Abstract
Distinct macrophage subsets populate the developing embryo and fetus in distinct waves. However little is known about the functional differences between in utero macrophage populations or how they might contribute to fetal and neonatal immunity. Here we tested the innate immune response of mouse macrophages derived from the embryonic yolk sac and from fetal liver. When isolated from liver or lung, CD11bHI fetal liver derived macrophages responded to the TLR4 agonist LPS by expressing and releasing inflammatory cytokines. However F4/80HI macrophages from the yolk sac did not respond to LPS treatment. While differences in TLR4 expression did not appear to explain these data, F4/80HI macrophages had much lower NLRP3 inflammasome expression compared to CD11bHI macrophages. Gene expression profiling also demonstrated LPS-induced expression of inflammatory genes in CD11bHI macrophages, but not in F4/80HI cells. Genes expressed in LPS-treated CD11bHI macrophages were more likely to contain predicted NF-κB binding sites in their promoter regions. Our data show that CD11bHI macrophages derived from fetal liver are the major pro-inflammatory cells in the developing fetus. These findings could have important implications in better understanding the fetal inflammatory response and the unique features of neonatal immunity.
Subject terms: Alveolar macrophages, Inflammasome
Introduction
Macrophages are key components of the innate immune system. Ubiquitous throughout the body, macrophages defend against harmful microbes, remove apoptotic cells, and promote tissue repair after injury1. Upon sensing microbial products, activated macrophages release inflammatory cytokines and chemokines that recruit additional inflammatory cells and cause both local and systemic inflammation. A robust inflammatory response by macrophages can also lead to significant tissue injury2,3. Dysregulation of macrophage activation and inflammation contributes to multiple diseases, including atherosclerosis, diabetes, and cancer4–6. When playing a trophic role, macrophages can drive tissue fibrosis and tumor growth and metastases7–9. Therefore understanding macrophages and their diverse functions could generate new strategies for combatting human disease.
Tissue macrophages are heterogeneous. For example, the lung contains alveolar macrophages, interstitial macrophages, patrolling monocytes, and airway dendritic cells that originate from macrophage/monocyte precursors. The macrophage populations in various tissues appear to arise from unique progenitors during different stages of development. Macrophages populate the embryo and fetus in three successive waves10,11. In mice, Csf1r+ erythromyeloid progenitors within the yolk sac endothelium give rise to F4/80HI macrophages throughout the embryo beginning at embryonic day 7 (E7). At E9, Myb+ precursors from the yolk sac establish a second site of hematopoiesis within the embryonic liver. From the liver, a second wave of CD11bHI macrophages appear around E12, differentiate into tissue-specific macrophages, and can persist into adulthood. In the lung, these CD11bHI cells differentiate into alveolar macrophages through GM-CSF and TGFβ signaling12,13. A third wave occurs after definitive hematopoiesis moves to the bone marrow, partially replacing embryonic yolk sac derived cells with bone marrow derived macrophages via the circulation14. While recent publications have shed new light on the origins of macrophage populations, less is known about the functional differences each population plays in immunity.
The fetal and newborn periods present unique immunological challenges. The maternal-fetal immune systems must maintain a tolerant state to prevent attack of the developing fetus by the maternal immune system and also fetal response against maternal antigens15. Persistence of tolerance after birth may allow colonization of the newborn with beneficial microbiota and minimize overzealous responses to ingested food antigens16,17. The newborn, however, must also be prepared at birth to fend off myriads of microbial pathogens suddenly encountered in the ex utero environment. This unique period in immune development renders newborns susceptible to infection by opportunistic pathogens18. In addition, an overzealous immune response in the newborn period, especially in infants born preterm, leads to serious pathology, chronic developmental abnormalities, and lifelong sequelae.
In infants born before 30 wk gestation, macrophage-mediated lung inflammation leads to bronchopulmonary dysplasia19–23. A chronic developmental lung disease, bronchopulmonary dysplasia is the most common serious complication of prematurity. In response to mechanical ventilation, infection, and high oxygen exposure, activated lung macrophages stimulate inflammation that prevents normal postnatal airway branching and alveolar formation24,25. Both patient and animal studies have implicated macrophage-derived IL-1β as a key cytokine that drives inflammation, injury, and abnormal structural development22,26,27. IL-1β release requires both NF-κB mediated Il1b transcriptional activation and processing of the pro-IL-1β peptide by inflammasome associated caspase activity. While multiple inflammasome versions exist, the NLRP3-ASC-CASP1 complex is required for lung inflammation and injury in mouse models22,27.
Inflammasome function and IL-1β release in the lung is developmentally regulated. Inflammatory stimuli and macrophage activation only impact lung development during later stages of embryonic development22,28. The molecular and cellular mechanisms producing this developmental window of susceptibility however are not clear. Here we use flow sorting techniques to isolate macrophage populations from embryonic mice and show that inflammasome function and IL-1β release is specifically restricted to the population of macrophages derived from the fetal liver. By identifying the cell populations that produce tissue inflammation and injury within the developing embryo, our findings will lead to more targeting therapeutic approaches for combatting neonatal inflammatory diseases.
Material and Methods
Approvals
Animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at University of California, San Diego. All experimental methods were carried out in accordance with the rules, regulations, and guidelines established by the University of California, San Diego Institutional Animal Care and Use Program.
Mouse strains
C57BL/6 mice were obtained from Harlan Laboratories. LysM-Cre-NLRP3L351P mice were developed and described previously29. The morning of plug identification was defined as embryonic day 0 (E0). Embryos were harvested at E13, E15 or E18. Dissections were performed in cold PBS.
Fetal macrophage isolation
Fetal organs (lung, liver, brain) and yolk sacs were collected in cold PBS containing EDTA (2 mM) and fetal bovine serum (FBS-2%). Tissues were homogenized and enzymatically digested with collagenase IV (2 mg/ml) for 15 min. red blood cells were lysed with ACK buffer (Life Technologies) for 5 min. Cells suspensions were passed through a 70-μm cell strainer.
Flow cytometry and cell sorting
Isolated single cell suspensions were first incubated with FC block and Zombie NIR or Aqua live/dead stain (Biolegend) for 15 min in PBS. Conjugated antibodies in staining buffer (2% FBS + 2%EDTA in PBS) were then added for an additional 30 min incubation. For intracellular staining, cells were fixed using IC fixation and permeabilization buffers according to manufacturer’s recommendation (eBioscience). The following antibodies were used for flow sorting: CD45-FITC, CD64-Percp-Cy5.5, F4/80-PE and CD11b-V450. For flow cytometry analysis and intracellular staining, the following additional antibodies were used: CD68-AF647, pro-IL1β-PE-Cy7, TNF-APC-Cy7, NLRP3-APC and CD45-V500.
Flow cytometry measurements were performed on a BD Canto II (BD Biosciences). Sorting was performed on a FACS Aria cell sorter. The following gating strategy was used: doublets were excluded based on forward scatter-A against forward scatter-W, followed by side scatter-A against side scatter-W. Live cells were selected using Zombie LIVE/DEAD stain. CD45+ and CD64+ cells were then selected and further separated based on F4/80 and CD11b expression. Yolk sac derived macrophages express higher F4/80 and lower CD11b levels while fetal monocytes express lower F4/80 and higher CD11b levels. Sorted cells were cultured in suspension in DMEM with 10% FBS with or without gel purified lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from 055:B5 E. coli (Sigma L2637). This low-protein preparation of LPS does not appear to activate other Toll-Like Receptors30,31.
RNA isolation and real-time PCR measurement
Cells were homogenized in TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and RNA was isolated using Direct-Zol RNA miniprep kit (Zymo Research). After RNA isolation, cDNA was synthesized using first-strand cDNA synthesis kit (Invitrogen). Real-time PCR was performed in CFX96 thermocycler (Bio-Rad) using unlabeled oligonucleotides (IDT) and SYBR Green (Bio-Rad). Gene expression data was presented using the 2−ΔCt method, using TBP as reference gene. The sequences of qPCR primers used are as followed: Tbp: 5′-ACA TCT CAG CAA CCC ACA CA and 5′-CTG CTG TGG CAG GAG TGA TA; Il1b: 5′-GAC CTG TTC TTT GAA GTT GAC GGA CC and 5′-CAA TGA GTG ATA CTG CCT GCC TGA AG; Il6: 5′-ACA ACC ACG GCC TTC CCT AC and 5′-ACA ATC AGA ATT GCC ATT GCA C; Nlrp3: 5′-GAC CAT CGG CCG GAC TAA AA and 5′-CTT GCA CAC TGG TGG GTT TG; Pf4: 5′-CCG AAG AAA GCG ATG GAG ATC T and 5′-CCA GGC AAA TTT TCC TCC CA; Igf1: 5′-GTG AGC CAA AGA CAC ACC CA and 5′-.ACC TCT GAT TTT CCG AGT TGC.
ELISA
For measurements of IL-1β and IL-6 in culture supernatants, we used the Ready-Set-GO ELISAs kits according to manufacturer’s protocol (eBioscience).
Monocyte depletion
For Ly6C+ monocyte depletion, pregnant mice received 3 intraperitoneal injections of anti-Ly6G/Ly6C (clone RB6-8C5, Bioxcell) antibody or the isotype control (rat IgG2b anti-KLH, clone LTF-2, Bioxcell), starting at E12. For the first injection, mice received 1 mg of antibodies, then 2 mg for the second and third injections. Embryos were collected at E15.
Gene expression analysis with Nanostring nCounter technology
The nCounter analysis system (NanoString Technologies) was used to assess gene expression by CD11b and F4/80 macrophages. RNA from sorted cells was amplified then hybridized with the Mouse Myeloid Innate Immunity Panel v2 (734 immunology-related mouse genes + 20 internal reference controls) according to manufacturer’s protocol. Processing was performed in the UCSD Stem Cell Genomics Core at the Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine. Data analysis was performed using nSolver 4.0 according to NanoString guidelines. Raw mRNA counts were normalized to account for hybridization efficiency, background noise, and sample content. Genes with mean counts less than 20 were excluded, and differential expression of remaining genes was calculated and represented on a volcano plot, using a nonparametric t-test and correction for multiple testing using the BH false discovery rate (FDR). Mouse single site analysis of conserved transcription factor (TF) binding sites in the list of differentially expressed genes was performed using oPOSSUM 3.0 (http://opossum.cisreg.ca/oPOSSUM3/), using JASPAR core profile and the oPOSSUM gene database as background.
Results
CD11bHI fetal lung macrophages are the primary sources of IL-1β and IL-6
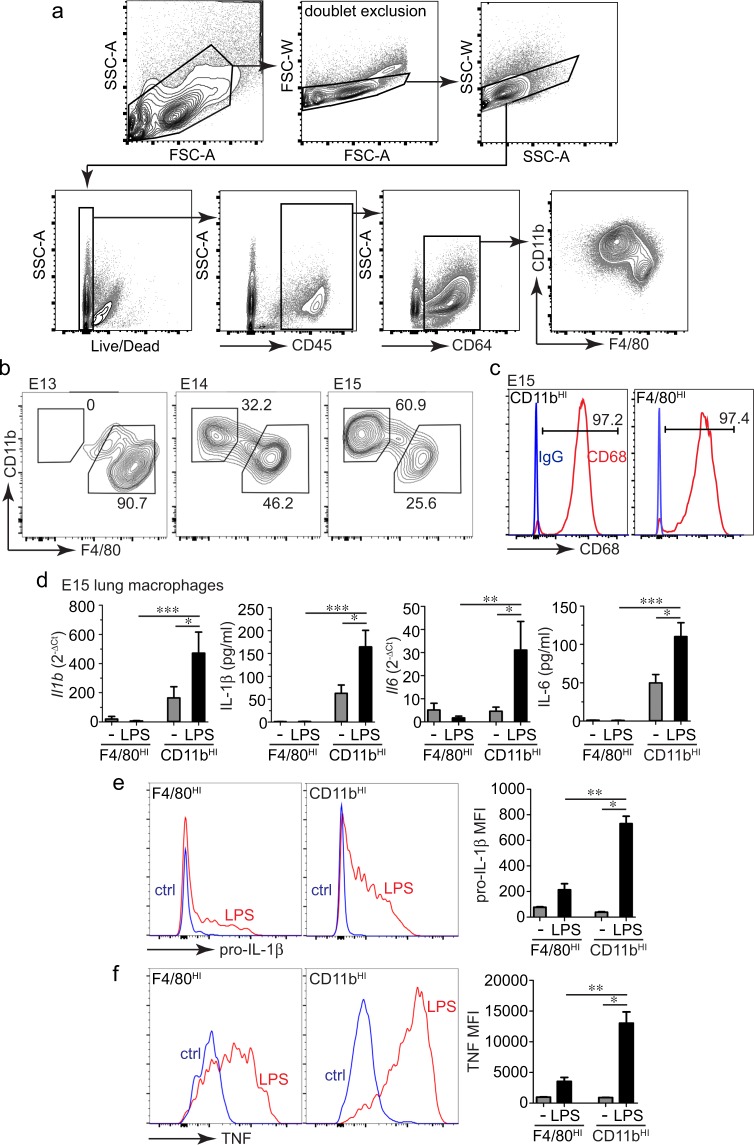
Fetal lung inflammation following macrophage activation increases during the later stages of development. Here we tested if this temporal change was due to inflammatory differentiation of resident tissue macrophages or appearance of new pro-inflammatory cells later in development. Using a flow sorting approach (Fig. 1a), we first demonstrated the timing of when different macrophage populations appeared in the developing mouse lung (Fig. 1b). The E13 lung contained primarily F4/80HI/CD11bLO (F4/80HI) macrophages (with macrophages defined as CD45+/CD64+). These F4/80HI macrophages are derived from myeloid precursor cells in the embryonic yolk sac. Beginning at E14, F4/80LO/CD11bHI (CD11bHI) macrophages appeared, derived from fetal liver monocytes. The percentage of CD11bHI macrophages increased further at E15. Both CD11bHI and F4/80HI cells expressed the macrophage marker CD68 (Fig. 1c).
Figure 1.
Fetal lung macrophages have differential responses to LPS. (a) Gating strategy used to isolate live, CD45+, CD64+ fetal macrophage populations. (b) FACS analysis of E13, E14, and E15 mouse lung macrophages (CD45+, CD64+) identified two different macrophage populations beginning at E14 based on relative CD11b and F4/80 expression. Percentage of CD45+, CD64+ cells in each population indicated. (c) Both CD11bHI and F4/80HI populations expressed the macrophage marker CD68 (red). Isotype control IgG staining is included as a control (blue), and the percentage of cells expressing CD68 is indicated. (d) Using the differential relative expression of CD11b and F4/80, two different macrophage populations were sorted and collected from E15 mouse lungs. After sorting, cells were cultured in suspension under control conditions or in the presence of E. coli LPS (O55:B5, gel-purified, 250 ng/ml). After two hours, cells were harvested by centrifugation and solubilized in TRIzol. Media was collected for ELISA. Il1b and Il6 mRNA was measured by real time PCR; IL-1β and IL-6 in the media was measured by ELISA. Compared to F4/80HI macrophages, CD11bHI macrophages expressed higher levels of cytokines both under basal conditions and following LPS treatment (+/− s.e.m.; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; n = 5–8). (e,f) Measurement of IL-1β and TNF expression in fetal lung macrophages by intracellular immunostaining and FACS. Single cell suspensions from E15 mouse lungs were treated with LPS for 2 h followed by fixation, staining, and FACS. LPS induced higher IL-1β and TNF expression in CD11bHI macrophages compared to F4/80HI macrophages (+/− s.e.m.; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, n = 3).
To test if yolk sac F4/80HI and fetal liver derived CD11bHI lung macrophage populations had distinct functional properties, we sorted both macrophage populations from E15 lungs and stimulated them with the TLR4 agonist LPS (gel purified from E. coli, O55:B5). Importantly, freshly sorted cells were kept in suspension and treated with LPS immediately upon sorting to reduce potential phenotypic changes with cell culture. LPS increased both Il1b and Il6 mRNA expression and IL-1β and IL-6 protein release in CD11bHI macrophages (Fig. 1d). F4/80HI macrophages expressed very low cytokine mRNA levels and did not release detectable amounts of cytokine peptides either under control conditions or upon LPS treatment. We also measured intracellular IL-1β and TNF within LPS-treated E15 lung cell suspensions using FACS (Fig. 1e,f). Similar to our real time PCR and ELISA data, inflammatory cytokine expression was restricted to CD11bHI lung macrophages and not detected in F4/80HI cells. LPS did not significantly increase cell death in either F4/80HI or CD11bHI macrophages as assayed by live-dead staining (not shown). CD11bHI macrophages appearing in the fetal lung after E13 were therefore more pro-inflammatory after LPS stimulation and with higher cytokine expression and release.
LPS-induced cytokine release is also restricted to CD11bHI macrophages in the fetal liver
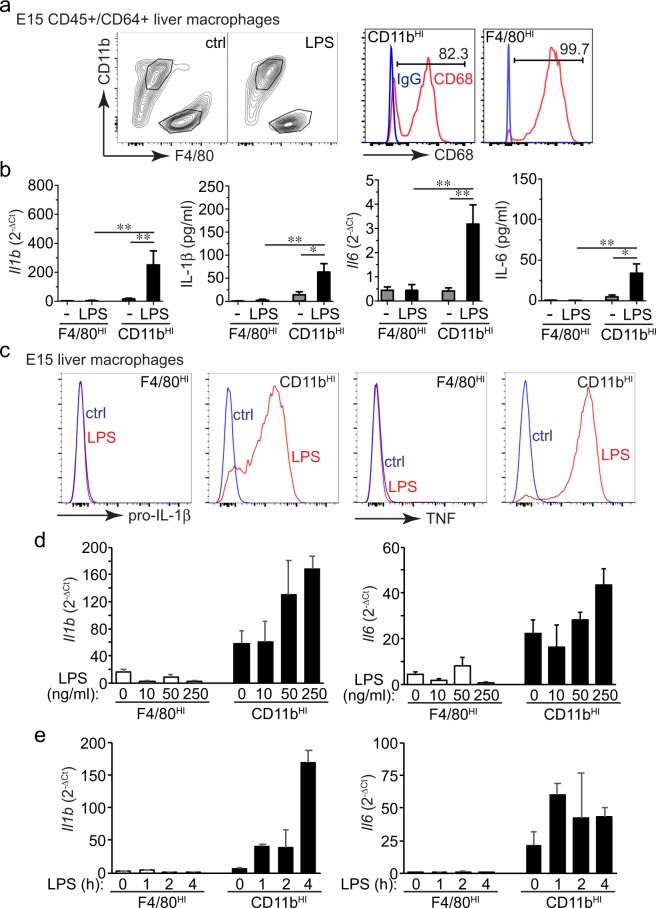
To test if the functional differences between macrophage populations were tissue specific, we next isolated F4/80HI and CD11bHI macrophages from E15 fetal liver and measured their LPS response (Fig. 2a). Similar to lung macrophages, LPS stimulated cytokine expression and release in CD11bHI fetal liver macrophages but not in F4/80HI macrophages (Fig. 2b,c). Of note, cytokine expression was lower in E15 liver CD11bHI macrophages compared to CD11bHI cells isolated from E15 lung as measured in Fig. 1. We next compared the dose response and time course of LPS activation between the two fetal macrophage populations. As shown in Fig. 2d, F4/80HI macrophages failed to respond at all LPS concentrations tested. We also did not detect increased Il1b or Il6 mRNA in LPS-treated F4/80HI macrophages over a 4 h time course. These data further confirm the proinflammatory phenotype in fetal CD11bHI macrophages and the resistance to LPS in fetal F4/80HI macrophages.
Figure 2.
Differential response to LPS between fetal liver macrophage populations. (a) E15 fetal mouse livers contain both CD11bHI and F4/80HI macrophage populations that also express CD68 (red). Isotype control IgG staining is included as a control (blue) and the percentage of cells expressing CD68 is indicated. (b) In sorted CD11bHI macrophages from E15 liver, LPS increased IL-1β and IL-6 gene expression and cytokine release into the media. However, LPS did not increase expression or release in F4/80HI macrophages. (+/− s.e.m.; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, n = 4–7). (c) Intracellular immunostaining and FACS analysis only detected pro-IL-1β and TNF in CD11bHI macrophages. F4/80HI cells did not express either cytokine, even following LPS treatment. Data shown are from a single experiment representative of three independent experiments. (d) Dose response data measuring Il1b and Il6 expression by real time PCR in CD11bHI and F4/80HI macrophage populations treated for 4 h with 0, 10 ng/ml, 50 ng/ml, or 250 ng/ml LPS (n = 3). (e) Time course of the LPS response (250 ng/ml) in both CD11bHI and F4/80HI macrophage populations (n = 3).
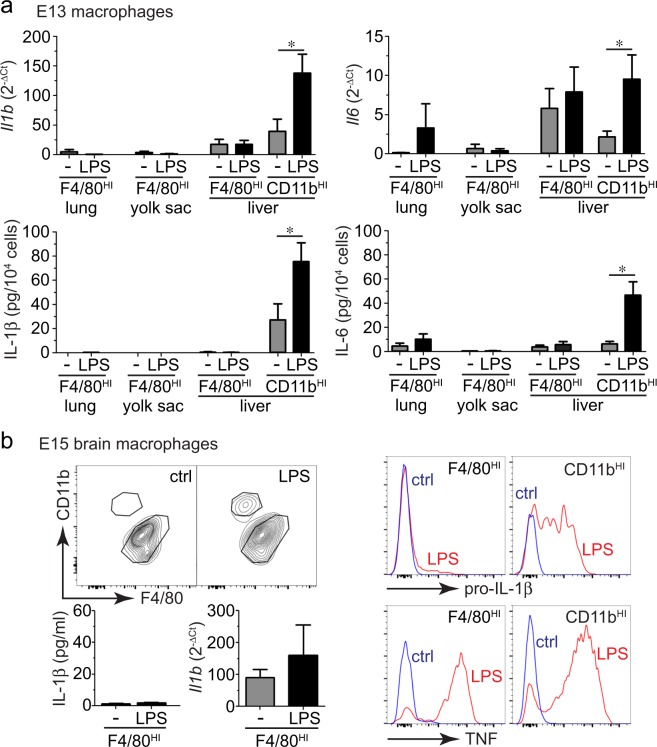
To test if the differential response to LPS was present earlier in development, we isolated macrophage populations from yolk sac, liver, and lung at E13 (Fig. 3a). LPS did not induce cytokine expression in F4/80HI E13 macrophages from any of the tissue sources tested. At E13, only the liver contained CD11bHI macrophages, and these cells did express IL-1β and IL-6 following LPS treatment. Interestingly, F4/80HI cells from the E13 liver appeared to express higher basal levels of Il1b and Il6 mRNA compared to macrophages from yolk sac and lung, but cytokine expression did not change with LPS. E13 liver F4/80HI macrophages also did not release cytokine peptides into the media after LPS treatment. While both F4/80HI and CD11bHI macrophages populate most tissues within the developing embryo, the brain contains primarily F4/80HI yolk sac macrophages. LPS treatment of F4/80HI macrophages from E15 brain did not induce IL-1β expression or release (Fig. 3b), similar to the results obtained with other F4/80HI macrophage populations. However F4/80HI brain macrophages did express TNF after LPS treatment. The unique brain microenvironment therefore appears to promote at least a partially competent inflammatory state in F4/80HI macrophages.
Figure 3.
(a) LPS responsiveness is only present in CD11bHI macrophages as early as E13. Macrophage populations from E13 mouse lung, yolk sac, and liver were sorted, isolated, and stimulated with LPS. Only F4/80HI macrophages could be isolated from E13 lung and yolk sac. LPS did not increase cytokine expression or release from E13 F4/80HI macrophages (+/− s.e.m.; *P < 0.05, n = 3–7). (b) F4/80HI macrophages in E15 mouse brains have a partial response to LPS. The majority of macrophages in E15 brain were F4/80HI, and LPS treatment did not increase IL-1β release or mRNA expression (+/− s.e.m.; n = 6–7). Intracellular staining and FACS did demonstrate increased TNF expression in F4/80HI macrophages from E15 brain, but only minimal pro-IL-1β expression (representative data from three independent experiments shown).
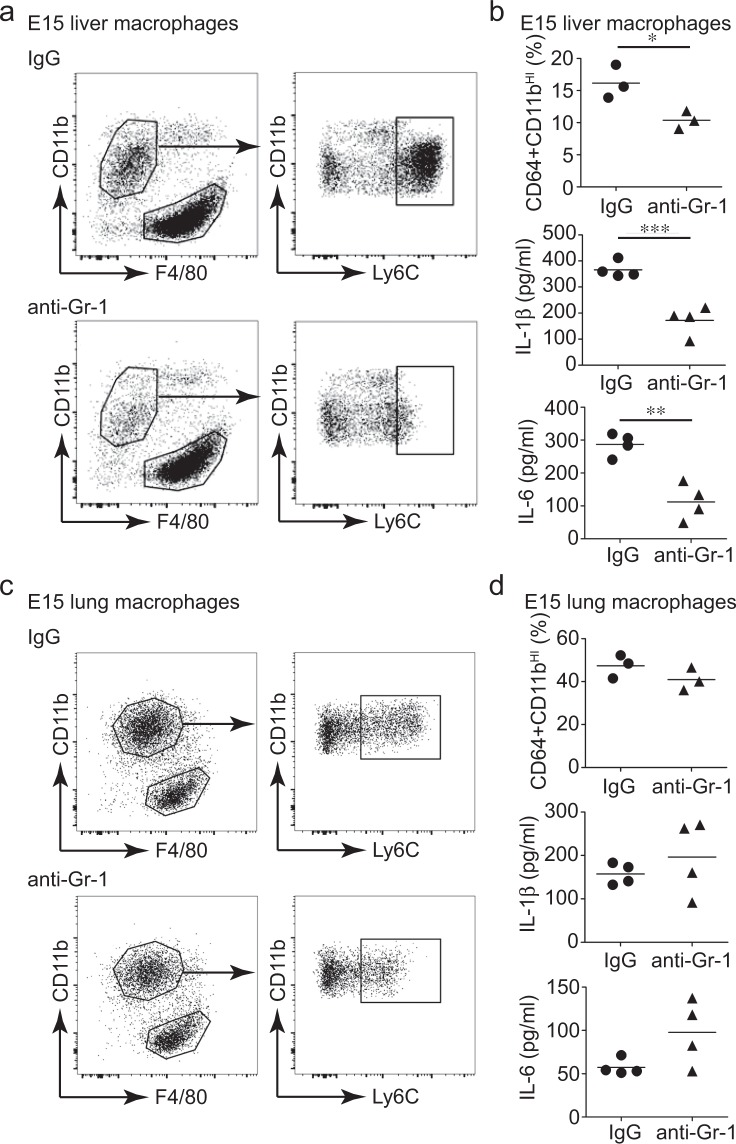
Based on these data, we hypothesized that CD11bHI macrophages were the primary inflammatory cells in the developing embryo. To test the requirement of CD11bHI macrophages in mediating inflammation, we injected pregnant dams with monoclonal anti-Gr-1 IgG to immunodeplete CD11bHI cells from developing embryos32,33. Figure 4 shows that anti-Gr-1 injection reduced the number of Ly6C+/CD11bHI macrophages in the fetal liver at E15. When the total liver cell suspension was treated with LPS, Gr-1 depleted samples had reduced levels of IL-1β and IL-6 release equivalent with the level of depletion (Fig. 4a,b). These data supported CD11bHI macrophages as a major population of cells in the fetal liver releasing IL-1β and IL-6 following LPS treatment. While anti-Gr-1 IgG immunodepleted Ly6C+ cells from the E15 lung, the number of CD11bHI macrophages was unchanged (Fig. 4c,d). LPS stimulated IL-1β and IL-6 release was unaffected by anti-Gr-1 depletion in E15 lung samples, consistent with our hypothesis that CD11bHI macrophages were the main cellular source of IL-1β.
Figure 4.
Depletion of CD11bHI/Ly6C+ macrophages reduces IL-1β production in E15 fetal liver. Pregnant mice were injected with nonimmune IgG or anti-GR-1 antibody. At E15, macrophages were isolated from fetal liver (a,b) and fetal lung (c,d) Anti-Gr-1 injection reduced the percentage of CD11bHI/Ly6C+ macrophages in the E15 fetal liver (a) with a corresponding reduction in IL-1β and IL-6 release following treatment of the total fetal liver cell suspension with LPS (*P < 0.05, n = 3; **P < 0.01, n = 4, ***P < 0.001, n = 4). Anti-Gr-1 injections did not reduce CD11bHI/Ly6C+ macrophages from fetal lungs or reduce IL-1β or IL-6 production following LPS treatment.
Tlr4 and Nlrp3 inflammasome expression in CD11bHI fetal macrophages
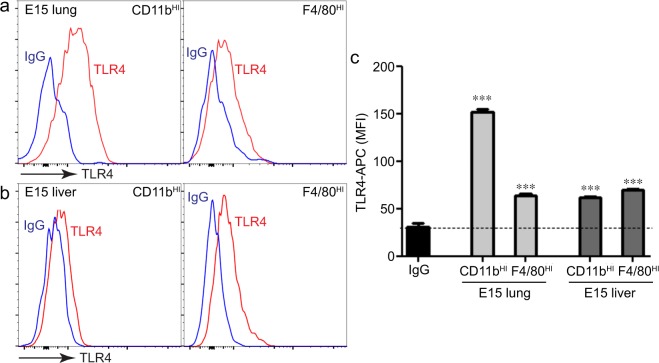
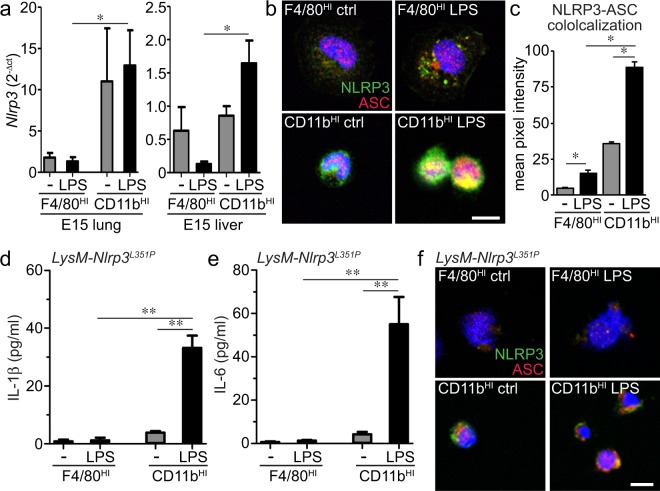
IL-1β expression and release following LPS exposure requires both TLR4 signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome expression, assembly, and activation. We next tested if fetal lung macrophage populations had differential TLR4 or NLRP3 expression. CD11bHI macrophages from the lung did express higher levels of TLR4 compared to F4/80HI macrophages (Fig. 5a,c). However E15 liver macrophage populations expressed similar TLR4 levels (Fig. 5b,c). Potential differences in TLR4 expression therefore did not appear to explain why F4/80HI macrophages failed to express inflammatory cytokines after LPS treatment. NLRP3 expression in the developing lung is restricted to macrophages and increases during the later stages of lung development. CD11bHI macrophages from E15 lung expressed higher Nlrp3 compared to F4/80HI macrophages (Fig. 6a). LPS increased Nlrp3 expression in CD11bHI cells with minimal effect on F4/80HI macrophages. Similar results were seen by immunostaining macrophages with antibodies against NLRP3 and the inflammasome linker protein ASC (Fig. 6b). Expression and co-localization were more prevalent in CD11bHI cells. LPS treatment increased co-localization in both macrophage populations, with much higher ASC-NLRP3 co-localized signal in CD11bHI macrophages (Fig. 6c).
Figure 5.
Both fetal macrophage populations express the LPS receptor TLR4. (a,b) E15 lung macrophages were immunolabeled with anti-TLR and analyzed by FACS. (c) TLR4-APC median fluorescence intensity (MFI) values measured TLR4 surface expression in each macrophage population. While CD11bHI macrophages from E15 lung appeared to express higher levels of TLR4 compared to F4/80HI lung macrophages, the relative expression of TLR4 in liver macrophage populations was similar (+/− s.e.m.; ***P < 0.001 compared to IgG isotype control, n = 4–6).
Figure 6.
Proinflammatory CD11bHI fetal macrophages express higher levels of the NLRP3 inflammasome. (a) Real time PCR measured higher Nlrp3 mRNA levels in LPS treated CD11bHI macrophages compared to F4/80HI macrophages in both E15 lung and E15 liver (+/− s.e.m.; *P < 0.05, n = 3–5). (b) CD11bHI macrophages from fetal liver expressed higher levels of NLRP3 and the linker protein ASC compared to F4/80HI macrophages as visualized by laser scanning confocal microscopy. (c) LPS increased NLRP3-ASC colocalization in both macrophage populations. For colocalization measurements, pixel intensities in the red, green, and yellow (colocalized) channels were measured in identically sized regions of interest. Higher pixel intensity was measured in CD11bHI macrophages (+/− s.e.m.; *P < 0.05, n = 3). (d,e) Macrophage populations were sorted from E15 LysM-Nlrp3L351P inflammasome gain of function mice and treated with LPS. IL-1β (d) and IL-6 (e) were only detected in the media from LPS-treated CD11bHI macrophages (+/− s.e.m.; **P < 0.01, n = 6). (f) Expression of NLRP3 and ASC inflammasome components were lower in F4/80HI macrophages from E15 LysM-Nlrp3L351P mice.
We next tested if constitutively active NLRP3 was sufficient to drive cytokine release in both CD11bHI and F4/80HI macrophages. We isolated E15 liver macrophages from Nlrp3L351P mice expressing a gain of function mutation within the Nlrp3 gene. At E15, neither macrophage population released significant IL-1β under control conditions (Fig. 6d,e). LPS treatment however stimulated both IL-1β and IL-6 release only in CD11bHI macrophages. F4/80HI macrophages from E15 Nlrp3L351P mice failed to express high levels of NLRP3 by confocal immunofluorescence, even after LPS treatment (Fig. 6f). Nlrp3L351P CD11bHI macrophages expressed both NLRP3 and ASC, with expression and colocalization increased after LPS treatment. Consistent with our data in wild type macrophages, these results show that fetal CD11bHI macrophages express NLRP3 inflammasome components and have the capacity to express and release IL-1β upon TLR4 stimulation. F4/80HI macrophages however failed to express NLRP3, preventing their ability to release IL-1β. Coupled with the lack of both Il1b and Il6 mRNA in F4/80HI macrophages, these data suggest that F4/80HI macrophages lack an innate immune transcriptional response as well as the machinery necessary for generating pro-inflammatory activation.
Differential myeloid gene expression in LPS-treated fetal macrophages
The above experiments focused on Il1b, Il6, and Nlrp3 in initially assessing the LPS-induced inflammatory response in F4/80HI and CD11bHI fetal macrophages. To measure expression of additional genes, we used Nanostring nCounter gene expression profiling of 734 myeloid genes in LPS treated F4/80HI and CD11bHI macrophages from E15 mouse lung (Fig. 7a). A total of 89 genes were differentially expressed between the 2 macrophage populations (log2 fold change >1; adjusted P < 0.05). CD11bHI cells expressed higher levels of Il1a, Il1b, Ccl9, and Cxcl3, while F4/80HI cells had higher expression of Pf4 (also known as Cxcl4), Igf1, and the complement genes C1qa, C1qb and C1qc (Fig. 7a). Real time PCR confirmed higher C1qa and Pf4 expression in F4/80HI macrophages and LPS did not increase expression of either gene (Fig. 7b). To identify the molecular mechanisms of differential gene expression in the two macrophage populations, we examined TF binding sites enriched in LPS-induced genes in CD11bHI macrophages compared to F4/80HI macrophages using Opossum 3.0 (Fig. 7c). Overexpressed genes in CD11bHI macrophages were notably enriched in NF-κB binding sites, while the F4/80HI macrophage gene signature contained motifs predicted to bind SRF, IRF1, and IRF2. In addition, RUNX1 predicted sites in F4/80HI samples were consistent with data showing Runx1 expression is restricted to yolk sac derived macrophages34. In summary, our data suggest fetal macrophage populations have inherent differences in the transcriptional response machinery following exposure to LPS.
Figure 7.
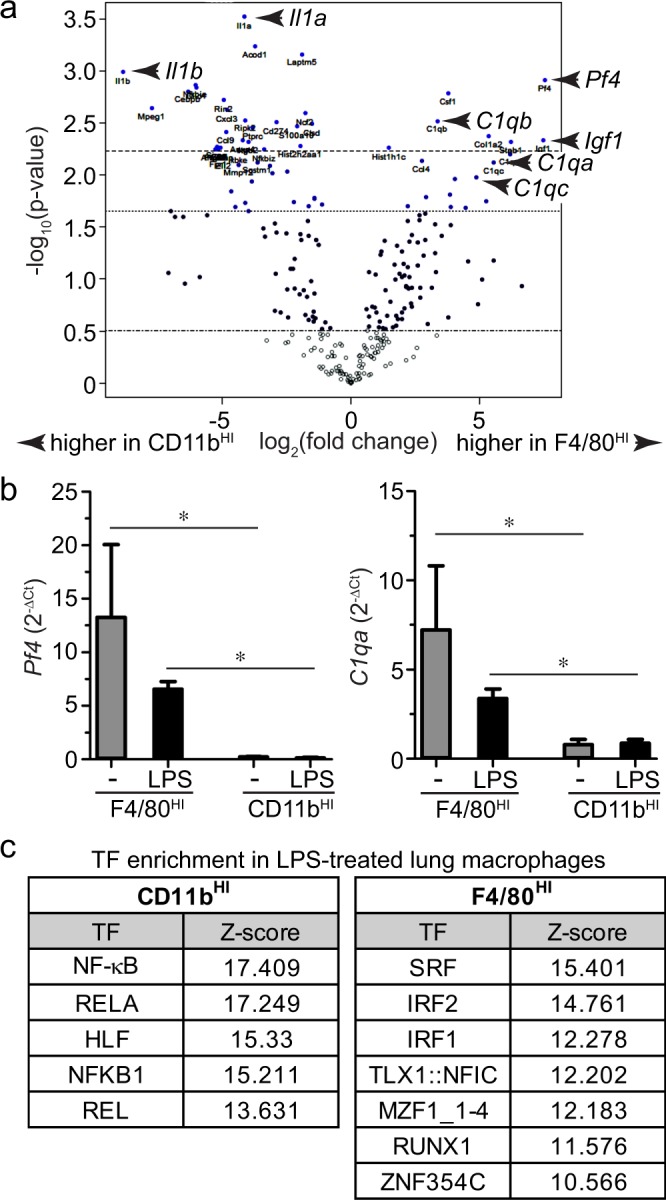
Differential gene expression in LPS-treated CD11bHI macrophages vs. F4/80HI macrophages from E15 mouse lung. (a) Volcano plot of myeloid gene expression as measured by Nanostring assay. Genes more highly expressed in CD11bHI samples are shifted to the left. Genes higher in F4/80HI macrophages are shifted to the right. Il1a and Il1b (higher in CD11bHI macrophages) and C1qa, C1qb, C1qc, Pf4, and Igf1 (higher in F4/80HI macrophages) are noted by arrowheads (n = 3 for F4/80HI, n = 4 for CD11bHI). (b) Real time PCR confirmed higher Pf4 and C1qa expression in F4/80HI macrophages. Neither gene was increased by LPS treatment (+/− s.e.m.; *P < 0.05, n = 3–4). (c) Transcription factor binding sites enriched in differentially expressed genes identified using oPOSSUM.
Discussion
Fetal lung inflammation is developmentally regulated, with macrophage activation and cytokine release impacting airway morphogenesis only during the later stages of in utero development22. Here we show that developmental regulation of lung inflammation is due to the programmed accumulation of pro-inflammatory macrophages in the lung after E15. While we and others have shown macrophages do populate the lung from the initial days of embryonic development12,23,35, these early yolk sac derived macrophages appear resistant to pro-inflammatory TLR mediated activation. Our data here clearly demonstrate the functional differences between F4/80HI yolk sac derived macrophages and CD11bHI fetal liver derived macrophages. CD11bHI macrophages express higher levels of inflammasome components and release IL-1β and IL-6 upon LPS treatment, while F4/80HI macrophages fail to release these inflammatory mediators that play important roles in injury and disease.
Macrophage populations may share common functional properties in the moments following their differentiation from myeloid progenitors during fetal hematopoiesis. Upon trafficking to the circulation and into various tissues, the local microenvironment then shapes macrophage biology and promotes specialized, tissue specific functions11,36. While the adult lung contains multiple immune cell populations including dendritic cells and lymphocytes, many of these cells appear after birth37,38. However we still have not determined the relative heterogeneity within the various fetal macrophage populations studied here. At E15 when fetal liver derived CD11bHI macrophages are first trafficking to various tissues, cells isolated from the fetal lung had a slightly higher expression of inflammatory cytokines compared to cells still residing within the liver. The high levels of GM-CSF present in the lung could mediate these differences39. F4/80HI cells from the yolk sac, liver, and lung remained resistant to LPS stimulation. The strikingly different situation identified for F4/80HI cells is the developing fetal brain. Macrophages in the fetal brain are primarily F4/80HI cells from the yolk sac, and these cells eventually differentiate into microglia34,40. Not only do brain microglia have inflammatory potential, they also play a key role in forming mature synapses41–43. Interestingly, F4/80HI macrophages from the E15 fetal brain did respond to LPS by increasing TNF expression. However they appeared to lack functional NLRP3 inflammasome expression and therefore failed to release IL-1β. Identifying the factors within the brain that give F4/80HI cells their unique functional properties could provide important insight into both macrophage biology and neuroinflammatory disease processes.
The functional differences between fetal macrophage populations suggest unique molecular regulatory mechanisms. While both macrophage populations expressed similar levels of the LPS receptor TLR4, F4/80HI macrophages did not express the same levels of NF-κB dependent genes after LPS treatment. Therefore F4/80HI macrophages could have reduced expression of proteins required for the TLR-IKK-NF-κB or MAPK signaling pathways. Differential transcription factor expression or epigenetic chromatin modifications between CD11bHI and F4/80HI macrophages could also explain why LPS generated unique responses in each cell population. Our informatics analysis clearly identified NF-κB promoter sites activated in CD11bHI macrophages that were apparently not accessible in F4/80HI cells. Ongoing experiments are exploring the potential upstream mechanisms responsible for these differences.
If CD11bHI cells mount inflammatory responses to microbes in the developing embryo, then what are the roles of F4/80HI macrophages? F4/80HI cells migrate throughout the entire embryo very early in development. The ubiquitous locations and lack of TLR-mediated inflammatory function suggest they play a role in tissue morphogenesis or homeostasis. Macrophages remove dying and apoptotic cells from both developing and mature tissues44. Multiple receptors on phagocytic cells bind outer leaflet phosphatidylserine on apoptotic and necrotic cells45. The complement component C1q promotes phagocytosis of dying cells by macrophages46–48. We measured higher levels of the C1q genes C1qa, C1qb, and C1qc in F4/80HI macrophages from fetal lung compared to CD11bHI macrophages. These data suggest that yolk sac derived F4/80HI macrophages play important roles in removing apoptotic or necrotic cells during tissue morphogenesis. F4/80HI macrophages also expressed IGF-1, a major promoter of both developmental morphogenesis and tissue repair and regeneration. Macrophage IGF-1 contributes to muscle repair following injury49. In the lung, macrophage phagocytosis of apoptotic cells in the lung releases IGF-1, which then stimulates additional phagocytic function in adjacent airway epithelial cells50. The transcription factors MafB and C/EBPγ were both detected in Nanostring analysis of F4/80HI macrophages, and both factors drive anti-inflammatory cell phenotypes51,52. Data therefore suggest that anti-inflammatory fetal F4/80HI macrophages could be tasked with removing damaged cells and cellular debris during morphogenesis while pro-inflammatory CD11bHI macrophages respond to microbial products and innate immune activators.
The unique functions of fetal macrophage populations could impact disease processes. Early in development, the lack of proinflammatory macrophages prevents a robust innate immune response. Upon appearance of activation competent CD11bHI macrophages in various tissues, TLR activation can lead to regional or systemic inflammation in the developing fetus. Future experiments will need to implement novel approaches for depleting specific fetal macrophage populations, as our antibody-based strategy was inefficient at cell depletion. Intrauterine fetal inflammation plays a major role in causing preterm birth and the long-term sequelae of extreme prematurity53. Inflammatory processes and tissue injury are associated with necrotizing enterocolitis54, bronchopulmonary dysplasia55, and retinopathy of prematurity56. If our data in mice translate to the development of human innate immunity, interventions targeting macrophage activation and inflammation processes will need to focus on specific pro-inflammatory macrophage populations.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (HL126703, HL086324, HL097195), the Gerber Foundation (1823–3830, 20180324), and an award from the UCSD Stem Cell Program at the Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine. We are especially thankful to our colleagues at UCSD and Rady Children’s Hospital for their helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author Contributions
O.L. performed a majority of the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. A.Y., G.H., K.A., S.L. and G.O.N. each performed experiments, analyzed the data, and contributed to the revisions of the manuscript. H.H. and L.P. reviewed both raw and analyzed data and analysis and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the manuscript prior to submission.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Gordon S, Martinez-Pomares L. Physiological roles of macrophages. Pflugers Arch. 2017;469:365–374. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-1945-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sarantis H, Grinstein S. Subversion of phagocytosis for pathogen survival. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;12:419–431. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Arango Duque G, Descoteaux A. Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front Immunol. 2014;5:491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013;496:445–455. doi: 10.1038/nature12034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schultze JL, Schmieder A, Goerdt S. Macrophage activation in human diseases. Semin Immunol. 2015;27:249–256. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2015.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Parisi L, et al. Macrophage Polarization in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Killers or Builders? J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:8917804. doi: 10.1155/2018/8917804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Noy R, Pollard JW. Tumor-associated macrophages: from mechanisms to therapy. Immunity. 2014;41:49–61. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Byrne AJ, Maher TM, Lloyd CM. Pulmonary Macrophages: A New Therapeutic Pathway in Fibrosing Lung Disease? Trends Mol Med. 2016;22:303–316. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2016.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhou D, et al. Macrophage polarization and function: new prospects for fibrotic disease. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017;95:864–869. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Perdiguero EG, Geissmann F. The development and maintenance of resident macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:2–8. doi: 10.1038/ni.3341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ginhoux F, Guilliams M. Tissue-Resident Macrophage Ontogeny and Homeostasis. Immunity. 2016;44:439–449. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guilliams M, et al. Alveolar macrophages develop from fetal monocytes that differentiate into long-lived cells in the first week of life via GM-CSF. J Exp Med. 2013;210:1977–1992. doi: 10.1084/jem.20131199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yu X, et al. The Cytokine TGF-beta Promotes the Development and Homeostasis of Alveolar Macrophages. Immunity. 2017;47:903–912 e904. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hoeffel G, Ginhoux F. Fetal monocytes and the origins of tissue-resident macrophages. Cell Immunol. 2018;330:5–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.PrabhuDas M, et al. Immune mechanisms at the maternal-fetal interface: perspectives and challenges. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:328–334. doi: 10.1038/ni.3131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fulde M, Hornef MW. Maturation of the enteric mucosal innate immune system during the postnatal period. Immunol Rev. 2014;260:21–34. doi: 10.1111/imr.12190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Harbeson D, Ben-Othman R, Amenyogbe N, Kollmann TR. Outgrowing the Immaturity Myth: The Cost of Defending From Neonatal Infectious Disease. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1077. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Maddux AB, Douglas IS. Is the developmentally immature immune response in paediatric sepsis a recapitulation of immune tolerance? Immunology. 2015;145:1–10. doi: 10.1111/imm.12454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Balany J, Bhandari V. Understanding the Impact of Infection, Inflammation, and Their Persistence in the Pathogenesis of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Front Med (Lausanne) 2015;2:90. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2015.00090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jobe AH. Mechanisms of Lung Injury and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am J Perinatol. 2016;33:1076–1078. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1586107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee DD, et al. Endothelial Monocyte-Activating Polypeptide II Mediates Macrophage Migration in the Development of Hyperoxia-Induced Lung Disease of Prematurity. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016;55:602–612. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0091OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stouch AN, et al. IL-1beta and Inflammasome Activity Link Inflammation to Abnormal Fetal Airway Development. J Immunol. 2016;196:3411–3420. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Blackwell TS, et al. NF-kappaB signaling in fetal lung macrophages disrupts airway morphogenesis. J Immunol. 2011;187:2740–2747. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shahzad T, Radajewski S, Chao CM, Bellusci S, Ehrhardt H. Pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: when inflammation meets organ development. Mol Cell Pediatr. 2016;3:23. doi: 10.1186/s40348-016-0051-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Husain AN, Siddiqui NH, Stocker JT. Pathology of arrested acinar development in postsurfactant bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Hum Pathol. 1998;29:710–717. doi: 10.1016/S0046-8177(98)90280-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bry K, Whitsett JA, Lappalainen U. IL-1beta disrupts postnatal lung morphogenesis in the mouse. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007;36:32–42. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0116OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liao J, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome is critically involved in the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8977. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stouch AN, et al. IkappaB kinase activity drives fetal lung macrophage maturation along a non-M1/M2 paradigm. J Immunol. 2014;193:1184–1193. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Brydges SD, et al. Inflammasome-mediated disease animal models reveal roles for innate but not adaptive immunity. Immunity. 2009;30:875–887. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.05.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pupo E, Lindner B, Brade H, Schromm AB. Intact rough- and smooth-form lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli separated by preparative gel electrophoresis exhibit differential biologic activity in human macrophages. FEBS J. 2013;280:1095–1111. doi: 10.1111/febs.12104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Prince LS, Dieperink HI, Okoh VO, Fierro-Perez GA, Lallone RL. Toll-like receptor signaling inhibits structural development of the distal fetal mouse lung. Dev Dyn. 2005;233:553–561. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schumak B, et al. Specific depletion of Ly6C(hi) inflammatory monocytes prevents immunopathology in experimental cerebral malaria. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dunay IR, Fuchs A, Sibley LD. Inflammatory monocytes but not neutrophils are necessary to control infection with Toxoplasma gondii in mice. Infect Immun. 2010;78:1564–1570. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00472-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ginhoux F, et al. Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science. 2010;330:841–845. doi: 10.1126/science.1194637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sorokin SP, Hoyt RF., Jr. Pure population of nonmonocyte derived macrophages arising in organ cultures of embryonic rat lungs. Anat Rec. 1987;217:35–52. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092170107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhao Y, Zou W, Du J, Zhao Y. The origins and homeostasis of monocytes and tissue-resident macrophages in physiological situation. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:6425–6439. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.de Kleer IM, et al. Perinatal Activation of the Interleukin-33 Pathway Promotes Type 2 Immunity in the Developing Lung. Immunity. 2016;45:1285–1298. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.10.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cohen M, et al. Lung Single-Cell Signaling Interaction Map Reveals Basophil Role in Macrophage Imprinting. Cell. 2018;175:1031–1044 e1018. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Berclaz PY, et al. GM-CSF regulates a PU.1-dependent transcriptional program determining the pulmonary response to LPS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007;36:114–121. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0174OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sheng J, Ruedl C, Karjalainen K. Most Tissue-Resident Macrophages Except Microglia Are Derived from Fetal Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Immunity. 2015;43:382–393. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Weinhard L, et al. Microglia remodel synapses by presynaptic trogocytosis and spine head filopodia induction. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1228. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03566-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schafer DP, et al. Microglia sculpt postnatal neural circuits in an activity and complement-dependent manner. Neuron. 2012;74:691–705. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Paolicelli RC, et al. Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development. Science. 2011;333:1456–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.1202529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Henson PM, Hume DA. Apoptotic cell removal in development and tissue homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 2006;27:244–250. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2006.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gordon S, Pluddemann A. Macrophage Clearance of Apoptotic Cells: A Critical Assessment. Front Immunol. 2018;9:127. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fraser DA, Laust AK, Nelson EL, Tenner AJ. C1q differentially modulates phagocytosis and cytokine responses during ingestion of apoptotic cells by human monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2009;183:6175–6185. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hulsebus HJ, O’Conner SD, Smith EM, Jie C, Bohlson SS. Complement Component C1q Programs a Pro-Efferocytic Phenotype while Limiting TNFalpha Production in Primary Mouse and Human Macrophages. Front Immunol. 2016;7:230. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Pulanco MC, et al. Complement Protein C1q Enhances Macrophage Foam Cell Survival and Efferocytosis. J Immunol. 2017;198:472–480. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tonkin J, et al. Monocyte/Macrophage-derived IGF-1 Orchestrates Murine Skeletal Muscle Regeneration and Modulates Autocrine Polarization. Mol Ther. 2015;23:1189–1200. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Han CZ, et al. Macrophages redirect phagocytosis by non-professional phagocytes and influence inflammation. Nature. 2016;539:570–574. doi: 10.1038/nature20141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tran MTN, et al. MafB is a critical regulator of complement component C1q. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1700. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01711-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Huggins CJ, et al. C/EBPgamma suppresses senescence and inflammatory gene expression by heterodimerizing with C/EBPbeta. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:3242–3258. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01674-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gilman-Sachs A, et al. Inflammation induced preterm labor and birth. J Reprod Immunol. 2018;129:53–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2018.06.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Neu J, Pammi M. Necrotizing enterocolitis: The intestinal microbiome, metabolome and inflammatory mediators. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;23:400–405. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2018.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Savani RC. Modulators of inflammation in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Semin Perinatol. 2018;42:459–470. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2018.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rivera JC, et al. Retinopathy of prematurity: inflammation, choroidal degeneration, and novel promising therapeutic strategies. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14:165. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0943-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]