Abstract
Background
The World Health Organization recommends intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy (IPTp) with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine for malaria for all women who live in moderate to high malaria transmission areas in Africa. However, parasite resistance to sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine has been increasing steadily in some areas of the region. Moreover, HIV‐infected women on cotrimoxazole prophylaxis cannot receive sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine because of potential drug interactions. Thus, there is an urgent need to identify alternative drugs for prevention of malaria in pregnancy. One such candidate is mefloquine.
Objectives
To assess the effects of mefloquine for preventing malaria in pregnant women, specifically, to evaluate:
• the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of mefloquine for preventing malaria in pregnant women; and • the impact of HIV status, gravidity, and use of insecticide‐treated nets on the effects of mefloquine.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group Specialized Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in the Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, Embase, Latin American Caribbean Health Sciences Literature (LILACS), the Malaria in Pregnancy Library, and two trial registers up to 31 January 2018. In addition, we checked references and contacted study authors to identify additional studies, unpublished data, confidential reports, and raw data from published trials.
Selection criteria
Randomized and quasi‐randomized controlled trials comparing mefloquine IPT or mefloquine prophylaxis against placebo, no treatment, or an alternative drug regimen.
Data collection and analysis
Two review authors independently screened all records identified by the search strategy, applied inclusion criteria, assessed risk of bias, and extracted data. We contacted trial authors to ask for additional information when required. Dichotomous outcomes were compared using risk ratios (RRs), count outcomes as incidence rate ratios (IRRs), and continuous outcomes using mean differences (MDs). We have presented all measures of effect with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We assessed the certainty of evidence using the GRADE approach for the following main outcomes of analysis: maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery, clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy, placental malaria, maternal anaemia at delivery, low birth weight, spontaneous abortions and stillbirths, dizziness, and vomiting.
Main results
Six trials conducted between 1987 and 2013 from Thailand (1), Benin (3), Gabon (1), Tanzania (1), Mozambique (2), and Kenya (1) that included 8192 pregnant women met our inclusion criteria.
Two trials (with 6350 HIV‐uninfected pregnant women) compared two IPTp doses of mefloquine with two IPTp doses of sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine. Two other trials involving 1363 HIV‐infected women compared three IPTp doses of mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole with cotrimoxazole. One trial in 140 HIV‐infected women compared three doses of IPTp‐mefloquine with cotrimoxazole. Finally, one trial enrolling 339 of unknown HIV status compared mefloquine prophylaxis with placebo.
Study participants included women of all gravidities and of all ages (four trials) or > 18 years (two trials). Gestational age at recruitment was > 20 weeks (one trial), between 16 and 28 weeks (three trials), or ≤ 28 weeks (two trials). Two of the six trials blinded participants and personnel, and only one had low risk of detection bias for safety outcomes.
When compared with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, IPTp‐mefloquine results in a 35% reduction in maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (RR 0.65, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.86; 5455 participants, 2 studies; high‐certainty evidence) but may have little or no effect on placental malaria infections (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.86; 4668 participants, 2 studies; low‐certainty evidence). Mefloquine results in little or no difference in the incidence of clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy (incidence rate ratio (IRR) 0.83, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.05, 2 studies; high‐certainty evidence). Mefloquine decreased maternal anaemia at delivery (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.76 to 0.94; 5469 participants, 2 studies; moderate‐certainty evidence). Data show little or no difference in the proportions of low birth weight infants (RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.17; 5641 participants, 2 studies; high‐certainty evidence) and in stillbirth and spontaneous abortion rates (RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.58; 6219 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; moderate‐certainty evidence). IPTp‐mefloquine increased drug‐related vomiting (RR 4.76, 95% CI 4.13 to 5.49; 6272 participants, 2 studies; high‐certainty evidence) and dizziness (RR 4.21, 95% CI 3.36 to 5.27; participants = 6272, 2 studies; moderate‐certainty evidence).
When compared with cotrimoxazole, IPTp‐mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole probably results in a 48% reduction in maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.30 to 0.93; 989 participants, 2 studies; moderate‐certainty evidence) and a 72% reduction in placental malaria (RR 0.28, 95% CI 0.14 to 0.57; 977 participants, 2 studies; moderate‐certainty evidence) but has little or no effect on the incidence of clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy (IRR 0.76, 95% CI 0.33 to 1.76, 1 study; high‐certainty evidence) and probably no effect on maternal anaemia at delivery (RR 0.94, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.20; 1197 participants, 2 studies; moderate‐certainty evidence), low birth weight rates (RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.60; 1220 participants, 2 studies; moderate‐certainty evidence), and rates of spontaneous abortion and stillbirth (RR 1.12, 95% CI 0.42 to 2.98; 1347 participants, 2 studies; very low‐certainty evidence). Mefloquine was associated with higher risks of drug‐related vomiting (RR 7.95, 95% CI 4.79 to 13.18; 1055 participants, one study; high‐certainty evidence) and dizziness (RR 3.94, 95% CI 2.85 to 5.46; 1055 participants, 1 study; high‐certainty evidence).
Authors' conclusions
Mefloquine was more efficacious than sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine in HIV‐uninfected women or daily cotrimoxazole prophylaxis in HIV‐infected pregnant women for prevention of malaria infection and was associated with lower risk of maternal anaemia, no adverse effects on pregnancy outcomes (such as stillbirths and abortions), and no effects on low birth weight and prematurity. However, the high proportion of mefloquine‐related adverse events constitutes an important barrier to its effectiveness for malaria preventive treatment in pregnant women.
2 April 2019
Up to date
All studies incorporated from most recent search
All eligible published studies found in the last search (31 Jan, 2018) were included and one ongoing study was identified (see 'Characteristics of ongoing studies' section)
Plain language summary
Mefloquine for preventing malaria in pregnant women
What is the aim of this review?
The aim of this Cochrane Review was to find out whether the antimalarial drug mefloquine is efficacious and safe for prevention of malaria in pregnant women living in stable transmission areas. We found six relevant studies to help us answer this question.
Key messages
The antimalarial drug mefloquine is efficacious for malaria prevention in pregnant women. The drug has been found to be safe in terms of adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as low birth weight, prematurity, stillbirths and abortions, and congenital malformations. However, it is worse tolerated than other antimalarial drugs.
What was studied in the review?
Pregnant women are vulnerable to malaria infection, especially if they are living with HIV. The consequences of malaria during pregnancy can be severe and include poor health outcomes for both women and their children. For this reason, in malaria‐endemic areas of stable transmission, women are recommended to prevent malaria infection by sleeping under mosquito bed‐nets and by taking effective drugs (such as sulphadoxine‐pyrimethamine or cotrimoxazole in case of HIV infection) as chemoprevention against malaria throughout pregnancy.
This Cochrane Review looked at the effects of mefloquine for prevention of malaria in both HIV‐uninfected and HIV‐infected pregnant women.
What are the main results of the review?
We found five relevant studies conducted in sub‐Saharan Africa and one in Thailand between 1987 and 2013. These studies compared mefloquine with placebo or other antimalarial drugs currently recommended for prevention of malaria in pregnant women. The review shows the following:
• Compared with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, mefloquine chemoprevention in HIV‐uninfected women:
◦reduces risks of maternal peripheral parasitaemia (presence of malaria parasites in the blood of women) and anaemia at delivery; ◦ makes no difference in the prevalence of adverse maternal outcomes (such as low birth weight, prematurity, stillbirths and abortions, and congenital malformations) and in the incidence of clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy; and ◦ increases risks of drug‐related adverse events including vomiting, fatigue/weakness, and dizziness.
• Compared with cotrimoxale prophylaxis alone, mefloquine chemoprevention plus cotrimoxazole in HIV‐infected women:
◦ reduces the risk of maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery and the risk of placental malaria; ◦ makes no difference in the prevalence of adverse pregnancy outcomes (such as low birth weight, prematurity, stillbirths and abortions, and congenital malformations) and in the incidence of clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy; and ◦ increases the risk of drug‐related adverse events such as vomiting and dizziness.
Overall, the high proportion of mefloquine‐related adverse events constitutes an important barrier to its effectiveness for malaria preventive treatment in pregnant women.
How up‐to‐date is this review?
The review authors searched for studies up to 31 January 2018.
Summary of findings
Background
Description of the condition
Malaria is the most important parasitic disease worldwide and is endemic in parts of Africa, Asia, and South America. Pregnant women are at higher risk of malaria infection than non‐pregnant women in the same age group, and are at higher risk of severe illness (Brabin 1983; Desai 2007). Malaria infection during pregnancy, particularly the first or second pregnancy, is also associated with adverse outcomes for both mother (severe anaemia) and infant (low birth weight, neonatal mortality; Ataíde 2014; Guyatt 2004; Menendez 2010; Radeva‐Petrova 2014; Schwarz 2008; Steketee 2001). Symptoms most commonly reported by semi‐immune pregnant women with clinical malaria include headache, arthromyalgias, and fever (Bardaji 2008). In areas of low transmission, pregnant women with malaria parasitaemia frequently present with symptoms and signs such as fever, malaise, headache, and vomiting. The infection may develop into severe complications such as cerebral malaria and pulmonary oedema if untreated, and may be a cause of maternal mortality (Bardaji 2008).
To reduce the burden and consequences of malaria in pregnancy, the World Health Organization (WHO) currently recommends that pregnant women who live in moderate to high malaria transmission areas in Africa sleep under an insecticide‐treated net (ITN), as described in Gamble 2006, and receive intermittent preventive treatment (IPT) with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine at each scheduled antenatal care visit (provided that doses are at least one month apart) (WHO 2013). IPT is a form of malaria chemoprevention that was tested and adopted as policy in response to both malaria parasites developing resistance to weekly prophylaxis with chloroquine and low compliance with the weekly regimen (WHO 2004). The long elimination half‐life of sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine allows intermittent dosing while still providing prophylactic cover for the intervening weeks (White 2005). IPT is therefore defined as "administration of a curative treatment dose of an effective antimalarial drug at predefined intervals during pregnancy" regardless of the presence or absence of current infection (White 2005).
Sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine remains the drug used for IPT in pregnancy, even though resistance has spread in many parts of southern and eastern Africa (ter Kuile 2007; WHO 2012a), which is spurring researchers and policy makers to seek safe and effective alternatives to sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine (Desai 2018).
Description of the intervention
Mefloquine is a 4‐methanolquinoline that is related to quinine. It was originally developed by the US military for preventing malaria in soldiers and has been widely used for preventing malaria in travellers (Schlagenhauf 2010). Like sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, mefloquine has a long elimination half‐life of two to four weeks; in travellers, weekly dosing consists of 250 mg (FDA 2004), and in pregnant women monthly dosing at treatment doses is feasible (Briand 2009).
Mefloquine was first investigated in the 1990s as prophylactic treatment for pregnant women. An observational study raised concerns that mefloquine may be associated with increased risk of stillbirth (Nosten 1999); however other trials did not confirm this finding (Pekyi 2016; Steketee 1996). A systematic review considered the safety of mefloquine in pregnancy and concluded that no evidence indicates that mefloquine use in pregnancy carries increased risk for the foetus (Gonzalez 2014). The drug is known to be associated with a range of mild dose‐related transient side effects, such as vomiting, nausea, and dizziness (Bardaji 2012; Lee 2017; Sevene 2010; ter Kuile 1995). Researchers have described severe neuropsychiatric side effects that occur in about one in 10,000 travellers taking mefloquine as chemoprophylaxis (Phillips‐Howard 1995; Steffen 1993). Studies conducted in Beninese pregnant women found that dizziness and vomiting are the most frequent adverse effects related to use of mefloquine as IPT in pregnancy (Briand 2009; Denoeud‐Ndam 2012).
Data show resistance to mefloquine in multi‐drug resistance areas of Thailand (Carrara 2009; Nosten 2000), but it remains rare in Africa (Aubouy 2007; MacArthur 2001; Oduola 1987).
How the intervention might work
Malaria chemoprevention is thought to work through clearance or suppression of asymptomatic malaria infection in the peripheral blood of the mother and the placenta (White 2005). This reduction in malaria parasitaemia may, however, be insufficient to justify recommendations for widespread prophylactic prescriptions that do not provide subsequent benefit for clinically important outcomes for mother and baby. These outcomes may include a reduction in episodes of maternal malaria, reduced risk of anaemia, and improved birth weight, as well as more substantive outcomes such as a reduction in severe maternal illness or lower rates of spontaneous pregnancy loss and maternal, neonatal, and infant mortality (see Figure 1).
1.
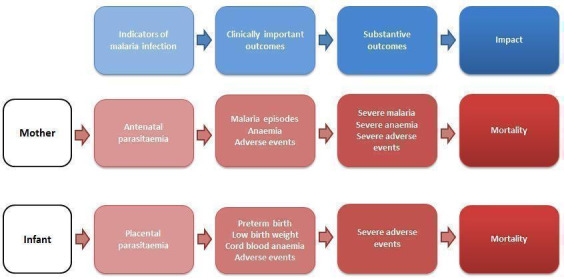
Indicators and impact of malaria infection in mothers and infants.
Effects of malaria chemoprevention may depend on the local malaria epidemiology and thus the level of acquired immunity against malaria in pregnant women. In stable transmission areas, women of reproductive age may be partially immune to malaria, presenting parasitaemia without clinical disease; however, asymptomatic infections may have detrimental effects, such as anaemia and low birth weight. In contrast, in unstable malaria transmission areas, naturally acquired malaria immunity is usually low among adults and malaria infection may be associated with clinical episodes and severe illness.
Primigravidae women are at higher risk of adverse effects of malaria infection than multigravidae women. This is thought to result from women developing antibodies specific to placental‐type parasites when exposed to Plasmodium falciparum during their first pregnancy. These antibodies are then present in subsequent pregnancies (Ataíde 2014). This is seen in multigravidae women as a more specific and efficient immune response and clearing the infection at an earlier stage than in primigravidae women (Walker 2013).
Another potential effect modifier of the susceptibility to malaria infection is HIV status (Menéndez 2011). In many malaria‐endemic areas, data show that the prevalence of HIV infection, which has been observed to increase the risk of malaria infection, is high among pregnant women (Gonzalez 2012; van Eijk 2003). Compared with HIV‐uninfected women, HIV‐infected women are more likely to carry malaria parasites in their blood, to have higher parasite densities, and to develop placental parasitaemia, anaemia, and malaria symptoms (Ayisi 2003; van Eijk 2002; van Eijk 2003). This increased risk of malaria is the same in multigravidae (women in their third pregnancy or higher) and in women in their first or second pregnancy (ter Kuile 2004; van Eijk 2003). Placental malaria infection may also increase the risk of perinatal mother‐to‐child transmission of HIV (Ayisi 2003).
Use of ITNs during pregnancy has been shown to have a beneficial impact on pregnancy outcomes (reduced prevalence of low birth weight, miscarriage, and placental parasitaemia) in malaria‐endemic Africa (Gamble 2007), and this approach could modify the effect of IPT (Menéndez 2008).
Why it is important to do this review
The WHO recommends IPT with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine for all pregnant women who live in moderate to high malaria transmission areas in Africa (WHO 2004; WHO 2013). However, studies have shown that resistance to sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine in some regions of Eastern Africa has been increasing steadily during the past two decades (Iriemenam 2012; Mockenhaupt 2008). Thus, there is an urgent need for more effective antimalarials to prevent malaria during pregnancy.
This review aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of mefloquine for preventing malaria in pregnant women. These findings could serve as the basis for future guidelines on preventive agents for malaria in pregnant women.
Objectives
To assess the effects of mefloquine for preventing malaria in pregnant women ‐ specifically, to evaluate:
the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of mefloquine for preventing malaria in pregnant women; and
the impact of HIV status, gravidity, and use of insect‐treated nets (ITNs) on the effects of mefloquine.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi‐RCTs.
Types of participants
Pregnant women of any gravidity regardless of HIV status, living in malaria‐endemic areas (CDC 2017).
Types of interventions
Interventions
Mefloquine given to pregnant women as intermittent preventive treatment or as chemoprophylaxis.
Controls
Placebo, no intervention, or an alternative drug regimen.
Types of outcome measures
Maternal
Maternal peripheral parasitaemia during pregnancy
Maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery
Placental malaria¹
Mean haemoglobin and maternal anaemia (moderate and severe) at delivery
Clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy
Foetal/infant
Cord blood parasitaemia
Cord blood haemoglobin and anaemia (as defined in the original studies)
Mean birth weight
Low birth weight prevalence (< 2500 g)
Prematurity prevalence (< 37 weeks of gestation)
Morbidity in first year of life
Adverse events
-
Serious adverse events (SAEs)²
Illnesses that were life threatening or required hospitalization during pregnancy (SAEs in pregnancy)
Adverse pregnancy outcomes: spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, congenital malformation
Maternal mortality
Perinatal, neonatal, infant mortality
Mother‐to‐child transmission of HIV frequency (at six weeks of age)
-
Non‐serious adverse events
Frequency and severity of reported all‐cause and drug‐related adverse events
¹Placental malaria diagnosed by histology, microscopy, or any method used in the included study. Figure 2 shows the relations between different outcomes.
2.
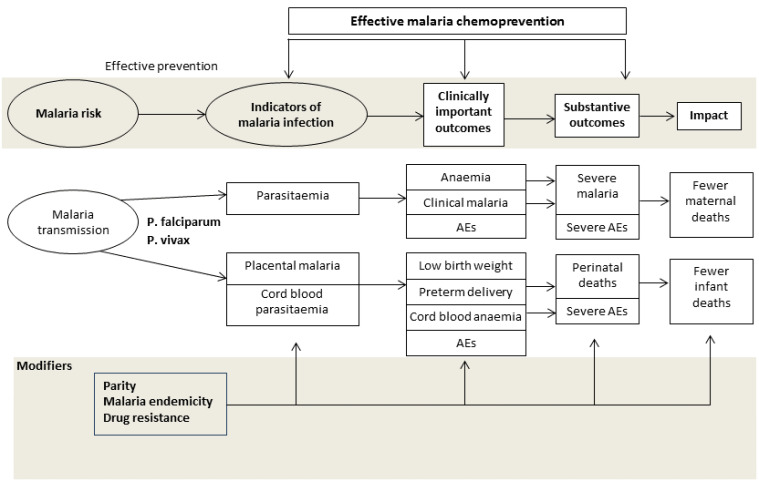
Conceptual framework of malaria chemoprevention. Reproduced under the terms of a Creative Commons Licence from Radeva‐Petrova 2014.
²Review authors acknowledge the limitation of analyzing rare serious adverse events because randomized controlled trials usually are not powered enough to detect them.
Search methods for identification of studies
We attempted to identify all relevant trials regardless of language or publication status (published, unpublished, in press, and in progress).
Electronic searches
We searched the following databases using the search terms and strategy described in Appendix 1: the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group Specialized Register (up to 31 January 2018); the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), published in the Cochrane Library (January 2018); MEDLINE (PubMed; from 1966 to 31 January 2018); Embase (OVID; 1974 to 31 January 2018); and Latin American Caribbean Health Sciences Literature (LILACS) (BIREME; 1982 to 31 January 2018). We also searched the Malaria in Pregnancy (MiP) Library (www.mip‐consortium.org/resources/index.htm), the WHO International Clinical Trial Registry Platform (ICTRP; www.who.int/ictrp/search/en), ClinicalTrials.gov, and the International Standard Randomized Controlled Trial Number (ISRCTN) registry (www.isrctn.com/), using ‘mefloquine', ‘malaria', and ‘pregnan*' as search terms.
Searching other resources
We contacted researchers working in the field to ask for unpublished data, confidential reports, and raw data from published trials. We also checked the citations of all trials identified by the methods described.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
Two review authors independently screened all trials identified by the search strategy by title or abstract, or both (Appendix 1). We coded studies as ‘retrieve' or ‘do not retrieve'. We retrieved the full‐text copies of trials deemed potentially relevant. Two review authors then independently assessed study eligibility using a form based on the review inclusion criteria. We resolved disagreements through discussion or by consultation with a third review author. Any review author who participated in trials that potentially met the review inclusion criteria did not participate in the procedure to select studies for inclusion. We listed all studies excluded after full‐text assessment and reasons for their exclusion in a ‘Characteristics of excluded studies' table. We illustrated the study selection process in a PRISMA diagram.
Data extraction and management
Three review authors (RG, CPD, and MP) used a data extraction form to independently extract data on trial characteristics, including trial site, year, local malaria transmission estimates, antimalarial resistance pattern of mefloquine and the comparator drug (when possible), trial methods, participants, interventions, doses, and outcomes.
We extracted the number of participants randomized and the number of participants analyzed in experimental and control groups for each outcome. For dichotomous outcomes, we extracted the number of participants experiencing the event and the number assessed in each treatment group. For continuous outcomes, we extracted the arithmetic means, standard deviations for each treatment group (when provided), and the number of participants assessed in each group. We also extracted medians and ranges when provided. For outcomes reported as incidences, we extracted the number of participants experiencing the event (cases) and the person‐years at risk.
Any review author who participated in any of the trials included in the review did not participate in data extraction nor ‘Risk of bias' assessment of their own articles.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors independently assessed the risk of bias for each included trial using the Cochrane ‘Risk of bias' assessment tool (Higgins 2011). This approach assesses the risk of bias across seven domains: sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective outcome reporting, and other potential sources of bias (Higgins 2011). For each domain, we assigned a judgment of low, high, or unclear risk of bias. We judged the risk of bias for blinding on the presence of blinding and whether lack of blinding could potentially influence the results.
Measures of treatment effect
We presented dichotomous outcomes using risk ratios (RRs), count outcomes as incidence rate ratios (IRRs), and continuous outcomes as mean differences (MDs). We presented all measures of effect with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Unit of analysis issues
When conducting a meta‐analysis, we ensured that participants and cases in the placebo group were not counted more than once.
Dealing with missing data
We aimed to conduct the analysis according to the intention‐to‐treat principle. However, when there was loss to follow‐up, we used a complete‐case analysis such that participants for whom no outcome was reported were excluded from the analysis. This analysis assumes that participants for whom an outcome is available are representative of the original randomized patients. We aimed to conduct a sensitivity analysis to evaluate the robustness of this method, but this was not possible, as described below. If data from trial reports were insufficient, unclear, or missing, we contacted the study authors for additional information.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We calculated the I2 statistic using values of 30% to 59%, 60% to 89%, and 90% to 100% to denote moderate, substantial, and considerable levels of heterogeneity, respectively.
Assessment of reporting biases
We aimed to assess the risk of publication bias by constructing funnel plots and looking for asymmetry, but the small number of trials included in each comparison of the meta‐analysis made this assessment impossible.
Data synthesis
We performed data analysis using Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5) (RevMan 2014). We intended to perform subgroup analysis by gravidity and HIV status when possible. HIV status subgroup analysis was not possible in any case owing to different study designs for different HIV status populations. In the absence of heterogeneity, we used a fixed‐effect model for the meta‐analysis; when we detected moderate or considerable heterogeneity, we used a random‐effects model. Additionally, we assessed the certainty of evidence using the GRADE approach (GRADEpro GDT 2015) for the following main outcomes of analysis: maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery, clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy, placental malaria, maternal anaemia at delivery, low birth weight, spontaneous abortion and stillbirth, dizziness, and vomiting.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
We aimed to investigate heterogeneity by conducting prespecified subgroup analysis to evaluate the contributions of differences in trial characteristics such as risk of bias, geographical region, malaria transmission pattern, antimalarial resistance, drug regimen, use of ITNs, gravidity (primigravidae versus multigravidae), HIV status (uninfected, infected, unknown), and trial methods. Only the gravidity subgroup analysis was possible for one outcome of the main comparison. The other subgroup analyses were not possible because of the small number of trials included in each comparison.
Sensitivity analysis
We planned to conduct a sensitivity analysis to restore the integrity of the randomization process and to test the robustness of our results; however, the small number of trials included in each comparison – two at most – made this impossible. Additionally, missing outcome data were balanced in numbers across intervention groups, and reasons for missing data were similar across groups.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
The literature search, conducted up to 31 January 2018, identified 254 references, of which two were duplicate trial reports. Of the 252 remaining articles, we excluded 231 articles and one ongoing trial after title/abstract screening. We assessed 20 full‐text articles for eligibility, of which we excluded 14 articles. Six trials (in six publications) met the inclusion criteria of the review (Figure 3).
3.
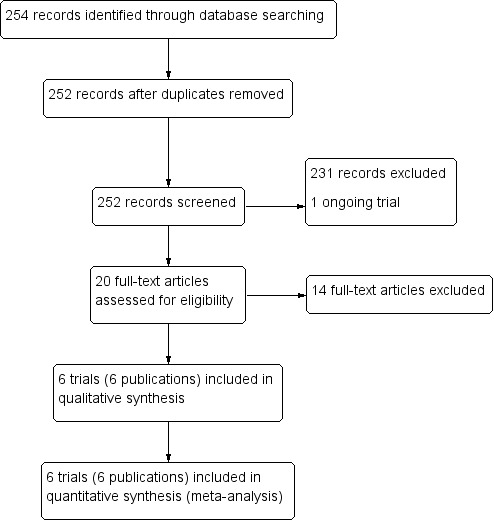
Study flow diagram.
Included studies
Six chemoprevention trials that included 8192 pregnant women met our inclusion criteria (see the Characteristics of included studies section). These trials were conducted between 1987 and 2013 in Thailand (one trial), Benin (three trials), Gabon (one trial), Kenya (one trial), Mozambique (two trials), and Tanzania (two trials).
The included trials recruited women of all gravidities of all ages (four trials) or over 18 years of age (two trials). Gestational age at recruitment was greater than 20 weeks (one trial), between 16 and 28 weeks (three trials), or ≤ 28 weeks (two trials).
Two trials evaluated mefloquine against sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine as IPTp in HIV‐uninfected pregnant women. Three trials evaluated mefloquine IPTp alone (or in combination with daily cotrimoxazole) against cotrimoxazole in HIV‐infected pregnant women. Finally, one trial in Thailand compared weekly mefloquine prophylaxis against placebo in women of unknown HIV status. All included trials reported that drug administration was supervised.
All included trials recruited women in all gravidity groups; five reported aggregate results and one disaggregated by gravidity for the primary outcome. In five trials, all women in both intervention and control groups received a long‐lasting ITN at recruitment and iron, and investigators routinely administered folic acid.
Excluded studies
We excluded one trial for the reasons given in the ‘Characteristics of excluded studies' table.
Risk of bias in included studies
See Figure 4 and Figure 5 for a summary of the ‘Risk of bias' assessments. We have presented further details in the ‘Characteristics of included studies' table.
4.
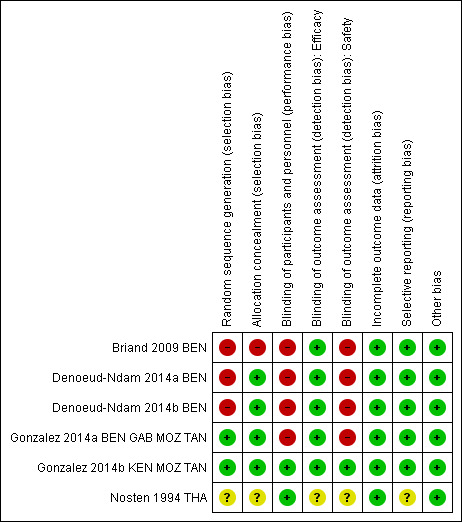
‘Risk of bias' summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
5.
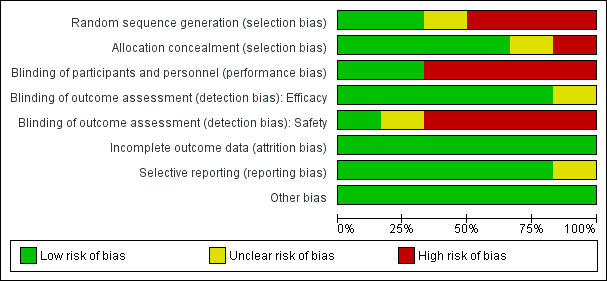
‘Risk of bias' graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
Allocation
Random sequence generation (selection bias)
Two trials adequately described methods of sequence generation (Gonzalez 2014a BEN GAB MOZ TAN; Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN), three described a non‐random component in the sequence generation process (Briand 2009 BEN; Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN; Denoeud‐Ndam 2014b BEN), and in the remaining trial, the risk was unclear (Nosten 1994 THA).
Allocation concealment (selection bias)
Four trials described adequate methods of allocation concealment (Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN; Denoeud‐Ndam 2014b BEN; Gonzalez 2014a BEN GAB MOZ TAN; Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN), one trial reported no concealment of allocation (Briand 2009 BEN), and in the remaining trial, the risk was unclear (Nosten 1994 THA).
Blinding
Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias)
Four trials were open (Briand 2009 BEN; Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN; Denoeud‐Ndam 2014b BEN; Gonzalez 2014a BEN GAB MOZ TAN), and we assessed these as having high risk of performance risk. Two trials were double‐blind and placebo‐controlled (Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN; Nosten 1994 THA), and we assessed these as having low risk of performance bias.
Blinding of efficacy outcome assessment (detection bias)
For five trials, we judged the efficacy outcome as not influenced by blinding or lack of blinding. In the remaining trial, the risk of detection bias for efficacy outcomes was unclear (Nosten 1994 THA).
Blinding of safety outcome assessment (detection bias)
For the four open trials, we judged the risk of detection bias as high for assessment of safety outcomes (Briand 2009 BEN; Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN; Denoeud‐Ndam 2014b BEN; Gonzalez 2014a BEN GAB MOZ TAN). In one trial, the risk of detection bias was unclear (Nosten 1994 THA). For the remaining trial, which was double‐blinded, we judged the risk of detection bias as low (Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN).
Incomplete outcome data
In all included trials, missing outcome data were balanced in numbers across groups, and we judged the risk of attrition bias to be low.
Selective reporting
We considered the risk of reporting bias as low in five trials and unclear in one (Nosten 1994 THA).
Other potential sources of bias
All included trials appeared to be free of other sources of bias, and we judged this risk as low.
Effects of interventions
Summary of findings for the main comparison. Mefloquine compared with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine for preventing malaria in pregnant women.
| Mefloquine compared with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine for preventing malaria in pregnant women | ||||||
| Patient or population: HIV‐uninfected pregnant women Setting: Benin, Gabon, Mozambique, and Tanzania Intervention: mefloquine Comparison: sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | Number of participants (trials) | Certainty of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments (compared with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine) | |
| Risk with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine | Risk with mefloquine | |||||
| Clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy | ‐ | ‐ | IRR 0.83 (0.65 to 1.05) | ‐ (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ HIGHa | Mefloquine results in little or no difference in the incidence of clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy |
| Maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery | 43 per 1000 | 28 per 1000 (20 to 37) |
RR 0.65 (0.48 to 0.86) |
5455 (2 RCTs) |
⊕⊕⊕⊕ HIGHa | Mefloquine results in lower maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery |
| Placental malaria | 52 per 1000 | 54 per 1000 (30 to 97) | RR 1.04 (0.58 to 1.86) | 4668 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝
LOWa,b,c Due to imprecision and heterogeneity |
Mefloquine may result in little or no difference in placental parasitaemia |
| Maternal anaemia at delivery | 219 per 1000 | 184 per 1000 (166 to 206) | RR 0.84 (0.76 to 0.94) | 5469 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝
MODERATEa,d Due to imprecision |
Mefloquine probably results in fewer women anaemic at delivery |
| Low birth weight | 117 per 1000 | 111 per 1000 (91 to 137) | RR 0.95 (0.78 to 1.17) | 5641 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ HIGHa,e | Mefloquine results in little or no difference in low birth weight |
| Stillbirths and abortions | 31 per 1000 | 37 per 1000 (28 to 49) | RR 1.20 (0.91 to 1.58) | 6219 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝
MODERATEa,b Due to imprecision |
Mefloquine probably results in little or no difference in stillbirths or abortions |
| AEs: vomiting | 82 per 1000 | 390 per 1000 (338 to 449) | RR 4.76 (4.13 to 5.49) | 6272 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ HIGHa | Mefloquine results in a four‐fold increase in vomiting |
| AEs: dizziness | 94 per 1000 | 396 per 1000 (316 to 496) | RR 4.21 (3.36 to 5.27) | 6272 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝
MODERATEa,f Due to risk of bias |
Mefloquine probably results in a four‐fold increase in dizziness |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). Abbreviations: CI: confidence interval; IRR: incidence rate ratio; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: risk ratio. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. High certainty: we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. Moderate certainty: we are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. Low certainty: our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. Very low certainty: we have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect. | ||||||
aNot downgraded for risk of bias: although one trial has serious risk of bias, the other is of good quality and exclusion of the smaller trial has little effect on the estimate of effect. bDowngraded by 1 for imprecision: confidence intervals range from considerable benefit to considerable harm. cDowngraded by 1 for heterogeneity: substantive qualitative heterogeneity is evident in the meta‐analysis. dDowngraded by 1 for imprecision: CIs include little or no important difference to a 24% reduction in anaemic women. eNot downgraded for imprecision: we consider that a 22% reduction or 17% increase in birth weight is not a clinically significant change. fDowngraded by 1 for performance bias: both trials are unblinded.
Summary of findings 2. Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole compared with cotrimoxazole for preventing malaria in pregnant women.
| Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole compared with cotrimoxazole for preventing malaria in pregnant women | ||||||
| Patient or population: HIV‐infected pregnant women Setting: Benin, Kenya, Mozambique, and Tanzania Intervention: mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole Comparison: cotrimoxazole | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | Number of participants (trials) | Certainty of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments (compared with cotrimoxazole) | |
| Risk with cotrimoxazole | Risk with mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole | |||||
| Clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy | ‐ | ‐ | IRR 0.76 (0.33 to 1.76) | ‐ (1 RCT) |
⊕⊕⊕⊕ HIGH | Mefloquine results in little or no difference in the incidence of clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy |
| Maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (PCR) | 66 per 1000 | 34 per 1000 (20 to 62) |
RR 0.52 (0.30 to 0.93) |
989 (2 RCTs) |
⊕⊕⊕⊝
MODERATEa Due to risk of bias |
Mefloquine probably results in lower maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery |
| Placental malaria (PCR) | 68 per 1000 | 19 per 1000 (10 to 39) | RR 0.28 (0.14 to 0.57) | 977 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ MODERATEa | Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole results in fewer women with placental malaria at delivery |
| Maternal anaemia at delivery | 178 per 1000 | 168 per 1000 (130 to 214) | RR 0.94 (0.73 to 1.20) | 1197 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝
MODERATEa Due to risk of bias |
Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole probably results in little or no difference in maternal anaemia cases at delivery |
| Low birth weight | 118 per 1000 | 141 per 1000 (105 to 188) | RR 1.20 (0.89 to 1.60) | 1220 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝
MODERATEa Due to risk of bias |
Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole probably results in little or no difference in the proportion of births that are low birth weight |
| Spontaneous abortions and stillbirths | 50 per 1000 | 56 per 1000 (21 to 149) | RR 1.12 (0.42 to 2.98) | 1347 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOWa,b,c | We do not know if mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole results in a difference in spontaneous abortions and stillbirths |
| AEs: vomiting | 30 per 1000 | 239 per 1000 (144 to 396) |
RR 7.95 (4.79 to 13.18) |
1055 (1 RCT)d |
⊕⊕⊕⊕ HIGH | Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole results in an eight‐fold increase in vomiting |
| AEs: dizziness | 75 per 1000 | 296 per 1000 (214 to 411) |
RR 3.94 (2.85 to 5.46) |
1055 (1 RCT)e |
⊕⊕⊕⊕ HIGH | Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole results in a four‐fold increase in dizziness |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). Abbreviations: CI: confidence interval; IRR: incidence rate ratio; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: risk ratio. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. High certainty: we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. Moderate certainty: we are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. Low certainty: our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. Very low certainty: we have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect. | ||||||
aDowngraded by 1 for risk of bias: one of the included trials is at serious risk of bias. bDowngraded by 1 for inconsistency: trials showed substantial heterogeneity. cDowngraded by 1 for imprecision: confidence intervals range from considerable benefit to considerable harm. dA second RCT, Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN, reported 50 events in the mefloquine+cotrimoxazole group and 0 in the control group (cotrimoxazole), with RR 101 (95% CI 6.29 to 1621.68). This trial was open and participants knew to which group they were allocated. Meta‐analysis causes a paradoxically very wide CI. Because of this distortion, we have used the results from Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN in the grade table. eA second RCT, Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN, reported 52 events in the mefloquine+cotrimoxazole group and 0 in the control group (cotrimoxazole), with RR 105 (95% CI 6.54 to 1685.03). This trial was open and participants knew to which group they were allocated. Meta‐analysis causes a paradoxically very wide CI with the lower 95% CI. Because of this distortion, we have used the results from Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN in this ‘Summary of findings' table.
Comparison 1: Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine (HIV‐uninfected pregnant women)
See Table 1.
Maternal outcomes
We included in this comparison two trials that evaluated two doses of IPTp (Briand 2009 BEN; Gonzalez 2014a BEN GAB MOZ TAN). Data show a decrease in the number of clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy among mefloquine recipients, but this does not clearly constitute an effect of mefloquine because the 95% CIs do not exclude the possibility of no different effects (IRR 0.83, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.05; 2 studies; high‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.1). Overall, IPTp‐mefloquine was associated with a 35% reduction in the risk of maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (RR 0.65, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.86; 5455 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 16%; high‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.2), but the absolute difference between treatments was small. We found no significant evidence of an effect of mefloquine or sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine on placental malaria infections (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.86; 4668 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 63%; low‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.3). The mefloquine group showed a slight increase in the mean haemoglobin level at delivery (MD 0.10, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.19; 5588 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 1.4) and a decrease in maternal anaemia cases at delivery (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.76 to 0.94; 5469 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; moderate‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.5), but the data show no significant differences in severe maternal anaemia at delivery between groups (RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.48; 5469 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 41%; Analysis 1.6). The original definitions of maternal moderate anaemia and severe maternal anaemia were different in the two trials included in the analysis (Gonzalez 2014a BEN GAB MOZ TAN defined anaemia as haemoglobin < 11 g/dL and severe anaemia as haemoglobin < 7 g/dL), but we homogenized data for the analysis as < 9.5 g/dL and < 8 g/dL (as defined in Briand 2009 BEN), respectively.
1.1. Analysis.
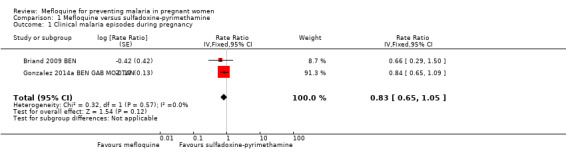
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 1 Clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy.
1.2. Analysis.
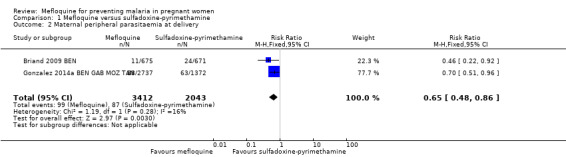
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 2 Maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery.
1.3. Analysis.
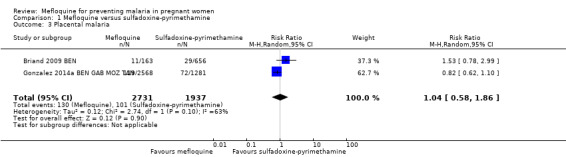
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 3 Placental malaria.
1.4. Analysis.
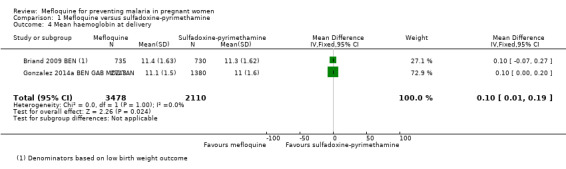
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 4 Mean haemoglobin at delivery.
1.5. Analysis.
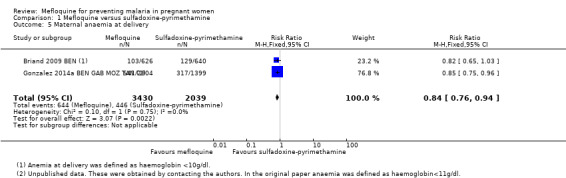
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 5 Maternal anaemia at delivery.
1.6. Analysis.
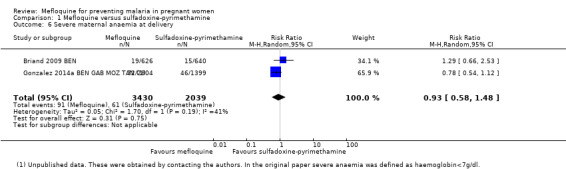
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 6 Severe maternal anaemia at delivery.
Foetal/infant outcomes
No effect was evident for the outcomes of cord blood parasitaemia (RR 0.44, 95% CI 0.13 to 1.46; 5309 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 33%; Analysis 1.7) and cord blood anaemia (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.87 to 1.23; 4006 participants, 1 study; Analysis 1.8).
1.7. Analysis.
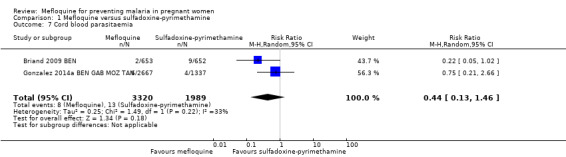
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 7 Cord blood parasitaemia.
1.8. Analysis.
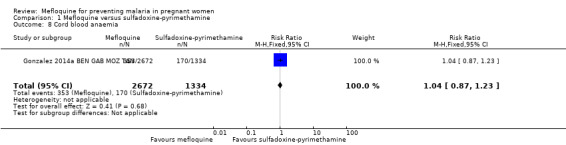
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 8 Cord blood anaemia.
Regarding newborn outcomes, mean birth weight did not show significant differences between groups (MD 2.52, 95% CI ‐25.66 to 30.69; 5241 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 1.9). Low birth weight (RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.17; 5641 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 33%; high‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.10) and prematurity prevalence (RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.40; 4640 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 1.12) also showed no differences between groups. Subgroup analysis of low birth weight by gravidity yielded results that did not vary (primigravidae: RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.80 to 1.30; 1576 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 3%; Analysis 1.11; multigravidae: RR 0.94, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.14; 4065 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 1.11).
1.9. Analysis.
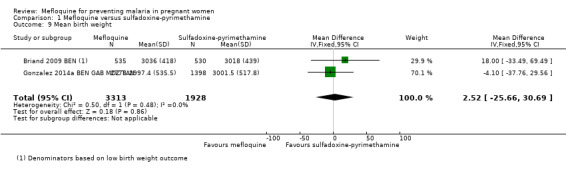
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 9 Mean birth weight.
1.10. Analysis.
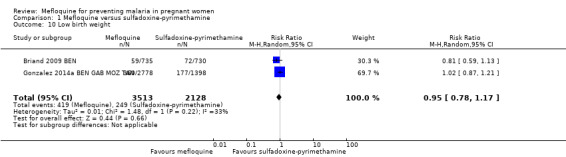
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 10 Low birth weight.
1.12. Analysis.
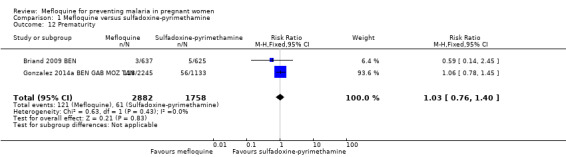
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 12 Prematurity.
1.11. Analysis.
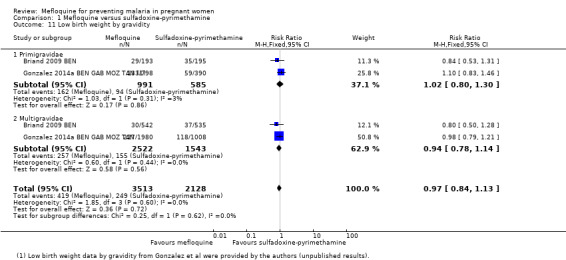
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 11 Low birth weight by gravidity.
Only one trial reported data on infant morbidity, and results followed the same trend; the IRR was near 1, and the CIs did not discard the possibility of no difference between mefloquine and sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine. Chosen proxies for infant morbidity were malaria in the first year of life (IRR 0.97, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.15; 1 study; Analysis 1.13) and hospital admissions in the first year of life (IRR 0.93, 95% CI 0.75 to 1.17; 1 study; Analysis 1.14).
1.13. Analysis.
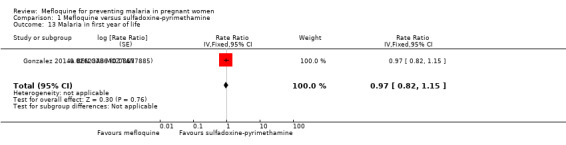
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 13 Malaria in first year of life.
1.14. Analysis.
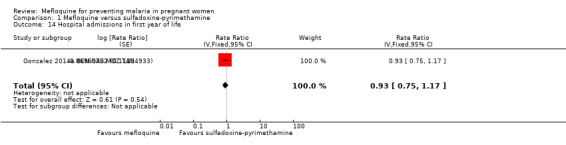
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 14 Hospital admissions in first year of life.
Safety outcomes
No difference was evident between mefloquine and sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine in overall serious adverse events reporting (RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.20; 4674 participants, 1 study; Analysis 1.15). Definitions of stillbirth and abortion were different for the two trials included in this comparison; therefore we aggregated both outcomes into a single outcome (RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.58; 6219 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; moderate‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.16). Congenital malformation cases were also similar in both intervention groups (RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.51 to 2.37; 5931 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 33%; Analysis 1.17).
1.15. Analysis.
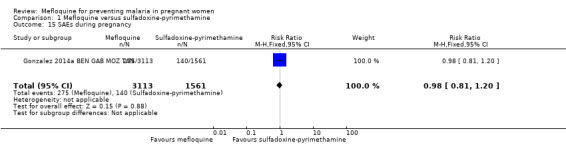
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 15 SAEs during pregnancy.
1.16. Analysis.
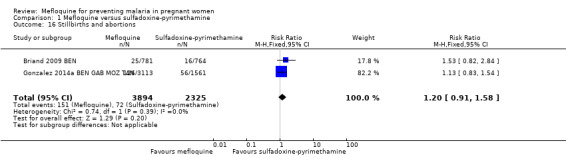
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 16 Stillbirths and abortions.
1.17. Analysis.
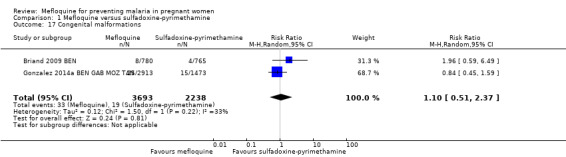
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 17 Congenital malformations.
Regarding maternal mortality, one of the trials reported maternal deaths only in the mefloquine group, and the other trial showed a similar proportion of maternal deaths in both IPTp groups; the CI of the meta‐analysis was wide, and heterogeneity was moderate (RR 2.41, 95% CI 0.27 to 21.23; 6219 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 54%; Analysis 1.18). Only one of the trials reported neonatal and infant mortality (Gonzalez 2014a BEN GAB MOZ TAN), but we obtained neonatal mortality rates for the other trial by contacting the study authors (Briand 2009 BEN). Neither of the two outcomes showed a significant effect of mefloquine or sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine (neonatal deaths: RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.67 to 1.43; 6134 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 1.19; incidence of infant deaths: IRR 1.00, 95% CI 0.66 to 1.52; 1 study; Analysis 1.20).
1.18. Analysis.
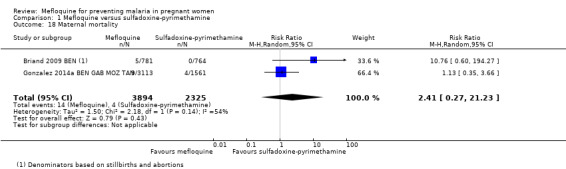
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 18 Maternal mortality.
1.19. Analysis.
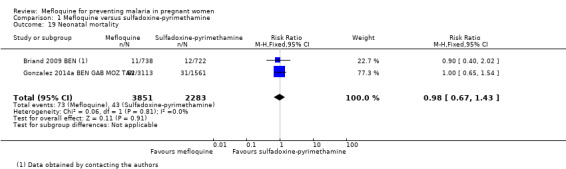
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 19 Neonatal mortality.
1.20. Analysis.
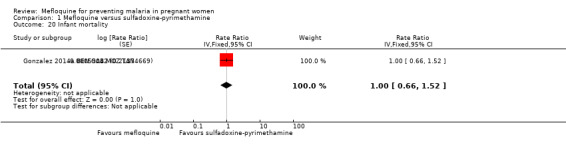
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 20 Infant mortality.
Overall, IPTp‐mefloquine increased the risk of adverse events; results of individual trials and of meta‐analyses were significant for vomiting (RR 4.76, 95% CI 4.13 to 5.49; 6272 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; high‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.21), fatigue/weakness (RR 4.62, 95% CI 1.80 to 11.85; 6272 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 91%; high‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.22), and dizziness (RR 4.21, 95% CI 3.36 to 5.27; 6272 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 66%; moderate‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.23), with the exception of headache (RR 0.70, 95% CI 0.25 to 1.94; 6272 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 85%; Analysis 1.24).
1.21. Analysis.
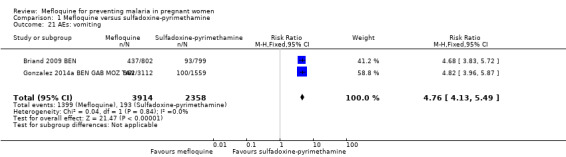
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 21 AEs: vomiting.
1.22. Analysis.
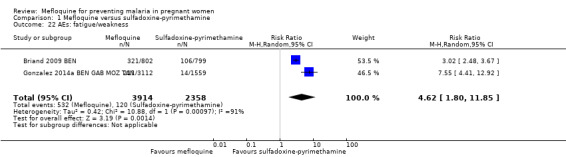
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 22 AEs: fatigue/weakness.
1.23. Analysis.
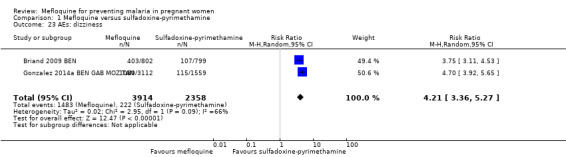
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 23 AEs: dizziness.
1.24. Analysis.
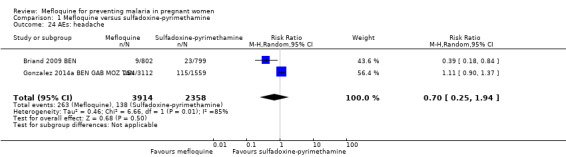
Comparison 1 Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, Outcome 24 AEs: headache.
Comparison 2: Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole (HIV‐infected pregnant women)
See Table 2.
Maternal outcomes
This comparison included two trials evaluating three IPTp doses of mefloquine (Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN; Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN). Only one of the trials reported clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy, noting no significant differences in malaria episodes between groups (IRR 0.76, 95% CI 0.33 to 1.76; 1 study; high‐certainty evidence; Analysis 2.1). IPTp‐mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole prophylaxis was associated with a 48% reduction in the risk of maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery measured by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.30 to 0.93; 989 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; moderate‐certainty evidence; Analysis 2.2), a 49% reduction in the risk of placental malaria measured by blood smear (RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.29 to 0.89; 1144 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 2.3), and a 72% reduction in the risk of placental malaria measured by PCR (RR 0.28, 95% CI 0.14 to 0.57; 977 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; moderate‐certainty evidence; Analysis 2.4). The other maternal‐related outcomes at delivery included in this comparison did not show evidence that they were effects of mefloquine owing to the wideness of the CIs (mean haemoglobin: MD 0.07, 95% CI ‐0.32 to 0.46; 1167 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 62%; Analysis 2.5; maternal anaemia: RR 0.94, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.20; 1197 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 12%; moderate‐certainty evidence; Analysis 2.6; severe maternal anaemia: RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.41 to 2.08; 1167 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 2.7). The original definitions of maternal anaemia were different in the two trials included in the analysis (Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN defined anaemia as haemoglobin < 11 g/dL), but we homogenized definitions for the analysis as < 9.5 g/dL (as defined in Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN). The two trials defined severe maternal anaemia as haemoglobin < 7 g/dL.
2.1. Analysis.
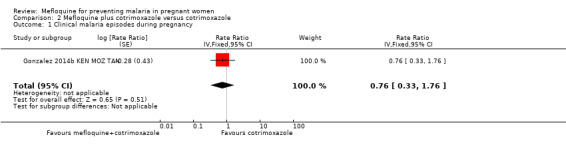
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 1 Clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy.
2.2. Analysis.
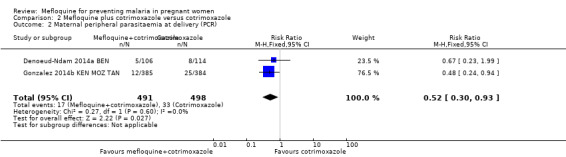
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 2 Maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (PCR).
2.3. Analysis.
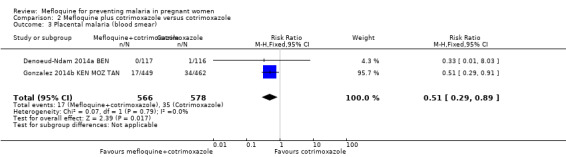
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 3 Placental malaria (blood smear).
2.4. Analysis.
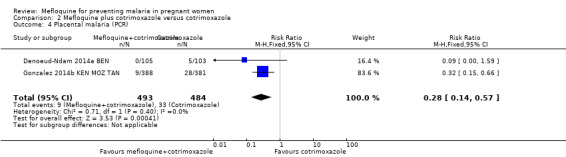
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 4 Placental malaria (PCR).
2.5. Analysis.
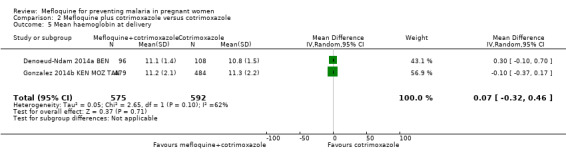
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 5 Mean haemoglobin at delivery.
2.6. Analysis.
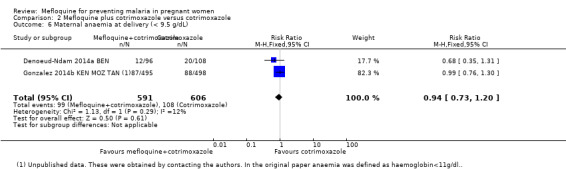
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 6 Maternal anaemia at delivery (< 9.5 g/dL).
2.7. Analysis.
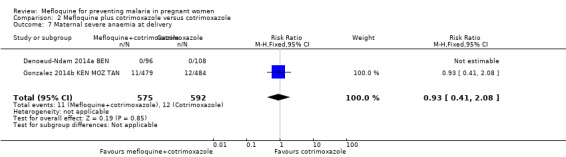
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 7 Maternal severe anaemia at delivery.
Foetal/infant outcomes
Meta‐analyses of foetal and neonatal outcomes were underpowered to detect significant effects of mefloquine on cord blood parasitaemia (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.03 to 3.13; 1166 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 2.8), mean birth weight (MD ‐25.75, 95% CI ‐86.99 to 35.49; 1220 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 2.9), low birth weight rates (RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.60; 1220 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; moderate‐certainty evidence; Analysis 2.10), and prematurity rates (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.72; 824 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 32%; Analysis 2.11). These CIs did not exclude the possibility of no different effects between groups.
2.8. Analysis.
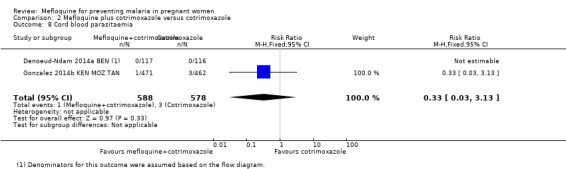
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 8 Cord blood parasitaemia.
2.9. Analysis.
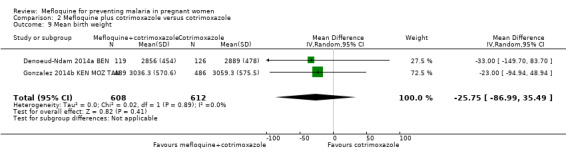
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 9 Mean birth weight.
2.10. Analysis.
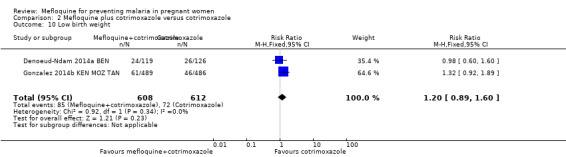
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 10 Low birth weight.
2.11. Analysis.
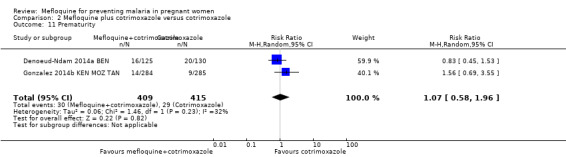
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 11 Prematurity.
Safety outcomes
Overall, serious adverse events during pregnancy were significantly less frequent in the group of IPTp‐mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole prophylaxis than in the cotrimoxazole alone group (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.95; 1347 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 2.12). However, analysis of individual adverse events did not show differences between groups, for example, spontaneous abortions and stillbirths (RR 1.12, 95% CI 0.42 to 2.98; 1347 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 69%; very low‐certainty evidence; Analysis 2.13) and congenital malformations (RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.22 to 1.67; 1312 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 2.14). Definitions of spontaneous abortion and stillbirth were different in the two included trials (that is, difference in the gestational age cutoff for classifying miscarriage or stillbirth); therefore, we combined both indicators and analyzed them as one. Only one trial included information on maternal deaths (Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN), and we obtained this information by contacting the authors in the other trial (Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN). Analyses of maternal deaths revealed no significant differences between groups (RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.13 to 2.01; 1347 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 2.15). Also, we found that neonatal mortality rates were not significantly different among groups, as revealed by the CI (RR 1.32, 95% CI 0.65 to 2.69; 1239 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 2.16). It is important to note that mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole recipients were at 1.92 times greater risk of mother‐to‐child transmission of HIV than the group that took only cotrimoxazole (RR 1.92, 95% CI 1.13 to 3.25; 1019 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 0%; Analysis 2.17).
2.12. Analysis.
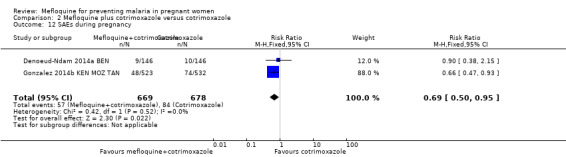
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 12 SAEs during pregnancy.
2.13. Analysis.
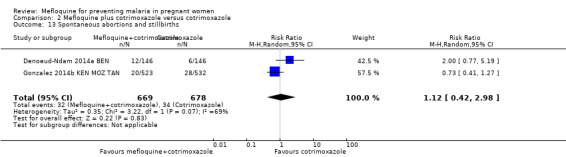
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 13 Spontaneous abortions and stillbirths.
2.14. Analysis.
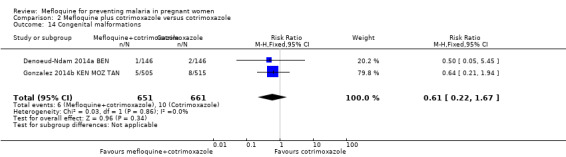
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 14 Congenital malformations.
2.15. Analysis.
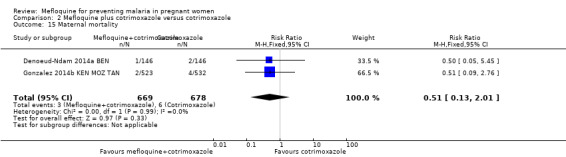
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 15 Maternal mortality.
2.16. Analysis.
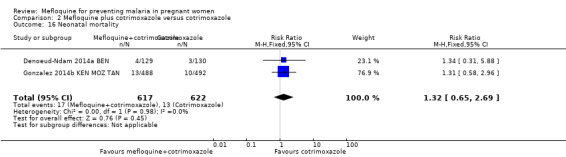
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 16 Neonatal mortality.
2.17. Analysis.
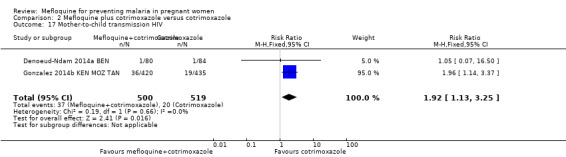
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 17 Mother‐to‐child transmission HIV.
Vomiting, fatigue/weakness, and dizziness displayed substantial and considerable levels of heterogeneity in the meta‐analysis. Individual trials showed significant increases in three drug‐related adverse events in the groups given IPTp‐mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole prophylaxis, but random‐effects analyses show a significant effect of IPTp‐mefloquine only in the case of vomiting (RR 20.88, 95% CI 1.40 to 311.66; 1347 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 74%; Analysis 2.18), while fatigue (RR 2.95, 95% CI 0.26 to 32.93; 1347 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 91%; Analysis 2.19) and dizziness (RR 16.34, 95% CI 0.39 to 684.99; 1347 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 86%; Analysis 2.20) show no significant evidence. In the three cases, CIs are considerably wide. Headache cases were not significantly different across groups (RR 0.76, 95% CI 0.28 to 2.10; 1347 participants, 2 studies; I2 statistic = 30%; Analysis 2.21).
2.18. Analysis.
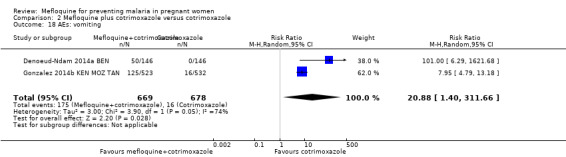
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 18 AEs: vomiting.
2.19. Analysis.
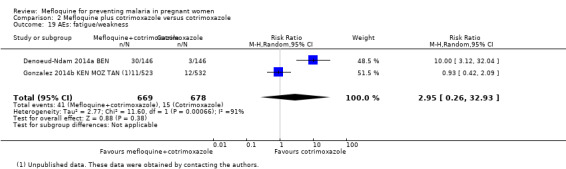
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 19 AEs: fatigue/weakness.
2.20. Analysis.
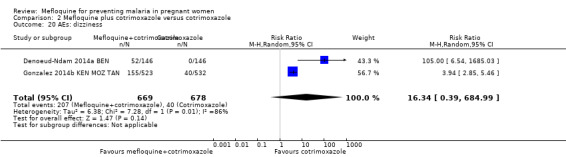
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 20 AEs: dizziness.
2.21. Analysis.
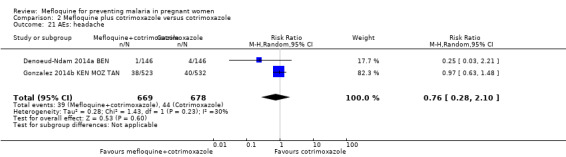
Comparison 2 Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 21 AEs: headache.
Comparison 3: Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole (HIV‐infected pregnant women)
Maternal outcomes
Only one trial conducted in Benin provided data on this comparison of three IPTp‐mefloquine doses versus cotrimoxazole prophylaxis (Denoeud‐Ndam 2014b BEN). The few observations reported in the trial made the analyses, in general, underpowered to detect differences between groups. Efficacy outcomes directly related to malaria yielded RR indicating beneficial effects of IPTp‐mefloquine in reducing infection, but CIs did not exclude the possibility of no difference between groups (maternal peripheral parasitaemia during pregnancy measured by PCR: RR 0.21, 95% CI 0.03 to 1.72; 98 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.1; placental malaria measured by PCR: RR 0.73, 95% CI 0.13 to 4.15; 94 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.2; placental malaria measured by blood smear: RR 0.35, 95% CI 0.01 to 8.30; 108 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.3). Data show no differences across groups for mean haemoglobin (MD ‐0.10, 95% CI ‐0.67 to 0.47; 100 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.4) or maternal anaemia at delivery (RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.26 to 3.16; 100 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.5).
3.1. Analysis.
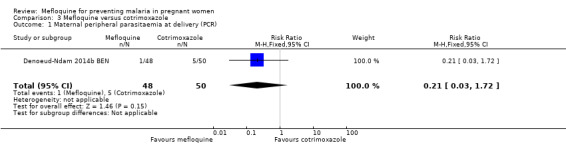
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 1 Maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (PCR).
3.2. Analysis.
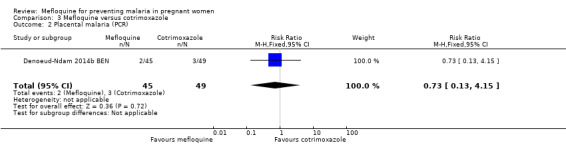
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 2 Placental malaria (PCR).
3.3. Analysis.
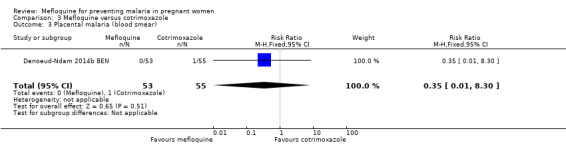
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 3 Placental malaria (blood smear).
3.4. Analysis.
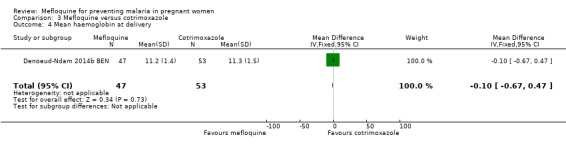
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 4 Mean haemoglobin at delivery.
3.5. Analysis.
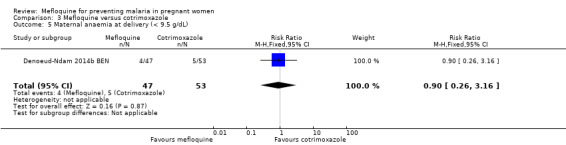
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 5 Maternal anaemia at delivery (< 9.5 g/dL).
Foetal/infant outcomes
All newborn outcomes included in the trial displayed wide CIs, providing no evidence of differences between groups (mean birth weight: MD ‐102.00, 95% CI ‐255.52 to 51.52; 120 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.6; low birth weight rate: RR 1.52, 95% CI 0.56 to 4.13; 120 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.7; prematurity rate: RR 1.08, 95% CI 0.33 to 3.56; 125 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.8).
3.6. Analysis.
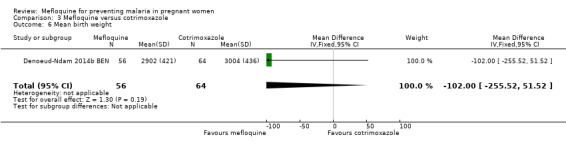
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 6 Mean birth weight.
3.7. Analysis.
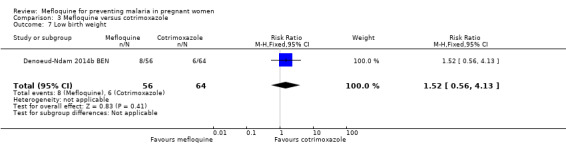
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 7 Low birth weight.
3.8. Analysis.
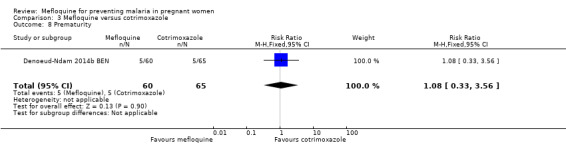
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 8 Prematurity.
Safety outcomes
Serious adverse events reported in the trial were balanced across groups and were infrequent. The CIs reveal the possibility of no different effects between interventions in overall serious adverse events (RR 1.06, 95% CI 0.28 to 4.07; 140 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.9), stillbirths (RR 4.30, 95% CI 0.49 to 37.49; 139 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.10), spontaneous abortions (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.07 to 16.84; 139 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.11), and congenital malformations (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.16 to 7.41; 139 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.12). No maternal deaths occurred during the trial (139 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.13), and only one neonate in each intervention group died (RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.07 to 16.39; 129 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.14). The trial did not record infant mortality and regarded infant deaths after seven days of birth until six weeks of age as a proxy; small numbers of observations and infant deaths made demonstration of differences between groups impossible (RR 2.10, 95% CI 0.19 to 22.54; 129 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.15).
3.9. Analysis.
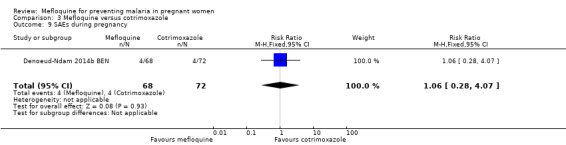
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 9 SAEs during pregnancy.
3.10. Analysis.
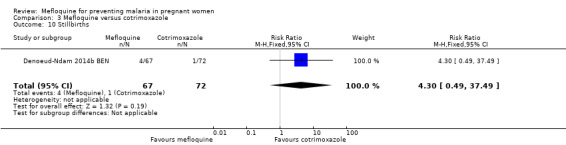
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 10 Stillbirths.
3.11. Analysis.
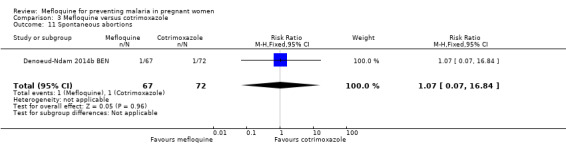
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 11 Spontaneous abortions.
3.12. Analysis.
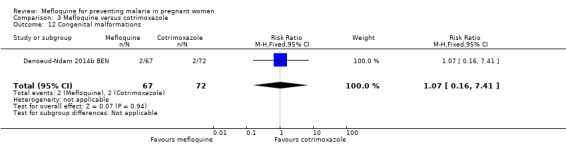
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 12 Congenital malformations.
3.13. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 13 Maternal mortality.
3.14. Analysis.
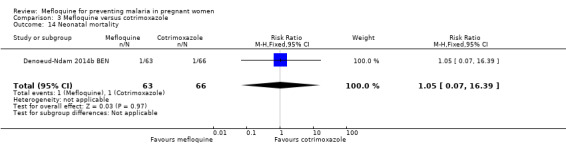
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 14 Neonatal mortality.
3.15. Analysis.
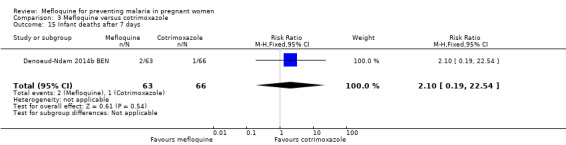
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 15 Infant deaths after 7 days.
Drug‐related adverse events were significantly more frequent in the mefloquine group. Despite wide CIs, results show an effect of mefloquine in increasing the frequency of vomiting (RR 13.43, 95% CI 3.31 to 54.54; 139 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.16), fatigue/weakness (RR 6.99, 95% CI 1.64 to 29.81; 139 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.17), and dizziness (RR 52.60, 95% CI 3.26 to 848.24; 139 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.18). Data show no differences between groups in drug‐related headache (RR 0.21, 95% CI 0.01 to 4.39; 139 participants, 1 study; Analysis 3.19).
3.16. Analysis.
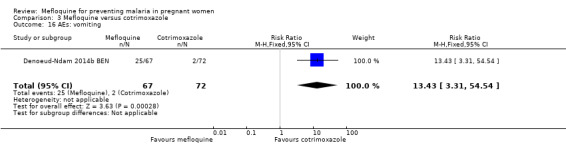
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 16 AEs: vomiting.
3.17. Analysis.
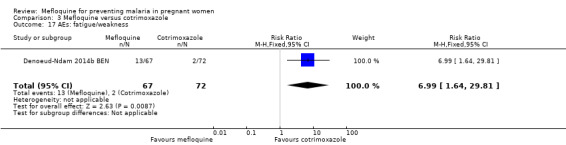
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 17 AEs: fatigue/weakness.
3.18. Analysis.
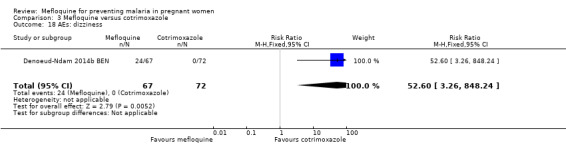
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 18 AEs: dizziness.
3.19. Analysis.
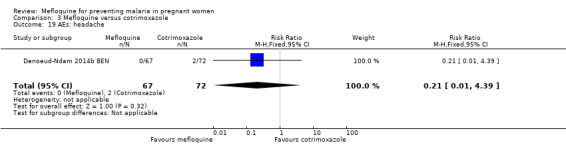
Comparison 3 Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole, Outcome 19 AEs: headache.
Comparison 4: Mefloquine versus placebo (pregnant women of unknown HIV status)
Maternal and foetal/infant outcomes
Only one trial provided data on this comparison, which comprised two phases of mefloquine prophylaxis with different doses of the drug (Nosten 1994 THA); the results belong to the pooled samples of both trial phases. This trial did not report clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy, maternal anaemia at delivery, cord blood parasitaemia and anaemia, serious adverse events, neonatal mortality, and adverse events, or data reporting was incomplete.
The only observed significant effect that could be attributed to mefloquine was the decrease in maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (RR 0.13, 95% CI 0.05 to 0.33; 339 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.1). The other efficacy outcomes evaluated in this trial ‐ both maternal and newborn‐related outcomes ‐ showed wide CIs and did not demonstrate different effects between placebo and mefloquine prophylaxis (placental malaria: RR 0.14, 95% CI 0.01 to 2.68; 220 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.2; mean birth weight: MD ‐80.00, 95% CI ‐184.65 to 24.65; 290 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.3; low birth weight: RR 1.39, 95% CI 0.78 to 2.48; 290 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.4; prematurity: RR 0.48, 95% CI 0.15 to 1.53; 199 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.5).
4.1. Analysis.
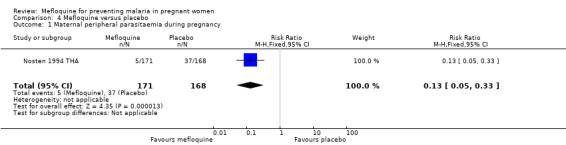
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 1 Maternal peripheral parasitaemia during pregnancy.
4.2. Analysis.
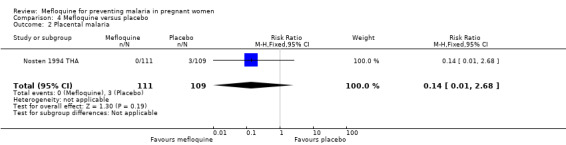
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 2 Placental malaria.
4.3. Analysis.
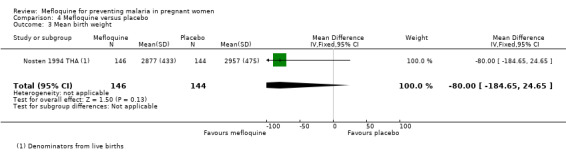
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 3 Mean birth weight.
4.4. Analysis.
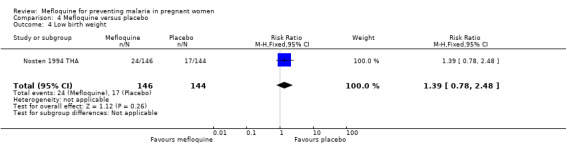
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 4 Low birth weight.
4.5. Analysis.
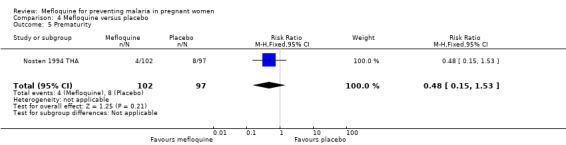
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 5 Prematurity.
Safety outcomes
This trial reported only serious adverse events, and adverse events data were not complete in the published article. Stillbirths were more prevalent in the group given mefloquine prophylaxis, but the small number of observed events made the analysis unpowered to detect differences between groups (RR 2.63, 95% CI 0.86 to 8.08; 311 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.6). Investigators reported only three spontaneous abortions and five congenital malformations, thus the CIs of analyses were very wide to detect differences in effects (spontaneous abortion: RR 0.48, 95% CI 0.04 to 5.22; 311 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.7; congenital malformation: RR 3.82, 95% CI 0.43 to 33.83; 311 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.8). During the trial, only one maternal death occurred in the mefloquine group, but the power of the analysis was too low to attribute the effects to an intervention (RR 2.95, 95% CI 0.12 to 71.85; 339 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.9). Infant deaths were equally frequent in both trial groups (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.63 to 1.74; 288 participants, 1 study; Analysis 4.10).
4.6. Analysis.
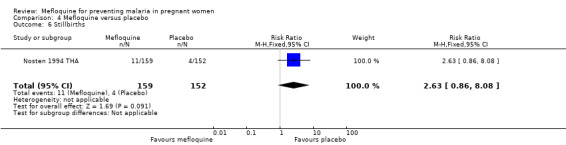
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 6 Stillbirths.
4.7. Analysis.
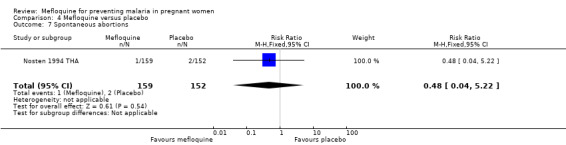
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 7 Spontaneous abortions.
4.8. Analysis.
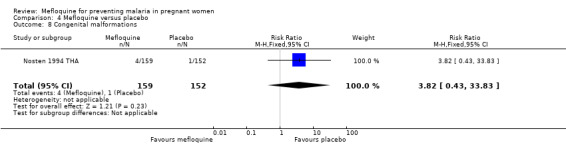
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 8 Congenital malformations.
4.9. Analysis.
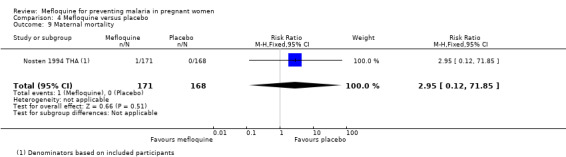
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 9 Maternal mortality.
4.10. Analysis.
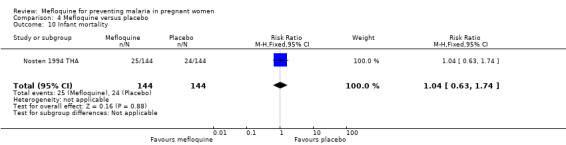
Comparison 4 Mefloquine versus placebo, Outcome 10 Infant mortality.
Discussion
Summary of main results
We included in this Cochrane Review six trials, enrolling 8192 pregnant women.
For HIV‐uninfected women, two doses of intermittent preventive mefloquine treatment in pregnancy (IPTp‐mefloquine) reduced the risk of maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery by 35% (high‐certainty evidence) and the risk of anaemia by 16% (moderate‐certainty evidence) compared with two doses of intermittent preventive sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine treatment in pregnancy (IPTp‐sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine). Investigators have reported no significant evidence of an effect of mefloquine on placental malaria, cord blood parasitaemia and anaemia, mean birth weight, prevalence of low birth weight, prematurity, stillbirths and abortions, and congenital malformations. Overall, IPTp‐mefloquine increases by approximately four‐fold the risk of drug‐related adverse events including vomiting, fatigue/weakness, and dizziness (high‐ or moderate‐certainty evidence), when compared with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine.
For HIV‐infected women, three doses of IPTp‐mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole prophylaxis compared with cotrimoxazole alone reduced the risk of maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (measured by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)) by 48% (moderate‐certainty evidence) and the risk of placental malaria (measured by PCR) by 72% (high‐certainty evidence). Meta‐analyses were underpowered to detect differences between effects of mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole and cotrimoxazole on other maternal, foetal, and neonatal outcomes. Regarding drug‐related adverse events, random‐effects analyses showed a significant effect of IPTp‐mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole prophylaxis compared with cotrimoxazole alone only in the case of vomiting (RR 7.95, 95% CI 4.79 to 13.18; 1055 participants; high‐certainty evidence). It is important to note that mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole recipients were at 1.92 times greater risk of mother‐to‐child transmission of HIV than the group that received cotrimoxazole alone (RR 1.92, 95% CI 1.13 to 3.25; 1019 participants). A secondary analysis of one of the included trials revealed this finding (Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN).
One trial among HIV‐infected women comparing three doses of IPTp‐mefloquine and cotrimoxazole was underpowered to detect an effect of mefloquine on maternal, foetal, infant, and safety outcomes, except for drug‐related adverse events, which were more frequent in the mefloquine group.
Finally, the single trial conducted in Thailand (where Plasmodium vivax coexists) found a significant effect attributable to mefloquine weekly prophylaxis (compared with placebo) only in reducing the risk of maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (RR 0.13, 95% CI 0.05 to 0.33; 339 participants).
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
Trials were carried out in sub‐Saharan Africa, except for one conducted in Thailand, and were published between 1994 and 2014. Findings evidenced that mefloquine chemoprevention reduces the risk of maternal parasitaemia at delivery in both HIV‐uninfected and HIV‐infected women compared with other antimalarials or placebo. Additionally, in HIV‐infected women, Mefloquine was found to reduce the risk of placental malaria. Results from these trials show fairly consistent clinically important benefits for women and their infants. However, the risk of drug‐related adverse events was increased among mefloquine recipients, and it is notable that mefloquine increased the risk of mother‐to‐child transmission in one trial.
Included trials evaluated two or three IPTp doses of sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine as per World Health Organization (WHO) recommendations, whereas current evidence suggests that monthly doses may provide a better prophylactic effect (Kayentao 2013). Additionally, the WHO currently recommends IPTp administration at each scheduled antenatal contact (WHO 2012b).
The findings of this review, derived from a variety of sub‐Saharan African settings and comparing mefloquine chemoprevention in pregnancy with varied antimalarial drugs and placebo, may be applied worldwide. Mefloquine is currently recommended as malaria chemoprevention for pregnant women of all gestational ages travelling to malaria‐endemic areas (CDC 2016). This drug is also recommended for treatment of uncomplicated malaria episodes in combination with artesunate (WHO 2015), and a fixed‐dose formulation is available in some malaria‐endemic countries. In 2013, the WHO Evidence Review Group (ERG) on IPTp met to assess evidence obtained from IPTp‐mefloquine trials, and the WHO Malaria Policy Advisory Committee (MPAC) reviewed ERG recommendations and agreed that mefloquine at the 15‐mg/kg dose regimen should not be recommended for IPTp, given its adverse events and poor tolerability (WHO MPAC 2013).
Certainty of the evidence
We assessed the certainty of evidence in this review by using the GRADE approach and presented the evidence in two ‘Summary of findings' tables for efficacy and safety outcomes (Table 1; Table 2).
For HIV‐uninfected pregnant women, evidence that IPTp‐mefloquine was superior to IPTp‐sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine in reducing the risk of maternal peripheral parasitaemia and anaemia at delivery was of moderate certainty, and evidence that IPTp‐mefloquine increased drug‐related adverse effects (namely, vomiting and dizziness) compared with IPTp‐sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine was of high and moderate certainty (respectively). We considered the effects of IPTp‐mefloquine in decreasing placental malaria risk compared with IPTp‐sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine to be of low certainty because of substantial heterogeneity among trials. Finally, we considered evidence of no effects of mefloquine compared with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine on low birth weight and stillbirths and abortions to be of moderate certainty.
For HIV‐infected women, evidence that cotrimoxazole plus IPTp‐mefloquine was superior to cotrimoxazole in reducing the risk of maternal peripheral parasitaemia and anaemia at delivery was of moderate certainty, whereas evidence regarding lack of effect on risk of placental malaria was of high certainty. Evidence of no effects of cotrimoxazole plus IPTp‐mefloquine compared with cotrimoxazole on low birth weight and stillbirths and abortions was of moderate and very low certainty, respectively, because of serious risk of bias of one of the included trials and substantial heterogeneity. Finally, we considered evidence of mefloquine increasing risks of vomiting and dizziness to be of low certainty because heterogeneity among trials was substantial and the 95% CI was wide.
Potential biases in the review process
It seems unlikely that we have missed any trials examining mefloquine for prevention of malaria in pregnant women.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
A previous Cochrane Review on drugs for preventing malaria in pregnant women in endemic areas analyzed the effects of mefloquine for prevention of malaria (Radeva‐Petrova 2014). Our results are consistent with those previously reported but include more trials and thus may be more robust.
The findings of this Cochrane Review are also consistent with those of a previous systematic review assessing the safety and tolerability of mefloquine in pregnancy (González 2013).
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
In past decades, many clinical trials have tested mefloquine chemoprevention to prevent malaria and its consequences in pregnant women.
For HIV‐uninfected pregnant women, IPTp‐mefloquine better reduces malaria effects compared with IPTp‐sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, but the drug is worse tolerated than sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine. For HIV‐infected pregnant women, IPTp‐mefloquine added to cotrimoxazole prophylaxis reduces the risk of important malaria consequences better than cotrimoxazole alone, but drug tolerability constitutes a health issue.
The data show that mefloquine is an efficacious and safe antimalarial drug in terms of pregnancy outcomes for prevention of malaria in pregnancy. However, the high proportion of mefloquine‐related adverse events constitutes an important barrier to its effectiveness for malaria preventive treatment in pregnant women.
Implications for research.
Mefloquine efficacy to prevent malaria effects in pregnancy is well established. Future research should concentrate on finding a dose that would provide the same antimalarial beneficial effects while reducing its drug‐related adverse events, especially as weekly prophylaxis (for example, at a dose of 5 mg/kg) for HIV‐uninfected women living in areas of high sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine resistance. Researchers also should further examine findings on the two‐fold increased risk of mother‐to‐child transmission of HIV among mefloquine recipients.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 November 2018 | Amended | Following feedback from the Cochrane Editorial and Methods department, the review authors checked and corrected the GRADE assessments, 'Summary of findings' tables, and review text for consistency. |
| 12 November 2018 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | Due to inconsistencies between the review sections, we corrected the GRADE assessments and review text. |
Acknowledgements
We thank David Sinclair and Ragna Boerma for their contributions to protocol development and analysis inputs for this review. We thank Valérie Briand, Michel Cot, and Lise Denoeud‐Ndam for contributing unpublished data. Finally, we thank Vittoria Lutje, Anne‐Marie Stephani, and Paul Garner from the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group, and Marta Roqué from the Iberoamerican Cochrane Centre. for support and help provided throughout all phases of development of this Cochrane Review.
The editorial base of the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group is funded by UK aid from the UK Government for the benefit of low‐ and middle‐income countries (Grant: 5242). The views expressed in this review do not necessarily reflect UK government policy.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Search strategies
| Search set | CIDG Specialized Register | CENTRAL | MEDLINE | Embase | LILACS |
| 1 | malaria | Malaria ti, ab, MeSH | Malaria ti, ab, MeSH | Malaria ti, ab, Emtree | malaria |
| 2 | Mefloquine OR Lariam | Mefloquine ti, ab, MeSH | Mefloquine ti, ab, MeSH | Mefloquine ti, ab, Emtree | Mefloquine |
| 3 | Pregnan* | Lariam ti, ab | Lariam ti, ab | Lariam ti, ab | Lariam |
| 4 | 1 and 2 and 3 | 2 or 3 | 2 or 3 | 2 or 3 | 2 or 3 |
| 5 | ‐ | 1 and 4 | 1 and 4 | 1 and 4 | 1 and 4 |
| 6 | ‐ | Pregnan* ti, ab | Pregnan* ti, ab | Pregnan* ti, ab | Pregnan$ |
| 7 | ‐ | Pregnancy [Mesh] | Pregnancy [Mesh] | Pregnancy [Emtree] | 5 and 6 |
| 8 | ‐ | 6 or 7 | 6 or 7 | 6 or 7 | ‐ |
| 9 | ‐ | 5 and 8 | 5 and 8 | 5 and 8 | ‐ |
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy | 2 | Rate Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.65, 1.05] | |
| 2 Maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery | 2 | 5455 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.48, 0.86] |
| 3 Placental malaria | 2 | 4668 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.58, 1.86] |
| 4 Mean haemoglobin at delivery | 2 | 5588 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.10 [0.01, 0.19] |
| 5 Maternal anaemia at delivery | 2 | 5469 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.76, 0.94] |
| 6 Severe maternal anaemia at delivery | 2 | 5469 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.58, 1.48] |
| 7 Cord blood parasitaemia | 2 | 5309 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.44 [0.13, 1.46] |
| 8 Cord blood anaemia | 1 | 4006 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.87, 1.23] |
| 9 Mean birth weight | 2 | 5241 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.52 [‐25.66, 30.69] |
| 10 Low birth weight | 2 | 5641 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.78, 1.17] |
| 11 Low birth weight by gravidity | 2 | 5641 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.84, 1.13] |
| 11.1 Primigravidae | 2 | 1576 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.80, 1.30] |
| 11.2 Multigravidae | 2 | 4065 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.78, 1.14] |
| 12 Prematurity | 2 | 4640 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.76, 1.40] |
| 13 Malaria in first year of life | 1 | Rate Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.82, 1.15] | |
| 14 Hospital admissions in first year of life | 1 | Rate Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.75, 1.17] | |
| 15 SAEs during pregnancy | 1 | 4674 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.81, 1.20] |
| 16 Stillbirths and abortions | 2 | 6219 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.20 [0.91, 1.58] |
| 17 Congenital malformations | 2 | 5931 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.51, 2.37] |
| 18 Maternal mortality | 2 | 6219 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.41 [0.27, 21.23] |
| 19 Neonatal mortality | 2 | 6134 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.67, 1.43] |
| 20 Infant mortality | 1 | Rate Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.66, 1.52] | |
| 21 AEs: vomiting | 2 | 6272 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.76 [4.13, 5.49] |
| 22 AEs: fatigue/weakness | 2 | 6272 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.62 [1.80, 11.85] |
| 23 AEs: dizziness | 2 | 6272 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.21 [3.36, 5.27] |
| 24 AEs: headache | 2 | 6272 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.25, 1.94] |
Comparison 2. Mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole versus cotrimoxazole.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clinical malaria episodes during pregnancy | 1 | Rate Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.33, 1.76] | |
| 2 Maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (PCR) | 2 | 989 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.52 [0.30, 0.93] |
| 3 Placental malaria (blood smear) | 2 | 1144 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.51 [0.29, 0.89] |
| 4 Placental malaria (PCR) | 2 | 977 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.28 [0.14, 0.57] |
| 5 Mean haemoglobin at delivery | 2 | 1167 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [‐0.32, 0.46] |
| 6 Maternal anaemia at delivery (< 9.5 g/dL) | 2 | 1197 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.73, 1.20] |
| 7 Maternal severe anaemia at delivery | 2 | 1167 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.41, 2.08] |
| 8 Cord blood parasitaemia | 2 | 1166 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.03, 3.13] |
| 9 Mean birth weight | 2 | 1220 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐25.75 [‐86.99, 35.49] |
| 10 Low birth weight | 2 | 1220 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.20 [0.89, 1.60] |
| 11 Prematurity | 2 | 824 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.58, 1.96] |
| 12 SAEs during pregnancy | 2 | 1347 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.50, 0.95] |
| 13 Spontaneous abortions and stillbirths | 2 | 1347 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.12 [0.42, 2.98] |
| 14 Congenital malformations | 2 | 1312 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.22, 1.67] |
| 15 Maternal mortality | 2 | 1347 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.51 [0.13, 2.01] |
| 16 Neonatal mortality | 2 | 1239 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.32 [0.65, 2.69] |
| 17 Mother‐to‐child transmission HIV | 2 | 1019 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.92 [1.13, 3.25] |
| 18 AEs: vomiting | 2 | 1347 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 20.88 [1.40, 311.66] |
| 19 AEs: fatigue/weakness | 2 | 1347 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.95 [0.26, 32.93] |
| 20 AEs: dizziness | 2 | 1347 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 16.34 [0.39, 684.99] |
| 21 AEs: headache | 2 | 1347 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.28, 2.10] |
Comparison 3. Mefloquine versus cotrimoxazole.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Maternal peripheral parasitaemia at delivery (PCR) | 1 | 98 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.03, 1.72] |
| 2 Placental malaria (PCR) | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.73 [0.13, 4.15] |
| 3 Placental malaria (blood smear) | 1 | 108 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.01, 8.30] |
| 4 Mean haemoglobin at delivery | 1 | 100 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.10 [‐0.67, 0.47] |
| 5 Maternal anaemia at delivery (< 9.5 g/dL) | 1 | 100 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.26, 3.16] |
| 6 Mean birth weight | 1 | 120 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐102.0 [‐255.52, 51.52] |
| 7 Low birth weight | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.52 [0.56, 4.13] |
| 8 Prematurity | 1 | 125 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.08 [0.33, 3.56] |
| 9 SAEs during pregnancy | 1 | 140 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.28, 4.07] |
| 10 Stillbirths | 1 | 139 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.30 [0.49, 37.49] |
| 11 Spontaneous abortions | 1 | 139 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.07, 16.84] |
| 12 Congenital malformations | 1 | 139 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.16, 7.41] |
| 13 Maternal mortality | 1 | 139 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 14 Neonatal mortality | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.07, 16.39] |
| 15 Infant deaths after 7 days | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.10 [0.19, 22.54] |
| 16 AEs: vomiting | 1 | 139 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 13.43 [3.31, 54.54] |
| 17 AEs: fatigue/weakness | 1 | 139 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.99 [1.64, 29.81] |
| 18 AEs: dizziness | 1 | 139 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 52.60 [3.26, 848.24] |
| 19 AEs: headache | 1 | 139 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.01, 4.39] |
Comparison 4. Mefloquine versus placebo.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Maternal peripheral parasitaemia during pregnancy | 1 | 339 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.13 [0.05, 0.33] |
| 2 Placental malaria | 1 | 220 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.68] |
| 3 Mean birth weight | 1 | 290 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐80.0 [‐184.65, 24.65] |
| 4 Low birth weight | 1 | 290 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.39 [0.78, 2.48] |
| 5 Prematurity | 1 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.48 [0.15, 1.53] |
| 6 Stillbirths | 1 | 311 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.63 [0.86, 8.08] |
| 7 Spontaneous abortions | 1 | 311 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.48 [0.04, 5.22] |
| 8 Congenital malformations | 1 | 311 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.82 [0.43, 33.83] |
| 9 Maternal mortality | 1 | 339 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.95 [0.12, 71.85] |
| 10 Infant mortality | 1 | 288 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.63, 1.74] |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Briand 2009 BEN.
| Methods | Trial design: open‐label, randomized, 2‐arm trial of 2 doses of IPTp Follow‐up: the second IPTp dose was administered from 30 weeks of gestation and at least 1 month after administration of the first dose. Women were visited at home, at delivery, and until 6 weeks after the end of pregnancy. Adverse event (AE) monitoring: AEs were recorded via an open‐labelled questionnaire during visits at home occurring within 1 week after each IPTp intake. |
|
| Participants | Numbers of participants randomized: 802 (IPTp‐mefloquine), 799 (IPTp‐sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine) Inclusion criteria: HIV‐uninfected women of all gravidities at 16 to 28 weeks of gestation who had no history of a neurological or psychiatric disorder and who had not previously used sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine or mefloquine nor reported having adverse reactions to medications containing sulfa. Exclusion criteria: pregnant women not meeting inclusion criteria. |
|
| Interventions |
|
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Country: Benin Setting: antenatal care clinics from Ouidah,a semi‐rural town Transmission: perennial with seasonal peaks Resistance: in 2005, rates of sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine and mefloquine resistance in vivo in children < 5 years of age were estimated to be 50% and 2.5% by day 28 of treatment, respectively. Dates: 2005 to 2008 Funding: Fonds de Solidarité Prioritaire (French Ministry of Foreign Affairs; project no. 2006–22); Institut de Recherche pour le Développement; Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (grant FDM20060907976 to V.B.); Fondation de France; and Fondation Mérieux |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Quote: "Randomization of subjects was stratified according to maternity clinic and gravidity". |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Allocation was not concealed. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | No blinding was reported, and safety outcomes are likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Efficacy | Low risk | No blinding of outcome assessment was reported, but the review authors judge that the efficacy outcome measurement is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Safety | High risk | No blinding of outcome assessment was reported; thus the review authors judge that the safety outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Missing outcome data were balanced in numbers across intervention groups, and similar reasons for missing data were reported across groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol is not available, but it is clear that published reports describe all expected outcomes, including those that were prespecified. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free of other sources of bias. |
Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN.
| Methods | Trial design: randomized, open‐label trial of 3 doses of IPTp Follow‐up: 3 scheduled IPTp administrations with at least a 1‐month interval between them. IPTp‐mefloquine administration and provision of cotrimoxazole. Clinical and adherence information, complete blood count, CD4 count, malaria screening, and treatment of malaria. At delivery: blood smears from placenta and umbilical cords and evaluation of newborns. Infant evaluation at 6 weeks, 4 months, and 2 months after weaning Adverse event (AE) monitoring: self‐reporting of all AEs. All adverse events were recorded at each visit. In addition, direct observation of early adverse reactions to mefloquine within 30 minutes after supervised intake was noted and later reactions were collected by phone the same day/evening or on the next day. Medical examination was performed 2 weeks after cotrimoxazole initiation to search for cutaneous reactions. An independent data and safety monitoring board reviewed all SAEs. |
|
| Participants | Numbers of participants randomized: 146 (cotrimoxazole), 146 (cotrimoxazole+mefloquine) Inclusion criteria: HIV‐infected pregnant women of all gravidities aged > 18 years, living permanently in the study area, between 16 and 28 weeks of gestation; last dosage of IPTp taken 1 month before enrolment; women requiring antimalarial treatment enrolled at least 2 weeks after completion of treatment Exclusion criteria: history of neuropsychiatric disorder; severe kidney or liver disease; serious adverse reaction to mefloquine, sulfa drugs, or quinine |
|
| Interventions |
IPTp with mefloquine plus cotrimoxazole
Cotrimoxazole
All study participants were given LLITNs and daily supplementation with 100 mg ferrous sulphate and 5 mg folic acid. The first dose was given at ≥ 16 weeks of gestation. All women were observed for 30 minutes following IPTp administration. Women vomiting within the first 30 minutes were given a second full IPTp dose. Asymptomatic women and women with low parasitaemia (< 1000 parasites/µL) were treated by the IPTp‐mefloquine dose in the mefloquine groups. Otherwise, women received artemether‐lumefantrine or oral quinine. Those with severe malaria were treated with intravenous quinine. |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Country: Benin Setting: 5 urban hospitals with PMTCT programmes Malaria transmission: intense and perennial transmission, with peaks during rainy seasons Resistance: increasing risk of resistance to sulfa drugs. Parasite resistance to cotrimoxazole Dates: 2009 to 2012 Funding: Sidaction Grant AI19‐3‐01528 |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Quote: "Randomization was stratified according to the study site and the number of previous pregnancies". |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The study coordination center retained the master list and assigned treatment by phone". |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | The trial blinded only the microscopist who evaluated blood smears. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Efficacy | Low risk | No blinding of outcome assessment was reported, but the review authors judge that the efficacy outcome measurement is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Safety | High risk | No blinding of outcome assessment was reported; thus the review authors judge that the safety outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Missing outcome data were balanced in numbers across groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Protocol was not available, but published report describes all expected outcomes including those prespecified. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free of other sources of bias. |
Denoeud‐Ndam 2014b BEN.
| Methods | Trial design: randomized, open‐label trial of 3 doses of IPTp Follow‐up: 3 scheduled IPTp administrations with at least a 1‐month interval between them. IPTp‐mefloquine administration and provision of cotrimoxazole. Clinical and adherence information, complete blood count, CD4 count, malaria screening, and treatment of malaria. At delivery: blood smears from placenta and umbilical cords and evaluation of newborns. Infant evaluation at 6 weeks, 4 months, and 2 months after weaning Adverse event (AE) monitoring: self‐reporting of all AEs. All adverse events were recorded at each visit. In addition, direct observation of early adverse reactions to mefloquine within 30 minutes after supervised intake was noted and later reactions were collected by phone the same day/evening or on the next day. Medical examination was performed 2 weeks after cotrimoxazole initiation to search for cutaneous reactions. An independent data and safety monitoring board reviewed all SAEs. |
|
| Participants | Numbers of participants randomized: 72 (cotrimoxazole), 68 (mefloquine) Inclusion criteria: HIV‐infected pregnant women of all gravidities aged > 18 years, living permanently in the study area, between 16 and 28 weeks of gestation, last dosage of IPTp taken 1 month before enrolment, women requiring antimalarial treatment enrolled at least 2 weeks after completion of treatment Exclusion criteria: history of neuropsychiatric disorder; severe kidney or liver disease; serious adverse reaction to mefloquine, sulfa drugs, or quinine |
|
| Interventions |
IPTp with mefloquine
Cotrimoxazole
All study participants were given LLITNs and daily supplementation with 100 mg ferrous sulphate and 5 mg folic acid. The first dose was given at ≥ 16 weeks of gestation. All women were observed for 30 minutes following IPTp administration. Women vomiting within the first 30 minutes were given a second full IPTp dose. Asymptomatic women and women with low parasitaemia (< 1000 parasites/µL) in the mefloquine groups were treated by the IPTp‐mefloquine dose. Otherwise, women received artemether‐lumefantrine or oral quinine. Thos with severe malaria were treated with intravenous quinine. |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Country: Benin Setting: 5 urban hospitals with PMTCT programmes Malaria transmission: intense and perennial transmission, with peaks during rainy seasons Resistance: increasing risk of resistance to sulfa drugs. Parasite resistance to cotrimoxazole Dates: 2009 to 2012 Funding: Sidaction Grant AI19‐3‐01528 |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Quote: "Randomization was stratified according to the study site and the number of previous pregnancies". |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The study coordination center retained the master list and assigned treatment by phone". |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | The trial blinded only the microscopist who evaluated blood smears. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Efficacy | Low risk | No blinding of outcome assessment was reported, but the review authors judge that the efficacy outcome measurement is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Safety | High risk | No blinding of outcome assessment was reported; thus the review authors judge that the safety outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Missing outcome data were balanced in numbers across groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Protocol was not available, but published report describes all expected outcomes including those prespecified. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free of other sources of bias. |
Gonzalez 2014a BEN GAB MOZ TAN.
| Methods | Trial design: open‐label, randomized, 3‐arm trial of 2 doses of IPTp Follow‐up: at each scheduled and unscheduled visit, a standardized symptom questionnaire was completed, as were blood smears for malaria parasites, and haemoglobin if symptoms and/or signs were suggestive of malaria. At delivery, blood samples were collected for haematological and parasitological evaluation. Weighting of newborns and gestational age at birth were recorded. Malaria parasite was determined 6 weeks after the end of pregnancy. Adverse event monitoring: home visits by field workers were done 2 days after IPTp administration to assess drug tolerability. Solicited and unsolicited adverse events (AEs) were assessed. The former were assessed by directed questioning regarding malaria‐related signs and symptoms during unscheduled visits, whereas the latter were assessed through open questioning during scheduled visits. |
|
| Participants | Numbers of participants randomized: 1578 (sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine), 1580 (mefloquine full dose), 1591 (mefloquine split) Inclusion criteria: HIV‐uninfected women of all gravidities attending the antenatal care clinic for the first time, did not receive IPTp during current pregnancy, permanent residence in the study area, gestational age of ≤ 28 weeks Exclusion criteria: HIV‐positive; history of allergy to sulfa drugs or mefloquine; history of severe renal, hepatic, psychiatric, or neurological disease; mefloquine or halofantrine treatment in the preceding 4 weeks; participating in other intervention studies |
|
| Interventions |
IPTp with sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, 3 tablets
IPTp with mefloquine
IPTp with mefloquine (split dose)
All study participants were given LLITNs. The first dose was given at > 13 weeks of gestation. All women were observed for 60 minutes following IPT administration. Women vomiting within the first 30 minutes were given a second full IPT dose, and those vomiting 30 to 60 minutes after drug intake were given a half replacement dose. Uncomplicated malaria episodes were treated with oral quinine (first trimester) or artemether‐lumefantrine (second and third trimesters); severe malaria episodes were treated with parenteral quinine. |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Country: Tanzania, Mozambique, Benin, and Gabon Setting: antenatal care clinics Transmission: mesoendemic in Tanzania and Mozambique, hyperendemic in Benin and Gabon Resistance: resistance to sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine due to long‐term sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine for IPTp Dates: 2009 to 2013 Funding: this study was funded by the European Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP; IP.2007.31080.002), the Malaria in Pregnancy Consortium, and the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI08/0564), in Spain. RG and MR were partially supported by grants from the Spanish Ministry of Health (ref. CM07/0015 and CM11/00278, respectively). The CISM receives core funding from the Spanish Agency for International Cooperation (AECID). LLITNs (Permanet) were donated by Vestergaard Frandsen. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The allocation of the participants to the study arms was done centrally by randomization stratified by country according to a 1:1:1 scheme. The sponsor’s institution biostatistician produced the computer‐generated randomization list for each recruiting site". |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Treatment allocation for each participant was concealed in opaque sealed envelopes that were opened only after recruitment. Study participants were assigned a unique study number linked to the allocated treatment group". |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Quote: "The study was designed as an open‐label, randomized, three‐arm trial to compare two‐dose mefloquine with two‐dose SP for IPTp". |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Efficacy | Low risk | No blinding of outcome assessment was reported, but the review authors judge that the efficacy outcome measurement is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Safety | High risk | No blinding of outcome assessment was reported; thus the review authors judge that the safety outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | All excluded participants, at any stage of the trial, are counted in the flow chart (both ITT and ATP cohorts). Missing outcome data were balanced in numbers across groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Not observed. Protocol available |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free of other sources of bias. |
Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN.
| Methods | Trial design: individually randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of 3 doses of IPTp Follow‐up: at each scheduled and unscheduled visit, a standardized symptom questionnaire was completed, as were blood smears for malaria parasites, and haemoglobin if symptoms and/or signs were suggestive of malaria. On a monthly basis, adherence to cotrimoxazole and LLITN was assessed. At delivery, blood samples were collected for haematological and parasitological evaluation with CD4 cell count and HIV viral load. Weighting of newborns and gestational age at birth were recorded. Malaria parasite was determined 6 weeks after the end of pregnancy. Adverse event monitoring: home visits by field workers were done 2 days after IPTp administration to assess drug tolerability. Solicited and unsolicited adverse events (AEs) were assessed. The former were assessed by directed questioning of malaria‐related signs and symptoms during unscheduled visits, whereas the latter were assessed through open questioning during scheduled visits. |
|
| Participants | Numbers of participants randomized: 537 (placebo+cotrimoxazole), 534 (mefloquine+cotrimoxazole) Inclusion criteria: HIV‐infected women of all gravidities attending the antenatal care clinic for the first time, did not receive IPTp during current pregnancy, permanent residence in the study area, gestational age of ≤ 28 weeks, HIV positive Exclusion criteria: history of allergy to sulfa drugs or mefloquine; history of severe renal, hepatic, psychiatric, or neurological disease; mefloquine or halofantrine treatment in the preceding 4 weeks; participating in other intervention studies |
|
| Interventions |
IPTp with mefloquine
IPTp with placebo
All study participants had monthly cotrimoxazole prophylaxis (fixed combination 800 mg of trimethroprim and 160 mg of sulfamethoxazole/tablet). All study participants were given LLITNs. The first dose was given at > 13 weeks of gestation. All women were observed for 60 minutes following IPT administration. Women vomiting within the first 30 minutes were given a second full IPTp dose, and those vomiting 30 to 60 minutes after drug intake were given a half replacement dose. Uncomplicated malaria episodes were treated with oral quinine (first trimester) or artemether‐lumefantrine (second and third trimesters); severe malaria episodes were treated with parenteral quinine. |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Countries: Tanzania, Mozambique, and Kenya Setting: antenatal care clinics Transmission: mesoendemic in Tanzania and Mozambique, holoendemic in Kenya Resistance: resistance to sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine due to long‐term sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine for IPTp Dates: 2010 to 2013 Funding: this study was funded by the European Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP; IP.2007.31080.002), the Malaria in Pregnancy Consortium, and the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI08/0564), in Spain. RG and MR were partially supported by grants from the Spanish Ministry of Health (ref. CM07/0015 and CM11/00278, respectively). The CISM receives core funding from the Spanish Agency for international Cooperation (AECID). LLITNs (Permanet) were donated by Vestergaard Frandsen, and cotrimoxazole tablets (Septrin) by UCB Pharma, in Spain. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The allocation of the participants to the study arms was done centrally by block randomization (block size of 6) stratified by country". |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The Pharmacy Department of the Hospital Clinic in Barcelona produced and safeguarded the computer‐generated randomization list for each recruiting site until unblinding, and carried out the masking, labelling, and packaging of all study interventional drugs. Study number allocation for each participant was concealed in opaque sealed envelopes that were sequentially numbered and opened only after recruitment by study health personnel". |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Study participants were assigned a unique study
number linked to the allocated treatment group. Investigators, laboratory staff, care providers, and study participants were blinded to intervention throughout the study". Placebo tablets were identical to mefloquine tables in shape and colour. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Efficacy | Low risk | Quote: "Investigators, laboratory staff, care providers, and study participants were blinded to intervention throughout the study". |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Safety | Low risk | Quote: "Investigators, laboratory staff, care providers, and study participants were blinded to intervention throughout the study". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | All excluded participants, at any stage of the trial, are counted in the flow chart (both ITT and ATP cohorts). Missing outcome data were balanced in numbers across groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Not observed. Protocol available |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free of other sources of bias. |
Nosten 1994 THA.
| Methods | Trial design: double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Phase 1 and phase 2 Follow‐up: in both phases, weekly visits included assessment of weight, temperature, pulse, blood pressure, fundal height, presence of oedema and anaemia, a symptom questionnaire on gastrointestinal and central nervous system side effects, malaria blood smear, electrocardiogram, and haematology and biochemistry every 2 weeks. Treatment of malaria and anaemia and food supply were provided when needed. At phase 2, expanded questionnaires and Romberg test were used. At delivery, measurement of newborn weight, details of labour, cord and maternal blood samples (malaria and anaemia), and placental biopsy were included. At phase 2, autopsy of death was performed in newborns. Follow‐up consisted of different measurements in children until 2 years of age (weight, height, head and arm circumferences) and determination of age when baby could first crawl, sit, walk, and talk. At phase 2, age at first symptomatic malaria, malaria blood smear, haematocrit, and full clinical examination were performed. Adverse event monitoring: weekly symptom questionnaire focusing on gastrointestinal, neurological, dermatological, and systemic symptoms |
|
| Participants | Numbers of participants randomized: 170 (mefloquine ‐ 60 phase 1, 110 phase 2), 169 (placebo ‐ 59 phase 1, 110 phase 2) Inclusion criteria: women of all gravidities and unknown HIV status (not tested) who attended the ANC clinic and were at > 20 weeks of estimated gestation. Exclusion criteria: women not meeting inclusion criteria. |
|
| Interventions |
IPTp with mefloquine
IPTp with placebo
The first dose was given at > 20 weeks of gestation. Anaemia was treated with ferrous sulphate and folic acid. Uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria was treated with quinine sulphate, P vivax with chloroquine sulphate, and severe malaria with intravenous quinine dihydrochloride. |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Country: Thailand Setting: 3 camps for displaced people: phase 1 antenatal clinics, phase 2 hospital Dates: 1987 to 1990 Transmission: seasonal malaria transmission (mesoendemic) Resistance: resistances to mefloquine, quinine, chloroquine, and antifolates Funding: United Nations Development Programme/World Bank/World Health Organization Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases; Wellcome Trust of Great Britain; Prevention Fundation |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Women were randomized to receive mefloquine or placebo. Not well explained how women were randomized |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not explained |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Double‐blind trial Quote: "The investigators were unaware of the randomization". Placebo tablets were identical to mefloquine tablets. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Efficacy | Unclear risk | Not explained |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) Safety | Unclear risk | Not explained |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | All excluded participants and those who decided to drop out are correctly reported along with reasons. Missing outcome data were balanced in numbers across groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Results of cord and maternal blood smears are not shown (published elsewhere?). No protocol is available. Nothing else was observed. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free of other sources of bias. |
Abbreviations: AE: adverse event; AECID: Spanish Agency for International Cooperation; ANC: antenatal care; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; CISM: Centro de Investigação em Saúde da Manhiça; IPTp: intermittent preventive treatment for malaria in pregnancy; IPTp‐mefloquine: intermittent preventive mefloquine treatment in pregnancy; IPTp‐sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine: intermittent preventive sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine treatment in pregnancy; ITT: intention‐to‐treat; LLITN: long‐lasting insecticide‐treated net; PCR: polymerase chain reaction; PMTCT: prevention of mother‐to‐child transmission; SAE: serious adverse event.
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Balocco 1992 | Letter to editor reporting on the results of pregnancy of 24 women exposed to mefloquine in early pregnancy. The report was excluded because it did not meet the inclusion criteria. |
| Briand 2015 | This publication reports the findings of a re‐analysis of previous published data comparing mefloquine with sulphadoxine‐pyrimethamine for IPTp in Benin using a multiple outcome approach, which allowed the joint assessment of efficacy and tolerability. This analysis was not included in the review because the original study (Briand 2009 BEN) was already included and it did not add additional data. |
| Denoeud‐Ndam 2012 | Study comparing mefloquine tolerability as IPTp between HIV‐infected and uninfected women participating in three included trials from Benin (Briand 2009 BEN and Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a and b). This analysis was excluded from the review because it did not provide additional data from already included trials. |
| Nosten 1990 THA | The study was designed as a dose‐finding pharmacokinetic study in 20 pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy who received mefloquine as prophylaxis. The trial did not compare the safety and efficacy of mefloquine with another antimalarial drug and thus, it did not meet inclusion criteria. |
| Phillips‐Howard 1998 | Publication reporting on a data analysis of reported use of mefloquine during the 1st trimester of pregnancy in European travellers. This analysis was excluded from the review because it did not meet inclusion criteria. |
| Schlagenhauf 2012 | This publication presents the analysis of the reports of exposure to mefloquine in pregnancy received by the Roche post‐marketing surveillance system. This analysis was excluded from the review because it did not meet inclusion criteria. |
| Smoak 1997 | This publication reports a case series of 72 US soldiers who inadvertently took mefloquine during pregnancy for prophylaxis. This publication was excluded from the review because it did not meet inclusion criteria. |
| Steketee 1996 MAL | We were not convinced that allocation was unbiased. Quote: "The assignment of regimens was based on the clinic day of enrolment. All women making their first antenatal clinic visit on a given day were assigned to the same regimen; the following clinic day, enrolled women were assigned a different regimen". We noted bias in allocation supported by statistically and clinically significant differences between intervention groups (3 groups under different chloroquine regimens versus 1 group under mefloquine regimen). |
| Vanhauwere 1998 | Study evaluating 1627 reports of mefloquine exposure pregnancy, mainly for chemoprophylaxis received by the Roche Post‐marketing surveillance system between 1986 and 1996.This analysis was excluded from the review because it did not meet inclusion criteria. |
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
Akinyotu 2015 NIG.
| Trial name or title | A comparative study of mefloquine and SP as prophylaxis against malaria in pregnant HIV‐infected patients |
| Methods | Allocation: randomized Intervention model: parallel assignment Masking: single‐blind (outcomes assessor) Primary purpose: prevention |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | No information available |
| Starting date | September 2015 |
| Contact information | Oriyomi O Akinyotu, MBBS; Ibadan: +2348035044590; oriyomiddoc@yahoo.com |
| Notes | We contacted the study authors, but they could not provide the data to us because the study was part of a thesis not yet defended. |
Differences between protocol and review
In the protocol, we indicated that for the safety evaluation of mefloquine in pregnancy, we would include studies that used mefloquine to prevent malaria in pregnant women travelling to malaria‐endemic areas. However, evaluation of mefloquine safety compared with the safety of other antimalarials was not possible because of the study design employed by retrieved studies. Consequently, no observational studies met the inclusion criteria and only randomized controlled trials met the inclusion criteria of this review.
In the protocol, we listed neonatal morbidity in the first 28 days of life as an analysis outcome. Similarly, we listed mean haemoglobin and maternal anaemia during pregnancy were as outcomes. However, the included trials did not report on these effects; consequently, we were unable to perform the analyses.
One included trial reported an unexpected increased risk of mother‐to‐child transmission (MTCT) of HIV associated with IPTp‐mefloquine. Given the clinical relevance of this finding, we included the frequency of MTCT of HIV as an outcome of the analysis.
Contributions of authors
RG, JJA, FtK, and CM designed the study. RG, JJA, and FtK wrote the protocol. RG, CPD, and MP assessed trial eligibility and risk of bias. RG, CPD, and MP extracted data. RG and CPD performed analyses. RG and CPD wrote the first version of the review. All review authors interpreted trial results, contributed to writing of this review, and approved the final version of the review.
Sources of support
Internal sources
Barcelona Institute of Global Health (ISGlobal), Hospital Clínic‐ Universitat de Barcelona, Spain.
Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, UK.
External sources
-
Department for International Development, UK.
Grant: 5242
Declarations of interest
RG, JJA, and CM are authors of two trials of mefloquine to prevent malaria in pregnancy (published in 2014) that are candidates for inclusion in this review. MP has no known conflicts of interest. CPD has no known conflicts of interest. FtK has no known conflicts of interest.
Unchanged
References
References to studies included in this review
Briand 2009 BEN {published and unpublished data}
- Briand V, Bottero J, Noël H, Masse V, Cordel H, Guerra J, et al. Intermittent treatment for the prevention of malaria during pregnancy in Benin: a randomized, open‐label equivalence trial comparing sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine with mefloquine. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2009;200(6):991‐1001. [DOI: 10.1086/605474] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Denoeud‐Ndam 2014a BEN {published and unpublished data}
- Denoeud‐Ndam L, Zannou DM, Fourcade C, Taron‐Brocard C, Porcher R, Atadokpede F, et al. Cotrimoxazole prophylaxis versus mefloquine intermittent preventive treatment to prevent malaria in HIV‐infected pregnant women: two randomized controlled trials. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 2014;65(2):198‐206. [DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000058] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Denoeud‐Ndam 2014b BEN {published and unpublished data}
- Denoeud‐Ndam L, Zannou DM, Fourcade C, Taron‐Brocard C, Porcher R, Atadokpede F, et al. Cotrimoxazole prophylaxis versus mefloquine intermittent preventive treatment to prevent malaria in HIV‐infected pregnant women: two randomized controlled trials. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 2014;65(2):198‐206. [DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000058] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gonzalez 2014a BEN GAB MOZ TAN {published and unpublished data}
- González R, Mombo‐Ngoma G, Ouédraogo S, Kakolwa MA, Abdulla S, Accrombessi M, et al. Intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy with mefloquine in HIV‐negative women: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. PLoS Medicine 2014;11(9):e1001735. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001733] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupérez M, González R, Mombo‐Ngoma G, Kabanywanyi AM, Sevene E, Ouédraogo S, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and developmental outcomes in infants born to women who received either mefloquine or sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine as intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy: a cohort study. PLoS Medicine 2016;13(2):e1001964. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001964] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gonzalez 2014b KEN MOZ TAN {published and unpublished data}
- González R, Mombo‐Ngoma G, Ouédraogo S, Kakolwa MA, Abdulla S, Accrombessi M, et al. Intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy with mefloquine in HIV‐infected women receiving cotrimoxazole prophylaxis: a multicenter randomized placebo‐controlled trial. PLoS Medicine 2014;11(9):e1001735. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001735] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nosten 1994 THA {published data only}
- Nosten F, ter Kuile F, Maelankiri L, Chongsuphajaisiddhi T, Nopdonrattakoon L, Tangkitchot S, et al. Mefloquine prophylaxis prevents malaria during pregnancy: a double‐ blind, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1994;169(3):595‐603. [DOI: 10.1093/infdis/169.3.595] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Balocco 1992 {published data only}
- Balocco R, Bonati M. Mefloquine prophylaxis against malaria for female travellers of childbearing age. Lancet 1992;340(8814):309‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Briand 2015 {published data only}
- Briand V, Escolano S, Journot V, Massougbodji A, Cot M, Tubert‐Bitter P. Mefloquine versus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine for intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy: a joint analysis on efficacy and tolerability. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2015;93(2):300‐4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Denoeud‐Ndam 2012 {published data only}
- Denoeud‐Ndam L, Clément MC, Briand V, Akakpo J, Agossou VK, Atadokpédé F, et al. Tolerability of mefloquine intermittent preventive treatment for malaria in HIV‐infected pregnant women in Benin. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 2012;61(1):64‐72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nosten 1990 THA {published data only}
- Nosten F, Karbwang J, White NJ, Honeymoon, Na Bangchang K, Bunnag D, et al. Mefloquine antimalarial prophylaxis in pregnancy:dose finding and pharmacokinetic study. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1990;30(1):79‐85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Phillips‐Howard 1998 {published data only}
- Phillips‐Howard PA, Steffen R, Kerr L, Vanhauwere B, Schildknecht J, Fuchs E, et al. Safety of mefloquine and other antimalarial agents in the first trimester of pregnancy. Journal of Travel Medicine 1998;5(3):121‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schlagenhauf 2012 {published data only}
- Schlagenhauf P, Blumentals WA, Suter P, Regep L, Vital‐Durand G, Schaerer MT, et al. Pregnancy and fetal outcomes after exposure to mefloquine in the pre‐ and periconception period and during pregnancy. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2012;54(11):e124‐31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Smoak 1997 {published data only}
- Smoak BL, Writer JV, Keep LW, Cowan J, Chantelois JL. The effects of inadvertent exposure of mefloquine chemoprophylaxis on pregnancy outcomes and infants of US Army servicewomen. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1992;176(3):831‐3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Steketee 1996 MAL {published data only}
- Steketee RW, Wirima JJ, Hightower AW, Slutsker L, Heymann DL, Breman JG. The effect of malaria and malaria prevention in pregnancy on offspring birthweight, prematurity, and intrauterine growth retardation in rural Malawi. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;55(Suppl 1):33‐41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steketee RW, Wirima JJ, Slutsker L, Breman JG, Heymann DL. Comparability of treatment groups and risk factors for parasitemia at the first antenatal clinic visit in a study of malaria treatment and prevention in pregnancy in rural Malawi. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;55(Suppl 1):17‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steketee RW, Wirima JJ, Slutsker L, Heymann DL, Breman JG. The problem of malaria and malaria control in pregnancy in sub‐Saharan Africa. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;55(Suppl 1):2‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steketee RW, Wirima JJ, Slutsker L, Khoromana CO, Heymann DL, Breman JG. Malaria treatment and prevention in pregnancy: indications for use and adverse events associated with use of chloroquine or mefloquine. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;55(Suppl 1):50‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steketee RW, Wirima JJ, Slutsker L, Roberts JM, Khoromana CO, Heymann DL, et al. Malaria parasite infection during pregnancy and at delivery in mother, placenta, and newborn: efficacy of chloroquine and mefloquine in rural Malawi. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;55(Suppl 1):24‐32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steketee RW, Wirima JJ, Slutsker WL, Khoromana CO, Breman JG, Heymann DL. Objectives and methodology in a study of malaria treatment and prevention in pregnancy in rural Malawi: the Mangochi Malaria Research Project. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;55(Suppl 1):8‐16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vanhauwere 1998 {published data only}
- Vanhauwere B, Maradit H, Kerr L. Post‐marketing surveillance of prophylactic mefloquine (Lariam) use in pregnancy. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1998;58(1):17‐21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to ongoing studies
Akinyotu 2015 NIG {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- A comparative study of mefloquine and SP as prophylaxis against malaria in pregnant HIV‐infected patients. Ongoing study September 2015.
Additional references
Ataíde 2014
- Ataíde R, Mayor A, Rogerson SJ. Malaria, primigravidae, and antibodies: knowledge gained and future perspectives. Trends in Parasitology 2014;30(2):85‐94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Aubouy 2007
- Aubouy A, Fievet N, Bertin G, Sagbo JC, Kossou H, Kinde‐Gazard D, et al. Dramatically decreased therapeutic efficacy of chloroquine and sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine, but not mefloquine, in southern Benin. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2007;12(7):886‐94. [PUBMED: 17596256] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ayisi 2003
- Ayisi JG, Eijk AM, ter Kuile FO, Kolczak MS, Otieno JA, Misore AO, et al. The effect of dual infection with HIV and malaria on pregnancy outcomes in western Kenya. AIDS 2003;17:585‐94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bardaji 2008
- Bardaji A, Sigauque B, Bruni L, Romagosa C, Sanz S, Mabunda S, et al. Clinical malaria in African pregnant women. Malaria Journal 2008;7:27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bardaji 2012
- Bardaji A, Bassat Q, Alonso PL, Menendez C. Intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnant women and infants: making best use of the available evidence. Expert Opinion in Pharmacotherapy 2012;13(12):1719‐36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Brabin 1983
- Brabin BJ. An analysis of malaria in pregnancy in Africa. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 1983;61(6):1005‐16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Briand 2009
- Briand V, Bottero J, Noel H, Masse V, Cordel H, Guerra J, et al. Intermittent treatment for the prevention of malaria during pregnancy in Benin: a randomized, open‐label equivalence trial comparing sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine with mefloquine. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2009;200(6):991‐1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Carrara 2009
- Carrara VI, Zwang J, Ashley EA, Price RN, Stepniewska K, Barends M, et al. Changes in the treatment responses to artesunate‐mefloquine on the northwestern border of Thailand during 13 years of continuous deployment. PLoS ONE 2009;4(2):e4551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
CDC 2016
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Yellow Book ‐ Malaria, Chapter 3. Travelers' Health. Available from wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2016/infectious‐diseases‐related‐to‐travel/malaria (accessed 13 February 2018).
CDC 2017
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Malaria Maps. Available from https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/travelers/about_maps.html (accessed 13 February 2018).
Desai 2007
- Desai M, ter Kuile FO, Nosten F, McGready R, Asamoa K, Brabin B, et al. Epidemiology and burden of malaria in pregnancy. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2007;7(2):93‐104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Desai 2018
FDA 2004
- US Food, Drug Administration. Lariam‐brand of mefloquine hydrochloride. 2004. Available from www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/019591s024s025lbl.pdf (accessed 1 December 2014).
Gamble 2006
- Gamble C, Ekwaru JP, ter Kuile FO. Insecticide‐reated nets for preventing malaria in pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003755.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gamble 2007
- Gamble C, Ekwaru PJ, Garner P, ter Kuile FO. Insecticide‐treated nets for the prevention of malaria in pregnancy: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. PLoS Medicine 2007;4(3):e107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gonzalez 2012
- Gonzalez R, Ataide R, Naniche D, Menéndez C, Mayor A. HIV and malaria interactions: where do we stand?. Expert Review of Anti‐infective Therapy 2012;10(2):153‐65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gonzalez 2014
- Gonzalez R, Hellgren U, Greenwood B, Menendez C. Mefloquine safety and tolerability in pregnancy: a systematic literature review. Malaria Journal 2014;13(1):75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
González 2013
- González R, Hellgren U, Greenwood B, Menéndez C. Mefloquine safety and tolerability in pregnancy: a systematic literature review. Malaria Journal 2014;13:75. [DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-75] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. www.gradeworkinggroup.org/. Version accessed 6 August 2017. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Guyatt 2004
- Guyatt HL, Snow RW. Impact of malaria during pregnancy on low birth weight in sub‐Saharan Africa. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2004;17(4):760‐9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC, editor(s). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org. The Cochrane Collaboration.
Iriemenam 2012
- Iriemenam NC, Shah M, Gatei W, Eijk AM, Ayis J, Kariuki S, et al. Temporal trends of sulphadoxine‐pyrimethamine (SP) drug‐resistance molecular markers in Plasmodium falciparum parasites from pregnant women in western Kenya. Malaria Journal 2012;11:134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kayentao 2013
- Kayentao A, Garner P, Eijk AM, Naidoo I, Roper C, Mulokozi A, et al. Intermittent preventive therapy for malaria during pregnancy using 2 vs 3 or more doses of sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine and risk of low birth weight in Africa: systematic review and meta‐analysis. JAMA 2013;309(6):594–604. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2012.216231] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lee 2017
- Lee SJ, ter Kuile FO, Price RN, Luxemburger C, Nosten F. Adverse effects of mefloquine for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria in Thailand: a pooled analysis of 19,850 individual patients. PLoS ONE 2017;12(2):e0168780. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168780] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
MacArthur 2001
- MacArthur J, Stennies GM, Macheso A, Kolczak MS, Green MD, Ali D, et al. Efficacy of mefloquine and sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum infection in Machinga District, Malawi, 1998. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2001;65(6):679‐84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Menendez 2010
- Menendez C, Bardaji A, Sigauque B, Sanz S, Aponte JJ, Mabunda S, et al. Malaria prevention with IPTp during pregnancy reduces neonatal mortality. PLoS ONE 2010;5(2):9438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Menéndez 2008
- Menéndez C, Bardají A, Sigauque B, Romagosa C, Sanz S, Serra‐Casas E, et al. A randomized placebo‐controlled trial of intermittent preventive treatment in pregnant women in the context of insecticide treated nets delivered through the antenatal clinic. PLoS ONE 2008;3(4):e1934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Menéndez 2011
- Menéndez C, Serra‐Casas E, Scahill MD, Sanz S, Nhabomba A, Bardají A, et al. HIV and placental infection modulate the appearance of drug‐resistant Plasmodium falciparum in pregnant women who receive intermittent preventive treatment. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2011;52(1):41‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mockenhaupt 2008
- Mockenhaupt FP, Bedu‐Addo G, Eggelte TA, Hommerich L, Holmberg V, von Oertzen, C, et al. Rapid increase in the prevalence of sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine resistance among Plasmodium falciparum isolated from pregnant women in Ghana. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2008;198(10):1545‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nosten 1999
- Nosten F, Vincenti M, Simpson J, Yei P, Thwai KL, Vries A, et al. The effects of mefloquine treatment in pregnancy. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1999;28(4):808‐15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nosten 2000
- Nosten F, Vugt M, Price R, Luxemburger C, Thway KL, Brockman A, et al. Effects of artesunate‐mefloquine combination on incidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria and mefloquine resistance in western Thailand: a prospective study. Lancet 2000;356(9226):297‐302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Oduola 1987
- Oduola AM, Milhous WK, Salako LA, Walker O, Desjardins RE. Reduced in‐vitro susceptibility to mefloquine in West African isolates of Plasmodium falciparum. Lancet 1987;2(8571):1304‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pekyi 2016
- PREGACT Study Group, Pekyi D, Ampromfi AA, Tinto H, Traoré‐Coulibaly M, Tahita MC, et al. Four artemisinin‐based treatments in African pregnant women with malaria. New England Journal of Medicine 2016;374(10):913‐27. [DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1508606] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Phillips‐Howard 1995
- Phillips‐Howard PA, ter Kuile FO. CNS adverse events associated with antimalarial agents. Fact or fiction?. Drug Experience 1995;12(6):370‐83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Radeva‐Petrova 2014
- Radeva‐Petrova D, Kayentao K, ter Kuile FO, Sinclair D, Garner P. Drugs for preventing malaria in pregnant women in endemic areas: any drug regimen versus placebo or no treatment. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000169.pub3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schlagenhauf 2010
- Schlagenhauf P, Adamcova M, Regep L, Schaerer MT, Rhein HG. The position of mefloquine as a 21st century malaria chemoprophylaxis. Malaria Journal 2010;9:357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schwarz 2008
- Schwarz NG, Adegnika AA, Breitling LP, Gabor J, Agnandji ST, Newman RD, et al. Placental malaria increases malaria risk in the first 30 months of life. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2008;47(8):1017‐25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sevene 2010
- Sevene E, Gonzalez R, Menendez C. Current knowledge and challenges of antimalarial drugs for treatment and prevention in pregnancy. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2010;11(8):1277‐93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Steffen 1993
- Steffen R, Fuchs E, Schildknecht J, Naef U, Funk M, Schlagenhauf P, et al. Mefloquine compared with other malaria chemoprophylactic regimens in tourists visiting east Africa. Lancet 1993;341(8856):1299‐303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Steketee 1996
- Steketee RW, Wirima JJ, Slutsker L, Roberts JM, Khoromana CO, Heymann DL, et al. Malaria parasite infection during pregnancy and at delivery in mother, placenta, and newborn: efficacy of chloroquine and mefloquine in rural Malawi. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;55(1 Suppl):24‐32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Steketee 2001
- Steketee RW, Nahlen BL, Parise ME, Menendez C. The burden of malaria in pregnancy in malaria‐endemic areas. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2001;64:28‐35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
ter Kuile 1995
- ter Kuile FO, Nosten F, Luxemburger C, Kyle D, Teja‐Isavatharm P, Phaipun L, et al. Mefloquine treatment of acute falciparummalaria: a prospective study of non‐serious adverse effects in 3673 patients. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 1995;73(5):631‐42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
ter Kuile 2004
- ter Kuile FO, Parise ME, Verhoeff FH, Udhayakumar V, Newman RD, Eijk AM, et al. The burden of co‐infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and malaria in pregnant women in sub‐Saharan Africa. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2004;72(Suppl 2):41‐54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
ter Kuile 2007
- ter Kuile FO, Eijk AM, Filler SJ. Effect of sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine resistance on the efficacy of intermittent preventive therapy for malaria control during pregnancy: a systematic review. Journal of the American Medical Association 2007;297(23):2603‐16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
van Eijk 2002
- Eijk AM, Ayisi JG, Ter Kuile FO, Misore AO, Otieno JA, Kolczak MS, et al. Malaria and human immunodeficiency virus infection as risk factors for anemia in infants in Kisumu, western Kenya. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2002;67:44‐53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
van Eijk 2003
- Eijk AM, Ayisi JG, ter Kuile FO, Misore AO, Otieno JA, Rosen DH, et al. HIV increases the risk of malaria in women of all gravidities in Kisumu, Kenya. AIDS 2003;17(4):595‐603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Walker 2013
- Walker PGT, Griffin JT, Cairns M, Rogerson SJ, Eijk AM, ter Kuile F, et al. A model of parity‐dependent immunity to placental malaria. Nature Communications 2013;4:1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
White 2005
- White NJ. Intermittent presumptive treatment for malaria. PLoS Medicine 2005;2(1):e3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
WHO 2004
- World Health Organization. A strategic framework for malaria prevention and control during pregnancy in the African Region. World Health Organization Regional Office for Africa 2004; Vol. AFR/MAL/04/01.
WHO 2012a
- World Health Organization. World malaria report. World Health Organization 2012; Vol. ISBN 978 92 4 156453 3.
WHO 2012b
- World Health Organization. Intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy using sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine (IPTp‐SP). Updated WHO Policy Recommendation October 2012.
WHO 2013
- World Health Organization. Policy brief for the implementation of intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy using sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine (IPTp‐SP). WHO/HTM/GMP/2014.4. Available from www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/iptp‐sp‐updated‐policy‐brief‐24jan2014.pdf?ua=1 (accessed 1 December 2014).
WHO 2015
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria, 3rd edition. Available from www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/9789241549127/en/ (accessed 13 February 2018).
WHO MPAC 2013
- World Health Organization. Malaria Policy Advisory Committee and Secretariat. Malaria Policy Advisory Committee to the WHO: conclusions and recommendations of September 2013 meeting. Malaria Journal 2013;12:346. [PUBMED: 24359206] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
González 2015
- González R, Boerma RS, Sinclair D, Aponte JJ, ter Kuile FO, Menéndez C. Mefloquine for preventing malaria in pregnant women. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011444] [DOI] [Google Scholar]


