Abstract
Background
Skeletal muscle wasting and weakness are significant complications of critical illness, associated with degree of illness severity and periods of reduced mobility during mechanical ventilation. They contribute to the profound physical and functional deficits observed in survivors. These impairments may persist for many years following discharge from the intensive care unit (ICU) and can markedly influence health‐related quality of life. Rehabilitation is a key strategy in the recovery of patients after critical illness. Exercise‐based interventions are aimed at targeting this muscle wasting and weakness. Physical rehabilitation delivered during ICU admission has been systematically evaluated and shown to be beneficial. However, its effectiveness when initiated after ICU discharge has yet to be established.
Objectives
To assess the effectiveness of exercise rehabilitation programmes, initiated after ICU discharge, for functional exercise capacity and health‐related quality of life in adult ICU survivors who have been mechanically ventilated longer than 24 hours.
Search methods
We searched the following databases: the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Ovid SP MEDLINE, Ovid SP EMBASE and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) via EBSCO host to 15 May 2014. We used a specific search strategy for each database. This included synonyms for ICU and critical illness, exercise training and rehabilitation. We searched the reference lists of included studies and contacted primary authors to obtain further information regarding potentially eligible studies. We also searched major clinical trials registries (Clinical Trials and Current Controlled Trials) and the personal libraries of the review authors. We applied no language or publication restriction. We reran the search in February 2015 and will deal with the three studies of interest when we update the review.
Selection criteria
We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs), quasi‐RCTs and controlled clinical trials (CCTs) that compared an exercise intervention initiated after ICU discharge versus any other intervention or a control or ‘usual care’ programme in adult (≥ 18 years) survivors of critical illness.
Data collection and analysis
We used standard methodological procedures as expected by the Cochrane Collaboration.
Main results
We included six trials (483 adult ICU participants). Exercise‐based interventions were delivered on the ward in two studies; both on the ward and in the community in one study; and in the community in three studies. The duration of the intervention varied according to length of hospital stay following ICU discharge (up to a fixed duration of 12 weeks).
Risk of bias was variable for all domains across all trials. High risk of bias was evident in all studies for performance bias, although blinding of participants and personnel in therapeutic rehabilitation trials can be pragmatically challenging. For other domains, at least half of the studies were at low risk of bias. One study was at high risk of selection bias, attrition bias and other sources of bias. Risk of bias was unclear for the remaining studies across domains. We decided not to undertake a meta‐analysis because of variation in study design, types of interventions and outcome measurements. We present a narrative description of individual studies for each outcome.
All six studies assessed functional exercise capacity, although we noted wide variability in the nature of interventions, outcome measures and associated metrics and data reporting. Overall quality of the evidence was very low. Individually, three studies reported positive results in favour of the intervention. One study found a small short‐term benefit in anaerobic threshold (mean difference (MD) 1.8 mL O2/kg/min, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.4 to 3.2; P value = 0.02). In a second study, both incremental (MD 4.7, 95% CI 1.69 to 7.75 watts; P value = 0.003) and endurance (MD 4.12, 95% CI 0.68 to 7.56 minutes; P value = 0.021) exercise testing results were improved with intervention. Finally self reported physical function increased significantly following use of a rehabilitation manual (P value = 0.006). Remaining studies found no effect of the intervention.
Similar variability was evident with regard to findings for the primary outcome of health‐related quality of life. Only two studies evaluated this outcome. Individually, neither study reported differences between intervention and control groups for health‐related quality of life due to the intervention. Overall quality of the evidence was very low.
Four studies reported rates of withdrawal, which ranged from 0% to 26.5% in control groups, and from 8.2% to 27.6% in intervention groups. The quality of evidence for the effect of the intervention on withdrawal was low. Very low‐quality evidence showed rates of adherence with the intervention. Mortality ranging from 0% to 18.8% was reported by all studies. The quality of evidence for the effect of the intervention on mortality was low. Loss to follow‐up, as reported in all studies, ranged from 0% to 14% in control groups, and from 0% to 12.5% in intervention groups, with low quality of evidence. Only one non‐mortality adverse event was reported across all participants in all studies (a minor musculoskeletal injury), and the quality of the evidence was low.
Authors' conclusions
At this time, we are unable to determine an overall effect on functional exercise capacity, or on health‐related quality of life, of an exercise‐based intervention initiated after ICU discharge for survivors of critical illness. Meta‐analysis of findings was not appropriate because the number of studies and the quantity of data were insufficient. Individual study findings were inconsistent. Some studies reported a beneficial effect of the intervention on functional exercise capacity, and others did not. No effect on health‐related quality of life was reported. Methodological rigour was lacking across several domains, influencing the quality of the evidence. Wide variability was noted in the characteristics of interventions, outcome measures and associated metrics and data reporting.
If further trials are identified, we may be able to determine the effects of exercise‐based intervention following ICU discharge on functional exercise capacity and health‐related quality of life among survivors of critical illness.
Plain language summary
Exercise rehabilitation following intensive care unit discharge for recovery from critical illness
Review question
We reviewed the evidence about the effects of exercise rehabilitation on functional exercise capacity and health‐related quality of life for patients who have been critically unwell in the intensive care unit (ICU). Functional exercise capacity is a term used to express how well individuals perform activities such as walking or climbing the stairs.
Background
Adults often develop muscle wasting and weakness during ICU admission. This may occur as a result of the illness itself, and because patients tend to be less mobile and physically active whilst they are receiving treatment. As they recover, this muscle weakness can cause difficulty in their ability to exercise and carry out normal activities of daily living. Adult patients can become depressed or low in mood as a result of the illness and the effects of their reduced strength, which can last for many years.
We wanted to measure health‐related quality of life to determine whether exercise programmes can help patients recover from critical illness‐related physical deconditioning and muscle weakness after they have been discharged from the ICU, and can help them to feel better about themselves.
Study characteristics
We included six studies that involved 483 participants (298 male, 185 female) over the age of 18 years. Participants had received breathing support from a machine (been mechanically ventilated) for longer than 24 hours whilst in the ICU and had begun an exercise programme after leaving the ICU. Studies were carried out in the UK, Australia, the USA and Italy.
Exercise programmes were delivered on the ward in two studies; on the ward and in the community in one study; and in the community in three studies. The duration of the intervention varied according to length of hospital stay after ICU discharge up to a fixed time of 12 weeks. Exercises included arm or leg cycling, walking and general muscle strengthening at home, provision of self help manuals and hospital‐based multi‐exercise programmes carried out in physiotherapist‐led gymnasiums.
Three of the six studies were funded by government health research funding agencies. One study was supported by combined funding from an independent charity and a commercial company (with no interest in the results of the study). One study did not report a funding source, and another was funded by an academic health research agency.
Key results
We were unable to determine an overall result for the effects of exercise‐based interventions. Three studies reported improvement in functional exercise capacity following completion of the exercise programme, and the other three found no effects of treatment.
Only two studies measured patient‐reported health‐related quality of life, and both of these studies showed no effects related to treatment. Again, we were unable to reach an overall conclusion. No study included an evaluation of acceptance of the treatment by patients or the experience of patient participation in an exercise‐based programme.
Quality of the evidence
We found considerable differences across included studies regarding types of exercise, how measurements of functional exercise capacity were collected, ways by which results were presented and people who had been critically ill. Exercise programmes were compared with usual care, with lack of acknowledgement of the standard level of rehabilitation and exercise in usual practice. In addition, we found variability in how well the studies were performed. We were unable to perform any statistical tests on study findings or to make firm conclusions because of this variability. The overall quality of the evidence was very low for these reasons. .
Currency of the evidence
Evidence is current to May 2014. We reran the search in February 2015 and will deal with studies of interest when we update the review.
Summary of findings
Summary of findings for the main comparison. Summary of findings for main comparison.
| Exercise rehabilitation compared with usual care for adult survivors of critical illness | ||||
|
Patient or population: adult survivors of critical illness Settings: any Intervention: exercise rehabilitation or training initiated after intensive care unit discharge Comparison: usual care | ||||
| Outcomes | Effectsa | Number of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments |
|
Functional exercise capacity Multiple different outcome measures used SF‐36 PF and AT (at 9 and 26 weeks) (Batterham 2014) SF‐36 PF and 6MWT (at 8 and 26 weeks) (Elliott 2011) ABC, Katz, TUAG (at 3 months) (Jackson 2012) SF‐36 PCS (follow‐up period not specified) (Jones 2003) Incremental and endurance exercise test (follow‐up period not specified) (Porta 2005) RMI, TUAG, 10m Walk Test, ISWT, HGD (at 3 months) (Salisbury 2010) |
Most studies found no difference in functional exercise capacity as a result of the intervention When a beneficial effect was reported, this was noted on a physiological exercise‐based outcome measure following targeted cardiopulmonary exercise training (AT at 9 weeks, n = 13 rehabilitation group vs n = 17 control group, 12.5 (1.9) vs 10.7 (1.9) mL O2/kg/min, MD 1.8 (95% CI 0.4 to 3.2), P value = 0.02) (Batterham 2014) |
Variable according to individual study and outcome measure (6) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowb | All studies reported data for functional exercise capacity albeit variable with regard to outcome measure and metrics. Pooling of data inappropriate because of differences in outcome measures |
|
Health‐related quality of life Multiple different outcome measures used EQ‐5D and EQ‐5D VAS (9 and 26 weeks) (Batterham 2014) SF‐36 PCS and MCS (8 and 26 weeks) (Elliott 2011) |
No study found a difference between control and intervention groups for health‐related quality of life | Variable according to individual study and outcome measure (2) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowb | Only 2 studies reported data for health‐related quality of life; pooling of data was inappropriate because of differences in outcome measures. Individual study findings are reported separately |
|
Withdrawals Participant withdrawal following randomization before or during receipt of the intervention because of consent or medical reason |
4 out of 6 studies reported data; no difference between intervention and control groups Total withdrawal rates (combined control and intervention groups): 13/59 (Batterham 2014); 16/195 (Elliott 2011) 3/22 (Jackson 2012) 16/66 (Porta 2005) |
341 (4) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowc | |
|
Adherence Participant completion of the intervention as described in the trial method |
Only 1 study reported rates of adherence to the intervention Overall adherence: Mean = 12 (out of 16 supervised sessions) and mean = 6 (out of 8 unsupervised sessions) (Batterham 2014) |
21 (1) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowd | |
|
Mortality Death at any point during the trial duration |
All studies reported data for mortality: no deaths reported in 2 studies (Batterham 2014; Porta 2005); no difference in mortality rates between intervention and control groups in the remaining 4 studies Total mortality rates (combined control and intervention groups): 11/195 (Elliott 2011) 1/22 (Jackson 2012) 10/126 (Jones 2003) 3/16 (Salisbury 2010) |
483 (6) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowe | |
|
Loss to follow‐up Non‐completion of outcome measures due to non‐attendance or other reasons as reported |
All studies reported data for loss to follow‐up; no loss to follow‐up in 2 studies (Jackson 2012; Porta 2005); no difference in loss to follow‐up rates between intervention and control groups in the remaining 4 studies Rates of total loss to follow‐up (combined control and intervention groups): 4/59 (Batterham 2014) 7/195 (Elliott 2011) 14/126 (Jones 2003) 2/16 (Salisbury 2010) |
483 (6) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowf | |
|
Other adverse events Non‐mortality |
3 out of 6 studies reported no adverse events (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Jones 2003). 1 study reported occurrence of adverse events, but this was not significantly different between groups and represented only 1 event overall (Jackson 2012). 2 studies did not report data on adverse events (Porta 2005; Salisbury 2010) | 376 (4) |
⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowg | |
|
Summary of included study settings: Batterham 2014; study conducted in the United Kingdom; intervention delivered after hospital discharge in an outpatient setting Elliott 2011; study conducted in Australia; intervention delivered after hospital discharge in the community Jackson 2012; study conducted in the United States; intervention delivered after hospital discharge in the community Jones 2003; study conducted in the United Kingdom; intervention delivered after ICU discharge in the hospital ward and in the community Porta 2005; study conducted in Italy; intervention delivered after ICU discharge in the high dependency unit of a respiratory rehabilitation department Salisbury 2010; study conducted in the United Kingdom; intervention delivered after ICU discharge in the hospital ward | ||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. High quality: Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: We are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||
aStudies could not be pooled because of insufficient data and variability in data when reported.
bDowngraded by 3 levels because of variability in multiple aspects of study methodology across all studies, risk of bias and differences in data reporting.
cDowngraded by 2 levels because of lack of reported data from 2 studies and serious imprecision (small overall sample size).
dDowngraded by 3 levels because of lack of reported data from 5 studies, and incomplete data from 1 study (mean values only).
eDowngraded by 2 levels because of serious inconsistency (data were not combined because of variation in study design) and imprecision (small overall sample size).
fDowngraded by 2 levels because of serious risk of bias and serious imprecision.
gDowngraded by 2 levels because of lack of reported data from 2 studies and serious imprecision.
Abbreviations: SF‐36 PF = Short Form 36 questionnaire Physical Function domain. AT = anaerobic threshold. 6MWT = Six Minute Walk Test. ABC = Activities and Balance Confidence scale. TUAG = Timed Up And Go. SF‐36 PCS/MCS = Short Form 36 questionnaire Physical Component Score/Mental Component Score. RMI = Rivermead Mobility Index. ISWT = Incremental Shuttle Walk Test. HGD = handgrip dynamometry. EQ‐5D = EuroQol 5‐domain. VAS = visual analogue scale.
Background
Admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) with critical illness can result in profound and physical impairment for survivors, which frequently persists for many years following resolution of the index illness, and which contributes to ‘post intensive care syndrome’ (Needham 2012a). Peripheral skeletal muscle wasting and weakness during the period of mechanical ventilation and immobilization associated with ICU admission are considered significant drivers underlying much of the physical functional deficit observed. In recent years, the importance of exercise‐based rehabilitation, which spans the whole recovery pathway, commencing within the ICU and continuing after transfer to the ward and beyond hospital discharge, has gained recognition as a strategy for targeting critical illness‐related physical deconditioning, as well as skeletal muscle wasting and weakness (NICE 2009).
Description of the condition
Advances in intensive care medicine have resulted in higher survival rates, including among patients with complex and chronic co‐morbidity. As a consequence, the prevalence of impairment and disability among survivors of critical illness has significantly increased. A wealth of longitudinal observational follow‐up data obtained for up to five years from the post critical illness population characterizes the varying and often pronounced morbidity related to physical functional (Cheung 2006; Dennis 2011; Herridge 2003; Herridge 2011; Needham 2012b; Needham 2013a); cognitive (Hopkins 2005a; Hopkins 2005b; Hopkins 2012; Pandharipande 2013); and psychological capacity (Sukantarat 2007a; Sukantarat 2007b; Wade 2012); and to health‐related quality of life (Cuthbertson 2010; Dowdy 2006; Kvale 2003; Oeyen 2010). Furthermore, data are available that highlight the healthcare utilization and socioeconomic impact of critical illness (Cheung 2006; Griffiths 2013; Unroe 2010) and are used to evaluate the burden experienced by family and care‐givers (Davidson 2012; de Miranda 2011; Kentish‐Barnes 2009). Recently, an international multi‐disciplinary stakeholder consensus indicated that the clinical term ‘post intensive care syndrome’ should be used to describe the multi‐faceted spectrum of sequelae following critical illness (Needham 2012a).
One component of this syndrome — peripheral skeletal muscle wasting and dysfunction developing during critical illness — is described as intensive care unit‐acquired weakness (ICU‐AW) and contributes significantly to residual deficits in physical function. In a recent detailed, observational study of muscle wasting in critically ill patients, serial ultrasound measurements of quadriceps rectus femoris cross‐sectional area demonstrated a 20% loss of muscle within the first 10 days of ICU admission (Puthucheary 2013). This muscle wasting was found to be significantly greater among sicker patients with multi‐organ failure, and in association with muscle necrosis and macrophage infiltrate on histological examination of comparative muscle biopsies. The negative effects of critical illness on multiple parameters of peripheral skeletal muscle architecture characterized by the use of ultrasound have been summarized in a recent systematic review (Connolly 2014b) and, in addition to the aforementioned loss of muscle bulk (Puthucheary 2013), include loss of muscle layer thickness (Baldwin 2014; Campbell 1995; Cartwright 2013; Gruther 2008) and muscle composition or quality as determined by assessment of echogenicity (Cartwright 2013; Grimm 2013). In addition, critically ill patients are more likely to develop muscle weakness, as demonstrated by both volitional and non‐volitional methods, when compared with control study participants and those with other chronic respiratory disease (Ali 2008; Baldwin 2013; Connolly 2014; Eikermann 2006; Ginz 2005; Harris 2000; Pickles 2005; Vivodtzev 2014).
One key long‐term outcome associated with ICU‐AW is a marked reduction in physical and functional capacity. In a landmark study, Herridge et al (Herridge 2011) reported the five‐year assessment of a cohort of acute respiratory distress syndrome survivors. At this time point, median (interquartile range) six‐minute walking distance was 436 (324 to 512) metres (m) — 76% that of an age‐ and sex‐matched control population, and representing persistent impairment in functional exercise capacity, which correlated with self reported physical health‐related quality of life (HRQL). Furthermore, self reported physical HRQL scores were well below the range reported by a control population. Notably, these patients had return of normal or near‐normal volumetric and spirometric lung function, indicating that results observed from objective and subjective physical assessments were a consequence of skeletal muscle impairment, not of respiratory capacity. Although participants examined in this study represented a relatively young, previously healthy cohort with a specific ICU‐related diagnosis, it is plausible to consider that the results may have been markedly worse if extrapolated to a general, older and chronically co‐morbid post ICU population. These findings are echoed by several studies that reported similar findings within time frames ranging up to the five‐year point (Cheung 2006; Conti 2011; Fan 2014; Needham 2012b; Needham 2013b). Indeed it has been suggested that even longer‐term follow‐up beyond five years may be required for full appreciation of the physical and functional consequences associated with post intensive care syndrome and critical illness survivorship (Iwashyna 2010).
Description of the intervention
Exercise‐based rehabilitation is advocated in the management of physical and functional disability secondary to ICU‐AW. Interventions delivered at all stages of the patient pathway have been reported, and rehabilitation ideally should follow a seamless transition from the ICU to the ward, and after hospital discharge (NICE 2009).
Early mobilization of patients in the ICU is characterized by a hierarchical progression of increasingly functional activities ranging from passive‐ and active‐assisted exercises whilst patients are in bed, sitting over the edge of the bed, standing, marching‐on‐the‐spot and ultimately walking (Hodgson 2014), depending on the level of active participation of patients. In addition, use of assistive technologies such as electrical muscle stimulation (Parry 2013), passive cycle ergometry (Pires‐Neto 2013) and interactive video‐game systems (Kho 2012) can facilitate prompt commencement of exercise. The safety (Berney 2012; Pires‐Neto 2013; Schweickert 2009; Sricharoenchai 2014) and feasibility (Bailey 2007; Bourdin 2010; Drolet 2012; Pohlman 2010) of early mobilization interventions have been extensively investigated, and clinical management algorithms based on consensus of expert opinion have been developed to facilitate decision making regarding appropriateness of physical treatments depending on patient status such as level of consciousness, physiological stability and degree of deconditioning (Hanekom 2011). Furthermore, the effectiveness of early mobilization in ICU patients has been examined in several systematic reviews (Calvo‐Ayala 2013; Kayambu 2013; Li 2013; Stiller 2013); early mobilization has been shown to result in significant improvement in health‐related quality of life, physical function, respiratory and peripheral skeletal muscle strength, length of hospital and ICU stay and duration of mechanical ventilation. This topic is the subject of a current Cochrane systematic review (Doiron 2013).
After transfer to the ward, physical management of post ICU patients is typically directed towards planning hospital discharge and ensuring adequate levels of the mobility required to expedite this. Only one study has specifically examined rehabilitation delivery at this stage of recovery, investigating the effects of a combined physical and nutritional rehabilitation package delivered by a generic rehabilitation assistant — a position found to be beneficial for facilitating continuity of care among patients during the ICU‐ward transition (Salisbury 2010a) and associated with significantly increased input on the frequency of physiotherapy sessions (median (interquartile range, IQR) 8.2 (7.1 to 10.6) vs 2.6 (1.8 to 4.2) visits; P value < 0.002) and dietetic sessions (4.9 (3.4 to 8.4) vs 1.2 (0.6 to 2.1) visits; P value < 0.001) (Salisbury 2010). Exercise interventions included transfer practice, walking and climbing stairs, and this model of intervention is currently under investigation in a larger randomized controlled trial (Ramsay 2014; Walsh 2015). Other randomized controlled trials have investigated interventions that include ward‐based components and are continued after hospital discharge (e.g. Denehy 2013).
Data are emerging regarding the effectiveness of exercise‐based post hospital discharge rehabilitation interventions. Whilst three recent randomized controlled trials failed to show benefit, this may have been a result of the methodology employed, the differing nature of the interventions and failure of investigators to stratify patients according to the presence of peripheral skeletal muscle weakness (Batterham 2014; Denehy 2013; Elliott 2011). Furthermore, lack of acknowledgement of the standard level of rehabilitation and exercise therapy provided in usual practice may have reduced differences evident between control and intervention arms. Exercise‐based interventions provided in these trials included self directed home‐based walking programmes, outpatient and hospital‐based exercise classes and specific cardiopulmonary exercise training. At present, no consensus has been reached on the optimal ‘dose’ of exercise‐based intervention, timing of delivery, structure and format of interventions and outcomes used to evaluate effectiveness (Connolly 2012).
How the intervention might work
Exercise‐based rehabilitation aims to primarily ameliorate the effects of ICU‐AW and residual physical function deficits in survivors of critical illness following ICU discharge. However, it is acknowledged that physical exercise therapy confers additional benefits, including improved psychological and cognitive outcomes, enhanced social participation and the opportunity to return to work. Physical rehabilitation represents one strategy for supporting recovery following critical illness and addressing symptoms of post intensive care syndrome (Needham 2012a).
Why it is important to do this review
Rehabilitation for survivors of critical illness is increasingly recognized as a vital component in the management of post intensive care syndrome. Exercise‐based interventions target the physical functional impairment evident in these patients, which persists long after ICU discharge (Herridge 2011). Whilst several systematic reviews have examined exercise‐based early mobilization delivered to critically ill patients in the ICU, none have evaluated the effects of interventions initiated after ICU discharge, albeit data available from randomized controlled trials are increasing. Given increasing survival rates following an ICU admission, and the increasing profile and integration of rehabilitation into the long‐term management of this patient population, it is important for investigators to determine the effects of exercise‐based rehabilitation programmes following critical illness and the optimal characteristics of interventions needed to assist in future services.
Objectives
To assess the effectiveness of exercise rehabilitation programmes, initiated after ICU discharge, for functional exercise capacity and health‐related quality of life in adult ICU survivors who have been mechanically ventilated longer than 24 hours.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs), quasi‐RCTs and controlled clinical trials (CCTs) that compared an exercise intervention initiated after ICU discharge versus any other intervention or a control or ‘usual care’ programme in adult survivors of critical illness.
Types of participants
We included studies of adults (age 18 years or older) who had been mechanically ventilated for 24 hours or longer and admitted to an ICU or critical care environment. In addition, we clarified from the original review protocol that participants in included studies were extubated at the time of receiving the intervention, and had been discharged from the ICU (see Differences between protocol and review).
We excluded studies on participants receiving palliative care. We also excluded studies that involved participants with head injury or trauma, and studies examining participants after cardiac surgery, as these patient groups have targeted rehabilitation pathways in place.
Types of interventions
We included studies that evaluated an intervention of exercise rehabilitation or training of any duration, initiated at any time point after ICU discharge, versus usual care or no intervention. Specifically for the purpose of this review, exercise included any structured or taught programmes with the aim of improving functional ability and quality of life. We excluded studies of interventions that focused solely on respiratory or inspiratory muscle training.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
Functional exercise capacity (with physical objective assessment and/or subjective assessment). This was defined as an individual’s maximal ability to perform functional exercise beneficial for activities of daily living, including walking, stair climbing, sit‐to‐stand exercises and strength.
Health‐related quality of life, as measured by reliable assessment scales (see Differences between protocol and review).
Secondary outcomes
Withdrawal (defined as participant withdrawal following randomization before, or during, receipt of the intervention because of consent or medical reasons).
Adherence (defined as participant completion of the intervention as described in the trial methods).
Mortality (defined as death at any point during the trial duration).
Loss to follow‐up (defined as non‐completion of outcome measures due to non‐attendance or other reasons, if reported).
Adverse events (non‐mortality).
These secondary outcomes were clarified (definition of ‘adherence’) and extended (addition of ‘loss to follow‐up’) from the original review protocol, as it was considered that this would provide more information on participant enrolment, feasibility of interventions employed, burden of outcomes used for evaluation and other factors influencing participant attrition (see Differences between protocol and review).
Search methods for identification of studies
The search for studies was based on a combination of controlled vocabulary and free‐text terms, consistent with the search strategy used for MEDLINE.
Electronic searches
We searched the literature using the standard strategy of the Cochrane Anaesthesia, Critical and Emergency Care Review Group of The Cochrane Collaboration. We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (2014, Issue 5), Ovid SP MEDLINE (1966 to 15 May 2014), Ovid SP EMBASE (1988 to 15 May 2014) and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) via EBSCO host (1982 to 15 May 2014).
We used a specific search strategy for each database that included synonyms for ICU and critical illness, exercise training and rehabilitation and RCTs to reflect the clinical population, intervention and study design, respectively. We presented search strategies for each database in the appendices (Appendix 1, MEDLINE; Appendix 2, EMBASE; Appendix 3, CENTRAL; Appendix 4, CINAHL). We imposed no language or publication restrictions during the search.
We reran the search in February 2015 and will deal with studies of interest when we update the review.
Searching other resources
We searched the reference lists of included studies for additional potentially relevant studies, and when data were available only in abstract form, we contacted authors of studies via electronic mail to determine if full publication had been completed. We manually searched journals and conference proceedings not included in electronic search databases. In addition to the original review protocol, we undertook searches of the major clinical trials registries (Clinical Trials, www.clinicaltrials.gov, up to 15 May 2014; Current Controlled Trials, www.controlled‐trials.com/isrctn/, up to 15 May 2014), as well as the personal libraries of the review authors, whom we consider to represent an expert panel.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
The lead review author (BC) undertook an initial screening of the search results to remove duplicates and non‐relevant subject material. Subsequently, two review authors (BC, BO’N) independently scanned identified titles and abstracts, and excluded records not meeting eligibility criteria as described previously. We obtained full‐text versions of potentially relevant studies and independently determined final eligibility by joint agreement of two review authors using a standardized form (BC, BO’N) (Appendix 5). Additional arbitration by a third review author was not required.
Data extraction and management
Two review authors (LG, LS) independently extracted data from all included studies, with the exception of one study, for which LS was the primary author (Salisbury 2010). This study underwent independent data extraction by LG and BC. Review authors extracted data using a standardized paper form (Appendix 5) that included information on study design, participants, trial characteristics, details of the intervention and outcomes. Following independent data extraction, these review authors met to resolve disagreements through discussion and consultation. Arbitration by a fourth review author was not required.
BC initially transferred into RevMan (RevMan 5.3) data manually collected on paper forms, and LS double‐checked the data entered.
We reviewed qualitatively all data derived from included studies (see Differences between protocol and review).
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors (BB, LS) independently assessed risk of bias of all included studies, with the exception of one study, for which LS was the primary author (Salisbury 2010). BB and BC independently assessed risk of bias for this study. Arbitration by a fourth review author was not required. We used the domain‐based evaluation presented in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Chapter 8, version 5.1.0 (Higgins 2011). We used an updated version of the ‘Risk of bias’ form,originally presented in the protocol,to evaluate each included study (see Differences between protocol and review). Review authors’ judgements were directed by criteria outlined in Chapter 8.5.3 and Table 8.5d. We categorized each study judgement as having ‘low risk of bias’ (yes), ‘uncertain risk of bias’ (unclear) or ‘high risk of bias’ (no) for the following domains.
Random sequence generation (selection bias).
Allocation concealment (selection bias).
Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias).
Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias).
Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias).
Selective reporting (reporting bias).
Other sources of bias (sample size, study design, etc).
We categorized risk of bias across all included studies according to the following criteria.
Low risk of bias — plausible bias unlikely to seriously alter the results if most information was obtained from studies at low risk of bias.
Unclear risk of bias — plausible bias that raised some doubt about the results if most information was obtained from studies at low or unclear risk of bias.
High risk of bias — plausible bias that seriously weakens confidence in results if the proportion of information obtained from studies at high risk of bias was sufficient to affect interpretation of results.
We reported all assessments in the ‘Risk of bias’ tables in this review (Characteristics of included studies) and in the Risk of bias in included studies section. Furthermore, in the Results section of the review, we discussed the impact of methodological quality on study results.
Measures of treatment effect
We combined data using RevMan 5.3 (RevMan 5.3), when possible, according to intervention, outcome and population. We expressed continuous data as mean differences (MDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), or as median values (interquartile range — IQR) when the sample size was too small for conversion, and dichotomous data as risk ratios (RRs) with 95% CIs.
Unit of analysis issues
The participant was the unit of analysis in each trial. Participants were randomly allocated to one of two parallel intervention groups, and a single measurement for each outcome for each participant was collected and analysed.
Dealing with missing data
We extracted all available data from included studies. Three studies reported data regarding intention‐to‐treat (ITT) analysis (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Porta 2005), one study was not clear on this although rates of attrition were reported (Jones 2003) and the remaining two studies were pilot feasibility studies, for which ITT analysis was not applicable (Jackson 2012; Salisbury 2010). We investigated attrition rates in detail, including withdrawals, adherence, mortality and loss to follow‐up, and noted when reasons for this were reported (see Secondary outcomes), to consider pertinent aspects of trial design relevant to the intervention under examination and the target population.
Assessment of heterogeneity
Review authors (BC, LS) judged clinical heterogeneity following extraction of data from included studies (LS, LG, BC) and noted these judgements in the results. We (LS, BB, BC) evaluated methodological heterogeneity by assessing risk of bias. We intended to assess statistical heterogeneity by visually inspecting the forest plot for the first primary outcome of functional exercise capacity for which data were reported by all included studies, using a standard Chi2 test with a significance level of α = 0.1, as the power of this test is low, and by calculating the I2 statistic to assess impact on meta‐analysis (Higgins 2002; Higgins 2003), wherein a value greater than 50% represents at least moderate heterogeneity (Higgins 2011). However, on closer examination of the included studies, we found that only two studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011) used the same outcome measure for functional exercise capacity (Short Form‐36 questionnaire Physical Function domain, SF‐36 PF) at a similar time frame with the potential for pooling data and assessing heterogeneity, albeit for one dataset (Elliott 2011) this would have also required estimation of between‐group differences at the specified time point derived from baseline characteristic data and reporting of mean change from baseline. Following discussion with the review statistician (AD), we considered statistical analysis of heterogeneity to be inappropriate because of the small number of included studies.
Assessment of reporting biases
To assess the level of publication bias when 10 or more studies reported a given outcome, we intended to use funnel plots to assess small‐study effects, according to guidance provided by the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Chapter 10 (Higgins 2011), regarding analysis and interpretation. Study numbers were ultimately insufficient for review authors to undertake this process.
Data synthesis
BC entered data into RevMan 5.3 (RevMan 5.3), and LS and BO'N independently checked these data. All included studies reported data for the primary outcome of functional exercise capacity, albeit data metrics varied: Investigators reported means with 95% CIs (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Porta 2005), medians with IQRs (Jackson 2012; Salisbury 2010) or no numerical data at all (Jones 2003). We calculated the standard deviation (SD) for data using the RevMan (RevMan 5.3) calculator, as well as means, 95% CIs and sample sizes reported by Batterham 2014, Elliott 2011 and Porta 2005. We considered sample sizes for Jackson 2012 and Salisbury 2010 too small to feasibly convert values to means (SDs) (Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions;Higgins 2011). We contacted the lead author for Jones 2003 to request raw data but received no response. Only two studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011) reported data for the second primary outcome of quality of life (similarly, for each study, means with 95% CIs, from which SDs were calculated).
All studies demonstrated variability in selection of outcome measures used to evaluate functional exercise capacity (n = 6) and, when included, health‐related quality of life (n = 2), as well as the timing with which these outcomes were measured. We were unable to perform a meta‐analysis of findings to determine the overall effect of the intervention and the degree of heterogeneity across studies, as this analysis was inappropriate because of the small number of studies with similar data available for pooling. Hence the description of findings was qualitative only, and results of individual studies are summarized in tables (Table 2; Table 3; Table 4; Table 5) with available mean differences, 95% CIs and P values.
1. Study characteristics of interventions.
| Study | Protocol intervention | Usual care |
| Batterham 2014 | Intervention comprised an 8‐week programme of 2 hospital‐based, physiotherapist‐led supervised exercise sessions per week Participants exercised individually, or in pairs, for 40 minutes (including 5 minutes each of warm‐up and cool‐down on a cycle ergometer; exercise intensity set at levels 12 to 14 on the 6‐ to 20‐point Borg scale of perceived exertion, corresponding to moderate intensity Pedal resistance increased progressively over the course of the programme as fitness increased, to ensure exercise intensity levels continued to be met Participants were encouraged to add 1 unsupervised session each week of the same duration and intensity (e.g. a 30‐minute walk at a moderate pace) |
Usual care comprised "...follow‐up by appropriate medical and surgical specialities, but no formal rehabilitation programme" |
| Elliott 2011 | Intervention comprised 8‐week, self delivered, home‐based physical rehabilitation programme focusing on strength training and walking Home visits were performed at weeks 1, 3 and 6 by qualified trainers (physiotherapist, exercise physiologist, registered nurse with additional training) to provide individualised verbal and written instructions; each home visit lasted for 60 to 90 minutes; additional telephone calls to monitor progress made at weeks 2, 4, 5 and 7 Endurance walk training prescription was based on results of each patient's Six Minute Walk Test, with intensity commenced at 80% baseline peak walking speed; extra activities were prescribed to achieve a level of perceived exertion of Level 3 to 4 on the modified Borg score; 12 walking levels were described, ranging from 1 to 60 minutes of walking (walk‐rest‐walk approach), and participants progressed towards achieving training of 5 days/wk for 20 to 30 minutes of walking Strength training included upper (biceps, triceps, shoulder abductors/adductors) and lower limb (quadriceps, hamstrings, hip abductors and extensors) muscle groups, with initial prescription of 1 set of 8‐repetition maximum (8RM) for each activity, progressing to 3 sets; further progression was based on increasing weight (0.25 to 1.5 kg for arm exercises) and increasing step height or weight for lower limb exercises An illustrated exercise manual accompanied the training programme |
Usual care comprised "...usual community‐based care after hospital discharge, for example, visits to their general practitioner, as well as the three study assessment visits, but no other placebo or sham interventions" |
| Jackson 2012 | Intervention comprised usual care plus a 12‐week, 3‐pronged rehabilitation programme including cognitive, physical and functional 12 visits were included of 60 to 75 minutes' duration (6 in‐person for delivery of cognitive rehabilitation, and 6 televisits for physical and functional rehabilitation); weekly telephone calls were also made Specifically, for physical rehabilitation, exercise trainers communicated in "real‐time" with patients via teletechnology and with assistance of a trained social worker in the home Exercises targeted lower extremity function and endurance with activities that could be performed easily in the home (e.g. chair stands, stair climbing and walking); exercise prescription was individually 'dosed' to correspond to current functional status, and intensity was progressively increased according to patient ability |
Usual care comprised "usual care" rehabilitation‐related interventions during and after hospitalization, as determined by medical providers. The scope of “usual care” interventions used with intensive care unit survivors may include physical therapy, occupational therapy and nursing care delivered to inpatient, outpatient or home‐health settings. Neither cognitive therapy nor speech therapy with a predominant cognitive focus is considered usual care among intensive care unit survivors without frank neurologic injuries" |
| Jones 2003 | Intervention comprised 6‐week rehabilitation manual including self directed exercise programme with 3 weekly phone calls to oversee use and a diary to document adherence | Usual care comprised routine intensive care unit follow‐up — participants were "followed up on the general wards post‐intensive care unit discharge, were contacted by telephone three times once they had gone home to ask how they were getting on, and finally were seen in a dedicated intensive care unit follow‐up clinic at 8 weeks and 6 months" |
| Porta 2005 | Intervention comprised control group management plus 15 daily, 20‐minute, supervised sessions of upper arm cycling of increasing intensity | Usual care comprised general physiotherapy, which consisted of "six weekly 45‐min daily sessions of assisted passive and progressively active lower‐ and upper‐limb mobilisation, chest physiotherapy, assisted deambulation, functional and strengthening exercises, reinforcement techniques for head and trunk control, sitting and standing balance, transfers, and safe energy‐efficient reciprocal pattern for gait with or without walking aids" |
| Salisbury 2010 | Intervention comprised specifically enhanced physical and nutritional rehabilitation delivered by a generic rehabilitation assistant and overseen by the research physiotherapist (for physiotherapy component) Physical rehabilitation included additional interventions of supervised passive, active and strengthening exercises, facilitation of additional transfers and mobility practice, balance exercises and advice |
Usual care comprised standard therapy input |
2. Review of functional exercise capacity findings.
| Study | Functional capacity measure | Rehabilitation group | Control group | Difference in mean | 95% CI | P value | ||
| n | Mean (SD) | n | Mean (SD) | |||||
| Batterham 2014 | SF‐36 PF 9 weeks |
18 | 43.5 (7.8) | 23 | 40.1 (7.8) | 3.4 | ‐1.4 to 8.2 | 0.2* |
| SF‐36 PF 26 weeks |
21 | 46.7 (10.5) | 25 | 46.6 (10.5) | 0.1 | ‐6.0 to 6.2 | 1.0* | |
| AT (mL O2/kg/min) 9 weeks |
13 | 12.5 (1.9) | 17 | 10.7 (1.9) | 1.8 | 0.4 to 3.2 | 0.02* | |
| AT (mL O2/kg/min) 26 weeks |
18 | 12.7 (3.5) | 20 | 12.1 (3.5) | 0.6 | ‐1.6 to 2.8 | 0.6* | |
| Elliott 2011 | SF‐36 PF (change from baseline to 8 weeks) |
85 | 12.9 (10.2) | 88 | 12.2 (10.9) | 0.7 | ‐2.5 to 3.8 | 0.7* |
| SF‐36 PF (change from baseline to 26 weeks) |
76 | 14.7 (12.9) | 85 | 13.7 (10.7) | 0.9 | ‐2.7 to 4.6 | 0.6* | |
| 6MWT (m) (change from baseline to 8 weeks) |
85 | 88.7 (121.0) | 88 | 80.3 (132.1) | 8.4 | ‐29.6 to 46.4 | 0.7* | |
| 6MWT (m) (change from baseline to 26 weeks) |
76 | 125.8 (118.6) | 85 | 116.2 (141.9) | 9.6 | ‐31.4 to 50.5 | 0.6* | |
| Jackson 2012a | ABC scale 3 months |
7 | 82 (78 to 89) | 8 | 83 (38 to 91) | ‐ | ‐ | 0.35˜ |
| Katz^ (% moderate to severe dependency) 3 months |
7 | 0 | 8 | 25 | ‐ | ‐ | 0.78˜ | |
| TUAG (s) 3 months |
7 | 9.0 (8.5 to 11.8) | 8 | 10.2 (9.2 to 11.7) | Adjusted treatment effect: ‐1.1 |
‐4.1 to 2.0 | 0.51˜ | |
| Jones 2003b | SF‐36 PF | P value = 0.006 | ||||||
| Porta 2005 | Incremental exercise test (maximum workload, W) | 25 | 17.0 (8.8) | 25 | 11.0 (6.4) | 6.0 | 1.7 to 10.3 | 0.008* |
| Incremental exercise test (change in Borg scale muscle fatigue) |
25 | ‐2.2 (2.5) | 25 | ‐0.87 (2.5) | ‐1.35 | ‐2.77 to 0.07 | 0.091* | |
| Endurance exercise test (time) | 25 | 14.1 (8.7) | 25 | 9.6 (6.4) | 4.5 | 0.3 to 8.7 | 0.04* | |
| Endurance exercise test (change in Borg scale muscle fatigue) |
25 | ‐2.24 (2.7) | 25 | ‐0.7 (2.7) | ‐1.54 | ‐3.05 to ‐0.33 | 0.056* | |
| Salisbury 2010c | RMI 3months |
5 | 12.0 (3.0 to 12.5) | 6 | 11.0 (8.0 to 14.3) | ‐ | ‐ | 0.4˜ |
| TUAG (s) 3 months |
4 | 12.5 (8.5 to 28.9) | 5 | 12.8 (9.2 to 17.5) | ‐ | ‐ | 1.0˜ | |
| 10m Walk Test (s) 3 months |
4 | 11.3 (7.7 to 43.2) | 5 | 11.0 (8.7 to 14.2) | ‐ | ‐ | 1.0˜ | |
| ISWT (m) 3 months |
4 | 168.0 (44.5 to 317.0) | 5 | 149.0 (91.0 to 333.0) | ‐ | ‐ | 0.8˜ | |
| Handgrip strength (% normal) (improvement between baseline and 3 months) |
4 | 13.5 (5.5 to 47.0) | 6 | 21.0 (13.8 to 25.8) | ‐ | ‐ | 0.8˜ | |
Abbreviations: SF‐36 PF = Short Form 36 questionnaire Physical Function domain. AT = anaerobic threshold. 6MWT = Six Minute Walk Test. ABC = Activities and Balance Confidence scale. RMI = Rivermead Mobility Index. TUAG = Timed Up And Go. ISWT = Incremental Shuttle Walk Test.
Notes: *Derived from t‐test. ˜Derived from Mann‐Whitney U test or Chi2 test. ^Katz scale is an ordinal scale of functional capacity; data in this study collapsed into binary outcome of presence of moderate to severe dependency and reported as numerical data. a+cData reported as median (interquartile range) or % due to small sample size and numerical data. bNo numerical data available; lead study author contacted for raw data but no response; P value derived from repeated measures analysis of variance group‐by‐time interaction effect (premorbid, 8 weeks, 6 months), as reported in published dataset.
3. Review of health‐related quality of life findings.
| Study | Quality of life measure | Rehabilitation group | Control group | Difference in mean | 95% CI | P value | ||
| n | Mean (SD) | n | Mean (SD) | |||||
| Batterham 2014 | EQ‐5D 9 weeks |
18 | 0.7 (0.2) | 23 | 0.684 (0.2) | 0.016 | ‐0.104 to 0.137 | 0.8* |
| EQ‐5D 26 weeks |
21 | 0.669 (0.2) | 25 | 0.712 (0.2) | ‐0.043 | ‐0.174 to 0.088 | 0.5* | |
| EQ‐5D VAS 9 weeks |
18 | 70.1 (13.6) | 22 | 70.3 (13.6) | ‐0.2 | ‐8.7 to 8.3 | 1.0* | |
| EQ‐5D VAS 26 weeks |
20 | 70.0 (18.2) | 24 | 74.1 (18.2) | ‐4.1 | ‐14.9 to 6.7 | 0.5* | |
| Elliott 2011 | SF‐36 PCS (change from baseline to 8 weeks) |
85 | 8.6 (9.3) | 88 | 9.9 (10.9) | ‐1.3 | ‐4.3 to 1.7 | 0.4* |
| SF‐36 PCS (change from baseline to 26 weeks) |
76 | 10.9 (11.8) | 85 | 10.6 (10.2) | 0.3 | ‐3.2 to 3.7 | 0.9* | |
| SF‐36 MCS (change from baseline to 8 weeks) |
85 | 9.7 (15.3) | 88 | 7.8 (14.4) | 1.8 | ‐2.6 to 6.2 | 0.4* | |
| SF‐36 MCS (change from baseline to 26 weeks) |
76 | 9.6 (15.3) | 85 | 8.1 (14.3) | 1.5 | ‐3.1 to 6.2 | 0.5* | |
| Jackson 2012 | Not assessed | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Jones 2003 | Not assessed | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Porta 2005 | Not assessed | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Salisbury 2010 | Not assessed | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
Abbreviations: EQ‐5D = EuroQol 5‐domain. VAS = visual analogue scale. SF‐36 PCS/MCS = Short Form 36 questionnaire Physical Component Score/Mental Component Score. *derived from t‐test.
4. Review of secondary outcome measure findings.
| Study | Rehabilitation group | Control group | Risk ratio | 95% CI | P value |
| n/N (%) | n/N (%) | ||||
| Withdrawals | |||||
| Batterham 2014 | 8/29 (27.6) | 5/30 (16.7) | 1.7 | 0.6 to 4.5 | 0.3 |
| Elliott 2011 | 8/97 (8.2) | 8/98 (8.2) | 1.0 | 0.4 to 2.6 | 1.0 |
| Jackson 2012 | 3/13 (23.1) | 0/8 (0) | 4.5 | 0.3 to 77.2 | 0.3 |
| Jones 2003 | Not reported | Not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Porta 2005 | 7/32 (21.9) | 9/34 (26.5) | 0.8 | 0.3 to 2.0 | 0.7 |
| Salisbury 2010 | Not reported | Not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Adherence | |||||
| Batterham 2014 | Mean = 12 (out of 16 supervised sessions) Mean = 6 (out of 8 unsupervised sessions) |
n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Elliott 2011 | Not reported | n/a | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Jackson 2012 | Not reported | n/a | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Jones 2003 | Not reported | n/a | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Porta 2005 | Not reported | n/a | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Salisbury 2010 | Not reported | n/a | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Mortality | |||||
| Batterham 2014 | 0/29 (0) | 0/30 (0) | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Elliott 2011 | 8/97 (8.2) | 3/98 (3.1) | 2.7 | 0.7 to 9.9 | 0.1 |
| Jackson 2012 | 1/13 (7.7) | 0/8 (0) | 1.9 | 0.09 to 42.3 | 0.7 |
| Jones 2003 | 5/69 (7.2) | 5/57 (8.8) | 0.8 | 0.3 to 2.7 | 0.8 |
| Porta 2005 | 0/32 (0) | 0/34 (0) | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Salisbury 2010 | 2/8 (25) | 1/8 (12.5) | 2.0 | 0.2 to 17.9 | 0.5 |
| Loss to follow‐up | |||||
| Batterham 2014 | 3/29 (10.3) | 1/30 (3.3) | 3.1 | 0.3 to 28.1 | 0.3 |
| Elliott 2011 | 5/97 (5.2) | 2/98 (2.0) | 2.5 | 0.5 to 12.7 | 0.3 |
| Jackson 2012 | 0/13 (0) | 0/8 (0) | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Jones 2003 | 6/69 (8.7) | 8/57 (14.0) | 0.6 | 0.2 to 1.7 | 0.3 |
| Porta 2005 | 0/32 (0) | 0/34 (0) | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Salisbury 2010 | 1/8 (12.5) | 1/8 (12.5) | 1.0 | 0.07 to 13.4 | 1.0 |
| Other adverse events | |||||
| Batterham 2014 | 0/29 (0) | 0/30 (0) | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Elliott 2011 | 0/97 (0) | 0/98 (0) | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Jackson 2012 | 1/13 (7.7) | 0/8 (0) | 1.9 | 0.09 to 42.3 | 0.7 |
| Jones 2003 | 0/69 (0) | 0/57 (0) | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Porta 2005 | Not reported | Not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Salisbury 2010 | Not reported | Not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
N/A = not applicable.
If further trials with greater consistency regarding data reporting are identified in the future, we will endeavour to calculate pooled estimates of differences using appropriate analyses.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
To explore potential heterogeneity, we planned subgroup analyses based on exercise type, intervention duration and frequency, age‐related variation or duration of the acute phase of critical illness. However, studies were insufficient for review authors to perform these analyses.
Sensitivity analysis
We planned to perform sensitivity analysis to determine whether level of risk of bias affected the estimate of effect; however, studies were insufficient for review authors to do this.
'Summary of findings' table
We assessed the quality of the total body of evidence associated with our primary and secondary outcomes using the GRADE (Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach (Guyatt 2008) and reported this in Table 1. The GRADE approach appraises the quality of a body of evidence according to the extent to which one can be confident that an estimate of effect or association reflects the object being assessed. Assessment of the quality of the evidence considers within‐study risk of bias (methodological quality), directness of the evidence, heterogeneity of data, precision of effect estimates and risk of publication bias. As we conducted a systematic review but determined that a meta‐analysis was not appropriate because study numbers and data were limited, our appraisal is restricted (Guyatt 2008), and applied ratings are more subjective in nature.
In the future, if further trials with data that permit analysis of pooled estimates of effect and assessment of heterogeneity are identified, we will be able to construct a more robust 'Summary of findings' table with GRADE levels applied to incorporate results of these quantitative analyses.
Results
Description of studies
Studies included were RCTs of exercise rehabilitation interventions initiated after ICU discharge for adult survivors of critical illness who had been mechanically ventilated for at least 24 hours.
Results of the search
Searches of electronic databases and additional sources revealed a total of 3942 and 17 citations, respectively, totaling 3992 records. Two review authors (BC, BO’N) reviewed these records and identified 22 records for possible inclusion. We then retrieved full‐text publications for these citations. We presented in Figure 1 our flow diagram detailing study screening and selection.
1.
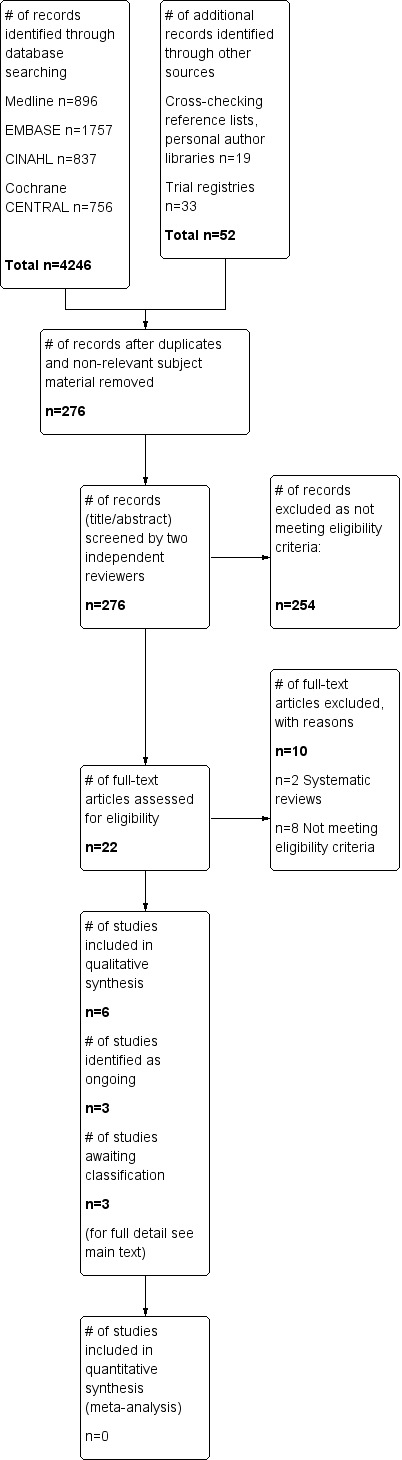
Study flow diagram.
Rerunning the search (15 May 2014 to 18 February 2015) yielded 306 citations. We will deal with studies of interest when we update the review.
Included studies
We included in this review six trials (five RCTs and one minimized controlled trial) conducted on 483 adult survivors of critical illness who had received mechanical ventilation for at least 24 hours (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Jackson 2012; Jones 2003; Porta 2005; Salisbury 2010). Intervention groups received structured or taught exercise programmes of any duration initiated at any time point after ICU discharge, excluding respiratory or inspiratory muscle training. Control groups received any other intervention or ‘usual care’.
Participants and settings
We reported full participant details in the Characteristics of included studies section. All studies reported eligibility criteria, which centred on duration of ventilatory support and length of ICU stay, functional ability status and, in those studies involving an outpatient hospital‐based intervention, residential location that permitted travel to the study site, albeit individual study variation was noted in the specific details of these eligibility criteria. Exclusion criteria were generally related to medical preclusions to undertaking exercise and absence of existing rehabilitation pathways in place. All participants were recruited from ICUs in both teaching and district hospitals.
Individual study sample size ranged from 16 (Salisbury 2010) to 195 (Elliott 2011). In three studies, researchers specified a minimum age of 18 years as an eligibility criterion (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Jackson 2012), and in one study, investigators detailed a maximum age of 65 years (Batterham 2014). In the remaining three studies (Jones 2003; Porta 2005; Salisbury 2010), age was not an inclusion criterion but was reported in the baseline characteristics of groups; all participants were older than 18 years of age.
Baseline characteristics were generally similar in intervention and control groups. Only two studies reported differences between groups (Jackson 2012; Salisbury 2010). The control group in the study by Jackson 2012 had higher levels of illness severity with a greater number of medical co‐morbidities and longer ICU length of stay and duration of mechanical ventilation than individuals in the intervention group. Whilst these differences were not statistically significant, they were acknowledged as potentially clinically relevant. Salisbury 2010 reported that older patients receiving the intervention had greater illness severity, greater duration of mechanical ventilation and longer ICU and ward lengths of stay than those in the control group. Whether these differences were statistically significant was not stated, although reporting of statistically significant differences between control and intervention groups is not methodologically required in RCTs.
Trials were conducted in the UK (Batterham 2014; Jones 2003; Salisbury 2010), Australia (Elliott 2011), the USA (Jackson 2012) and Italy (Porta 2005).
Interventions
We summarized interventions reported in included studies in the Characteristics of included studies and in Table 2. Study authors evaluated a range of interventions that varied according to timing of delivery, structure of the programme and frequency, intensity, timing and type of exercise prescription. Interventions were delivered primarily by specialist exercise personnel (e.g. physiotherapists, exercise trainers). Three studies involved interventions delivered post ICU while patients were still in‐hospital (i.e. based in high‐dependency units and hospital wards) (Jones 2003; Porta 2005; Salisbury 2010), one of which continued after hospital discharge (Jones 2003). Interventions in the remaining three studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Jackson 2012) were commenced after hospital discharge. Three studies incorporated in their programmes use of rehabilitation manuals and self directed components (Elliott 2011; Jackson 2012; Jones 2003).
Control group
Control group participants in all included studies were documented as undergoing standard practice operation for post critical illness at their respective institutions, with research study‐specific assessments surplus to this. The exact descriptions provided in study publications of what constituted usual or standard care are presented in the Characteristics of included studies tables. Only Salisbury 2010 reported objective quantifiable data on frequency and types of services provided to control group participants, and these were analysed in comparison with those given to intervention group participants. Jackson 2012 acknowledged that the exact quantity of post ICU outpatient rehabilitation provided to control group participants was difficult to assess because data for more than half of participants were missing.
Outcomes
All included studies reported data for outcomes related to functional exercise capacity, albeit variability was observed in outcome measures selected for assessment. Both subjective (self reported) and objective measures were used in all studies, with the exception of Jones 2003, for which only a subjective measure was employed. The most common subjective measure, which was used in three studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Jones 2003), was the Physical Function domain of the SF‐36 health‐related quality of life questionnaire (SF‐36 PF). In other studies, investigators used the Activities and Balance Confidence (Powell 1995) and Katz (Katz 1963) scales (Jackson 2012), a Borg (Borg 1992) scale for perceived muscle fatigue (Porta 2005) and the Rivermead Mobility Index (Collen 1991; Salisbury 2010).
Objective functional exercise capacity was measured by using a combination of clinical field tests — Six Minute Walk Test (6MWT) (Elliott 2011), Timed Up And Go (Jackson 2012; Salisbury 2010) and Incremental Shuttle Walk Test, 10 metre Timed Walk Test and handgrip dynamometry (Salisbury 2010) — and physiological cardiopulmonary exercise tests — anaerobic threshold using lower limb cycle ergometry (Batterham 2014) and incremental and endurance exercise testing from arm cycle ergometry (Porta 2005).
Only two studies examined health‐related quality of life. Batterham 2014 reported data from the EuroQol 5 Domain scale (EuroQol‐5D), and Elliott 2011 used Physical (PCS) and Mental (MCS) Component Scores of the SF‐36 questionnaire.
Three studies reported primary outcomes (Batterham 2014, anaerobic threshold and SF‐36; Elliott 2011, SF‐36 PF; and Jackson 2012, Timed Up And Go). Two studies (Jones 2003; Porta 2005) did not specify which of the reported outcomes was the primary outcome, and Salisbury 2010 did not identify a primary outcome because of the feasibility nature of the study design.
All included studies reported data for dichotomous secondary outcomes such as mortality, loss to follow‐up and attrition. Four studies reported withdrawals (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Jackson 2012; Porta 2005), and four described adverse events (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Jackson 2012; Jones 2003). Only one study objectively reported adherence to the intervention (Batterham 2014). Jones 2003 included a subjective comment regarding intervention adherence, although this was not quantifiable.
Excluded studies
We excluded 10 studies. These comprised two systematic reviews, for which cross‐checking of reference lists revealed no further relevant studies (Calvo‐Ayala 2013; Mehlhorn 2013), and eight studies not meeting eligibility criteria related to the intervention (Brummel 2014; Chen 2011; Chen 2012; Cuthbertson 2009; Denehy 2013; Nava 1998), the study design (Mah 2013) and the population (Paratz 2012). We presented the details in the Characteristics of excluded studies section.
Ongoing studies
We identified three studies as ongoing (Battle 2013; McWilliams 2013; O'Neill 2014), and confirmed trial status through direct contact with lead authors. We presented in the Characteristics of ongoing studies section details of participants, interventions, control groups and outcomes for these trials.
Studies pending classification
Three studies (Connolly 2015; Jones 2015; Walsh 2015) are awaiting classification (see Characteristics of studies awaiting classification). We will deal with these studies of interest when we update the review.
Risk of bias in included studies
We assessed risk of bias using the domain‐based evaluation of risk of bias tool of The Cochrane Collaboration (Higgins 2011). We identified low or unclear risk across most of the six domains for the majority of included studies. We presented our judgement on the classification of bias for individual studies in the Characteristics of included studies section, as well as a summary in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
2.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
3.
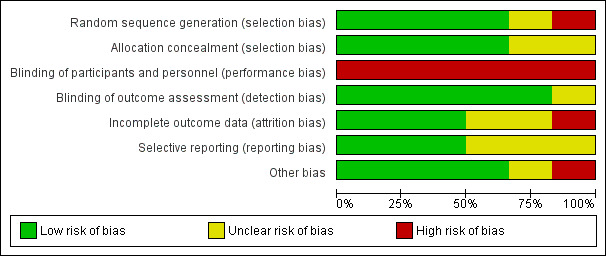
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
Allocation
Four studies demonstrated adequate random sequence generation and allocation concealment (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Porta 2005; Salisbury 2010). Jones 2003 demonstrated unclear risk of bias for both of these domains, and Jackson 2012 presented high risk of bias for random sequence generation.
Blinding
All six included studies demonstrated high risk of performance bias related to blinding of participants and trial personnel. However, all included subjective self reported measures for the primary outcome of functional capacity. Outcome assessors were blinded to intervention assignment in all but one study, in which the outcome assessor was reported as independent of study involvement but was not explicitly reported as blinded (Porta 2005).
Incomplete outcome data
We judged three studies to have low risk of bias for incomplete outcome reporting (Elliott 2011; Jones 2003; Salisbury 2010). Risk of bias was unclear for two studies for which data were missing and the degree of imputation was difficult to assess (and was not reported clearly in the trial flow diagram) (Batterham 2014), and for which the approach to statistical analysis (intention‐to‐treat (ITT) for all randomly assigned, or per‐protocol for all completed) was not clear from the results (Porta 2005). We excluded from analyses participants with missing data and noted a high withdrawal rate for the intervention group in the study conducted by Jackson 2012, which led to high risk of bias.
Selective reporting
Risk of selective reporting bias was low in three included studies (Batterham 2014; Jackson 2012; Salisbury 2010) and was unclear in another three included studies (Elliott 2011; Jones 2003; Porta 2005). Lack of clarity in reporting of all secondary outcomes and absence of trial registration and/or trial protocol to confirm reporting of all intended outcomes led to the unclear judgement.
Other potential sources of bias
Other potential sources of bias were not identified in three studies (Elliott 2011; Porta 2005; Salisbury 2010). In one study (Batterham 2014), potential bias was judged as unclear for outcomes related to imbalance in sample size between groups, and as high in another study (Jackson 2012) because of differences in baseline characteristics between groups that could have influenced results.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1
Primary analysis: comparison of exercise rehabilitation versus control
Primary outcome 1: functional exercise capacity
Data availability and outcome reporting
All six studies reported the primary outcome of functional exercise capacity. We summarized the data in Table 3. We obtained all data from published literature and contacted the lead authors of two studies to request raw data to facilitate further analysis (Jones 2003; Salisbury 2010). No additional data were provided by Jones 2003, so review authors could report in Table 3 only minimal data obtained through data extraction. Salisbury 2010 provided additional data. However, sample sizes were too small for their outcomes of functional exercise capacity (ranging between four and six in the control group or the intervention group) to facilitate conversion of non‐parametric median (IQR) data to parametric means (SD). However, by using the raw data, we were able to calculate P values for differences between control and intervention groups. Insufficient sample size was evident for the study reported by Jackson 2012 (control and intervention groups ranging between seven and eight participants), although results of statistical testing were published. For these two studies (Jackson 2012; Salisbury 2010), we reported median (IQR) data in Table 3. For all remaining studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Porta 2005), we reported mean values (SD), differences in the mean, 95% CIs and P values.
Data on findings of functional exercise capacity were individually variably characterized with regard to types and details of outcome measures and timing and nature of data acquisition (see Table 3). For example, Batterham 2014 reported between‐group differences in the SF‐36 PF domain at nine weeks and at 26 weeks. In contrast, Elliott 2011 reported between‐group differences for changes in the SF‐36 PF domain from baseline to weeks eight and 26. Objective exercise testing employed by these studies also differed, namely, cardiopulmonary exercise testing measuring anaerobic threshold (Batterham 2014) and 6MWT (Elliott 2011). Furthermore, the 'baseline' time point for Batterham 2014 was up to 16 weeks post hospital discharge, whereas for Elliott 2011, baseline data were collected at one week post hospital discharge.
Whilst Jones 2003 also employed the SF‐36 PF domain as the outcome measure for functional exercise capacity, researchers provided minimal data. Furthermore, Porta 2005 assessed cardiopulmonary exercise testing but used different methods and different parameters, with an unspecified time frame, and reported a mix of absolute between‐group differences and between‐group differences in changing variables. Both Jackson 2012 and Salisbury 2010 reported on a battery of clinical functional exercise capacity measures.
As a result of this diversity in functional exercise capacity reporting, we presented data for each outcome according to reporting by investigators in each included study (see Table 3). We made no post hoc decisions to influence presentation or analysis of data. We reviewed the data to determine a pooled value for the effect of the intervention on functional exercise capacity, and to assess for degree of heterogeneity. However, only two studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011) provided data with the potential for pooling (SF‐36 PF). On further inspection with the review statistician (AD), we confirmed that for this small sample, pooling of data and assessment of heterogeneity would not be appropriate.
For a summary of findings, see Table 1. The GRADE quality of evidence was very low.
Individual study findings
Batterham 2014 demonstrated a small benefit for anaerobic threshold at nine weeks among intervention versus control participants (MD 1.8 mL O2/kg/min, 95% CI 0.4 to 3.2; P value = 0.02), although this was not sustained at the 26‐week follow‐up point. However, researchers found no differences between groups for self reported physical function (SF‐36 PF) at either time point. Likewise, Elliott 2011 observed no significant effects of their intervention on both objective and subjective measures. Changes in 6MWT distance were 80 m and 89 m at eight weeks, and 116 m and 126 m at 26 weeks, for control and intervention groups, respectively, and changes in SF‐36 PF were 12 points and 13 points at eight weeks, and 14 points and 15 points at 26 weeks. Results for SF‐36 PF, whilst non‐statistically significant, were noted to represent clinically important improvement in both groups.
No significant differences between groups were found for the Activities and Balance Confidence scale, the Katz scale and Timed Up And Go at three‐month follow‐up (Jackson 2012). At a similar time point, Salisbury 2010 reported non‐significant differences between groups across their range of outcomes (Rivermead Mobility Index, Timed Up And Go, 10 m Walk Test, Incremental Shuttle Walk Test, improvement in handgrip strength). In contrast, Jones 2003 reported significant improvement (P value = 0.006) in subjective physical function (SF‐36 PF domain) at both time points assessed by investigators, but lack of raw data made further interpretation difficult. Data graphically presented suggest a similar, albeit lower‐level, trajectory of recovery for participants in the control group. Finally, Porta 2005 reported significant improvement in both incremental (MD 4.7, 95% CI 1.69 to 7.75 watts; P value = 0.003) and endurance (MD 4.12, 95% CI 0.68 to 7.56 minutes; P value = 0.021) exercise testing among participants receiving the intervention.
Primary outcome 2: health‐related quality of life
Data availability and outcome reporting
Investigators assessed health‐related quality of life in only two studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011). Data are summarized in Table 4. We obtained all data from published literature and reported all as means (SD), differences in the mean, 95% CIs and P values. These studies employed different measures of health‐related quality of life, at different time points, and reported different types of data. Batterham 2014 reported between‐group differences in the EuroQol‐5D and the EuroQol‐5D visual analogue scale at nine weeks and at 26 weeks. In contrast, Elliott 2011 reported changes in SF‐36 PCS and MCS from baseline to weeks eight and 26.
As a result of this diversity in health‐related quality of life reporting, we presented data for each outcome according to how they were presented in each included study (see Table 3). We made no post hoc decisions to influence presentation or analysis of data. After discussion with the review statistician (AD), we concluded that it would not be appropriate to pool these limited data and to assess study heterogeneity.
For a summary of findings, see Table 1. The GRADE quality of evidence was very low.
Individual study findings
Neither Batterham 2014 nor Elliott 2011 demonstrated statistically significant differences between control and intervention groups for health‐related quality of life following delivery of an exercise‐based intervention (Table 4).
Review authors addressed diversity in functional exercise capacity reporting by presenting data for each outcome according to how they were presented in each included study (see Table 3). We made no post hoc decisions to influence presentation or analysis of data. We reviewed the data to determine a pooled value for effects of the intervention on functional exercise capacity, and to assess the degree of heterogeneity. However, only two studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011) provided data with the potential for pooling (SF‐36 PF). On further inspection with the review statistician (AD), we confirmed that given this small sample, it would not be appropriate to pool these data and to assess heterogeneity.
Secondary outcomes
Secondary outcomes included withdrawal (defined as participant withdrawal following random assignment before, or during, receipt of the intervention for consent or medical reasons), adherence (defined as participant completion of the intervention as described in the trial method), mortality (defined as death at any point during the trial duration), loss to follow‐up (defined as non‐completion of outcome measures due to non‐attendance or for other reasons as reported) and adverse events (non‐mortality). We presented data for these outcomes in Table 5. We obtained all data from published literature. We found no studies that reported their own statistical analysis of differences between groups for secondary outcomes, and we learned that numerical data were reported for differing numbers of outcomes in each study (Table 5). When we entered and analysed data in RevMan (RevMan 5.3), we found no significant differences in risk ratios between groups across all secondary outcomes. For many secondary outcomes across all included studies, rates were zero for both control and intervention groups.
For a summary of findings, see Table 1.
Secondary outcome 1: withdrawals
In the study by Batterham 2014, all withdrawals occurred before the start of the intervention, with no causal reason specified, whereas participant withdrawals were reported at each assessment point in the study by Elliott 2011 (intervention vs control; baseline, n = 3 vs n = 6; week eight, n = 3 vs n = 0; week 26, n = 2 vs n = 2). All withdrawals occurred in the intervention group in the study by Jackson 2012 following intervention allocation. Documented reasons for these withdrawals included participant‐reported inconvenience of participation, participant‐reported personal circumstances and significant medical issues necessitating rehospitalization. Porta 2005 reported that their "drop‐outs" could be patients who prematurely failed to complete the intervention programme because of clinical worsening or for whom for any reason final assessment was lacking. Ultimately, all reported withdrawals occurred for medical reasons.
The GRADE quality of evidence was low (Table 1).
Secondary outcome 2: adherence
Intervention adherence did not apply to control participants in any study, and only Batterham 2014 made some reference to adherence rates in their intervention group, although they reported mean values only.
The GRADE quality of evidence was very low (Table 1).
Secondary outcome 3: mortality
No deaths occurred in two studies (Batterham 2014; Porta 2005). Both Elliott 2011 and Jones 2003 reported mortality across each of their assessment points (intervention vs control; Elliott 2011, baseline, n = 1 vs n = 1; week eight, n = 2 vs n = 2; week 26, n = 5 vs n = 0; Jones 2003, week 8, n = 2 vs n = 3; 6 months, n = 3 vs n = 2). Only one death was reported in the control group of Jackson 2012 (overall mortality rate = 4.8%), and the study by Salisbury 2010 reported three deaths (overall mortality rate = 18.8%).
The GRADE quality of evidence was low (Table 1).
Secondary outcome 4: loss to follow‐up
Two studies reported no loss to follow‐up (Jackson 2012; Porta 2005). In the remaining four studies, loss to follow‐up in intervention or control groups ranged from 2.0% (Elliott 2011) to 14.0% (Jones 2003). Reasons for loss to follow‐up included medical reasons, return to work and ‘did not attend’ (Batterham 2014). Salisbury 2010 did not classify one loss to follow‐up, and the second was attributable to medical status at the time of assessment. Elliott 2011 and Jones 2003 did not report reasons for loss to follow‐up.
The GRADE quality of evidence was low (Table 1).
Secondary outcome 5: adverse events (non‐mortality)
Non‐mortality adverse events were minimal. Only one study reported occurrence of a single adverse event (Jackson 2012; a minor musculoskeletal injury sustained by a participant in the intervention group, which did not require formal medical attention and did not preclude further participation).
The GRADE quality of evidence was low (Table 1).
Discussion
A systematic review of the literature revealed six completed and fully published trials that were eligible for inclusion in the current review (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Jackson 2012; Jones 2003; Porta 2005; Salisbury 2010). Another six studies identified in the search were pending trials, and relevant information was reported for these (Battle 2013; Connolly 2015; Jones 2015; McWilliams 2013; O'Neill 2014; Walsh 2015). These search results indicate that the evidence base for exercise rehabilitation initiated after ICU discharge is growing. We were unable to perform a meta‐analysis of findings to determine the overall effect of the intervention and the degree of heterogeneity across studies, as this analysis was inappropriate because only a small number of studies provided similar data for pooling. Hence the description of findings was qualitative only. Consequently, authors of the current review were not able to determine the effects of exercise rehabilitation on functional exercise capacity and on health‐related quality of life among survivors of critical illness after ICU discharge. Non‐significant differences between intervention and control groups across several studies could be due to the extent of methodological variation in intervention ‘dose’ and outcomes used for evaluation of effectiveness.
Summary of main results
Most included studies demonstrated non‐significant differences between intervention and control groups, indicating lack of effect of exercise therapy on functional exercise capacity and health‐related quality of life. When a significant difference was reported, this was noted in physiological outcome measures following specific cycling ergometry programmes targeting the lower limbs in an outpatient, post hospital discharge intervention (anaerobic threshold during exercise, Batterham 2014), and the upper limbs in an in‐hospital intervention (incremental exercise capacity (watts), endurance exercise capacity (time), Porta 2005). These findings could be considered attributable to the specificity of the training programme employed and the corresponding outcome measure used to assess for treatment effect, which therefore limits their generalizability to interventions of an alternative nature. Furthermore, the slight improvement reported by Batterham 2014 was not maintained at later follow‐up (week 26) and was not observed in self reported physical function at either time point. Quality of life, measured only in two studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011), was similar between intervention and control groups for short‐ and longer‐term outcomes. Dichotomous secondary outcomes were also similar when reported. Because of the extent of variability in the characteristics of interventions, the range of outcome measures tested and limitations in data availability and sample size, it was not possible for review authors to tabulate a comprehensive summary of the findings.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
Consistency in participant eligibility criteria was evident across studies. These criteria included duration of ICU admission and mechanical ventilation, which is particularly relevant, as it indicates that patients were exposed to factors associated with critical illness muscle wasting. As expected, medical stability for participation in exercise therapy in the absence of clinical (e.g. palliation), logistical (e.g. resident beyond the geographical coverage of the study site for attendance at hospital‐based rehabilitation sessions) and pragmatic (e.g. no existing rehabilitation pathway in place) factors was an additional criterion. However, the inherent heterogeneity of the critical illness population meant that even the application of somewhat ‘standard’ inclusion and exclusion factors may not produce a cohort of patients who behave and respond similarly to interventions and demonstrate a smooth trajectory of recovery.
Furthermore, whilst meta‐analyses of findings were not possible, the results of individual studies lack generalizability because of individual specificity in the timing of delivery, the structure of the programme and the frequency, intensity, timing and type of exercise prescription characterizing the intervention. Exercise interventions ranged from targeted cycle ergometry to composite programmes including strength training, functional activities, balance and cardiovascular exercise. In addition, usual care demonstrated some variability across studies. Limited detail was reported across studies regarding treatment fidelity and the extent to which interventions were delivered as intended throughout the duration of the trial. Only one study (Batterham 2014) reported data on adherence. Hence it is difficult to establish whether non‐significant findings of included studies represent failure of the intervention to cause an effect, or failure of the intervention to be implemented appropriately.
No study included evaluation of acceptance of the treatment by patients or the experience of patient or the experience of patient participation in an exercise‐based intervention. Such qualitative research can provide valuable data for understanding the patient perspective on effectiveness of post critical illness rehabilitation.
The current review was limited to physical rehabilitation interventions that commenced following ICU discharge. In the future however, inclusion of interventions delivered across the patient pathway would better characterize the approach to physical rehabilitation in the context of the recovery trajectory of patients. In addition, this would account for variability in the timing of delivery of the intervention, patient location and illness acuity according to the definitions by which 'critical care' environments are classified by different international healthcare systems.
Quality of the evidence
Methodological quality of the evidence was inconsistent when evaluated by review authors using the risk of bias tool of The Cochrane Collaboration (Higgins 2011). For most domains, evidence of low risk of bias ranged from 50% to 75%, although one study was judged to have high risk of bias for random sequence generation, incomplete outcome data and other sources of bias. Furthermore, all included studies demonstrated high risk of bias for blinding of participants and trial personnel. Whilst it is acknowledged that blinding of a physical rehabilitation intervention can be feasibly challenging with regards to clinicians delivering the actual treatment, concealment of participant assignment could be possible if naivete on the part of participants is assumed with regards to what constitutes usual care for rehabilitation practice. When participants are aware of their group allocation, consideration of this is important in the interpretation of findings from self reported outcome measures. Blinding of outcome assessors was judged to confer low risk in five of the six studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Jackson 2012; Jones 2003; Salisbury 2010) and unclear risk in the only remaining study (Porta 2005).
Sample sizes ranged from 16 (Salisbury 2010) to 195 (Elliott 2011) randomly assigned participants. The study with the smallest sample size (n = 16, Salisbury 2010) exhibited the greatest methodological quality, which could be a result of the pilot, feasibility element of this trial, with attention paid to all aspects of trial conduct for purposes of evaluation.
Notably several studies reporting non‐significant differences between control and intervention groups following exercise‐based intervention failed to meet intended sample sizes (Elliott 2011, n = 195 recruited from n = 200 required) or were intended as pilot feasibility trials, which did not require power calculations and for which data were acquired with the aim of informing a future, larger‐scale trial (Batterham 2014; Jackson 2012; Salisbury 2010). Hence these findings could be attributable to type II error and could be a function of a reduced sample size that was inadequate to demonstrate a treatment effect. Furthermore, examination of screening and enrolment rates in included studies highlights the challenges associated with recruitment into post critical illness rehabilitation trials. Batterham 2014 recruited 59 participants from a cohort of 740 screened. Elliott 2011 achieved a successful randomization rate of approximately one participant for every 30 screened (n = 195 recruited, n = 5980 screened). These findings are echoed in similar trials by Denehy 2013 (n = 150 participants randomly assigned from n = 764 screened) and Connolly 2015 (n = 20 randomly assigned from n = 763 screened).
In addition, studies differed as to whether investigators reported findings of a comparison of the change from baseline in outcome measures between groups, or of differences between groups at the time point of assessment. This variability in outcome reporting further limits comparison across studies. Likewise, use of multiple outcomes in all studies is associated with the potential for type I error, thus further decreasing the likelihood of detecting the true effects of interventions.
Limitations in study number and data and discussion with the review statistician (AD) precluded a quantitative meta‐analysis of findings, which was deemed by review authors to be inappropriate, and we conducted a systematic review only. This, in turn, influenced the robustness by which we were able to use the GRADE approach (Guyatt 2008) to assess the quality of the overall body of evidence for each primary and secondary outcome. Hence the GRADE levels reported in our 'Summary of findings' table (Table 1) require interpretation with caution because of the more subjective nature of their rating assignment. For the primary outcomes of functional exercise capacity and health‐related quality of life, the overall quality of the evidence was very low. For secondary outcomes, the quality of the evidence was as follows: withdrawals — low, adherence — very low, mortality — low, loss to follow‐up — low, other non‐mortality adverse events — low.
Potential biases in the review process
Several processes minimized bias in the conduct of this review, including independent screening for trial inclusion, data extraction and assessment of risk of bias involving four of the review authors. Furthermore data entry was double‐checked. Following adoption of the protocol by an updated review authorship group, we engaged the assistance of the Cochrane Anaesthesia, Critical and Emergency Care Review Group Search Trials Co‐ordinator to resolve queries noted with the proposed search strategies detailed in the original protocol, and to conduct thorough and rigorous searches of the electronic databases identified. In an update of the original protocol, we searched international clinical trial registries and the personal libraries of review authors to maximize relevant search results, further clarified the definition of eligible participants to ensure accuracy of included studies and expanded and clarified dichotomous secondary outcomes. This latter point was particularly important, as it related to interpretation of different aspects of trial conduct in included studies. We acknowledge that we did not search sources of grey literature, and this could have contributed to the results, although we believe our comprehensive search identified all relevant studies available at the time. However, because of insufficient numbers of included studies with data to permit pooling, we were unable to perform quantitative synthesis of findings, as a meta‐analysis was not appropriate; this in turn influenced our overall rating of evidence quality according to GRADE (Guyatt 2008) presented in our 'Summary of findings' table (Table 1).
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
To our knowledge, this is the first published systematic review of exercise rehabilitation in survivors of critical illness initiated after ICU discharge. Qualitative descriptive findings regarding variability in intervention structure, format, type, content and timing, and selection of outcome measures used for evaluation mirror those reported in a previous integrative review (Connolly 2012).
Findings from this review were consistent with those described in a recently published, large RCT of a three‐stage exercise‐based rehabilitation intervention that spanned the patient pathway, commencing in the ICU, and continuing after ward transfer and post hospital discharge (Denehy 2013). Specifically, the post hospital discharge stage involved a structured, 16‐session, outpatient, hospital‐based programme involving cardiovascular, strength, functional and balance exercises individually tailored and progressed according to patient ability. For the primary outcome of 6MWT at 12 months post ICU discharge, review authors reported no significant differences between groups (usual care vs intervention, mean (standard error) 404.9 (23.0) vs 409.6 (22.9) m; MD 4.7, 95% CI ‐59.7 to 69.2; P value = 0.884), although rate of recovery in the short term up to three months was greater in the intervention arm (Denehy 2013). Connolly 2015 adopted an intervention similar to the post hospital discharge intervention investigated by Denehy 2013, and found no differences between groups for a range of physical, clinical, physiological and health‐related quality of life outcomes, although this study was designed as a pilot feasibility evaluation and was not powered to detect statistical differences. Published data in abstract form from pending trials show contrasting findings. Both McWilliams 2013 and Battle 2013 reported some differences as a result of post hospital discharge interventions. Improvement in health‐related quality of life (SF‐36 PCS, usual care vs intervention group, 4.1 vs 8.0 points, P value = 0.048; MCS 4.0 vs 10.6 points; P value = 0.017), but not in exercise capacity (anaerobic threshold, usual vs intervention, 16.2 vs 13.9%; P value = 0.74; peak oxygen consumption, 15.3 vs 17.7%; P value = 0.68) was observed after a seven‐week exercise programme (McWilliams 2013). In contrast, Battle 2013 reported that a six‐week exercise programme resulted in significantly greater improvement in cardiopulmonary fitness (Six Minute Walk Test, P value < 0.001) and balance (P value < 0.05), and numerically but not statistically significant greater improvements in anxiety, depression and handgrip strength in intervention versus control groups. However, the limited detail reported in abstracts requires that these results should be interpreted with caution in comparison with results of fully published trials. In addition three studies were identified as awaiting classification (Connolly 2015; Jones 2015; Walsh 2015) and will be dealt with when the review is updated. Data from these studies will further inform our understanding of the effect of post ICU rehabilitation interventions.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Authors of this systematic review were unable to determine the average effect of exercise‐based rehabilitation interventions initiated after ICU discharge on functional exercise capacity or health‐related quality of life among survivors of critical illness. Variation between characteristics of the studies prevented us from combining data. Among individual studies examined to date, effectiveness has been shown only in trials of specific exercise training involving cycle ergometry using physiological cardiopulmonary outcome measures, although our assessment indicates that the quality of evidence on functional outcomes overall is very low. Two small studies have provided very low‐quality evidence on the effects of interventions on health‐related quality of life. This area of practice remains highly profiled, and extensive observational data on recovery post intensive care highlight the clinical need to provide rehabilitation services for this patient population. Data from currently ongoing trials published in the future will contribute to the evidence base and will allow further examination of this topic in a subsequently updated review, at which point a more robust conclusion may be made.
Implications for research.
The relatively small number of trials included in the current review, of considerable variability on numerous levels including sample size and nature of the intervention, limits the conclusions that can be drawn on the effectiveness of post ICU discharge exercise rehabilitation for survivors of critical illness. At this time, insufficient studies have provided data for pooling and for assessment of heterogeneity for the outcome of functional exercise capacity or health‐related quality of life.
Rehabilitation for post critical illness patients is a complex intervention delivered to an equally complex patient group (MRC 2008). Several considerations in the design, conduct and evaluation of future trials have been identified that may facilitate quantitative evaluation in a subsequent review on this topic. Further research must focus on identifying the target population that would benefit from physical exercise‐based rehabilitation, which will facilitate optimising eligibility and recruitment into trials to ensure that target sample sizes are achieved, and that findings are robust. In addition, the optimum ‘dose’ of intervention must be determined, including frequency, intensity and timing and type of exercise therapy, as well as overall programme duration, structure and timing of delivery. With regard to the latter, data from longitudinal follow‐up studies may reveal the trajectory of recovery in this patient population, with the rationale that rehabilitation should be delivered at a point when the natural recovery trajectory has plateaued. Detailed descriptions of usual or standard care are additionally required in any future trial conducted to determine the true effect of any enhanced intervention (Parker 2013). This would be particularly necessary in multi‐centre studies, in which a range of usual practice approaches may be evident.
Standardisation of outcomes, outcome measures and their associated metrics, used for evaluation of intervention effectiveness, would facilitate comparison across multiple datasets, albeit this would have to be applicable to the recovery stage of patients and representative of the goals of treatment (e.g. interventions delivered during ward‐based care may be directed towards achieving adequate functional status for hospital discharge, whereas interventions delivered following hospital discharge may be targeting achievement of higher‐intensity exercise performance). Outcome measures therefore may represent activities of daily living, functional status, exercise capacity and health‐related quality of life, but also dichotomous outcomes such as those included as secondary outcomes in the current review. Instruments used to capture these data must be validated for the post critical illness population, particularly with regards to responsiveness to change. Development of new tools for this purpose may be a goal of future studies. An understanding of trial withdrawal rates, intervention adherence, loss to follow‐up and outcome measure attrition can lead to accumulation of valuable data on differing aspects of the trial process. Finally, embedding in future trials qualitative evaluation of both patient and carer perspectives will enhance our understanding of how interventions can be optimized to maximize participation from, and effect for, those affected by an experience of critical illness. Ideally these outcomes would be Incorporated into a core set comprising patient‐centred, clinical, mechanistic and healthcare utilisation‐centred measures.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 14 December 2018 | Amended | Editorial team changed to Cochrane Emergency and Critical Care |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 8, 2010 Review first published: Issue 6, 2015
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 9 August 2010 | Amended | Typo in Acknowledgements section corrected |
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Karen Hovhannisyan, Cochrane Search Trials Co‐ordinator, and Jane Cracknell, Managing Editor, Cochrane Anaesthesia, Critical and Emergency Care Review Group(ACE), for assistance provided during this review process. We would also like to thank Anna Lee (content editor); Vibeke E Horstmann (statistical editor); Tom J Overend, Sue Berney and Terri Hough (peer reviewers); and Janet Wale (consumer editor) for help and editorial advice provided during preparation of this systematic review.
BC, AD and NH are supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre based at Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust and King's College London. The views expressed are those of the review author(s) and are not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
The ERACIP (Enhanced Recovery After Critical Illness Programme) Group additionally includes Stephen Brett, David Griffith, Stephen Shepherd, Judith Merriweather, Nazir Lone, Simon Baudouin, Stephen Bonner, Kathryn McDowell, Dorothy Wade, Natalie Pattison, Danielle Bear, Sallie Lamb, Rebecca Cusack, Daniel F McAuley, Robert Hatch, David Parkin, Mark Foster, Laura Price, Liesl Wandrag and Pamela Ramsay.
Appendices
Appendix 1. MEDLINE (Ovid SP) search strategy
1 exp Exercise‐Therapy/ 2 exp Exercise/ 3 exp Physical‐Fitness/ 4 exp Weight‐Lifting/ 5 exp Physical‐Medicine/ 6 exp Physical‐Therapy‐Modalities/ 7 (rehabilitation adj3 (Exercise or Physical)).mp. 8 (Exercise or Physiatrics or Physiatry or Physiotherapy or mobili?ation).ti,ab. 9 Activit*.ti. 10 (movement adj3 (Active or Whole body)).mp. 11 (Exercise adj3 (training* or Progressive or therapy or intervention)).mp. 12 (training adj3 (Aerobic or endurance or Strength or resistance or weight or Fitness or Interval or Circuit)).mp. 13 (Physical therapy).mp. or (Weight lifting).mp. 14 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 15 Critical‐Care/ or exp Critical‐Illness/ 16 Intensive‐Care/ or Intensive‐Care‐Units/ 17 Atrophy/ 18 Ventilator‐Weaning/ 19 Shock‐Septic/ 20 Sepsis/ 21 (care adj3 (Critical or Intensive)).ti,ab. 22 (unit adj3 (Intensive care or High dependency or Intensive therapy or Intensive treatment)).mp. 23 (Critical adj3 (collapse or illness)).mp. 24 ((Critical illness) adj3 (neuropath* or myopath* or polyneuropath* or polyneuromyopathy)).mp. 25 (ICU or HDU or ITU or CIN or CIM or CIPN or CIPNM or ARDS).ti,ab. 26 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25 27 14 and 26 28 ((low back pain) or ((head or brain) adj3 injury) or pregnancy or stroke or (cardiac surg*)).mp. 29 27 not 28 30 CLINICAL‐TRIAL.pt. 31 randomized.ab. 32 placebo.ab. 33 (clinical trials).sh. 34 randomly.ab. 35 trial.ti. 36 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 or 34 or 35 37 (animals not (humans and animals)).sh 38 36 not 37 39 29 and 38
Appendix 2. EMBASE (Ovid SP) search strategy
1 exercise therapy.mp. 2 exercise.mp. 3 physical fitness.mp. 4 Physical Medicine.mp. 5 Weight Lifting.mp. 6 physical therapy modalities.mp. 7 (exercise or physiatrics or physiatry or physiotherapy or mobili*ation).ti. 8 activit*.ti. 9 (physical therapy or weight lifting).mp. 10 (rehabilitation and (exercise or physical)).mp. 11 (movement and (active or whole body)).mp. 12 (exercise and (training* or progressive or therapy or intervention)).mp. 13 (training and (aerobic or endurance or strength or resistance or weight or fitness or interval or circuit)).mp. 14 (1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13).mp. 15 (critical care or critical illness).mp. 16 (intensive care or intensive care units).mp. 17 atrophy.mp. 18 Artificial Ventilation/ 19 Septic Shock.mp. 20 sepsis.mp. 21 (care and (critical or intensive)).ti. 22 (unit and (intensive care or high dependency or intensive therapy or intensive treatment)).mp. 23 (critical and (collapse or illness)).mp. 24 (critical illness and (neuropath* or myopath* or polyneuropath* or polyneuromyopathy)).mp. 25 (ICU or HDU or ITU or CIN or CIM or CIPN or CIPNM or ARDS).mp. 26 (15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25).mp. 27 (14 and 26).mp. 28 (low back pain or ((head or brain) and injury) or pregnancy or stroke or cardiac surg*).mp. 29 (27 not 28).mp. 30 (crossover.mp. or multicenter.ab. or placebo.sh. or ((singl* or doubl* or tripl*) adj3 blind).mp. or controlled study.ab. or random*.ti,ab. or trial*.ti,ab.) not (animals not (humans and animals)).sh. 31 29 and 30
Appendix 3. CENTRAL search strategy
#1 MeSH descriptor Exercise Therapy explode all trees #2 MeSH descriptor Exercise explode all trees #3 MeSH descriptor Physical Fitness explode all trees #4 MeSH descriptor Weight Lifting explode all trees #5 MeSH descriptor Physical Medicine explode all trees #6 MeSH descriptor Physical Therapy Modalities explode all trees #7 (rehabilitation near (Exercise or Physical)) #8 (Exercise or Physiatrics or Physiatry or Physiotherapy or mobili?ation):ti,ab #9 Activit*:ti #10 (movement near (Active or Whole body)) #11 (Exercise near (training* or Progressive or therapy or intervention)) #12 (training near (Aerobic or endurance or Strength or resistance or weight or Fitness or Interval or Circuit)) #13 (Physical therapy) or (Weight lifting) #14 (#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13) #15 MeSH descriptor Critical Care explode all trees #16 MeSH descriptor Critical Illness explode all trees #17 MeSH descriptor Intensive Care explode all trees #18 MeSH descriptor Intensive Care Units explode all trees #19 MeSH descriptor Atrophy explode all trees #20 MeSH descriptor Ventilator Weaning explode all trees #21 MeSH descriptor Shock, Septic explode all trees #22 MeSH descriptor Sepsis explode all trees #23 (care near (Critical or Intensive)):ti,ab #24 (unit near (Intensive care or High dependency or Intensive therapy or Intensive treatment)) #25 (Critical near (collapse or illness)) #26 ((Critical illness) near (neuropath* or myopath* or polyneuropath* or polyneuromyopathy)) #27 (ICU or HDU or ITU or CIN or CIM or CIPN or CIPNM or ARDS):ti,ab #28 (#15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20 OR #21 OR #22 OR #23 OR #24 OR #25 OR #26 OR #27) #29 (#14 AND #28) #30 (low back pain) or ((head or brain) near injury) or pregnancy or stroke or (cardiac surg*) #31 (#29 AND NOT #30)
Appendix 4. CINAHL (EBSCOhost) search strategy
S1 (MH "Therapeutic Exercise+") OR (exercise AND therap*) OR (MH "Exercise+") OR (MH "Physical Fitness+") OR (MH "Weight Lifting") OR (MH "Physical Medicine") OR (MH "Physical Therapy+") OR (rehabilitation N5 (exercise OR physical)) OR AB (exercise OR physiatrics OR physiatry OR physiotherapy OR mobili*ation) OR TI activit* OR (movement AND (active OR "whole body")) OR (exercise AND (training* OR progressive OR therapy OR intervention)) OR (training AND (aerobic OR endurance OR strength OR resistance OR weight OR fitness OR interval OR circuit)) OR (physical therapy OR weight lifting) S2 critical care OR critical illness OR (MM "Intensive Care Units") OR (MH "Atrophy+") OR (MH "Ventilator Weaning") OR (MH "Ventilators, Mechanical") OR (MH "Shock, Septic") OR (MH "Sepsis+") OR (care AND (TI critical OR TI intensive)) OR (unit AND (high dependency OR intensive therapy OR intensive treatment OR intensive care)) OR (critical AND (collapse OR illness)) OR (critical illness AND (neuropath* OR myopath* OR polyneuropath* OR polyneuromyopath*)) OR ICU OR HDU OR ITU OR CIN OR CIM OR CIPN OR CIPNM OR ARDS S3 S1 AND S2 S4 ((MM "Randomized Controlled Trials") OR (MM "Random Assignment") OR (MH "Prospective Studies") OR (MH "Multicenter Studies") OR (MH "Double‐Blind Studies") OR (MH "Single‐Blind Studies") OR (MH "Triple‐Blind Studies") OR (MH "Placebos") ) OR ( random* OR (controlled AND (stud* or trial*)) OR ((blind* or mask*) AND (single or double or triple))) S5 S4 AND S3
Appendix 5. Study selection, quality assessment and data extraction
ACE 172 Exercise rehabilitation for recovery from critical illness
Study selection, quality assessment & data extraction form
| First author | Journal/Conference proceedings, etc | Year |
| |
Study eligibility
| RCT/Quasi/CCT (delete as appropriate) |
Relevant participants Adults ≥ 18 years old ICU/Critical care admission with mechanical ventilation |
Relevant interventions Exercise taught/structured/supervised |
Relevant outcomes Functional exercise capacity Quality of life Withdrawal rates Adherence Mortality Other adverse events |
| Yes/No/Unclear |
Yes/No/Unclear | Yes/No/Unclear | Yes/No*/Unclear |
*Issue relates to selective reporting when study authors may have taken measurements for particular outcomes that were not reported these within the paper(s). Review authors should contact trial lists for information on possible non‐reported outcomes and reasons for exclusion from publication. Study should be listed in ‘Studies awaiting assessment’ until clarified. If no clarification is received after 3 attempts, study should then be excluded.
| Do not proceed if any of the above answers is ‘No’. If study is to be included in ‘Excluded studies’ section of the review, record below the information to be inserted into ‘Table of excluded studies’. |
| |
| Freehand space for comments on study design and treatment: |
References to trial
Check other references identified in searches. If further references to this trial are found, link the papers now and list below. All references to a trial should be linked under one Study ID in RevMan.
| Code each paper | Author(s) | Journal/Conference proceedings, etc | Year |
| A |
The paper listed above |
||
| B |
Further papers |
||
Participants and trial characteristics
| Participant characteristics | |
| Further details | |
| Age (mean, median, range, etc) | |
| Sex of participants (numbers/%, etc) | |
| Disease status/type, etc (if applicable) | |
| Time on mechanical ventilation (mean, median, range, etc) | |
| Other | |
| Trial characteristics | |
| Further details | |
| Single‐centre/Multi‐centre | |
| Country/Countries | |
| How was participant eligibility defined? |
|
| How many people were randomly assigned? | |
| Number of participants in each intervention group | |
| Number of participants who received intended treatment | |
| Number of participants who were analysed | |
| Treatment(s) used | |
| Dose/Frequency of administration | |
| Duration of treatment (State weeks/months, etc; if cross‐over trial, give length of time in each arm) | |
| Median (range) length of follow‐up reported in this paper (state weeks, months or years, or if not stated) | |
| Time points when measurements were taken during the study | |
| Time points reported in the study | |
| Time points you are using in RevMan | |
| Trial design (e.g. parallel/cross‐over*) | |
| Other | |
*If cross‐over design, please refer to the Cochrane Editorial Office for further advice on how to analyse these data.
Methodological quality
| Allocation of intervention | |
| State here method used to generate allocation and reasons for grading | Grade (circle) |
| Note reason for allocation: |
Adequate (random) |
| Inadequate (e.g. alternate) | |
| Unclear | |
|
Concealment of allocation Process used to prevent foreknowledge of group assignment in an RCT, which should be seen as distinct from blinding | |
| State here method used to conceal allocation and reasons for grading | Grade (circle) |
| Note reason for allocation: | Adequate |
| Inadequate | |
| Unclear | |
| Blinding | |
| Person responsible for participant care | Yes/No |
| Participant | Yes/No |
| Outcome assessor | Yes/No |
| Other (please specify) | Yes/No |
|
Intention‐to‐treat An intention‐to‐treat analysis is one in which all participants in a trial are analysed according to the intervention to which they were allocated, whether or not they received it. | |
| All participants entering trial | |
| 20% or less excluded | |
| More than 20% excluded | |
| Not analysed as ‘intention‐to‐treat’ | |
| Unclear | |
Were withdrawals described? Yes? No? Not clear?
Discuss if appropriate.
Data extraction
| Outcomes relevant to your review | |
| Reported in paper (circle) | |
| Outcome 1: Functional capacity (subjective/objective) including 1 or more of VO2max and/or VO2peak Muscle mass and/or morphology Body composition Strength and/or endurance tests Resting HR and/or BP |
Yes/No Specify: |
| Outcome 2: Quality of life | Yes/No |
| Outcome 3: Withdrawal rates | Yes/No |
| Outcome 4: Adherence | Yes/No |
| Outcome 5: Mortality | Yes/No |
| Outcome 6: Other adverse events | Yes/No |
| For continuous data | |||||||
| Code of paper |
Outcomes |
Unit of measurement |
Intervention group | Control group | Details if outcome described only in text | ||
| n | Mean (SD) | N | Mean (SD) | ||||
| A, etc | Functional capacity subjective | ||||||
| Functional capacity objective | |||||||
| Quality of life | |||||||
| VO2max and/or VO2peak | |||||||
| Muscle mass or morphology | |||||||
| Body composition | |||||||
| Strength test | |||||||
| Endurance test | |||||||
| Resting HR | Beats/min | ||||||
| Resting BP | mmHg systole/diastole | ||||||
| For dichotomous data | |||
| Code of paper | Outcomes | Intervention group (n) n = number of participants, not number of events |
Control group (n) n = number of participants, not number of events |
| Withdrawal | |||
| Adherence | |||
| Mortality (i.e. death) | |||
| Adverse events (not death) | |||
|
Other information which you feel is relevant to the results Indicate if any data were obtained from the primary author; if results were estimated from graphs, etc; or if results were calculated by you using a formula (this should be stated and the formula given). In general, if results not reported in paper(s) are obtained, this should be made clear here to be cited in the review. |
| Freehand space for writing actions such as contact with study authors and changes: |
References to other trials
| Did this report include any references to published reports of potentially eligible trials not already identified for this review? | ||
| First author | Journal/Conference | Year of publication |
| Did this report include any references to unpublished data from potentially eligible trials not already identified for this review? If yes, give contact name and details | ||
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Batterham 2014.
| Methods | Multi‐centre, exploratory, parallel‐group, minimized controlled trial Trial dates: Recruitment occurred from June 2008 to November 2010, with final follow‐up data collection completed in May 2011 |
|
| Participants |
Setting: 2 ICUs at 2 large teaching hospitals, North Tyneside, England, UK Inclusion criteria: age 18 to 65 years. Minimum of 3 days of ventilator support (for emergency management of trauma or sepsis), discharged home within 6 months of hospital admission Exclusion criteria: inability to climb a flight of stairs, enrolment in another rehabilitation programme, medical contraindication to cardiopulmonary exercise testing Participant numbers: 59 minimized (M:F 38:21); 30 to the control arm (M:F 19:11) (25 received allocated intervention, 5 withdrawals before start of intervention, 1 loss to follow‐up for physical assessment) and 29 to the intervention arm (M:F 19:10) (21 received allocated intervention, 8 withdrawals before start of intervention, 3 losses to follow‐up for physical assessment) Numbers of participants analysed varied for both follow‐up time points, and for different measures: control group, Anaerobic threshold, week 9 n = 17, week 26 n = 20, Physical function and mental health, week 9 n = 23, week 26 n = 25. Intervention group, Anaerobic threshold week 9 n = 13, week 26 n = 18, Physical function and mental health, week 9 n = 18, week 26 n = 21 |
|
| Interventions |
|
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Funded by national government health research agency (United Kingdom National Institute for Health Research, Research for Patient Benefit Programme) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants were allocated to trial groups (control or intervention) using minimization to balance arms for potentially important a priori determined prognostic factors. Eligible patients were allocated remotely via e‐mail by the trial statistician. Trial personnel in charge of recruitment were unaware of the specific minimization factors adopted to preclude deducing future group assignment. Minimization was performed using Minim software13 with a 1:1 allocation ratio and equal weighting for the 3 minimization factors |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Allocation was concealed from those assessing eligibility and recruiting patients, with eligible patients allocated remotely via e‐mail by the trial statistician |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Neither participants nor trial personnel were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcome assessors were blind to group allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Difficult to assess whether imputation of data was performed as described, and also unclear from CONSORT diagram |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN65176374 (http://www.controlledtrials.com/ISRCTN65176374). Outcomes reported as registered |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Difficult to assess, some imbalance reported between groups for 3 outcomes, although this was a pilot study, hence a small sample size |
Elliott 2011.
| Methods | Multi‐centre, parallel‐group, randomized controlled trial Trial dates: Recruitment occurred from June 2005 to August 2008, with final follow‐up data collection completed in February 2009 |
|
| Participants |
Setting: 12 ICUs (6 teaching hospitals, 5 district hospitals, 1 private hospital) based in Sydney, Brisbane and Perth, Australia Inclusion criteria: age 18 years or older; ICU length of stay at least 48 hours; received mechanical ventilation at least 24 hours; discharged home to self care or carer (non‐institutional care); resided within the hospitals' local geographical areas to enable home visits (an approx 50‐km radius); had no neurological, spinal or skeletal dysfunction preventing participation in physical rehabilitation; not receiving palliative care; no organized rehabilitation related to ongoing chronic disease management (e.g. pulmonary or cardiac rehabilitation); cognitively able to complete self report measures and comply with physical testing instructions Exclusion criteria: not specifically reported Participant numbers: 195 randomly assigned (M:F 123:72); 97 to the intervention group (M:F 62:30) (92 received allocated intervention, 3 withdrawals before start of intervention, 1 loss to follow‐up, 1 death) and 98 to the control group (M:F 61:30) (91 received allocated intervention, 6 withdrawals, 1 death). Number of participants analysed is unclear. An intention‐to‐treat analysis is stated, but no details were reported on management of missing data due to withdrawal, death or other attrition Participants underwent baseline assessment and randomization 1 week post hospital discharge, at which point interventions commenced |
|
| Interventions |
|
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Funded by national government health research agency (Australian National Health and Medical Research Council) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Following participant consent, the site project officer contacted an independent telephone randomization service for the participant study number and group allocation. The service used blocked random allocation sequences (1 for each recruitment site) generated by the trial statistician using SAS software |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Following participant consent, the site project officer contacted an independent telephone randomization service for the participant study number and group allocation. The service used blocked random allocation sequences (1 for each recruitment site) generated by the trial statistician using SAS software |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Neither participants nor trial personnel were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcome assessors were blind to group allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Intention‐to‐treat analysis was used; numbers of withdrawals were small and appeared balanced between groups, with all participants accounted for |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | ACTRN12605000166673: retrospectively registered trial protocol Protocol published 2005. Primary measures reported, although some secondary measures not included |
| Other bias | Low risk | None apparent |
Jackson 2012.
| Methods | Single‐centre, parallel‐group, randomized controlled trial Trial dates: Enrolment occurred between August 2008 and February 2009 |
|
| Participants |
Setting: single ICU at a university medical hospital, Nashville, Tennessee, USA Inclusion criteria: adult (older than 18 years), English speaking, medical and surgical ICU patients enrolled in National Institutes of Health sponsored observational cohort study, the BRAIN‐ICU study (5R01AG027472‐05) Exclusion criteria: discharge to a nursing home or rehabilitation centre planned (this criterion was relaxed during the trial to include these participants), presence of normal cognitive and physical function, lack of telephone service with an analogue telephone line (required for telephonic and televideo interventions), lived outside a 125‐mile radius Participant numbers: 22 enrolled, with 1 withdrawal before randomization (M:F 11:10). 20 randomly assigned (1 pilot participant allocated to the intervention group to test the intervention, and subsequently included in the analysis); 13 allocated to the intervention group (M:F 8:5) (13 received the intended intervention, 9 analysed, 1 death, 3 withdrawals), and 8 to the control group (M:F 3:5) (8 received the allocated intervention, 8 analysed) |
|
| Interventions |
|
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Funded by national government health research agency (US National Institutes of Health) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Although randomization with block sizes of 3 and 6 was used, and trial personnel enrolling study participants were blinded regarding which group the next eligible patient would be randomly assigned to, the Results section refers to 1 participant (the study’s initial pilot patient) assigned to the intervention group and not randomly assigned. Reasons for this are unclear and may have biased the results of this small pilot study |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomization was concealed via tri‐folded randomization sheets placed in sealed opaque envelopes |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Neither participants nor trial personnel were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcome assessors were blind to group allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | Recruitment and attrition described (flow chart) with reasons — although withdrawal in the intervention group was high, with just over half completing. Participants with missing data were excluded from analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Registered at clinicaltrials.gov (NCT00715494). Outcomes reported as per protocol registration |
| Other bias | High risk | Sample size was small, with some differences in baseline characteristics between groups that may have affected the results |
Jones 2003.
| Methods | Multi‐centre, parallel‐group, randomized controlled trial Trial dates: not reported |
|
| Participants |
Setting: ICUs at Merseyside, Manchester and Reading, UK Inclusion criteria: admitted to ICU and mechanically ventilated Exclusion criteria: ICU admission less than 48 hours; patients were suffering a burn injury (due to prolonged recovery), were unable to follow the manual or had language difficulties, were neurosurgical patients, had pre‐existing psychotic illness (confounding factor for psychological illness) or were discharged for terminal care and unlikely to survive the 6‐month follow‐up period Participant numbers: 126 randomly assigned (M:F 70:56); 69 to intervention group (M:F 37:32), 57 to control group (M:F 33:24). Numbers of participants receiving intended treatment allocation not reported. Numbers of participants analysed varied according to follow‐up time point: 8 weeks, Intervention group 63/69 (91%), Control group 51/57 (89%); 6 months, Intervention group 58/69 (84%), Control group 44/57 (77%) |
|
| Interventions |
|
|
| Outcomes |
Primary outcome not specified |
|
| Notes | Funded in part by independent charity (Stanley Thomas Johnson Foundation, Switzerland) and commercial company with no interest in the findings (REMEDI, UK) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Participants were assigned to treatment or control groups through a closed envelope technique, randomly assigned in blocks of 6. Intervention participants were not told that they were receiving anything extra. Not clear if the envelopes were opaque and who managed the randomization |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Reference is made to ‘a closed envelope’ technique; however, no specific appropriate safeguards are described (e.g. non‐opaque envelopes, sequential numbering) |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Neither participants nor trial personnel were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Blinded assessors were used. Patients’ follow‐up appointments were staggered so that study participants did not sit in the waiting room together. Outcome assessors may have been unblinded by participants, but this was unlikely to affect the outcome |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Intention‐to‐treat analysis not reported. Attrition stated, although reasons for missing data not reported. Similar numbers of deaths/missing data in both groups |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Study protocol not available for judgement. Trial registered; however, primary/secondary outcomes not stated at the time of registration. Outcomes stated in the paper reported in the results |
| Other bias | Low risk | None apparent |
Porta 2005.
| Methods | Multi‐centre, parallel‐group, randomized controlled trial Trial dates: Recruitment occurred from September 1999 to January 2002 |
|
| Participants |
Setting: 3 respiratory ICUs of Salvatore Maugeri Scientific Institutes of Gussago and Montescano and Gaiato Onlus Villa, Pineta, Italy Inclusion criteria: weaned from mechanical ventilation (invasive or non‐invasive) for 48 to 96 hours, clinically stable (arterial blood gases pH > 7.35; PaO2 > 60 mmHg at FiO2 < 0.4), absence of hyperthermia or infection, stability in haemodynamics, conscious and co‐operative mental state Exclusion criteria: primary neurologic disease, cerebrovascular disease, myopathy, cardiovascular instability, severe arrhythmia, orthopaedic problems, insufficient co‐operative state, any other condition involving inability to perform arm ergometry and/or to maintain the sitting upright position Participant numbers: 66 randomly assigned (M:F 45:21); 32 to the intervention group (M:F 22:10) (25 received the intended intervention, 7 drop‐outs) and 34 to the control group (M:F 23:11) (25 received the intended intervention, 9 drop‐outs). Study authors state that analyses were intention‐to‐treat (on all randomly assigned participants) or per‐protocol (all completers), but it is unclear when either approach was used. Hence it is not clear whether only the 25 completers per group were included in the analyses, or all included participants |
|
| Interventions |
|
|
| Outcomes |
Primary outcome not specified |
|
| Notes | Funding source not reported | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Consecutive patients were enrolled and were randomly assigned to 1 of the 2 groups by means of a computer‐generated randomization list |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Methods not reported; a computer‐generated list is reported, but it is unclear whether this was concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Neither participants nor trial personnel were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Baseline exercise tests were performed by an independent physician. All measurements were performed and recorded under the supervision of a nurse not involved in the study, although it is not explicitly stated that this person was blind to group allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Whilst it is documented that data will be analysed as intention‐to‐treat (all randomly assigned participants) or per‐protocol (all completers), it is not clear from the results when either approach has been used |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | No study protocol (no reference to one nor independently locatable). Primary and secondary outcomes not clearly stated |
| Other bias | Low risk | None apparent |
Salisbury 2010.
| Methods | Single‐centre, parallel‐group, pilot feasibility randomized controlled trial Trial dates: Recruitment occurred from 27 February 2007 to 28 August 2007 |
|
| Participants |
Setting: ICU at a university teaching hospital, Edinburgh, UK Inclusion criteria: received mechanical ventilation for longer than 4 days during ICU admission Exclusion criteria: underlying illness already with an established rehabilitation service (e.g. stroke, head injury, liver transplant), referred to palliative care, an intravenous drug abuser, participating in other randomized controlled trials or pregnant Participant numbers: 16 randomly assigned (M:F 11:5); 8 to the intervention group (M:F 5:3) (5 analysed, 2 death, 1 acute confusion) and 8 to the control group (M:F 6:2) (6 analysed, 1 death, 1 loss to follow‐up) |
|
| Interventions |
|
|
| Outcomes |
No primary outcome selected because of pilot, feasibility nature of the study. Additional nutrition‐related outcome measures collected but not reported in this review |
|
| Notes | Funded by academic health research agency (Centre for Integrated Healthcare Research, Edinburgh, UK) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants were randomly assigned to either trial arm (intervention or control) after baseline outcome measures had been collected, using a computer‐generated randomization list held by an independent researcher; participants were allocated in consecutive order following face‐to‐face or telephone contact with the independent researcher |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants were randomly assigned to either trial arm (intervention or control) after baseline outcome measures had been collected, using a computer‐generated randomization list held by an independent researcher; participants were allocated in consecutive order following face‐to‐face or telephone contact with the independent researcher |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Participants were not blinded, but it is unclear whether trial personnel were blinded; whilst it was not possible to blind the generic assistant delivering the intervention, study authors did not report whether other clinicians (dietician, physiotherapist) were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcomes: Patients were assessed 3 months after discharge from intensive care, according to standard procedures, by a research nurse blinded to group allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Some potentially eligible patients were not included. 3‐month follow‐up was completed in 11 patients (69%), although intention‐to‐treat analysis was potentially not applicable to pilot feasibility studies. Explanation given for loss at follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Feasibility study; all outcomes reported. Reasons for non‐completion of outcomes reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | None apparent |
Abbreviations: ICU = intensive care unit. SF‐36 = Short Form 36. EQ‐5D = EuroQol‐5 domain. CONSORT = Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials. ACTRN = Australia New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry Number. PaO2 = partial pressure of arterial oxygen. FiO2 = fraction of inspired oxygen. M = male. F = female.
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Brummel 2014 | Intervention initiated in the intensive care unit |
| Calvo‐Ayala 2013 | Systematic review ‐ no additional relevant articles identified |
| Chen 2011 | Intervention initiated in the intensive care unit |
| Chen 2012 | Intervention initiated in the intensive care unit |
| Cuthbertson 2009 | Intervention involving self directed programme and follow‐up clinic |
| Denehy 2013 | Intervention initiated in the intensive care unit |
| Mah 2013 | Non‐randomized controlled trial study design with unclear intervention |
| Mehlhorn 2013 | Systematic review ‐ no additional relevant articles identified |
| Nava 1998 | Intervention initiated in the intensive care unit |
| Paratz 2012 | Involved excluded population (burn (trauma) patients) |
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
Connolly 2015.
| Methods | Pilot feasibility randomized controlled trial, with a nested observational cohort study |
| Participants | 20 adult patients, mechanically ventilated for longer than 48 hours and presenting with a diagnosis of intensive care unit‐acquired weakness (Medical Research Council Sum score < 48/60) were recruited into the randomized controlled trial. 21 patients without intensive care unit‐acquired weakness were recruited into the observational cohort study. All patients were recruited at ICU discharge |
| Interventions | 16‐session, exercise‐based rehabilitation programme delivered to participants in the intervention group after hospital discharge. Control group and observational cohort participants received usual care (no post hospital discharge rehabilitation programme) |
| Outcomes | Feasibility, clinical and patient‐centred outcomes measured at hospital discharge and at 3 months. Intervention feasibility demonstrated by high adherence and patient acceptability, and absence of adverse events. Low proportion of enrolment against numbers screened for eligibility. Study underpowered to detect effectiveness of intervention. Process evaluation of the trial identified methodological factors, categorized by 'Population', 'Intervention', 'Control Group' and 'Outcome' |
| Notes | Data extracted from the publication abstract. Full study will be assessed and dealt with when the review is updated |
Jones 2015.
| Methods | 2 x 2 factorial design randomized controlled trial |
| Participants | 93 intensive care patients aged 45 years or older with a combined intensive care unit stay/pre‐intensive care unit stay of 5 days or more |
| Interventions | Two factors: i) Six‐week programme of enhanced physiotherapy and structured exercise (PEPSE) ii) Essential amino acid supplement drink (glutamine and essential amino acid mixture, GEAA) |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome was an improvement in 6‐minute walking test at 3 months. Patients receiving combination of both interventions demonstrated larges gains in distance walked in six minutes (P value < 0.001) |
| Notes | Data extracted from the publication abstract. Full study will be assessed and dealt with when the review is updated |
Walsh 2015.
| Methods | Parallel‐group, randomized clinical trial with blinded outcome assessment at 2 hospitals |
| Participants | 240 adult patients discharged from the ICU, who had required at least 48 hours of mechanical ventilation |
| Interventions | Standard physiotherapy and dietetic, occupational and speech/language therapy delivered to control and intervention group participants after ICU discharge, during the ward‐based stay. Participants in the intervention group received rehabilitation that typically increased the frequency of mobility and exercise therapies 2‐ to 3‐fold, increased dietetic assessment and treatment, used individualized goal setting and provided more illness‐specific information. This Intervention therapy was co‐ordinated and delivered by a dedicated rehabilitation practitioner |
| Outcomes | Rivermead Mobility Index (RMI) (range 0 to 15) at 3 months. Secondary outcomes included HRQL, psychological outcomes, self reported symptoms, participant experience and cost‐effectiveness during 12‐month follow‐up |
| Notes | Data extracted from the publication abstract. Full study will be assessed and dealt with when the review is updated |
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
Battle 2013.
| Trial name or title | Early results of a 6‐week exercise programme in post‐ICU patients |
| Methods | Single‐centre pragmatic, blinded randomized controlled trial |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria 1. Male or female patients age 18 years or older (no upper age limit) 2. Patients who have had a length of stay on ICU longer than 48 hours 3. Patients who have been discharged home and are attending follow‐up clinic within 6 months of discharge from the ICU 4. Patients who can follow instructions 5. Patients who are not already enrolled in a rehabilitation programme 6. Patients who live within commutable distance Exclusion criteria 1. Patients who do not consent to participation in the study 2. Patients younger than 18 years of age 3. Patients hospitalized longer than 6 months since their discharge from ICU 4. Patients who lack capacity to follow instructions 5. Patients who are already enrolled in a rehabilitation programme 6. Patients who live outside of commutable distance 7. Patients with any medical contraindications to exercise, including: 7.1. Unstable angina or myocardial infarction in the preceding month 7.2. Unmanaged valvular problems 7.3. Awaiting further definitive treatment (e.g. open abdominal wound) 7.4. Pregnancy during which the patient has been advised against exercise |
| Interventions |
Intervention group 6‐week, twice‐weekly, supervised exercise programme (supervisory personnel not specified) that includes the following. 1. Cardiovascular exercise on treadmill, cycle ergometer, rowing machine and stepper 2. Balance exercises 3. Strengthening exercises Control group No treatment |
| Outcomes |
Primary outcome Cardiopulmonary fitness (6‐minute walk test) Secondary outcomes 1. Balance (Berg Balance Score) 2. Grip strength (JAMAR® grip dynamometer) 3. Anxiety and depression (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale) |
| Starting date | 01/11/2011 |
| Contact information | Dr Ceri Battle; ceri.battle@wales.nhs.uk |
| Notes | Supplemented with additional detail from trial registration available at www.controlled‐trials.com/isrctn/pf/11853373 |
McWilliams 2013.
| Trial name or title | Outpatient‐based physical rehabilitation for survivors of prolonged critical illness — a randomized controlled trial |
| Methods | Single‐centre randomized controlled trial |
| Participants | Post ICU patients who had been invasively ventilated for at least 5 days |
| Interventions |
Intervention group 7‐week exercise and education programme. Supervisory personnel not specified Control group No intervention |
| Outcomes |
Primary outcomes
Secondary outcomes
|
| Starting date | Unknown |
| Contact information | Mr David McWilliams; david.mcwilliams@uhb.nhs.uk |
| Notes |
O'Neill 2014.
| Trial name or title | Effectiveness of a programme of exercise on physical function in survivors of critical illness following discharge from the ICU: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial (REVIVE) |
| Methods | Multi‐centre, phase II, allocation‐concealed, assessor‐blinded, randomized controlled trial |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria 1. Age 18 years or older 2. ICU admission requiring mechanical ventilation longer than 96 hours 3. Planned discharge to home (self/carer) 4. Willing and able to participate in exercise and deemed medically fit to participate in the intervention Exclusion criteria 1. Declined consent, or unable to give consent 2. Inability to participate due to any neurological, spinal or skeletal dysfunction affecting ability to exercise 3. Cognitive impairment affecting ability to consent, participate in the intervention or complete questionnaires 4. Participation in another structured rehabilitation programme due to ongoing chronic disease 5. Medical contraindication to participation in an exercise programme |
| Interventions |
Intervention group 6‐week programme comprising 3 exercise sessions per week (2 supervised and 1 unsupervised), of up to 60 minutes including rest periods and aerobic components, strengthening exercise and an exercise manual to facilitate independent exercise. The programme will be delivered by trained physiotherapists Control group Standard care including appropriate medical and nursing care, with referral to other disciplines as necessary, but with no specific post critical illness support |
| Outcomes |
Primary outcome Physical function (measured using the Physical Function domain of the SF‐36 questionnaire) Secondary outcomes 1. Physical function (Rivermead Mobility Index) 2. Hand strength and dexterity (dynamometry and Nine Hole Peg Test) 3. Exercise capacity (Incremental Shuttle Walk Test) 4. Health‐related quality of life (other subscales of the Short Form 36 Health Survey (role limitations due to physical health, bodily pain, general health perceptions, vitality, social functioning, role limitations due to emotional problems and mental health; Functional Limitations Profile; EuroQol 5 dimension questionnaire 5‐level version) 5. Breathlessness (Medical Research Council Dyspnoea Scale) 6. Anxiety and depression (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale) 7. Readiness to exercise (Readiness to Change Questionnaire) 8. Self efficacy to exercise (Chronic Disease Self Efficacy Scale) 9. Healthcare resource use (Resource Use Questionnaire) |
| Starting date | January 2012 |
| Contact information | Dr Brenda O'Neill; b.oneill@ulster.ac.uk |
| Notes | Supplemented with additional detail from trial registration; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01463579 |
Abbreviations: ICU = intensive care unit. SF‐36 = Short Form 36. RCT = randomized controlled trial. NHS = National Health Service. SF‐12 = Short Form 12. EQ‐5D = EuroQol‐5 domain.
Differences between protocol and review
The following items represent differences between the original protocol (Geneen 2010) and the current review.
Extended title to clarify that this review examines exercise rehabilitation during recovery from critical illness specifically at the post ICU stages of recovery and excludes the period of recovery that occurs whilst patients remain in the ICU (itself the subject of a current Cochrane review, Doiron 2013).
New authorship list (BC, BO'N, AD, MPWG, NH, BB) with updated affiliations, including three original protocol author group members (LG, LS, TSW), and with new authorship order to reflect relative contributions to the review.
As a result of the time frame between publication of the original protocol and completion of the review, we have written the Background section with a much more updated context and reference list to reflect the current state of the evidence in the field and the rationale for the intervention under review.
Clarified participant eligibility from the original protocol aims to assess the effectiveness of exercise rehabilitation programmes initiated after ICU discharge — patients received a minimum of 24 hours of mechanical ventilation during their admission, but were discharged from the ICU and were no longer ventilated at the time of intervention receipt.
Clarified terminology of the primary outcome from the original protocol wording of 'Quality of life' to 'Health‐related quality of life' for more accurate reporting of this measure as quality of life pertaining to the illness experience — inclusion of trial registry searches (Clinical Trials and ISRCTN) and personal author libraries in ‘Other sources’.
Clarification of dichotomous secondary outcomes.
Quantitative methods for combining data from included studies according to population, intervention and outcomes were intended but were not possible with the current dataset. These methods would still be used in future updates of the review, when the data were suitable for such analyses.
Use of an updated 'Risk of bias' form based on that originally presented in the protocol.
Limited number of studies and degree of variability restricted ability to conduct meta‐analysis and subgroup and sensitivity analyses and to prepare funnel plots for assessment of reporting bias.
Contributions of authors
Conceiving the review: Lisa Salisbury (LS), Louise Geneen (LG), Timothy Walsh (TW).
Co‐ordinating the review: Bronwen Connolly (BC).
Undertaking manual searches: BC (with assistance from Cochrane Search Trials Co‐ordinator).
Screening search results: BC, Brenda O’Neill (BO’N).
Organizing retrieval of papers: BC.
Screening retrieved papers against inclusion criteria: BC, BO’N.
Appraising quality of papers: LS, Bronagh Blackwood (BB), BC (one paper only).
Abstracting data from papers: LS, LG, BC (one paper only).
Writing to authors of papers for additional information: BC.
Providing additional data about papers: BC.
Obtaining and screening data on unpublished studies: BC, BO’N.
Managing data for the review: BC.
Entering data into Review Manager (RevMan 5.3): BC.
Analysing RevMan statistical data: BC.
Performing other statistical analysis not using RevMan: BC, LS, AD.
Performing double entry of data (data entered by person one: BC; checked by person two: LS/BO'N).
Interpreting data: BC, LS, BO’N, LG, Michael Grocott (MG), Nicholas Hart (NH), TW, BB.
Making statistical inferences: BC, AD.
Writing the review: BC (lead), with iterative review by remaining authors.
Securing funding for the review: n/a.
Performing previous work that served as the foundation of the present study: LS, TW, BC, NH.
Serving as guarantor for the review (one author): BC.
Taking responsibility for reading and checking the review before submission: BC.
Sources of support
Internal sources
-
Lane Fox Respiratory Unit Patient Association, Guy's & St.Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK.
Salary for the lead author
-
Guy’s & St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London NIHR Biomedical Research Centre, UK.
Infrastructure support
External sources
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
Bronwen Connolly: lead author of one study awaiting classification (Connolly 2015), which could be included in a future update of this review.
Lisa Salisbury: lead author of one included study (Salisbury 2010). LS did not extract data from this study nor check interpretation against the study report. This was carried out by other authors working on the review. LS is also a co‐author of one study awaiting classification (Walsh 2015), which could be included in a future update of this review.
Brenda O'Neill: lead author of one currently ongoing study (O'Neill 2014), which could be included in a future update of this review. Also Chief Investigator for a funding grant received from a national intensive care unit charity to fund the aforementioned currently ongoing study.
Louise Geneen: none known.
Abdel Douiri: none known.
Michael PW Grocott: Editor‐in‐Chief, Extreme Physiology and Medicine (BioMedCentral journal). Board member, Evidence Based Perioperative Medicine (EBPOM) — small group organizing academic meeting in anaesthesia, perioperative and critical care medicine and extreme environment physiology.
MPWG also leads the Xtreme‐Everest oxygen research consortium, which has received unrestricted grant funding from BOC Medical (Linde Group), Ely‐Lilly Critical Care, Smith's Medical, Deltex Medical, London Clinic and Rolex. No funding paid directly to MG: all funds paid directly to the home institutions of researchers within the consortium. MPWG has received honoraria for speaking (NOT related to this review) and/or travel expenses from Baxter, Fresenius‐Kabi, BOC Medical (Linde Group) and Ely‐Lilly Critical Care.
Nicholas Hart: senior author for one study awaiting classification (Connolly 2015), which could be included in a future update of this review.
Timothy S Walsh: senior author for one included study (Salisbury 2010). TSW did not extract data from this study nor check interpretation against the study report. This was carried out by other authors working on the review. TSW is lead author for one study awaiting classification (Walsh 2015), which could be included in a future update of this review. TSW has no competing interests related to the current review. TSW has received grants for post ICU recovery studies and trials from the Chief Scientists Office Scotland and the Health Services Research unit, NHS Lothian. These grants were paid to his institution. Studies are all investigator led; none are commercial. The investigator‐initiated grant funded studies reflect his content expertise but do not represent a competing interest. Results of the review will not benefit this work nor TW personally in any way.
Bronagh Blackwood: co‐applicant for a funding grant received from a national intensive care unit charity to fund a currently ongoing study (O'Neill 2014). This ongoing study is referred to in this review and may be included in a future update of this review.
The ERACIP Group: none known.
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Batterham 2014 {published and unpublished data}
- Batterham AM, Bonner S, Wright J, Howell SJ, Hugill K, Danjouz G. Effect of supervised aerobic exercise rehabilitation on physical fitness and quality‐of‐life in survivors of critical illness: an exploratory minimized controlled trial (PIX study). British Journal of Anaesthesia 2014;113(1):130‐7. [PUBMED: 24607602] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Elliott 2011 {published and unpublished data}
- Elliott D, McKinley S, Alison J, Aitken LM, King M, Leslie GD, et al. Health‐related quality of life and physical recovery after a critical illness: a multi‐centre randomised controlled trial of a home‐based physical rehabilitation program. Critical Care 2011;15(3):R142. [PUBMED: 21658221] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jackson 2012 {published and unpublished data}
- Jackson J, Ely EW, Morey M, Anderson V, Denne L, Clune J, et al. Cognitive and physical rehabilitation of intensive care unit survivors: results of the RETURN randomized controlled pilot investigation. Critical Care Medicine 2012;40(4):1088‐97. [PUBMED: 22080631] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jones 2003 {published and unpublished data}
- Jones C, Skirrow P, Griffiths R, Humphris GH, Ingleby S, Eddleston J, et al. Rehabilitation after critical illness: a randomized, controlled trial. Critical Care Medicine 2003;31:2456‐61. [PUBMED: 14530751] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Porta 2005 {published and unpublished data}
- Porta R, Vitacca M, Gilè LS, Clini E, Bianchi L, Zanotti E, et al. Supported arm training in patients recently weaned from mechanical ventilation. Chest 2005;128(4):2511‐20. [PUBMED: 16236917] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Salisbury 2010 {published and unpublished data}
- Salisbury L, Merriweather J, Walsh T. The development and feasibility of a ward‐based physiotherapy and nutritional rehabilitation package for people experiencing critical illness. Clinical Rehabilitation 2010;24:489‐500. [PUBMED: 20410151] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Brummel 2014 {published and unpublished data}
- Brummel NE, Girard TD, Ely EW, Pandharipande PP, Morandi A, Hughes CG, et al. Feasibility and safety of early combined cognitive and physical therapy for critically ill medical and surgical patients: the Activity and Cognitive Therapy in ICU (ACT‐ICU) trial. Intensive Care Medicine 2014;40(3):370‐9. [PUBMED: 24257969] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Calvo‐Ayala 2013 {published and unpublished data}
- Calvo‐Ayala E, Khan BA, Farber MO, Ely EW, Boustani MA. Interventions to improve the physical function of ICU survivors: a systematic review. Chest 2013;144(5):1469‐80. [PUBMED: 23949645] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chen 2011 {published and unpublished data}
- Chen S, Su CL, Wu YT, Wang LY, Wu CP, Wu HD, et al. Physical training is beneficial to functional status and survival in patients with prolonged mechanical ventilation. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association 2011;110(9):572‐9. [PUBMED: 21930067] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chen 2012 {published and unpublished data}
- Chen YH, Lin HL, Hsiao HF, Chou LT, Kao KC, Huang CC, et al. Effects of exercise training on pulmonary mechanics and functional status in patients with prolonged mechanical ventilation. Respiratory Care 2012;57(5):727‐34. [PUBMED: 22152978] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cuthbertson 2009 {published and unpublished data}
- Cuthbertson BH, Rattray J, Campbell MK, Gager M, Roughton S, Smith A, et al. The PRaCTICaL study of nurse led, intensive care follow‐up programmes for improving long term outcomes from critical illness: a pragmatic randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2009;339:b3723. [PUBMED: 19837741] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Denehy 2013 {published and unpublished data}
- Denehy L, Skinner E, Edbrooke L, Haines K, Warrillow S, Hawthorne G, et al. Exercise rehabilitation for patients with critical illness: a randomized controlled trial with 12 months of follow‐up. Critical Care 2013;17(4):R156. [PUBMED: 23883525] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mah 2013 {published and unpublished data}
- Mah JW, Staff I, Fichandler D, Butler KL. Resource‐efficient mobilization programs in the intensive care unit: who stands to win?. American Journal of Surgery 2013;206(4):488‐93. [PUBMED: 23806826] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mehlhorn 2013 {published and unpublished data}
- Mehlhorn J, Freytag A, Schmidt K, Brunkhorst FM, Graf J, Troitzsch U, et al. Rehabilitation Interventions for postintensive care syndrome: a systematic review. Critical Care Medicine 2014;42(5):1263‐71. [PUBMED: 24413580] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nava 1998 {published and unpublished data}
- Nava S. Rehabilitation of patients admitted to a respiratory intensive care unit. Archives of Physical and Medical Rehabilitation 1998;79(7):849‐54. [PUBMED: 9685104] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Paratz 2012 {published and unpublished data}
- Paratz JD, Stockton K, Plaza A, Muller M, Boots RJ. Intensive exercise after thermal injury improves physical, functional, and psychological outcomes. Journal of Trauma & Acute Care Surgery 2012;73(1):186‐94. [PUBMED: 2011604226] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies awaiting assessment
Connolly 2015 {published and unpublished data}
- Connolly B, Thompson A, Douiri A, Moxham J, Hart N. Exercise‐based rehabilitation following hospital discharge for survivors of critical illness with intensive care unit‐acquired weakness: a pilot feasibility trial. Journal of Critical Care 2015;30(3):589‐98. [PUBMED: 25703957] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jones 2015 {published and unpublished data}
- Jones C, Eddleston J, McCairn A, Dowling S, McWilliams D, et al. Improving rehabilitation after critical illness through outpatient physiotherapy classes and essential amino acid supplement: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Critical Care 2015;published ahead of print:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.05.002. [PUBMED: 26004031] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Walsh 2015 {published and unpublished data}
- Walsh T, Salisbury LG, Merriweather JL, Boyd JA, Griffith DM, Huby G, et al. for the RECOVER Investigators. The effectiveness of increased hospital‐based physical rehabilitation and information provision following intensive care discharge: the RECOVER randomized controlled trial. JAMA Internal Medicine 2015;published ahead of print:doi:10.1001/jamainternalmed.2015.0822. [PUBMED: 25867659] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to ongoing studies
Battle 2013 {published data only}
- Battle C, James K, Temblett P, Hutchings H. Early results of a 6‐week exercise programme in post‐ICU patients. Critical Care 2013;17(Suppl 2):P541. [Google Scholar]
McWilliams 2013 {published data only}
- McWilliams D, Benington S, Atkinson J. Outpatient‐based physical rehabilitation for survivors of prolonged critical illness ‐ a randomised controlled trial. Journal of the Intensive Care Society 2013;14(1):S‐9. [Google Scholar]
O'Neill 2014 {published data only}
- O'Neill B, McDowell K, Bradley J, Blackwood B, Mullan B, Lavery G, et al. Effectivness of a programme of exercise on physical function in survivors of critical illness following discharge from the ICU: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (REVIVE). Trials 2014;15:146. [PUBMED: 24767671] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Ali 2008
- Ali NA, O'Brien JM, Hoffmann SP, Phillips G, Garland A, Finley JCW, et al. Acquired weakness, handgrip strength, and mortality in critically ill patients. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2008;178(3):261‐8. [PUBMED: 18511703] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bailey 2007
- Bailey P, Thomsen GE, Spuhler VJ, Blair R, Jewkes J, Bezdjian L, et al. Early activity is feasible and safe in respiratory failure patients. Critical Care Medicine 2007;35(1):139‐45. [PUBMED: 17133183] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Baldwin 2013
- Baldwin CE, Paratz JD, Bersten AD. Muscle strength assessment in critically ill patients with handheld dynamometry: an investigation of reliability, minimal detectable change, and time to peak force generation. Journal of Critical Care 2013;28(1):77‐86. [PUBMED: 22520490] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Baldwin 2014
- Baldwin CE, Bersten AD. Alterations in respiratory and limb muscle strength and size in patients with sepsis who are mechanically ventilated. Physical Therapy 2014;94:68‐82. [PUBMED: 24009347] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Berney 2012
- Berney S, Haines K, Skinner EH, Denehy L. Safety and feasibility of an exercise prescription approach to rehabilitation across the continuum of care for survivors of critical illness. Physical Therapy 2012;92(12):1524‐35. [PUBMED: 22879441] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Borg 1992
- Borg GAV. Psychophysical basis of perceived exertion. Medicine & Science in Sports and Exercise 1992;14:377‐81. [PUBMED: 7154893] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bourdin 2010
- Bourdin G, Barbier J, Burle JF, Durante G, Passant S, Vincent B, et al. The feasibility of early physical activity in intensive care unit patients: a prospective observational one‐center study. Respiratory Care 2010;55(4):400‐7. [PUBMED: 20406506] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Campbell 1995
- Campbell IT, Watt T, Withers D, England R, Sukumar S, Keegan MA, et al. Muscle thickness, measured with ultrasound, may be an indicator of lean tissue wasting in multiple organ failure in the presence of edema. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;62(3):533‐9. [PUBMED: 7661114] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cartwright 2013
- Cartwright MS, Kwayisi G, Griffin LP, Sarwal A, Walker FO, Harris JM, et al. Quantitative neuromuscular ultrasound in the intensive care unit. Muscle and Nerve 2013;47:255‐9. [PUBMED: 23041986] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cheung 2006
- Cheung A, Tansey C, Tomlinson G, Diaz‐Granados N, Matte A, Barr A, et al. Two‐year outcomes, health care use, and costs of survivors of acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006;174(5):538‐44. [PUBMED: 16763220] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Collen 1991
- Collen FM, Wade DT, Robb GF, Bradshaw CM. The Rivermead Mobility Index: a further development of the Rivermead Motor Assessment. International Disability Studies 1991;13:50‐4. [PUBMED: 1836787] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Connolly 2012
- Connolly B, Denehy L, Brett S, Elliott D, Hart N. Exercise rehabilitation following hospital discharge in survivors of critical illness: an integrative review. Critical Care 2012;16(3):R226. [PUBMED: 22713336] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Connolly 2014
- Connolly B, Maddocks M, Bernal W, Hopkins P, Rafferty G. A novel technique for the assessment of peripheral skeletal muscle strength in critically ill patients. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2014;271:A4497. [Google Scholar]
Connolly 2014b
- Connolly B, MacBean V, Crowley C, Lunt A, Moxham J, Rafferty GF, et al. Ultrasound for the assessment of peripheral skeletal muscle architecture in critical illness: a systematic review. Critical Care Medicine 2015;43(4):897‐905. [PUBMED: 25559437] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Conti 2011
- Conti M, Friolet R, Eckert P, Merlani P. Home return 6 months after an intensive care unit admission for elderly patients. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2011;55(4):387‐93. [PUBMED: 21348865] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cuthbertson 2010
- Cuthbertson B, Roughton S, Jenkinson D, MacLennan G, Vale L. Quality of life in the five years after intensive care: a cohort study. Critical Care 2010;14(1):R6. [PUBMED: 20089197] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Davidson 2012
- Davidson J, Jones C, Bienvenu OJ. Family response to critical illness: postintensive care syndrome‐family. Critical Care Medicine 2012;40(2):618‐24. [PUBMED: 22080636] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
de Miranda 2011
- Miranda S, Pochard F, Chaize M, Megarbane B, Cuvelier A, Bele N, et al. Postintensive care unit psychological burden in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and informal caregivers: a multicenter study. Critical Care Medicine 2011;39(1):112‐8. [PUBMED: 21037472] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dennis 2011
- Dennis DM, Hebden‐Todd TK, Marsh LJ, Cipriano LJ, Parson RW. How do Australian ICU survivors fare functionally 6 months after admission?. Critical Care & Resuscitation 2011;13(1):9‐16. [PUBMED: 21355823] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Doiron 2013
- Doiron KA, Hoffmann T, Beller EM. Early intervention (mobilization or active exercise) for critically ill patients in the intensive care unit (Protocol). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013;10:CD010754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dowdy 2006
- Dowdy DW, Eid MP, Dennison CI, Mendez‐Tellez P, Herridge MS, Guallar E, et al. Quality of life after acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta‐analysis. Intensive Care Medicine 2006;32:1115‐24. [PUBMED: 16783553] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Drolet 2012
- Drolet A, DeJuilio P, Harkless S, Henricks S, Kamin E, Leddy EA, et al. Move to improve: the feasibility of using an early mobility protocol to increase ambulation in the intensive and intermediate care settings. Physical Therapy 2012;93:197‐207. [PUBMED: 22976447] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Eikermann 2006
- Eikermann M, Koch G, Gerwig M, Ochterbeck C, Beiderlinden M, Koeppen S, et al. Muscle force and fatigue in patients with sepsis and multiorgan failure. Intensive Care Medicine 2006;32(2):251‐9. [PUBMED: 16468072] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fan 2014
- Fan E, Dowdy DW, Colantuoni E, Mendez‐Tellez PA, Sevransky JE, Shanholtz C, et al. Physical complications in acute lung injury survivors: a two‐year longitudinal prospective study. Critical Care Medicine 2014;42(4):849‐59. [PUBMED: 24247473] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Geneen 2010
- Geneen L, Mercer TH, Salisbury L, Walsh T, Thomson CE. Exercise rehabilitation for recovery from critical illness CD008632. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010;8:CD008632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ginz 2005
- Ginz H, Iaizzo P, Girard T, Urwyler A, Pargger H. Decreased isometric skeletal muscle force in critically ill patients. Swiss Medical Weekly 2005;135:555‐61. [PUBMED: 16333766] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Griffiths 2013
- Griffiths J, Hatch R, Bishop J, Morgan K, Jenkinson C, Cuthbertson B, et al. An exploration of social and economic outcome and associated health‐related quality of life after critical illness in general intensive care unit survivors: a 12‐month follow‐up study. Critical Care 2013;17(3):R100. [PUBMED: 23714692] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Grimm 2013
- Grimm A, Teschner U, Porzelius C, Ludewig K, Zielske J, Witte OW, et al. Muscle ultrasound for early assessment of critical illness neuromyopathy in severe sepsis. Critical Care 2013;17:R227. [PUBMED: 24499688] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gruther 2008
- Gruther W, Benesch T, Zorn C, Paternostro‐Sluga T, Quittan M, Fialka‐Moser V, et al. Muscle wasting in intensive care patients: ultrasound observation of the M. quadriceps femoris muscle layer. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2008;40(3):185‐9. [PUBMED: 18292919] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Guyatt 2008
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Vist GE, Falck‐Ytter Y, Schunemann HJ, et al. What is “quality of evidence” and why is it important to clinicians?. BMJ 2008;336:995‐8. [PUBMED: 18456631] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hanekom 2011
- Hanekom S, Gosselink R, Dean E, Aswegen H, Roos R, Ambrosino N, et al. The development of a clinical management algorithm for early physical activity and mobilization of critically ill patients: synthesis of evidence and expert opinion and its translation into practice. Clinical Rehabilitation 2011;25(9):771‐87. [PUBMED: 21504951] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Harris 2000
- Harris M, Lou Y, Watson A, Rafferty G, Polkey M, Green M, et al. Adductor pollicis twitch tension assessed by magnetic stimulation of the ulnar nerve. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2000;162(1):240‐5. [PUBMED: 10903248] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Herridge 2003
- Herridge MS, Cheung AM, Tansey CM, Matte‐Martyn A, Diaz‐Granados N, Al‐Saidi F, et al. One‐year outcomes in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348:683‐93. [PUBMED: 12594312] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Herridge 2011
- Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matté A, Tomlinson G, Diaz‐Granados N, Cooper A, et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2011;364(14):1293‐304. [PUBMED: 21470008] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2002
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. [PUBMED: 12111919] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2003
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta‐analyses. British Medical Journal 2003;327:557‐60. [PUBMED: 12958120] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011, Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. [Google Scholar]
Hodgson 2014
- Hodgson C, Needham D, Haines K, Bailey M, Ward A, Harrold M, et al. Feasibility and inter‐rater reliability of the ICU Mobility Scale. Heart and Lung 2014;43(1):19‐24. [PUBMED: 24373338] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hopkins 2005a
- Hopkins RO, Brett S. Chronic neurocognitive effects of critical illness. Current Opinion in Critical Care 2005;11(4):369‐75. [PUBMED: 16015118] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hopkins 2005b
- Hopkins RO, Weaver LK, Collingridge D, Parkinson RB, Chan KJ, Orme JF Jr. Two‐year cognitive, emotional, and quality‐of‐life outcomes in acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2005;171(4):340‐7. [PUBMED: 15542793] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hopkins 2012
- Hopkins RO, Suchyta MR, Farrer TJ, Needham D. Improving post–intensive care unit neuropsychiatric outcomes. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2012;186(12):1220‐8. [PUBMED: 23065013] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Iwashyna 2010
- Iwashyna TJ. Survivorship will be the defining challenge of critical care in the 21st century. Annals of Internal Medicine 2010;153(3):204‐5. [PUBMED: 20679565] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Katz 1963
- Katz S, Ford AB, Moskowitz RW, Jackson BA, Jaffe MW. Studies of illness in the aged. The index of ADL: a standardized measure of biological and psychological function. Journal of the American Medical Association 1963;185:914‐19. [PUBMED: 14044222] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kayambu 2013
- Kayambu G, Boots R, Paratz J. Physical therapy for the critically ill in the ICU: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Critical Care Medicine 2013;41(6):1543‐54. [PUBMED: 23528802] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kentish‐Barnes 2009
- Kentish‐Barnes N, Lemiale V, Chaize M, Pochard F, Azoulay E. Assessing burden in families of critical care patients. Critical Care Medicine 2009;37(10 Suppl):S448‐56. [PUBMED: 20046134] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kho 2012
- Kho, ME, Damluji A, Zanni JM, Needham DM. Feasibility and observed safety of interactive video games for physical rehabilitation in the intensive care unit: a case series. Journal of Critical Care 2012;27(2):219.e1‐219.e6. [PUBMED: 21944880] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kvale 2003
- Kvale R, Flaatten H. Changes in health‐related quality of life from 6 months to 2 years after discharge from intensive care. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2003;1(1):2. [PUBMED: 12685930] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Li 2013
- Li Z, Peng X, Zhu B, Zhang Y, Xi X. Active mobilization for mechanically ventilated patients: a systematic review. Archives of Physical and Medical Rehabilitation 2013;94(3):551‐61. [PUBMED: 23127305] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
MRC 2008
- Medical Research Council. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: new guidance. 2008; Vol. http://wwwmrcacuk/Utilities/Documentrecord/indexhtm?d=MRC004871 (accessed 26 October 2013).
Needham 2012a
- Needham DM, Davidson J, Cohen H, Hopkins RO, Weinert C, Wunsch H, et al. Improving long‐term outcomes after discharge from intensive care unit: report from a stakeholders' conference. Critical Care Medicine 2012;40(2):502‐9. [PUBMED: 21946660] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Needham 2012b
- Needham D, Colantuoni E, Mendez‐Tellez PA, Dinglas V, Sevransky J, Himmelfarb C, et al. Lung protective mechanical ventilation and two year survival in patients with acute lung injury: prospective cohort study. British Medical Journal 2012;344:e2124. [PUBMED: 22491953] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Needham 2013a
- Needham DM, Dinglas VD, Morris PE, Jackson JC, Hough CL, Mendez‐Tellez PA, et al. Physical and cognitive performance of patients with acute lung injury 1 year after initial trophic versus full enteral feeding: EDEN trial follow‐up. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2013;188(5):567‐76. [PUBMED: 23805899] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Needham 2013b
- Needham D, Dinglas V, Bienvenu OJ, Colantuoni E, Wozniak AW, Rice TW, et al. One year outcomes in patients with acute lung injury randomised to initial trophic or full enteral feeding: prospective follow‐up of EDEN randomised trial. British Medical Journal 2013;346:f1532. [PUBMED: 23512759] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NICE 2009
- NICE. NICE Clinical Guideline 83: Rehabilitation After Critical Illness. London, UK: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2009. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG83. [Google Scholar]
Oeyen 2010
- Oeyen SG, Vandijck DM, Benoit DD, Annemans L, Decruyenaere JM. Quality of life after intensive care: a systematic review of the literature. Critical Care Medicine 2010;38(12):2386‐400. [PUBMED: 20838335] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pandharipande 2013
- Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, Jackson JC, Morandi A, Thompson JL, Pun BT, et al. Long‐term cognitive impairment after critical illness. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;369(14):1306‐16. [PUBMED: 24088092] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Parker 2013
- Parker A, Tehranchi K, Needham D. Critical care rehabilitation trials: the importance of 'usual care'. Critical Care 2013;17(5):183. [PUBMED: 24103735] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Parry 2013
- Parry S, Berney S, Granger C, Koopman R, El‐Ansary D, Denehy L. Electrical muscle stimulation in the intensive care setting: a systematic review. Critical Care Medicine 2013;41(10):2406‐18. [PUBMED: 23921276] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pickles 2005
- Pickles J, Kondili E, Harikumar G, Kaul S, Bernal W, Wendon J, et al. Respiratory and limb muscle strength following critical illness. American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine 2005;171:A787. [Google Scholar]
Pires‐Neto 2013
- Pires‐Neto R, Kawaguchi Y, Hirota A, Fu C, Tanaka C, Caruso P, et al. Very early passive cycling exercise in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: physiological and safety aspects — a case series. Public Library of Science ONE 2013;8(9):e74182. [PUBMED: 24040200] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pohlman 2010
- Pohlman MC, Schweickert WD, Pohlman AS, Nigos C, Pawlik AJ, Esbrook CL, et al. Feasibility of physical and occupational therapy beginning from initiation of mechanical ventilation. Critical Care Medicine 2010;38(11):2089‐94. [PUBMED: 20711065] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Powell 1995
- Powell LE, Myers AM. The Activities‐specific Balance Confidence (ABC) scale. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 1995;50A:M28‐M34. [PUBMED: 7814786] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Puthucheary 2013
- Puthucheary ZA, Rawal J, McPhail M, et al. Acute skeletal muscle wasting in critical illness. Journal of the American Medical Association 2013;310(15):1591‐600. [PUBMED: 24108501] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ramsay 2014
- Ramsay P, Salisbury LG, Merriweather JL, Huby G, Rattray JE, Hull AM, et al. A rehabilitation intervention to promote physical recovery following intensive care: a detailed description of construct development, rationale and content together with proposed taxonomy to capture processes in a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2014;15(1):38. [PUBMED: 24476530] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen. Review Manager (RevMan) 5.3. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Salisbury 2010a
- Salisbury LG, Merriweather JL, Walsh TS. Rehabilitation after critical illness: could a ward‐based generic rehabilitation assistant promote recovery?. Nursing Critical Care 2010;15(2):57‐65. [PUBMED: 20236432] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schweickert 2009
- Schweickert WD, Pohlman MC, Pohlman AS, Nigos C, Pawlik AJ, Esbrook CL, et al. Early physical and occupational therapy in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009;373(9678):1874‐82. [PUBMED: 20711065] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sricharoenchai 2014
- Sricharoenchai T, Parker A, Zanni J, Nelliot A, Dinglas V, Needham D. Safety of physical therapy interventions in critically ill patients: a single‐center prospective evaluation of 1110 intensive care unit admissions. Journal of Critical Care 2014;29:395‐400. [PUBMED: 24508202] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Stiller 2013
- Stiller K. Physiotherapy in intensive care: an updated systematic review. Chest 2013;144(3):825‐47. [PUBMED: 23722822] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sukantarat 2007a
- Sukantarat K, Greer S, Brett S, Williamson R. Physical and psychological sequelae of critical illness. British Journal of Health Psychology 2007;12(1):65‐74. [PUBMED: 17288666] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sukantarat 2007b
- Sukantarat KT, Williamson RC, Brett SJ. Psychological assessment of ICU survivors: a comparison between the Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale and the Depression, Anxiety and Stress scale. Anaesthesia 2007;62(3):239‐43. [PUBMED: 17300300] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Unroe 2010
- Unroe M, Kahn JM, Carson SS, Govert JA, Martinu T, Sathy SJ, et al. One‐year trajectories of care and resource utilization for recipients of prolonged mechanical ventilation: a cohort study. Annals of Internal Medicine 2010;153(3):167‐75. [PUBMED: 20679561] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vivodtzev 2014
- Vivodtzev I, Devost AA, Saey D, Villeneuve S, Boilard G, Gagnon P, et al. Severe and early quadriceps weakness in mechanically ventilated patients. Critical Care 2014;18:R431. [PUBMED: 25033092] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wade 2012
- Wade D, Howell D, Weinman J, Hardy R, Mythen M, Brewin C, et al. Investigating risk factors for psychological morbidity three months after intensive care: a prospective cohort study. Critical Care 2012;16(5):R192. [PUBMED: 23068129] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All six studies reported the primary outcome of functional exercise capacity. We summarized the data in Table 3. We obtained all data from published literature and contacted the lead authors of two studies to request raw data to facilitate further analysis (Jones 2003; Salisbury 2010). No additional data were provided by Jones 2003, so review authors could report in Table 3 only minimal data obtained through data extraction. Salisbury 2010 provided additional data. However, sample sizes were too small for their outcomes of functional exercise capacity (ranging between four and six in the control group or the intervention group) to facilitate conversion of non‐parametric median (IQR) data to parametric means (SD). However, by using the raw data, we were able to calculate P values for differences between control and intervention groups. Insufficient sample size was evident for the study reported by Jackson 2012 (control and intervention groups ranging between seven and eight participants), although results of statistical testing were published. For these two studies (Jackson 2012; Salisbury 2010), we reported median (IQR) data in Table 3. For all remaining studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011; Porta 2005), we reported mean values (SD), differences in the mean, 95% CIs and P values.
Data on findings of functional exercise capacity were individually variably characterized with regard to types and details of outcome measures and timing and nature of data acquisition (see Table 3). For example, Batterham 2014 reported between‐group differences in the SF‐36 PF domain at nine weeks and at 26 weeks. In contrast, Elliott 2011 reported between‐group differences for changes in the SF‐36 PF domain from baseline to weeks eight and 26. Objective exercise testing employed by these studies also differed, namely, cardiopulmonary exercise testing measuring anaerobic threshold (Batterham 2014) and 6MWT (Elliott 2011). Furthermore, the 'baseline' time point for Batterham 2014 was up to 16 weeks post hospital discharge, whereas for Elliott 2011, baseline data were collected at one week post hospital discharge.
Whilst Jones 2003 also employed the SF‐36 PF domain as the outcome measure for functional exercise capacity, researchers provided minimal data. Furthermore, Porta 2005 assessed cardiopulmonary exercise testing but used different methods and different parameters, with an unspecified time frame, and reported a mix of absolute between‐group differences and between‐group differences in changing variables. Both Jackson 2012 and Salisbury 2010 reported on a battery of clinical functional exercise capacity measures.
As a result of this diversity in functional exercise capacity reporting, we presented data for each outcome according to reporting by investigators in each included study (see Table 3). We made no post hoc decisions to influence presentation or analysis of data. We reviewed the data to determine a pooled value for the effect of the intervention on functional exercise capacity, and to assess for degree of heterogeneity. However, only two studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011) provided data with the potential for pooling (SF‐36 PF). On further inspection with the review statistician (AD), we confirmed that for this small sample, pooling of data and assessment of heterogeneity would not be appropriate.
For a summary of findings, see Table 1. The GRADE quality of evidence was very low.
Investigators assessed health‐related quality of life in only two studies (Batterham 2014; Elliott 2011). Data are summarized in Table 4. We obtained all data from published literature and reported all as means (SD), differences in the mean, 95% CIs and P values. These studies employed different measures of health‐related quality of life, at different time points, and reported different types of data. Batterham 2014 reported between‐group differences in the EuroQol‐5D and the EuroQol‐5D visual analogue scale at nine weeks and at 26 weeks. In contrast, Elliott 2011 reported changes in SF‐36 PCS and MCS from baseline to weeks eight and 26.
As a result of this diversity in health‐related quality of life reporting, we presented data for each outcome according to how they were presented in each included study (see Table 3). We made no post hoc decisions to influence presentation or analysis of data. After discussion with the review statistician (AD), we concluded that it would not be appropriate to pool these limited data and to assess study heterogeneity.
For a summary of findings, see Table 1. The GRADE quality of evidence was very low.


