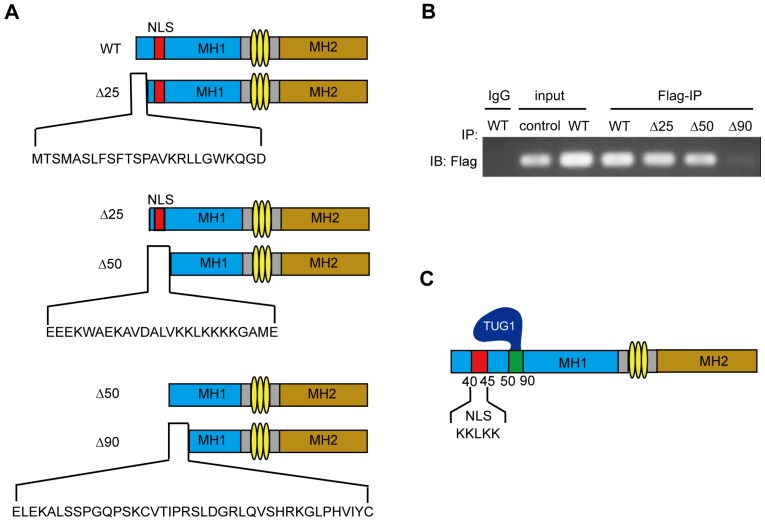
Figure 5.
The main domain of Smad5 interacting with TUG1 is near to NLS of Smad5. (A)The schematic illustration of Smad5 deletion constructs. WT: wild-type Smad5, ∆25: ∆25 deletion constructs, ∆50: ∆50 deletion constructs, ∆90: ∆90 deletion constructs. (B) RIP assay to detect the interaction between TUG1 and the Smad5 deletion constructs. IgG: negative control; Input: positive control; Flag-IP (Anti-flag immunoprecipitation): PCR detection of the indicated RNAs retrieved by Flag-specific antibody within BM-MSCs. Control: BM-MSCs, WT: BM-MSCs transfected with flag-tagged wild-type Smad5, ∆25: BM-MSCs transfected with the flag-tagged ∆25 deletion constructs, ∆50: BM-MSCs transfected with the flag-tagged ∆50 deletion constructs, ∆90: BM-MSCs transfected with the flag-tagged ∆90 deletion constructs. (C) The schematic diagram of TUG1 bound to Smad5. Abbreviations: Flag-IP: Anti-flag immunoprecipitation, NLS: nuclear localization sequence, IgG: immunoglobulin G, WT: wild type.