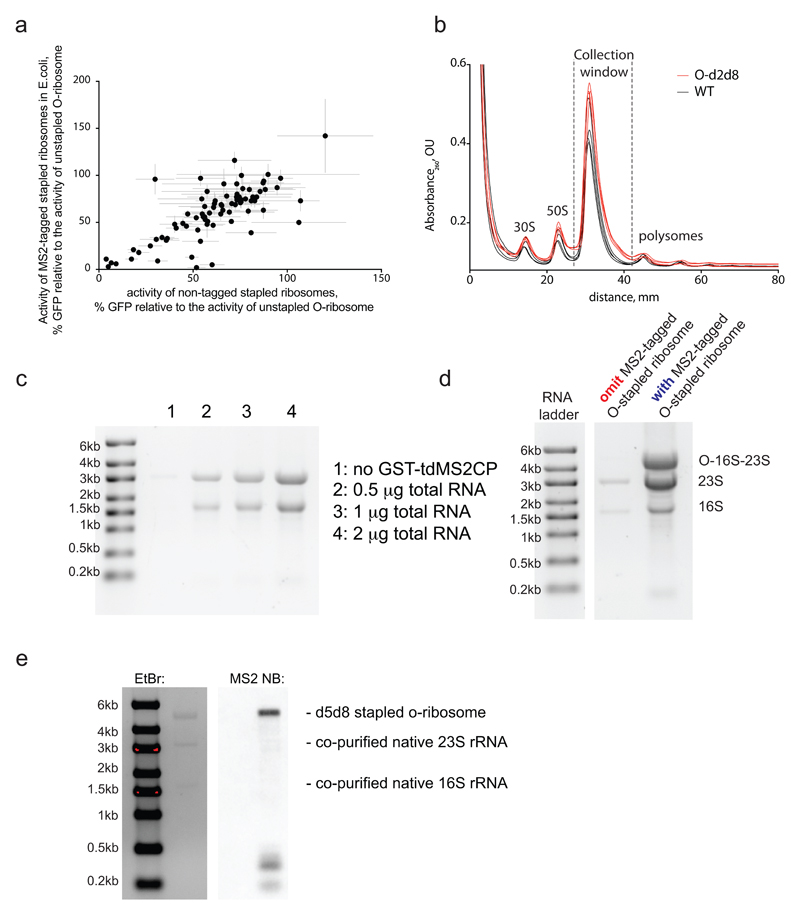
Extended Data Figure 2. MS2 tagged O-stapled ribosomes.
a Tagging O-stapled ribosomes with an MS2 stem loop minimally perturbs in vivo ribosome activity. We measured in vivo ribosome activities via GFP production from an O-sfGFP150TAG reporter, in cells expressing an intact or MS2-tagged linker-length variant of O-stapled ribosome along with the M. mazei pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNACUA pair (encoded by PylS/pylT) in the presence of 1 mM BocK. GFP fluorescence was normalized to that produced from a non-stapled O-ribosome. For numbers of replicates (n) and statistics, see Methods and Supplementary Data 2. b, Sucrose gradient analysis of an E. coli lysate with and without an O-stapled ribosome variant; n = 3 biological replicates. c, Affinity purification of a non-stapled O-ribosome depends on the presence of GST-tdMS2CP (a fusion between glutathiose-S-transferase (GST) and a mutant of a tandem dimer of the MS2 coat protein (tdMS2CP)) on resin. Affinity purification of MS2-tagged ribosomes was performed on glutathione–sepharose resin with bound GST-tdMS2CP (lanes 2–4) and without GST-tdMS2CP (lane 1). Varying amounts of total RNA were loaded in lanes 2–4. d, Affinity purification depends on the presence of the MS2 RNA stem loop on ribosomes. Pellets of O-p2d6 ribosomes were collected through sucrose cushions. Affinity purifications were performed on glutathione–sepharose resin with bound GST-tdMS2CP. e, O-d5d8-MS2 was affinity purified, and MS2 stem-loop-containing species were probed by northern blot (NB). EtBr, ethidium bromide (a fluorescent stain for nucleic acid). The experiments in c–e were each performed once. For source data regarding gels, see Supplementary Fig. 1.