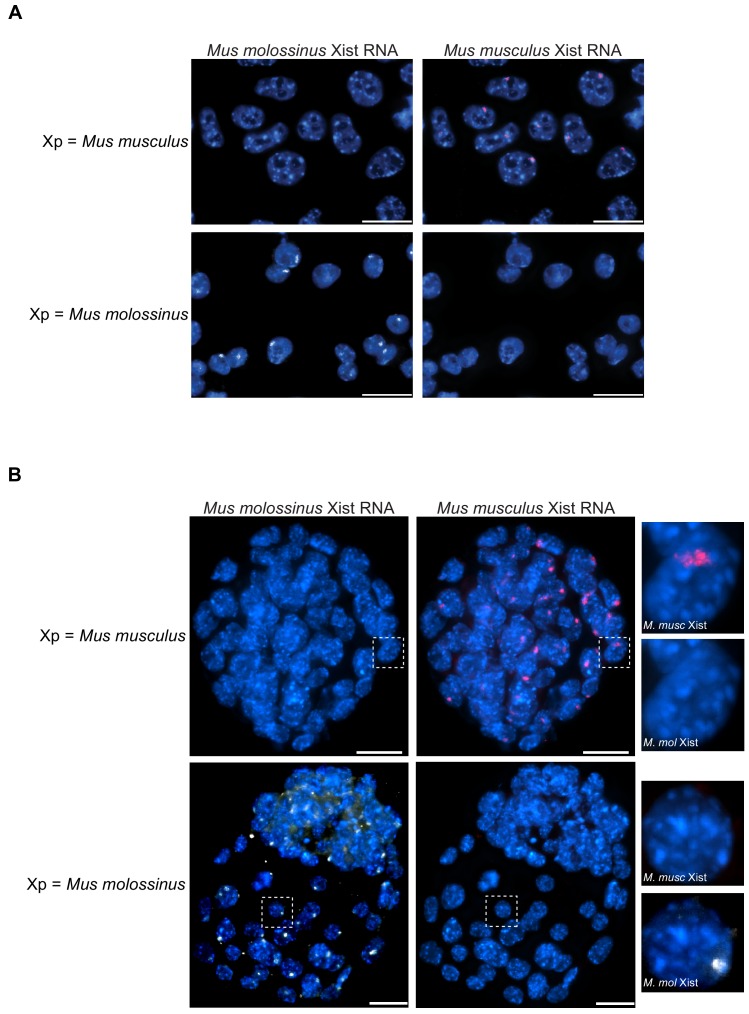
(
A) Female Trophoblast stem (TS) cells (top panel) and extraembryonic endoderm (XEN) stem cells (bottom panel) stained with an allele-specific Xist RNA FISH probe. Both TS cells and XEN cells express
Xist from and undergo imprinted X-inactivation of the paternal X-chromosome (
Kunath et al., 2005;
Tanaka et al., 1998). The TS cells are derived from a cross of JF1
Mus molossinus dam with a 129/S1-derived
Mus musculus sire. The XEN cells are generated from a cross of 129/S1
Mus musculus dam and JF1
Mus molossinus-derived sire. In the TS cells, the paternal-X is therefore
Mus musculus derived while in the XEN cells the paternal-X is JF1
Mus molossinus derived.
Mus musculus-specific Xist RNA FISH probe detects the complimentary Xist RNA in red and the
Mus molossinus-specific Xist RNA FISH probe detects its complimentary Xist RNA in white. (
B)
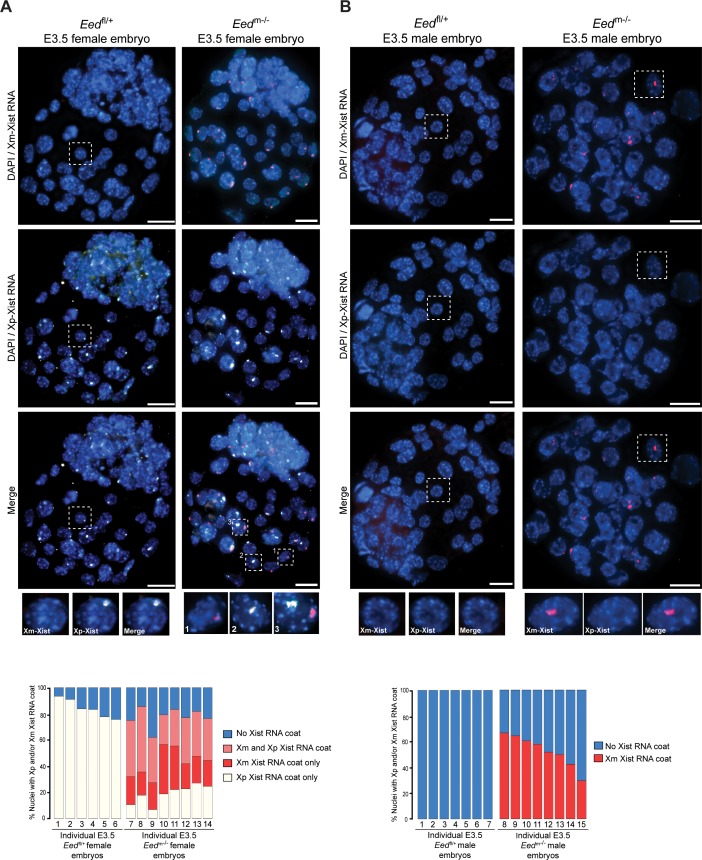
Eedfl/+ female E3.5 embryos stained with the same allele-specific Xist RNA FISH probe as in (
A). Top panels, representative stained embryo derived from a cross of
Eedfl/fl;
XJF1XJF1
Mus molossinus-derived dam with a
Mus musculus sire. Bottom panels, representative stained embryo from an
Eedfl/fl Mus musculus-derived dam with a JF1
Mus molossinus-derived sire (this embryo is also shown in
Figure 6A). Due to imprinted X-inactivation, both E3.5 embryos are expected to express Xist RNA from their paternal X-chromosome.