Abstract
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida is a temperature-dependent opportunistic pathogen which is associated with a variety of diseases in fish. During the development of “white nodules” disease, the expression of htpG in P. plecoglossicida was found to be significantly up-regulated at its virulent temperature of 18°C. The infection of htpG-RNAi strain resulted in the onset time delay, reduction in mortality and infection symptoms in spleen of Epinephelus coioides, and affected the bacterial tissue colonization. In order to reveal the effect of htpG silencing of P. plecoglossicida on the virulence regulation in P. plecoglossicida and immune response in E. coioides, dual RNA-seq was performed and a pathogen-host integration network was constructed. Our results showed that infection induced the expression of host genes related to immune response, but attenuated the expression of bacterial virulence genes. Novel integration was found between host immune genes and bacterial virulence genes, while IL6, IL1R2, IL1B, and TLR5 played key roles in the network. Further analysis with GeneMANIA indicated that flgD and rplF might play key roles during the htpG-dependent virulence regulation, which was in accordance with the reduced biofilm production, motility and virulence in htpG-RNAi strain. Meanwhile, IL6 and IL1B were found to play key roles during the defense against P. plecoglossicida, while CELA2, TRY, CPA1, CPA2, and CPB1 were important targets for P. plecoglossicida attacking to the host.
Keywords: pathogen-host molecular integration, dual RNA-seq, Pseudomonas plecoglossicida, Epinephelus coioides, htpG
Introduction
To date, infection of ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis) (1), large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) (2), orange spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) (3), and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) (4) with Pseudomonas plecoglossicida has been reported. Outbreaks of P. plecoglossicida infection in cage-farmed large yellow croaker are mainly recorded in the seawater temperature range of 15–20°C, which is characterized by granulomas in internal organs and lead to severe economic losses (5). In order to find an effective way to prevent or cure the “white nodules” disease, and reduce the economic losses caused by P. plecoglossicida infection, it is critical to understand the mechanism underlying P. plecoglossicida induced “white nodules” disease (6, 7). Multiple strategies have been adopted to investigate the virulence regulation of P. plecoglossicida, including genomics, secretomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. Moreover, some studies have investigated the immune response of the host to P. plecoglossicida infection with RNA-seq. However, these efforts did not directly reflect the intense struggle between the pathogen and the host.
Environmental adaptation has been reported to play an important role in the survival of pathogens, especially in the constantly changing host internal environment (8, 9). When an infection occurs, the gene expression patterns of both the pathogen and the host change dynamically, so that both sides engage in mutual attack (10). Thus, simultaneous monitoring of host-pathogen gene expression profiles during the infection is critical to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of pathogenic mechanisms (11). Hence, the possibility to simultaneously profile host and pathogen transcriptomes via dual RNA-seq in infection biology was proposed in 2012 (12). Recently, dual RNA-seq was successfully used for pathogen-host interactions analysis in Salmonella typhimurium-infected HeLa cells (13) and Streptococcus pneumonia-infected lung epithelial cells (14). For S. pneumonia-lung epithelial cells infection model, dual RNA-seq was used to track transcriptional changes at various time points post-infection, indicating that dynamic transcriptional adjustments are necessary during in vitro infection progression (14). However, the study did not examine dynamic interactions between pathogens and the entire host organism during in vivo infection progression, which overlooked almost entirely the influence of whole host context on immune response and did not truly reflect the complexities of in vivo infection (15). Thus, further studies are required to simultaneously capture the dynamics of transcriptome changes of both a bacterial pathogen and its eukaryotic host during the infection in vivo (11). We believe that dual RNA-seq would be an ideal strategy to facilitate our understanding of “white nodules” disease.
Our previous research evaluating the transcriptome, proteome and metabolome of P. plecoglossicida incubated under virulent (18°C) and avirulent (28°C) temperatures confirmed that P. plecoglossicida was a temperature-dependent facultative pathogen, and showed that htpG was significantly highly expressed under 18°C (16, 17). htpG encodes the protein HtpG, a member of heat-shock proteins (HSPs) family (18, 19), which was first described in Escherichia coli (20). Null mutation of this gene is not lethal to bacterial cells and only results in impaired growth at high temperatures (21). HtpG acts as a chaperone that enables the optimal folding of newly synthesized proteins under stress conditions. The HtpG-mediated folding mechanism does not involve co-chaperones and the identity of proteins acting as substrates in this process remains unknown (22). In E. coli, HtpG interacts with the DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE chaperone complex (23). Null mutation of htpG affects many physiological processes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including those that are important for virulence, such as motility, biofilm formation, proteolytic activity, and pigment and biosurfactant production (21). Many virulence factors of P. aeruginosa are extracellular and HtpG could play a role in their secretion (21). In addition, HtpG participates in bacterial immunity via the CRISPR system (24), in the virulence of some bacteria like extra-intestinal pathogenic E. coli strains, Edwardsiella tarda, or Salmonella typhimurium, and plays a role in the biosynthesis of antibiotic and toxins (25–27). The role of htpG remains highly elusive in bacterial pathogenicity, and its function during pathogen infection has not been reported (28).
Given the major harm caused by P. plecoglossicida to cultured fish and the potential important role of htpG in its virulence, the virulence of wild-type and htpG-RNAi P. plecoglossicida to E. coioides were compared. The spleens of E. coioides infected with wild-type and htpG-RNAi P. plecoglossicida were subjected to dual RNA-seq for further comparison. The aim of this study was to reveal the effect of htpG silencing of P. plecoglossicida on the virulence regulation in P. plecoglossicida and immune response in E. coioides. To the best of our knowledge, this was the first attempt to use tissue dual RNA-seq to simultaneously monitor the dynamics of gene expression changes of a bacterial pathogen and its eukaryotic host and infer molecular inter-species interactions between them, which could simultaneously obtain high-resolution dynamic transcriptome data from the interacting species in prokaryotic and eukaryotic biological systems, as well as predict molecular inter-species interactions based on the dual-transcriptomics data, and further predict and identify crucial virulence genes during infection.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
The pathogenic P. plecoglossicida strain (NZBD9) was isolated from the spleen of naturally infected large yellow croaker (2). Physiological saline with 10% glycerol was used to store the NZBD9 strain at −80°C. The NZBD9 strain was routinely grown in Luria Bertani (LB) medium at 18 or 28°C with shaking at 220 rpm. E. coli DH5α was obtained from TransGen Biotech (Beijing, China), and grown in LB medium (37°C, 220 rpm).
Construction of P. plecoglossicida RNAi Strain
RNAi strain was constructed according to previously described methods (5). Five short hairpin RNA sequences targeting htpG, rplF, and flgD were designed and synthesized by Shanghai Generay Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) (Table S1). After linearizing pCM130/tac vectors with the restriction enzymes NsiI and BsrGI (New England Biolabs, U.S.A), the oligonucleotides were annealed and ligated to the linearized pCM130/tac vectors using T4 DNA ligase (New England Biolabs) based on the manufacturer's recommendations. The recombinant pCM130/tac vectors were transformed into competent E. coli DH5a cells by heat shock, and then extracted and electroporated into P. plecoglossicida. Finally, the expression level of the target gene of each RNAi strain was evaluated by qRT-PCR.
Artificial Infection and Sampling
E. coioides (average weight 50.0 ± 2.0 g) fish were obtained from Zhangzhou (Fujian, China) and acclimatized at 18°C for 1 week under specific pathogen-free laboratory conditions. Fish were tested to be healthy by sera agglutination and bacteriological recovery tests as described by Pang et al. (29). E. coioides were divided into several groups (n = 40 in each group, triplicates were used for each experiment) and grown in 500 L tanks with constant aeration and a flow-through set-up.
For survival assays, weight-matched E. coioides were intrapleurally injected with 103 cfu/g of P. plecoglossicida (wild-type or RNAi strain). E. coioides that were intrapleurally injected with PBS were used as negative control. The water temperature during infection was 18 ± 1°C. The daily mortality of infected E. coioides was recorded. For dual RNA-Seq, the spleens of six weight-matched E. coioides infected with wild-type P. plecoglossicida or RNAi strain were sampled at 48 h post-infection (hpi). Every two spleens were mixed as one sample. For the tissue distribution assays, the spleens, livers, head kidneys, trunk kidneys and blood of three E. coioides were sampled at 24, 48, 72, and 96 hpi, respectively.
DNA Isolation
DNA from spleens, livers, head kidneys and trunk kidneys was purified with an EasyPure Marine Animal Genomic DNA kit (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer's instructions (30). The EasyPure Blood Genomic DNA kit (TransGen Biotech) was used for DNA isolation from blood samples.
RNA Isolation
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The mixed genomic DNA in total RNA was digested with the Turbo DNA-free DNase (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA) (31). The RNA quality was assessed using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The rRNA in total RNA was removed using the Ribo-Zero rRNA removal kit (Epicenter, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions (32).
Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
qRT-PCR was performed using a QuantStudio 6 Flex real-time PCR system (Life Technologies, USA) (33). All primer sequences are listed in Table S2. The expression of bacterial genes was normalized using 16s rDNA. In E. coioides, the expression of genes was normalized to β-actin. The 2−ΔΔCt method was used to calculate the relative levels of gene expression (34).
To evaluate the dynamic distribution of P. plecoglossicida in host, the copy number of the gyrB gene was used to estimate P. plecoglossicida abundance in spleens, trunk kidneys, head kidneys, blood and livers. The primers are listed in Table S2. The gyrB DNA copy number per milligram of tissue was used to express the results.
Transcriptomic Analysis
Library Preparation and Sequencing
The RNA-seq libraries were prepared using protocols supplied with the TruSeq™ RNA sample preparation kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Briefly, the rRNA-depleted RNA sample was fragmented in fragmentation buffer, and cDNA was synthesized using a SuperScript double-stranded cDNA synthesis kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). After end reparation, phosphorylation and poly (A) addition, the cDNA library was amplified using Phusion DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs). An Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies) was used to validate the library quality. Sequencing was performed on the Illumina HiSeq4000 sequencing platform at Majorbio Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
Processing and Mapping of Reads
The trimming and quality control of raw Illumina reads were performed using Sickle (https://github.com/najoshi/sickle) and SeqPrep (https://github.com/jstjohn/SeqPrep), with the default settings. For RNA-seq, clean data were mapped to the genome of P. plecoglossicida strain NZBD9 [NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession number SRP062985] using Bowtie2 (35). Mapped reads were classified as reads of P. plecoglossicida, and leftover reads were used for de novo assembly to obtain the E. coioides unigenes.
De novo Assembly and Annotation of mRNAs in the Host
All clean reads, which were not mapped to the P. plecoglossicida genome from the wild-type and RNAi strain-infected spleens, were treated as a pool of reads. This pool was assembled de novo into unigenes using Trinity (36). To remove any possible prokaryote contamination, all unigenes were first aligned to the bacterial NCBI non-redundant (NR) protein database. For annotation of mRNAs, the clean unigenes were compared with different databases, including NCBI NR protein, STRING, SWISS-PROT and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) using BLASTX to identify the proteins that shared the highest sequence similarity with the identified unigenes. Gene Ontology (GO) annotations were conducted using the Blast2GO software (http://www.blast2go.com) (37). Finally, KEGG was used for metabolic pathway analysis (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/) (38).
Analysis of Differential Gene Expression
Expression analyses of transcriptome data from E. coioides were performed based on the annotations from NCBI (NZ_ASJX00000000.1) and the reference transcriptome annotation described above (annotation for the host transcriptome), respectively. After obtaining uniquely mapped read counts, the package edgeR (targeting mRNAs of host) (39) was used to test for differentially expressed genes (DEGs), which were determined by the following thresholds: |log2foldchange| ≥ 1 and a false discovery rate (FDR) <0.05.
Analysis of htpG-Dependent Virulence Gene Distribution and Their Transcription Factors
To classify the gene distribution of the htpG-dependent proteins derived from the dual RNA-seq, we adopted the following filtration analysis (40). First, a gene cluster is defined as at least two neighboring genes and tolerant to only one gene missed among at least three genes in a cluster. Second, the genes must be located on the same DNA sequence strand, either positive or negative. Finally, the distance between the neighboring members of a gene cluster must be within −50 to +100 base pairs.
When the clusters were identified, we identified the starting position of the first gene in each gene cluster and submitted all the sequences on the scaffolds corresponding to that location for transcription factor prediction by BPROM (http://linux1.softberry.com/berry.phtml?topic=bprom&group=programs&subgroup=gfindb).
Prediction of a Gene Regulatory Network in Pathogen-Host Interactions
Network inference was implemented using the NetGenerator algorithm (41, 42). Briefly, the DEGs from the pathogenic enriched pathways of modules in P. plecoglossicida and the immune response-related pathways in E. coioides were used for the prediction of a gene regulatory network. The robustness of the putative gene regulatory network was checked, and edges identified by >50% of the iterations were chosen as the final network.
Gene Co-expression Network Prediction
For candidate modules, a gene co-expression network was constructed, where a gene was represented using each node and co-expression correlation was expressed as the connecting line (edge) between two genes. The nodes of most connections in the gene network were considered as hub genes. The Cytoscape software was used to visualize the network.
Growth Curves
The wild-type and gene-silenced P. plecoglossicida were grown at 28°C in LB overnight and then the OD600nm of the cultures was adjusted to 0.2. The P. plecoglossicida strains were then incubated at 18°C (n = 3). The values of OD600nm were measured at 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24 h, and growth curves were plotted to compare the wild-type and silenced strains (43).
Biofilm Assay
The biofilm assay for P. plecoglossicida was conducted as previously described (44). P. plecoglossicida strains were grown at 28°C in LB overnight and then the OD600nm of the cultures was adjusted to 0.2.150 μl of LB was mixed with 50 μl of bacterial culture, and then incubated at 18°C. After incubation for 24 h, it was washed three times using sterile PBS, stained for 15 min with 200 μl 1% crystal violet, rinsed again with sterile PBS, and then air dried. Two hundred microliter acetic acid (33%) was used for solubilizing the stained biofilm, which was quantitated by measuring OD590nm. Six replicates were performed for each treatment.
Soft Agar Plate Motility Assay
To assay the motility of P. plecoglossicida strains, the soft agar method was adapted (45). Overnight cultures were diluted to OD660 = 0.03. 1 μl drop of the cell suspension was spotted on to the center of the LB plates (0.3% agar) at 37°C for 20 h. The diameters of the colonies were measured at 24 h.
Statistical Analyses
All data are expressed as the means ± standard deviation (SD) from at least three sets of independent experiments. Data analysis was performed using the SPSS 17.0 software (Chicago, IL, USA), and one-way analysis of variance with Dunnett's test were used. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Associations between the expression of hub virulence genes and htpG in the spleen during the infection were analyzed with bivariate correlations tests followed by Pearson's correlation coefficient via SPSS 18.0 software. P < 0.05 was used to indicate significant correlation.
Data Access
The RNA sequencing reads data were deposited at the GenBank SRA database under the accession number PRJNA497501.
Ethics Statement
All animal experiments were conducted strictly based on the recommendations in the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” set by the National Institutes of Health. The animal protocols were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Jimei University (Acceptance No. JMULAC201159).
Results
Construction of the htpG-RNAi Strain
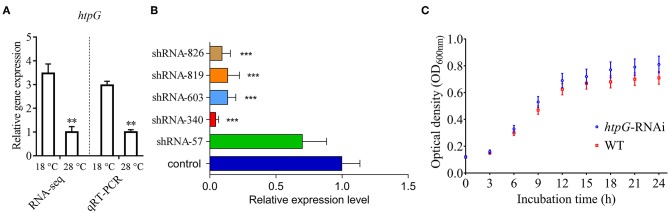
qRT-PCR results showed that the expression of P. plecoglossicida htpG was significantly higher at 18°C than at 28°C in vitro (Figure 1A), which was consistent with the results of previous RNA-seq.
Figure 1.
Construction and growth curve of htpG-RNAi strain of P. plecoglossicida. (A) Expression of htpG at 18 and 28°C in wild-type strain. (B) The htpG expression levels of 5 htpG-RNAi silencing strain. (C) Growth curve of wild-type strain and htpG-RNAi strain. Data are shown as means ± SD from three independent biological replicates. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Four of the five shRNAs significantly reduced the expression of htpG, with different efficiencies (Figure 1B). The htpG-RNAi-340 strain exhibited the best efficiency of gene silencing, and was chosen for further studies. Although htpG was silenced, htpG-RNAi strain growth rate was similar to the control strain (Figure 1C).
Effect of htpG Gene on the Virulence of P. plecoglossicida
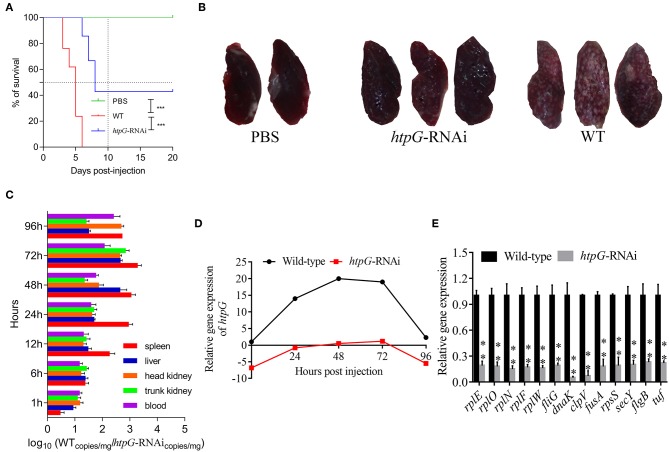
As compared to the counterparts injected with wild-type P. plecoglossicida, the E. coioides injected with htpG-RNAi strain exhibited a significant delay in the time of death and a significant decrease in mortality (Figure 2A). At 96 hpi, the spleens of the E. coioides injected with wild-type P. plecoglossicida showed typical symptoms (the surface of the spleen was covered with numerous white spots), while white spots were almost undetectable on the surface of spleens of E. coioides injected with RNAi strain (Figure 2B).
Figure 2.
The virulence of wild-type and htpG-RNAi strain of P. plecoglossicida. (A) Survival rate of E. coioides infected by P. plecoglossicida (n = 3). (B) Symptoms of spleen of E. coioides infected by P. plecoglossicida. (C) Spatial and temporal distribution of htpG-RNAi strain compared to wild-type strain. (D) Expression level of htpG of P. plecoglossicida in the spleen of E. coioides. (E) qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of randomly selected novel genes among wild type P. plecoglossicida in vitro, wild type P. plecoglossicida in vivo, and htpG-RNAi strain in vivo. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001.
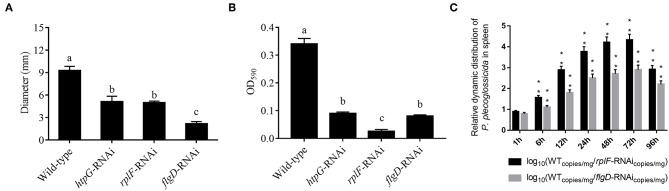
The dynamic distribution of htpG-RNAi strain and wild-type strain of P. plecoglossicida in E. coioides was compared (Figure 2C). The abundances of htpG-RNAi strain in the spleen, liver, head kidney, trunk kidney, and blood were significantly reduced as compared to the wild-type P. plecoglossicida at majority of the time points post-injection.
The expression level of htpG of wild-type and htpG-RNAi strains in spleens at different times post-injection under 18°C was evaluated (Figure 2D, Figure S1). The expression level of htpG gene in the spleen infected with wild-type strain peaked at 48 hpi and then gradually decreased (Figure S1). For 96 h post-infection, the expression of htpG in htpG-RNAi strain was always lower than wild-type strain in the spleen (Figure 2D).
RNA-Seq of P. plecoglossicida in Infected Spleen of E. coioides
The gene expression profile was calculated by edgeR, and there was obvious statistical difference when the changes in the expression level that met FDR <0.05 & |log2FC|≥1. According to the heat map generation and hierarchical clustering, the individual strain repeats of P. plecoglossicida, naturally separated and clustered according to their respective sample groups, which indicated the remarkable transcriptomic alterations among wild-type P. plecoglossicida in vitro and in vivo, and htpG-RNAi strain in vivo. As compared to wild-type P. plecoglossicida in vitro and in vivo, numerous genes were down-regulated in htpG-RNAi strain in vivo, which indicated that the htpG gene probably plays an important role in the pathogenesis of P. plecoglossicida by regulating other genes. A total of 4,914 genes were identified from profiled transcripts of P. plecoglossicida in infected spleen of E. coioides. As compared to the wild-type P. plecoglossicida in infected spleen of E. coioides, 159 genes from the htpG-RNAi strain in infected spleen of E. coioides were significantly differentially expressed, with 157 down-regulated genes and two up-regulated genes (Figure S2).
To validate the results from the transcriptomic analysis, qRT-PCR was performed. As compared to the wild-type strain in vivo, the qRT-PCR results revealed significant down-regulation of rplE, rplO, rplN, rplF, rplW, fliG, dnaK, clpV, fusA, rpsS, secY, flgB, and tuf in htpG-RNAi strain in vivo (Figure 2E). The qRT-PCR results matched those of the sequencing, which reinforced the reliability of the RNA-seq.
The functions of these 159 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were analyzed by GO, and the number of genes mapped to every term was counted. This analysis categorized the 159 DEGs into 30 enriched functional groups. Most of the DEGs were involved in the following functional categories: cellular process, metabolic process, single-organism process, cell, cell part, macromolecular complex, organelle, binding, and catalytic activity.
Pathway analysis of DEGs based on the latest version of the KEGG database was also conducted. According to the KEGG database, the 159 DEGs were enriched in 36 KEGG pathways, including pathways closely related to bacterial virulence regulation such as flagellar assembly, RNA degradation, ribosome, TCA cycle, glycolysis, and plant-pathogen interaction.
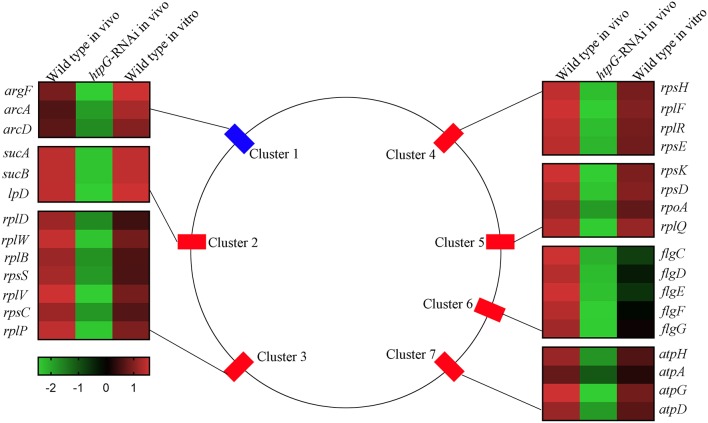
To elucidate htpG-related gene expression profiles, the 159 DEGs were further analyzed by K-Means Cluster analysis. Generally, K-means cluster analysis is based on the assumption that genes involved in either a similar function or a common pathway will have similar expression profiles and can likely be grouped together. The analysis was performed among wild-type P. plecoglossicida in vitro and in vivo, and htpG-RNAi strain in vivo. The 159 DEGs were clustered into five primary clusters and then grouped into three different groups based on significant changes in expression patterns (Figure S3). Group 1, the largest group, consisted of 155 genes that were further divided into two sub-groups. All the genes in this group exhibited low expression levels in htpG-RNAi strain in vivo, but high levels in wild-type P. plecoglossicida in vitro and in vivo. Two DEGs from group 2 showed similar expression pattern as group 1, but were slightly down-regulated in wild-type P. plecoglossicida in vitro. Group 3 included two DEGs, which showed elevated expression in htpG-RNAi strain in vivo and low expression in wild-type P. plecoglossicida in vitro and in vivo. According to the results of K-Means Cluster analysis, DEGs included in group 1 seemed to be positively related to htpG, whose distribution was classified into seven gene clusters covering 30 genes (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
The genomic localization for the P. plecoglossicida DEGs included in group 1 that were filtered by cluster analysis. Central panel represents the genomics localization for the DEGs. Right and left panels represent the fold changes of abundance of each DEG. The lower panel with color gradient represents the changes of gene abundance from down-regulated (green) to up-regulated (red).
Cluster 1 consisted of three genes, including argF, arcA, and arcD, which belonged to the arginine biosynthesis pathway. Cluster 2 consisted of three genes, including sucA, sucB, and lpD, which belonged to the TCA cycle pathway. Cluster 3 (including rplD, rplW, rplB, rpsS, rplV, rpsC, and rplP), Cluster 4 (including rpsH, rplF, rplR, and rpsE) and Cluster 5 (including rpsK, rpsD, rpoA, and rplQ) consisted of seven genes, four genes and four genes, respectively, which encoded the ribosomal proteins. Cluster 6 consisted of five flagellar assembly genes, including flgC, flgD, flgE, flgF, and flgG. Cluster 7 consisted of four genes, including atpH, atpA, atpG, and atpD, which belonged to the oxidative phosphorylation pathway.
Because of genes involved in ribosome assembly and flagellar assembly were usually chief virulence genes, the 20 genes belonging to Clusters 3, 4, 5, and 6 were chosen for further analysis of pathogen-host interactions.
Tissue RNA-Seq of Infected Spleen of E.coioides
There was obvious statistical difference when the changes in the expression level that met FDR <0.05 & |log2FC|≥1. According to the heat map generation and hierarchical clustering, the individual samples of E. coioides spleen, naturally separate and cluster according to their respective sample groups, which indicated the remarkable transcriptomic alterations among E. coioides injected with PBS, wild-type P. plecoglossicida and htpG-RNAi strain. This indicated that under these different conditions, the physiological status of the host was very different, and these differences might be closely related to the immune response of the host. A total of 180,502 genes were identified from profiled transcripts of E. coioides spleen. As compared to the wild-type P. plecoglossicida infected spleen of E. coioides, 17,512 genes from the htpG-RNAi strain infected spleen of E. coioides were significantly differentially expressed, with 10,694 down-regulated genes and 6,818 up-regulated genes (Figure S4). The large number of DEGs indicated that htpG gene plays an important role in the immune response of E. coioides to P. plecoglossicida.
To validate the results from the transcriptomic analysis, qRT-PCR was performed. As compared to the wild-type P. plecoglossicida infected spleen of E. coioides, the qRT-PCR results revealed significant down-regulation of TLR5, IL1B, C47569_g2, C7 and C2; and significant up-regulation of C321660_g6, pldA and C129279_g3 in htpG-RNAi strain infected spleen of E. coioides (Figure 4). The qRT-PCR results matched the sequencing results, which reinforced the reliability of the RNA-seq.
Figure 4.
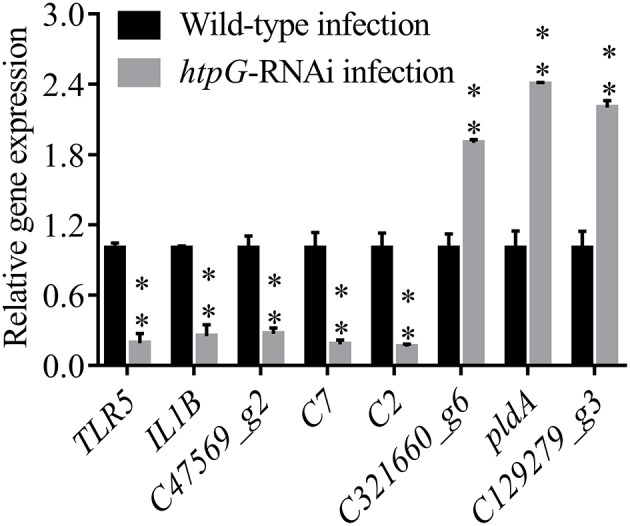
qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of randomly selected novel genes among E. coioides accepted injection of PBS, wild type P. plecoglossicida and htpG-RNAi strain. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). **P < 0.01.
The functions of the 17,512 DEGs were analyzed by GO, and the number of genes mapped to every term was counted. This analysis categorized the 17,512 DEGs into 56 enriched functional groups while some DEGs were involved in the immune response such as cell killing, immune system, and response to stimulus.
Pathway analysis of DEGs based on the latest version of the KEGG database was also conducted. According to the KEGG database, the 17,512 DEGs were enriched in 67 KEGG pathways, including pathways closely related to Immunoregulation such as cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, complement and coagulation cascades, lysosome, intestinal immune network for IgA production, systemic lupus erythematosus, primary immunodeficiency, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, antigen processing and presentation, chemokine signaling pathway, and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway.
K-Means Cluster analysis was performed on the 17,512 DEGs among E. coioides injected with PBS, wild-type P. plecoglossicida and htpG-RNAi strain. The 17,512 DEGs were clustered into 10 primary clusters and then grouped into five different groups based on significant changes in expression patterns (Figure S5). Group 1, the largest group, consisted of 17,319 genes, which displayed horizontal expression profiles among samples. Group 2 consisted of 58 genes, which exhibited high expression levels in healthy E. coioides, but low levels in E. coioides injected with wild-type P. plecoglossicida and htpG-RNAi strain. Meanwhile, genes in this group exhibited slightly elevated expression in E. coioides injected with htpG-RNAi strain than those injected with wild-type P. plecoglossicida. This indicated that P. plecoglossicida probably attenuated the expression of these genes in the host, which might be one of the key pathogenic mechanisms of P. plecoglossicida regulated by htpG. Moreover, htpG was critical for this modulation. KEGG analysis showed that genes in this group were involved in the metabolism of proteins, fats and other substances in the host. Group 3 consisted of 82 genes, which exhibited low expression in healthy E. coioides, but high expression in E. coioides injected with wild-type P. plecoglossicida and htpG-RNAi strain. This indicated that the expression of P. plecoglossicida htpG gene had no significant effect on the expression of genes involved in Group 3, but this part of the host gene must be involved in the host's defense against P. plecoglossicida infection, which is the key to the host's resistance to P. plecoglossicida. Subsequent studies with KEGG database showed that these genes were involved in immune defense-related processes such as host complement production, interleukin production and signaling, and gene expression regulation. Group 4 consisted of 29 genes, whose expression levels in E. coioides injected with wild-type P. plecoglossicida, htpG-RNAi strain and PBS decreased in turn. This indicated that the expression of htpG activated the expression of these host genes. Therefore, this part of the gene may be another key to pathogenesis of P. plecoglossicida regulated by htpG, or it may be involved in interactions between P. plecoglossicida and host immune system regulated by htpG. KEGG analysis revealed that these genes were involved in immune defense-related processes including cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, intestinal immune network for IgA production, and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Group 5 consisted of 24 genes that were further divided into six sub-groups. Genes in this group did not show obvious regularity. Based on these findings, the protein metabolism-related genes from Group 2, and immune response-related genes from Groups 3 and 4, were chosen for further analysis of pathogen-host interactions.
Prediction of htpG-Dependent Key Genes in Pathogen-Host Interactions
To predict the htpG-dependent key genes of P. plecoglossicida involved in infection, the genes from P. plecoglossicida and E. coioides mentioned above were subjected to further analysis.
-
(1) Prediction of gene regulatory networks in pathogen-host interactions.
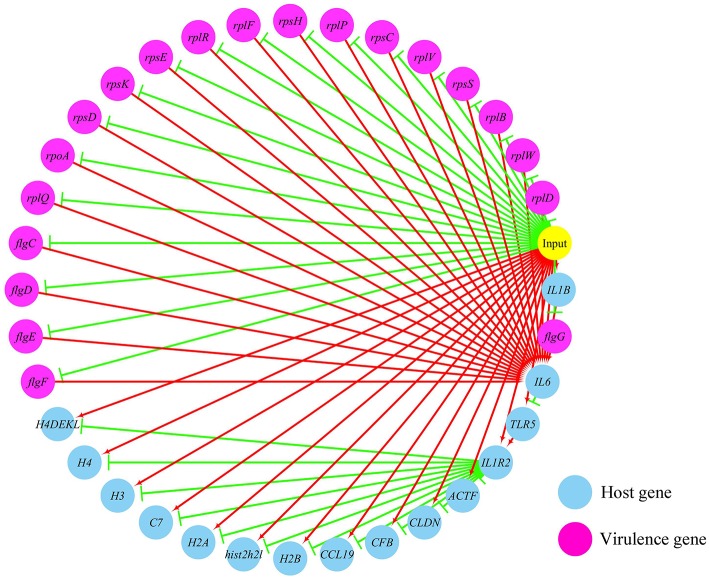
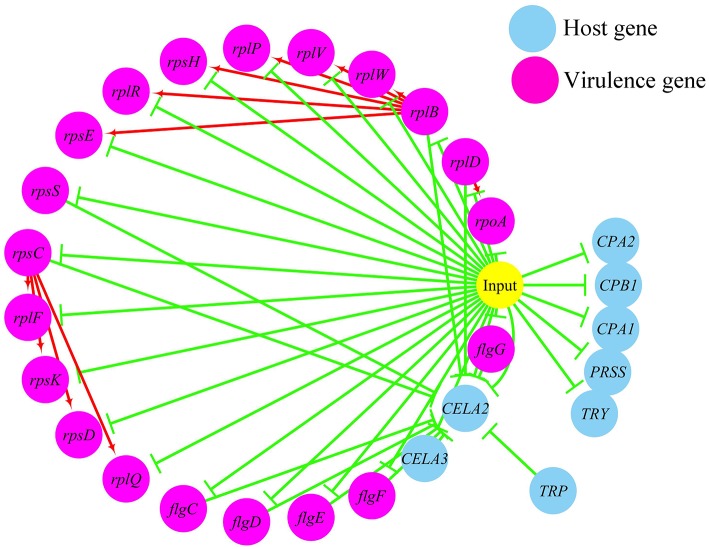
Figures 5, 6 show the pathogen-host gene regulatory prediction networks. In terms of the correlations between the virulence genes and host immune response-related genes (Figure 5), first of all, occurrence of infection activated the expression of immune-related genes, which then attenuated the expression of virulence genes. Secondly, there were interactions between pathogenic genes and host genes. Virulence genes such as rplD, rplW, rplQ, flgD, and flgE could influence host immunity and thus activate the expression of IL6, indicating that IL6 played a key role in the interaction between pathogen and host. Finally, there were mutual regulatory relationships between host genes, such as IL6 inhibited TLR5; TLR5 promoted IL1R2; IL1R2 inhibited H4DEKL, H4, H3, C7, H2A, H2B, CCL19, CFB, CLDN, and other 11 host genes. Therefore, pathogenic virulence genes could activate the expression of 11 host immune genes to facilitate all-round encirclement and suppression of pathogens, by stimulating the expression of IL6 and then amplifying through signal transduction cascade. Notably, four host immune-related genes, IL6, IL1R2, IL1B, and TLR5, performed key regulatory roles in the interaction network. Moreover, IL6 and IL1R2 belonged to Group 4 of the host genes, so the expression of htpG could influence host immunity and thus activate the expression of IL6 and IL1R2.
In terms of the correlations between the virulence genes and host protein metabolism-related genes (Figure 6), firstly, it seems that when the infection occurs, the host immune and tissue cells could sense the presence of P. plecoglossicida, which will influence host immunity and then attenuate the expression of the pathogen virulence genes. Interestingly, the expression of host protein metabolism-related genes were also attenuated when infection happened, suggesting that P. plecoglossicida might cause white spot symptoms by disrupting host protein metabolism and damaging host spleen. Secondly, there were interactions between pathogenic genes and host genes. Among them, virulence genes such as rpsS, rpsC, rplD, rplB, flgC, flgD, flgE, flgF, and flgG could activated the expression of CELA2, indicating that CELA2 might be an important host target for P. plecoglossicida. Moreover, there were mutual regulatory relationships between virulence genes. For example, rplB could promote the expression of rplW, rplV, rplP, rpsH, rplR, and rpsE; rpsC could promote the expression of rplF, rpsK, rpsD, and rplQ; and rplD could promote the expression of rpoA.
-
(2) Identification and visualization of hub virulence genes of P. plecoglossicida.
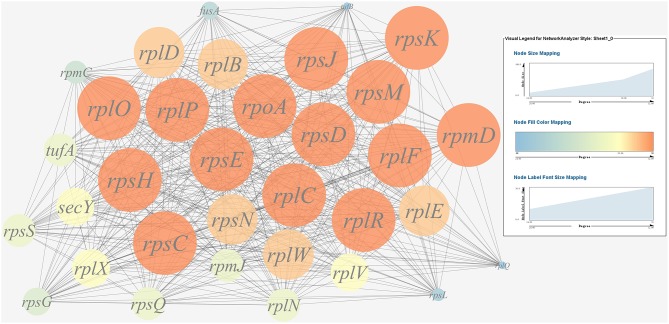
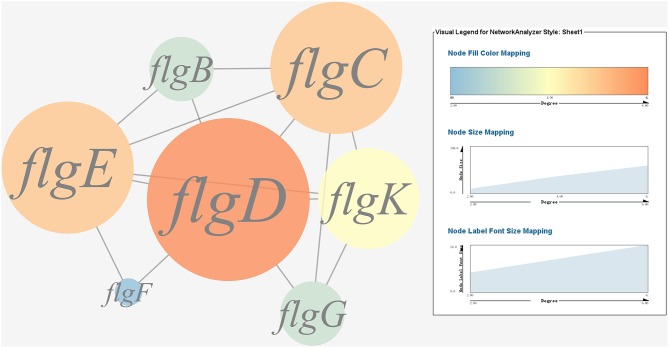
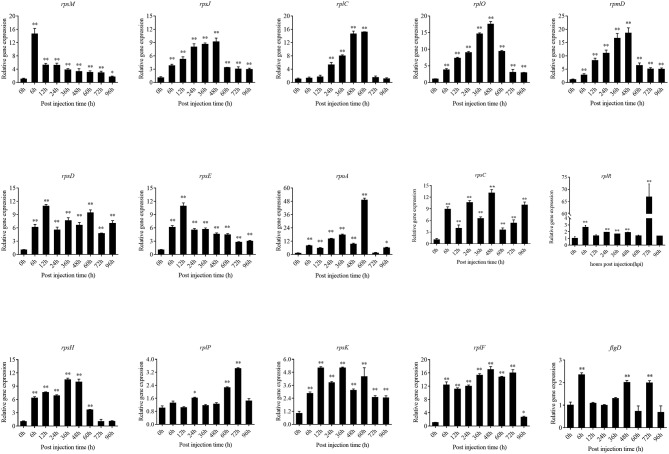
A gene co-expression network of the virulence genes mentioned above was constructed and visualized (Figures 7, 8). Among the ribosomal genes, rpsM, rpsJ, rplC, rplO, rpmD, rpsD, rpsE, rpoA, rpsC, rplR, rpsH, rplP, rpsK, and rplF were the nodes of most connections in the network and considered as hub genes (Figure 7). Among flagellar genes, flgD was considered as a hub gene (Figure 8).
-
(3) Identification and visualization of hub response genes of E. coioides.
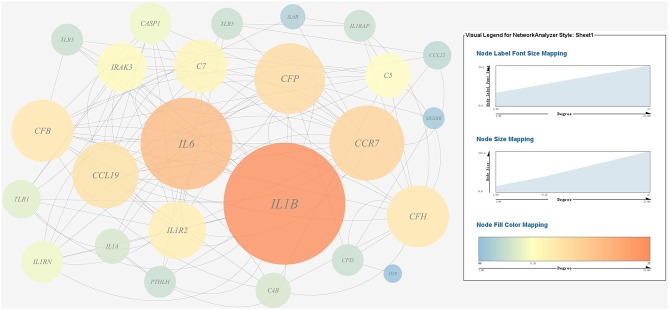
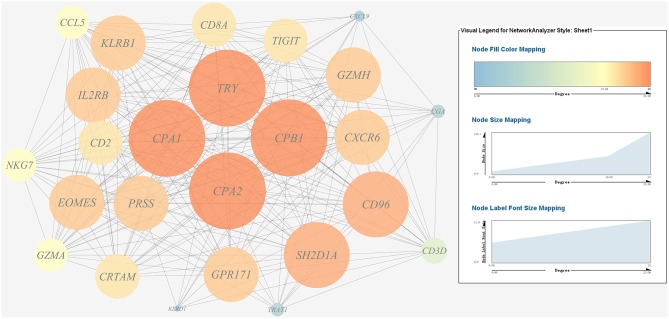
A gene co-expression network of the host immune response-related genes and host protein metabolism-related genes mentioned above was constructed and visualized, respectively (Figures 9, 10). Among host immune response-related genes, IL1B was the node of most connections in the network and considered as a hub gene (Figure 9). Among host protein metabolism-related genes, TRY, CPA1, CPA2, and CPB1 were considered as hub genes (Figure 10).
Figure 5.
The predicted regulation network between the virulence genes and host immune response related genes. For the predicted regulation network, the yellow circle represents the occur of infection; each blue circle represents an input host immune response related genes; each purple circle represents an input virulence gene; each red line represents a positive correlation; and each green line represents a negative correlation.
Figure 6.
The predicted regulation network between the virulence genes and host protein metabolism related genes. For the predicted regulation network, the yellow circle represents the occur of infection; each blue circle represents an input host immune response related genes; each purple circle represents an input virulence gene; each red line represents a positive correlation; and each green line represents a negative correlation.
Figure 7.
Gene co-expression network of ribosomal genes in P. plecoglossicida. For the predicted regulation network, each circle represents a gene; each line represents a correlation. For the genes, the diameter, color and symbol size of each node is directly proportional to the number of nodes associated with it. Among ribosomal genes, rpsM, rpsJ, rplC, rplO, rpmD, rpsD, rpsE, rpoA, rpsC, rplR, rpsH, rplP, rpsK, and rplF were the nodes of most connections in the network and considered as hub genes.
Figure 8.
Gene co-expression network of flagellar genes in P. plecoglossicida. For the predicted regulation network, each circle represents a gene; each line represents a correlation. The candidate key virulence gene flgD is marked in red.
Figure 9.
Gene co-expression network of host immune response related genes. For the predicted regulation network, each circle represents a gene; each line represents a correlation. For the genes, the diameter, color and symbol size of each node is directly proportional to the number of nodes associated with it. Among these genes, IL6 and IL1B were the nodes of most connections in the network and considered as hub genes.
Figure 10.
Gene co-expression network of host protein metabolism related genes. For the predicted regulation network, each circle represents a gene; each line represents a correlation. For the genes, the diameter, color and symbol size of each node is directly proportional to the number of nodes associated with it. Among these genes, TRY, CPA1, CPA2, and CPB1 were the nodes of most connections in the network and considered as hub genes.
Effects of the htpG Dependent Key Virulence Genes on the Pathogenicity of P. plecoglossicida in E. coioides
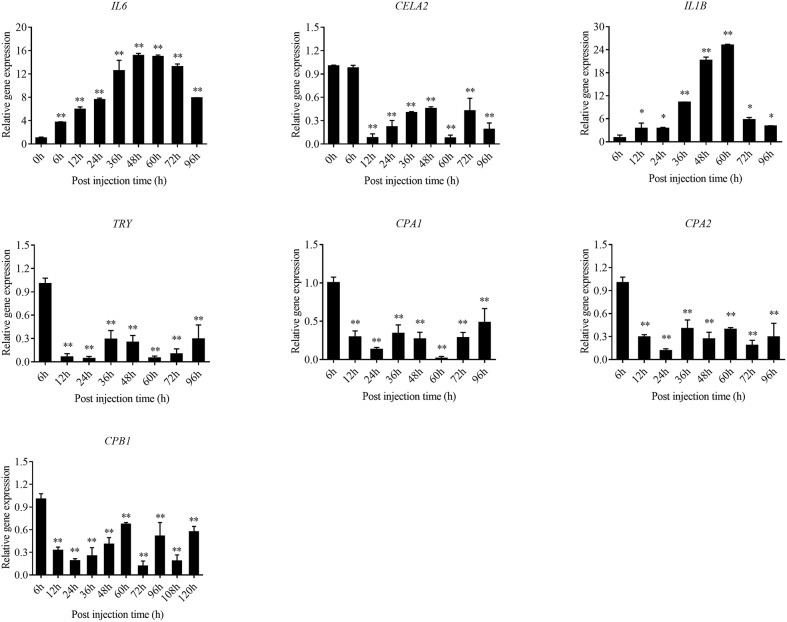
The expression level of the predicted htpG dependent key genes in pathogen-host interactions were evaluated in the wild-type P. plecoglossicida infected spleen at different stages of infection with qRT-PCR (Figure 11). The results showed that hub virulence genes of P. plecoglossicida were generally up-regulated throughout the infection process. For the hub response genes of E. coioides, IL6 and IL1B were induced, while CELA2, TRY, CPA1, CPA2, and CPB1 were repressed throughout the infection process (Figure 12). Meanwhile, the correlation tests showed that among the hub virulence genes of P. plecoglossicida, the ribosomal gene rplF was most significantly associated with htpG in the spleen during the infection (Table S3). Therefore, the ribosomal gene rplF and the flagellar gene flgD were chosen for further research.
Figure 11.
qRT-PCR analysis of the expression level of the predicted htpG dependent key genes during pathogen-host interactions in the wild type P. plecoglossicida infected spleen at different stages of infection. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Figure 12.
qRT-PCR analysis of the expression level of the hub response genes of E. coioides in the wild type P. plecoglossicida infected spleen at different stages of infection. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
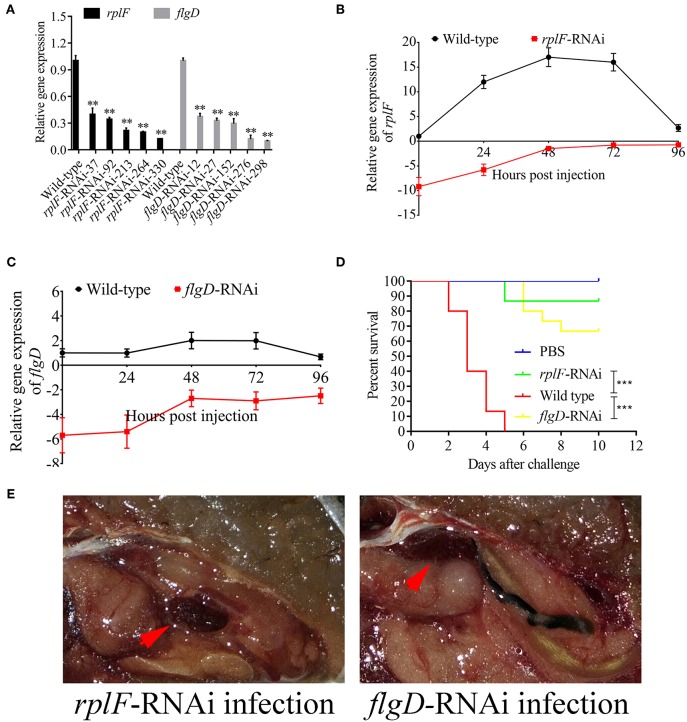
rplF and flgD were stably silenced with different shRNAs resulting in different knockdown efficiencies (Figure 13A). The strains containing pCM130/tac-rplF-shRNA-330 (named the rplF-RNAi strain), and pCM130/tac-flgD-shRNA-298 (named the flgD-RNAi strain) showed the best efficiencies for silencing the rplF and flgD genes, respectively, and were used for further experiments. For 96 h post-infection, the expression of rplF (Figure 13B) and flgD (Figure 13C) in RNAi strains was always lower than wild-type strain in the spleen. The motility (Figure 14A) and biofilm formation (Figure 14B) of P. plecoglossicida was significantly decreased in the silenced strains. Meanwhile, the dynamic distributions of the rplF- and flgD-RNAi strains in E. coioides spleen were significantly reduced as compared to wild-type P. plecoglossicida at most of the time points after injection (Figure 14C). As compared to the wild-type strain, the mortality of E. coioides injected with RNAi strains decreased substantially (Figure 13D). Injection of RNAi strains also led to a delay in the time of death. Moreover, the spleens of all the E. coioides that received rplF or flgD-RNAi strains did not develop visible nodules (Figure 13E).
Figure 13.
Construction of rplF- and flgD-RNAi strains and their effects on virulence. (A) Screening of shRNAs targeting rplF and flgD transcripts. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001. (B) Expression level of rplF gene of P. plecoglossicida in the spleen of E. coioides. (C) Expression level of rplF gene of P. plecoglossicida in the spleen of E. coioides. (D) The cumulative survival of E. coioides injected with Wild type and RNAi strains during 10 days post challenge. (E) E. coioides that received rplF- or flgD-RNAi strains failed to develop visible nodules.
Figure 14.
(A) Stable gene silencing reduces the motility behavior on soft agar plates of P. plecoglossicida. Diameter of the colony of each strain was presented as mean ± SD, n = 6. Means of treatments not sharing a common letter are significantly different at P < 0.05. (B) Biofilm formation of wild-type and stable silenced strains. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 6). Means of treatments not sharing a common letter are significantly different at P < 0.05. (C) The dynamic distribution of Wild type and RNAi strains in host spleen. Data are shown as means ± SD from three independent biological replicates. **P < 0.01.
Discussion
Dual RNA-seq was believed to be an ideal strategy to facilitate the understanding of “white nodules” disease, since it was capable of simultaneously monitoring host-pathogen transcriptome alterations during natural infections and offering a (46). However, the greatest obstacle to pathogen transcriptome sequencing in dual RNA-seq for pathogen-host interaction tissue samples is the extremely low abundance of pathogens (11). Therefore, simultaneous monitoring of the dynamics of gene expression changes between a bacterial pathogen and its host through tissue dual RNA-seq is currently lacking. The present study showed that P. plecoglossicida significantly accumulated in the spleen at 48 h, which was an ideal model for dual RNA-seq in vivo (Figure 2C). Therefore, we used a dual RNA-seq strategy to identify host-pathogen interaction regulators controlled by the expression of htpG.
The role of htpG remains highly elusive in bacterial pathogenicity recently, and the function of htpG during pathogen infection has not been reported (28). In the present study, htpG was found to be remarkably induced during the infection process. Meanwhile, silencing of htpG significantly reduced the distribution and virulence, but not the growth. Thus, htpG is a key activator of P. plecoglossicida virulence.
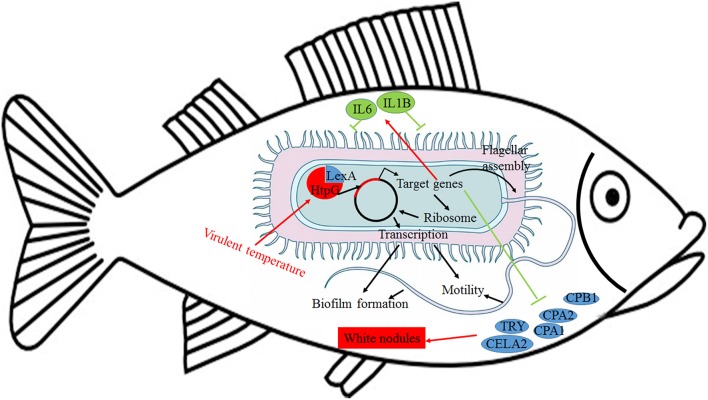
According to the results of dual RNA-seq, htpG was found to control the expression of 159 genes in P. plecoglossicida, directly or indirectly. Several pathways closely related to bacterial virulence regulation were involved, such as flagellar assembly, RNA degradation, ribosome, TCA cycle, glycolysis, and plant-pathogen interaction. Notably, distribution of DEGs positively related to htpG was classified, which finally achieved seven gene clusters covering 30 genes.
Further analysis of the seven gene clusters offered clues to how and why the htpG-dependent transcriptomes were generated. First, according to the RNA-seq data, the members in each gene cluster had similar expression profiles. Second, the members in each gene cluster were involved in a common pathway and performed similar functions. Third, distance analysis of the neighboring genes to these clusters indicated that most of the distances were within −10 to +50 base pairs, which are typical distances of operon structure genes in bacteria. These features led to a hypothesis that gene transcription in these seven clusters probably act as operons, whose activities are very sensitive to htpG expression level. HtpG has not yet been reported as a transcription factor. It acts as a chaperone that enables the optimal folding of newly synthesized proteins under stress conditions (22). Therefore, a hypothetical transcriptional regulator should exist. Transcription factor prediction analysis by BPROM showed that the seven clusters shared a common transcription factor LexA. Thus, HtpG probably ensured the optimal folding of LexA in adverse environment during infection, and then regulated the virulence-related genes in the seven clusters (Figure 15). Although further study is necessary to validate the hypothesis, lexA has been identified as a key gene of interest. Furthermore, as compared to the wild-type P. plecoglossicida infected spleen of E. coioides, numerous DEGs were identified from the htpG-RNAi strain infected spleen of E. coioides. Numerous pathways closely related to immune response regulation were identified, such as cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, complement and coagulation cascades, lysosome, intestinal immune network for IgA production, systemic lupus erythematosus, primary immunodeficiency, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, antigen processing and presentation, chemokine signaling pathway, and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway (47, 48). This indicated that htpG gene played an important role in the immune response of E. coioides to P. plecoglossicida. In order to validate this, correlations between the virulence genes and host immune response-related genes were analyzed. Both htpG-independent (Group 3) and htpG-dependent (Group 4) defense mechanisms were observed. Infection activated the expression of immune-related genes and attenuated the expression of virulence genes. Meanwhile, there were interactions between pathogenic genes and host genes. Virulence genes such as rplD, rplW, rplQ, flgD, and flgE could influence host immunity and thus activate the expression of IL6 expression, indicating that IL6 played a key role in the interaction between pathogen and host. Finally, there were mutual regulatory relationships between host genes. Collectively, these observations strongly suggested that pathogenic virulence genes could activate the expression of 11 host immune genes to facilitate all-round encirclement and suppression of pathogens, by stimulating the expression of IL6 and then amplifying through signal transduction cascade (Figure 15). Among the host immune response-related genes, IL1B was considered as a hub gene.
Figure 15.
Schematic diagram to illustrate the hypothetical model of P. plecoglossicida htpG gene functions during host-pathogen interactions with E. coioides.
Interleukins (ILs) are the largest group of cytokines and play crucial roles in host innate/acquired immune response (49). To date, more than 30 ILs have been identified in fish (50). IL-6 as a key member of cytokines plays key roles in immune process, including acute phase response, hematopoiesis, energy sensor, and immune cell differentiation through modulating immune-signaling pathways (51, 52). Simultaneously, as a pro-inflammatory factor, up-regulation of IL-6 transcripts was detected in many fish defending against various pathogenic infections (53–55). Furthermore, IL-6 was found to drive lymphocyte differentiation after stimulation of trout head-kidney cells (56), indicating that it might be involved in fish immune response. Recent studies also revealed that IL-6 might be involved in large yellow croaker immune response and improve the inflammatory response through activating TNF-α expression. IL-1b, the first IL to be characterized, is crucial for the initiation and regulation of immune and inflammatory responses in many economically important teleost (57). Teleost IL-1b is also important for the host defense against pathogen infection (58). Recent studies suggested that LcIL-1β plays an important role in the large yellow croaker immune response against V. alginolyticus (57). Considering their crucial roles in fish inflammatory response, especially in the large yellow croaker, IL-6 and IL-1b may play important roles in the immune response of E. coioides to P. plecoglossicida during the process of white spot disease, and are closely related to the formation of granuloma. In the present study, IL-6 and IL-1B were proven to be induced throughout the infection process by qRT-PCR, which reinforced the hypothesis.
Inflammation is associated with high levels of flagellin, the principal bacterial flagellar protein (59). Furthermore, TLR5 dependent innate-immunity-directed development of flagellin-specific adaptive immune responses can modulate the production of flagella in a three-way interaction that helps to avoid inflammation and tissue damage in mice. TLR5 could inhibit bacterial motility and down-regulate flagellar gene expression (60). In the present study, TLR5 was proven to be a key immune-related gene and activated by P. plecoglossicida infection through dual RNA-seq. Meanwhile, flagellar assembly genes were predicted to be repressed during infection. Although the specific principles need to be further explored, these results indicated a three-way interaction dependent on TLR5 in E. coioides, which is closely related to the occurrence, development and regulation of inflammation during white spot disease.
The enzootic disease was characterized by granulomas in internal organs in cage-farmed large yellow croaker. The appearance of granulomas is usually caused by chronic inflammation in tissues (61). Previous histological analysis showed the accumulation of macrophages in the granulomatous lesions, which also indicated the presence of inflammation (62). However, the pathological cause of granulomas is unclear. Unexpectedly, we discovered correlations between the virulence genes and host protein metabolism-related genes. Interestingly, the expression of host protein metabolism-related genes were attenuated when infection occurred. Meanwhile, there were interactions between pathogenic genes and host genes. Among them, virulence genes such as rpsS, rpsC, rplD, rplB, flgC, flgD, flgE, flgF, and flgG could activate the expression of CELA2, indicating that CELA2 might be an important target for P. plecoglossicida attacking to the host. Finally, there were mutual regulatory relationships among host protein metabolism-related genes. TRY, CPA1, CPA2, and CPB1 were considered as hub genes and proven to be repressed throughout the infection process by qRT-PCR. Taken together, these results suggested that P. plecoglossicida might cause white spot symptoms by disrupting host protein metabolism and damaging the host spleen (Figure 15).
In the present study, rplF and flgD were predicted as htpG-dependent key virulence genes involved in host-pathogen interactions. Ribosomal protein L6, encoded by rplF, is essential for the assembly of functional 50S subunits at the late stage (63). FlgD, one of the flagellar scaffolding proteins, is required for flagellar hook assembly and acts as a hook-capping protein to enable assembly of hook protein subunits (64). Silencing of htpG, rplF, and flgD significantly reduced motility, biofilm formation, distribution and virulence. Taken together, these results indicated that rplF and flgD were htpG-dependent key virulence genes in E. coioides-P. plecoglossicida interactions. These results reflect the high sensitivity and accuracy of dual RNA-seq for predicting key virulence genes involved in host-pathogen interactions.
Conclusion
This is the first report of the successful use of tissue dual RNA-seq to simultaneously monitor the dynamics of gene expression changes of pathogen and host in the context of prokaryotic and eukaryotic biological systems, which obtained high-resolution transcriptome data. Dual RNA-seq not only increased our knowledge of HtpG control of virulence gene expression in P. plecoglossicida during infection but also revealed the htpG-independent and htpG-dependent defense mechanisms of E. coioides against P. plecoglossicida. Furthermore, dual RNA-seq analysis also offered new clues underlying the pathological cause of granulomas. Notably, HtpG acts as a chaperone that enables the optimal folding of newly synthesized proteins under stress conditions, especially the change of temperature, while the virulence of P. plecoglossicida is temperature-dependent. Therefore, HtpG might act as a temperature sensor and effector, by regulating the expression of virulence genes, and then initiate the infection process at the pathogenic temperature. The ability of HtpG to respond to the environment is also likely to be activated by the adverse environment inside the host after the pathogen invasion, and then regulate the expression of virulence genes and interact with the host. In the future, we intend to validate these results and explain the molecular factors that govern these interactions during infection.
Author Contributions
QY and YS conceived the experiments. LH, LZ, WL, XX, and YQ conducted the experiments. All authors assisted in the collection and interpretation of data. LH and QY wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract No. 31702384 and 31672694.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00984/full#supplementary-material
Expression level of htpG of wild type P. plecoglossicida in the spleen of E. coioides during the infection. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.0001.
Hierarchical clustering of genes among wild type P. plecoglossicida in vitro, wild type P. plecoglossicida in vivo, and htpG-RNAi strain in vivo. For hierarchical clustering, green and red indicate decreased and increased expression, respectively. Transcripts were clustered by hierarchical clustering using the complete linkage algorithm and Pearson correlation metric in R.
K-means cluster analysis of 159 P. plecoglossicida genes from the htpG-RNAi strain in infected spleen of E. coioides exhibited significant difference.
Hierarchical clustering of genes among E. coioides accepted injection of PBS, wild type P. plecoglossicida and htpG-RNAi strain. For hierarchical clustering, green and red indicate decreased and increased expression, respectively. Transcripts were clustered by hierarchical clustering using the complete linkage algorithm and Pearson correlation metric in R.
K-means cluster analysis of 17512 E. coioides genes from the htpG-RNAi strain infected spleen of E. coioides exhibited significant difference.
Oligonucleotides used in producing shRNA for stable gene silencing.
Primers for qRT-PCR.
Correlations between gene expressions.
References
- 1.Nishimori E, Kita-Tsukamoto K, Wakabayashi H. Pseudomonas plecoglossicida sp. nov., the causative agent of bacterial hemorrhagic ascites of ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. (2000) 50:83–9. 10.1099/00207713-50-1-83 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hu J, Zhang F, Xu XJ, Su YQ, Qin YX, Ma Y, et al. Isolation, identification and virulence of the pathogen of white-spots disease in internal organs of Pseudosciaena crocea. Oceanol Limnol Sin. (2014) 45:409–417. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang B, Luo G, Zhao L, Huang L, Qin Y, Su Y, et al. Integration of RNAi and RNA-seq uncovers the immune responses of Epinephelus coioides to L321_RS19110 gene of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 81:121–9. 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.06.051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Akayli T, Canak O, Basaran B. A new Pseudomonas species observed in cultured young rainbow trout. (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792): Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. Res J Biol Sci. (2011) 4:107–11. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sun Y, Luo G, Zhao L, Huang L, Qin Y, Su Y, et al. Integration of RNAi and RNA-seq reveals the immune responses of Epinephelus coioides to sigX gene of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1624. 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tao Z, Zhou T, Zhou S, Wang G. Temperature-regulated expression of type VI secretion systems in fish pathogen Pseudomonas plecoglossicida revealed by comparative secretome analysis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. (2016) 363:fnw261. 10.1093/femsle/fnw261 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhang J, Wang Y, Guo H, Mao Z, Ge C. Identification and characterization of a phospholipase A1 activity type three secreted protein, PP_ExoU from Pseudomonas plecoglossicida NB2011, the causative agent of visceral granulomas disease in large yellow croaker. (Larimichthys crocea). J Fish Dis. (2017) 40:831–40. 10.1111/jfd.12565 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Luo L, Lu J, Wang Q, Chen S, Xu A, Yuan S. Autophagy participates in innate immune defense in lamprey. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 83:416–24. 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.09.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sun W, Feng J. Differential lncRNA expression profiles reveal the potential roles of lncRNAs in antiviral immune response of Crassostrea gigas. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 81: 233–41. 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.07.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Baddal B, Muzzi A, Censini S, Calogero RA, Torricelli G, Guidotti S, et al. Dual RNA-seq of Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae and host cell transcriptomes reveals novel insights into host-pathogen cross talk. mBio. (2015) 6:e01765–15. 10.1128/mBio.01765-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nuss AM, Beckstette M, Pimenova M, Schmühl C, Opitz W, Pisano F, et al. Tissue dual RNA-seq allows fast discovery of infection-specific functions and riboregulators shaping host-pathogen transcriptomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2017) 114:E791–800. 10.1073/pnas.1613405114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Westermann AJ, Gorski SA, Vogel J. Dual RNA-seq of pathogen and host. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2012) 10:618–30. 10.1038/nrmicro2852 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Westermann AJ, Förstner KU, Amman F, Barquist L, Chao Y, Schulte LN, et al. Dual RNA-seq unveils noncoding RNA functions in host-pathogen interactions. Nature. (2016) 529:496–501. 10.1038/nature16547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Aprianto R, Slager J, Holsappel S, Veening JW. Time-resolved dual RNA-seq reveals extensive rewiring of lung epithelial and pneumococcal transcriptomes during early infection. Genome Biol. (2016) 17:198. 10.1186/s13059-016-1054-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Colgan AM, Cameron AD, Kröger C. If it transcribes, we can sequence it: mining the complexities of host-pathogen-environment interactions using RNA-seq. Curr Opin Microbiol. (2017) 36:37–46. 10.1016/j.mib.2017.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huang L, Liu W, Jiang Q, Zuo Y, Su Y, Zhao L, et al. Integration of transcriptomic and proteomic approaches reveals the temperature-dependent virulence of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2018) 8:207. 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Huang L, Zuo Y, Jiang Q, Su Y, Qin Y, Xu X, et al. A metabolomic investigation into the temperature-dependent virulence of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida from large yellow croaker. (Pseudosciaena crocea). J Fish Dis. (2019) 42:431–46. 10.1111/jfd.12957 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Song C, Cui Y, Liu B, Xie J, Ge X, Xu P, et al. HSP60 and HSP90β from blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala: molecular cloning, characterization, and comparative response to intermittent thermal stress and Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 74:119–32. 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.12.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hong Y, Huang Y, Yan G, Pan C, Zhang J. Antioxidative status, immunological responses, and heat shock protein expression in hepatopancreas of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis under the exposure of glyphosate. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 86:840–5. 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.12.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Garcie C, Tronnet S, Garénaux A, McCarthy AJ, Brachmann AO, Pénary M, et al. The bacterial stress-responsive Hsp90 chaperone. (HtpG) is required for the production of the genotoxin colibactin and the siderophore yersiniabactin in Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. (2016) 214:916–24. 10.1093/infdis/jiw294 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Grudniak AM, Klecha B, Wolska KI. Effects of null mutation of the heat-shock gene htpG on the production of virulence factors by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Fut Microbiol. (2018) 13:69–80. 10.2217/fmb-2017-0111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Buchner J. Bacterial Hsp90-desperately seeking clients. Mol Microbiol. (2010) 76:540–4. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07140.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Doyle SM, Hoskins JR, Wickner S. Collaboration between the ClpB AAA+ remodeling protein and the DnaK chaperone system. Proc Natl Acad. Sci USA. (2007) 104:11138–44. 10.1073/pnas.0703980104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yosef I, Goren MG, Kiro R, Edgar R, Qimron U. High-temperature protein G is essential for activity of the Escherichia coli clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. (CRISPR)/Cas system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2011) 108:20136–41. 10.1073/pnas.1113519108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vivien E, Megessier S, Pieretti I, Cociancich S, Frutos R, Gabriel DW, et al. Xanthomonas albilineans HtpG is required for biosynthesis of the antibiotic and phytotoxin albicidin. FEMS Microbiol Lett. (2005) 251:81–9. 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.07.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dang W, Hu YH, Sun L. HtpG is involved in the pathogenesis of Edwardsiella tarda. Vet Microbiol. (2011) 152:394–400. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.05.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Verbrugghe E, Van Parys A, Leyman B, Boyen F, Haesebrouck F, Pasmans F. HtpG contributes to Salmonella Typhimurium intestinal persistence in pigs. Vet Res. (2015) 46:118. 10.1186/s13567-015-0261-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Honoré FA, Méjean V, Genest O. Hsp90 is essential under heat stress in the bacterium Shewanella oneidensis. Cell Rep. (2017) 19:680–7. 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.03.082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pang H, Qiu M, Zhao J, Hoare R, Monaghan SJ, Song D, et al. Construction of a Vibrio alginolyticus hopPmaJ. (hop) mutant and evaluation of its potential as a live attenuated vaccine in orange-spotted grouper. (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 76:93–100. 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.02.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huang LX, Xi ZH, Wang CG, Zhang YY, Yang ZB, Zhang SQ, et al. Phenanthrene exposure induces cardiac hypertrophy via reducing miR-133a expression by DNA methylation. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:20105. 10.1038/srep20105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Huang LX, Huang L, Yan QP, Qin YX, Ma Y, Lin M, et al. The TCA pathway is an important player in the regulatory network governing Vibrio alginolyticus adhesion under adversity. Front Microbiol. (2016) 40: 1–13. 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Guo L, Huang L, Su Y, Qin Y, Zhao L, Yan Q. secA, secD, secF, yajC and yidC contribute to the adhesion regulation of Vibrio alginolyticus. Microbiol Open. (2018) 7:e00551. 10.1002/mbo3.551 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Huang L, Wang L, Lin X, Su Y, Qin Y, Kong W, et al. mcp, aer, cheB, and cheV contribute to the regulation of Vibrio alginolyticus. (ND-01) adhesion under gradients of environmental factors. Microbiol Open. (2017) 6:e517. 10.1002/mbo3.517 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Huang L, Zuo Z, Zhang Y, Wang C. Toxicogenomic analysis in the combined effect of tributyltin and benzo [a] pyrene on the development of zebrafish embryos. Aquatic Toxicol. (2015) 158:157–64. 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.10.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. (2011) 9:357–9. 10.1038/nmeth.1923 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol. (2011) 29:644. 10.1038/nbt.1883 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M, Robles M. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. (2005) 21:3674–6. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. (2000) 28:27–30. 10.1093/nar/28.1.27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK. edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. (2010) 26:139–40. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chen Z, Wen B, Wang Q, Tong W, Guo J, Bai X, et al. Quantitative proteomics reveals the temperature-dependent proteins encoded by a series of cluster genes in Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis. Mol Cell Proteomics. (2013) 12:2266–77. 10.1074/mcp.M112.025817 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schulze S, Schleicher J, Guthke R, Linde J. How to predict molecular interactions between species. Front Microbiol. (2016) 7:442. 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00442 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schulze S, Henkel SG, Driesch D, Guthke R, Linde J. Computational prediction of molecular pathogen-host interactions based on dual transcriptome data. Front Microbiol. (2015) 6:65. 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liu W, Huang L, Su Y, Qin Y, Zhao L, Yan Q. Contributions of the oligopeptide permeases in multistep of Vibrio alginolyticus pathogenesis. MicrobiologyOpen. (2017) 6:e511. 10.1002/mbo3.511 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Luo G, Huang L, Su Y, Qin Y, Xu X, Zhao L, et al. flrA, flrB, and flrC regulate adhesion by controlling the expression of critical virulence genes in Vibrio alginolyticus. Emerg Microbes Infect. (2016) 5:e85. 10.1038/emi.2016.82 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Qin Y, Lin G, Chen W, Xu X, Yan Q. Flagellar motility is necessary for Aeromonas hydrophila adhesion. Microbial Pathog. (2016) 98:160–6. 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.07.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Luo G, Sun Y, Huang L, Veening J-W. Time-resolved dual RNA-seq of tissue uncovers key virulence genes in host-pathogen interaction. BMC Genomics. (2019) 17:198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Musthafa MS, Asgari SM, Elumalai P, Hoseinifar SH, Doan HV. Protective efficacy of Shilajit enriched diet on growth performance and immune resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 82:147–52. 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.08.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tharuka MDN, Priyathilaka TT, Yang H, Pavithiran A, Lee J. Molecular and transcriptional insights into viperin protein from Big-belly seahorse. (Hippocampus abdominalis), and its potential antiviral role. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 86:599–607. 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.12.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hoseinifar SH, Yousefi S, Capillo G, Paknejad H, Khalili M, Tabarraei A, et al. Mucosal immune parameters, immune and antioxidant defence related genes expression and growth performance of zebrafish. (Danio rerio) fed on Gracilaria gracilis powder. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 83:232–7. 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.09.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Nerbøvik IK, Solheim MA, Eggestøl HØ, Rønneseth A, Jakobsen RA, Wergeland HI, et al. Molecular cloning of MDA 5, phylogenetic analysis of RIG-I-like receptors. (RLRs) and differential gene expression of RLRs, interferons and proinflammatory cytokines after in vitro challenge with IPNV, ISAV, and SAV in the salmonid cell line TO. J Fish Dis. (2017) 40:1529–44. 10.1111/jfd.12622 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fogelson SB, Fast MD, Leary J, Camus AC. Pathologic features of mycobacteriosis in naturally infected Syngnathidae and novel transcriptome assembly in association with disease. J Fish Dis. (2017) 40:1681–94. 10.1111/jfd.12634 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Fan Y, Zhou Y, Zeng L, Jiang N, Liu W, Zhao J, et al. Identification, structural characterization, and expression analysis of toll-like receptors 2 and 3 from gibel carp. (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2018) 72:629–38. 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.11.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mallo N, DeFelipe AP, Folgueira I, Sueiro RA, Lamas J, Leiro JM. Combined antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory effects of the natural polyphenol curcumin on turbot scuticociliatosis. J Fish Dis. (2017) 40:205–17. 10.1111/jfd.12503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Jin JW, Kim YC, Hong S, Kim MS, Jeong JB, Jeong HD. Cloning and expression analysis of innate immune genes from red sea bream to assess different susceptibility to megalocytivirus infection. J Fish Dis. (2017) 40:583–95. 10.1111/jfd.12537 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rozas-Serri M, Pe-a A, Arriagada G, Enríquez R, Maldonado L. Comparison of gene expression in post-smolt Atlantic salmon challenged by LF-89-like and EM-90-like Piscirickettsia salmonis isolates reveals differences in the immune response associated with pathogenicity. J Fish Dis. (2018) 41:539–52. 10.1111/jfd.12756 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kittana H, Gomes-Neto JC, Heck K, Geis AL, Segura Mu-oz RR, Cody LA, et al. Commensal Escherichia coli strains can promote intestinal inflammation via differential interleukin-6 production. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2318. 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02318 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Dixon B, Barreda DR, Sunyer JO. Perspective on the development and validation of Ab reagents to fish immune proteins for the correct assessment of immune function. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2957. 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02957 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Khalil SR, Reda RM, Awad A. Efficacy of Spirulina platensis diet supplements on disease resistance and immune-related gene expression in Cyprinus carpio L. exposed to herbicide atrazine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2017) 67:119–28. 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.05.065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sanders DS. Mucosal integrity and barrier function in the pathogenesis of early lesions in Crohn's disease. J Clin Pathol. (2005) 58:568–72. 10.1136/jcp.2004.021840 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Cullender TC, Chassaing B, Janzon A, Kumar K, Muller CE, Werner JJ, et al. Innate and adaptive immunity interact to quench microbiome flagellar motility in the gut. Cell Host Microbe. (2013) 14:571–581. 10.1016/j.chom.2013.10.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhang JT, Zhou SM, An SW, Chen L, Wang GL. Visceral granulomas in farmed large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea. (Richardson), caused by a bacterial pathogen, Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. J Fish Dis. (2014) 37:113–21. 10.1111/jfd.12075 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Mao Z, Li M, Chen J. Draft Genome Sequence of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida Strain NB2011, the causative agent of white nodules in large yellow croaker. (Larimichthys crocea). Genome Announc. (2013) 1:e00586–13. 10.1128/genomeA.00586-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Shigeno Y, Uchiumi T, Nomura T. Involvement of ribosomal protein L6 in assembly of functional 50S ribosomal subunit in Escherichia coli cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2016) 473:237–42. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.085 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zhang M, Wu H, Li X, Yang M, Chen T, Wang Q, et al. Edwardsiella tarda flagellar protein FlgD: a protective immunogen against edwardsiellosis. Vaccine. (2012) 30:3849–56. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.04.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Expression level of htpG of wild type P. plecoglossicida in the spleen of E. coioides during the infection. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.0001.
Hierarchical clustering of genes among wild type P. plecoglossicida in vitro, wild type P. plecoglossicida in vivo, and htpG-RNAi strain in vivo. For hierarchical clustering, green and red indicate decreased and increased expression, respectively. Transcripts were clustered by hierarchical clustering using the complete linkage algorithm and Pearson correlation metric in R.
K-means cluster analysis of 159 P. plecoglossicida genes from the htpG-RNAi strain in infected spleen of E. coioides exhibited significant difference.
Hierarchical clustering of genes among E. coioides accepted injection of PBS, wild type P. plecoglossicida and htpG-RNAi strain. For hierarchical clustering, green and red indicate decreased and increased expression, respectively. Transcripts were clustered by hierarchical clustering using the complete linkage algorithm and Pearson correlation metric in R.
K-means cluster analysis of 17512 E. coioides genes from the htpG-RNAi strain infected spleen of E. coioides exhibited significant difference.
Oligonucleotides used in producing shRNA for stable gene silencing.
Primers for qRT-PCR.
Correlations between gene expressions.