The character of the methylhydrazine carbothioamide moiety in the title compound is a thiosemicarbazone Schiff base was confirmed by its bond lengths and bond angles. In the crystal, molecules of the title compound are mediated into sheets parallel to the ab plane by N—H⋯S hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrazine carbothioamide, Schiff base, intermolecular interaction
Abstract
In the title compound, C10H13N3OS, the azomethine C=N double bond has an E configuration. The phenyl ring and methylhydrazine carbothioamide moiety [maximum deviation = 0.008 (2) Å] are twisted slightly with a dihedral angle of 14.88 (10)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked into sheets parallel to the ab plane via N—H⋯S hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions.
Chemical context
Schiff base compounds are very important and can be used for multidisciplinary applications. They are widely used in the food and dye industries and exhibit many types of biological activity (Gaur, 2000 ▸) such as antibacterial, antifungal, and antimalarial (Annapoorani & Krishnan, 2013 ▸). The azomethine C=N group of Schiff bases plays an important role in the biological activity. Metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones have also received much attention. The metal chelation typically improves the lipophilicity of the ligand and facilitates the penetration of the complexes into bacterial membranes (Lobana et al., 2009 ▸; Rogolino et al., 2017 ▸). Thiosemicarbazones have multi-donor characteristics because of the presence of nitrogen and sulfur atoms in their molecular backbone. This results in a variety of coordination modes and many different physiochemical properties (Sharma et al., 2016 ▸). As part of our ongoing studies on thiosemicarbazone Schiff bases (Arafath et al., 2018a
▸), we report herein the synthesis and structural determination of the title compound.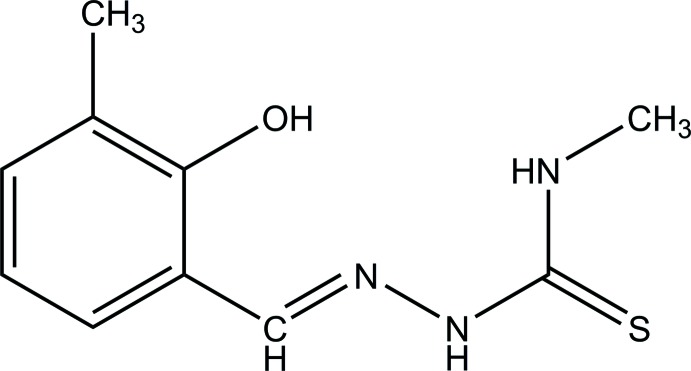
Structural commentary
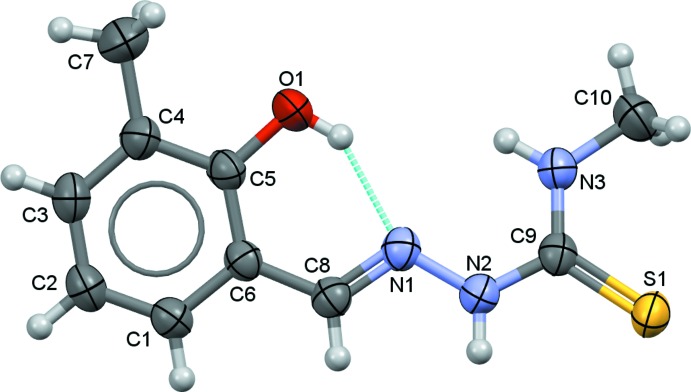
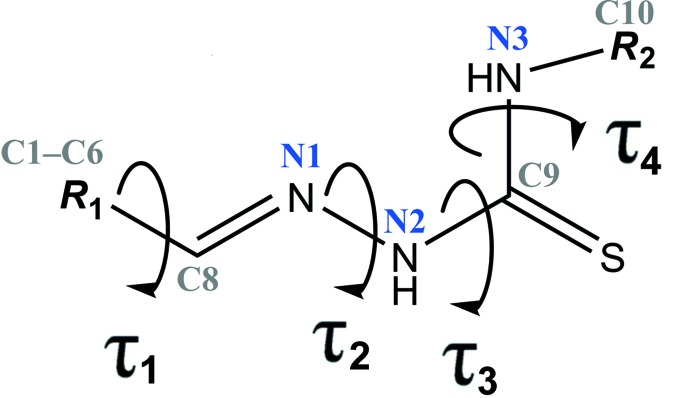
The title compound (I) crystallizes in the non-centrosymmetric orthorhombic space group Iba2 and exhibits an E configuration with respect to the azomethine C=N double bond (Fig. 1 ▸). The C8=N1 and C9=S1 bond lengths of 1.288 (3) and 1.689 (2) Å, respectively, confirm the presence of the double bonds while the C6—C8, N2—C9 and C9—N3 bond lengths of 1.452 (3), 1.354 (3) and 1.321 (3) Å, respectively, confirm their single-bond character. The C6—C8—N1 and N2—C9—N3 angles are 122.5 (2) and 117.8 (2)°, respectively, and are consistent with an sp 2-hybridized character for atom C8 and C9 (Arafath et al., 2018b ▸; Khalaji et al., 2012 ▸). The unique molecular conformation of (I) can be characterized by four torsion angles, viz. τ 1 (C5—C6—C8—N1), τ 2 (C8—N1—N2—C9), τ 3 (N1—N2—C9—N3) and τ 4 (N2—C9—N3—C10), respectively (Fig. 2 ▸). The torsion angles τ 3 and τ 4 are 0.4 (3) and 179.9 (2)°, signifying the planarity of the methylhydrazine carbothioamide moiety [N1—N2—(C9=S1)—N3—C10; mean deviation σ = 0.002 Å, maximum deviation = 0.008 (2) Å for atom C9]. τ 1 and τ 2 are slightly twisted [τ 1 = −4.2 (3) and τ 2 = 170.4 (2)°, respectively], and the C1–C6 phenyl ring and the methylhydrazine carbothioamide moiety subtend a dihedral angle of 14.88 (10)°. In the molecule, the hydroxy group acts as a hydrogen-bond donor for the adjacent hydrazine group, forming a intramolecular hydrogen bond with an S(6) ring motif (Fig. 1 ▸, Table 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
The atom labelling scheme and displacement ellipsoids of the molecular structure at the 50% probability level.
Figure 2.
General chemical diagram showing torsion angles, τ1, τ2, τ3 and τ4 in the title compound.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 phenyl ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1O1⋯N1 | 0.84 (4) | 1.94 (4) | 2.681 (3) | 147 (4) |
| N2—H1N2⋯S1i | 0.89 (3) | 2.51 (3) | 3.387 (2) | 173 (3) |
| C10—H10A⋯Cg1ii | 0.96 | 2.70 | 3.577 (4) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 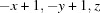 ; (ii)
; (ii) 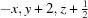 .
.
Supramolecular features
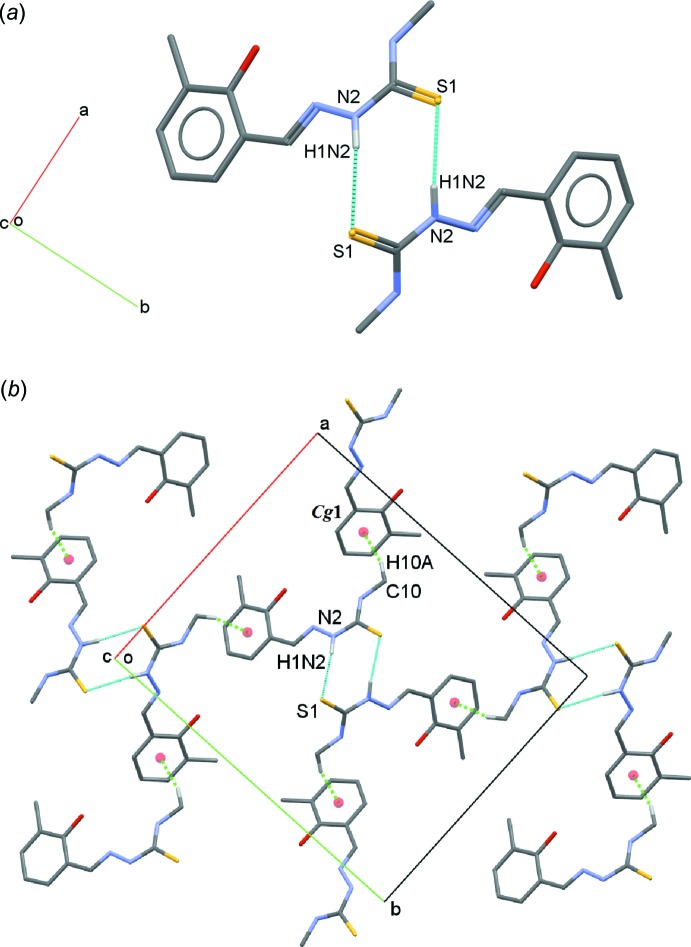
In the crystal, molecules are linked into dimers with an 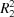 (8) ring motif via N2—H1N2⋯S1 hydrogen bonds (Fig. 3 ▸
a, Table 1 ▸). The dimers are connected into sheets parallel to the ab plane through C—H⋯π interactions (Fig. 3 ▸
b, Table 1 ▸).
(8) ring motif via N2—H1N2⋯S1 hydrogen bonds (Fig. 3 ▸
a, Table 1 ▸). The dimers are connected into sheets parallel to the ab plane through C—H⋯π interactions (Fig. 3 ▸
b, Table 1 ▸).
Figure 3.
(a) A view of a dimer of C10H13N3OS with N2—H1N2⋯S1 hydrogen bonds shown as cyan dotted lines. (b) A view of a dimeric sheet with C10—H10A⋯Cg1 interactions shown as green dotted lines. Hydrogen atoms not involved in with these interactions are omitted for clarity.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD version 5.39, last update February 2018; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) using (E)-2-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-(λ1-methyl)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide as reference moiety found 44 structures containing the 2-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazinecarbothioamide moiety with different substituents. The basic structural motif (E)-2-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-(λ1-methyl)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide is shown in Fig. 2 ▸ and the different substituents (R 1 and R 2) together with the torsion angles of the C—CH=N—NH—C(=S)—NH—C backbone are summarized in Table 2 ▸. In these structures, the torsion angle τ1 exists in either the syn-periplanar (range from 0 to 12°) or anti-periplanar (range from 167 to 179°) conformation. As for the torsion angle τ2, all structures adopt an anti-periplanar conformation (169–179°). Similar to the title compound, torsion angles τ3 and τ4 for most of the structures are syn-periplanar (0–16°) and anti-periplanar (171-180°), respectively. However, there are two outliers (YOCJOR and YOCJUX; (Chumakov et al., 2014 ▸)) where the 2-(2-hydroxybenzylidene) hydrazinecarbothioamide is substituted with a pyridine ring. In contrast to most of the structures, torsion angles τ3 and τ4 for YOCJOR and YOCJUX are anti-periplanar (178 and 177°, respectively) and syn-periplanar (1 and 3°, respectively).
Table 2. Torsion angles τ1, τ2, τ3 and τ4 (°).
| Compound | R 1 | R 2 | τ1 | τ2 | τ3 | τ4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | 2-hydroxy-3-methylbenzylidenyl | methyl | 4 | 170 | 0 | 180 |
| AWAZOP (Hussein & Guan, 2015 ▸) | 5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 1 | 175 | 12 | 179 |
| AWEBEL (Hussein & Guan, 2015 ▸) | 3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 176 | 174 | 4 | 180 |
| CIVZAK (Hussein et al., 2014b ▸) | 5-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 2 | 174 | 15 | 180 |
| CIWBAN (Hussein et al., 2014b ▸) | 5-allyl-3-ethyl-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 169 | 173 | 5 | 178 |
| DAGVOZ (Arafath et al., 2017b ▸) | 2-hydroxy-5-methoxy-3-nitrobenzylidenyl | methyl | 177 | 176 | 7 | 179 |
| EFUPAX (Rubčić et al., 2008 ▸) | 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidenyl | phenyl | 2 | 173 | 4 | 174 |
| EROVIR (Lo & Ng, 2011 ▸) | 5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 8 | 172 | 14 | 176 |
| GOZQIX (Hussein et al., 2015a ▸) | 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 3 | 175 | 14 | 180 |
| GOZQIX01 (Salam et al., 2016 ▸) | 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 3 | 175 | 15 | 180 |
| GOZQIX02 (Subhashree et al., 2017 ▸) | 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 2 | 175 | 13 | 180 |
| HABDEW (Hussein et al., 2015c ▸) | 3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 177 | 176 | 5 | 180 |
| HABFEY (Hussein et al., 2015c ▸) | 5-allyl-2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 173, 173 | 176, 179 | 6, 8 | 178, 177 |
| HAXROO (Vrdoljak et al., 2005 ▸) | 2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 1 | 176 | 11 | 178 |
| HAXROO01 (Liu, 2015 ▸) | 2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 2 | 175 | 11 | 178 |
| HAXSAB (Vrdoljak et al., 2005 ▸) | 2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 177 | 174 | 5 | 178 |
| IBAZUJ (Haque et al., 2015 ▸) | 2,3-dihydroxybenzyliden | methyl | 1 | 170 | 1 | 175 |
| IBEDOL (Haque et al., 2015 ▸) | 2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidenyl | methyl | 3, 2 | 175, 173 | 16, 16 | 175, 175 |
| IFUXEN (Tan et al., 2008b ▸) | 2,4-dihydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 2 | 179 | 0 | 176 |
| IFUXEN01 (Hussein et al., 2014b ▸) | 2,4-dihydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 2 | 179 | 0 | 176 |
| IFUXEN02 (Ramaiyer & Frank, 2015 ▸) | 2,4-dihydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 1 | 175 | 4 | 179 |
| IFUXEN03 (Ramaiyer & Frank, 2015 ▸) | 2,4-dihydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 5 | 171 | 6 | 178 |
| IGALUY (Tan et al., 2008c ▸) | 2,4-dihydroxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 5 | 174 | 9 | 176 |
| IGALUY01 (Salam et al., 2015 ▸) | 2,4-dihydroxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 2 | 177 | 16 | 178 |
| IMAFIN (El-Asmy et al., 2016 ▸) | 2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 1 | 177 | 13 | 177 |
| JAJHUA (Li et al., 2016 ▸) | 5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | methyl | 1 | 175 | 12 | 179 |
| JOFHIW (Tan et al., 2008a ▸) | 2,5-dihydroxybenzyliden | methyl | 1 | 175 | 11 | 178 |
| KOCLIY (Đilović et al., 2008 ▸) | 4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | phenyl | 2 | 172 | 12 | 174 |
| LAQCIR (Jacob & Kurup, 2012 ▸) | 5-bromo-2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidenyl | cyclohexyl | 172 | 177 | 4 | 179 |
| NUQNAP (Shawish et al., 2010 ▸) | 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 167 | 176 | 8 | 174 |
| OBOLOJ (Arafath et al., 2017a ▸) | 5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | cyclohexyl | 175 | 176 | 6 | 177 |
| PAXCAU (Jacob et al., 2012 ▸) | 5-bromo-2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidenyl | phenyl | 177 | 180 | 6 | 177 |
| RIVFAE (Seena et al., 2008 ▸) | 2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | phenyl | 2, 5, 2 | 179, 175, 178 | 12, 9, 2 | 171, 177, 180 |
| RIVFAE01 (Rubcic et al., 2008 ▸) | 2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | phenyl | 11, 3 | 177, 171 | 2, 2 | 175, 170 |
| SUKQOG (Hussein et al., 2015d ▸) | 5-allyl-2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidenyl | phenyl | 168 | 172 | 4 | 179 |
| WEXDAG (Orysyk et al., 2013 ▸) | 2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | allyl | 4 | 170 | 7 | 173 |
| XOTPED (Hussein et al., 2015b ▸) | 2-hydroxy-3-methylbenzylidenyl | ethyl | 2 | 179 | 7 | 179 |
| YOCJOR (Chumakov et al., 2014 ▸) | 5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | pyridin-2-yl | 0 | 179 | 178 | 1 |
| YOCJUX (Chumakov et al., 2014 ▸) | 2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidenyl | pyridin-2-yl | 3 | 178 | 177 | 3 |
| YOPHUI (Hussein et al., 2014a ▸) | 3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 4, 8 | 171, 169 | 4, 18 | 179, 180 |
| YOPLIA (Hussein et al., 2014a ▸) | 2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidenyl | ethyl | 4 | 171 | 10 | 180 |
| YUKYOU (Salam & Haque, 2015 ▸) | 3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 179 | 180 | 2 | 178 |
| YUXJOS (Arafath et al., 2018a ▸) | 3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | cyclohexyl | 12 | 170 | 12 | 176 |
| ZIJKIO (Li & Sato, 2013 ▸) | 5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 6 | 172 | 12 | 176 |
| ZIJKIO02 (Hussein et al., 2015b ▸) | 5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidenyl | ethyl | 7 | 173 | 13 | 177 |
Note: there is more than one torsion angle for compounds HABFEY, IBEDOL, RIVFAE, RIVFAE01 and YOPHUI because there are more than one independent molecules in their asymmetric units.
Synthesis and crystallization
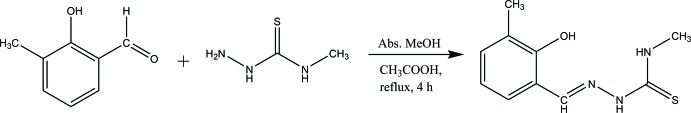
2-Hydroxy-3-methylbenzaldehyde (0.68 g, 5.00 mmol) was dissolved in 20.0 mL of methanol. 0.20 mL of glacial acetic acid was added and the mixture was refluxed for 30 minutes. A solution of 0.52 g (5.00 mmol) of N-methyl hydrazinecarbothioamide in 20.0 mL of methanol was added dropwise with stirring to the aldehyde solution (Fig. 4 ▸). The resulting colourless solution was heated under reflux for 4 h with stirring. The crude product was washed with 5.0 mL of n-hexane. The recovered product was dissolved in DMSO for purification and recrystallization. Light-yellow single crystals (m.p. 454–455 K; yield 94%) suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of the solvent.
Figure 4.
Reaction scheme for the synthesis of C10H13N3OS.
Analysis calculated for C10H13N3OS (FW: 223.29 g mol−1); C, 53.74; H, 5.83; N, 18.81; found: C, 53.71; H, 5.79; N, 18.83%. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d 6, Me4Si ppm): δ 11.38 (s, N—NH), δ 9.39 (s, OH), δ 8.34 (s, HC=N), δ 8.44 (q, CS–NH), δ 7.42–6.81 (multiplet, aromatic), δ 3.00 (d, J = 4.5 Hz, N—CH3), δ 2.20 (s, Ph—CH3). 13C NMR (DMSO-d 6, Me4Si ppm): δ 177.48 (C=S), δ 154.24 (C=N), δ 143.64–119.10 (C-aromatic), δ 31.05 (N—CH3), δ 15.91(Ph—CH3) ppm. IR (KBr pellets υmax/cm−1): 3418 υ(NH), 3133 υ(OH), 2983(NC—H3, sp3), 1618 υ(C=N), 1553 υ(C=C, aromatic), 1270 υ(C=S), 1251 υ(CH, bend., aromatic), 1085 υ(C—O). 1043 υ(C—N).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å) and refined using a riding model with U iso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5 U eq(C). All N- and O-bound H atoms were located from a difference-Fourier map and freely refined.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C10H13N3OS |
| M r | 223.29 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, I b a2 |
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 14.6474 (14), 17.522 (2), 8.9048 (8) |
| V (Å3) | 2285.4 (4) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.26 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.46 × 0.26 × 0.16 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.853, 0.879 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 14825, 3359, 2949 |
| R int | 0.020 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.705 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.033, 0.094, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 3359 |
| No. of parameters | 150 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.17, −0.16 |
| Absolute structure | Flack parameter determined using 1222 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.04 (3) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019004444/nr2074sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019004444/nr2074Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019004444/nr2074Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1485713
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C10H13N3OS | Dx = 1.298 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 223.29 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Iba2 | Cell parameters from 5563 reflections |
| a = 14.6474 (14) Å | θ = 2.3–29.5° |
| b = 17.522 (2) Å | µ = 0.26 mm−1 |
| c = 8.9048 (8) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 2285.4 (4) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 8 | 0.46 × 0.26 × 0.16 mm |
| F(000) = 944 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3359 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2949 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.020 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 30.1°, θmin = 1.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | h = −20→20 |
| Tmin = 0.853, Tmax = 0.879 | k = −23→24 |
| 14825 measured reflections | l = −12→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0497P)2 + 0.3888P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.094 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.06 | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 3359 reflections | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
| 150 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack parameter determined using 1222 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: 0.04 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.35594 (4) | 0.50006 (3) | 0.20442 (10) | 0.05018 (16) | |
| O1 | 0.45729 (12) | 0.77741 (11) | 0.6162 (3) | 0.0621 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.48391 (12) | 0.65142 (9) | 0.4511 (3) | 0.0414 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.46275 (13) | 0.59332 (10) | 0.3526 (2) | 0.0436 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.31035 (13) | 0.60707 (11) | 0.4029 (2) | 0.0459 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.69785 (15) | 0.72085 (14) | 0.6081 (2) | 0.0443 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.735599 | 0.683585 | 0.567182 | 0.053* | |
| C2 | 0.73506 (15) | 0.77658 (13) | 0.6987 (3) | 0.0493 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.797160 | 0.776261 | 0.720393 | 0.059* | |
| C3 | 0.67936 (16) | 0.83287 (14) | 0.7568 (3) | 0.0492 (5) | |
| H3A | 0.704945 | 0.871242 | 0.815398 | 0.059* | |
| C4 | 0.58596 (16) | 0.83349 (12) | 0.7297 (3) | 0.0479 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.54896 (14) | 0.77591 (12) | 0.6405 (3) | 0.0424 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.60427 (14) | 0.71939 (12) | 0.5768 (2) | 0.0380 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.5255 (2) | 0.89533 (18) | 0.7931 (5) | 0.0783 (10) | |
| H7A | 0.491901 | 0.918970 | 0.713173 | 0.117* | |
| H7B | 0.562565 | 0.932944 | 0.842504 | 0.117* | |
| H7C | 0.483746 | 0.873420 | 0.864103 | 0.117* | |
| C8 | 0.56962 (15) | 0.65960 (11) | 0.4793 (3) | 0.0410 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.610876 | 0.625925 | 0.435625 | 0.049* | |
| C9 | 0.37548 (14) | 0.57095 (11) | 0.3289 (2) | 0.0397 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.21430 (16) | 0.58990 (19) | 0.3892 (4) | 0.0647 (7) | |
| H10A | 0.179253 | 0.629791 | 0.435460 | 0.097* | |
| H10B | 0.201496 | 0.542285 | 0.438227 | 0.097* | |
| H10C | 0.198298 | 0.586205 | 0.284940 | 0.097* | |
| H1N2 | 0.5065 (18) | 0.5680 (16) | 0.307 (4) | 0.056 (8)* | |
| H1N3 | 0.3243 (19) | 0.6428 (16) | 0.471 (4) | 0.054 (7)* | |
| H1O1 | 0.444 (3) | 0.7429 (19) | 0.555 (5) | 0.076 (10)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0523 (3) | 0.0455 (3) | 0.0527 (3) | −0.0030 (2) | −0.0095 (3) | −0.0097 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0328 (8) | 0.0601 (11) | 0.0936 (16) | −0.0015 (7) | −0.0014 (8) | −0.0230 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0439 (9) | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0436 (8) | −0.0042 (6) | −0.0024 (9) | 0.0006 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0412 (9) | 0.0404 (9) | 0.0491 (10) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0030 (8) | −0.0060 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0409 (9) | 0.0495 (10) | 0.0475 (9) | 0.0000 (8) | −0.0055 (7) | −0.0078 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0380 (10) | 0.0490 (12) | 0.0460 (11) | 0.0012 (9) | 0.0008 (9) | 0.0009 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0379 (9) | 0.0576 (12) | 0.0525 (11) | −0.0059 (9) | −0.0058 (10) | 0.0016 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0478 (12) | 0.0485 (11) | 0.0513 (11) | −0.0119 (10) | −0.0057 (10) | −0.0017 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0446 (11) | 0.0416 (10) | 0.0575 (15) | −0.0049 (9) | 0.0020 (9) | −0.0064 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0327 (10) | 0.0401 (10) | 0.0544 (12) | −0.0048 (8) | 0.0031 (8) | 0.0002 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0357 (9) | 0.0380 (10) | 0.0401 (10) | −0.0037 (8) | 0.0010 (8) | 0.0033 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0642 (17) | 0.0641 (17) | 0.107 (3) | 0.0081 (14) | −0.0021 (18) | −0.0325 (17) |
| C8 | 0.0413 (10) | 0.0387 (9) | 0.0428 (11) | −0.0008 (8) | −0.0006 (8) | 0.0020 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0439 (10) | 0.0365 (9) | 0.0387 (9) | −0.0016 (8) | −0.0064 (8) | 0.0033 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0403 (12) | 0.0802 (18) | 0.0736 (17) | −0.0043 (12) | −0.0015 (12) | −0.0148 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C9 | 1.689 (2) | C2—H2A | 0.9300 |
| O1—C5 | 1.360 (3) | C3—C4 | 1.389 (3) |
| O1—H1O1 | 0.84 (4) | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C8 | 1.288 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.393 (3) |
| N1—N2 | 1.379 (3) | C4—C7 | 1.509 (4) |
| N2—C9 | 1.354 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.400 (3) |
| N2—H1N2 | 0.88 (3) | C6—C8 | 1.452 (3) |
| N3—C9 | 1.321 (3) | C7—H7A | 0.9600 |
| N3—C10 | 1.444 (3) | C7—H7B | 0.9600 |
| N3—H1N3 | 0.90 (3) | C7—H7C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.379 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.399 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9300 | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.381 (4) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C5—O1—H1O1 | 108 (3) | C4—C5—C6 | 121.21 (19) |
| C8—N1—N2 | 115.18 (18) | C1—C6—C5 | 118.25 (19) |
| C9—N2—N1 | 121.68 (18) | C1—C6—C8 | 118.35 (19) |
| C9—N2—H1N2 | 118.0 (19) | C5—C6—C8 | 123.40 (18) |
| N1—N2—H1N2 | 120.2 (19) | C4—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C9—N3—C10 | 124.2 (2) | C4—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C9—N3—H1N3 | 120.5 (18) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C10—N3—H1N3 | 115.1 (18) | C4—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.1 (2) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 119.4 | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—H1A | 119.4 | N1—C8—C6 | 122.5 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.4 (2) | N1—C8—H8A | 118.7 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.3 | C6—C8—H8A | 118.7 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.3 | N3—C9—N2 | 117.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.5 (2) | N3—C9—S1 | 123.86 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.3 | N2—C9—S1 | 118.37 (16) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.3 | N3—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.4 (2) | N3—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 121.2 (2) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 120.3 (2) | N3—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| O1—C5—C4 | 117.4 (2) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| O1—C5—C6 | 121.4 (2) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—N2—C9 | 170.4 (2) | O1—C5—C6—C1 | −179.2 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.4 (4) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.9 (4) | O1—C5—C6—C8 | 1.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.6 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C8 | −178.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | −179.8 (3) | N2—N1—C8—C6 | 178.06 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5—O1 | 179.6 (2) | C1—C6—C8—N1 | 176.1 (2) |
| C7—C4—C5—O1 | −1.1 (4) | C5—C6—C8—N1 | −4.2 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.2 (3) | C10—N3—C9—N2 | 179.9 (2) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 178.0 (3) | C10—N3—C9—S1 | 1.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.3 (3) | N1—N2—C9—N3 | 0.4 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C8 | 179.4 (2) | N1—N2—C9—S1 | 179.17 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 phenyl ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1O1···N1 | 0.84 (4) | 1.94 (4) | 2.681 (3) | 147 (4) |
| N2—H1N2···S1i | 0.89 (3) | 2.51 (3) | 3.387 (2) | 173 (3) |
| C10—H10A···Cg1ii | 0.96 | 2.70 | 3.577 (4) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, z; (ii) −x, y+2, z+1/2.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Universiti Sains Malaysia grants 1001/PKIMIA/811269 and USM-TWAS fellowship. The World Academy of Sciences grant USM-TWAS fellowship to Md. Azharul Arafath. Malaysian Government grant MyBrain15 to Huey Chong Kwong.
References
- Annapoorani, S. & Krishnan, C. (2013). Synthesis, 5, 180–185.
- Arafath, M. A., Adam, F. & Razali, M. R. (2017a). IUCrData, 2, x161997.
- Arafath, M. A., Adam, F., Razali, M. R., Ahmed Hassan, L. E., Ahamed, M. B. K. & Majid, A. M. S. A. (2017b). J. Mol. Struct. 1130, 791–798.
- Arafath, M. A., Kwong, H. C., Adam, F. & Razali, M. R. (2018a). Acta Cryst. E74, 687–690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Arafath, M. A., Kwong, H. C., Adam, F. & Razali, M. R. (2018b). Acta Cryst. E74, 1460–1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2012). Bruker AXS Inc., Madison. Wisconsin, USA.
- Chumakov, Y. M., Petrenko, P. A., Codita, T. B., Tsapkov, V. I., Poirier, D. & Gulea, A. P. (2014). Crystallogr. Rep. 59, 207–212.
- Đilović, I., Rubčić, M., Vrdoljak, V., Pavelić, S. K., Kralj, M., Piantanida, I. & Cindrić, M. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16, 5189–5198. [DOI] [PubMed]
- El-Asmy, A. A., Jeragh, B. & Ali, M. S. (2016). Private communication (Refcode CCDC 1478956. CCDC, Cambridge, England.
- Gaur, S. (2000). Asian J. Chem. 43, 250–254.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Haque, R. A., Salam, M. A. & Arafath, M. A. (2015). J. Coord. Chem. 68, 2953–2967.
- Hussein, M. A. & Guan, T. S. (2015). Eur. J. Chem. 6, 451–460.
- Hussein, M. A., Guan, T. S., Haque, R. A., Ahamed, M. B. K. & Majid, A. M. S. A. (2015a). Polyhedron, 85, 93–103.
- Hussein, M. A., Guan, T. S., Haque, R. A., Khadeer Ahamed, M. B. & Abdul Majid, A. M. S. (2014a). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 421, 270–283.
- Hussein, M. A., Guan, T. S., Haque, R. A., Khadeer Ahamed, M. B. & Abdul Majid, A. M. S. (2015b). Spectrochim. Acta A, 136, 1335–1348. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hussein, M. A., Iqbal, M. A., Asif, M., Haque, R. A., Ahamed, M. B. K., Majid, A. M. S. A. & Guan, T. S. (2015c). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon, 190, 1498–1508.
- Hussein, M. A., Iqbal, M. A., Umar, M. I., Haque, R. A. & Guan, T. S. (2015d). Arab. J. Chem. In the Press.
- Hussein, M. A., Guan, T. S., Haque, R. A., Ahamed, M. B. K. & Majid, A. M. S. A. (2014b). J. Coord. Chem. 67, 714–727.
- Jacob, J. M. & Kurup, M. R. P. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o836–o837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J. M., Sithambaresan, M. & Kurup, M. R. P. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1871–o1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Khalaji, A. D., Fejfarova, K. & Dusek, M. (2012). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 42, 263–266.
- Li, Z. & Sato, O. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-Y., Ohtsu, H., Kojima, T., Dai, J.-W., Yoshida, T., Breedlove, B. K., Zhang, W.-X., Iguchi, H., Sato, O., Kawano, M. & Yamashita, M. (2016). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 5184–5189. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-X. (2015). J. Struct. Chem. 56, 1420–1425.
- Lo, K. M. & Ng, S. W. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lobana, T. S., Sharma, R., Bawa, G. & Khanna, S. (2009). Coord. Chem. Rev. 253, 977–1055.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Orysyk, S. I., Bon, V. V., Zholob, O. O., Pekhnyo, V. I., Orysyk, V. V., Zborovskii, Y. L. & Vovk, M. V. (2013). Polyhedron, 51, 211–221.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ramaiyer, V. & Frank, R. (2015). Private communication (Refcode CCDC 1058555. CCDC, Cambridge, England.
- Rogolino, D., Gatti, A., Carcelli, M., Pelosi, G., Bisceglie, F., Restivo, F. M., Degola, F., Buschini, A., Montalbano, S., Feretti, D. & Zani, C. (2017). Sci. Rep. 7, 11214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rubčić, M., Đilović, I., Cindrić, M. & Matković-Čalogović, D. (2008). Acta Cryst. C64, o570–o573. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Salam, M. A. & Haque, R. A. (2015). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 435, 103–108.
- Salam, M. A., Hussein, M. A., Ramli, I. & Islam, M. S. (2016). J. Organomet. Chem. 813, 71–77.
- Salam, M. A., Hussein, M. A. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, 58–61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Seena, E. B., Prathapachandra Kurup, M. R. & Suresh, E. (2008). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 38, 93–96.
- Sharma, R., Lobana, T. S., Kaur, M., Thathai, N., Hundal, G., Jasinski, J. P. & Butcher, R. J. (2016). J. Chem. Sci. 128, 1103–1112.
- Shawish, H. B., Maah, M. J. & Ng, S. W. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Subhashree, G. R., Haribabu, J., Saranya, S., Yuvaraj, P., Anantha Krishnan, D., Karvembu, R. & Gayathri, D. (2017). J. Mol. Struct. 1145, 160–169.
- Tan, K. W., Ng, C. H., Maah, M. J. & Ng, S. W. (2008a). Acta Cryst. E64, o1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tan, K. W., Ng, C. H., Maah, M. J. & Ng, S. W. (2008b). Acta Cryst. E64, o2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tan, K. W., Ng, C. H., Maah, M. J. & Ng, S. W. (2008c). Acta Cryst. E64, o2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vrdoljak, V., Cindrić, M., Milić, D., Matković-Čalogović, D., Novak, P. & Kamenar, B. (2005). Polyhedron, 24, 1717–1726.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019004444/nr2074sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019004444/nr2074Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019004444/nr2074Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1485713
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report