Parker KL, Chen KH, Kingyon JR, Cavanagh JF, Narayanan NS. Medial frontal ~4-Hz activity in humans and rodents is attenuated in PD patients and in rodents with cortical dopamine depletion. J Neurophysiol 114: 1310–1320, 2015. First published July 1, 2015; doi: 10.1152/jn.00412.2015.
The authors issue corrections to their article “Medial frontal ~4-Hz activity in humans and rodents is attenuated in PD patients and in rodents with cortical dopamine depletion.” These corrections do not affect any conclusions in this article and stemmed from errors in their code. Although they do not affect any interpretations of data in the manuscript, they are issued as part of the authors' commitment to scientific accuracy.
CORRECTIONS
On page 1314, the sentence beginning: “Around 12-s peaks . . . ” should now read: “Around 12-s peaks, humans with PD response-time distributions trended to be less curved [curvature index 0.18 ± 0.07 vs. 0.00 ± 0.05; t(1,24)=2.18, P < 0.04], while around 3-s peaks, curvature was not significantly different [curvature index 0.04 ± 0.02 vs. 0.06 ± 0.02; t(1,24) = 0.56, P < 0.58].”
On page 1314, the sentence beginning “Rodent dopamine depletion also decreased . . . ” should now read: “Rodent dopamine depletion trended to decrease curvature indices for 12-s trials only [Int 12: 0.15 ± 0.05 vs. −0.07 vs. 0.08; paired t(1,10) = 1.9, P < 0.09; Int 3: −0.47 ± 0.04 vs. −0.49 ± 0.08; paired t(1,10) = 0.21, P < 0.84; Fig. 1C].”
Fig. 1.
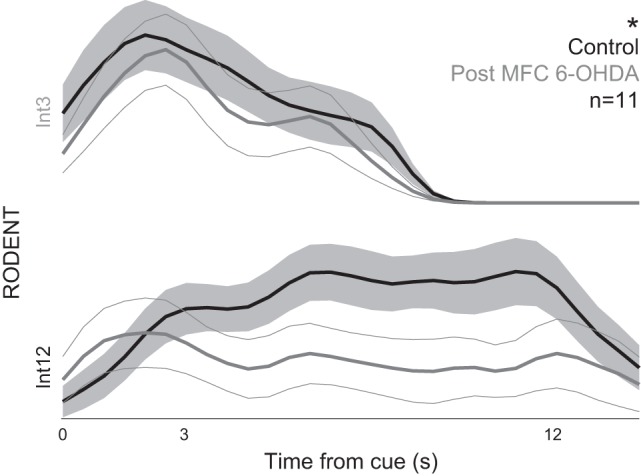
Replacement image for Fig. 1C.
Table 2 should read as shown below.
Table 2.
Response time medians and means
| Species | Condition | Interval Length | Median | Mean | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | Young | 3 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 0.03 |
| 12 | 12.2 | 11.9 | 0.1 | ||
| Control | 3 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 0.02 | |
| 12 | 12.1 | 11.8 | 0.04 | ||
| PD | 3 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 0.02 | |
| 12 | 11.4 | 11.5 | 0.05 | ||
| Rodent | Control | 3 | 4.1 | 4.4 | 0.3 |
| 12 | 8.8 | 9.2 | 0.4 | ||
| MFC 6-OHDA | 3 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 0.2 | |
| 12 | 8.6 | 7.7 | 0.9 |
All values are in seconds. Statistics are given in the text. MFC, medial frontal cortex; 6-OHDA, 6-hydroxydopamine.
Figure 1C should appear as shown below.
TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
On page 1314, the text “greater SEs for humans compared with rats” should now read “greater SEs for rats compared with humans.”
In Fig. 4's legend on page 1315, the word “normalized” should be deleted from the first line.
CLARIFICATIONS
Finally, on page 1312, the authors would like to clarify the rodent animal numbers. Eleven animals had MFC cannula and were included in behavioral analyses; eight animals had MFC cannula and were included in neurophysiological analyses. In Fig. 3 the authors' goal was to compare human EEG to rodent LFP in sessions without any drug infusions into frontal cortex. The authors had these sessions for five animals; data from these animals were previously published (Parker et al. 2014).
Crucially, these clarifications and corrections do not affect any conclusions or interpretations of this manuscript.
REFERENCE
- Parker KL, Chen KH, Kingyon JR, Cavanagh JF, Narayanan NS. D1-dependent 4 Hz oscillations and ramping activity in rodent medial frontal cortex during interval timing. J Neurosci 34: 16774–16783, 2014. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2772-14.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


