Abstract
Nowadays most plant textiles used for clothing and household are made of cotton and viscose. Before the 19th century however, plant textiles were mainly made from locally available raw materials, in Scandinavia these were: nettle, hemp and flax. It is generally believed that in Viking and early Middle Ages Scandinavia hemp was used only for coarse textiles (i.e. rope and sailcloth). Here we present an investigation of 10 Scandinavian plant fibre textiles from the Viking and Early Middle Ages, believed to be locally produced. Up till now they were all believed to be made of flax. We show that 4 textiles, including two pieces of the famous Överhogdal Viking wall-hanging are in fact made with hemp (in three cases hemp and flax are mixed). This indicates that hemp was important, not only for coarse but also for fine textile production in Viking and Early Middle Ages in Scandinavia.
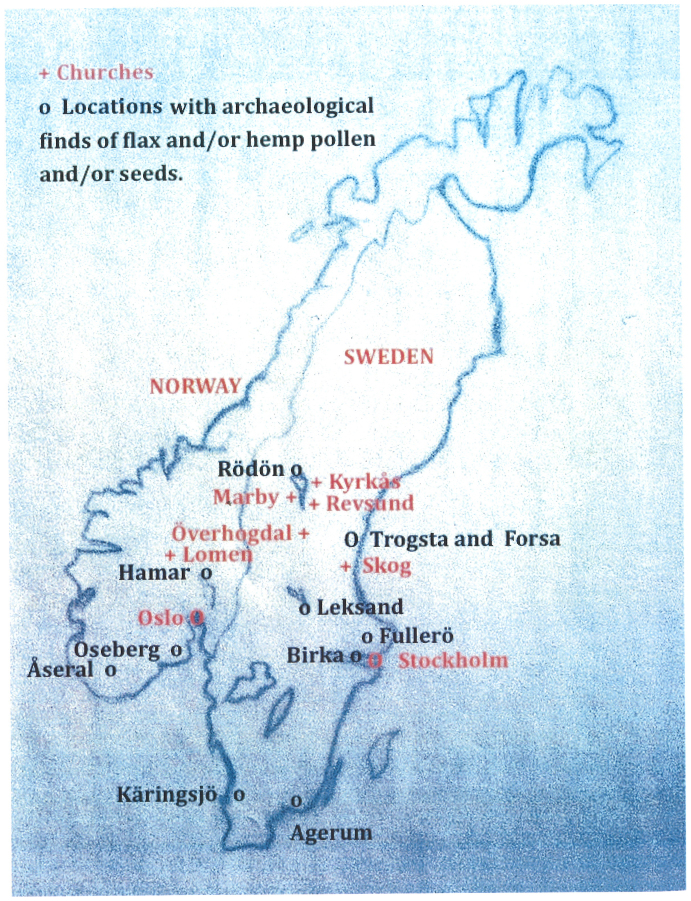
There is archaeological evidence, based mainly on the finds of pollen and seeds, that hemp (Cannabis sativa) and flax (Linum usitatissimum) were grown in northern Scandinavia (Norway and Sweden). An overview of the locations of different finds can be found on the map in Fig. 1.
Figure 1. Map of Northern Scandinavia (Sweden and Norway) showing the archaeological sites discussed in the main text and the churches where the textiles investigated were originally placed.
Map prepared for this publication by author GS. The Map outline was traced from Wikimedia file Scandinavia.svg (Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license, Author Hayden 120).
In Norway there are early finds of hemp and flax pollen from the inner Oslo Fjord area, about 350 BC–450 AD (considerably more hemp than flax pollen was found1). Pollen and hemp seeds were found in a settlement in Hamar from around 400 AD2. There are finds of hemp pollen from around 650 and 800 AD, from the inland of Åseral in Vest-Agder3 and both hemp and flax seeds were found in the famous Viking burial mound, the Oseberg ship in Vestfold county from around 800 AD4,5,6.
From Sweden in Jämtland, Rödön parish, near Lake Storsjön there are finds of hemp pollen, about 100–200 AD7. The first flax seeds were found in Hälsingland, in Trogsta about 200 century AD8,9. Another early find from Hälsingland of flax seeds, in a bog near a settlement in Forsa indicate that flax was cultivated and retted there about 300 AD8,10. There are also finds of bundles of flax from Kärinsjö, in the province of Halland, from about 200–300 AD8,11. From the Viking Age, 800–1050 AD there are more finds of hemp pollen and hemp seeds, for example from the area Lake Mälaren, near Stockholm, and in the area Lake Storsjön, near Rödön. In addition there are finds of pollen, seeds and fibres of hemp from the area of Lake Siljan in Dalarna7. Both flax and hemp seeds were found in the area south of Lake Siljan, near Leksand12.
The finds of hemp and flax pollen and seeds do not prove conclusively that textile production really took place. Only finds of retted fibres can do that. It is possible that the plants were grown for other purposes, i.e. the use of the seeds as food or oil. This applies both to hemp and flax. Unfortunately the preservation conditions in Scandinavia are such that plant fibre textiles normally do not survive well. There are some early remains of plant fibre textiles from Sweden from around 400–500 AD, from Fullerö in the province Uppland, and from Augerum in Blekinge in the south8. More textile remains are preserved from the Viking and Middle Ages, for example at the Viking site of Birka at Lake Mälaren13. There is also a find from Norway, in the Oseberg ship, from about 800 AD, consisting of a woven tapestry made of wool together with plant fibres, but the plant fibres were largely decomposed14.
Despite the archeological finds showing that hemp and flax were both grown in the north of Scandinavia in the Viking and Early Middle Ages and despite the fact that hemp fibres can be almost as fine as flax fibres15 it has hitherto generally been believed that hemp was used primarily for coarse textiles i.e. ropes and sailcloth4,16,17,18,19 and that flax was the common textile plant for fine clothing and household textiles in Northern Scandinavia in this period.
This is reflected in the fact that throughout the literature, including but not restricted to the literature on Scandinavian Viking and Early Middle Ages, most fine plant fibre textile remains are referred to as flax without any mentioning of analytical tests. One of the few exceptions from this is Agnes Geijer, who in the 1930s investigated the textile finds from the Swedish Viking settlement Birka, near Lake Mälaren. She introduced the term FH (Flax/Hemp) for all plant fibre material13 and called for a scientific method for proper identification “It was the difficulty involved in firmly distinguishing between the two bast species that led me to employ the cryptic designation FH (Flax/Hemp) in the original classification. Such finds were made in about forty-five graves.”20. To this day these fibres remain unidentified.
Part of the problem is that a systematic investigation of plant fibre textiles has been hampered by the difficulty of fibre identification. Fibres from animals (wool, fur and hair) and plant fibres in general can easily be distinguished because animal fibres have scales21, but to distinguish between individual plant fibres is much more difficult22. Samples have often been identified as flax purely on the basis of examinations with standard, white light, compound microscopy. This is insufficient to secure a proper identification23,43.
The 10 textiles that we investigate here are all woven and made of plant fibres combined with wool. They have been carbon-14 dated to 780–1420 AD4. They are believed to be locally produced on the basis of the patterns and textile techniques24. They all belonged to different churches and are among the oldest and finest preserved Scandinavian textiles found above ground. A considerable number of medieval textiles have been preserved in Swedish churches. The reason is that the Reformation in Sweden did not cause such immediate, drastic changes in the church décor as, in most other countries, for example Denmark25. The old church textiles in Sweden were widely used even after the Reformation26.
Results
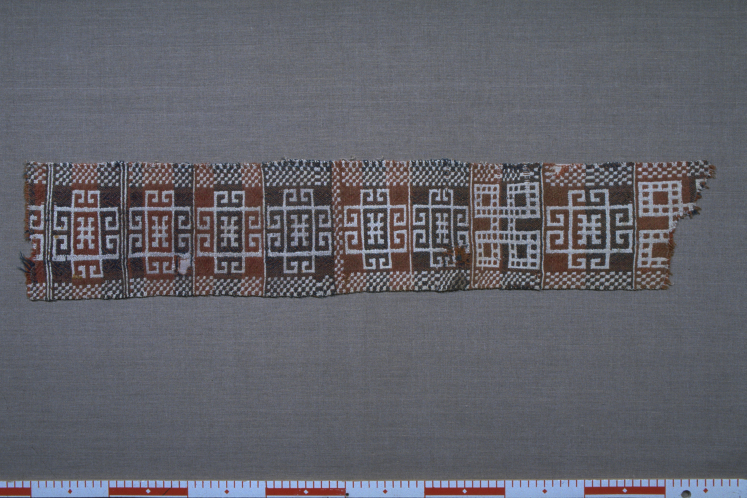
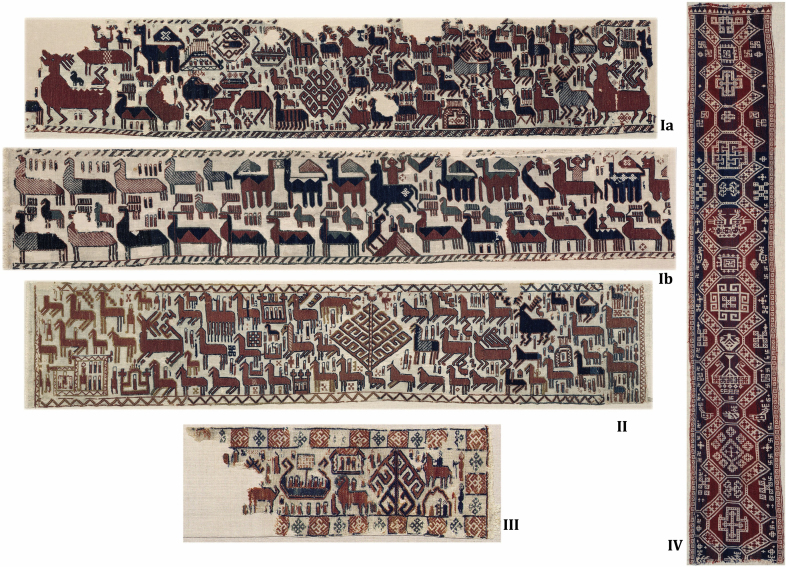
All 5 pieces of the famous Swedish Överhogdal Viking wall-hanging were examined, see Fig. 2 for a picture. For a picture of the Norwegain Lomen coverlet see Fig. 3 and for a picture of the Marby hanging, Fig. 4. For an overview of all textiles, including fibre identification, see Table 1. The locations where the textiles were found are indicated on the map in Fig. 1. In the literature all these textiles are listed as being flax, without any proper references to the methods that have been used for the fibre identifications.
Figure 2. The Överhogdal Viking wall-hangings.
The two top pieces Ia (Length: 164 cm (top edge, Width: 33, 4–33, 5 cm) and Ib (Length: 195 cm, Width: 33–35 cm) are shown to be made of a mixture of hemp and flax. For the other pieces only flax were found (see Table 1). Published with permission of Jamtli Museum, Sweden.
Figure 3. The Lomen coverlet (Length: 130 cm, Width: 82 cm).
Published with permission of the National Museum of Art, Architecture and Design, Oslo, Norway.
Figure 4. The Marby hanging (Length: 81–85 cm, Width: 16–17, 5 cm).
Published with permission of The Swedish History Museum © Gabriel Hildebrand/Statens Historiska Museum.
Table 1. Overview of all the analysis results: The samples are listed in chronological order. Microscopy images can be found in the online supplementary information.
| Textile items/Museum Inv. No. | Dated4 | Location See map (Fig. 1) Province/Country | Warp or Weft | Result Z/S |
| Revsund hanging | 780–980 | Revsund | Warp | Flax |
| Jamtli Museum, Östersund | Jämtland | S-twist | ||
| No. 76 | Sweden | |||
| Överhogdal wall-hanging Ia | 900–1100 | Överhogdal | Warp | Hemp and Flax |
| Jamtli Museum, Östersund | Härjedalen | Z-twist and S-twist | ||
| No. 8090 | Sweden | |||
| Överhogdal wall-hanging Ib | 900–1100 | Överhogdal | Warp | Hemp and Flax |
| Jamtli Museum, Östersund | Härjedalen | Z-twist and S-twist | ||
| No. 8090 | Sweden | |||
| Överhogdal wall-hanging II | 900–1100 | Överhogdal | ? | Flax |
| Jamtli Museum, Östersund | Härjedalen | S-twist | ||
| No. 8090 | Sweden | |||
| Överhogdal wall-hanging III | 900–1100 | Överhogdal | Warp | Flax |
| Jamtli Museum, Östersund | Härjedalen | S-twist | ||
| No. 8090 | Sweden | |||
| Överhogdal wall-hanging IV | 900–1100 | Överhogdal | Warp | Both Flax |
| Jamtli Museum, Östersund | Härjedalen | Weft | S-twist | |
| No. 8090 | Sweden | |||
| Kyrkås coverlet | 990–1160 | Jämtland/Sweden | ? | Flax |
| Nordiska Museet, Stockholm | S-twist | |||
| No. 33154: 1–4 | ||||
| Marby hanging | 1030–1160 | Jämtland/Sweden | ? | Hemp and Flax |
| The Swedish History museum, Stockholm | Z-twist and S-twist | |||
| No. 17786 | ||||
| Lomen coverlet | 1165–1260 | Valdres/Norway | ? | Hemp |
| The National Museum of Art, Architecture and Design, Oslo | Z-twist | |||
| No. 1217 | ||||
| Skog wall-hanging | 1240–1410 | Hälsingland/Sweden | Weft | Flax |
| The Swedish History museum, Stockholm | S-twist | |||
| No. 15275 |
Our results show that 4 of the 10 investigated textile samples contained hemp fibres. They do not differ in quality from the other textiles. The Lomen coverlet was the only sample were only hemp fibres were found. Three other samples were found to contain a mixture of hemp and flax: The Marby hanging and the Överhogdal wall-hangings Ia and Ib. In the other Överhogdal pieces only flax fibres were identified. This is an important result in its own right, since it provides an independent support for the theory that the pieces Ia and Ib are woven on the same warp4,24. To the best of our knowledge the Överhogdal and Marby measurements provide the first proof that mixed plant fibres were used in the Scandinavian Viking and Early Medieval Textile production.
It is possible that mixed fibres may have been used in other textiles as well and that we just did not find them. In some cases the museums only provided threads from the warp or weft. It is possible that different material may have been used in the warp and the weft. We can also not know for sure if the plant fibre material used in the examined textiles is really locally produced. In principle it could be imported. A strontium isotope analysis could possible one day provide the answer to this34.
Discussion
Our results show that the role of hemp in the Scandinavian cultural history needs to be reconsidered. Hemp was not used solely for the production of coarse textiles such as ropes and sailcloth; it was also used in the production of fine household textiles in Scandinavian Viking and Middle Ages. The big question, from a cultural history and historical research management point of view is: Why use one material instead of another? When hemp and when flax?
Until the true distribution of the use of hemp and flax in Scandinavia and other places has been properly investigated through detailed fibre identification analysis, we cannot hope to come up with a conclusive answer to this, but we may speculate on the reasons:
While hemp and flax can both grow well on most good soil suitable for crops35, hemp can also, to some extend grow on soils with high pH and muddy soils not suitable for many other crops without the need for much soil preparation (i.e. plowing, burn-beating, rotation of crop or lie fallow)36. This type of soil is often found in mountain areas and in coniferous forest areas, in swamps and marshes and around lakes. The Överhogdal wall-hangings and Lomen coverlet were found in mountain areas and in march- and lake rich areas. The literature says that hemp cultivation was especially common in Jämtland during the 1700s and 1800s because the area has the characteristic soil needed. For optimal growth of flax the requirements are different37. For example a nitrogen rich soil does not give a nice flax fibre35,36. Flax grows well in a climate with uniform high humidity and rainfall where early summer drought does not occur. The coastal area of Hälsingland, a region that was known for flax cultivation from the Middle Ages has such a climate and also weeding was not so important here, due to good availability of suitable soil and favorable crop rotation36,38.
The simple answer to the question “when hemp and when flax?” could be that the preference for hemp or flax varied depending on the local growth conditions.
In later times flax became the most common textile plant for clothes and household textiles. It became so common that the word linen, became essentially synonymous with a flax textile. The origin of the word “linen” is debated, but it seems that originally it simply meant a woven fabric of a plant fibre39. During the end of the eighteenth century in the European linen trade, flax and hemp was often blended40. In “The workwoman's guide” from 1840, in a chapter about different qualities of linen, it is written that “The Suffolk hemp is considered the best”41. In another earlier book “The English Housewife” from 1683, the author Markham describes linen and its characteristics and writes that housewives must become proficient in the design of all types of linen fabric, whether it be of hemp or flax, he writes; "For from these two only the largest cloth come, and do so both in England and in other countries"42.
Eventually flax and hemp lost their important position to cotton and nowadays the word linen is often used for a plain weave fabric of cotton and cloth made of flax sometimes mistakenly referred to as cotton.
To summarize: In this paper we have shown that hemp was used in Northern Scandinavia in the Viking and Early Middle Ages for the production of fine household textiles. Of the 10 textiles investigated, 4 were found to be made with hemp: The famous Swedish Överhogdal wall-hangings Ia and Ib, supporting the theory that the two pieces are woven on the same warp, the Marby hanging and the Norwegian Lomen coverlet. The three first textiles were found to be made with mixed fibres. To the best of our knowledge these measurements provide the first proof that mixed plant fibres were used in the Scandinavian Viking and Early Medieval Textile production. Our results show that the role of hemp in the Scandinavian cultural history needs to be reconsidered. More generally it demonstrates how the lack of proper fibre identification in textile research can lead to a distorted view of the relative importance of different textile plants.
Methods
Hemp and flax are both bast fibres. Bast fibres (with the exception of wood bast) originate from the stem of a plant. Bast fibres are very similar in appearance and cannot be distinguished conclusively using standard white light, compound microscopy, as discussed in the previous section. DNA analysis of bast fibres is usually not possible. It is generally difficult to extract DNA even from modern bast fibres27. Further, the removal of the fibres from the plant stem (retting) involves exposure to water, thus increasing the likelihood of extensive hydrolytic damage to the DNA28,29. Fortunately there is one characteristic feature, which can be used for identification purposes. The cell walls in bast fibres contain the so-called fibrils. Fibrils are bundles of cellulose chains. In one of the cell wall layers these cellulose bundles rotate around the fibre. This is referred to as S-twist or Z twist of a fibre. Flax and nettle are S-twist and hemp is Z-twist (Fig. 5).
Figure 5. Fibrillar orientations of bast fibres.
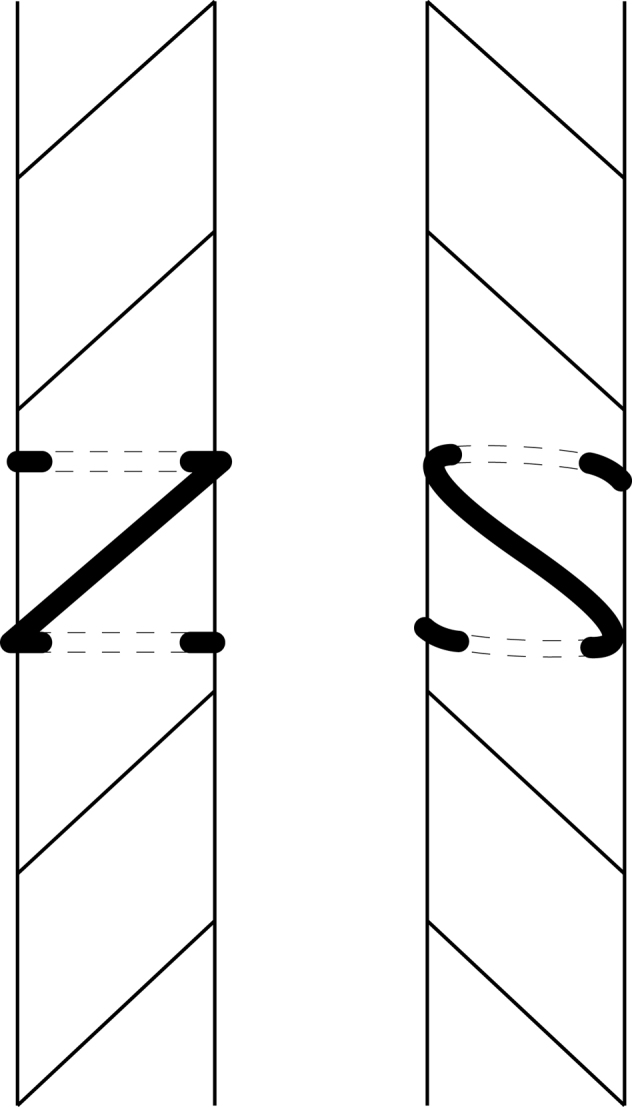
To the left: Z-twist, to the right, S-twist.
For more than 60 years the so-called modified Herzog test has been available as a way of measuring the fibrillar orientation of fibres using polarized light microscopy28. The modified Herzog test exploits the fact that the cellulose chains are bifringent. Unfortunately the Herzog test has not been widely used in the textile research community, except for a few cases, for example in reference30,31. Part of the problem with the Herzog test is that it was based on empirical evidence and sometimes it does not work. Recently one of the authors of this paper (Holst) and co-worker (Haugan) published an analytical model for the Herzog test32 showing why it works, why it never gives a false result and why it is sometimes not possible to identify a fibrillar orientation with the test.
In the modified Herzog test the fibre sample is placed between crossed polars and rotated to extinction (sample turns black). A red plate compensator is then inserted. A color change, dependent on the fibrillar orientation, will then occur in the sample part that was at extinction before. A S-twist fibre will turn yellow and a Z-twist fibre blue when close to parallel to the analyzer. The exact color change and angle will vary depending on the thickness of the fibre, cell membrane etc.32.
Samples of threads, about 1–3 cm long were collected from each textile by conservators at the associated museums. Single fibres were extracted from each sample and mounted on microscope slides following the procedure described in reference33. It is important that the mounting is done with great care. Only a few single fibre fragments, about 1–3 mm is needed for identification, but the older textile material tends to be brittle and this makes the procedure more difficult. All experiments were done using an Olympus BX-51P compound microscope equipped with a full wave compensator of wavelength 530 nm and objectives of the type UiS2 series, Ach N. After mounting, the microscope slides were labeled solely with numbers so that it was possible for one of the authors (Holst) and two assistants, who did not prepare the fibres to perform identifications as an independent blind test. The fibre identifications were also performed by the person who prepared the fibres (Skoglund). No conflicting measurements were obtained. For each sample 2–3 fibres were tested separately.
The fibrillar orientation of all textile samples could successfully be identified. The results are listed in Table 1. Note that strictly speaking we can only identify the hemp samples, since the samples with S-twist could in principle also be nettle15. A complete overview with images of all experimental results can be found in the online supplementary material for this paper.
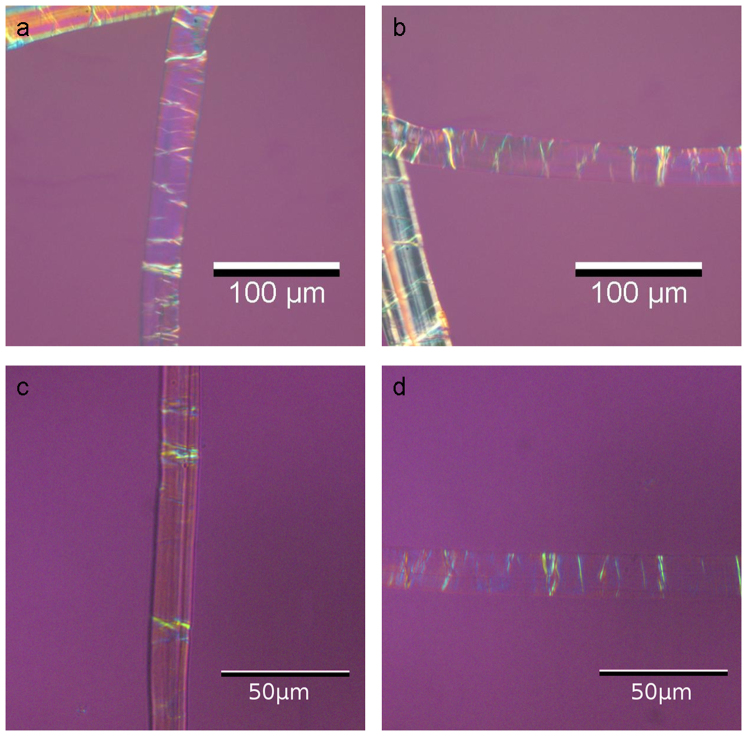
Images of the modified Herzog test performed on the Överhogdal wall-hanging Ia can be found in Fig. 6.
Figure 6. The modified Herzog Test performed on the Överhogdal Viking wall-hanging piece Ia.
The two top pictures (a and b) show a Z-twist fibre (Hemp) and the two bottom pictures (c and d) show a S-twist fibre (Flax). The analyzer is oriented vertically.
Supplementary Material
Online Supplementary Information for: Viking and Early Middle Ages Northern Scandinavian Textiles proven to be made with Hemp
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The Agnes Geijer Foundation for Nordic Textile Research History and Bergens Research Foundation. We thank the museums in Sweden and Norway for their support and for allowing us to borrow textile threads from their collections. We thank A. S. Dinger and A. S. Palau for additional fibre tests. We also thank A. S. Dinger for preparing the images used in Figure 6 and in the online supplementary material document.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author Contributions Authors G.S. and B.H. were responsible for writing the main manuscript text. G.S. was responsible for selecting the samples and preparing the microscopy slides. B.H. was responsible for the microscopy analysis, which was performed in cooperation with G.S. and two assistants (see acknowledgements). G.S. and M.N. were responsible for the interpretation of the data in a textile historical context.
References
- Hafsten U. Jordbrukskulturens historie i Oslo och Mjøstrakten belyst ved pollenanalytiske undersøkelser. Viking. Norsk arkeologisk årsbok. Oslo 70 (1958). [Google Scholar]
- Soltveg E.-C. Makrofossilanalyse av prøver fra hustomt I, II, III og V, Valum, Hamar k., Hedmark. Oppdragsrapport, Universitetet i Stavanger, Arkeologisk museum 1994, Arkeologisk museum i Stavanger. Stavanger (1994).
- Jessen C. & Stylegar F.-A. Ødegården Sosteli i Åseral fra romertid til vikingtid. Viking. Norsk arkeologisk årbok. Oslo 139 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Nockert M. & Possnert G. Att datera textilier. Gidlunds förlag. Södertälje 10, 69–89 (2002). [Google Scholar]
- Hafsten U. Jordbrukskulturens historie i Oslo och Mjøstrakten belyst ved pollenanalytiske undersøkelser. Viking. Norsk arkeologisk årsbok. Oslo 71 (1958). [Google Scholar]
- Brügger A. W. & Shetelig H. Osebergfundet. Bind V. Kristiania (1927). [Google Scholar]
- Robertsson A.-M. Vikingatida hampodling. Jämten. Östersund 183–188 (1992). [Google Scholar]
- Nockert M. The Högom find and other Migration Period textiles and costumes in Scandinavia. University of Umeå. Department of archaeology. Riksantikvarieämbetet. Umeå 66, 67 (1991). [Google Scholar]
- Liedgren L. Järnåldersgårdar i Hälsingland. Gårdar, borgar och hamnar i det äldsta Hälsingland. Red. G. Skoglund. Umeå (1981). [Google Scholar]
- Viklund K. Jordbrukskris i Norrland i slutet av den äldre järnåldern. Arkeologi i norr 2. Umeå 95–105 (1989). [Google Scholar]
- Arbman H. Käringsjön. Studier i halländsk järnålder. Kungl. Vitterhets-, historie-och antikvitetsakademiens handlingar. Stockholm (1945). [Google Scholar]
- Påhlsson I. Västannorstjärn: en pollenalytisk undersökning. Rapport. The Central Board of National Antiquities and the National Historical museum. RAÄ 1981:6. Stockholm 12 (1981). [Google Scholar]
- Geijer A. Birka III: Die Textilfunde aus den Gräbern, Untersuchungen und Studien/von Agnes Geijer. Vitterhets-, historie-och antikvitetsakademien. Stockholm (1938).
- Christensen A. E. & Nockert M. Osebergfunnet. Bd 4. Textilene. Kulturhistorisk museum. Oslo (2006). [Google Scholar]
- Bergfjord C. et al. Nettle as a distinct Bronze Age textile plant. Scientific Reports 2, 664 10.1038/srep00664 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson E. The common thread. Textile production during the Late Iron Age – Viking Age. Institutionen för arkeologi. Lund 36 (1999). [Google Scholar]
- Gutarp E. M. Medieval Manner of Dress, Documents, Images and Surviving Examples of Northern Europé, Emphasizing Gotland in the Baltic Sea. Gotlands Fornsals Förlag. Visby 46 (2001). [Google Scholar]
- Nylén Hemslöjd A.-M. Den svenska hemslöjden fram till 1800-talets slut av Anna-Maja Nylén. Stockholm (First published 1968) 118 (1995). [Google Scholar]
- Barber E. J. W. Prehistoric Textiles: the development of cloth in the Neolithic and Bronze Ages with special reference to Aegean. Princeton University Press, Princeton, N. J. 15 (1992). [Google Scholar]
- Geijer Agnes A. The Textile Finds from Birka. Cloth and Clothing in Medieval Europe. Essays in Memory of Professor E. M Carus-Wilson. London 87 (1983). [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. G. Handbook of Textile Fibres. 1. Natural Fibres. Redwood Books. Wiltshire. (First published 1959) 99 (1993). [Google Scholar]
- Catling D. & Grayson J. Identification of vegetable fibres. J. W. Arrowsmith Ltd. Bristol (1982). [Google Scholar]
- Bergfjord C. et al. Comment on ‘‘30,000-Year-Old Wild Flax Fibres’’. Science 325 634-b (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzen A.-M. & Nockert M. Bonaderna från Skog och Överhogdal. Almqvist & Wiksell Internationel. Stockholm (1992). [Google Scholar]
- Geijer A. Oriental Textiles in Sweden. Copenhagen 13 (1951).
- Estham I. Kyrkliga textilier: arv, utveckling och vård/Inger Estham; under medverkan av Gertrud Ingers och Gerd Reimers. Skeab. Stockholm (First published 1976) 12 (1980). [Google Scholar]
- Dunbar M. & Murphy T. M. DNA analysis of Natural Fiber Rope. Journal of Forensic Sciences 54, 108–13 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature 362, 709–715 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofreiter M., Serre D., Poinar H. N., Kuch M. & Pääbo S. S. Ancient DNA. Nature Reviews Genetics 2, 353–359 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog A. Mikrophotographischer Atlas der technisch wictigen Pflanzenfasern, second ed., Akademie-Verlag. Leipzig (1955). [Google Scholar]
- Goodway M. Fibre identification in practice. Journal of the American Institute for Conservation 26, 27–44 (1987). [Google Scholar]
- Haugan E. & Holst B. Determining the fibrillar orientation of bast fibres with polarized light microscopy: The modified Herzog test (red plate test) explained, Accepted. Journal of Microscopy 10.1111/jmi.12079 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergfjord C. & Holst B. A procedure for identifying textile bast fibres using microscopy: Flax, nettle/ramie, hemp and jute. Ultramicroscopy 110, 1192–1197 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson L. V., Hattori E. M., Taylor H. E., Poulson S. R. & Jolie E. A. Isotopesourcing of prehistoric willow and tule textiles recovered from western Greate Basin rock shelters and caves – proof of concept. Journal of Archealogical Science 33, 1588–1599 (2006). [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski S. & Carus M. Ecological benefits of hemp and flax cultivation and products. Nova-Institute (2011). http://eiha.org/attach/643/11-0513_Ecological_benefits_of_hemp_and_flax.pdf (Retrieved 2013-05-08). [Google Scholar]
- Fröier K. Lin och Hampa. Lts Förlag. Stockholm 91, 33 (1960). [Google Scholar]
- Frankow I. Ingrid 1982. Hampa som textilmaterial. Orsaker till användning. Materialets roll i självhushållet. Institutet för folklivsforskning. Stockholm 10, 10–12 (1982). [Google Scholar]
- Guinchard J. Sweden: historical and statistical handbook/Second part: industries. VII: 494 (1914). http://runeberg.org/sweden14/2/0508.html (Retrieved 2013-05-08). [Google Scholar]
- Geijer A. A History of Textile Art. (transl. by Roger Tanner) Pasold research fund in ass. with Sotheby Parke Bernet. London (1979).
- Montgomery F. Textiles in America, 1650–1870: a dictionary based on original documents, prints and paintings, commercial records, American merchant's papers, shopkeepers'advertisements, and pattern books with original swatches of cloth. Montgomery;foreword by Linda Eaton. W. W. Norton & Company Ltd. New York 277–278 (2007). [Google Scholar]
- The workwoman’s guide, containing instructions in cutting out and completing articles of wearing apparel, by a lady, Repr. Bloomfield books & Publ. Doncaster (First published 1840) (1975). [Google Scholar]
- Markham G. The english Housewife. Containing the inward and outward virtues which ought to be in a complete woman; as her skill in physic, cookery, banquetingstuff, distillation, perfumes, wool, hemp, flax, dairies, brewing, baking, and all other things belonging to a household. Printed for Hannah. London (Gervase Markham 1568–1637). [Google Scholar]
- Haugan E. & Holst B. Flax look-alikes: Pitfalls of ancient plant fibre identification. Archaeometry 10.1111/arcm.12054 (2013). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Online Supplementary Information for: Viking and Early Middle Ages Northern Scandinavian Textiles proven to be made with Hemp