Abstract
Objective:
This review synthesizes findings from the peer-reviewed evaluation literature on condom availability programs (CAPs) in secondary schools.
Data Source:
Peer reviewed evaluation literature indexed in MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsychINFO, ERIC, CINAHL, Sociological Abstracts, SCOPUS, and POPLINE.
Study Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:
Manuscripts had to be peer-reviewed, written in English, and report evaluation data from a U.S., school-based CAP.
Data Extraction:
Articles were coded independently by two authors. Discrepancies were resolved through open discussion.
Data Synthesis:
We grouped findings into outcome evaluation and process evaluation findings. Outcome evaluation findings included STIs, pregnancy rates, condom use, contraception use, sexual risk, and substance use. Process evaluation findings included awareness of CAPs, attitudes towards CAPs, attitudes towards condoms, and receipt of education and instruction.
Results:
Of the 138 citations reviewed, twelve articles published between 1995 and 2012 met the inclusion criteria, representing 8 programs. Evaluations indicate CAPs yield condom acquisition rates between 23% and 48%, have mixed results related to condom use, and are not associated with increases in sexual and other risk behaviors. One program found CAPs were associated with a decrease in a combined rate of chlamydia and gonorrhea. One program found no association between CAPs and unintended pregnancy. Students’ attitudes toward CAPs were favorable and awareness was high.
Conclusions:
CAPS are accepted by students and can be an appropriate and relevant school-based intervention for teens. CAPs can increase condom use, but more evaluations are needed on CAPs impact on rates of HIV, STIs, and unintended pregnancy.
Purpose
In 2015, youth aged 13 to 24 accounted for 22% of new HIV diagnoses in the United States [1], and nearly half of the 20 million sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) reported each year are among young people aged 15–24 years [2]. Although declining, the U.S. has one of the highest teenage pregnancy rates compared to other industrialized nations [3, 4]. This group is at risk of these negative health issues due to biological, social, and behavioral risk factors. For example, in 2015, 43.1% of currently sexually active high school students did not use a condom at last sex, and while condom use at last sex has increased overall from 1991–2015, there has been a significant decrease from 2003–2015 [5]. Condoms are an effective method to prevent STIs, HIV, and pregnancy [6–10] However, there are barriers to condom use such as cost and access [11, 12]. Furthermore, condom use among teens is declining [13]. This information demonstrates a need for effective prevention efforts to improve access to condoms and to increase condom use among adolescents.
School-based condom availability programs (CAPs) have existed since the early 1990s in high schools as one strategy to prevent unplanned pregnancy and to reduce the transmission of STIs and HIV [14]. These programs make condoms available to students in places like the school nurse office, school-based health centers (SBHCs), classrooms, and vending machines. While some programs include things like advertisements for CAPs [15], most program descriptions do not include such detail. In general, most programs provide condoms to students free of charge and are implemented simultaneously with other sexual health promotion strategies (e.g., sexual health education, or HIV/STI testing and referral to treatment) [14].
By 1995, it was estimated that 431 CAPs existed, in more than 50 school districts across 21 states, including most if not all high schools of the Los Angeles and New York City school districts [14]. In 2014, 7.2% of high schools made condoms available to students [16]. Some of the first CAPs were met with public scrutiny and challenged in court with competing legal decisions that left programs without a clear directive on whether or not to include parental consent, which may explain some variation in implementation of parental consent procedures [17].
The public debate was in part fueled by questions about CAPs effectiveness and concerns about possible unintended negative consequences by promoting sexual activity among adolescents [18, 19]. This underscores the need to evaluate CAPs for effects on biological outcomes and sexual behavior. The Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine and the American Academy of Pediatrics have called for support of CAPs [20, 21]. Previous studies have found that CAPs are associated with increases in condom use [22, 23]. However, these analyses focus primarily on condom use behavior. Given the complexity of circumstances related to CAPs in schools, it is important to understand if and when CAPs in schools are effective at changing biological and behavioral outcomes, and to identify key programmatic components of CAPs.
The purpose of this review is to provide a comprehensive summary and synthesis of the peer-reviewed evaluation literature on CAPs in secondary schools in the United States. We summarize the literature based on outcome and process evaluation findings with the intent to summarize program effectiveness, identify gaps in the program evaluation literature, identify important programmatic components of CAPs, and provide future directions for research and evaluation.
Methods
Data Sources
We conducted a systematic search of MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsychINFO, ERIC, CINAHL, Sociological Abstracts, SCOPUS, and POPLINE using keywords related to CAPs (“condom availability program”, “condom distribution program”, “condom availability campaign”, and “condom distribution campaign”) and adolescents (“adolescent”, “adolescents”, “school”, “schools”, “student”, and “students”). Additionally, we reviewed references of publications meeting inclusion criteria during title and abstract screening as well as reference lists of other CAPs-related reviews. Forward citation searches were conducted in Google Scholar to identify any publication indexed there as having cited one of our included articles.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Two authors (JA, NL) reviewed titles and abstracts identified through searches using a standard form. To be eligible for full text review, manuscripts had to be peer-reviewed, written in English, and report data from a U.S. CAP evaluation that included an adolescent sample of middle or high school students. No inclusion criteria based on publication date was used. Qualitative studies were excluded from the synthesis due to differences in analyses performed among a limited number of studies. Discrepancies between screeners were settled through open discussion until both authors agreed. In the case of uncertainty, articles were included in the full text review.
Data Extraction
A standard coding workbook was used to extract information from each article including study characteristics, programmatic information, and outcomes. The research team used an iterative process of coding and group discussion to refine the coding workbook and ensure consistent data abstraction. Each full text article was then coded independently by a minimum of two authors. Discrepancies in full text coding were resolved through open discussion until consensus was achieved among all authors (JA, NL, and SL).
Data Synthesis
To summarize the literature on CAPs in schools, we grouped findings into outcome evaluation and process evaluation findings. Outcome evaluation findings addressed biological outcomes (i.e., STIs and pregnancy rates) and behavioral outcomes, that is condom use, contraception use (e.g., oral contraception and any contraception), and sexual risk (e.g., ever had sex and number of sex partners) and substance use behavior (e.g., alcohol use before sex and any substance use). Process evaluation findings included findings about awareness of CAPs, attitudes towards CAPs (e.g., approval of program), attitudes towards condoms (e.g., belief that condoms affect sexual pleasure), and receipt of education and instruction (e.g., read accompanying information sheet with condom).
Outcome evaluation.
For each outcome, we summarized program level findings, with significant findings defined as having a p-value less than .05. We report study level findings for each outcome of interest. We then synthesize the outcomes across studies using vote counting. Findings reported by only 1 program were not synthesized. If the majority of studies agree, the synthesis is then reported as the same as the findings from the majority of studies. Otherwise, the findings are reported as mixed.
Process Evaluation.
After grouping the process evaluation findings into categories (e.g., program awareness, attitudes, etc.), each author independently reviewed the process evaluation findings. Through open discussion, themes both within and across the categories of findings emerged. A brief summary of the findings are listed in the results, and the themes are presented in the discussion.
Results
Figure 1 illustrates the results of the search and screening process. We identified 265 citations through key word searches. No additional unique citations that met our inclusion criteria were identified through the other search strategies. After removing duplicates, we retained 138 citations for title and abstract screening, of which we excluded 124 citations, leaving 14 articles for full text review. Two articles were excluded during full text review; one did not present evaluation data and the other only included qualitative data.
Figure 1.
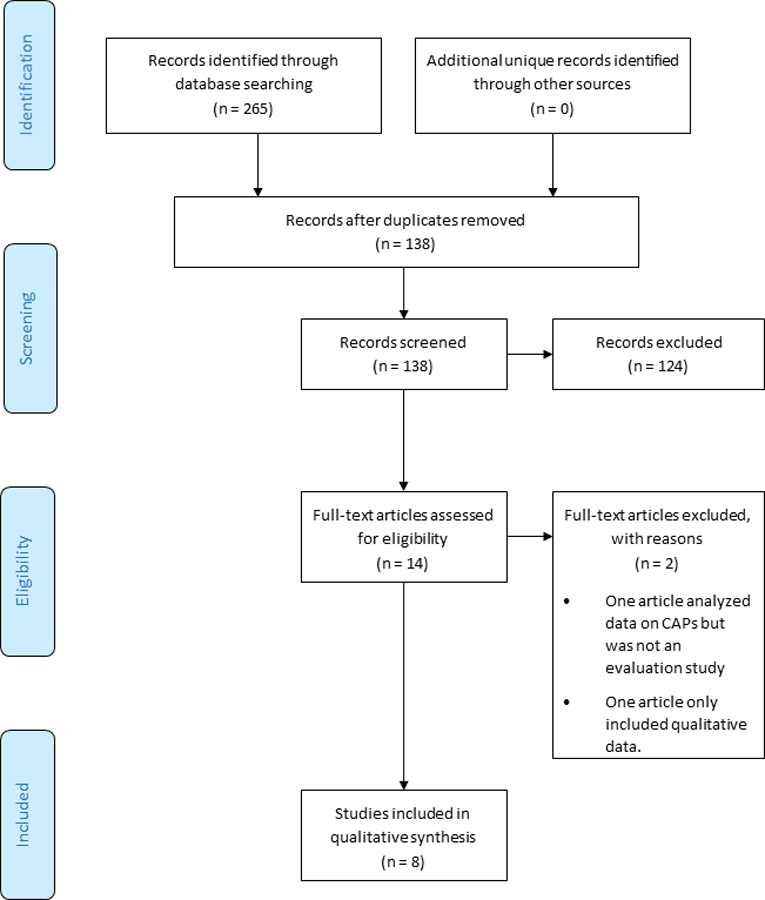
Screening for inclusion criteria
Table 1 presents study characteristics of the 12 included articles. Five publications included both process and outcome evaluation findings, three contained only process findings, and four contained only outcome findings. Of the nine publications that contained outcome findings, four used cross-sectional data with a comparison group, four used both a comparison group and multiple time points of data, and one used multiple time points of data with no comparison group
Table 1.
Select Characteristics of Included Publications
| Citation | Data type | Evaluation Type | Comparison Group | Number of Time Points | Unit of Analysis | Analyses Performed | Study Sample Size* | Race/Ethnicity* | Percent Female* | Percent Sexually Experienced* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blake et al., 2003 | Survey | Process & Outcome | Yes | 1 | Student | Analysis of covariance, logistic regression | 4166 | White 75.4%, Black 6.4%, Hispanic 8.2%, Asian 4.3%, American Indian or Alaskan Native .9%, other 4.9% | 49.3% | 47% |
| Brown, Pennylegion & Hillard, 1997 | Survey, focus groups | Process | NA | 1 | Student | Summary statistics, qualitative coding | Survey: 7830 Focus group: 130 | Survey: White 35.1%, African American 15.9%, Hispanic 4.0%, Asian 27.8%, American Indian/Alaskan Native 1.1%, Multi-ethnic/other 16.0%. Focus groups: White 35.3%, African American 40.0%, Hispanic 3.8%, Asian 8.5%, American Indian/Alaskan Native 3.1%, Multi-ethnic/other 9.2% | Survey: 50.8%. Focus groups: 66.2% | 49% |
| De Rosa et al., 2012a | Survey | Process & Outcome | Yes | 5 | Student | Multi-level hierarchical linear model | Control: 2635. Intervention: 3295 |
Control: Latino 75.8%, Black 10.5%, other 13.8%. Intervention: Latino 76.7%, Black 12.5%, other 10.8% | Control: 55.9%. Intervention: 54.9% |
Control: 46.1%. Intervention: 47.8% |
| Furstenberg et al., 1997 | Survey | Process & Outcome | Yes | 2 | Student | Weighted Logistic regression | No HRCc: 319. HRCc: 171 |
No HRCc: White 28%, Black 57%. HRCc: White 19.3%, Black 69.6% | No HRCc: 75.7%. HRCc: 75.4 | No HRCc 56%. HRCc 64% |
| Guttmacher et al., 1995 | Survey | Process | No | 1 | Student | T-tests, Chi-squared test | 6881 | African-American 24%, African-Caribbean 16%, Hispanic/Latino 31%, Asian 7%, White 13%, Other 9% | 60% | Males: 63% Females 46% |
| Guttmacher et al., 1997 | Survey | Outcome | Yes | 1 | Student | Multivariate logistic regression | 12857 | New York: African-American/Caribbean 47.1%, Hispanic/Latino 28.3%, Asian 6.9%, White 17.1% Native American 0.6%. Chicago: African-American/Caribbean 46.6%, Hispanic/Latino 28.5%, Asian 7.1%, White 17.2% Native American 0.6% | New York: 53.8%. Chicago: 53.2% |
New York continuing students:
59.7%. Chicago continuing students 60.1% |
| Guttmacher, Lieberman & Ward, 1998 | Survey | Outcome | Yes | 1 | Student | Multivariate logistic regression | 12857 | New York: African-American/Caribbean 47.1%, Hispanic/Latino 28.3%, Asian 6.9%, White 17.1% Native American 0.6%. Chicago: African-American/Caribbean 46.6%, Hispanic/Latino 28.5%, Asian 7.1%, White 17.2% Native American 0.6% | New York: 53.8%. Chicago: 53.2% | New York continuing students: 59.7%. Chicago continuing students 60.1% |
| Kirby et al., 1999 | Survey | Process & Outcome | Yes | 2 | Student | 2-way ANOVA with random effects for school | Seattle: 6636. National YRBSd: 16296 |
Seattle: White 40%, Black 19%, Hispanic 5%, Asian 31%, American Indian 1%, other 4%. National YRBSSd: White 71%, Black 14%, Hispanic 9%, Asian 3%, American Indian 1%, other 3% | Seattle: 50%. National YRBSd: 52% |
Seattle: 46%. National YRBSd: 49% |
| Schuster et al., 1997 | Survey | Process | No | 1 | Student | Weighted logistic regression | 1112 | African-American 8%, Asian and Pacific Islander 10%, Latino 27%, White 48%, other 7% | 49% | 51% |
| Schuster et al., 1998 | Survey | Outcome | No | 2 | Student | Weighted logistic regression | 1945 | African-American 9%, Asian and Pacific Islander 10%, Latino 27%, White 48%, other 6% | 48% | Male: 51%. Female: 38% |
| Wolk & Rosenbaum, 1995 | Survey | Process & Outcome | Yesb | 1 | Student | Chi-square, z-test, Mantel-Haenszel test for linear association, Spearman correlation coefficient, | 152 | . | 51.3% | 60% |
| Wretzel, Visintainer & Koenigs, 2011 | Reportable incidence data | Outcome | Yes | 7 | City | Poisson regression | 2 | . | . | . |
Baseline data reported for studies with multiple waves of data collection.
The authors evaluated an intervention to improve CAPs and used existing programs as a comparison group.
The authors only compared sexual activity in the school to the state as a whole.
Health Resource Center
Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System
The 12 articles represent findings from 8 different programs. Table 2 summarizes each CAP, however two programs did not provide detailed program descriptions in the literature. Two programs did not require consent for participating in the CAP, three programs employed passive consent procedures and one was not specified. Four programs distributed condoms confidentially, while four did not explicitly state that condoms could be obtained confidentially. Six programs provided educational material along with condoms and implemented the program in conjunction with other school-based sexual health promotion activities.
Table 2.
High School Condom Availability Program Characteristics
| CAP | State | Urban | Evaluation Citations | Parental Consent to Receive Condom | Received Condoms Confidentially | Educational Material Provided with Condom | Location of Condoms in Schools | Sexual Health Programing in School | Donation Solicited for Condom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Los Angeles Unified School District | CA | Yes | De Rosa et al., 2012 | Passive | . | Yes | . | Yes | No |
| Los Angeles County | CA | Yes | Schuster et al., 1997; Schuster et al., 1998 | None | Yes | Yes | Classroom, nurse’s office | Yes | Yes |
| Adams City High | CO | No | Wolk & Rosenbaum, 1995 | Consent was required but did not specify if it was passive or active | Yes | Yes | Classroom, nurse’s office, community health services office | Yes | No |
| Massachusetts a | MA | . | Blake et al., 2003 | . | . | . | . | . | No |
| Holyoke a | MA | No | Wretzel, Visintainer & Koenigs, 2011 | . | . | . | . | . | No |
| New York City Schools | NY | Yes | Guttmacher et al., 1995; Guttmacher et al., 1997; Guttmacher, Lieberman & Ward, 1998 | Passive | Yes | Yes | Classroom | Yes | No |
| School District of Philadelphia | PA | Yes | Furstenberg et al., 1997 | Passive | . | Yes | School-based health center, classroom, or office space | Yes | No |
| Seattle Public School District | WA | Yes | Brown, Pennylegion & Hillard, 1997; Kirby et al., 1999 | None | Yesb | Yes | School-based health center, vending machines in different places such as nurse’s office, activities center, or hallway | Yes | Yes |
Programmatic descriptions were not provided for these two CAPs.
At least one location allowed students to receive condoms confidentially.
Outcome Evaluation Findings
All 8 programs reported outcome evaluation measures, resulting in 30 unique findings summarized in Table 3 and Table 4.
Table 3.
Condom Availability Program Outcome Evaluation Findings: STIs, Pregnancy, Condom Use, and Contraception Use
| Program | STIs | Pregnancy | Condom use at last sex | Current condom use | Past year 100% condom use | Contraception use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Los Angeles Unified School District | NA | NA | Not Significant | NA | NA | NA |
| Los Angeles County | NA | NA | NA | NA | Positive | NA |
| Adams City | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Massachusetts | NA | Not Significant | Positive | NA | NA | Mixeda |
| Holyoke | Negative | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| New York City Schools | NA | NA | Positive | NA | NA | NA |
| School District of Philadelphia | NA | NA | Not Significant | Not Significant | NA | NA |
| Seattle Public School District | NA | NA | Negative | NA | NA | Positive |
| Synthesis | NA | NA | Mixed | NA | NA | Mixed |
Positive means CAPs are significantly positively associated with the outcome. Negative means CAPs are significantly negatively associated with the outcome. NA means the outcome was not assessed. The p-value for significant findings is less than .05.
This program found both positive and negative associations with different measures of contraception use.
Table 4.
Condom Availability Program Outcome Evaluation Findings: Sexual Risk and Substance Use
| Program | Substance Use | Ever Had Sex | Sexual Debut | Number of Sex Partners | Currently Sexually Active | Frequency of Sex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Los Angeles Unified School District | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Los Angeles County | NA | Not Significant | NA | NA | Not Significant | Not Significant |
| Adams City | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not Significant | NA |
| Massachusetts | Not Significant | Negative | Not Significant | Not Significant | Negative | NA |
| Holyoke | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| New York City Schools | Not Significant | Not Significant | NA | Not Significant | Not Significant | NA |
| School District of Philadelphia | NA | Not Significant | NA | NA | Not Significant | NA |
| Seattle Public School District | NA | Not Significant | Not Significant | Negative | Negative | NA |
| Synthesis | Not Significant | Not Significant | Not Significant | Not Significant | Not Significant | NA |
Positive means CAPs are significantly positively associated with the outcome. Negative means CAPs are significantly negatively associated with the outcome. NA means the outcome was not assessed. The p-value for significant findings is less than .05.
STIs and pregnancy.
One program assessed the effect of CAPs on STI rates. Wretzel, Visintainer [24] found that combined chlamydia and gonorrhea rates decreased in the city with CAPs in its high schools (47% per year), and increased in the city without a CAP (23% per year). One program assessed the effect of CAPs on pregnancy. Sexually active students in schools with CAPs did not differ from students in schools without a CAP in their likelihood of having ever been pregnant/gotten someone pregnant or the mean number of times pregnant [25].
Condom use.
Three programs assessed students’ use of CAP condoms. Use of condoms obtained from school was as high as 30% among all students [26, 27] and 74% among sexually active students [26, 27]. Kirby, Brener [27] found that students who initiated sex at a younger age, who had more frequent sex in the previous three months, and who had more sexual partners were all more likely to have used a condom obtained at school.
Six programs assessed the effect of CAPs on condom use, with five programs measuring condom use at last sex, one program measuring current condom use, and one program measuring past year 100% condom use. For condom use at last sex, the evidence is mixed, with one program showing a significant decrease in condom use, two programs showing no significant association, and two programs showing a significant increase in condom use. For example, one study found that sexually active students at schools with CAPs were more likely to have used a condom during most recent sex (adjusted odds ratio (AOR) =2.1) and were more likely to have used a condom to prevent pregnancy during most recent sex (AOR=2.1) than students at schools without a CAP [25]. Similarly all students in New York City high schools that had CAPs were more likely to use a condom at last sex (AOR=1.36) than the comparison schools without CAPs in Chicago [28, 29]. This relationship was similar among males (AOR=1.29), females (AOR=1.73), and high risk students (i.e., three or more sex partners in past six months) (AOR=1.85). One study found a decrease in condom use at last sex (57%−51%) with a significant relative difference compared to the National Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) (53%−56%) [27].
One study found no association with the presence of a CAP and recent condom use [30]. Finally, Schuster, Bell [31] found that 100% condom use for vaginal intercourse increased at follow up among male students (from 37% to 50%).
Contraception use.
Two programs assessed the effect of CAPs on the use of contraceptive methods, including general measures (i.e., any contraception including condoms) and more specific measures (i.e., oral contraception). Overall, the results are mixed with one program showing mixed results and one showing positive association between CAPs and contraception use. Blake, Ledsky [25] found that among sexually-active students, those in schools with CAPs were more likely to have used any contraception at most recent sex (AOR=1.67) than those in schools without CAPs, but less likely to have used other contraception methods (i.e., excluding condoms) (AOR=.5). It is unclear if other contraception methods include all methods such as withdrawal or only more effective methods such as oral contraception. However, in Seattle schools, the percent of students who used oral contraception at last sex remained the same (16%) with a significant relative difference compared to the decrease in the National YRBS (16%−13%) [27].
Sexual and substance use behavior.
Six of the programs assessed CAPs effect on different sexual and substance use behaviors. Our synthesis found no association between CAPs and substance use, ever having sex, sexual debut, number of sex partners, and being currently sexually active [25, 27–29, 31].
Process Evaluation Findings
Six of the 8 programs published process evaluation findings that largely addressed differences in program use among subgroups of students (e.g., boys versus girls).
Awareness of CAPs was high in two studies that reported percentages (88% and 93%) [26, 32], and 90% of students supported one program [33], although many had concerns about programmatic elements such as confidentiality and consent [26]. One study found 75% of students believed parental permission should not be required, 79% believed parental permission would make students obtain condoms less frequently, and 57% believed parental permission would make students use condoms less frequently [26].
Between 23% to 48% of all students sampled and 41% to 48% of sexually active students reported getting condoms from their school’s CAP [25, 26, 30, 33]. Male students, sexually experienced students, sexually active students, and older students were all more likely to have obtained condoms than female students or those who were not sexually experienced, students who are not currently sexually active, and younger students respectively [26, 34].
Discussion
Our analysis found a mixed association between CAPs and condom use. These results help replicate findings from another review that found similar results but drew stronger conclusions [23]. While two programs reported increases in condom use at last sex and one program reported an increase in past year 100% condom use, one program reported a decrease in condom use at last sex [27]. Kirby, Brener [27] presented two possible reasons why condom use decreased. First, condoms were already widely available in the community, which resulted in a substitution effect (i.e., students changed where they obtained condoms without increasing use). Second, the program did not address reasons students gave for not using condoms such as they trusted their partners, or had been tested for STDs. While it is clear that condom use increased in some cases, it is unclear what underlies these increases given such high variability in program implementation and evaluation. More data are needed to clarify if and when CAPs produce the desired effects of increases in condom use.
Given the preventive benefits of condom use, CAPs could lead to broader and long-term impacts on biological outcomes such as STIs or pregnancy [6]. We found limited data on associations between CAPs and biological outcomes. No program evaluations measured HIV incidence, and one looked at STI incidence, finding no significant associations between CAPs and gonorrhea or chlamydia rates separately. However, the same program did find a significant decrease in a combined rate of gonorrhea and chlamydia [24]. Additionally, one study found no association between CAPs and unintended pregnancy [25]. More data are needed to determine the effect of CAPs on biological outcomes.
Consistent with previous research [35], our review suggests that CAPs do not increase sexual behavior; in fact, the only significant associations between CAPs and sexual behaviors were protective (i.e., ever had sex, number of sex partners, and currently sexually active) [25, 27]. There were no significant associations between CAPs and increases in ever having sex, sexual initiation, currently sexually active, frequency of sex, or substance use. Thus, we found no evidence of increases in sexual risk associated with CAPs.
Additionally, there has been concern that CAPs may cause students to substitute using highly effective forms of contraception (e.g., long acting reversible contraception) with less effective ones (i.e., condoms) [36]. Our review shows mixed results for an association between CAPs and contraceptive use. The study that found CAPs to be associated with a greater likelihood of using “any” form of contraception (including condoms) at last sex, also found lower likelihood of using “other” contraception [25]. It may follow from these findings that young people are using condoms as contraception at the expense of using other forms of contraception. It is unclear from the evaluation whether such contraception replacement is, in fact, occurring and if condoms are used instead of only highly effective forms of contraception (e.g., oral contraception) or less effective forms as well (e.g., withdrawal). This same study found no changes in teen pregnancy, with similar rates in both schools with and without a CAP. Therefore, our review does not reveal data to suggest any unintended negative consequences of CAPs on teen pregnancy. Rather, our findings point to the need for further research into possible associations between CAPs and contraceptive use and for CAPs and related sexual health programs to emphasize the importance of preventing both unintended pregnancy and STIs/HIV. For example, education material could include dual prevention messages that promote using highly effective birth control methods for pregnancy prevention as well as condoms for STI and HIV prevention.
Several emergent themes from the process evaluation findings provide insight into best practices for implementing and evaluating a CAP. Every CAP was implemented in concert with other sexual health or HIV prevention programming; however, aspects of other programmatic activities were generally not considered in the evaluations. Therefore, it is unclear whether the impact of CAPs on condom use and sexual behavior is due to condom provision, other programmatic activities like sexual health education or both. Additionally, other organizational, community, and policy factors may play a role in shaping students’ sexual behavior and should also be considered. For example, one study [27] learned through focus groups with students that free condoms were already widely available to students in other venues, which may have explained why they did not see an increase in condom use even though students were taking condoms from school. Without the use of more rigorous evaluation methods (i.e., randomized controlled trials), it is recommended that evaluations consider other elements of sexual health programing in schools and other organizational, community, and policy factors that may be associated with sexual behavior, HIV, STIs, and unplanned pregnancy.
While six of the 8 programs provided information regarding the programmatic elements of CAPs, there is no consensus as to what the core elements of a program are, in order to distinguish a CAP from simply making condoms available. One evaluation however, provides insights into the elements of effective implementation of CAPs [15]. This intervention worked with partially implemented programs in schools to bring them up to full program implementation. Their action steps towards full program implementation included: 1. develop an oversight committee, 2. identify (additional) condom distributors, 3. identify a person to order and store condoms and informational material, 4. implement advertising strategies to promote condom availability, 5. disseminate parental notification, and 6. establish procedures for receiving and recording non-consent letters. De Rosa, Jeffries [15] reported significant increases in awareness and use of CAPs in intervention schools among all students, sexually experienced students, and sexually active students. This evidence suggests that partially implemented programs may be less visible to students thereby resulting in lower use of the program.
Two programs measured student attitudes of the program and found that students approved of the programs and felt their schools should make condoms available [26, 33]. However, consent procedures, confidentiality, and location of the condoms may contribute to which students use the program. One study demonstrated that students would be less likely to obtain condoms from a CAP if parental permission were required [26]. Programs should engage parents, students, and other stakeholders to develop consent procedures that fit the needs of parents and students. Similarly, qualitative research demonstrates student concerns about privacy and confidentiality suggesting students would be less likely to obtain condoms if they were not able to do so confidentially [33, 37]. Programs should consider providing at least one confidential and private location for students to obtain condoms, consistent with state laws and regulations.
CAP use differed among subgroups of students. Sexually active students had higher rates of condom acquisition and use of CAP condoms. Kirby, Brener [27] found that students with more sexual risk behavior were more likely to have used a CAP condom for sex than students with less risk behavior. This evidence indicates that CAPs may be particularly important for preventing negative health outcomes among students at disproportionate risk. Future evaluations should consider subgroup analyses based on student’s levels of sexual behavior.
Finally, we observed several differences in attitudes towards condoms and condom use between male and female students. Boys were more likely to obtain and use condoms and girls were more likely to be embarrassed if someone saw them taking a condom [26, 34]. While it is unclear if or how normative beliefs have changed, the 2015 National Youth Risk Behavior Survey demonstrated that condom use at last sex was higher among male students (61.5%) than female students (52.0%) [5]. These differences suggest that CAPs and other sexual health programs should explore and address differences in normative beliefs about condoms among boys and girls, in order to decrease disparities in use.
A final point regarding our findings pertains to the limited number of programs in existence and to the limited number of published evaluations revealed in our search. As noted, about 7% of public high schools in the United States reported making condoms available in 2015 [16], and only 8 programs have published evaluation findings. It may be speculated that the limited number of programs is related to controversy over this type of intervention or that the limited number of evaluations is related to a lack of financial resources. Further investigation is required to understand why most schools do not have CAPs, and why so few have been evaluated. While our review cannot conclude definitively that CAPs are effective, it is clear that in some cases CAPs have and therefore can achieved the goal of increasing condom use among sexually active students. Evaluation of new and existing programs are needed, and the dissemination of their findings via professional presentations, peer reviewed literature, and other avenues would help advance the fields of sexual health and school health.
Limitations.
There are several limitations to this analysis. First, due to a lack of homogeneity across a limited number of studies, meta-analysis could not be performed. Second, there is a lack of evaluation of CAPs in rural settings, potentially limiting the generalizability of these findings. Third, we included all evaluations that met our inclusion criteria, regardless of the study design and without assessment of study quality. Fourth, it is notable that the evidence from this review comes primarily from studies that were conducted in the 1990s, which may limit the generalizability to the present. Finally, our synthesis did not include grey literature which may bias our findings towards evaluations with significant findings.
Conclusions
These data suggest CAPs are not associated with increases in sexual or other risk behavior. Therefore, CAPs can be an appropriate and relevant school-based intervention for increasing condom use among teens. The association between CAPs and condom use is mixed, with more studies showing an increase in condom use. There is limited data on the associations between CAPs and biological outcomes. Considering the limited evaluation data on CAPs, existing and new programs should consider conducting evaluations and disseminating their findings. Future evaluation studies should focus on the impact of CAPs on biological outcomes as well as include measures of correct and consistent condom use. Additionally, evaluations should consider higher-level social ecological factors including other elements of sexual health programs in schools. Finally, due to subgroup differences related to CAP use and condom use, program evaluators should consider stratifying their analyses by biological sex and students’ level of risk behavior to understand differential effects of CAPs.
So What?
What is already know about this topic? CAPs have previously been found to be associated with increases condom use among students.
What does this article add? Few studies have measured the association between CAPs and biological outcomes, however some show promising results. Programmatic elements such as privacy, confidentiality, parental consent, the development of an oversight committee, and the implementation of advertising strategies may effect program use by students. Additionally, use of the program differed by biological sex and sexual risk behavior.
What are the implications for health promotion practice or research? CAPs should be implemented in a way that carefully considers the elements of confidentiality, privacy, and parental consent that best fits the needs of the students and their parents. Evaluators should consider stratifying their analyses by biological sex, and by level of risk behavior to understand differential program effects on these subgroups.
Acknowledgments
The findings and conclusions in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Footnotes
Potential Conflicts of Interest: The Authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
References
- 1.HIV Surveillance Report, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Editor. 2015, U.S. Department of health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2015, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Editor. 2016, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hamilton Brady E., Martin Joyce A., and Osterman Michelle J.K., Births: Preliminary Data for 2015. National Vital Statistics Reports, 2016. 65(3). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kearney MS and Levine PB, Why is the Teen Birth Rate in the United States So High and Why Does It Matter? Journal of Economic Perspectives, 2012. 26(2): p. 141–166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kann L, et al. , Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance -United States, 2015. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 2016. 65(6): p. 1–174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Paz-Bailey G, et al. , The effect of correct and consistent condom use on chlamydial and gonococcal infection among urban adolescents. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 2005. 159(6): p. 536–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Niccolai L, et al. , Condom effectiveness for prevention of Chlamydia trachomatis infection. Sexually Transmitted Infections, 2005. 81(4): p. 323–325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Alfonsi GA and Shlay JC, The effectiveness of condoms for the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. Current Women’s Health Reviews, 2005. 1(2): p. 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weller SC and Davis‐Beaty K, Condom effectiveness in reducing heterosexual HIV transmission. The Cochrane Library, 2002. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 10.Sundaram A, et al. , Contraceptive Failure in the United States: Estimates from the 2006–2010 National Survey of Family Growth. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 2017. 49(1): p. 7–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hock‐Long L, et al. , Access to adolescent reproductive health services: Financial and structural barriers to care. Perspectives on sexual and reproductive health, 2003. 35(3): p. 144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sarkar N, Barriers to condom use. The European Journal of Contraception & Reproductive Health Care, 2008. 13(2): p. 114–122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Harper CR, et al. , Variability in Condom Use Trends by Sexual Risk Behaviors: Findings from the 2003–2015 National Youth Risk Behavior Surveys. Sex Transm Dis, 2018. 45(6): p. 400–405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kirby DB and Brown NL, Condom availability programs in U.S. schools. Family planning perspectives, 1996. 28(5): p. 196–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.De Rosa CJ, et al. , Improving the implementation of a condom availability program in urban high schools. Journal of Adolescent Health, 2012. 51(6): p. 572–579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Results from the School Health Policies and Practices Study 2014, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Editor. 2015, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mahler K, Condom availability in the schools: lessons from the courtroom. Family Planning Perspectives, 1996. 28(2): p. 75–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kirby D and Coyle K, School-based programs to reduce sexual risk-taking behavior. Children and Youth Services Review, 1997. 19(5–6): p. 415–436. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Guttmacher S, Parents’ Attitudes and Beliefs about HIV/AIDS Prevention with Condom Availability in New York City Public High Schools. The Journal of School Health, 1995: p. 101–106. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 20.Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine, Condom Availability in Schools: A Practical Approach to the Prevention of Sexually Transmitted Infection/HIV and Unintended Pregnancy. Journal of Adolescent Health, 2017. 60(6): p. 754–757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.O’Brien R, et al. , Condom Use by Adolescents. Pediatrics, 2013. 132(5): p. 973–981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Charania MR, et al. , Efficacy of structural-level condom distribution interventions: a meta-analysis of US and international studies, 1998–2007. AIDS and Behavior, 2011. 15(7): p. 1283–1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang T, et al. , The Effects of School-Based Condom Availability Programs (CAPs) on Condom Acquisition, Use and Sexual Behavior: A Systematic Review. AIDS and Behavior, 2018. 22(1): p. 308–320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wretzel SR, Visintainer PF, and Pinkston Koenigs LM, Condom availability program in an inner city public school: Effect on the rates of gonorrhea and chlamydia infection. Journal of Adolescent Health, 2011. 49(3): p. 324–326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Blake SM, et al. , Condom Availability Programs in Massachusetts High Schools: Relationships with Condom Use and Sexual Behavior. American Journal of Public Health, 2003. 93(6): p. 955–962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schuster MA, et al. , Students’ acquisition and use of school condoms in a high school condom availability program. Pediatrics, 1997. 100(4): p. 689–694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kirby D, et al. , The impact of condom distribution in Seattle schools on sexual behavior and condom use. American Journal of Public Health, 1999. 89(2): p. 182–187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guttmacher S, et al. , Condom availability in New York City public high schools: Relationships to condom use and sexual behavior. American Journal of Public Health, 1997. 87(9): p. 1427–1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Guttmacher S, Lieberman L, and Ward D, Does access to condoms influence adolescent sexual behavior? AIDS Reader, 1998. 8(4): p. 201–205+209. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Furstenberg FFG, Lynne M; Teitler Julien O; Weiss Christopher C, Does condom availability make a difference? An evaluation of Philadelphia’s health resource centers. Family Planning Perspectives, 1997. 29(3): p. 123–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schuster MA, et al. , Impact of a high school condom availability program on sexual attitudes and behaviors. Family Planning Perspectives, 1998. 30(2): p. 67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wolk LI and Rosenbaum R, The benefits of school-based condom availability: Cross-sectional analysis of a comprehensive high school-based program. Journal of Adolescent Health, 1995. 17(3): p. 184–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brown NL, Pennylegion MT, and Hillard P, A Process Evaluation of Condom Availability in the Seattle, Washington Public Schools. Journal of School Health, 1997. 67(8): p. 336–340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Guttmacher S, et al. , Gender differences in attitudes and use of condom availability programs among sexually active students in New York City public high schools. Journal of the American Medical Women’s Association, 1995. 50(3–4): p. 99–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kirby DB, The impact of schools and school programs upon adolescent sexual behavior. Journal of Sex Research, 2002. 39(1): p. 27–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Buckles KS and Hungerman DM, The Incidental Fertility Effects of School Condom Distribution Programs 2016. [PubMed]
- 37.Rafferty Y and Radosh A, AIDS prevention and condom availability in an urban school system: facilitating factors and programme challenges. Health Education Journal, 2000. 59(1): p. 50–68. [Google Scholar]


