FIG 3.
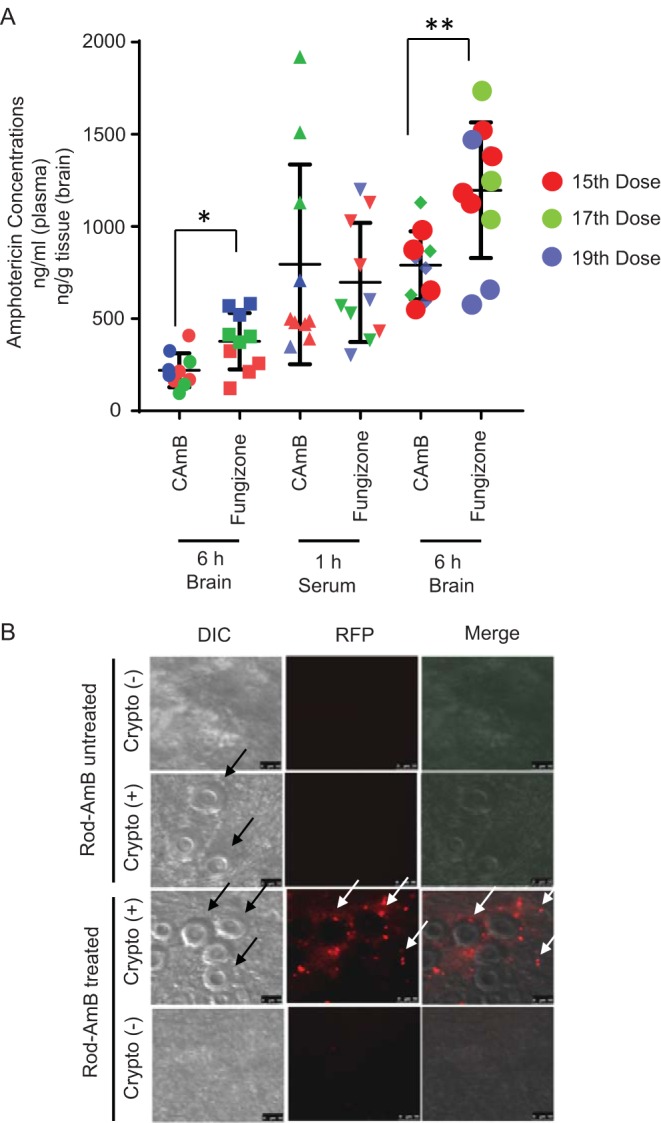
Treatment with an encochleated oral formulation of CAmB results in accumulation of amphotericin B in brains of C. neoformans-infected mice. (A) Mice were infected as in Fig. 1B above and treated with the indicated formulations of amphotericin B. After the indicated doses of each formulation, serum was obtained 1 h after dosing, serum and brains were harvested at 6 h from sacrificed animals, and amphotericin B concentrations were determined by HPLC-MS as described in Materials and Methods (n = 9 animals; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0. 01; error bars, ±SD). (B) Mice were infected intravenously with 104 CFU of C. neoformans [Crypto (+)] or remained uninfected [Crypto (-)]. Five days later, mice were treated daily for 3 days with fluorescent CAmB (Rod-AmB) p.o. and sacrificed. Brains were removed, homogenized, and subjected to microscopy using differential interference contrast (DIC) or fluorescence microscopy (RFP). Black arrows show C. neoformans, and white arrows show CAmB fluorescent puncta. Bar, 5 μm.
