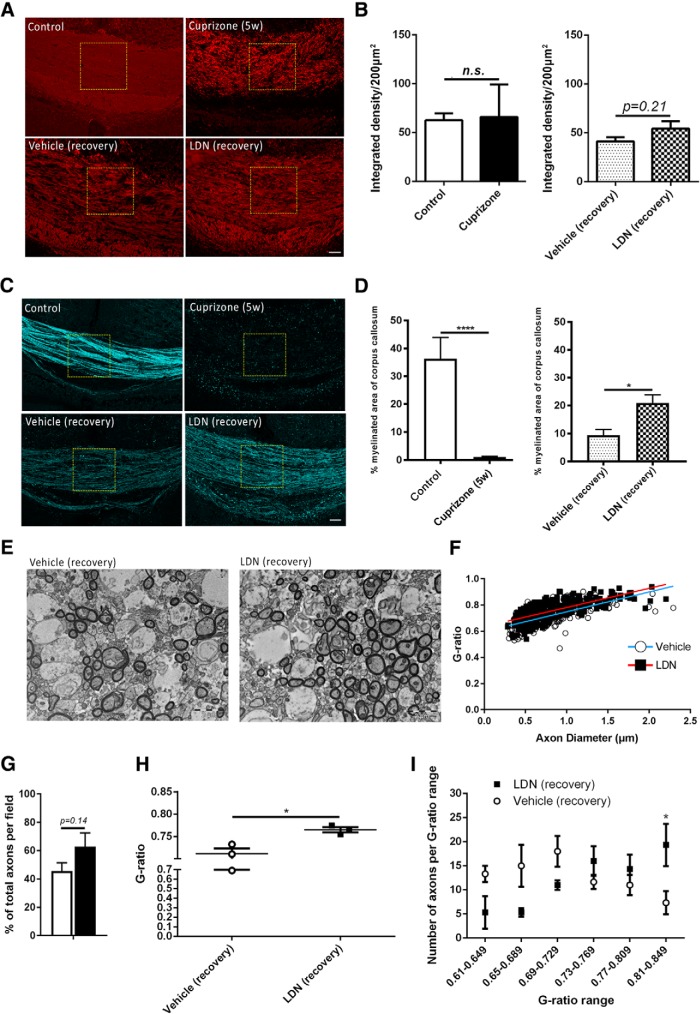
Figure 1.
Inhibiting BMP4/BMPRI signaling following demyelination promotes remyelination in vivo. A, Representative MBP IHC images showing myelin protein in the caudal corpus callosi of healthy control (control) and 5 week cuprizone-challenged mice (Cuprizone 5w, top panels); and 5 week cuprizone-challenged mice followed by 1 week of recovery with vehicle (Vehicle recovery) or LDN-193189 (LDN recovery) infusion (bottom panels). B, Quantification of integrated density of MBP immunostaining. No significant differences were observed between control and cuprizone-fed mice, or between vehicle- and LDN-infused mice. C, Representative SCoRe images to identify myelin in the caudal corpus callosi of healthy control (control) and 5 week cuprizone-challenged mice (Cuprizone (5w), top panels); and 5 week cuprizone-challenged mice followed by 1 week of recovery with vehicle (Vehicle recovery) or LDN-193189 (LDN recovery) infusion (bottom panels). D, Quantification of myelinated area (SCoRe signal that is pixelated) as a percentage of the total area measured. The SCoRe signal is significantly reduced in 5 week cuprizone-challenged mice [Cuprizone (5w) compared with healthy control (Ctrl) mice, confirming demyelination (B)]. LDN-193189-infused mice display a significantly greater SCoRe signal than the vehicle-infused control group (C), indicating greater remyelination. E, TEM cross-sectional images of caudal corpus callosum axons of 5 week cuprizone-challenged mice followed by 1 week of recovery with vehicle (Vehicle recovery) or LDN-193189 (LDN recovery) infusion. F, A scatterplot comparison of g-ratio distribution relative to axonal diameter. LDN-infused mice had a significantly higher average g-ratio than vehicle-infused controls (p = 0.016). G, Proportion of total myelinated axons in the caudal corpus callosum of vehicle- and LDN-infused mice following 5 weeks of cuprizone administration. A trend, but a nonsignificant increase, was observed in LDN-infused mice compared with vehicle controls. H, The average g-ratio of axons in the caudal corpus callosum of vehicle- and LDN-infused mice following 5 weeks of cuprizone treatment. Mice treated with LDN-193189 after 5 weeks of cuprizone had more thinly myelinated axons (high g-ratio) in the corpus callosum compared with vehicle-infused mice. I, Number of axons in the corresponding g-ratio range for vehicle- versus LDN-infused mice following 5 weeks of cuprizone treatment. EM analysis indicated a higher number of axons with thinner myelin in the LDN-treated group, indicating greater remyelination (N = 4-6 animals/group for SCoRe; N = 3 animals/group for EM). *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001. Scale bars: SCoRe images, 50 µm; TEM images, 2 µm.