x) versus peak area ratio of compound to internal standard (y) using a 1/(x2) weighting was used with Sciex Analyst software (version 1.6.2).
Method Validation
Preparation of Calibration Standards and Quality Control Samples
Blank hair supernatant was prepared by adding 5mL of hair extraction solvent (50:50 methanol:acetonitrile with 2% formic acid) to multiple glass vials each containing 20-50 mg of drug-free hair. The vials were sonicated for one hour and then incubated overnight (water bath temperature 40°C, shaker speed 80rpm). Following incubation, the contents of all of the vials were mixed together and stored at 4 °C. This pooled supernatant was used to generate the calibration standard and quality control (QC) samples
DTG stock solutions were prepared in duplicate at 1mg/mL in DMSO. One stock solution was used to prepare calibration standards and the second stock solution was used to prepare QC samples. A set of calibration standard spiking solutions was prepared at 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 2, 5, 20, 50, 170, and 200ng/mL, and a set of QC spiking solutions was prepared at 0.1, 0.3, 6, and 160ng/mL in 50:50 acetonitrile:water. Stock solutions and spiking solutions were stored at −80 °C.
Calibration standards and QC samples were prepared fresh daily by diluting the appropriate spiking solutions 20-fold with the blank hair supernatant. The concentrations of the resulting calibration standards were 5, 10, 25, 100, 250, 1000, 2500, 8500, and 10000pg/mL and the QC samples were 5 (LLOQ QC), 15 (Low QC), 300 (Mid QC), and 8000pg/mL (High QC).
The internal standard (DTG-IS) stock solution was prepared at 1mg/mL in DMSO and stored at −80 °C. This solution was diluted to 5000ng/mL with methanol and further diluted to 5ng/mL in 50:50 methanol:water for the final internal standard working solution. This working solution was stored at 4°C.
Recovery/Matrix Effects
Blank hair supernatant was spiked with DTG at the low, mid, and high QC concentrations prior to extraction (pre-extracted). Resulting peak areas for DTG and DTG-IS were compared with blank hair extracts spiked with DTG and DTG-IS corresponding to 100% recovered concentrations (post-extracted) and neat solution samples (unextracted) representing 100% recovery of DTG and DTG-IS. Recovery was calculated as the ratio of the mean peak area response of the compound in pre-extracted QCs to the mean peak area response in post-extracted QCs. Matrix effects (ionization enhancement or suppression) were calculated as the ratio of the mean peak area response of the compound in post-extracted QCs to mean peak area response of the compound in unextracted solvent QCs.
Matrix effects were also evaluated using the experiments previously described by Matuszewski [11]. Blank hair supernatant was prepared from six different lots of drug-free human hair. Samples were spiked at the low, mid, and high QC concentrations in each lot of hair and extracted in triplicate with the average peak area ratios from the analyses being plotted against QC concentrations for each of the six lots evaluated. Additionally, the mid QC samples from the six lots were quantified with a complete set of calibration standards prepared from a separate lot of drug-free hair for precision and accuracy assessments.
A final assessment of matrix effects was performed by extracting various ratios of hair mass (mg) to extraction solvent volume (mL). Different amounts of drug-free hair (5, 10, 25, and 50mg) were added to separate vials containing 5mL of the extraction solvent. The samples were spiked at the mid QC concentration and extracted to determine if the ratio of hair mass:extraction solvent volume (between 1-10mg hair/mL extraction solvent) impacts the ability to quantify DTG.
Clinical Sample Analysis
209 de-identified hair samples collected from WIHS participants on DTG based combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) were analyzed for DTG concentrations. Informed consent was provided by all participants via protocols approved by Institutional Review Committees at each affiliated institution. The regimens consisted of DTG (50mg once daily) in combination with two backbone nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). Samples were collected from the occipital region of the head, which has been shown to have the most consistent linear growth rate of approximately 1cm/month [12]. A vast majority (~97%) of the hair samples were either black or brown in color. The samples were cut with scissors into small pieces (1-2mm) and transferred into a tared glass vial where the mass was recorded. The total length cut was approximately 2cm, which should correspond to around 2 months of drug exposure. Many of the hair strands were collected in a manner indicating the proximal and distal ends relative to the scalp. In these cases, the samples were cut from proximal end to monitor the most recent time period of drug uptake. In cases where the hair strands were short (~2cm or less), the ends of the strands were unlabeled, and the whole strand was extracted. Extraction solvent (1-5mL depending on mass of hair extracted) was added to each sample vial resulting in ratios of 1-2 mg of hair per mL of solvent. Samples were sonicated for 1 hour and incubated at 40°C for overnight prior to extraction. Final concentrations of study samples were converted to pg/mg by multiplying the pg/mL result by the extraction volume (1-5mL) and dividing by the amount of hair extracted (mg). Peak areas for the degradation product were also recorded for the clinical samples.
Dolutegravir Stability Analysis
Following analysis of clinical samples, an additional peak was noticed in the DTG channel in many chromatograms around 1.9 min. This peak was not seen during the development or validation of the assay where DTG was spiked into drug-free hair. A series of experiments were performed to identify whether this additional peak was related to DTG, and if its presence may indicate degradation of DTG following uptake into the hair strand.
Results and Discussion
Method development
The development of this method required the use of clinical hair samples collected from subjects on DTG regimens (DTG dosed at 50mg once daily). These samples were used to determine the most effective conditions for extracting DTG from hair. In addition, since there were no literature values for DTG levels detected in hair, these samples served as a means to select an appropriate analytical range for the assay.
Five solvents (acetonitrile, methanol, 50:50 acetonitrile:methanol, , and 25:25:50 acetonitrile: methanol: water, and 50:50 acetonitrile:methanol with 2% formic acid) were initially evaluated for selection of optimal DTG extraction. Hair samples were placed in vials containing a solvent and were incubated at 40°C overnight (approximately 18 hours). The samples were mixed with internal standard prior to analyzing for DTG concentrations. The results are shown in Table 1. A mixture of 50:50 acetonitrile:methanol resulted in higher extraction efficiency than either solvent alone, while the acidification of the 50:50 acetonitrile:methanol with 2% formic acid provided the highest extraction efficiency of DTG.
Table 1.
Extraction solvent evaluation following incubation of clinical hair samples for 18 hours
| Extraction Solvent | Normalized DTG Response |
|---|---|
| Acetonitrile | 4% |
| Methanol | 13% |
| 50:50 Acetonitrile:Methanol | 29% |
| 25:25:50 Methanol:Acetonitrile:Water | 18% |
| 50:50 Acetonitrile:Methanol (2% Formic Acid) | 100% |
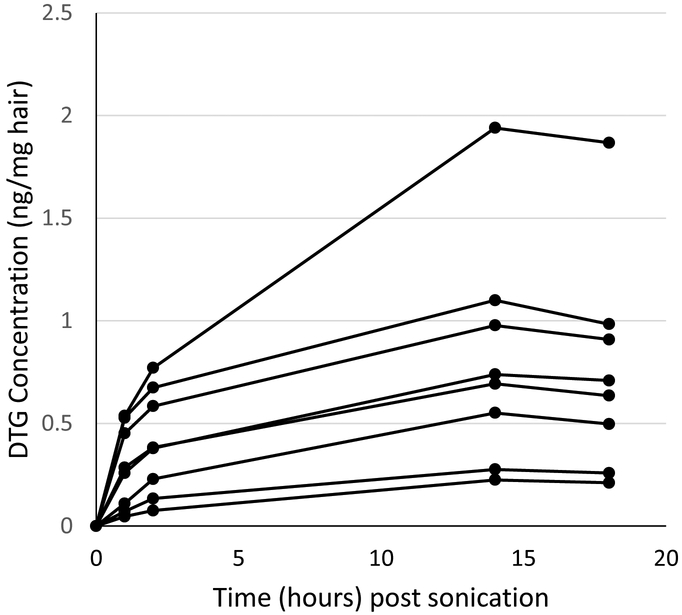
Once 50:50 methanol:acetonitrile with 2% formic acid was selected as the extraction solution, an evaluation of the required extraction time was performed. Hair samples (5-10mg) from eight subjects on DTG regimens was placed in vials containing 5mL of extraction solvent. The samples were sonicated for one hour followed by incubation for 18 hours at 40°C. Aliquots from the eight samples were removed at 1, 2, 14, and 18 hours following sonication and were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The results are shown in Fig. 1. This experiment showed the concentrations of DTG in the extraction solvent were very similar between the 14 and 18 hour evaluations indicating the extraction was complete following 14 hour of incubation. In addition, these samples provided guidance for the analytical range needed. The evaluated samples fell within a range of 200-2000pg DTG/mg hair.
Fig. 1.
DTG concentrations in extracts from 8 hair samples following incubation in 50:50 methanol:acetonitrile with 2% formic acid for 1, 2, 14, and 18 hours
The incorporation of drugs in hair has been shown to vary with hair color [13-16] with lighter hair colors resulting in lower concentrations than darker pigmented hair strands. To evaluate potential lower concentrations, we isolated grey hair strands and compared those concentrations with black strands from the head of the same subject. The grey hair strands produced concentrations of approximately 20pg DTG/mg hair, and the black strands produced concentrations of approximately 500pg DTG/mg hair. These results indicated that the initial low end of our expected concentration range needed to be lowered to account for possible concentrations present in hair with less melanin content. Based on these findings the analytical range of 5-10,000 pg/mL of DTG in the extraction solvent was selected for validation.
Method validation
Selectivity
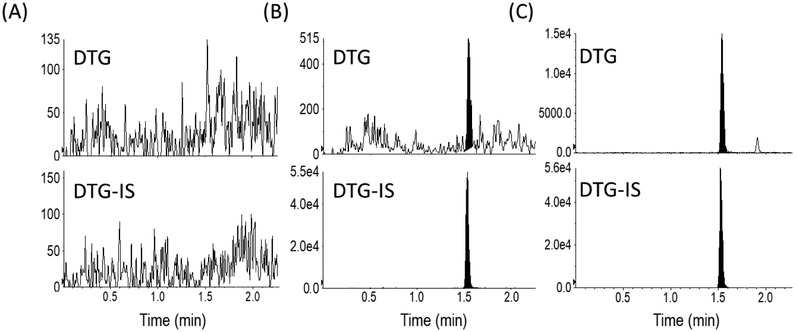
Selectivity was evaluated by the extraction of six lots of blank human hair. No Interfering peaks were detected at the retention time of DTG or DTG-IS in any of the samples evaluated. Samples from male and female donors with blonde, brown, and black hair were included in this evaluation. Fig. 2 shows example chromatograms from a drug-free hair sample, a drug-free hair sample spiked with DTG at the LLOQ, and a clinical hair sample from a subject on a DTG regimen.
Fig. 2.
Example chromatograms from a drug-free hair sample (Fig 2A) a LLOQ calibration standard (Fig 2B) and a clinical hair sample from subject on DTG regimen (Fig 2C)
Linearity
The validation consisted of three analytical runs to evaluate assay performance. Duplicate standard curves were injected at the beginning and end of each run. The standard curves were constructed using a linear regression algorithm with 1/x2 weighting to plot the peak area ratio of analyte to internal standard versus concentration. Acceptance criteria for accuracy of the calibration standards was ≤15% (≤20% at the LLOQ). Correlation coefficients for all runs exceeded 0.99.
Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy and precision was assessed by analysis of six replicates of QC samples at four concentrations (5, 15, 300, and 8000pg/mL) over three runs. Intra-assay statistics were determined for QCs (n=6) within the same analytical run. Inter-assay statistics were determined from the analysis of QC samples assayed in each of three separate analytical runs (n=18). Accuracy was reported as % bias from nominal concentration with acceptance criteria of ≤±15% (≤±20% at the LLOQ). Precision was reported as coefficient of variation (%CV) with acceptance criteria of ≤15% (≤20% at the LLOQ). All results were within the described acceptance criteria and are shown in Table 2.
Table 2.
Intra-assay and Inter-assay QC precision and accuracy statistics
| Nominal Con (pg/mL) |
Run 1 Accuracy (%Bias) |
Run 1 Precision (%CV) |
Run 2 Accuracy (%Bias) |
Run 2 Precision (%CV) |
Run 3 Accuracy (%Bias) |
Run 3 Precision (%CV) |
Inter-assay Accuracy (%Bias) |
Inter-assay Precision (%CV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | −3.4 | 13.2 | 1.7 | 8.2 | 1.6 | 10.3 | −2.9 | 10.3 |
| 15 | 5.2 | 11.8 | −1.1 | 5.3 | −4.2 | 5.6 | 1.7 | 8.8 |
| 300 | 6.5 | 3.3 | −5.7 | 3.5 | −0.8 | 4.1 | 4.9 | 6.2 |
| 8000 | −2.1 | 6.8 | −2.7 | 5.5 | 4.9 | 1.6 | −6.5 | 5.9 |
Dilution
The ability to dilute samples above the upper limit of quantitation was also demonstrated. A QC sample at 16000pg/mL was prepared in blank human hair supernatant. The QC was diluted 10-fold with blank human hair supernatant prior to extraction. Triplicate analysis of the 10-fold diluted QC produced acceptable accuracy (10.4% bias) and precision (1.7 %CV) meeting acceptance criteria of ≤±15%.
Recovery/Matrix Effects
The range of recoveries associated with this assay was 65.2%–71.8% for DTG and 71.6%–75.4% for DTG-IS. The recovery values of the analyte and internal standard are consistent and are concentration independent. The values reported for recovery in this assay only reflect the assay recovery following incubation. The recovery reported from these spiked QCs was not intended to represent the recovery associated with an incurred sample, since it is impossible to generate a hair sample with analyte incorporated into the strands at a known concentration. Additional experiments were performed with incurred samples to assess the extraction efficiency and stability of DTG during the extraction process.
The matrix effects ranged from 98.2%–101.7% for DTG and 85.1%–95.0% for DTG-IS across all QC levels. The matrix effects were minimal in this assay and were consistent between the analyte and internal standard throughout the concentration range evaluated.
The %CV from the six slope values for DTG generated in six lots of hair was 3.6% indicating the lack of matrix effect related to different lots of hair. Samples from male and female donors with blonde, brown, and black hair were included in this evaluation. The precision (%CV) and accuracy (% bias) for the quantitation of the 6 lots of hair spiked at the mid QC level were within the ±15% acceptance criteria. Data for the slope analysis and mid QC precision and accuracy assessment are presented in Table 3.
Table 3.
DTG slope analysis and mid QC precision and accuracy from 6 lots of human hair
| Hair Lot | Slope | Mid QC %Bias | Mid QC %CV |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00399 | −12.4 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 0.00400 | 5.3 | 5.0 |
| 3 | 0.00407 | 6.7 | 3.0 |
| 4 | 0.00408 | 8.0 | 4.8 |
| 5 | 0.00439 | −3.1 | 2.0 |
| 6 | 0.00413 | 9.3 | 3.0 |
| %CV (Slope) | 3.6 |
An assessment of ratios of hair mass (mg):extraction solvent (mL) was performed to determine if the amount of hair extracted would impact the ability to quantify DTG. Ratios of 1:1, 2:1, 5:1, and 10:1 mg hair:mL extraction solvent were evaluated at the mid QC level. Precision and accuracy for all four ratios were within acceptance criteria for precision and accuracy indicating the amount of hair relative to the amount of extraction solvent is not critical to assay performance. These results are shown in Table 4.
Table 4.
Precision and accuracy assessment of DTG QC samples prepared at mid QC level with multiple ratios of hair mass:extraction solvent volume
| Hair Mass | Solvent Added | Ratio (Hair:Solvent) | Target Conc | Mean Conc | % Bias | %CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | 5 mL | 1:1 | 300 pg/mL | 270 pg/mL | −10.1 | 3.6 |
| 10 mg | 5 mL | 2:1 | 300 pg/mL | 332 pg/mL | 10.6 | 5.8 |
| 25 mg | 5 mL | 5:1 | 300 pg/mL | 282 pg/mL | −6.0 | 5.5 |
| 50 mg | 5 mL | 10:1 | 300 pg/mL | 334 pg/mL | 11.4 | 4.7 |
Carryover
No carryover was observed for DTG or DTG-IS in a blank sample analyzed directly following the injection of the high calibration standard.
Stability
Stability of DTG throughout the extraction process was evaluated. DTG was spiked into extraction solvent (50:50 methanol:acetonitrile with 2% formic acid) at 800pg/mL. The sample was sonicated for 1 hour followed by an overnight (19 hour) incubation at 40 °C. Following incubation, this sample was analyzed in triplicate and compared with a freshly prepared sample spiked into extraction solvent at 800pg/mL. The incubated sample was only −3.8% different from the freshly prepared sample indicating DTG is stable in the extraction solvent during the incubation process.
QC samples at the low (15pg/mL) and high (8000 pg/mL) QC concentrations were allowed to sit at room temperature for approximately 28 hours following incubation. These QCs were assayed in triplicate and compared to nominal concentrations. The room temperature exposed QCs showed −6.9% and 1.8% deviation from nominal at the low and high QC levels respectively meeting the acceptance criteria of ±15%.
Following incubation, the stability of DTG after 3 freeze/thaw cycles between room temperature and - 80°C was evaluated. The first cycle was frozen for at least 24 hours and all other cycles were frozen for at least 12 hours between each cycle. Low (15pg/mL) and high (8000pg/mL) QC samples were assayed in triplicate after completing 3 freeze/thaw cycles. The freeze/thaw QCs showed −5.1% and 2.3% deviation from nominal at the low and high QC levels respectively meeting the acceptance criteria of ±15%.
Extracts from QC samples at the low (15pg/mL) and high (8000 pg/mL) concentrations were analyzed in triplicate following storage for 3 days in the autosampler at 15°C . The QCs stored in the autosampler for 3 days showed 11.7% and −0.8% deviation from nominal concentrations at the low and high QC levels respectively meeting the acceptance criteria of ±15%.
Clinical Evaluations
Assay Performance
Of the 209 samples provided from the WIHS, DTG was detected in 96%, indicating the analytical range selected was appropriate for this analysis. Calibration standard and QC performance during sample analysis was consistent with performance seen during method validation.
Degradation Product Analysis
While the assay performed as expected with regard to DTG quantitation, an additional peak was seen in the chromatograms for many of the incurred samples. This extra peak (retention time ~ 1.9 minutes) was fully resolved from the DTG peak (retention time ~1.5 minutes) but was present in 60% of samples analyzed. The extra peak did not occur in a specific ratio relative to DTG and was not present in all samples, even when DTG was detected at high concentrations. If this peak were a metabolite of DTG, its presence would likely be more consistently found in incurred hair samples.
A series of experiments were performed to identify whether this additional peak was related to DTG, and if its presence may indicate degradation of DTG following uptake into the hair strand. Additional MRM transitions for DTG were added to the assay to allow for assessments of fragment ions at m/z 127, 377, 136, and 177 from the parent ion at 420.
Ten drug-free hair samples were extracted and analyzed for DTG and the presence of a peak around 1.9 minutes. None of these samples had a peak at the retention time of DTG or the potential degradation product, indicating the additional peak was likely not an endogenous component (Fig. 3a). In addition, these ten samples were extracted with DTG spiked into the extraction solvent at 5000 pg/mL. These samples underwent the sonication and incubation at 40 °C prior to extraction and LC-MS/MS analysis. All ten of these samples showed large peaks for DTG in all five MRM channels with no peaks detected around 1.9 minutes (Fig. 3b). This test indicated that the sonication, incubation, and extraction from a hair sample containing high concentrations of DTG did not result in the generation of this additional peak.
Fig. 3.
Chromatograms from 5 MRM transitions [Q1/Q3] from a drug-free hair sample (Fig 3A) a drug-free hair sample spiked with DTG (Fig 3B) a clinical hair sample from subject on DTG regimen (Fig 3C) and a DTG solution in 50:50 methanol:water following exposure to sunlight for 3 hours (Fig 3D)
Six clinical samples in which the initial analysis demonstrated a chromatographic peak at approximately 1.9 minutes were re-extracted and analyzed with the revised assay. The peak at 1.9 minutes was present in all six samples, but only in the MRM channels with fragment ions at m/z 277 (transition monitored in original assay) and 127. No peaks were seen at 1.9 minutes for fragment ions at m/z 377, 136, or 177. DTG (retention time 1.5 minutes) had peaks present for all five transitions (Fig. 3c). In an attempt to further characterize the peak at 1.9 minutes, the eluent from the LC was collected from approximately 1.75-2 minutes from the clinical sample. This solution was infused into the mass spectrometer and additional fragment ions were found. However, upon injection of a clinical extract, none of the additional fragment ions resulted in a peak at 1.9 minutes. With the limited concentration available from a clinical extract, further identification of this component was not likely.
In an attempt to determine if this additional peak was from photodegradation of DTG, a solution of DTG (500ng/mL in 50:50 methanol:water) was placed outside and exposed to sunlight for 3 hours. The sample was analyzed following sunlight exposure with the revised LC-MS/MS assay. The chromatogram for the exposed sample showed peaks present at all five MRM transitions at 1.5 minutes and only two of the MRM transitions at 1.9 minutes. The two transitions with peaks detected at 1.9 minutes were the same (fragment ions at m/z 277 and 127) as seen in the clinical samples (Fig. 3d). The chromatography from this sample also indicated that multiple components may be present at approximately 1.5 minutes as the peak shape for several of the transitions (specifically m/z 127 and 177) were much broader than those seen for fragments at m/z 377 and 136.
The peaks present in all five MRM transitions for DTG and the peaks detected at 1.9 minutes in all samples described above (drug-free hair, drug-free hair spiked with DTG, clinical hair, and sun exposed DTG solution) were integrated. In each sample, the peak areas for the various transitions were normalized to the area detected in the m/z [420/227] transition. The results of this evaluation are shown in Table 5. The results indicate the ratio of peak intensity detected in the monitored MRM transitions is consistent between the ten drug-free spiked samples and the six clinical samples for the DTG peak detected at 1.5 minutes. In addition, the ratio of the peak areas detected in the m/z 420/277 and m/z 420/127 transitions of the clinical samples matched the ratio detected in the sun exposed DTG solution sample for the 1.9 minute component.
Table 5.
Normalized responses for peaks detected at 1.5 min and 1.9 min in a drug-free hair sample spiked with DTG, a clinical hair sample, and a 3-hour sun-exposed DTG solution with 5 MRM transitions
| Normalized Peak Area (Ret Time = 1.5 min) | Normalized Peak Area (Ret Time = 1.9 min) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRM Transition |
Drug-Free Spiked Hair |
Clinical Hair Sample |
Sun Exposed Solution |
Drug-Free Spiked Hair |
Clinical Hair Sample |
Sun Exposed Solution |
| 420/277 | 100% | 100% | 100% | Not Detected | 100% | 100% |
| 420/127 | 57% | 58% | 167% | Not Detected | 62% | 61% |
| 420/136 | 9% | 9% | 5% | Not Detected | Not Detected | Not Detected |
| 420/177 | 7% | 6% | 15% | Not Detected | Not Detected | Not Detected |
| 420/377 | 5% | 5% | 3% | Not Detected | Not Detected | Not Detected |
Although we are unable to completely identify the component present at 1.9 minutes in the chromatograms, the evidence presented demonstrates a correlation between sun exposure and production of a peak that is similar to that seen in chromatograms from clinically collected samples. If not accounted for, this degradation product may confound the interpretation of DTG drug adherence for those who may be exposed to more sun exposure. This should be taken into account with any analyses evaluating DTG hair concentrations as a measure of adherence.
Conclusion
An LC-MS/MS assay has been developed for the analysis of DTG concentrations in human hair. This method was fully validated showing good results in terms of linearity, sensitivity, accuracy, precision, and specificity. DTG in was shown to be stable during the 19 hour sonication/incubation procedure required to extract DTG from hair, at room temperature (up to 28 hours) following incubation, and stable through 3 freeze/thaw cycles following incubation. This is, to our knowledge, the first assay to assess DTG levels in human hair as a means to evaluate drug adherence. The assay has been used to effectively analyze clinical samples with 96% of samples having DTG detected within the calibrated range. However, the analysis of DTG in human hair may be confounded by potential photodegradation occurring with sun exposure, which is problematic for analysis in hair that is routinely exposed to sunlight. This potential degradant is easily detected with our assay. However, the correlation between DTG concentration and the presence of this potential degradant was not evaluated, as it is not possible to spike known amounts of analyte into hair to accurately evaluate the degradation. In addition it is impossible to track the amount of time hair that has been exposed to this type of degradation prior to being collected. Although there are potential complicating factors prior to sample collection, we have presented a validated assay for the analysis of DTG in human hair that can be used to aid in the determination of patient adherence to DTG-containing drug regimens.
Acknowledgements
This publication resulted from core activities of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Center for AIDS Research (CFAR), an NIH funded program (P30 AI50410) and the WIHS (Women’s Interagency HIV Study (U01 AI103390). ADM Kashuba is also supported by R01 AI111891 and R01 AI122319.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
References
- 1.Castillo-Mancilla JR, Phillips AN, Neaton JD, Neuhaus J, Collins S, Mannheimer S, Pett S, Touzeau-Römer V, Polizzotto MN, Lundgren JD, Gardner EM; INSIGHT SMART Study Group. Association of Suboptimal Antiretroviral Therapy Adherence With Inflammation in Virologically Suppressed Individuals Enrolled in the SMART Study. INSIGHT SMART Study Group. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017. December 22;5(1):ofx275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents Living with HIV. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf.
- 3.Anderson PL, Liu AY, Castillo-Mancilla JR, Gardner EM, Seifert SM, McHugh C, Wagner T, Campbell K, Morrow M, Ibrahim M, Buchbinder S, Bushman LR, Kiser JJ, MaWhinney S. Intracellular Tenofovir-Diphosphate and Emtricitabine-Triphosphate in Dried Blood Spots following Directly Observed Therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. December 21;62(1). pii: e01710–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Podsadecki TJ, Vrijens BC, Tousset EP, Rode RA, Hanna GJ. "White coat compliance" limits the reliability of therapeutic drug monitoring in HIV-1-infected patients. HIV Clin Trials. 2008. Jul-Aug;9(4):238–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Castillo-Mancilla JR, Zheng JH, Rower JE, Meditz A, Gardner EM, Predhomme J, Fernandez C, Langness J, Kiser JJ, Bushman LR, Anderson PL. Tenofovir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir diphosphate in dried blood spots for determining recent and cumulative drug exposure AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses, 29 (February (2)) (2013), 384–390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schauer AP, Sykes C, Cottrell ML, Prince H, Kashuba ADM. Validation of an LC-MS/MS Assay to Simultaneously Monitor the Intracellular Active Metabolites of Tenofovir, Emtricitabine, and Lamivudine in Dried Blood Spots. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017. October 31;149:40–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gandhi M, Ameli N, Bacchetti P, Anastos K, Gange SJ, Minkoff H, Young M, Milam J, Cohen MH, Sharp GB, Huang Y, Greenblatt RM. Atazanavir concentration in hair is the strongest predictor of outcomes on antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2011. May;52(10):1267–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.van Zyl GU, van Mens TE, McIlleron H, Zeier M, Nachega JB, Decloedt E, Malavazzi C, Smith P, Huang Y, van der Merwe L, Gandhi M, Maartens G. Low lopinavir plasma or hair concentrations explain second-line protease inhibitor failures in a resource-limited setting. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011. April;56(4):333–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gandhi M, Ameli N, Bacchetti P, Gange SJ, Anastos K, Levine A, Hyman CL, Cohen M, Young M, Huang Y, Greenblatt RM; Women's Interagency HIV Study (WIHS). Protease inhibitor levels in hair strongly predict virologic response to treatment. AIDS. 2009. February 20;23(4):471–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.https://www.nichd.nih.gov/research/supported/WIHS
- 11.Matuszewski. Standard line slopes as a measure of a relative matrix effect in quantitative HPLC-MS bioanalysis J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci, 830 (January (2)) (2006), pp. 293–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.LeBeau MA, Montgomery MA, Brewer JD. The Role of Variations in Growth Rate and Sample Collection on Interpreting Results of Segmented Analyses of Hair Forensic Sci Int. July 15:210(1-3):110–116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Slawson MH, Wilkins DG, Rollins DE. The Incorporation of Drugs into Hair: Relationship of Hair Color and Melanin Concentration to Phencyclidine Incorporation J Anal Toxicol (1998) 22 (6): 406–413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rollins DE, Wilkins DG, Krueger GG, Augsburger MP, Mizuno A, O’Neal C, Borges CR, Slawson MH. The Effect of Hair Color on the Incorporation of Codeine into Human Hair J Anal Toxicol (Nov-Dec 2003) 27 (8): 545–551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rothe M, Praqst F, Thor S, Hunger J. Effect of pigmentation on the drug deposition in hair of grey-haired subjects. Forensic Sci Int. 1997. January 17;84(1-3):53–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hubbard DL, Wilkins DG, Rollins DE. The Incorporation of Cocaine and Metabolites into Hair: Effects of Dose and Hair Pigmentation Drug Metab Dispos December 1, 2000. 28:1464–1469 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]