Correction to: BMC Evol Biol
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-019-1406-3
After publication of the original article [1], the authors have notified us that the incorrect version of Fig. 4 was used. Below you can find the both incorrect and correct versions of the figure.
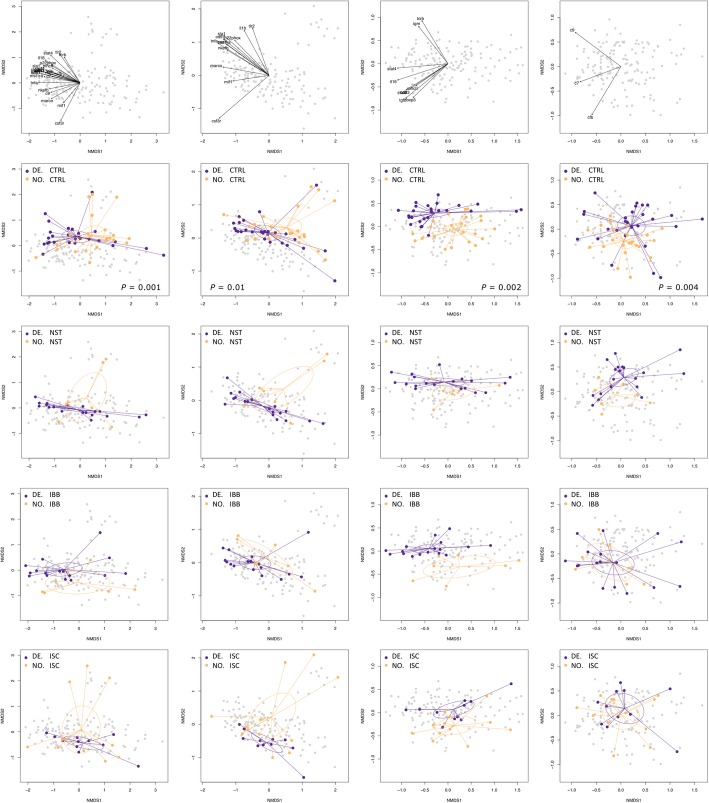
Fig. 4.
Multivariate gene expression patterns differ between DE and NO sticklebacks. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots on Euclidian distances and two dimensions comparing data from NO and DE sticklebacks (contrast 1). NMDS were based on log10-transformed calibrated normalized relative quantities (CNRQ values) of all 24 immune genes, twelve genes of innate immunity (marco, mst1ra, mif, il-1β, tnfr1, saal1, tlr2, csf3r, p22phox, nkef-b, sla1, cd97), nine genes of adaptive immunity (stat4, stat6, igm, cd83, foxp3, tgf-β, il-16, mhcII, tcr-β), or three genes of the complement system (cfb, c7, c9). Each dot represents one individual; colors refer to the host population. Ellipses represent 95% confidence intervals. P-values are shown if significant after FDR-correction. The contribution of each gene is shown in the first row. The second row shows data from sham-exposed (CTRL) sticklebacks. The third to sixth row show data from infected individuals. Function metaMDS() was used to plot the NMDS; the contribution of each gene was plotted by use of the envfit() function (both functions are implemented in R package vegan [74])
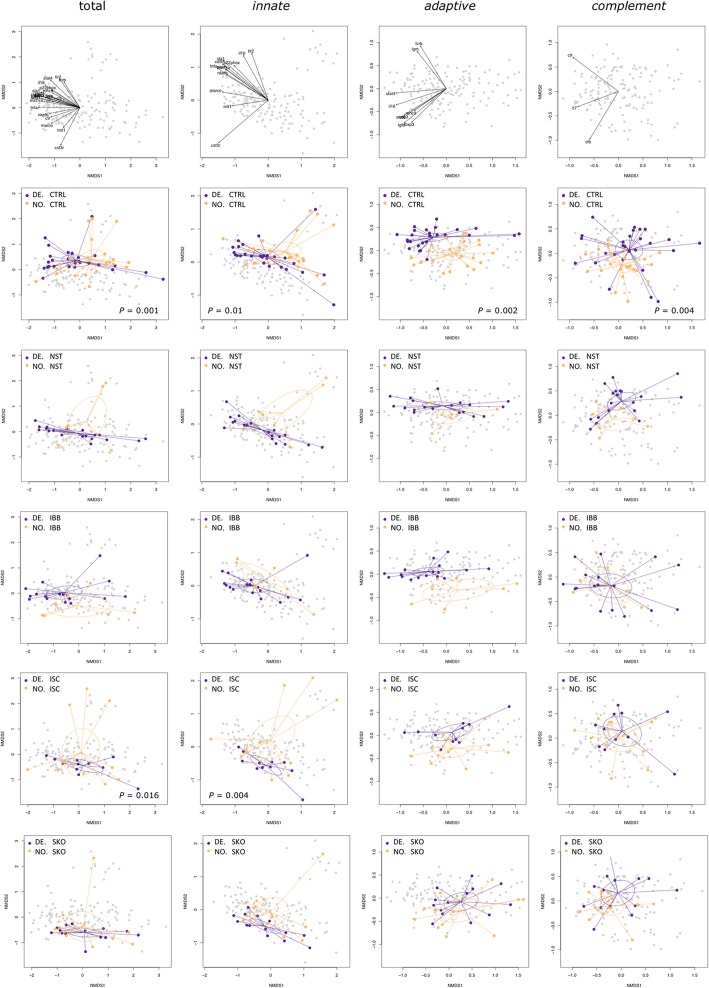
Fig. 4.
Multivariate gene expression patterns differ between DE and NO sticklebacks. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots on Euclidian distances and two dimensions comparing data from NO and DE sticklebacks (contrast 1). NMDS were based on log10-transformed calibrated normalized relative quantities (CNRQ values) of all 24 immune genes, twelve genes of innate immunity (marco, mst1ra, mif, il-1β, tnfr1, saal1, tlr2, csf3r, p22phox, nkef-b, sla1, cd97), nine genes of adaptive immunity (stat4, stat6, igm, cd83, foxp3, tgf-β, il-16, mhcII, tcr-β), or three genes of the complement system (cfb, c7, c9). Each dot represents one individual; colors refer to the host population. Ellipses represent 95% confidence intervals. P-values are shown if significant after FDR-correction. The contribution of each gene is shown in the first row. The second row shows data from sham-exposed (CTRL) sticklebacks. The third to sixth row show data from infected individuals. Function metaMDS() was used to plot the NMDS; the contribution of each gene was plotted by use of the envfit() function (both functions are implemented in R package vegan [74])
The original article has been corrected.
Footnotes
Martin Kalbe is deceased. This paper is dedicated to his memory.
Reference
- 1.Piecyk et al. (2019) Specificity of resistance and geographic patterns of virulence in a vertebrate hostparasite system (2019) 19:80: 10.1186/s12862-019-1406-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]