Abstract
Magnesium is an essential mineral naturally present in the human body, where it acts as cofactor in several enzymatic reactions. Magnesium is a key cardiovascular regulator, which maintains electrical, metabolic, and vascular homeostasis. Moreover, magnesium participates in inflammation and oxidative processes. In fact, magnesium deficiency is involved in the pathophysiology of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, endothelial dysfunction, coronary artery disease, cardiac arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death. In consideration of the great public-health impact of cardiovascular disease, the recognition of the negative effects of magnesium deficiency suggests the possible role of hypomagnesaemia as cardiovascular risk factor and the use of serum magnesium level for the screening and prevention of cardiovascular risk factors and cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, it might help with the identification of new therapeutical strategies for the management of cardiovascular disease through magnesium supplementation.
1. Introduction
Magnesium (Mg2+) is an essential mineral naturally present in the human body, where it plays an important role as a cofactor in about 325 enzymatic reactions such as the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the synthesis of nucleotides, glucose, and blood pressure control, and lipid peroxidation [1]. Mg2+ is the second most important intracellular cation after potassium (K+) and is fundamental in muscle contraction, nerve conduction, and bone strength. In an adult human body, there are approximately 0.4 g Mg2+/kg [2], with about 50–60% localized in bones, and the rest distributed in skeletal muscle and soft tissues. Serum Mg2+ represents a little percentage, less than 1% of all Mg2+ in the body [3], and the normal reference range is 0.76–1.15 mmol/L [4]. However, bone Mg2+ is largely exchangeable to counteract acute changes in serum levels of this mineral, while one-third of skeletal Mg2+ accomplishes the same function [5]. We can obtain Mg2+ from different types of food as green leafy vegetables, legumes, cereal and nuts, which have a great Mg2+ content, or fruits, meat, fish, and chocolate, providing a moderate amount of Mg2+. Moreover, water represents an important source of Mg2+, because it contains up to 30 mg/L of Mg2+ [6].
Scientific literature has reported the role of Mg2+ as important cardiovascular regulator, acting to maintain electrical, metabolic, and vascular homeostasis; additionally, Mg2+ modulates inflammation and oxidative processes that are known to be triggers for atherogenesis and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) [7]. More recently, several data have shown the association between Mg2+ intake and circulating Mg2+ with CV health [7–9]; hypomagnesaemia has been associated to increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D), metabolic syndrome (MetS), arterial hypertension, endothelial dysfunction, and CVD. Hence, new evidences suggest that hypomagnesaemia may have a detrimental effect on CV health and may increase the total risk of developing several metabolic conditions and CVD. Dietary surveys have shown deficient Mg2+ intake in a large proportion of population, probably due to Western dietary habits. Additionally, other known causes of hypomagnesaemia, such as intestinal malabsorption, gastrointestinal losses, and diuretics or lassative assumption, are very frequent in general population but often underestimated and undertreated, particularly among elderly individuals.
The recognition of the possible role of hypomagnesaemia as risk factor for CV health, along with the underestimation of the importance of this mineral in daily clinical practice, makes serum Mg2+ level suitable for the screening and prevention of CVD and opens new therapeutic scenarios with the possibility of reducing CV risk profile and treating CVDs through Mg2+ supplementation.
2. Mg2+ and Cardiovascular System: Pathophysiologic Insights
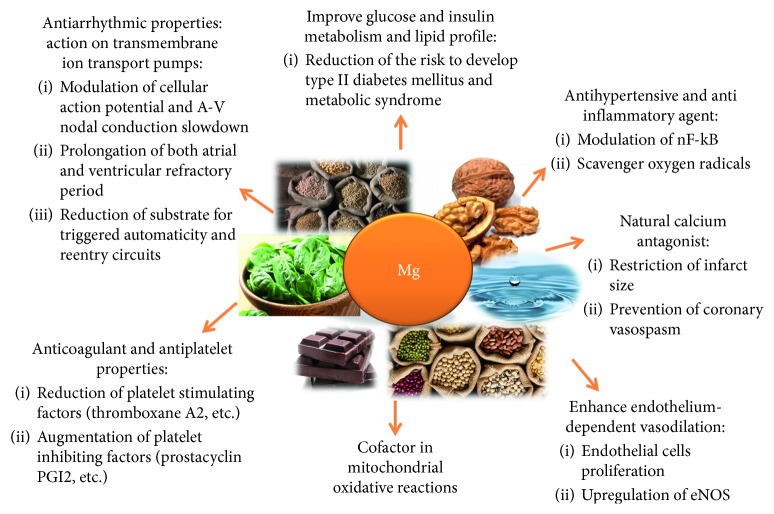
Mg2+ exerts beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system by acting on transmembrane ion transport pumps, improving glucose and insulin metabolism, enhancing endothelium-dependent vasodilation, improving lipid profile, and acting as an antihypertensive and anti-inflammatory agent [10]. Additionally, Mg2+ is a natural calcium antagonist, is an essential cofactor in mitochondrial oxidative reactions, and has anticoagulant and antiplatelet properties.
2.1. Magnesium as Ionic Channel Regulator
Mg2+ participates to the control of the activity of some ionic channels, such as sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), and calcium (Ca2+) [11, 12]. Mg2+ reduces the rapid inward component of the delayed rectifier K+ channel (IKr) [13] and exerts an antiarrhythmic action modulating the duration of action potential and myocardial excitability. In fact, Mg2+ infusion provokes the slowing of atrioventricular (AV) nodal conduction and also determines the prolongation of PR and QRS duration [14]. Mg2+ prolongs both atrial and ventricular refractory period, reducing proarrhythmic substrate for triggered automaticity and reentry circuits [15, 16]. On the contrary, Mg2+ deficiency is correlated with a prolonged QT interval potentially associated to the development of ventricular arrhythmias as the torsade de pointes. Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) is usually successfully used during the episodes of torsade de pointes, because it is able to stop early after depolarizations (EADs) and automaticity by decreasing IKr current and blocking long-lasting type (L-type) Ca2+ activity [17]. Through the inhibitory effect on two Ca2+ channels, transient-type (T-type) and L-type [18], Mg2+ exerts a protective effect against triggered activity, prevents coronary artery spasm, and plays a crucial role in modulating vascular muscle tone and, therefore, systemic arterial blood pressure. Furthermore, Mg2+ plays a critical role in the potassium-proton exchange and in the protection against potassium loss. Hypomagnesaemia weakens this mechanism and also promotes the augmentation of intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ concentrations. These concepts can explain how hypomagnesaemia can impact the physiological activity of muscle cells in general and cardiomyocytes and vascular muscle cells in specific, leading to cardiovascular diseases and coronary vasospasm [19]. Additionally, myocardial ischemia is related to intracellular Ca2+ overload that has detrimental effect on myocardial function. Competing for the same binding sites, Mg2+ may reduce intracellular Ca2+ overload during myocardial ischemia, and may restrict infarct size limiting coronary artery spasm, reducing postinfarction oxidative damage [20], and improving endothelial-dependent vasodilation through NO release [21].
2.2. Magnesium as Enzymatic Cofactor
Mg2+ acts as a cofactor in multiple cellular reactions, some of which take place in mitochondria, that also represent the main intracellular reservoir of this ion and, through the Mg2+ transporter, mediate the redistribution of Mg2+ inside cells according to physiological stimuli [22]. Dysregulation in homeostasis of mitochondrial Mg2+ has effects both on mitochondrial energy production and mitochondrial morphology, disrupting ATP production [22].
2.3. Magnesium and Metabolic Homeostasis
Mg2+ seems to have beneficial effects on CV health, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome [23, 24]. This ion improves glucose and insulin metabolism modulating the activity of glucose transporter protein 4 (GLUT 4) [25] and enhancing insulin sensibility. Particularly, it has been demonstrated that Mg2+ mediates pancreatic insulin release, postreceptor insulin signaling, and acts as a second messenger for insulin-mediated signal transduction [26, 27].
2.4. Magnesium and Inflammatory Response
Mg2+ has been associated to the regulation of inflammation and oxidative processes. Indeed, this ion has anti-inflammatory effect, modulating the release of nuclear factor-kB [28], and antioxidant properties, by scavenging oxygen radicals [28–34]. The inflammatory response that takes place in case of hypomagnesaemia also influences the lipid profile through lipoprotein peroxidation [35], with the increase of the triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, the accumulation of plasma concentrations of apolipoprotein B, decreased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels resulting in the development of dyslipidemia [34]. These lipoprotein changes, together with the chronic impairment of redox status, lead to the atherogenic effects of hypomagnesaemia and exalt the possible role of Mg2+ in the cardiovascular health.
2.5. Magnesium and Coagulation System
Mg2+ has anticoagulant [36] and antiplatelet properties. The latter is based on the Mg2+ capacity to reduce platelet activation, both by inhibiting the production of platelet stimulating factors, such as thromboxane A2 (TXA2), and e increasing the release of platelet inhibiting factors, such as prostacyclin (PGI2) [37, 38], and to counteract platelet aggregation, because it competes with Ca2+ ions for specific sites in the glycoprotein (Gp) IIb subunit, modifying the receptor conformation and hindering fibrinogen-Gp IIb-IIIa interaction. This effect could be observed greatly in case of Mg2+ supplementation, as highlighted by Gawaz et al. [39]. Moreover, Mg2+ is able to inhibit thrombin-induced Ca2+ influx [40].
2.6. Magnesium and Microvascular System
Of note, hypomagnesaemia could increase the susceptibility to CVD affecting the endothelial function and modulating microvascular functions. The role of coronary microcirculation and its endothelial or nonendothelial-dependent dysfunction in the pathogenesis of CVD, and specifically of myocardial ischemia, is well known. Recent evidences in this field assigned a new visibility and importance to the presence of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes encoding for coronary ion channels, most of all for the ATP-dependent K+ channel (K-ATP), as a possible substrate where endothelial dysfunction establishes itself. Starting from these considerations, it is more intelligible how Mg2+, as essential intracellular cation, can affect these mechanisms [41–43]. Indeed, Mg2+ prevents vasospasm and endothelial damage [44] by stimulating endothelial proliferation and angiogenesis, upregulating the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), thus increasing nitric oxide (NO) release. Conversely, low Mg2+ levels affect and reduce the synthesis of vasodilator molecules and slow the proliferation of endothelial cells and promote the adhesion of monocytes, increasing the susceptibility of the CV system to oxidative stress and contributing to the creation of a prothrombotic and atherogenic surface [26, 27, 33–35, 44–59]. The production of nitric oxide (NO) represents the main protective action performed by the coronary endothelium to avoid vasospasm or thrombosis and provides the endothelium-dependent vasodilation acetylcholine-induced. Pearson et al. demonstrated that Mg2+, infused after cardiac operations, affects endothelial-dependent vasodilation without interfere with NO production, and low extracellular Mg2+ levels affect NO-dependent vasodilation [60]. By reducing NO release and affecting Ca2+ handling system, Mg2+ deficiency modulates vascular tone and can increase the risk of developing hypertension [59, 61, 62]. It has been demonstrated that Mg2+ induces endothelial dysfunction reducing endothelial proliferation [63]. Particularly, the slowdown in endothelial cells proliferation is linked to the upregulation of interleukin-1 (IL-1), a potent inhibitor of endothelial growth [64], and, on the other hand, the downregulation of cell division cycle 25B (CDC25B) phosphatase with a role in the promotion of cells G2–M progression in cellular cycle [63, 65]. Furthermore, hypomagnesaemia results in the overexpression of adhesion molecules, like soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (sVCAM-1) and E-selectin, associated to the proinflammatory status with the increased release of interleukin-1a (IL-1) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) [52]. The upregulation of these endothelial-related markers results in an amplificated monocyte adhesion to the endothelium and promotes atherogenesis and CVD development [66].
3. Mg2+ and Cardiovascular System: Clinical Insights
As mentioned above, Mg2+ is a fundamental mineral in cardiac health, and its role is essential in various different cardiovascular and metabolic conditions. It is a defense against the oxidative damage [67–69], a physiological Ca2+ antagonist [18] that contributes to the modifications in the membrane potential [70], a regulator of platelet aggregation and adhesion [37, 38], and a modulator of endothelial function [60, 63, 64]. There are several studies reporting an inverse association between serum Mg2+ level, Mg2+ supplementation, and CVD. These evidences suggest that this ion could be monitored for screening and prevention of CVD and possibly supplemented as an adjunctive pharmacotherapy for CVD (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Molecular effects and role of Mg2+ in the cardiovascular system.
Prevention and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias are the most widely accepted indications for Mg2+ use in daily clinical practice, since Mg2+ deficiency can disrupt the homeostasis of intra- and extracellular ions leading to the prolongation of QT segment, ST-depression, and T waves characterized by a lower amplitude [71]. Salaminia et al. conducted a meta-analysis of twenty-two randomized trials that highlighted the role of MgSO4 in the reduction of cardiac arrhythmias, showing the lowering of the risk of ventricular arrhythmias about 32% and supraventricular arrhythmias 42% [72]. This effect was confirmed also by other meta-analyses [73–75]. This suggested that the administration of MgSO4 could be a safe, effective, and cost-effective strategy for the preservation of cardiac patient's health [72]. The importance of Mg2+ in the chapter of arrhythmias is greater in the prevention against postoperative atrial fibrillation arising after coronary artery bypass [75] or after cardiac surgery [76, 77]. In the same way, the Framingham Heart Study highlighted how in the comparison between individuals belonging to the lowest quartile or the upper quartiles of serum Mg2+, the first group was about 50% more likely to go to atrial fibrillation than the latter. Therefore, it resulted that low-serum Mg2+ levels are moderately associated with the onset of atrial fibrillation also in people without cardiovascular diseases [78]. The risk of the development of ventricular arrhythmias is influenced by Mg2+ concentrations also. In addition to the well-known answer of torsade de pointes episodes to MgSO4, Raghu et al. demonstrated the efficacy of the Mg2+ supplementation, adjuvant to thrombolytic therapy, in preventing ventricular arrhythmias and reducing short-term mortality after acute myocardial infarction [79]. As a result, the European Society of Cardiology incorporated Mg2+ in their guidelines regarding the prevention and the managing of some kind of cardiac arrhythmias [80].
Mg2+ deficiency, through abnormalities of Ca2+ handling system, dysregulation of vascular tone and endothelial dysfunction, contributes to induce hypertension. A recent meta-analysis showed a statistically significant inverse association between Mg2+ intake and arterial hypertension [23]. These results were consistent with those by Dibaba et al. that pointed out the reduction of both systolic and diastolic blood pressure through Mg2+ supplementation [81].
It has been demonstrated that hypomagnesaemia alters the normal lipid profile and induces insulin resistance (IR), T2D, and MetS. A recent meta-analysis demonstrated a linear dose-response relationship between Mg2+ intake and T2D: the higher the Mg2+ intake, the lower the risk of T2D [23]; Sarrafzadegan et al. showed that Mg2+ supplementation was associated with lower risk of MetS [82]. Through oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, Mg2+ deficiency has been linked to dyslipidemia, and in some meta-analysis, Mg2+ supplementation showed beneficial effects reducing triglycerides and total cholesterol [83, 84].
The association of Mg2+ deficiency with CV risk factors promoting the generation of atherosclerotic plaques is probably the reason of the increased risk of ischemic heart disease (IHD) seen in patients with hypomagnesaemia. Particularly, the risk of myocardial infarction is also referable to the role that Mg2+ plays in favoring oxidative stress, suggested by a lot of evidences both in humans and animal models [67]. Hans et al. studied in rats with Mg2+ deficiency the lowering of plasma anticoagulants and an increased lipid peroxidation [68], while Kuzniar et al. observed in mice that hypomagnesaemia led to the reduction of glutathione (GSH) levels and to a decrease of GSH reductase, superoxide dismutase, and GSH S-transferase activity in erythrocytes [69]. Kharb and Singh tried to understand if Mg2+ deficiency may promote oxidative injury in cardiovascular disease states and highlighted how actually low Mg2+ concentrations can accelerate and potentiate oxidative insult in the myocardium [85]. The link between hypomagnesaemia and IHD has been pointed out by a recent systematic review, showing that higher circulating Mg2+ levels are associated with lower risk of IHD and fatal IHD [9].
Another mechanism through which low Mg2+ levels can bring to IHD is coronary vasospasm, and this event is mostly due to the consequences of hypomagnesaemia on intracellular Ca2+. A lot of studies have already demonstrated that Mg2+ deficiency is correlated to coronary artery spasm [86–90]. Guo et al., who investigated the Mg2+ status in and out of cells in 12 women affected by variant angina, found that Mg2+ concentration in the cytoplasm of erythrocytes was well related to the activity of the variant angina [86]. Starting from this knowledge, Teragawa et al. studied whether Mg2+ could be useful in the prevention of coronary vasospasm in patients with vasospastic angina. They demonstrated that Mg2+ infusion can induce nonsite specific basal coronary vasodilation and block coronary spasm acetylcholine-induced in patients affected by vasospastic angina [87].
Recently, Joris et al. conducted a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled intervention trial in a group of overweight and obese adults to study the effects of Mg2+ on arterial stiffness, a known marker of CV health. They found that Mg supplementation reduced the arterial stiffness without any effects on blood pressure values, suggesting a potential way through which an increased Mg2+ intake could exert benefits for cardiovascular health [91, 92].
A systematic review and meta-analysis conducted by Del Gobbo et al. tried to draw a link between circulating and dietary Mg2+ and risk of cardiovascular disease, such as ischemic heart disease, and it was confirmed with significant results, supporting recommendations to increase Mg2+ intake, mostly the consumption of Mg2+-rich food, as vegetables and nuts [9].
New evidences suggest that Mg2+ supplementation could have beneficial effects in the early phase of acute coronary syndrome and after implantation of drug-eluting stent (DES). Gyamlani et al. found that Mg2+ levels during and after acute myocardium infarction (AMI) were lower in patients affected by AMI than controls and that intravenous Mg2+ administered in the immediate postinfarction period in the patients had a cardioprotective effect and the capacity to reduce arrhythmias, pump dysfunction, and death [93]. A study conducted by An et al. showed that Mg2+ levels could be considered, independently from other risk factors, as predictor of major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) in patients who undergo a DES implantation after AMI, but not unstable angina [94]. Similarly, Yuksel et al. identified low Mg2+ as independent predictor of electrocardiographic no-reflow and long-term mortality in 111 patients after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and primary percutaneous coronary implantation (p-PCI) [95]. In continuity with these results, Çiçek et al. analyzed the hypothetical association between Mg2+ levels and acute stent thrombosis after a p-PCI in people with STEMI. The results pointed out that Mg2+ was an independent predictor of acute stent thrombosis in these groups of patients [96]. Besides, since Mg2+ represents an important ion in the determination of membrane potential, dosing its plasma levels, together with calculation of the concentrations of the other main ions, could be useful in the identification of the membrane permittivity and conductivity, for the purpose of better understanding the mechanisms that are at the basis of the hemocompatibility of vascular stent materials [97].
Nevertheless, data regarding the protective role of Mg2+ in the reduction of mortality after acute myocardial infarction are not all concordant, and there are conflicting results, such as the MAGIC (Mg2+ in coronaries) trial that did not report any advantage of early Mg2+ administration in addition to the standard therapy in high-risk patients after STEMI, with no effects on 30-day mortality [98]. Vassalle et al. did not observe a significant role of low Mg2+ levels in predicting hard events (all causes of death and nonfatal myocardial infarction) in patients after AMI [99]. The results found in these studies are probably due to the different population features, pointing out that Mg2+ supplementation could exert the beneficial effect in low-risk patients with CVD or in prevention of CVD rather than in patients with high CV risk profiles.
Finally, a big number of studies published in the past decades links hypomagnesaemia to sudden cardiac death (SCD) because of different reasons, such as the major frequency of sudden death in areas where community water supplies have a little Mg2+ content or the lower Mg2+ concentrations in people who die of sudden death. A possible explanation of this correlation is referable to cardiac arrhythmias and coronary vasospasm, which are usually associated to Mg2+ deficiency. An important study related to this question was conducted by Peacock et al. in a cohort of more than fourteen thousand persons, distributed according to the value of their serum Mg2+. The results showed that people at the higher quartile of serum Mg2+ had a significantly lower risk of sudden death compared to individuals at the lower quartile, and these findings were confirmed also after the adjustment for the major potential confounders of Mg2+-SCD relationship, like hypertension, diabetes, serum K+ concentrations, or use of diuretics [100].
All these evidences suggest that hypomagnesaemia may predispose to the development of CV risk factors and CVD. The awareness of the possible role of this ion as risk factor for CVD may lead to use Mg2+ level for screening and prevention of CVD and Mg2+ supplementation as adjunctive pharmacotherapy for patients suffering from heart disease.
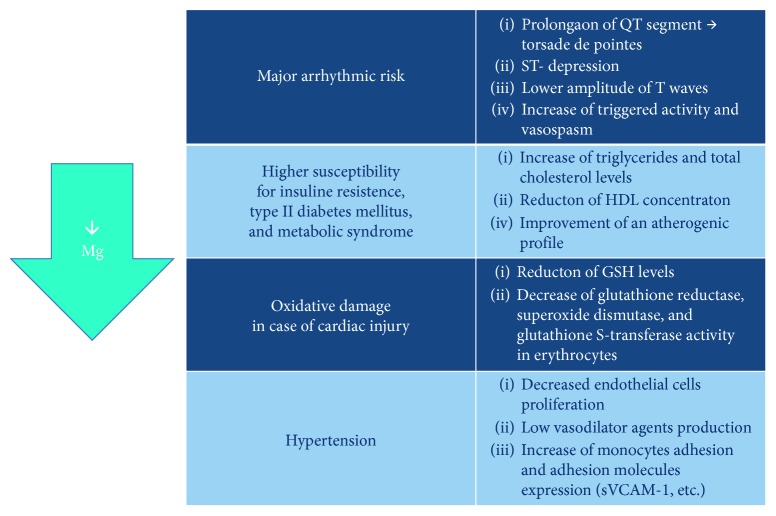
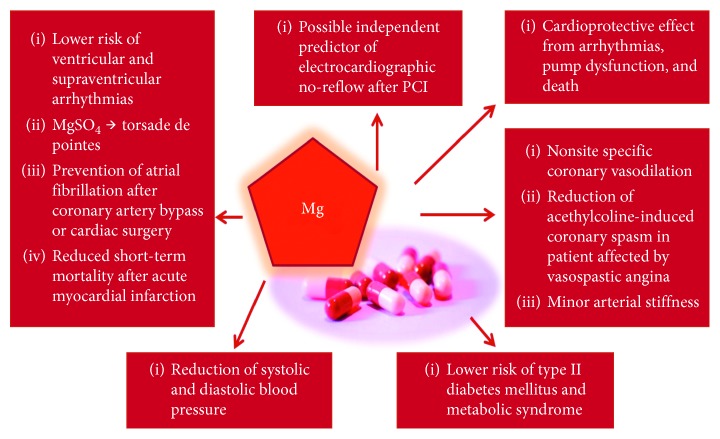
Nevertheless, the aforementioned studies have several limitations. First of all, serum Mg2+ does not unequivocally reflect the intracellular concentration of this ion, which better correlates with Mg2+ functions [101, 102], thus possibly affecting the results of the studies. Maybe, the evaluation of the intracellular amount of Mg2+ within lymphocytes and erythrocytes would be likely more accurate and would correlate better with intramyocardial Mg2+ [103]. Secondly, a possible limitation of the cited epidemiological studies is the use of indirect methods, such as food questionnaires, to determine Mg2+ intake; thus, it is not possible to discriminate among the effect of Mg2+ and residual effect derived from the intake of other microelements. Moreover, it is not possible to determine the amount of supplemented Mg2+ effectively absorbed and utilized. Another limitation is the different types of Mg2+ formulations used for the supplementation. The studies about the effect of Mg2+ intake on CV health use different Mg2+ formulations, both organic and inorganic, but it have been demonstrated that there are differences in the bioavailability among formulations. These differences could influence the results of the studies. Lastly, some cited meta-analyses present heterogeneity between the studies, possibly affecting the reliability of statistical analysis. These limitations suggest that new large prospective randomized trial is necessary to elucidate the association among Mg and CV health and to assess the benefits and the usefulness of Mg supplementation in the prevention and treatment of CVD (Figures 2 and 3).
Figure 2.
Detrimental consequences of Mg2+ deficiency on the cardiovascular health.
Figure 3.
Potential benefits and role of Mg2+ supplementation in the prevention and treatment of CVD.
4. Conclusions
The present review shows that a relationship between Mg2+ and cardiovascular health has been clearly demonstrated and underlines the possible pathophysiological mechanisms through which Mg2+ deficiency can promote the onset, progression, and maintenance of CVD. In fact, hypomagnesaemia influences negatively the CV health and is associated with an augmented incidence of hypertension, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, arrhythmias, and coronary artery disease. In consideration of the great public-health impact of CVD, the recognition of the detrimental effects of Mg2+ deficiency on CV health suggests the possible role of Mg2+ blood levels for the screening and prevention of CV risk factors and CVD and helps the identification of new therapeutical strategies for the management of CVD through Mg2+ supplementation. This concept is even more shareable if framed in a wider and more complete perspective, that aims to embrace in a global way any possible alteration or disease, even noncardiovascular ones, which can damage the heart health and whose treatment or correction can support specific cardiological therapies, from the standard one to the most innovative, in the pursuit of the healing and the well-being of the patients [104–106]. Considering the limitations of the present studies addressing a role of hypomagnesaemia on the development of CVD, large prospective randomized controlled trials are necessary to elucidate this multifaceted relationship, to assess the benefits of routine Mg2+ level assessment in cardiovascular patients and in the general population and the usefulness of Mg2+ supplementation in the prevention and treatment of CVD.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- 1.National Institutes of Health. Magnesium. Bethesda, Maryland, USA: National Institutes of Health; 2018. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Mg2+-HealthProfessional/ [Google Scholar]
- 2.Maguire M. E., Cowan J. A. Magnesium chemistry and biochemistry. Biometals. 2007;15(3):203–210. doi: 10.1023/A:1016058229972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Volpe S. L. Magnesium in disease prevention and overall health. Advances in Nutrition. 2013;4(3):378S–383S. doi: 10.3945/an.112.003483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gröber U., Schmidt J., Kisters K. Magnesium in prevention and therapy. Nutrients. 2015;7(9):8199–8226. doi: 10.3390/nu7095388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alfrey A. C., Miller N. L. Bone magnesium pools in uremia. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1973;52(12):3019–3027. doi: 10.1172/jci107500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Swaminathan R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clinical Biochemist Review. 2003;24:47–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Qu X., Jin F., Hao Y., et al. Magnesium and the risk of cardiovascular events: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS One. 2013;8(3) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057720.e57720 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fang X., Wang K., Han D., et al. Dietary magnesium intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMC Medicine. 2016;14(1):p. 210. doi: 10.1186/s12916-016-0742-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Del Gobbo L. C., Imamura F., Wu J. H., de Oliveira Otto M. C., Chiuve S. E., Mozaffarian D. Circulating and dietary magnesium and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2013;98(1):160–173. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.053132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shechter M. Magnesium and cardiovascular system. Magnesium Research. 2010;23:60–72. doi: 10.1684/mrh.2010.0202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Iseri L. T., Allen B. J., Ginkel M. L., Brodsky M. A. Ionic biology and ionic medicine in cardiac arrhythmias with particular reference to magnesium. American Heart Journal. 1992;123(5):1404–1409. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(92)91059-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mubagwa K., Gwanyanya A., Zakharov S., Macianskiene R. Regulation of cation channels in cardiac and smooth muscle cells by intracellular magnesium. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2007;458(1):73–89. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Williams B. A., Beatch G. N. Magnesium shifts voltage dependence of activation of delayed rectifier I(K) in Guinea pig ventricular myocytes. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 1997;272(3):H1292–H1301. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1997.272.3.h1292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rasmussen H. S., Thomsen P. E. B. The electrophysiological effects of intravenous magnesium on human sinus node, atrioventricular node, atrium, and ventricle. Clinical Cardiology. 1989;12(2):85–90. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960120204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Stiles M. K., Sanders P., Disney P., et al. Differential effects of intravenous magnesium on atrioventricular node conduction in supraventricular tachycardia. American Journal of Cardiology. 2007;100(8):1249–1253. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.05.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Satoh Y., Sugiyama A., Tamura K., Hashimoto K. Effect of magnesium sulfate on the haloperidol-induced QT prolongation assessed in the canine in vivo model under the monitoring of monophasic action potential. Japanese Circulation Journal. 2000;64(6):445–451. doi: 10.1253/jcj.64.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kaseda S., Gilmour R. F., Zipes D. P. Depressant effect of magnesium on early afterdepolarizations and triggered activity induced by cesium, quinidine, and 4-aminopyridine in canine cardiac Purkinje fibers. American Heart Journal. 1989;118(3):458–466. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(89)90258-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu J. Y., Lipsius S. L. Effects of extracellular Mg2+ on T- and L-type Ca2+ currents in single atrial myocytes. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 1990;259(6):H1842–H1850. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.6.h1842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sheehan J. P., Seelig M. S. Interactions of magnesium and potassium in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Magnesium. 1984;3(4–6):301–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Leor J., Kloner R. A. An experimental model examining the role of magnesium in the therapy of acute myocardial infarction. American Journal of Cardiology. 1995;75(17):1292–1293. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)80787-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Paravicini T. M., Chubanov V., Gudermann T. TRPM7: a unique channel involved in magnesium homeostasis. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 2012;44(8):1381–1384. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yamanaka R., Tabata S., Shindo Y., et al. Mitochondrial Mg2+ homeostasis decides cellular energy metabolism and vulnerability to stress. Scientific Reports. 2016;6(1) doi: 10.1038/srep30027.30027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fang X., Han H., Li M., et al. Dose-response relationship between dietary magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutrients. 2016;8(11):p. 739. doi: 10.3390/nu8110739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Guerrero-Romero F., Tamez-Perez H., González-González G., et al. Oral magnesium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic subjects with insulin resistance. A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Diabetes & Metabolism. 2004;30(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/s1262-3636(07)70116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gommers L. M. M., Hoenderop J. G. J., Bindels R. J. M., de Baaij J. H. F. Hypomagnesemia in type 2 diabetes: a vicious circle? Diabetes. 2016;65(1):3–13. doi: 10.2337/db15-1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Takaya J., Higashino H., Kobayashi Y. Intracellular magnesium and insulin resistance. Magnesium Research. 2004;17(2):126–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pham P.-C. T., Pham P.-M. T., Pham S. V., Miller J. M., Pham P.-T. T. Hypomagnesemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2007;2(2):366–373. doi: 10.2215/cjn.02960906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mazur A., Maier J. A. M., Rock E., Gueux E., Nowacki W., Rayssiguier Y. Magnesium and the inflammatory response: potential physiopathological implications. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2007;458(1):48–56. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.03.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Barbagallo M., Dominguez L. J., Galioto A., et al. Role of magnesium in insulin action, diabetes and cardio-metabolic syndrome X. Molecular Aspects of Medicine. 2003;24(1-3):39–52. doi: 10.1016/s0098-2997(02)00090-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.He K., Liu K., Daviglus M. L., et al. Magnesium intake and incidence of metabolic syndrome among young adults. Circulation. 2006;113(13):1675–1682. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.105.588327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Blache D., Devaux S., Joubert O., et al. Long-term moderate magnesium-deficient diet shows relationships between blood pressure, inflammation and oxidant stress defense in aging rats. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2006;41(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Freedman A. M., Atrakchi A. H., Cassidy M. M., Weglicki W. B. Magnesium deficiency-induced cardiomyopathy: protection by vitamin E. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1990;170(3):1102–1106. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90506-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Freedman A. M., Cassidy M. M., Weglicki W. B. Magnesium-deficient myocardium demonstrates an increased susceptibility to an in vivo oxidative stress. Magnesium Research. 1991;4(3-4):185–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.King D. E. Inflammation and elevation of C-reactive protein: does magnesium play a key role? Magnesium Research. 2009;22(2):57–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rayssiguier Y., Gueux E., Bussière L., Durlach J., Mazur A. Dietary magnesium affects susceptibility of lipoproteins and tissues to peroxidation in rats. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 1993;12(2):133–137. doi: 10.1080/07315724.1993.10718293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shechter M., Merz C. N. B., Paul-Labrador M., et al. Oral magnesium supplementation inhibits platelet-dependent thrombosis in patients with coronary artery disease. American Journal of Cardiology. 1999;84(2):152–156. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)00225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hwang D. L., Yen C. F., Nadler J. L. Effect of extracellular magnesium on platelet activation and intracellular calcium mobilization. American Journal of Hypertension. 1992;5(10):700–706. doi: 10.1093/ajh/5.10.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rukshin V., Shah P. K., Cercek B., Finkelstein A., Tsang V., Kaul S. Comparative antithrombotic effects of magnesium sulfate and the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors tirofiban and eptifibatide in a canine model of stent thrombosis. Circulation. 2002;105(16):1970–1975. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000014612.88433.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gawaz M., Ott I., Reininger A., Neumann F.-J. Effects of magnesium on platelet aggregation and adhesion. Magnesium modulates surface expression of glycoproteins on platelets in vitro and ex vivo. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 1994;72(6):912–918. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1648983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rukshin V., Santos R., Gheorghiu M., et al. A prospective, nonrandomized, open-labeled pilot study investigating the use of magnesium in patients undergoing nonacute percutaneous coronary intervention with stent implantation. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2003;8(3):193–200. doi: 10.1177/107424840300800304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fedele F., Severino P., Bruno N., et al. Role of ion channels in coronary microcirculation: a review of the literature. Future Cardiology. 2013;9(6):897–905. doi: 10.2217/fca.13.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fedele F., Mancone M., Chilian W. M., et al. Role of genetic polymorphisms of ion channels in the pathophysiology of coronary microvascular dysfunction and ischemic heart disease. Basic Research in Cardiology. 2013;108(6):p. 387. doi: 10.1007/s00395-013-0387-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Severino P., D’Amato A., Netti L., et al. Diabetes mellitus and ischemic heart disease: the role of ion channels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018;19(3):p. 802. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Barbagallo M., Dominguez L. J., Resnick L. M. Magnesium metabolism in hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. American Journal of Therapeutics. 2007;14(4):375–385. doi: 10.1097/01.mjt.0000209676.91582.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Olatunji L. A., Soladoye A. O. Increased magnesium intake prevents hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance and reduces lipid peroxidation in fructose-fed rats. Pathophysiology. 2007;14(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2006.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Garcia L. A., Dejong S. C., Martin S. M., Smith R. S., Buettner G. R., Kerber R. E. Magnesium reduces free radicals in an in vivo coronary occlusion-reperfusion model. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 1998;32(2):536–539. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rock E., Astier C., Lab C., et al. Magnesium deficiency in rats induces a rise in plasma nitric oxide. Magnesium Reseach. 1995;8(3):237–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dickens B. F., Weglicki W. B., Li Y.-S., Mak I. T. Magnesium deficiency in vitro enhances free radical-induced intracellular oxidation and cytotoxicity in endothelial cells. FEBS Letters. 1992;311(3):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wiles M. E., Wagner T. L., Weglicki W. B. Effect of acute magnesium deficiency (MgD) on aortic endothelial cell (EC) oxidant production. Life Sciences. 1996;60(3):221–236. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(96)00619-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kramer J. H., Mišík V., Weglicki W. B. Magnesium-deficiency potentiates free radical production associated with postischemic injury to rat hearts: vitamin E affords protection. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 1994;16(6):713–723. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(94)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kramer J. H., Mak I. T., Phillips T. M., Weglicki W. B. Dietary magnesium intake influences circulating pro-inflammatory neuropeptide levels and loss of myocardial tolerance to postischemic stress. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2003;228(6):665–673. doi: 10.1177/153537020322800604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bernardini D., Nasulewic A., Mazur A., Maier J. A. M. Magnesium and microvascular endothelial cells: a role in inflammation and angiogenesis. Frontiers in Bioscience. 2005;10(1–3):1177–1182. doi: 10.2741/1610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mylonas C., Kouretas D. Lipid peroxidation and tissue damage. In Vivo. 1999;13(3):295–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Morrill G. A., Gupta R. K., Kostellow A. B., et al. Mg2+ modulates membrane lipids in vascular smooth muscle: a link to atherogenesis. FEBS Letters. 1997;408(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)00420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bussière L., Mazur A., Gueux E., Nowacki W., Rayssiguier Y. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins from magnesium-deficient rats are more susceptible to oxidation by cells and promote proliferation of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Magnesium Research. 1995;8(2):151–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gueux E., Azais-Braesco V., Bussière L., Grolier P., Mazur A., Rayssiguier Y. Effect of magnesium deficiency on triacylglycerol-rich lipoprotein and tissue susceptibility to peroxidation in relation to vitamin E content. British Journal of Nutrition. 1995;74(6):849–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Altura B., Gebrewold A., Altura B., Brautbar N. Magnesium depletion impairs myocardial carbohydrate and lipid metabolism and cardiac bioenergetics and raises myocardial calcium content in-vivo: relationship to etiology of cardiac diseases. International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 1996;40(6):1183–1190. doi: 10.1080/15216549600201823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sontia B., Touyz R. M. Magnesium transport in hypertension. Pathophysiology. 2007;14(3-4):205–211. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2007.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Maier J., Bernardini D., Rayssiguier Y., Mazur A. High concentrations of magnesium modulate vascular endothelial cell behaviour in vitro. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease. 2004;1689(1):6–12. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(04)00025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Pearson P. J., Evora P. R. B., Seccombe J. F., Schaff H. V. Hypomagnesemia inhibits nitric oxide release from coronary endothelium: protective role of magnesium infusion after cardiac operations. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 1998;65(4):967–972. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(98)00020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kolte D., Vijayaraghavan K., Khera S., Sica D. A., Frishman W. H. Role of magnesium in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiology in Review. 2014;22(4):182–192. doi: 10.1097/crd.0000000000000003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Laurant P., Kantelip J. P., Berthelot A. Dietary magnesium supplementation modifies blood pressure and cardiovascular function in mineralocorticoid-salt hypertensive rats but not in normotensive rats. Journal of Nutrition. 1995;125(4):830–841. doi: 10.1093/jn/125.4.830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Maier J., Malpuech-Brugère C., Zimowska W., Rayssiguier Y., Mazur A. Low magnesium promotes endothelial cell dysfunction: implications for atherosclerosis, inflammation and thrombosis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease. 2004;1689(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(04)00006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Maier J. A., Statuto M., Ragnotti G. Endogenous interleukin 1 alpha must be transported to the nucleus to exert its activity in human endothelial cells. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 1994;14(3):1845–1851. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Nilsson I., Hoffmann I. Progress in Cell Cycle Research. Vol. 4. Boston, MA, USA: Springer; 2000. Cell cycle regulation by the Cdc25 phosphatase family; pp. 107–114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Chacko S. A., Song Y., Nathan L., et al. Relations of dietary magnesium intake to biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in an ethnically diverse cohort of postmenopausal women. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(2):304–310. doi: 10.2337/dc09-1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zheltova A. A., Kharitonova M. V., Iezhitsa I. N., Spasov A. A. Magnesium deficiency and oxidative stress: an update. BioMedicine. 2016;6(4):8–14. doi: 10.7603/s40681-016-0020-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hans C. P., Chaudhary D. P., Bansal D. D. Magnesium deficiency increases oxidative stress in rats. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 2002;40(11):1275–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kuzniar A., Mitura P., Kurys P., Szymonik-Lesiuk S., Florianczyk B., Stryjecka-Zimmer M. The influence of hypomagnesemia on erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme defence system in mice. Biometals. 2003;16(2):349–357. doi: 10.1023/a:1020632505289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Madden J. A., Willems W. J., Smith G. A., Mueller R. A. Sodium kinetics and membrane potential in aorta of magnesium-deficient rats. Magnesium. 1984;3(2):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Davis W. H., Ziady F. The effect of oral magnesium chloride therapy on the QTc and QUc intervals of the electrocardiogram. South African Medical Journal. 1978;53(15):591–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Salaminia S., Sayehmiri F., Angha P., Sayehmiri K., Motedayen M. Evaluating the effect of magnesium supplementation and cardiac arrhythmias after acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders. 2018;18(1):p. 129. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0857-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Horner S. M. Efficacy of intravenous magnesium in acute myocardial infarction in reducing arrhythmias and mortality. Meta-analysis of magnesium in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1992;86(3):774–779. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.3.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Shiga T., Wajima Z. i., Inoue T., Ogawa R. Magnesium prophylaxis for arrhythmias after cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. American Journal of Medicine. 2004;117(5):325–333. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2004.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Alghamdi A. A., Al-Radi O. O., Latter D. A. Intravenous magnesium for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Cardiac Surgery. 2005;20(3):293–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8191.2005.200447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Burgess D. C., Kilborn M. J., Keech A. C. Interventions for prevention of post-operative atrial fibrillation and its complications after cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis. European Heart Journal. 2006;27(23):2846–2857. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehl272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Miller S., Crystal E., Garfinkle M., Lau C., Lashevsky I., Connolly S. J. Effects of magnesium on atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis. Heart. 2005;91(5):618–623. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2004.033811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Khan A. M., Lubitz S. A., Sullivan L. M., et al. Low serum magnesium and the development of atrial fibrillation in the community: the Framingham heart study. Circulation. 2013;127(1):33–38. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.111.082511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Raghu C., Peddeswara Rao P., Seshagiri Rao D. Protective effect of intravenous magnesium in acute myocardial infarction following thrombolytic therapy. International Journal of Cardiology. 1999;71(3):209–215. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5273(99)00125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Priori S. G., Blomstrom-Lundqvist C., Mazzanti A., et al. 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Europace. 2015;17(11):1601–1687. doi: 10.1093/europace/euv319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Dibaba D. T., Xun P., Song Y., Rosanoff A., Shechter M., He K. The effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure in individuals with insulin resistance, prediabetes, or noncommunicable chronic diseases: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2017;106(3):921–929. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.117.155291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Sarrafzadegan N., Khosravi-Boroujeni H., Lotfizadeh M., Pourmogaddas A., Salehi-Abargouei A. Magnesium status and the metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition. 2016;32(4):409–417. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Mirmiran P., Shab-Bidar S., Hosseini-Esfahani F., Asghari G., Hosseinpour-Niazi S., Azizi F. Magnesium intake and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adults: tehran lipid and glucose study. Public Health Nutrition. 2012;15(4):693–701. doi: 10.1017/s1368980011002941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Bain L. K. M., Myint P. K., Jennings A., et al. The relationship between dietary magnesium intake, stroke and its major risk factors, blood pressure and cholesterol, in the EPIC-Norfolk cohort. International Journal of Cardiology. 2015;196:108–114. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.05.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kharb S., Singh V. Magnesium deficiency potentiates free radical production associated with myocardial infarction. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India. 2000;48(5):484–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Guo H., Cheng J., Lee J.-D., Ueda T., Shan J., Wang J. Relationship between the degree of intracellular magnesium deficiency and the frequency of chest pain in women with variant angina. Herz. 2004;29(3):299–303. doi: 10.1007/s00059-003-2471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Teragawa H., Kato M., Yamagata T., Matsuura H., Kajiyama G. The preventive effect of magnesium on coronary spasm in patients with vasospastic angina. Chest. 2000;118(6):1690–1695. doi: 10.1378/chest.118.6.1690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Turlapaty P., Altura B. Magnesium deficiency produces spasms of coronary arteries: relationship to etiology of sudden death ischemic heart disease. Science. 1980;208(4440):198–200. doi: 10.1126/science.7361117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Chadda K. D., Schultz N. A. Magnesium deficiency and coronary vasospasm: role in sudden cardiac death. Magnesium. 1982;1:86–94. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Yanagisawa-Miwa A., Ito H., Sugimoto T. Effects of insulin on vasoconstriction induced by thromboxane A2 in porcine coronary artery. Circulation. 1990;81(5):1654–1659. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.5.1654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Cohn J. N., Quyyumi A. A., Hollenberg N. K., Jamerson K. A. Surrogate markers for cardiovascular disease: functional markers. Circulation. 2004;109(25):4–31. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000133442.99186.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Joris P. J., Plat J., Bakker S. J., Mensink R. P. Long-term magnesium supplementation improves arterial stiffness in overweight and obese adults: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2016;103(5):1260–1266. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.116.131466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Gyamlani G., Parikh C., Kulkarni A. G. Benefits of magnesium in acute myocardial infarction: timing is crucial. American Heart Journal. 2000;139(4):p. 703. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(00)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.An G., Du Z., Meng X., et al. Association between low serum magnesium level and major adverse cardiac events in patients treated with drug-eluting stents for acute myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 2014;9(6) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098971.e98971 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Yuksel M., Isik T., Tanboga I. H., et al. The importance of magnesium values in patients with STEMI admitted to the emergency department. Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis. 2017;23(4):329–335. doi: 10.1177/1076029616658119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Çiçek G., Açikgoz S. K., Yayla Ç., Kundi H., İleri M. Magnesium as a predictor of acute stent thrombosis in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction who underwent primary angioplasty. Coronary Artery Disease. 2016;27(1):47–51. doi: 10.1097/mca.0000000000000318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Basoli C., Cametti A., Ginnari F., Satriani P., Severino P. Hemocompatibility of stent materials: alterations in electrical parameters of erythrocyte membranes. Vascular Health and Risk Management. 2012;8:197–204. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S28979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Antman E. M. Early administration of intravenous magnesium to high-risk patients with acute myocardial infarction in the magnesium in coronaries (magic) trial: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360(9341):1189–1196. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)11278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Vassalle C., Battaglia D., Vannucci A., et al. Low magnesium is not a significant predictor of hard events in acute myocardial infarction. BBA Clinical. 2016;5:130–133. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Peacock J. M., Ohira T., Post W., Sotoodehnia N., Rosamond W., Folsom A. R. Serum magnesium and risk of sudden cardiac death in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. American Heart Journal. 2010;160(3):464–470. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2010.06.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Haigney M. C. P., Silver B., Tanglao E., et al. Noninvasive measurement of tissue magnesium and correlation with cardiac levels. Circulation. 1995;92(8):2190–2197. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.8.2190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Shah S. A., Clyne C. A., Henyan N., et al. The impact of magnesium sulfate on serum magnesium concentrations and intracellular electrolyte concentrations among patients undergoing radio frequency catheter ablation. Connecticut Medicine. 2008;72(5):261–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Elin R. J. Status of the determination of magnesium in mononuclear blood cells in humans. Magnesium. 1988;7:300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Fedele F., Severino P., Calcagno S., Mancone M. Heart failure: TNM-like classification. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2014;63(19):1959–1960. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Nieminen M. S., Buerke M., Parissis J., et al. Pharmaco-economics of levosimendan in cardiology: a European perspective. International Journal of Cardiology. 2015;199:337–341. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.07.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Fedele F., Mancone M., Adamo F., Severino P. Heart failure with preserved, mid-range, and reduced ejection fraction: the misleading definition of the new guidelines. Cardiology in Review. 2017;25(1):4–5. doi: 10.1097/crd.0000000000000131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]