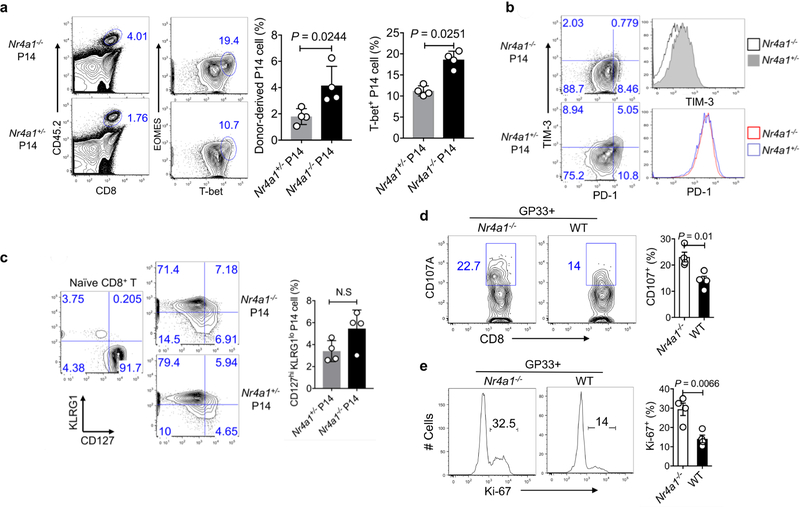
Extended Data Fig. 7. NR4A1 deficiency promotes CD8+ T cell effector function during viral infection.
a– c, Congenic CD45.1+B6SJL mice received equal amounts of CD45.2+ Nr4a1− /− cells or Nr4a1+/− P14 cells (1 × 104 per mouse) and were infected with LCMV-Armstrong at the dosage of 2 × 10 5 PFU. Eight days after infection, mice were euthanized and donor cells were assessed. a, Flow cytometry analysis and quantification of EOMES and T-bet expression in Nr4a1−/− and Nr4a1+/− P14 cells in the spleen. b, Flow cytometry analysis and quantification of PD-1 and TIM-3 expression in Nr4a1−/ − and Nr4a1+/− P14 cells in the spleen. c, Flow cytometry analysis and quantification of KLRG1 and CD127 expression in Nr4a1−/− and Nr4a1+/− P14 cells in the spleen. d, e, Chimeric mice were generated by transferring equal amounts of CD45.1+ wild-type and CD45.2+ Nr4a1−/− bone marrow cells into Rag1−/− mice. Eight weeks after reconstitution, mice were infected with LCMV-clone 13. Four weeks after infection, wild-type and Nr4a1−/− CD8+ T cells in the spleen were analysed by flow cytometry. d, Flow cytometry analysis of CD107A in splenic wild-type and Nr4a1−/− GP33+CD8+ T cells after GP33 peptide restimulation. e, Flow cytometry analysis of Ki-67 in splenic wild-type and Nr4a1−/− GP33 +CD8+ T cells after GP33 peptide restimulation. n = 4 per group. P values were calculated using a two-sided unpaired Student’s t-test. Data are representative of two individual experiments and graphs show mean ± s.d.