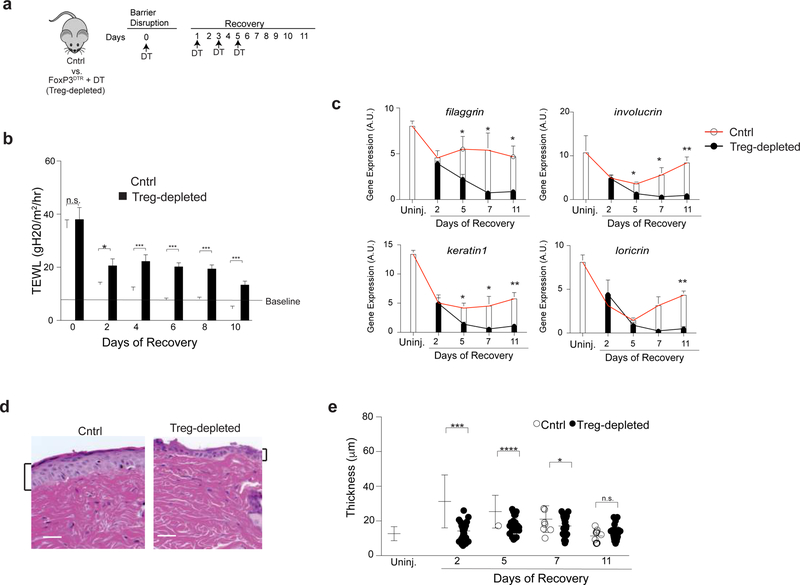
Figure 1. Regulatory T cells facilitate epidermal regeneration after injury.
(a) Schematic showing diphtheria toxin (DT) administration schedule after skin barrier disruption. Cntrl animals are DT-treated WT mice or FoxP3DTR littermates not given DT.
(b) Transepidermal water loss (TEWL) on the indicated days of recovery.
(c) qRT-PCR of epidermal differentiation genes normalized to β2m during barrier regeneration from the back affected back skin of Cntrl and Treg cell-depleted mice.
(d) Representative histology 2 days after barrier injury and
(e) quantification of epidermal thickness of affected back skin of Cntrl and Treg cell-depleted mice throughout the course of barrier repair. Results in b are representative of > 10 experiments (n=2–4 mice per group). Results in d & e are representative of 3 experiments (n = 3 mice per group) Scale bar in d is 50 μm. See also Supplementary Figures 1 and 2.