Abstract
NAD+ has gone in and out of fashion within the scientific community a number of times since its discovery in the early 1900s. Over the last decade, NAD+ has emerged as a potential target for combatting metabolic disturbances and the mitochondrial dysfunction that is mediated through sirtuin (SIRT) enzymes. The beneficial metabolic effects of the NAD+/SIRT axis have triggered an increased interest in NAD+ as an enhancer of energy metabolism. As a result, a myriad of publications have focused on NAD+ metabolism, with the majority of the work having been performed using in vitro models, and in vivo work largely consisting of interventions in Caenorhabditis elegans and rodents. Human intervention trials, on the other hand, are scarce. The aim of this review is to provide an overview of the state-of-the-art on influencing NAD+ metabolism in humans and to set the stage for what the future of this exciting field may hold.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s00125-019-4831-3) contains a slideset of the figures for download, which is available to authorised users.
Keywords: Diabetes, Energy metabolism, Human, Metabolic disease, NAD+, Review
Introduction
In recent years, a tremendous effort has been made to identify approaches for combatting metabolic disturbances and mitochondrial dysfunction, such as those seen in ageing [1] and type 2 diabetes mellitus [2, 3] by specifically targeting the sirtuin (SIRT) enzyme family [4]. SIRTs are NAD+-dependent deacetylating enzymes that regulate cellular metabolism [5]. To date, seven mammalian SIRT enzymes (SIRT1–7) have been identified, each having its own characteristic tissue and subcellular compartment expression, enzyme activity and targets. We kindly refer readers to Houtkooper et al [6] for a comprehensive review on SIRTs.
Several SIRT-targeting strategies have been deployed, demonstrating the metabolic benefits of SIRT activation. In mice, a SIRT1 gain-of-function mutation evoked a metabolic profile that protected against insulin-resistant diabetes by increasing hepatic insulin sensitivity, hepatic glucose tolerance and overall metabolic efficiency [7, 8]. Moreover, a proposed SIRT1 activator, SRT1720, increased mitochondrial respiration and improved insulin sensitivity [9], mimicking the signalling profile observed with caloric restriction [10] in high-fat-diet (HFD)-challenged mice. Resveratrol, an AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-activating polyphenol that activates SIRT1, improved skeletal muscle mitochondrial function in healthy obese men, in individuals with type 2 diabetes and in first-degree relatives of those with type 2 diabetes, although the observed metabolic health effects are inconsistent [11, 12]. Together, these studies indicate that SIRT activation promotes metabolic health.
Why NAD+?
The concept of influencing NAD+ bioavailability to activate the SIRTs was recently proposed for combatting metabolic disturbances and mitochondrial dysfunction in humans [13, 14]. This is supported by reports that decreased NAD+ bioavailability contributes to metabolic disturbances in ageing mice [15, 16] and humans [17, 18], and also in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes mellitus [16]. SIRTs are important consumers of NAD+ and depend on this rate-limiting substrate to act as metabolic sensors, responding to the level of available NAD+.
Considering the limited scope of this review, we will not digress into detail of the NAD+ metabolism and refer the reader to more comprehensive reviews on this topic [5, 19–21]. Briefly, however, as NADH is the predominant electron donor to the electron transport chain, NADH/NAD+ redox potential is an important indicator of the bioenergetic status of the cell and is tightly regulated [21]. The cytosolic and mitochondrial NADH/NAD+ and NADPH/NADP+ redox states are strongly connected. These states depend on the formation of NAD+ from NADH through cellular processes, such as the glycolytic enzyme activity, the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain [20], thereby exemplifying the essentiality of NAD+ and its redox potential within cellular metabolism. The NAD+ pool is maintained through a continuous process of biosynthesis and breakdown, stemming from the salvage and the Preiss–Handler pathways or from de novo biosynthesis at one end, and enzymatic consumption at the other [20] (Fig. 1). When NAD+ levels rise, SIRTs activate and deac(et)ylate or mono-ADP-ribosylate a variety of metabolic substrates, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) and forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1). This elicits an array of metabolic adaptations, including mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle [19] and enhanced oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle, brown adipose tissue and the liver [22, 23]. On a physiological level, this may lead to improved insulin sensitivity [24, 25], improved metabolic flexibility [26] and increased mitochondrial function [26, 27].
Fig. 1.
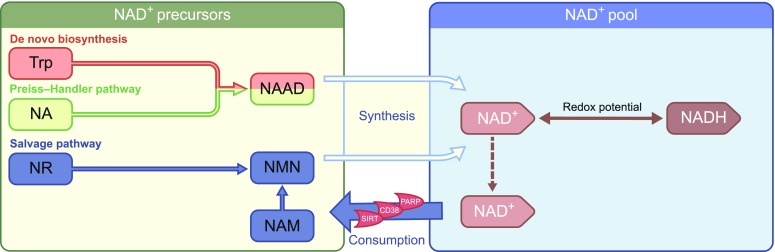
Summary of NAD+ metabolism. NAD+ can be synthesised from Trp through the de novo biosynthesis pathway in the liver and kidneys. Nicotinic acid (more commonly known as vitamin B3) enters the NAD+ pool through the Preiss–Handler pathway, whereas nicotinamide, nicotinamide riboside and NMN (re-)enter the NAD+ pool through the salvage pathway. NAD+ is consumed by SIRTs, CD38, and PARP enzymes, producing nicotinamide, which enters the pool of NAD+ precursors for resynthesis into NAD+. Dashed arrow, movement of NAD+ within the NAD+ pool. NA, nicotinic acid; NAAD, nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide; NAM, nicotinamide; NR, nicotinamide riboside. This figure is available as part of a downloadable slideset
NAD+ boosting strategies: preclinical evidence
Exercise and caloric restriction induce nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase expression through AMPK
Exercise and caloric restriction share a common denominator in that they affect AMPK activity, which can modulate NAD+ bioavailability (Fig. 2). To support this, AMPK activation in C2C12 myotubes increases cellular NAD+ levels and, in turn, activates SIRT1 and the subsequent PGC-1α-dependent upregulation of mitochondrial and lipid metabolism [28]. An increased demand for energy by the cell, such as during exercise, activates AMPK. With this in mind, it was shown that exercise induces the expression of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT), the rate-limiting enzyme that converts nicotinamide into NAD+ [29], thereby increasing NAD+ bioavailability [30, 31]. The induction of NAMPT expression through AMPK has been suggested to be a mechanistic adaptation to the metabolic stress derived from both exercise and caloric restriction [32–34]. Moreover, exercise in rats has been demonstrated to induce de novo biosynthesis of NAD+ from l-tryptophan (Trp), ultimately increasing NAD+ bioavailability [35].
Fig. 2.
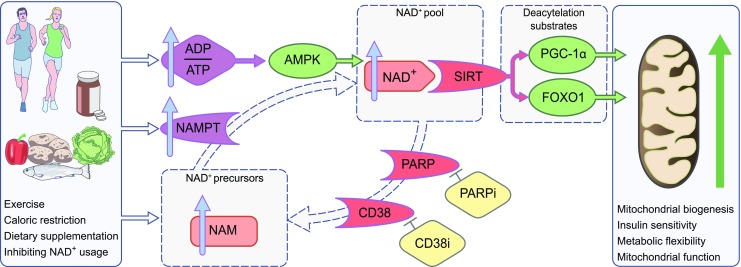
Effect of activating the NAD+/SIRT axis by increasing NAD+ bioavailability. Several approaches may be used to increase NAD+ bioavailability, including exercise, caloric restriction, dietary supplementation and inhibition of NAD+ consumption. These changes positively affect SIRT activation and subsequent PGC-1α and FOXO1 expression, resulting in mitochondrial changes and, as a consequence, metabolic adaptations. CD38i, CD38 inhibitor; FOXO1, forkhead box protein O1; NAM, nicotinamide; PARPi, PARP inhibitor. This figure is available as part of a downloadable slideset
NAD+ precursors increase NAD+ bioavailability and activate SIRTs
Various research groups have pursued sustained SIRT activation through an increase in endogenous NAD+ bioavailability. Preclinical research in ageing or HFD-challenged mice has shown that boosting NAD+ levels by supplementation with NAD+ precursors, such as nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) or nicotinamide riboside, attenuates age-related decline of muscle strength [1, 36], increases lifespan and healthspan [36]. In addition, oxidative metabolism and activation of SIRT1 and SIRT3 are enhanced in HFD-fed mice supplemented with NAD+ precursors [26]. In aged mice, NAD+ precursor supplementation also restored arterial SIRT1 activity, which was associated with improved vascular function and decreased aortic stiffness [37]. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of altering NAD+ bioavailability and subsequent SIRT activation.
More specifically, in HFD-fed mice, exogenous administration of the NAD+ precursor NMN was demonstrated to be a viable method of increasing endogenous NAD+ bioavailability and inducing SIRT1 activity, thereby attenuating the effects of the HFD and improving glucose tolerance and hepatic insulin sensitivity [16]. Long-term administration of NMN was also found to mitigate the age-associated decline in energy metabolism, insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism [36]. Similarly, supplementation of HFD-challenged mice with nicotinamide riboside (another NAD+ precursor), also improved hepatic insulin sensitivity [26]. Additionally, an improved glucose tolerance and lipid profile were observed in mouse models of age-induced type 2 diabetes upon NMN supplementation [16].
The NAD+ precursors nicotinic acid and nicotinamide have also been used to supplement HFD-challenged mice, increasing hepatic NAD+ levels and improving glucose tolerance. In one study, nicotinamide proved to be a more potent booster of NAD+ than nicotinic acid as it was also found to specifically alter the expression of SIRT1, SIRT2 and SIRT6 [38]. Lastly, Acipimox, a synthetic nicotinic acid analogue, has been shown to elevate NAD+ in C2C12 myotubes [39].
Together, these preclinical data suggest that dietary supplementation of NAD+ precursors can increase NAD+ levels and beneficially affect metabolic health.
Inhibition of NADases increases NAD+ bioavailability and SIRT1 activity
Preclinical research has explored compounds that can inhibit the NADases CD38 [40] and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1), reducing the enzymatic competition for their shared substrate, for example by reducing their NAD+-binding capacity, and thus enhancing SIRT1 activity (Fig. 2). Following this line of thought, a decrease in PARP-1 activity coincides with a rise in SIRT activity and NAD+ levels in worms [41] and mice [27], with PARP-1−/− mice displaying a leaner phenotype with higher energy expenditure compared with PARP-1+/+ mice. In line with this, in skeletal muscle, PARP-1 inhibitor-induced increases in SIRT1 activity were accompanied by improved mitochondrial function, enhanced energy expenditure and endurance performance [42]. In endothelial progenitor cells, PARP-1 inhibition also preserved cellular NAD+ content [43]. Similarly, Cd38 knockout mice have elevated NAD+ levels and are protected against HFD-induced metabolic inflexibility [44]. Moreover, the compounds apigenin, quercetin [45] and 78c [46] have all been demonstrated to enhance NAD+ levels and SIRT1 activity by inhibiting CD38.
How to boost NAD+ in humans?
Increasing NAD+ bioavailability through exercise and caloric restriction
Regular exercise and caloric restriction are well known to improve metabolic health in humans [47]. Alongside improving insulin sensitivity, metabolic flexibility and mitochondrial function, exercise also upregulates the expression of NAMPT in human skeletal muscle [48] (Fig. 2). Endurance-trained athletes have a twofold higher expression of NAMPT in skeletal muscle compared with baseline levels in sedentary obese, non-obese and type 2 diabetic individuals. After completing a 3 week training intervention, the non-obese group displayed increased NAMPT expression over baseline. NAMPT levels correlated positively with PGC-1α expression, mitochondrial content, maximal mitochondrial ATP synthesis in skeletal muscle and overall maximal aerobic capacity [48]. Concordantly, increased skeletal muscle SIRT3 content and PGC-1α expression were reported in men who were sedentary obese at baseline after a 12 week aerobic exercise intervention [49]. In a 6 week one-leg endurance exercise intervention, NAMPT protein levels only increased in the trained leg as compared with the untrained leg [34], further supporting the paradigm of activating the NAD+/SIRT axis through exercise and NAMPT induction.
Continuing, during a caloric restriction-induced weight-loss intervention, NAMPT and subsequent SIRT1 expression were found to be increased in adipose tissue of healthy obese participants [50] when compared with healthy lean participants. The participants were studied prior to, and after 5 months and 12 months, of the intervention, with the intervention resulting in a loss of 17.1% of body weight in the obese group. At baseline, gene expression of SIRT1, SIRT3, SIRT7 and NAMPT were significantly lower and PARP-1 activity significantly higher in the obese participants when compared with the lean group, indicating a state of low NAD+ bioavailability in obese individuals. With weight loss, SIRT1 expression increased, whereas PARP-1 activity declined in the subcutaneous adipose tissue of the obese group [50]. Evidence that a state of obesity or overnutrition indeed lowers NAD+ levels also comes from studies of longer-term overfeeding using an HFD for 8 weeks in young, healthy men. This resulted in reduced NAD+ levels and SIRT activity in skeletal muscle when compared with baseline [51]. This was further supported by PGC-1α hyperacetylation in the same skeletal muscle biopsies. Concurring with these findings, a study in young adult monozygotic twins (n = 26 obesity-discordant pairs and n = 14 obesity-concordant pairs) reported that obesity was associated with lower NAD+/SIRT axis activation in subcutaneous adipose tissue [14]. Together, these findings suggest that a state of energy abundance is prone to reduce the activity of the NAD+/SIRT axis and that inducing a state of energy demand may aid to restore NAD+ levels.
Supplementation of NAD+ precursors
From a human dietary perspective, Trp, nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and nicotinamide riboside are the predominant NAD+ precursors currently used in intervention trials, with nicotinamide riboside being the latest addition to the array of dietary NAD+ precursors (Fig. 1). The efficacy and safety of treatment with each of these NAD+ precursors are discussed in more detail below.
Nicotinamide
Phase 0 and phase 1 trials have demonstrated tolerance and safety of nicotinamide in daily pharmacological doses up to 3.5 g [52–56] and single doses of up to 6 g [57–59]. However, at doses above this, nicotinamide can become hepatotoxic [60].
Nicotinic acid and Acipimox
Nicotinic acid is the most effective pharmacological drug available for elevating HDL-cholesterol and lowering total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and triacylglycerol levels, thereby reducing the overall cardiovascular risk profile of the user [61]. However, nicotinic acid can elevate plasma glucose levels by inducing insulin resistance following a rebound increase in circulating NEFAs [62]. This poses a challenge when using nicotinic acid as (add-on to statin) therapy for dyslipidaemia in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance, impaired fasted glucose or type 2 diabetes, with the reduction in overall cardiovascular disease risk on one hand and compromised glycaemic control on the other. The worsening of hyperglycaemia with nicotinic acid use would possibly require additional therapeutic fine tuning to be implemented on an individual level to maintain glycaemic control. Alternatively, a reduction in the dose of nicotinic acid could improve glycaemic control, however, this may require acceptance of reciprocal compromise of the lipid profile or additional therapy to be initiated.
A large clinical trial evaluated the efficacy of nicotinic acid as a treatment for hypercholesterolaemia, with a daily dose of 1–3 g, for a duration of 96 weeks [63]. Overall, nicotinic acid was well tolerated. However, flushing was reported as a major adverse event. In contrast to nicotinamide, nicotinic acid is a vasoactive compound [64] and activates the G protein-coupled receptor, GPR109A, thereby inducing flushing [65]. In an attempt to reduce the occurrence of flushing and improve adherence, synthetic and extended- and sustained-release formulations of nicotinic acid were developed. Acipimox is a synthetic nicotinic acid analogue and, thereby, an NAD+ precursor that can be utilised by the Preiss–Handler pathway (Fig. 1). Although Acipimox displays the vasoactive properties that lead to flushing, we previously showed that treating individuals with type 2 diabetes with Acipimox for 2 weeks resulted in an improvement in skeletal muscle mitochondrial function [39]. In two other trials, Acipimox therapy improved insulin sensitivity [66, 67]. However, Acipimox is mainly used for lowering circulating NEFA levels and these human experiments do not allow us to conclude whether the beneficial effects observed were due to NAD+ boosting actions alone, although, in the first trial [39], the improved mitochondrial function with Acipimox therapy was accompanied with elevated (as opposed to lower) NEFA levels due to a known rebound effect. Unfortunately, the newer formulations of nicotinic acid have been associated with a higher occurrence of gastro-intestinal complaints, hepatotoxicity and hyperglycaemia, and a decreased HDL-cholesterol-raising efficacy compared with regular nicotinic acid [61]. Together, the side effects limit the use of nicotinic acid for further clinical exploration and implementation.
NADH
NADH supplementation has also been used to boost NAD+ levels in humans. In a small study, 80 adults with chronic fatigue syndrome received daily doses of 20 mg of NADH combined with 200 mg of coenzyme Q10 and were compared with placebo-treated individuals [68, 69]. The intervention improved reported fatigue [68] and increased maximal heart rate after 8 weeks of treatment [69] but did not alter body weight or blood pressure. Additionally, in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), the intervention significantly reduced NAD+ levels and increased NADH levels, thus, significantly lowering the NAD+/NADH ratio over baseline. Furthermore, ATP content and citrate synthase activity were significantly increased in PBMCs [68]. Unfortunately, it cannot be distinguished whether the observed results were solely attributed to NADH supplementation considering the co-administration of coenzyme Q10 in this study.
Nicotinamide riboside
In contrast to nicotinic acid, nicotinamide riboside is not vasoactive and does not cause flushing [70], thereby overcoming one of the adverse effects of nicotinic acid supplementation. In a recently published placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomised, phase 1 crossover trial, a daily dose of 1000 mg of nicotinamide riboside for 6 weeks was demonstrated to be well tolerated and adverse events were no more frequent than in the placebo arm [71]. These findings are confirmatory of the preceding phase 1 trials [72–74]. Additionally, nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (NAAD) has been confirmed as a reliable and sensitive biomarker for assessing changes in NAD+ levels following nicotinamide riboside supplementation [72].
Daily nicotinamide riboside supplementation of up to 2000 mg can effectively enhance blood NAD+ levels, achieving higher steady-state concentrations over baseline [73]. Concordantly, a more recent study demonstrated that nicotinamide riboside supplementation increased NAAD and NAD+ levels by ~60% in PBMCs. In this study, the effect of 6 weeks of nicotinamide riboside supplementation vs placebo was tested in healthy middle-aged and older adults. It was also found that 6 weeks of nicotinamide riboside supplementation tended to improve systolic blood pressure and pulse-wave velocity, both of which are markers of cardiovascular health [71]. However, no effect of nicotinamide riboside supplementation was found on physical performance outcomes, such as the 4 metre or 6 minute walk test, handgrip strength or maximum torque. Moreover, metabolic variables, such as during a treadmill exhaustion test, respiratory exchange ratio, and insulin sensitivity assessed by an IVGTT, did not differ between the groups. From these findings, it was concluded that long-term nicotinamide riboside supplementation is a viable strategy for enhancing NAD+ in humans and potentially has cardiovascular benefits that require further exploration in larger trials.
Most recently, an RCT of daily treatment with 2000 mg of nicotinamide riboside for 12 weeks was reported, evaluating safety, insulin sensitivity and other metabolic variables in 40 healthy, obese, middle-aged men [75]. Overall, nicotinamide riboside was well tolerated and only four adverse events were reported: pruritus, excessive sweating, bloating and transient changes in stools. Nicotinamide riboside supplementation increased NAD+ metabolism, as was seen by an increase in urinary metabolites. Using the hyperinsulinaemic–euglycaemic clamp technique, insulin sensitivity was found to be unchanged before and after supplementation and when compared with the placebo condition. In addition, resting energy expenditure and respiratory exchange ratio were not affected by nicotinamide riboside supplementation. Also, intrahepatic lipid content and body composition remained unchanged in the treatment group vs baseline and compared with the placebo group. Finally, a significant but modest increase in serum triacylglycerol levels was detected after nicotinamide riboside supplementation when compared with baseline values. The authors concluded that this study was underpowered and future studies should be larger and focus on other variables of metabolic health, such as intrahepatic lipid content, which showed significant changes in rodents [76, 77] treated with nicotinamide riboside and approached significance in this study.
Tryptophan
Another dietary NAD+ precursor, Trp, is an essential amino acid and is metabolised into NAD+ through de novo biosynthesis in the liver and kidneys [20]. This route is critical for maintaining the NAD+ pool, even though the conversion ratio of Trp to NAD+ is low in humans, averaging 60:1 [78]. Nonetheless, Trp is deemed capable of meeting the metabolic demands of NAD+ metabolism in nicotinic acid- and nicotinamide-deficient diets, and is well tolerated at high doses, between 30 and 50 mg/kg bodyweight, apart from drowsiness/sleepiness [79].
Recently, higher circulating Trp levels were identified as a predictive marker for the development of type 2 diabetes in a large prospective Chinese cohort [80]. However, to date, no dietary supplementation studies are available that directly assess whether boosting NAD+ through Trp might be metabolically beneficial in humans.
Inhibition of NAD+ consumers
The drawback of pharmacological strategies involving CD38 and PARP-1 inhibition is the original intended therapeutic use in malignancies [81, 82]. As such, no clinical trials with PARP-1 or CD38 inhibitors that focus on improving metabolic variables have been conducted in humans. This, however, does not imply that this strategy must be abandoned altogether, as a viable work-around to exploit the theoretical metabolic benefit of inhibition of NAD+ consumers may present itself in due time, allowing us to assess their efficacy in clinical trials.
Future perspective
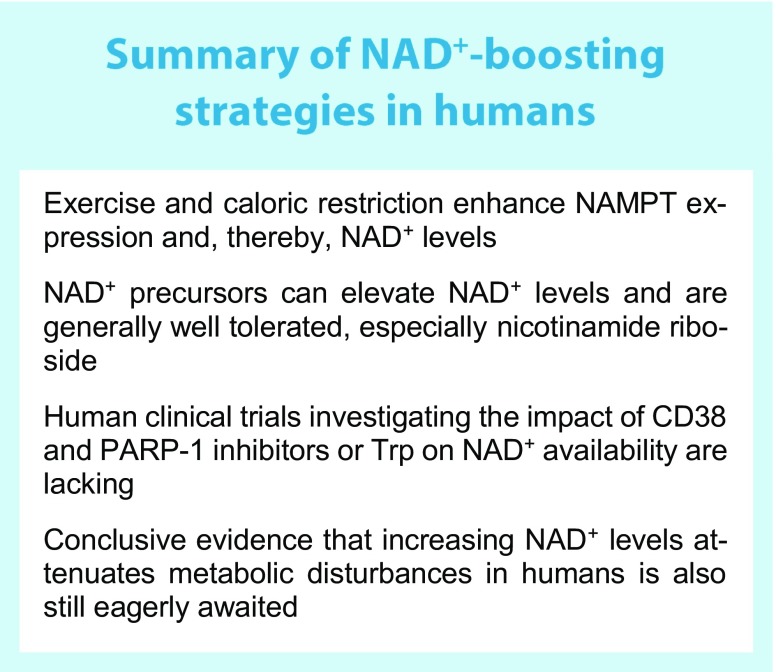
The current evidence base from preclinical research on NAD+ is setting the stage for trials in humans by identifying the points at which intervening in the NAD+ metabolism process seems to be clinically and physiologically relevant (see Summary text box). Even though many results have not been replicated in humans at this point in time, phase 0 and phase 1 trials have proven the feasibility and safety of NAD+ boosting in humans. As most evidence that increased NAD+ levels may be beneficial to human metabolism comes from indirect observations, such as exercise and weight loss interventions, the assessment of efficacy in well-powered phase 2 and phase 3 trials is urgently awaited in order to draw clear conclusions. Additionally, studies in metabolically disturbed individuals must be considered as these are more in line with the preclinical models used. To date, generally healthy populations have been included in studies in this area, in which the range of improvement may be too small to detect significant changes. The combination of strategies to increase NAD+, such as exercise, caloric restriction, or CD38 and PARP-1 inhibitors, with NAD+ precursor supplementation may also be considered, to evaluate added efficacy of such approaches, as seen in mice [15] (see Recommendations text box).
Currently, a number of clinical trials (Table 1) are underway in which NAD+ precursor supplementation is being used to improve (often disturbed) metabolic health variables. The coming years will prove whether the promising results observed in preclinical studies can indeed find human translation.
Table 1.
Overview of clinical trials on NAD+ metabolism in humans
| ClinicalTrials.gov registration no. | Title | Disease/condition | Interventions | Outcome measures | Sex | Participant age (years) and number | Study design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03540758 | Regulation of endogenous glucose production by central KATP channels | T2D; glucose metabolism disorders; high BG | Drugs: diazoxide ± nicotinic acid or placebo | EGP | M and F | 21–65 (adult, older adult) n = 45 |
Randomised, SGA, single maskeda, for basic science purposes |
| NCT03432871 | Nicotinamide riboside and mitochondrial biogenesis | Mitochondrial diseases | Dietary supplement: nicotinamide riboside | Bioavailability; safety (treatment-related AEs, blood analytes, temperature, BP, pulse); mitochondrial biogenesis (MRI, respiratory chain enzyme analysis, mitochondrial DNA quantification); mitochondrial disease symptoms (dynamometric measure of muscle strength, 6 minute walk test, QOL [SF-36; qualitative], TUG) | M and F | 18–70 (adult, older adult) n = 15 |
SGA, no masking (open label), for treatment purposes |
| NCT03310034 | NAD supplementation study (NADS) | Ageing | Dietary supplement: NAD+ precursors (nicotinic acid, nicotinamide and Trp) or control | Ex vivo mitochondrial respiration; basal metabolic rate; in vivo mitochondrial capacity; submaximal exercise energy expenditure; glucose tolerance; ectopic lipid accumulation; acetylcarnitine levels; physical function | M and F | 65–75 (older adult) n = 14 |
Randomised, crossover assignment, double maskingb, for basic science purposes |
| NCT03151707 | The effects of nicotinamide riboside supplementation on NAD+/NADH ratio and bioenergetics | Healthy | Drug: nicotinamide riboside | Brain NAD+/NADH ratio; brain PCr/ATP ratio; creatine kinase enzyme rate | M and F | 18–65 (adult, older adult) n = 60 |
SGA, no masking (open label), for treatment purposes |
| NCT03151239 | Effect of ‘nicotinamide mononucleotide’ (NMN) on cardiometabolic function | Glucose metabolism disorders | Dietary supplement: NMN or placebo | Insulin sensitivity; beta cell function | F | 55–75 (adult, older adult) n = 50 |
Randomised, parallel assignment, triple maskingc, for basic science purposes |
| NCT02950441 | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and skeletal muscle metabolic phenotype (NADMet) | Ageing | Dietary supplement: nicotinamide riboside or placebo | Mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle (high resolution respirometry); skeletal muscle NAD+ levels in vastus lateralis biopsy (targeted metabolomics); response to OGTT/HOMA-IR; lipid profile; muscle arterio-venous difference (tissue-specific metabolite trafficking, O2 consumption, CO2 production); muscle biopsy (adaptive expression profile [genomic]); RMR (indirect calorimetry); NAD+ metabolomics, changes in steroid ratios in 24 h urine collection (GC/MS); muscle strength (grip testing) | Male | 70–80 (older adult) n = 12 |
Randomised, crossover assignment, quadruple maskingd, for treatment purposes |
| NCT02835664e | Nicotinamide riboside and metabolic health | Obesity; insulin resistance | Dietary supplement: nicotinamide riboside or placebo | Muscle and liver insulin sensitivity; ex vivo muscle mitochondrial function; ectopic lipid accumulation; BAT activity; cardiovascular risk variables; whole body EE; body composition; acetylcarnitine levels | M and F | 45–65 (adult, older adult) n = 15 |
Randomised, crossover assignment, quadruple maskingd, for treatment purposes |
| NCT02689882e | Pharmacokinetic study of nicotinamide riboside | Metabolic disturbance | Dietary supplement: nicotinamide riboside | Average Css of nicotinamide riboside and NAD following up-titration to 1000 mg by mouth twice daily; serum levels of K+, creatine kinase, glucose, uric acid and ALT | M and F | 21–50 (adult) n = 8 |
SGA, no masking (open label) |
| NCT02303483e | The effect of vitamin B3 on substrate metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and body composition in obese men | Obesity | Dietary supplement: nicotinamide riboside or placebo | Insulin sensitivity; substrate metabolism; body composition; activation of satellite cells; lipid accumulation in liver and skeletal muscle; glucose turnover; insulin signalling in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue biopsies; palmitate turnover; gut microbiota; incretin hormone secretion | M | 40–70 (adult, older adult) n = 40 |
Randomised, parallel assignment, quadruple maskingd, for treatment purposes |
| NCT02300740e | Pharmacokinetic analysis of nicotinamide riboside | Healthy | Dietary supplement: nicotinamide riboside | Serum nicotinamide riboside; metabolites of nicotinamide riboside; AUC for serum nicotinamide riboside; T1/2, Cmax and Tmax of serum nicotinamide riboside |
M | 18–30 (adult) n = 12 |
Randomised, crossover assignment, no masking (open label), for treatment purposes |
| NCT01321034e | Effect of niacin in the lipoprotein (a) concentration | Hypercholesterolaemia | Drug: niacin/laropiprantf | Absolute and relative Lp(a) lowering effect of niacin/laropiprant at 1 g/20 mg and 2 g/40 mg per day in participants with normal, high and very high Lp(a) (<1.07 μmol/l, 1.07–2.14 μmol/l and > 2.14 μmol/l, respectively) and depending on number of KIV-2 repeated copies on the apo(a) gene | M an F | 18–80 (adult, older adult) n = 90 |
SGA, no masking (open label), for treatment purposes |
| NCT01216956e | Metabolic effects of an 8 week Niaspan treatment in patients with abdominal obesity and mixed dyslipidemia | Obesity and dyslipidaemia | Drug: ER nicotinic acid or placebo | NEFA and triacylglycerol concentrations over time; insulin sensitivity; lipoprotein metabolism; lipid profile | M | 18–65 (adult, older adult) n = 24 |
Randomised, crossover assignment, double maskingb, for treatment purposes |
| NCT00618995e | A study to evaluate the effects of ER niacin/laropiprant, laropiprant, ER niacin, and placebo on urinary prostanoid metabolites (0524A-079) | T2D | Drug: ER niacin + laropiprantf or ER niacin or laropiprantf or placebo | 11-dTxB2; PGIM | M and F | 18–65 (adult, older adult) n = 26 |
Randomised, crossover assignment, double maskingb, for treatment purposes |
| NCT00485758e | Extended niacin/laropiprant in patients with type 2 diabetes (0524A-069) | T2D | Drug: ER niacin/laropiprantf or placebo (unspecified) | LDL-c; HDL-c; triacyclglycerol | M and F | 18–80 (adult, older adult) n = 796 |
Randomised, parallel assignment, double maskingb, for treatment purposes |
Data are from trials registered on ClinicalTrials.gov
aParticipant only
bParticipant and investigator
cParticipant, care provider and investigator
dParticipant, care provider, investigator and outcomes assessor
eTrial has been completed
fLaropiprant: prostaglandin D2 receptor subtype DP1 receptor antagonist that combats nicotinic acid-induced flushing
AE, adverse event; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BAT, brown adipose tissue; BG, blood glucose; Css, steady-state concentration; 11-dTxB2, urinary 11-dehydrothromboxane B2; EE, energy expenditure; EGP, endogenous glucose production; ER, extended-release; F, female; HDL-c, HDL-cholesterol; KIV-2, kringle IV type 2; LDL-c, LDL-cholesterol; Lp(a), lipoprotein(a); M, male; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PCr, phosphocreatine; PGIM, prostaglandin I metabolite; QOL, quality of life; RMR, resting metabolic rate; SF-36, short form (36) health survey questionnaire; SGA, single group assignment; T2D, type 2 diabetes; TUG, timed up and go test
Electronic supplementary material
(PPTX 403 kb)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support from the Netherlands Cardiovascular Research Initiative: an initiative with support of the Dutch Heart Foundation (CVON2014-02 ENERGISE).
Abbreviations
- AMPK
AMP-activated protein kinase
- HFD
High-fat diet
- NAMPT
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase
- NMN
Nicotinamide mononucleotide
- PARP-1
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1
- PBMC
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- PGC-1α
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α
- SIRT
Sirtuin
- Trp
l-Tryptophan
Contribution statement
All authors were responsible for drafting the article and revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the version to be published.
Duality of interest
The authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Frederick DW, Loro E, Liu L, et al. Loss of NAD homeostasis leads to progressive and reversible degeneration of skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2016;24(2):269–282. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lowell BB, Shulman GI. Mitochondrial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Science. 2005;307(5708):384–387. doi: 10.1126/science.1104343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hesselink MK, Schrauwen-Hinderling V, Schrauwen P. Skeletal muscle mitochondria as a target to prevent or treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(11):633–645. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Milne JC, Lambert PD, Schenk S, et al. Small molecule activators of SIRT1 as therapeutics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2007;450(7170):712–716. doi: 10.1038/nature06261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Houtkooper RH, Auwerx J. Exploring the therapeutic space around NAD+ J Cell Biol. 2012;199(2):205–209. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201207019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Houtkooper RH, Pirinen E, Auwerx J. Sirtuins as regulators of metabolism and healthspan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(4):225–238. doi: 10.1038/nrm3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Banks AS, Kon N, Knight C, et al. SirT1 gain of function increases energy efficiency and prevents diabetes in mice. Cell Metab. 2008;8(4):333–341. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.08.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pfluger PT, Herranz D, Velasco-Miguel S, Serrano M, Tschop MH. Sirt1 protects against high-fat diet-induced metabolic damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(28):9793–9798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802917105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Minor RK, Baur JA, Gomes AP, et al. SRT1720 improves survival and healthspan of obese mice. Sci Rep. 2011;1(1):70. doi: 10.1038/srep00070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Smith JJ, Kenney RD, Gagne DJ, et al. Small molecule activators of SIRT1 replicate signaling pathways triggered by calorie restriction in vivo. BMC Syst Biol. 2009;3(1):31. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-3-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.de Ligt M, Bruls YMH, Hansen J, et al. Resveratrol improves ex vivo mitochondrial function but does not affect insulin sensitivity or brown adipose tissue in first degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol Metab. 2018;12:39–47. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Timmers S, de Ligt M, Phielix E, et al. Resveratrol as add-on therapy in subjects with well-controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(12):2211–2217. doi: 10.2337/dc16-0499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Imai S. “Clocks” in the NAD world: NAD as a metabolic oscillator for the regulation of metabolism and aging. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1804(8):1584–1590. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.10.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jukarainen S, Heinonen S, Ramo JT, et al. Obesity is associated with low NAD+/SIRT pathway expression in adipose tissue of BMI-discordant monozygotic twins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(1):275–283. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Camacho-Pereira J, Tarrago MG, Chini CCS, et al. CD38 dictates age-related NAD decline and mitochondrial dysfunction through an SIRT3-dependent mechanism. Cell Metab. 2016;23(6):1127–1139. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yoshino J, Mills KF, Yoon MJ, Imai S. Nicotinamide mononucleotide, a key NAD+ intermediate, treats the pathophysiology of diet- and age-induced diabetes in mice. Cell Metab. 2011;14(4):528–536. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhu XH, Lu M, Lee BY, Ugurbil K, Chen W. In vivo NAD assay reveals the intracellular NAD contents and redox state in healthy human brain and their age dependences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(9):2876–2881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417921112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Massudi H, Grant R, Braidy N, Guest J, Farnsworth B, Guillemin GJ. Age-associated changes in oxidative stress and NAD+ metabolism in human tissue. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e42357. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mouchiroud L, Houtkooper RH, Auwerx J. NAD+ metabolism: a therapeutic target for age-related metabolic disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;48(4):397–408. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.789479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Houtkooper RH, Canto C, Wanders RJ, Auwerx J. The secret life of NAD+: an old metabolite controlling new metabolic signaling pathways. Endocr Rev. 2010;31(2):194–223. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Canto C, Menzies KJ, Auwerx J. NAD+ metabolism and the control of energy homeostasis: a balancing act between mitochondria and the nucleus. Cell Metab. 2015;22(1):31–53. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Feige JN, Lagouge M, Canto C, et al. Specific SIRT1 activation mimics low energy levels and protects against diet-induced metabolic disorders by enhancing fat oxidation. Cell Metab. 2008;8(5):347–358. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ratajczak J, Joffraud M, Trammell SA, et al. NRK1 controls nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinamide riboside metabolism in mammalian cells. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1):13103. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schenk S, McCurdy CE, Philp A, et al. Sirt1 enhances skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in mice during caloric restriction. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(11):4281–4288. doi: 10.1172/JCI58554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang RH, Kim HS, Xiao C, Xu X, Gavrilova O, Deng CX. Hepatic Sirt1 deficiency in mice impairs mTorc2/Akt signaling and results in hyperglycemia, oxidative damage, and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(11):4477–4490. doi: 10.1172/JCI46243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Canto C, Houtkooper RH, Pirinen E, et al. The NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside enhances oxidative metabolism and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity. Cell Metab. 2012;15(6):838–847. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bai P, Canto C, Oudart H, et al. PARP-1 inhibition increases mitochondrial metabolism through SIRT1 activation. Cell Metab. 2011;13(4):461–468. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Canto C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Feige JN, et al. AMPK regulates energy expenditure by modulating NAD+ metabolism and SIRT1 activity. Nature. 2009;458(7241):1056–1060. doi: 10.1038/nature07813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Revollo JR, Grimm AA, Imai S. The NAD biosynthesis pathway mediated by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase regulates Sir2 activity in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(49):50754–50763. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408388200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Frederick DW, Davis JG, Davila A, Jr, et al. Increasing NAD synthesis in muscle via nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase is not sufficient to promote oxidative metabolism. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(3):1546–1558. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.579565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Costford SR, Brouwers B, Hopf ME, et al. Skeletal muscle overexpression of nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase in mice coupled with voluntary exercise augments exercise endurance. Mol Metab. 2018;7:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.10.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fulco M, Cen Y, Zhao P, et al. Glucose restriction inhibits skeletal myoblast differentiation by activating SIRT1 through AMPK-mediated regulation of Nampt. Dev Cell. 2008;14(5):661–673. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Canto C, Jiang LQ, Deshmukh AS, et al. Interdependence of AMPK and SIRT1 for metabolic adaptation to fasting and exercise in skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2010;11(3):213–219. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.02.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brandauer J, Vienberg SG, Andersen MA, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase regulates nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase expression in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2013;591(20):5207–5220. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.259515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ito Y, Yonekura R, Maruta K, et al. Tryptophan metabolism was accelerated by exercise in rat. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;527:531–535. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0135-0_61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mills KF, Yoshida S, Stein LR, et al. Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice. Cell Metab. 2016;24(6):795–806. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.de Picciotto NE, Gano LB, Johnson LC, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation reverses vascular dysfunction and oxidative stress with aging in mice. Aging Cell. 2016;15(3):522–530. doi: 10.1111/acel.12461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yang SJ, Choi JM, Kim L, et al. Nicotinamide improves glucose metabolism and affects the hepatic NAD-sirtuin pathway in a rodent model of obesity and type 2 diabetes. J Nutr Biochem. 2014;25(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.van de Weijer T, Phielix E, Bilet L, et al. Evidence for a direct effect of the NAD+ precursor acipimox on muscle mitochondrial function in humans. Diabetes. 2015;64(4):1193–1201. doi: 10.2337/db14-0667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Haffner CD, Becherer JD, Boros EE, et al. Discovery, synthesis, and biological evaluation of thiazoloquin(az)olin(on)es as potent CD38 inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2015;58(8):3548–3571. doi: 10.1021/jm502009h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fang Evandro F, Scheibye-Knudsen M, Brace Lear E, et al. Defective mitophagy in XPA via PARP-1 hyperactivation and NAD+/SIRT1 reduction. Cell. 2014;157(4):882–896. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pirinen E, Canto C, Jo YS, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases improves fitness and mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2014;19(6):1034–1041. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zha S, Li Z, Cao Q, Wang F, Liu F. PARP1 inhibitor (PJ34) improves the function of aging-induced endothelial progenitor cells by preserving intracellular NAD+ levels and increasing SIRT1 activity. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0961-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chiang SH, Harrington WW, Luo G, et al. Genetic ablation of CD38 protects against western diet-induced exercise intolerance and metabolic inflexibility. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0134927. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Escande C, Nin V, Price NL, et al. Flavonoid apigenin is an inhibitor of the NAD+ ase CD38: implications for cellular NAD+ metabolism, protein acetylation, and treatment of metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 2013;62(4):1084–1093. doi: 10.2337/db12-1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tarrago MG, Chini CCS, Kanamori KS, et al. A potent and specific CD38 inhibitor ameliorates age-related metabolic dysfunction by reversing tissue NAD+ decline. Cell Metab. 2018;27(5):1081–1095. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.03.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Smith RL, Soeters MR, Wust RCI, Houtkooper RH. Metabolic flexibility as an adaptation to energy resources and requirements in health and disease. Endocr Rev. 2018;39(4):489–517. doi: 10.1210/er.2017-00211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Costford SR, Bajpeyi S, Pasarica M, et al. Skeletal muscle NAMPT is induced by exercise in humans. Am J Phys Endocrinol Metab. 2010;298(1):E117–E126. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00318.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Vargas-Ortiz K, Perez-Vazquez V, Figueroa A, Diaz FJ, Montano-Ascencio PG, Macias-Cervantes MH. Aerobic training but no resistance training increases SIRT3 in skeletal muscle of sedentary obese male adolescents. Eur J Sport Sci. 2018;18(2):226–234. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2017.1406007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rappou E, Jukarainen S, Rinnankoski-Tuikka R, et al. Weight loss is associated with increased NAD+/SIRT1 expression but reduced PARP activity in white adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(3):1263–1273. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Seyssel K, Alligier M, Meugnier E, et al. Regulation of energy metabolism and mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle during lipid overfeeding in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(7):E1254–E1262. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-4379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mendola G, Casamitjana R, Gomis R. Effect of nicotinamide therapy upon B-cell function in newly diagnosed type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1989;32(3):160–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00265087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pozzilli P, Visalli N, Ghirlanda G, Manna R, Andreani D. Nicotinamide increases C-peptide secretion in patients with recent onset type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 1989;6(7):568–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1989.tb01229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Vague P, Picq R, Bernal M, Lassmann-Vague V, Vialettes B. Effect of nicotinamide treatment on the residual insulin secretion in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1989;32(5):316–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00265549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Pozzilli P, Visalli N, Signore A, et al. Double blind trial of nicotinamide in recent-onset IDDM (the IMDIAB III study) Diabetologia. 1995;38(7):848–852. doi: 10.1007/s001250050362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Visalli N, Cavallo MG, Signore A, et al. A multi-centre randomized trial of two different doses of nicotinamide in patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes (the IMDIAB VI) Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 1999;15(3):181–185. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-7560(199905/06)15:3<181::AID-DMRR31>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Stratford MR, Rojas A, Hall DW, et al. Pharmacokinetics of nicotinamide and its effect on blood pressure, pulse and body temperature in normal human volunteers. Radiother Oncol. 1992;25(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(92)90193-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Dragovic J, Kim SH, Brown SL, Kim JH. Nicotinamide pharmacokinetics in patients. Radiother Oncol. 1995;36(3):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(95)01581-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Petley A, Macklin B, Renwick AG, Wilkin TJ. The pharmacokinetics of nicotinamide in humans and rodents. Diabetes. 1995;44(2):152–155. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.2.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Winter SL, Boyer JL. Hepatic toxicity from large doses of vitamin B3 (nicotinamide) N Engl J Med. 1973;289(22):1180–1182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311292892208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Birjmohun RS, Hutten BA, Kastelein JJ, Stroes ES. Efficacy and safety of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol-increasing compounds: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45(2):185–197. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.10.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Poynten AM, Gan SK, Kriketos AD, et al. Nicotinic acid-induced insulin resistance is related to increased circulating fatty acids and fat oxidation but not muscle lipid content. Metabolism. 2003;52(6):699–704. doi: 10.1016/S0026-0495(03)00030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Capuzzi DM, Guyton JR, Morgan JM, et al. Efficacy and safety of an extended-release niacin (Niaspan): a long-term study. Am J Cardiol. 1998;82(12):74U–81U. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(98)00731-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ranchoff RE, Tomecki KJ. Niacin or niacinamide? Nicotinic acid or nicotinamide? What is the difference? J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(1):116–117. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(86)80149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Benyo Z, Gille A, Bennett CL, Clausen BE, Offermanns S. Nicotinic acid-induced flushing is mediated by activation of epidermal langerhans cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70(6):1844–1849. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.030833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Santomauro AT, Boden G, Silva ME, et al. Overnight lowering of free fatty acids with Acipimox improves insulin resistance and glucose tolerance in obese diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1999;48(9):1836–1841. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.48.9.1836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Cusi K, Kashyap S, Gastaldelli A, Bajaj M, Cersosimo E. Effects on insulin secretion and insulin action of a 48-h reduction of plasma free fatty acids with Acipimox in nondiabetic subjects genetically predisposed to type 2 diabetes. Am J Phys Endocrinol Metab. 2007;292(6):E1775–E1781. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00624.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Castro-Marrero J, Cordero MD, Segundo MJ, et al. Does oral coenzyme Q10 plus NADH supplementation improve fatigue and biochemical parameters in chronic fatigue syndrome? Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;22(8):679–685. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Castro-Marrero J, Saez-Francas N, Segundo MJ, et al. Effect of coenzyme Q10 plus nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide supplementation on maximum heart rate after exercise testing in chronic fatigue syndrome - a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Clin Nutr. 2016;35(4):826–834. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2015.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Bogan KL, Brenner C. Nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and nicotinamide riboside: a molecular evaluation of NAD+ precursor vitamins in human nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr. 2008;28(1):115–130. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.28.061807.155443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Martens CR, Denman BA, Mazzo MR, et al. Chronic nicotinamide riboside supplementation is well-tolerated and elevates NAD+ in healthy middle-aged and older adults. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1286. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03421-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Trammell SA, Schmidt MS, Weidemann BJ, et al. Nicotinamide riboside is uniquely and orally bioavailable in mice and humans. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1):12948. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Airhart SE, Shireman LM, Risler LJ, et al. An open-label, non-randomized study of the pharmacokinetics of the nutritional supplement nicotinamide riboside (NR) and its effects on blood NAD+ levels in healthy volunteers. PLoS One. 2017;12(12):e0186459. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Dellinger RW, Santos SR, Morris M, et al. Repeat dose NRPT (nicotinamide riboside and pterostilbene) increases NAD+ levels in humans safely and sustainably: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2017;3(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41514-017-0016-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Dollerup OL, Christensen B, Svart M, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial of nicotinamide riboside in obese men: safety, insulin-sensitivity, and lipid-mobilizing effects. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018;108(2):343–353. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Zhou CC, Yang X, Hua X, et al. Hepatic NAD+ deficiency as a therapeutic target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in ageing. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173(15):2352–2368. doi: 10.1111/bph.13513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gariani K, Menzies KJ, Ryu D, et al. Eliciting the mitochondrial unfolded protein response by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide repletion reverses fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatology. 2016;63(4):1190–1204. doi: 10.1002/hep.28245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Fukuwatari T, Shibata K. Nutritional aspect of tryptophan metabolism. Int J Tryptophan Res. 2013;6(Suppl 1):3–8. doi: 10.4137/IJTR.S11588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Fernstrom JD. Effects and side effects associated with the non-nutritional use of tryptophan by humans. J Nutr. 2012;142(12):2236S–2244S. doi: 10.3945/jn.111.157065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Chen T, Zheng X, Ma X, et al. Tryptophan predicts the risk for future type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 2016;11(9):e0162192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, et al. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(2):123–134. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0900212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.McKeage K. Daratumumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2016;76(2):275–281. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(PPTX 403 kb)