Abstract
Background
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves the therapeutic administration of 100% oxygen in a pressure chamber at pressures above one atmosphere absolute. This therapy has been used as an adjunct to surgery and antibiotics in the treatment of patients with necrotizing fasciitis with the aim of reducing morbidity and mortality.
Objectives
To review the evidence concerning the use of HBOT as an adjunctive treatment for patients with necrotizing fasciitis (NF). Specifically, we wish to address the following questions.
1. Does administration of HBOT reduce mortality or morbidity associated with NF?
2. What adverse effects are associated with use of HBOT in the treatment of individuals with NF?
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); MEDLINE Ovid (1966 to September 2014); the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) Ovid (1982 to September 2014); EMBASE Ovid (1980 to September 2014); and the Database of Randomised Controlled Trials in Hyperbaric Medicine (DORCTHIM, M Bennett) (from inception to September 2014). In addition, we performed a systematic search of specific hyperbaric literature sources. This included handsearching of relevant hyperbaric textbooks; hyperbaric journals (Hyperbaric Medicine Review, South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society Journal, European Journal of Underwater and Hyperbaric Medicine, Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine Journal); and conference proceedings of the major hyperbaric societies (Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society, South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society, European Underwater and Baromedical Society, International Congress of Hyperbaric Medicine).
Selection criteria
We included all randomized and pseudo‐randomized trials (trials in which an attempt at randomization has been made but the method was inappropriate, for example, alternate allocation) that compared the effects of HBOT with the effects of no HBOT (no treatment or sham) in the treatment of children and adults with necrotizing fasciitis.
Data collection and analysis
We planned independent data collection by two review authors using standardized forms.
Main results
We found no trials that met the inclusion criteria.
Authors' conclusions
This systematic review failed to locate relevant clinical evidence to support or refute the effectiveness of HBOT in the management of necrotizing fasciitis. Good quality clinical trials are needed to define the role, if any, of HBOT in the treatment of individuals with necrotizing fasciitis.
Plain language summary
Using oxygen at high pressure (in a compression chamber) for the treatment of individuals with severe soft tissue infection (necrotizing fasciitis)
Severe soft tissue infection (necrotizing fasciitis) is life threatening, is associated with prolonged hospital stay and carries high risk of long‐term loss of function. Routine treatment consists of immediate surgical removal of infected tissue and administration of antibiotics. Use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy, or HBOT, in addition to surgery and antibiotics has been suggested as a way to minimize tissue loss, decrease the number of limb amputations and reduce death. The aim of HBOT is to increase the supply of oxygen to the site. This approach may be toxic to bacteria, may improve the effectiveness of antibiotics and can improve healing.
We searched the databases to September 2014. This Cochrane review found no high‐quality trials to support or refute the use of HBOT in the treatment of individuals with necrotizing fasciitis. It should be noted that HBOT may very rarely result in serious adverse effects. Further studies are required to address the effectiveness of HBOT because currently it is provided as routine practice in some centres.
Background
Description of the condition
Necrotizing fasciitis (NF) is a rare soft tissue infection characterized by rapidly progressive death (necrosis) of the fascia and subcutaneous tissue with relative sparing of underlying muscle (Wilson 1952). It was first described in the scrotum and penis by Fournier in 1883, and subsequently by Meleney in a series of patients with streptococcal disease (Fournier 1883; Meleney 1924). This fulminant tissue necrosis is usually accompanied by generalized toxicity, which may progress to shock and multiple organ failure. Without prompt recognition and immediate aggressive management, NF is often rapidly fatal.
Necrotizing fasciitis may occur in a wide range of anatomical locations, and it has been labelled specifically when it occurs in certain locations, for example, Fournier's gangrene in the scrotum (Dellinger 1981; Elliott 1996; McHenry 1995). The initial event in the onset of necrotizing fasciitis is entry of bacteria into the fascia, which may be an apparently ‘spontaneous’ event or may occur secondary to trauma or surgery. Rapid bacterial proliferation in the fascia is followed by polymorphonuclear leukocyte (white cell) infiltration and liquefactive necrosis (tissue death). Progressive thrombosis (occlusion) of blood vessels in the fascia leads to occlusion of the perforating skin vessels and secondary cutaneous (skin) ischaemia and gangrene (Stamenkovic 1984; Wong 2005).
The key therapeutic intervention is immediate and radical surgical debridement of all dead tissue. It has been consistently shown that delay to the first surgical debridement is associated with increased mortality (Bilton 1998; Freischlag 1985; Majeski 1983; Majeski 1997; Sudarsky 1987; Wong 2003). Surgery should be accompanied by prompt commencement of broad‐spectrum antibiotics and appropriate high‐dependency supportive care. Necrotizing fasciitis may be monomicrobial (Type 2 or 3) or polymicrobial (Type 1) (Lancerotto 2012; Wong 2003). Group A streptococci (GAS) are the most commonly isolated organisms (Lancerotto 2012; Wong 2003); consequently antibiotic treatment should include good bactericidal streptococcal cover. Even with early aggressive surgical intervention and appropriate antibiotic treatment, mortality rates are in the region of 30% to 40% in relatively recently published case series (Clark 1999; Elliott 1996; McHenry 1995). Furthermore, patients frequently require multiple extensive debridements and not uncommonly are left with large soft tissue deficits. Prolonged hospital stay and rehabilitation are often required. Thus necrotizing fasciitis is a condition that incurs significant morbidity and both early and late mortality.
Description of the intervention
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves the therapeutic administration of 100% oxygen in a pressure chamber at pressures above one atmosphere absolute. This results in greatly increased arterial oxygen content and thus tissue oxygen pressure (PtO2). The precise details of treatments vary, but most treatments involve 60 to 90 minutes of exposure to oxygen at pressures between two and three atmospheres. Full critical care monitoring, including invasive blood pressure and central venous pressure (CVP) monitoring, is available during treatment if required. Patients can be mechanically ventilated throughout HBOT. Furthermore, use of multi‐occupant chambers permits constant medical supervision inside the chamber by critical care nurses and doctors.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is associated with some risk of adverse effects. The most common adverse event is pressure‐induced damage (barotrauma) to the middle ear, which occurs in approximately 4% of treatments (Plafki 2000). In the vast majority of cases, barotrauma is self‐limiting and has no long‐term effects on hearing (Beuerlein 1997). In ventilated patients, tympanostomies (holes in the tympanic membrane) may be performed under local anaesthetic before HBOT is given to prevent the occurrence of middle ear barotrauma. Pressure‐induced damage to the inner ears, lungs, sinuses and teeth has been reported but is extremely rare; a prospective study reported no cases among 11,376 HBOT treatments (Plafki 2000). Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may cause acute brain oxygen toxicity, which presents with seizures and occurs in approximately 0.03% of HBOT treatments (Hampson 2003; Plafki 2000). Seizures terminate when oxygen is removed, and their occurrence does not confer long‐term risk of seizures. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may cause pulmonary oxygen toxicity, resulting in a cough, but this does not affect lung function test results (Plafki 2000). Temporary worsening of short‐sightedness occurs but usually resolves by 10 weeks (Evanger 2004). Claustrophobia occurs in a minority of patients (Plafki 2000). Thus, although serious adverse events are rare, HBOT cannot be regarded as an entirely benign intervention.
How the intervention might work
Several of the physiological effects of HBOT indicate that it may be beneficial for individuals with necrotizing fasciitis. Infected necrotic fascia with disrupted vasculature is oedematous and relatively hypoxic (Hunt 1969). Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases tissue oxygen tension in necrotizing fasciitis wounds, thereby salvaging critically ischaemic areas (Korhonen 2000). Furthermore, hyperoxia potentiates antibiotic efficiency, improves white cell killing efficacy and is anti‐inflammatory—all of which may improve outcomes (Chapnick 1996; Clark 1999; Mader 1980; Mandell 1974; Park 1999; Thom 1997; Zamboni 1993).
Why it is important to do this review
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been used as adjunctive treatment for individuals with necrotizing soft tissue infection since the 1960s, when it was proposed to treat anaerobic infection (Brummelkamp 1961). However, non‐random evidence supporting the use of HBOT is conflicting. Some retrospective cohort studies report a significant reduction in mortality with adjunctive HBOT (Hollabaugh 1998; Riseman 1990; Wilkinson 2004), whilst others report no change in mortality (Brown 1994; Shupak 1995). As a result, clinical practice varies widely. At some centres HBOT is an integral part of the standard treatment regimen, whilst at others it is never used (Elliott 1996; McHenry 1995; Riseman 1990). In view of the significant mortality and morbidity associated with this condition and the risks inherent in the transfer of critically ill patients, it is important that potentially beneficial adjunctive treatments be closely evaluated.
Objectives
To review the evidence concerning the use of HBOT as an adjunctive treatment for patients with necrotizing fasciitis (NF). Specifically, we wish to address the following questions.
Does administration of HBOT reduce mortality or morbidity associated with NF?
What adverse effects are associated with use of HBOT in the treatment of individuals with NF?
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We planned to include all randomized and pseudo‐randomized trials (trials in which an attempt at randomization has been made but the method was inappropriate, for example, alternate allocation) that compared the effects of HBOT with the effects of no HBOT in the treatment of children and adults with necrotizing fasciitis.
Types of participants
We planned to include all human trials.
Types of interventions
The intervention was HBOT administered in a monoplace or multi‐place chamber at pressures between 1.5 and 3 atmospheres for 60 minutes or longer, at least once a day. The minimum accepted number of treatments was one. The comparator therapy was no HBOT treatment (no treatment or sham). Additional therapy provided concomitantly must have been applied to both groups and may have been diverse. We planned to accept any antibiotic and surgical regimens designed to control the infection.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
Mortaility during the presenting admission.
Secondary outcomes
Six‐month, one‐year and two‐year mortality.
Major amputation rate (above wrist or ankle in limb NF).
Number of surgical debridements.
Functional outcomes at any time, including quality of life measures.
Ventilator days.
Hospital length of stay.
Costs of therapy.
Adverse effects of all therapies.
Search methods for identification of studies
We aimed to capture all relevant published and unpublished studies.
Electronic searches
We performed electronic searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); MEDLINE Ovid (1966 to September 2014); the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) Ovid (1982 to September 2014); EMBASE Ovid (1980 to September 2014); and the Database of Randomised Controlled Trials in Hyperbaric Medicine (DORCTHIM, M Bennett) (from inception to September 2014). The search strategies used are included in Appendix 1 (MEDLINE Ovid); Appendix 2 (CINAHL Ovid); Appendix 3 (EMBASE Ovid); and Appendix 4 (CENTRAL).
Given the confusing and varied nomenclature used in the field of necrotizing fasciitis, these searches contain a wide variety of search terms including necrotizing fasciitis, Fournier’s gangrene, necrotizing soft tissue infection, haemolytic streptococcal gangrene, progressive synergistic bacterial gangrene, suppurative fasciitis, acute dermal gangrene, Meleney’s ulcer, Cullen’s ulcer, hospital gangrene and synergistic necrotizing cellulitis.
Searching other resources
In addition, we performed a systematic search of specific hyperbaric literature sources. This included handsearching of relevant hyperbaric textbooks (Bakker 2002; Jain 2004; Kindwall 1999; Mathieu 2006; Neuman 2008); hyperbaric journals (Hyperbaric Oxygen Review, South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society Journal, European Journal of Underwater and Hyperbaric Medicine, Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine Journal); and conference proceedings of the major hyperbaric societies (Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society, South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society, European Underwater and Baromedical Society, International Congress of Hyperbaric Medicine).
We considered all languages and handsearched the references of all identified studies to identify further relevant publications.
We contacted researchers in the field and leading hyperbaric treatment centres (as identified from personal communication and Internet searches) and asked for additional data in the form of published and unpublished studies.
We contacted the authors of relevant studies to request details of unpublished or ongoing investigations and to clarify unclear points.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
One review author (MB) was responsible for searching for and identifying potentially eligible studies. Two review authors (DL, IM) examined the search results and identified studies for inclusion. Identified studies were retrieved as full text independently by DL and IM for inclusion or exclusion.
Data extraction and management
We planned to extract data using a piloted data extraction form designed for this review. Data that we planned to extract included information regarding participants, interventions, outcomes and study quality. We planned that two review authors (DL, IM) would extract data independently. MB planned to review all extracted data and to arbitrate on unresolved disagreements between the other two review authors. We planned to contact study authors for clarification if we noted any ambiguity in the data. We planned that two review authors (DL, IM) would independently enter all data into Review Manager (RevMan 5.3).
We planned to extract the following data: citation; study design; methodological criteria; inclusion and exclusion criteria; participant characteristics; trial setting; HBOT treatment regimen and number of treatments;NF site and severity including microbiology, control group intervention details such as timing of first surgery, nature of the surgery, experience of the surgeon and type and time course of antibiotic treatment; all relevant outcome measures and all cost‐effectiveness data reported.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
We planned to assess and document the methodological quality of included controlled trials in accordance with the Cochrane approach, using the methods detailed in Section 6 of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011). We planned to use the following five parameters to assess quality: allocation concealment, method of allocation to treatment, documentation of exclusions, completeness of follow‐up and methods used to document complications. We planned to grade each parameter of trial quality as low risk of bias, high risk of bias or unclear risk of bias, and to perform an overall assessment of each controlled trial using the same three criteria.
Differences would have been settled by consensus, and further information was to be sought from study authors when information provided in the written report was insufficient. In addition, we planned to rank studies on the basis of sample size and to identify those with sufficient power to determine the clinically important effect for which the trial was designed.
Unit of analysis issues
Had we included cluster‐randomized trials, we would have adjusted samples sizes according to Gates 2004 using an estimate of the intracluster correlation co‐efficient (ICC) derived from the trial data, if possible. If ICCs from other sources were used, we would have reported this and conducted sensitivity analyses to assess the effects of variations in the ICC. We considered it reasonable to combine results from individual randomized and cluster‐randomized trials if study design was not heterogeneous and if any interaction between choice of randomization unit and intervention effect was unlikely.
Dealing with missing data
All extracted data would have reflected the original allocation group to allow an intention‐to‐treat analysis. Dropouts were identified when this information was given.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We planned to assess differences between studies in key characteristics of participants, interventions or outcome measures (clinical heterogeneity) and to give consideration to the appropriateness of pooling results and performing meta‐analyses. In the absence of significant clinical heterogeneity, differences in reported effects (statistical heterogeneity) would have been assessed. We planned to address statistical heterogeneity using the I2 statistic (Higgins 2002). We considered that statistically important heterogeneity was likely when I2 was greater than 40%.
Assessment of reporting biases
We planned to address publication bias by examining a funnel plot for signs of asymmetry.
Data synthesis
We planned to perform a random‐effects meta‐analysis of the effects of HBOT on hospital mortality.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
If data were available, we planned subgroup analyses on the basis of the following.
Time of onset to time of first treatment.
Severity of illness at outset.
Location of NF (limb vs trunk).
Age (children vs adults).
Intercurrent illness (considering diabetes and immune depression, if appropriate).
Sensitivity analysis
We planned to employ sensitivity analyses using different approaches to imputation of missing data. The best‐case scenario assumed that none of the participants originally enrolled in the treatment group and missing from the primary analysis had the negative outcome of interest, whilst all of those missing from the control group did. The worst‐case scenario was the reverse. We planned to employ sensitivity analyses on the basis of data quality.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
We searched the databases up to September 2013. Our search revealed 906 hits (see Figure 1). We screened 673 records after we removed duplicates. Upon scrutinizing all of these abstracts, we found no studies that fulfilled the inclusion criteria. We contacted experts in the field of hyperbaric medicine, but this effort failed to contribute any relevant studies, published or unpublished.
1.
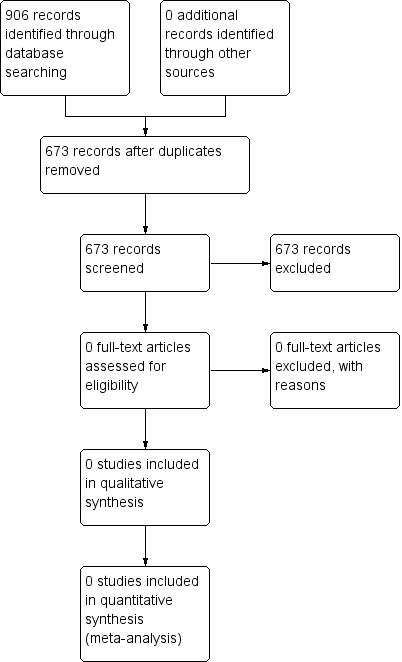
Flow diagram of identified studies.
Included studies
No eligible studies were identified (see Characteristics of included studies table).
Excluded studies
No eligible studies were identified for exclusion (see Characteristics of excluded studies table).
Risk of bias in included studies
No studies were included in this review.
Effects of interventions
No studies were included in this review.
Discussion
This review failed to locate evidence from any randomized trial to support or refute the treatment of patients with necrotizing fasciitis with hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). Although this result was disappointing, it was not entirely unexpected. Previous reviews of HBOT for necrotizing soft tissue infection have highlighted the absence of truly randomized trials in this area, and successful performance of randomized controlled trials in this area is highly problematic for several reasons. One reason is that these infections are now quite uncommon and research would require the co‐operation of a large number of treatment centres to generate adequate power to detect important differences between groups; also the disease itself is widely variable in terms of both affected anatomical locations and severity, suggesting that a multiple stratification approach would further increase the numbers required. Also considerable heterogeneity in surgical and antibiotic approaches has been noted and would need to be standardized across all participating centres.
Ultimately, centres with hyperbaric facilities in place are unlikely to participate because most of these would accept HBOT as a standard, routine approach to treatment of individuals with these infections and would refuse to accept withdrawal of this therapy on ethical grounds.
We are aware of several non‐random comparative studies in this area. Combining the results of these reports into a single meta‐analysis has been suggested in the past, but no one has acted upon this suggestion. We are aware of the potential for bias introduced by such an approach; however, we intend to explore a meta‐analysis of this evidence in a future publication.
The best course of action would be to conduct a multi‐centre randomised controlled trial, and we urge researchers to consider completing such a study. In the absence of this, a less desirable but feasible alternative would be to establish a large multi‐centre (probably multi‐national) prospective cohort study including centres with expertise and experience with these infections both with and without adjunctive HBOT. A prospective carefully prepared collection of data would prevent some of the biases that may be present in currently available data and would likely serve as a useful guide for practice.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Randomized evidence is insufficient to support or refute the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the treatment of patients with necrotizing fasciitis.
Implications for research.
Given current interest in the use of HBOT for this difficult clinical problem and the wide variation in international practice, the case can be made for new clinical trials of high methodological rigour specifically designed to assess the impact of HBOT as adjunctive therapy for individuals with necrotizing fasciitis. Specifically, information is required to identify the effects of adjunctive HBOT on functional outcome, amputation rate and mortality. Furthermore, adverse effects associated with use of HBOT in the treatment of these critically ill patients must be identified.
Future trials should include the following.
Appropriate sample sizes with power to detect expected differences.
Number of HBOT treatments required.
Number of surgical debridements required.
Major amputation rate.
Critical care length of stay, hospital length of stay.
Functional outcomes.
Costs of therapy.
Adverse effects of therapy.
We urge researchers to consider establishing a multi‐centre randomized controlled trial.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 14 December 2018 | Amended | Editorial team changed to Cochrane Emergency and Critical Care |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 3, 2009 Review first published: Issue 1, 2015
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 18 December 2007 | Amended | Converted to new review format |
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Harald Herkner (content editor); Jong‐Wook Ban, Dirk Jan Bakker and Bernard Coronel Wischmeyer (peer reviewers); and Ann E Fonfa (consumer referee) for help and editorial advice provided during the preparation of this systematic review.
We would also like to thank Harald Herkner (content editor); Bernard Coronel Wischmeyer, Dirk Jan Bakker and Richard Moon (peer reviewers); and the Cochrane Consumer Network (Suzanne Cunliffe and Kathie Godfrey) for help and editorial advice provided during preparation of the protocol (Levett 2009) for this systematic review.
Appendices
Appendix 1. MEDLINE (Ovid SP)
1. exp Hyperbaric Oxygenation/ or HBO*.mp. or (hyperbaric adj3 oxygen*).af. 2. exp Fasciitis, Necrotizing/ or ((necro* or suppurative) adj3 fasciit*).mp. or ((fasciitis.mp. or exp Fasciitis/) and exp Necrosis/) or exp Fournier Gangrene/ or exp Soft Tissue Infections/ or (gangren* adj5 (hospital or synergistic or bacterial or streptococcal or ha?molytic or dermal or acute)).mp. or synergistic necrotic?ing cellulitis.mp. or (ulcer* adj3 (meleney* or cullen*)).mp. or necroti?ing soft tissue infection$.mp. 3. 1 and 2
Appendix 2. CINAHL (EBSCO host)
S1 (MM "Hyperbaric Oxygenation") or (HBO* or hyperbaric oxygen*)
S2 (MM "Fournier's Gangrene") and (MM "Soft Tissue Infections") or (MM "Necrosis" and ((MM "Fasciitis") or "fasciitis") or (Fournier gangrene or Necrotizing fasc* or Meleney* or Necrotizing soft tissue infection or haemolytic streptococcal* or progressive synergistic bacterial gangrene or suppurative fasciitis or acute dermal gangrene or synergistic necrotizing cellulitis)
S3 S1 and S2
Appendix 3. EMBASE (Ovid SP)
1. exp hyperbaric oxygen/ or HBO*.mp. or (hyperbaric adj3 oxygen*).af. 2. exp necrotizing fasciitis/ or ((necro* or suppurative) adj3 fasciit*).mp. or ((fasciitis.mp. or exp fasciitis/) and exp necrosis/) or exp Fournier gangrene/ or exp soft tissue infection/ or (gangren* adj5 (hospital or synergistic or bacterial or streptococcal or ha?molytic or dermal or acute)).mp. or synergistic necrotic?ing cellulitis.mp. or (ulcer* adj3 (meleney* or cullen*)).mp. or necroti?ing soft tissue infection$.mp. 3. 1 and 2
Appendix 4. CENTRAL
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Hyperbaric Oxygenation] explode all trees #2 (hyperbaric and oxygen*) or HBO* #3 #1 or #2 #4 MeSH descriptor: [Fasciitis, Necrotizing] explode all trees #5 MeSH descriptor: [Fournier Gangrene] explode all trees #6 MeSH descriptor: [Soft Tissue Infections] explode all trees #7 ((necro* or suppurative) and fasciit*) or (gangren* and (hospital or synergistic or bacterial or streptococcal or ha?molytic or dermal or acute)) or (synergistic necrotic?ing cellulitis) or (ulcer* and (meleney* or cullen*)) or (necroti?ing soft tissue infection*) #8 #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 #9 #3 and #8
Contributions of authors
Conceiving of the review: Dr Denny Levett (DL), Dr Ian Millar (IM) and Professor Mike Bennett (MB). Co‐ordinating the review: DL. Undertaking manual searches: DL and MB designed search strategies for electronic searches and undertook handsearching of relevant journals. Screening search results: DL and IM. Organizing retrieval of papers: DL. Screening retrieved papers against inclusion criteria: DL and IM. Appraising quality of papers: DL and IM. Abstracting data from papers: DL and IM. Writing to authors of papers for additional information: IM. Providing additional data about papers: IM. Obtaining and screening data on unpublished studies: MB. Managing data for the review: DL. Entering data into Review Manager: DL. Analysing RevMan statistical data: under guidance of MB. Performing other statistical analysis not using RevMan: under guidance of MB. Performing double entry of data: data entered by person one, DL; data entered by person two, IM. Interpreting data: all review authors. Making statistical inferences: MB. Writing the review: DL wrote the first draft with input from other review authors. Securing funding for the review: funded by salary support at the review authors' institutions. Performing previous work that served as the foundation of the present study: Dr Ian Millar, necrotizing fasciitis and HBOT; Dr Mike Bennett, multiple Cochrane systematic reviews on the efficacy of HBOT. Serving as guarantor for the review (one review author): DL. Taking responsibility for reading and checking the review before submission: all review authors; DL submitted.
Sources of support
Internal sources
Salary support, The Alfred Hyperbaric Unit, Melbourne, Australia.
Salary support, Prince of Wales Hospital, Sydney, Australia.
External sources
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
Denny Levett: none known.
Michael H Bennett: none known.
Ian Millar: none known.
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
Additional references
Bakker 2002
- Bakker J. Hyperbaric Surgery—Perioperative Care. First Edition. North Palm Beach, FL, USA: Best Publishing Company, 2002. [Google Scholar]
Beuerlein 1997
- Beuerlein M, Nelson RN, Welling DB. Inner and middle ear hyperbaric oxygen‐induced barotrauma. Laryngoscope 1997;107(10):1350‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bilton 1998
- Bilton BD, Zibari GB, McMillan RW, Aultman DF, Dunn G, McDonald JC. Aggressive surgical management of necrotizing fasciitis serves to decrease mortality: a retrospective study. The American Surgeon 1998;64(5):397‐400. [PUBMED: 9585771] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Brown 1994
- Brown DR, Davis NL, Lepawsky M, Cunningham J, Kortbeek J. A multicenter review of the treatment of major truncal necrotizing infections with and without hyperbaric oxygen therapy. American Journal of Surgery 1994;167(5):485‐9. [PUBMED: 8185032 ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Brummelkamp 1961
- Brummelkamp WH. Treatment of anaerobic infections by drenching the tissue with oxygen under high atmospheric pressure. Surgery 1961;49:299‐302. [Google Scholar]
Chapnick 1996
- Chapnick EK, Abter EI. Necrotizing soft‐tissue infections. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America 1996;10(4):835‐55. [PUBMED: 8958171] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Clark 1999
- Clark LA, Moon RE. Hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of life‐threatening soft‐tissue infections. Respiratory Care Clinics of North America 1999;5(2):203‐19. [PUBMED: 10333449] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dellinger 1981
- Dellinger EP. Severe necrotizing soft‐tissue infections. Multiple disease entities requiring a common approach. JAMA 1981;246(15):1717‐21. [PUBMED: 7277653 ] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Elliott 1996
- Elliott DC, Kufera JA, Myers RA. Necrotizing soft tissue infections. Risk factors for mortality and strategies for management. Annals of Surgery 1996;224(5):672‐83. [PUBMED: 8916882] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Evanger 2004
- Evanger K, Haugen O, HIrgens A, Aanderud L, Thorsen E. Ocular refractive changes in patients receiving hyperbaric oxygen administered by oronasal mask or hood. Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica 2004;82(4):449‐53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fournier 1883
- Fournier AJ. Devastating gangrene of the penis [Gangrene Foudroyante de la Verge]. Seminars in Medicine 1883;3:345. [Google Scholar]
Freischlag 1985
- Freischlag JA, Ajalat G, Busuttil RW. Treatment of necrotizing soft tissue infections. The need for a new approach. American Journal of Surgery 1985;149(6):751‐5. [PUBMED: 4014552] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gates 2004
- Gates S. Statistical and methodological guidelines for Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group reviews. The Editorial Team. Pregnancy and Childbirth Group. About the Cochrane Collaboration (Cochrane Review Groups (CRGs)) Issue 3 (1465‐858) 2004.
Hampson 2003
- Hampson N, Atik D. Central nervous system oxygen toxicity during routine hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine 2003;30(2):147‐53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2002
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. [PUBMED: 12111919 ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hollabaugh 1998
- Hollabaugh RS Jr, Dmochowski RR, Hickerson WL, Cox CE. Fournier's gangrene: therapeutic impact of hyperbaric oxygen. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 1998;101(1):94‐100. [PUBMED: 9427921] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hunt 1969
- Hunt TK, Zederfeldt B, Goldstick TK. Oxygen and healing. American Journal of Surgery 1969;118(4):521‐5. [PUBMED: 4898193 ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jain 2004
- Jain KK. Textbook of Hyperbaric Medicine. Fourth. Cambridge, MA, USA: Hogrefe & Huber Publishers, 2004. [Google Scholar]
Kindwall 1999
- Kindwall EP. Hyperbaric Medicine Practice. Second Edition. North Palm Beach, FL, USA: Best Publishing Company, 1999. [Google Scholar]
Korhonen 2000
- Korhonen K, Kuttila K, Niinikoski J. Tissue gas tensions in patients with necrotising fasciitis and healthy controls during treatment with hyperbaric oxygen: a clinical study. European Journal of Surgery 2000;166(7):530‐4. [PUBMED: 10965830 ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lancerotto 2012
- Lancerotto L, Tocco I, Salmaso R, Vindigni V, Bassetto F. Necrotizing fasciitis: classification, diagnosis, and management. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 2012;72(3):560‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mader 1980
- Mader JT, Brown GL, Guckian JC, Wells CH, Reinarz JA. A mechanism for the amelioration by hyperbaric oxygen of experimental staphylococcal osteomyelitis in rabbits. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 1980;142(6):915‐22. [PUBMED: 7462700] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Majeski 1983
- Majeski JA, Alexander JW. Early diagnosis, nutritional support, and immediate extensive debridement improve survival in necrotizing fasciitis. American Journal of Surgery 1983;145(6):784‐7. [PUBMED: 6344676 ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Majeski 1997
- Majeski J, Majeski E. Necrotizing fasciitis: improved survival with early recognition by tissue biopsy and aggressive surgical treatment. Southern Medical Journal 1997;90(11):1065‐8. [PUBMED: 9386043] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mandell 1974
- Mandell GL. Bactericidal activity of aerobic and anaerobic polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Infection and Immunity 1974;9(2):337‐41. [PUBMED: 4361295] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mathieu 2006
- Mathieu D. Handbook of Hyperbaric Medicine. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Neuroscience, 2006. [Google Scholar]
McHenry 1995
- McHenry CR, Piotrowski JJ, Petrinic D, Malangoni MA. Determinants of mortality for necrotizing soft‐tissue infections. Annals of Surgery 1995;221(5):558‐63. [PUBMED: 7748037] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meleney 1924
- Meleney FL. Hemolytic streptococcus gangrene. Archives of Surgery 1924;9:317. [Google Scholar]
Neuman 2008
- Neuman TS, Thom SR. Physiology and Medicine of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. First Edition. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2008. [Google Scholar]
Park 1999
- Park M. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen in infectious diseases: basic mechanisms. Hyperbaric Medicine Practice. North Palm Beach, FL, USA: Best Publishing Company, 1999:205‐43. [PUBMED: 99] 99 [Google Scholar]
Plafki 2000
- Plafki C, Peters P, Almeling M, Welslau W, Busch R. Complications and side effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine 2000;71(2):119‐24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan) Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Riseman 1990
- Riseman JA, Zamboni WA, Curtis A, Graham DR, Konrad HR, Ross DS. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for necrotizing fasciitis reduces mortality and the need for debridements. Surgery 1990;108(5):847‐50. [PUBMED: 2237764] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shupak 1995
- Shupak A, Shoshani O, Goldenberg I, Barzilai A, Moskuna R, Bursztein S. Necrotizing fasciitis: an indication for hyperbaric oxygenation therapy?. Surgery 1995;118(5):873‐8. [PUBMED: 7482275] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Stamenkovic 1984
- Stamenkovic I, Lew PD. Early recognition of potentially fatal necrotizing fasciitis. The use of frozen‐section biopsy. The New England Journal of Medicine 1984;310(26):1689‐93. [PUBMED: 6727947] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sudarsky 1987
- Sudarsky LA, Laschinger JC, Coppa GF, Spencer FC. Improved results from a standardized approach in treating patients with necrotizing fasciitis. Annals of Surgery 1987;206(5):661‐5. [PUBMED: 3314752] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thom 1997
- Thom SR, Mendiguren I, Hardy K, Bolotin T, Fisher D, Nebolon M, et al. Inhibition of human neutrophil beta2‐integrin‐dependent adherence by hyperbaric O2. The American Journal of Physiology 1997;272(3 Pt 1):C770‐7. [PUBMED: 9124510] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wilkinson 2004
- Wilkinson D, Doolette D. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment and survival from necrotizing soft tissue infection. Archives of Surgery 2004;139(12):1339‐45. [PUBMED: 15611459 ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wilson 1952
- Wilson B. Necrotizing fasciitis. The American Surgeon 1952;18(4):416‐31. [PUBMED: 14915014] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wong 2003
- Wong CH, Chang HC, Pasupathy S, Khin LW, Tan JL, Low CO. Necrotizing fasciitis: clinical presentation, microbiology, and determinants of mortality. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 2003;85‐A(8):1454‐60. [PUBMED: 12925624 ] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wong 2005
- Wong CH, Wang YS. The diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases 2005;18(2):101‐6. [PUBMED: 15735411 ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zamboni 1993
- Zamboni WA, Roth AC, Russell RC, Graham B, Suchy H, Kucan JO. Morphologic analysis of the microcirculation during reperfusion of ischemic skeletal muscle and the effect of hyperbaric oxygen. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 1993;91(6):1110‐23. [PUBMED: 8479978] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Levett 2009
- Levett D, Bennett MH, Millar I. Adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen for necrotizing fasciitis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007937] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


