Fig. 7.
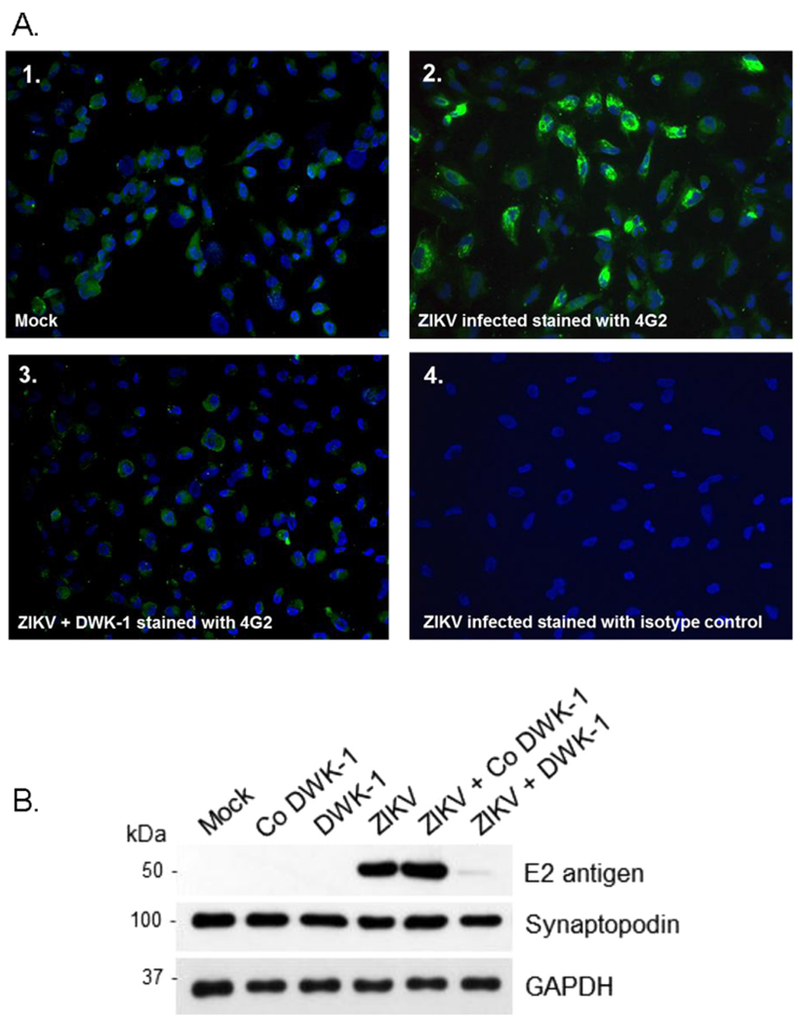
A. Immunostaining of ZIKV infected podocytes after treatment with DWK-1. Immunofluorescent staining of ZIKV infected podocytes using the 4G-2 antibody specific to the E protein of ZIKV. (1) Mock infected podocytes stained with 4G-2 antibody, (2) Podocytes infected with wildtype ZIKV for 72 h and stained with the 4G-2 antibody, (3) Podocytes pretreated with DWK-1 for 24 h, rinsed and infected with ZIKV for 72 h were stained with the 4G-2 antibody. (4) Isotype control for the 4G-2 antibody. Fluorescent images were taken on a Nikon TE2000S microscope mounted with a CCD camera at 200 × magnification. Nuclei (blue) were stained with DAPI. B. DWK-1 inhibits expression of E protein in ZIKV-infected podocytes. Western blot analysis of protein lysates from uninfected and ZIKV infected podocytes. Control protein lysates were prepared from mock infected podocytes and podocytes pretreated for 24 h with 10 μM DWK-1 or Co DWK-1, rinsed and cultured for additional 72 h without added morpholinos. Untreated podocytes or cells pretreated for 24 h with DWK-1 or Co DWK-1 were subsequently infected with ZIKV and protein lysates were prepared 72 h after ZIKV infection. The ZIKV expression of the E protein (E2 antigen) is shown in the top panel. The middle panel shows the podocyte biomarker Synaptopodin and the bottom panel shows GAPDH as a loading control.
