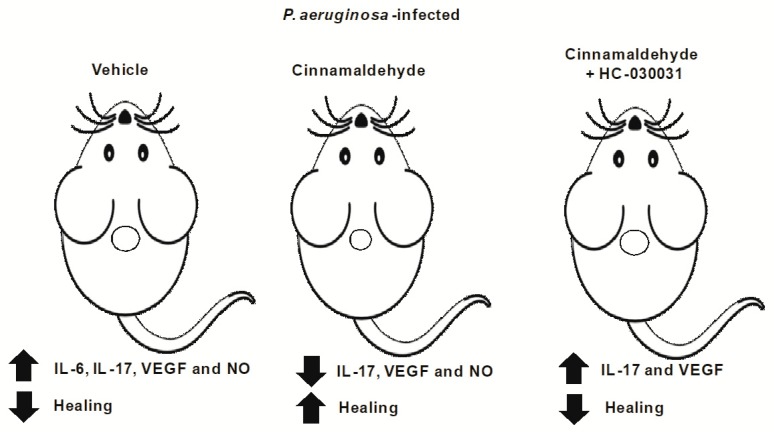
Figure 6.
Summary of cinnamaldehyde effects in the wound healing of mice infected with P. aeruginosa. Mice infected with P. aeruginosa have delayed healing, associated with increased production of inflammatory mediators in the wound beds in response to this bacterial infection. The topical application of cinnamaldehyde reduces the bacterial load in the wound tissue and promotes wound healing, as denoted by reduction of the wounded area. This effect is associated with diminished levels of IL-17, VEGF and NO in the wound beds. The systemic TRPA1 antagonism by HC-030031 prevents cinnamaldehyde’s pro-healing action by increasing IL-17 and NO levels.