Abstract
Ischemic diseases, which are caused by a reduction of blood supply that results in reduced oxygen transfer and nutrient uptake, are becoming the leading cause of disabilities and deaths. Therapeutic angiogenesis is key for the treatment of these diseases. Stem cells have been used in animal models and clinical trials to treat various ischemic diseases. Recently, the efficacy of stem cell therapy has increasingly been attributed to exocrine functions, particularly extracellular vesicles. Extracellular vesicles are thought to act as intercellular communication vehicles to transport informational molecules including proteins, mRNA, microRNAs, DNA fragments, and lipids. Studies have demonstrated that extracellular vesicles promote angiogenesis in cellular experiments and animal models. Herein, recent reports on the use of extracellular vesicles for therapeutic angiogenesis during ischemic diseases are presented and discussed. We believe that extracellular vesicles-based therapeutics will be an ideal treatment method for patients with ischemic diseases.
Keywords: Stem cells, Extracellular vesicles, Exosomes, Angiogenesis, Ischemic diseases
Background
With the development of society and improvement of living standards, ischemic diseases have become a leading cause of disabilities and deaths in humans. Ischemic diseases are characterized by a reduction of blood supply with limited oxygen transfer and nutrient uptake. Thus, angiogenesis and blood supply reconstruction are key for treatment of ischemic diseases. Current clinical treatments primarily involve medical therapy (thrombolytic drugs and vasodilator drugs [1]) and surgery [2]. However, it remains difficult to achieve the purpose of vascular remodeling using either drugs [3] or surgery [4]. Inspired by the fact that the body undergoes natural angiogenesis in response to an insufficient blood supply, scientists have learned to enhance the efficiency of angiogenesis as a treatment strategy. The concept of therapeutic angiogenesis involves introducing an agent to promote the growth of new blood vessels in ischemic tissue. Stem cell therapy is a technology that has shown great prospects for ischemic diseases [5, 6]. Indeed, stem cells have been used in animal models and clinical trials to treat various ischemic diseases. However, as transplantation of stem cells continues to be limited by ethical issues, tumorigenicity, and immune rejection, such therapies are not widely available in the clinic.
Recent studies have found that stem cell supernatants can promote repair of damaged tissue [7, 8]. Accordingly, researchers began to focus on the exocrine function of stem cells. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are secreted from cells, have been discovered for more than 30 years. In the past, scientists have thought of EVs as cellular dust. Today, EVs are thought to be carriers of intercellular biological information, as they may contain nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins, thereby playing an indispensable role in cell-to-cell communication [9]. Furthermore, the composition of EVs varies according to their origin, and the information they carry also varies [10]. Biological characteristics and functions of EVs suggest their potential application for cell-free regeneration strategies, which may avoid the disadvantages of current stem cell transplantation techniques.
In particular, recent studies have reported that EVs accelerate angiogenesis in cellular experiments and animal models [10–12]. Here, we first summarize the characteristics and properties of EVs (Table 1) and then discuss the emerging role of stem cell-derived EVs in ischemic diseases, such as chronic wound, ischemic cardiomyopathy, and ischemic stroke. We believe that EV-based therapeutics will be an ideal option for patients who suffer from ischemic diseases.
Table 1.
The main characteristics of extracellular vesicles
| Biological characteristics | Exosomes | Microvesicles | Apoptotic bodies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generation | MVEs fuse with cell membranes to release ILVs as exosomes into the extracellular space | budding from plasma membrane directly | budding from apoptotic membrane directly |
| Shape | Cup-shaped | Heterogeneous | Heterogeneous |
| Size(nm) | 50–150 | 100–1000 | 1000–5000 |
| Markers | Tetraspanins (CD9/63/81), Alix, TSG101, flollin, clathrin, MHC | Annexin V, selecns, integrins, flollin-2, CD40, metalloproteinases | Annexin V, Histones |
| Lipids | PtdSer, sphingomyelin cholesterol, ceramide, lysobisphoshadic acid etc. | PtdSer, cholesterol, sphingomyelin etc. | PtdSer etc. |
| Nucleic acids | mRNA, miRNA, lncRNAs | mRNA, miRNA, lncRNAs | mRNA, miRNA, lncRNAs, fragments of DNA |
Abbreviation: MVEs multi-vesicular endosomes, ILVs intraluminal vesicles, PtdSer phosphatidylserine
Biological characteristics of EVs
EVs have three distinct types including exosomes, microvesicles (MVs), and apoptotic bodies (ApoBDs) [13], as classified by their biogenesis and origin. Here, we mainly summarize the generation, composition, and isolation of EVs.
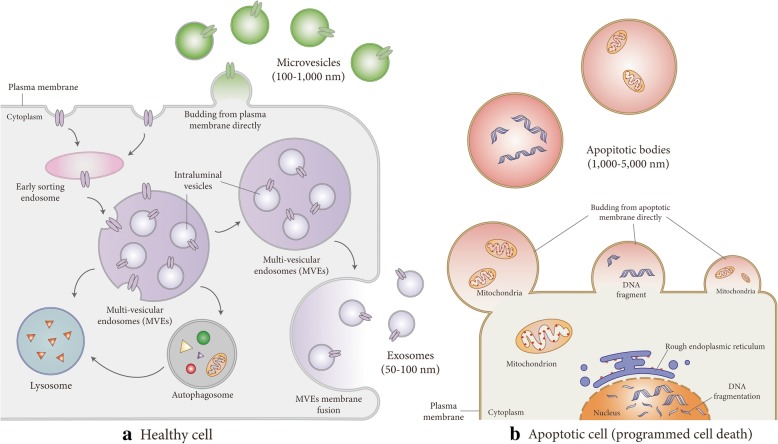
Generation of EVs (Fig. 1)
Fig. 1.
Generation and release of extracellular vesicles (EVs). a Healthy cells produce exosomes and MVs. Exosomes occur through three steps: cytomembrane recess inward to form early endosomes, intraluminal vesicle forming in multi-vesicular endosomes (MVEs) by intraluminal budding, and MVE fusing with cell membranes to release ILVs as exosomes. MVs bud outward directly from the plasma membrane. b Apoptotic cells produce ApoBDs. ApoBDs bud outward directly from the apoptotic membrane. ApoBDs are thought to be connected with self-cleaning of aging cells and intercellular immune regulation
Exosomes, defined as 50–150-nm-sized vesicles, were found and named in 1987 [14]. The process of exosome generation can be summarized into three parts. First, the cytomembrane recesses inward to form early endosomes. Second, these early endosomes further develop into multi-vesicular endosomes (MVEs) in which intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) are formed by intraluminal budding. Finally, MVEs fuse with cell membranes to release ILVs as exosomes into the extracellular space, where they can be taken up by donor cells [9]. Released exosomes can travel to distant tissues to affect the behavior and biological function of target cells [15], which bind to the surface of exosomes through specific ligands. There are two ways in which exosomes enter target cells [16], namely cellular endocytosis and membrane fusion, whereby they release their cargoes. Unlike exosomes, MVs are in the range of 100–1000 nm in diameter [17] and are usually larger than exosomes. MVs bud from plasma membrane directly and then are released extracellularly under the condition of various stresses including irradiation, injury, and hypoxia [18]. Many studies have shown that exosomes and MVs are generated from healthy cells, while ApoBDs are mainly produced by dying cells or apoptotic cells [19]. The role of ApoBDs in intercellular communication is currently unclear. Researchers consider the primary functions of ApoBDs are self-cleaning of aging cells and intercellular immune regulation [20–22].
Composition of EVs
Proteins
Proteins in EVs are mainly derived from plasma membrane, cytosol, Golgi, and nucleus [23, 24]. As more EV proteins are identified, it has been apparent that EVs contain a common set of EV proteins and cell-type-specific components. The common proteins include cytoskeletal proteins, heat-shock proteins, metabolic enzymes, annexins, ribosomal proteins, tetraspanins, vesicle trafficking-related proteins, and major histocompatibility complex (MHC). The purity of EV preparation is often demonstrated by protein markers enriched in EVs. In fact, tetraspanins including CD9, CD63, CD81, and CD82; heat-shock proteins (e.g., HSP70 and HSP90); MHC classes (I and II); Tsg101; 14-3-3 proteins; and the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT-3) binding protein Alix have been regarded as “specific” exosomes markers for years. However, these proteins can also be detectable in ApoBDs and MVs [24, 25]. In addition, the types of cell-type-specific proteins are dependent on their parental cells and conditions under which the EVs are secreted. These proteins include immune-modulating proteins, cell-surface antigens, proteases, angiogenic and molecules [26].
Lipids
EVs are rich in lipids such as cholesterol, phosphatidylserine, diglyceride, phospholipid, phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylinositol, polyglycerol, and phosphatidylethanolamine. Specifically, exosome plasma membranes contain a lot of cholesterol, sphingomyelin, ceramide, lipid rafts, and phosphatidylserine. MV and ApoBD membranes have high concentration of phosphatidylserine [27]. The stability of EV membrane is attributed in part to the lipid content of their membranes [28]. As a result of their high lipid content, EVs have the capacity to pass through biological barriers, escape phagocytosis by the reticuloendothelial system, and protect informational molecules contained within EVs [29]. Interestingly, lipids contained in EVs are somewhat different from other lipids present in their source cells, which might be affected by the micro-environment around EVs. For example, tumor micro-environments may lead to an enrichment of certain tumor progressive or immunosuppressive lipids, such as prostaglandins [30].
Nucleic acids
Besides proteins and lipids, EVs also incorporate coding RNA (mRNAs), non-coding RNAs (nc-RNAs), and DNA fragments [31–33]. According to nucleotide length, nc-RNAs are divided into long nc-RNAs (lncRNAs, longer than 200 nucleotides) [34] and small nc-RNAs (sncRNAs, smaller than 200 nucleotides) [35]. LncRNAs encompass the largest proportion of the non-coding transcriptome, but their functions are so far not well defined except for their role in tumor genesis [34]. SncRNAs in EVs include microRNAs (miRNAs), mitochondrial RNAs, piwi-RNA (pi-RNAs), small nuclear RNA, small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA), transfer RNA, Y-RNA, vault RNA, and small interfering RNA (siRNA) [36–38]. Among these sncRNAs, miRNAs [39], Y-RNAs [37, 40], pi-RNA [41], snoRNA [42], and siRNA [43] have been shown to mediate the therapeutic effect of EVs. MiRNAs in particular are the well-known group of sncRNAs and have already been studied extensively. In addition, DNA fragments in EVs such as ApoBDs may be related to cell apoptosis [19].
Isolation of EVs
The most common method for EVs isolation is differential centrifugation, which can separate similarly sized vesicle particles. Johnstone et al. originally developed differential centrifugation for the separation of EVs in reticulocyte tissue culture fluid [14]. Later, Théry et al. optimized and improved this method [15]. The first step involves centrifugation at 300×g, 2000×g, and 10,000×g to remove cells, dead cells, and cell debris, respectively. The second step is ultracentrifugation (> 100,000×g) to obtain a crude EV-rich extract. The third step repeats ultracentrifugation twice to remove contaminating proteins, which allows clear EVs to be obtained. Today, this method is widely used for various biological samples and considered a “gold standard” for isolating EVs. Advantages of this method are simple operation and production of a large number of EVs. However, the whole process is time-consuming and repeated centrifugation operations may damage the EVs. Thus, further improvement of this method is necessary.
EVs promote angiogenesis in chronic wound healing
Chronic wounds, which have the characteristics of complex pathogenesis, prolonged disease, easy recurrence, prolonged treatment time, high cost, and high disability rate, refer to wounds that cannot attain anatomical and functional wound healing standards after regular treatment for 4 weeks or more [44]. Most recalcitrant wounds result from pressure ulcers [45], diabetic ulcers [46], venous ulcers [47], vascular insufficiency (e.g., arteriosclerosis [48] or critical limb ischemia [49]), and trauma such as burns [50] and frostbite [51]. Difficulties associated with chronic wound healing have primarily been ascribed to a lack of angiogenesis [52]. Furthermore, without neovascularization, acute wounds will become chronic wounds [53]. Recently, EVs derived from many sources of stem cells have been reported as one of the most promising treatments for chronic wounds by promoting angiogenesis (Table 2).
Table 2.
Extracellular vesicles derived from stem cells promote angiogenesis in chronic wound healing
| EVs source | EVs type | EVs isolation | Experimental model (target cells/animal models) | Functional cargo | Molecules/pathways activated | Key functions/downstream genes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM-MSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) | STAT3 | Akt, ERK, and STAT3 | HGF, IL-6, IGF-1, NGF and SDF1↑ | Shabbir et al. [54] |
| BM-MSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation PEG-US-S purification Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) | Wnt3a | Wnt pathway | CD63+ exosomes are a significant carrier of exterior Wnt3a which results in angiogenesis in vitro. | McBride et al. [55] |
| ADSCs | MVs |
Differential centrifugation 100 KDa molecular filtration Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (mice/full-thickness wounds model) |
/ | PI3K-AKT and ERK signaling pathways | VEGFA, PDGFA, EGF and bFGF↑ | Ren et al. [56] |
| ADSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 0.2-μm pore membrane filtration Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (male BALB/c nude mice) |
miR-125a | Speculated to Notch signaling pathways |
proangiogenic genes Ang1 and Flk1 ↑ anti-angiogenic genes Vash1, TSP1 and DLL4 ↓ |
Liang et al. [57] |
| ADSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 0.2-μm pore membrane filtration Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (nude mice) |
/ | PKA signaling pathway |
proangiogenesis gene Angpt1 and Flk1↑ VEGF↑ anti-angiogenic gene Vash1↓ |
Xue et al. [58] |
| UC-MSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 0.2-μm pore membrane filtration Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HMECs) In vivo (male C57BL/6 mice/full-thickness excisional skin wounds model) |
miR-21-3p | PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling | PTEN and SPRY1↓ | Hu et al. [59] |
| UC-MSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 100 kDa molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) hollow fiber membrane Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (EA.hy926 cells) In vivo(rats/deep second-degree burn wounds model) |
Wnt4 | Wnt pathway | Wnt4 induces β-catenin activation in endothelial cells and exerts proangiogenic effects. | Zhang et al. [60] |
| PMSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 0.2-μm pore membrane filtration Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HMECs) In vivo (nude mice/auricle ischemic injury model) |
/ | / | PMSC-Exos enhanced angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo | Komaki et al. [61] |
| iPSCs | Exosomes | MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit | In vivo (male C57BLKS/J-Leprdb (db/db) mice/full-thickness excisional skin wounds and diabetes model) | / | / | iPSC-Exos significantly increased micro-vessel of full-thickness excisional skin wounds in diabetes mice | Kobayashi et al. [62] |
| iPSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 0.2-μm pore membrane filtration Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (female Sprague-Dawley rats/full-thickness skin defect model) |
/ | / | iPSC-Exos can increase proliferation, migration, and tube formation of HUVECs in a dose-dependent manner | Zhang et al. [63] |
| EPCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 0.2-μm pore membrane filtration Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HMECs) In vivo(male Sprague-Dawley rats) |
/ | / |
eNOS, IL-8, ANG-1, E-selectin, VEGFA, VEGFR-2, HIF- 1a, CXCL16 and PDGFA↑ PDGFB and MMP-9↓ |
Li et al. [64] |
| EPCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 0.2-μm pore membrane filtration Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HMECs) In vivo (male Sprague-Dawley rats/diabetic model) |
/ | / |
aFGF, eNOS, IL-8, ANG-1, E-selectin, VEGFA, VEGFR-2 and CXCL-16↑ MMP-9↓ |
Li et al. [65] |
Abbreviation: BM-MSCs bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells, ADSCs adipose-derived stem cells, UC-MSCs umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, PMSCs placenta tissue mesenchymal stem cells, iPSCs induced pluripotent stem cells, EPCs endothelial progenitor cells, MVs microvesicles, PEG-UC-S polyethylene glycol-sucrose cushion method, HUVECs human umbilical vein endothelial cells, HMECs human microvascular endothelial cells, HGF hepatocyte growth factor, IL-6 interleukin-6, IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor-1, NGF nerve growth factor, SDF1 stromal-derived growth factor-1, VEGFA vascular endothelial growth factor A, PDGFA platelet-derived growth factor subunit A, EGF epidermal growth factor, bFGF basic fibroblast growth factor, DLL4 delta-like 4, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, IL-8 interleukin-8, ANG-1 angiopoietin-1, VEGFR-2 vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, HIF-1a hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha, PDGFA platelet-derived growth factor subunit A, PDGFB platelet-derived growth factor subunit B, MMP-9 matrix metallopeptidase 9
BM-MSC-EVs
Bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) are a type of adult stem cells derived from the mesoderm, which mainly exist in bone marrow stroma to support hematopoiesis. Transplantation of BM-MSCs seeded in a collagen scaffold resulted in increased wound healing and enhanced angiogenesis [66]. Furthermore, when BM-MSCs were seeded directly onto the wound site and injected into the wound edges, increased dermal vascularity was observed in the wound [67]. Some studies have suggested that the paracrine functions of BM-MSCs elicit angiogenesis in the wound by activating vascular endothelial cells [68–70]. EVs as an important paracrine factor of BM-MSCs (BM-MSC-EVs) have been examined as potential BM-MSC-based therapies. Experiments showed that BM-MSC-EVs were internalized by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and promoted endothelial angiogenesis in vitro [54]. This finding is in line with many reports demonstrating the angiogenic potential of BM-MSC-conditioned medium. Further research demonstrated that BM-MSC-EVs activated important signaling cascades including AKT, STAT3, and ERK in recipient cells. These pathways were probably responsible for increased transcription of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), which can improve endothelial neovascularization. In another study, CD63+ exosomes were isolated by flow cytometry of magnetic beads coated with anti-CD63+ antibodies. For the first time, CD63+ exosomes containing Wnt3a exteriorly were found to stimulate tube length formation in vitro by activating the canonical Wnt signaling pathway [55].
ADSC-EVs
In addition to their self-renewal ability and multi-directional differentiation potential, adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) are an abundant resource that can rapidly expand in vitro. Indeed, ADSCs have been shown to maintain both a stable phenotype and multipotent differentiation ability after in vitro culture for 40 generations or cryopreservation [71]. In vivo experiments have revealed that ADSC-derived therapies can significantly improve mean capillary count in chronic wounds [72, 73]. Moreover, ADSC-induced acceleration of VEGF levels in diabetic wounds reportedly regulates local angiogenesis [74]. Recently, Ren et al. [56] demonstrated that ADSC-derived MVs (ADSC-MVs) promoted tube formation of HUVECs seeding in a transwell system. Similarly, ASC-MVs could also increase the establishment efficiency of newly formed vessels and mature vessels in vivo. Moreover, after the treatment of ADSC-MVs, the expression of many growth factors and receptors including platelet-derived growth factor subunit A(PDGFA), vascular endothelial growth factor A(VEGFA), bFGF, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2), and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) were significantly upregulated in HUVECs. Further study showed that ASC-MVs could increase the activation level of ERK and AKT signaling pathways in HUVECs, which may be responsible for the angiogenesis effect of ASC-MVs on endothelial cells. It was observed that loss of Nrf2/ARE activity increases oxidative stress, which can aggravate endothelial dysfunction and abnormal angiogenesis occurring in diabetes [75]. The researchers demonstrated that ADSC-derived exosomes (ADSC-Exo) overexpressing Nrf2 increased granulation tissue formation, promoted tube formation, and accelerated angiogenesis, suggesting that ADSC-Exo can potentially promote angiogenesis. Therefore, transplantation of exosomes may be suitable for clinical applications to treat diabetic foot ulcers. In addition to this study, other scientists reported that treatment of HUVECs with ADSC-Exo can promote the expression of proangiogenesis genes Angpt1 and Flk1 and inhibit the anti-angiogenesis gene Vash1, which improved wound healing [57]. Angpt1 and Flk1 are key for promoting tube formation, whereas Vash1 inhibits tube formation. Further study found that, by activating PKA pathway signaling, hypoxia-exposed ADSC-Exo promoted proangiogenesis gene expression, downregulated anti-angiogenic gene expression (Angpt1 and Flk1), and promoted tube formation (Vash1). In addition, in vivo experiments assessing vascular formation yielded similar results to in vitro cell models, suggesting that hypoxia-exposed exosomes can indeed enhance angiogenesis [58]. A large number of studies have reported that under conditions of hypoxia and inflammation, most cells can secrete VEGF, which can specifically act on vascular endothelial cells and promote blood vessel formation in vivo. As VEGF is known to activate the PKA signaling pathway [76], researchers examined the PKA signaling pathway in HUVECs after exosome treatment. They found that PKA signaling was activated, which further promoted endogenous VEGF expression in HUVECs and synergistically regulated the expression of downstream proangiogenic genes Angpt1 and Flk1, and decreased the anti-angiogenic gene Vash1, thus promoting angiogenesis. Therefore, this finding may represent a novel therapy for hypoxic-condition wounds, as well as the treatment of ischemic diseases with stem cell-derived products.
UCB-EVs, UC-MSC-EVs, and PMSC-EVs
Fetal appendage-derived MSCs are obtained from both maternal and fetal origins, such as umbilical cord blood MSCs (UCB-MSCs), umbilical cord MSCs (UC-MSCs), and placenta tissue MSCs (PMSCs). Fetal appendage-derived MSCs are an attractive source of transplantable stem cells for wound repair because they have no risk to donors, easy accessibility, and a low incidence of graft-versus-host disease [77, 78]. Many studies have shown that direct use of fetal-derived MSCs or their conditioned media can significantly increase neovascularization and promote chronic wound healing. MSCs derived from fetal appendages secrete proangiogenic molecules including VEGF, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), bFGF, TGF-β, and insulin-like growth factor-1 [79–83]. Hu et al. first demonstrated that local transplantation of umbilical cord blood-derived exosomes (UCB-Exo) induced prominent regenerative effects in wound healing, mainly through new blood vessel formation [59]. Further experiments demonstrated that UCB-Exo accelerated cutaneous wound healing through miR-21-3p-mediated promotion of angiogenesis. Zhang et al. later demonstrated that human UC-MSC-Exo improved the tube-formation ability of endothelial cells in vitro and promoted angiogenesis in a cutaneous burn model in vivo [60]. Further exploration of the underlying mechanism revealed that extracted exosomes contained wnt4 protein, which can promote β-catenin nuclear transfer, activate the wnt/β-catenin pathway in skin, and inhibit E-cadherin expression, thus promoting the angiogenesis of skin. Furthermore, exosomes derived from PMSC-conditioned media (PMSC-Exo) also contained angiogenic factors, which enhanced endothelial tube formation. In vivo laser Doppler blood flow analysis showed that PMSC-Exo also enhanced angiogenesis in a murine ischemic injury model [61].
iPSC-EVs
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are generated by reprogramming somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells with the characteristics and functions of embryonic stem cells (ESCs). iPSCs are an abundant potential source of autologous or donor-matched cells for therapy and, therefore, have emerged as a promising alternative to ESCs for stem cell transplantation therapy. Scientists found that use of iPSCs or iPSC-derived fibroblasts with three-dimensional structure could improve wound healing [84, 85]. Recently, EVs derived from iPSCs (iPSC-EVs) were also used to treat diabetic wounds in mice [62]. Newly formed vessels and average vessel density in the exosomes derived from iPSCs (iPSC-Exo)-treated group at day 7 were significantly higher, suggesting that iPSC-Exo can improve diabetic chronic wounds by enhancing vessel density and number. In a rat skin full-thickness defect model, exosomes were found to promote wound blood vessel regeneration and maturation. In addition, iPSC-Exo were also reported to promote HUVEC tube formation in vitro [63]. Although some studies have shown that iPSC-Exo has a great effect on wound angiogenesis, underlying mechanisms have not been clearly explained, which provides direction for our future research.
EPC-EVs
Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are mainly found in the bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, and peripheral blood. Recent studies indicate that EPCs can promote diabetic wound repair by facilitating neovascularization and the therapeutic effects of EPCs were attributed to a paracrine mechanism [86, 87]. Studies found that EVs derived from EPCs (EPC-EVs) accelerated the healing of diabetic skin wounds by promoting the regeneration of blood vessels. Experiments in vitro showed that EPC-Exo increased the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells and accelerated expression of vascular-related factors such as VEGF and HIF-1α [64]. Experiments in vivo demonstrated that transplantation of EPC-Exo could accelerate skin wound healing in diabetic rats by positively modulating vascular endothelial cell function [65]. Further research showed that Erk1/2 signaling pathway was the critical mediator during the angiogenic responses of endothelial cells induced by EPC-Exo [88]. However, what EPC-Exo components are transferred into vascular endothelial cells remains unclear.
EVs promote angiogenesis in myocardial ischemia
With advancements in basic and clinical research of cardiovascular disease, the current clinical treatment of myocardial ischemia involves interventions such as percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty and coronary artery bypass grafting, but only for patients whose arteries larger than 2 mm in diameter. Patients with arteries less than 2 mm in diameter, certain diffuse coronary artery lesions, history of multiple surgeries, or lack of arteriovenous grafts are unsuitable for such revascularization techniques [89]. Increasingly, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) leads to acute coronary block and reperfusion injury, which can cause acute ischemia and hypoxia in cardiomyocytes. Myocardial necrosis and apoptosis ultimately lead to myocardial remodeling. Therefore, many studies hope stem cells can proliferate and differentiate into new cardiomyocytes to replace damaged myocardial tissue and improve cardiac function after AMI [90, 91]. However, recent studies have shown that survival and differentiation rates of stem cells in transplanted hearts are very low. Therefore, stem cell transplantation may elicit benefits mainly through paracrine effects [92]. At present, different cell-derived EV therapies for AMI are considered to be the most promising method for repairing damaged myocardium and promoting myocardial vessel regeneration (Table 3).
Table 3.
Extracellular vesicles derived from stem cells promote angiogenesis in myocardial ischemia
| EVs source | EVs type | EVs isolation | Experimental model (target cells/animal models) | Functional cargo | Molecules/pathways activated | Key functions/downstream genes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation Exoquick Exosome Precipitation Solution Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HMECs) In vivo (male SCID mice) |
miR-146a | / | Enhanced angiogenesis and the density of micro-vessels both in vitro and in vivo | Ibrahim et al. [93] |
| CDCs | Exosomes |
Ultracentrifugation Exoquick exosome precipitation solution |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (male SCID-beige mice) |
/ | / |
In vitro: stimulate angiogenesis in a HUVEC angiogenesis assay. In vivo: stimulated capillary reorganization. |
Lang et al. [94] |
| CDCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) | miR-126, miR-130a, miR-210 | / |
Speculate: miR-210→EENA3↓→ tube formation↑ miR-130a→GAX and HoxA5↓→ VEGF and VEGFR2↑→tube formation↑ miR-126→VEGF and bFGF↑, Spred-1↓→ tube formation↑ |
Namazi et al. [95] |
| CDCs | Exosomes |
450 nm pore membrane filtration PEG ultrafiltration Centrifugation |
In vivo (female adult Yucatan mini-pigs/MI model) | / | / | decreased acute ischaemia-reperfusion injury, and halt chronic post-MI adverse remodeling in pigs | Gallet et al. [96] |
| BM-MSCs | Exosomes |
ExoQuick-TC reagent Centrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (female Sprague-Dawley rats/MI model) |
/ | / | Exosomes accounted for the cardioprotection through the formation of new blood vessels. | Teng et al. [97] |
| BM-MSCs | Exosomes | ExoQuick-TC reagent |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (female Sprague-Dawley rats/MI model) |
CXCR4 | PI3K/Akt signaling pathway |
VEGF ↑ Cardiomyocyte survival↑ |
Kang et al. [98] |
| BM-MSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs/HMECs) In vivo (male C57bl/6 mice) |
EMMPRIN | ERK/Akt signaling pathway | EMMPRIN has powerful proangiogenic effects both in vitro and in vivo | Vrijsen et al. [99] |
| UC-MSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 100 kDa molecular weight cut-off hollow fiber membrane Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (EA.hy926 cells) In vivo (male Sprague-Dawley rats/MI model) |
/ | / | protect myocardial cells and accelerate heart repair by angiogenesis after ischemic injury. | Zhao et al. [100] |
| ADSCs | MVs |
Differential centrifugation Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (male C57BL/6 J mice and nude mice) |
miR-31 | / | FIH1↓ | Kang et al. [101] |
| EnMSCs | Exosomes |
0.22-μm pore membrane filtration Exosome isolation reagent Centrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (male Sprague-Dawley rats/MI model) |
miR-21-5p | PTEN-Akt pathway |
PTEN↓ Akt and VEGF↑ |
Wang et al. [102] |
| ESCs | Exosomes | Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (male C57BL/6 mice/MI model) |
/ | / |
In vitro: increased tube formation; In vivo: decreased infarct size. |
Khan et al. [103] |
| iPSC | MVs |
Differential centrifugation Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (CECs) In vivo (C57BL/6 mice/MI model) |
/ | / |
In vitro: EVs impart cytoprotective properties to cardiac cells In vivo: induce superior cardiac repair with regard to LV function and vascularization. |
Adamiak et al. [104] |
|
iPSC-Pg iPSC-CM |
Exosomes | Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (nude mice/MI model) |
/ | / | EV may promote cell survival, proliferation of resident cardiac cells, and angiogenesis thereby improving left ventricular function. | EI Harane et al. [105] |
| CD34+ cells | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (nude mice) |
miR-126, miR-130a | / |
In vitro: promote tube formation in HUVECs In vivo: induced the formation of vessel-like endothelial structures in corneal angiogenesis assays. |
Sahoo et al. [106] |
Abbreviation: CDCs cardiosphere-derived cells, BM-MSCs bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells, UC-MSCs umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, ADSCs adipose-derived stem cells, EnMSCs human endometrium-derived mesenchymal stem cells, ESCs embryonic stem cells, iPSC-Pg human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiovascular progenitors, iPCS-CM human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, MVs microvesicles, HMECs human microvascular endothelial cells, HUVECs human umbilical vein endothelial cells, CECs murine cardiac endothelial cells, SCID severe combined immunodeficient, MI myocardial infarction model, EMMPRIN extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer, FIH1 hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha inhibitor
CDC-EVs
Cardiosphere-derived cells (CDCs) are cardiac progenitor cells that can differentiate into the three major cardiac cell types: cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells [107]. Previous studies demonstrated that CDCs stimulate angiogenesis and functional improvement by indirect mechanisms in the infarcted myocardium [108, 109]. Treating CDCs with exosome biosynthesis inhibitor GW4869 abolished their cardioprotective and regenerative properties. Subsequent studies paid more attention to the role of EVs derived from CDCs (CDC-EVs) and found CDC-EVs have similar therapeutic effects of CDCs in the treatment of myocardial ischemia [93]. When CDC-Exo were injected into the infarct border zone after AMI, the scar was reduced and necrotic myocardium was repaired with neovascularization. This effect of CDC-Exo was confirmed by Gallet et al. who observed a higher number of arterioles in both infarct and border zones of exosomes derived from CDCs (CDC-Exo)-treated pigs [94]. Further study demonstrated that the function of CDC-Exo in neovascularization of ischemic myocardium was related to the high content of miR-146a. Experiments in vitro also showed that CDC-Exo increased HUVEC tube formation and promoted angiogenesis [95]. In addition, the contents of CDC-Exo can be changed under given conditions. For example, exosomes isolated from CDCs cultured under hypoxia were enriched with proangiogenic miRNAs such as miR-126, miR-130a, and miR-210, which increased tube formation of HUVECs [96]. For treatment of ischemic heart disease, CDCs which are derived from myocardial tissue have lower immune responses compared with other stem cells. Furthermore, allogeneic CDC-Exo did not induce significant immune responses after repeated dosing [110].
MSC-EVs
As a treatment for ischemia, EVs play an important role as key transporters of paracrine factors during angiogenesis [111]. For example, scientists observed that BM-MSC-EVs can be internalized by endothelial cells and enhanced HUVEC tube formation. Moreover, fluorescence micrographs showed a large number of functional tubes forming in regions surrounding infarction areas. Subsequent in vivo experiments observed increased blood vessel density in hearts injected with BM-MSC-EVs [97]. CXCR4 serves as a major regulator of stem/progenitor cell activities. CXCR4-enriched BM-MSC-Exo activates PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, leading to an increase of VEGF and cardiomyocyte survival under hypoxic conditions [98]. In vitro models, BM-MSC-Exo stimulated endothelial cell migration and vessel formation via ERK/Akt signaling. To determine the angiogenic effect of BM-MSC-Exo in vivo, exosomes were added to the Matrigel plug and then implanted subcutaneously. The results suggested the enhancement of the influx of vascular cells and the blood vessel formation in the Matrigel plug. Analysis of proangiogenic factors revealed the level of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) was high in BM-MSC-Exo. Knockdown of EMMPRIN leads to, both in vitro and in vivo, a diminished proangiogenic effect [99]. The exosomes were isolated from UC-MSC. In vitro, UC-MSC-Exo could promote migration of endothelial cells and tube formation, which might be associated with the increased expression of Bcl-2 family [100]. Kang et al. observed that MVs from ADSCs, especially from endothelial differentiation medium-preconditioned ADSCs, also enhanced angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo, but the molecular mechanism was different. The level of miR-31 was found to be upregulated in preconditioned ADSCs. Further study showed miR-31 targeted factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (FIH1) in vascular endothelial cells to mediate the proangiogenic effect of MVs [101]. Another research assessed therapeutic properties of BM-MSCs, ADSCs, and endometrium-derived mesenchymal stem cells (EnMSCs) in a rat model of AMI and found that EnMSCs supported enhanced microvessel density. Analyses of exosomal microRNAs revealed miR-21 was the potential mediator of EnMSC therapy via the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)/Akt pathway [102].
ESC-EVs
ESCs have the ability to produce exosomes which are capable of instigating cell analogous response in target cells. In order to assess the therapeutic efficacy of ESC-derived exosome (ESC-Exo) in post-infarct myocardium, ESC-Exo were intramyocardially injected in mice at the time of AMI. After 4 weeks, immunohistochemical analysis showed the capillary density was remarkably increased in ESC-Exo transplanted hearts, but the underlying basis for the effect is unknown [103].
iPSC-EVs
In recent years, iPSC researches have offered exciting opportunities for tissue restoration. Scientists compared the angiogenesis ability of iPSCs with that of iPSC-EVs in heart failure. The results demonstrated that both iPSCs and iPSC-EVs significantly promoted the migration and tube formation of murine cardiac endothelial cells (CECs). Further experimental analysis of capillary density in vivo was performed in the infarct zone, border zone, and non-ischemic zone of infarcted mouse hearts respectively. IPSC-EV injection resulted in greater number of capillaries in the infarct zone compared with iPSC injection [104]. Another study observed the EVs from cardiovascular progenitor cells derived from iPSCs (iPSC-CPC-EVs) promoted the migration and tube formation of HUVECs. Moreover, iPSC-CPC-EVs could significantly improve chronic heart failure through decreasing left ventricular volumes and increasing left ventricular ejection fraction [105].
CD34+ cell-EVs
CD34 is selectively expressed on the surface of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and gradually weakens or even tends to disappear with the maturation of the cells. After intramyocardial injection, autologous CD34+ cells can enhance myocardial perfusion and function of patients with AMI by promoting angiogenesis [112]. Sahoo et al. investigated the mechanism of CD34+ cell-induced proangiogenic paracrine effects and found that the exosomes from CD34+ cells (CD34+-Exo) have the same effects on endothelial cell viability, proliferation and tube formation on Matrigel as CD34+ cells have [106]. Further study showed the therapeutic efficacy of CD34+ cell treatment could be increased by secretion of sonic hedgehog (Shh) and exosome-mediated delivery of Shh to AMI represents a major mechanism [113].
EVs promote angiogenesis in stroke
Stroke is a group of diseases characterized by cerebral ischemic and hemorrhagic injury, with ischemic stroke accounting for 60–80% of strokes [114]. Ischemia and hypoxia cause neuronal degeneration and necrosis, leading to irreversible damage in the ischemic core region [115]. Current effective therapies include the use of tissue plasminogen activator thrombolysis and intravascular thrombectomy. However, the time window for application of these treatments is only a few hours [116]. Moreover, most patients suffer from a certain degree of neurological dysfunction even after receiving effective thrombolytic therapy. Because of these limitations, more than 90% of ischemic strokes cannot be treated promptly and effectively. Therefore, how to reduce ischemic injury and promote the recovery of nerve function in ischemic areas has become a research hotspot. In recent years, a deeper understating of EVs has confirmed that the intercellular information exchange process regulated by EVs is widely involved in angiogenic processes of the cerebrovascular system [117] (Table 4).
Table 4.
Extracellular vesicles derived from stem cells promote angiogenesis in stroke
| EVs source | EVs type | EVs isolation | Experimental model (target cells/animal models) | Functional cargo | Molecules/pathways activated | Key functions/downstream genes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM-MSCs | Unclear |
0.22-μm pore membrane filtration PEG ultrafiltration Centrifugation |
In vivo (male C57BL6 mice/MCAO model) | / | / | Formation of new endothelial cells | Doeppner et al. [12] |
| BM-MSCs | Exosomes |
0.2-μm pore membrane filtration Differential centrifugation Ultracentrifugation |
In vivo (male Wistar rats/MCAO model) | / | / | Promote angiogenesis after stroke | Xin et al. [118] |
| ADSCs | Exosomes | Total exosome isolation kit |
In vitro (BMECs) In vivo (male Wistar rats/MCAO model) |
miR-181b-5p | TRPM7 axis | TRPM7↓→HIF-1α and VEGF↑ TIMP3↓ | Yang et al. [119] |
Abbreviation: BM-MSCs bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells, ADSCs adipose-derived stem cells, MCAO middle cerebral artery occlusion model, TRPM7 transient receptor potential melastatin 7, HIF-1a hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor
MSCs isolated from various tissues can promote angiogenesis not only in wound healing, but also in stoke [120]. In trying to understand the exact molecular mechanism by which different sources of MSCs exert protective roles in ischemic stroke, many studies have investigated the proangiogenesis ability of EVs. BM-MSC-Exos were used to treat middle cerebral artery occlusion of adult male Wistar rats. The results demonstrated that endothelial cell proliferation, compared with the PBS-treated control group, was significantly increased and new capillary network was formed, suggesting that BM-MSC-Exos promote angiogenesis post stroke [12, 118]. Another research also found that ADSC-Exos which contained miRNA-181b-5p could enhance the tube length of brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) after oxygen-glucose deprivation in vitro [119]. Direct targets of miR-181b-5p were further confirmed. Yang et al. found that the mRNA and protein levels of transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) were declined, and meanwhile, HIF-1α and VEGF were upregulated in BMECs after being cultured with 181b-Exos. These researches suggest that exosomes from stem cells may represent a novel therapeutic approach for stroke recovery.
EVs promote angiogenesis in other ischemic disease (Table 5)
Table 5.
Extracellular vesicles derived from stem cells promote angiogenesis in other ischemic diseases
| EVs source | EVs type | EVs isolation | Experimental model (target cells/animal models) | Functional cargo | Molecules/pathways activated | Key functions/downstream genes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iMSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 0.22-μm pore membrane filtration 30% sucrose/D2O cushion purification Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (mice/hindlimb ischemia model) |
/ | / | HIF-1α, TGF-β, VEGFA1, VEGFA2, angiogenin, bFGF, KDR, bFGFR, and VEGF↑ | Hu et al. [121] |
| PMSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (mice/hindlimb ischemia model) |
miR-126, VEGF | PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | miR-126↑→PIK3R2↓ pAKT↑ | Du et al. [122] |
| EPCs | MVs | Ultracentrifugation | In vivo (SCID mice/hindlimb ischemia model) | miR-126, miR-296 | / | VEGF↑ | Ranghino et al. [123] |
| CD34+ stem cells | Exosomes | Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (immunocompromised BalbC mice/hindlimb ischemia model) |
miR-126-3p | / | VEGF, angiogenin1, and MMP-9↑ | Mathiyalagan et al. [124] |
| BM-MSCs | Size is between in exosomes and MVs |
Differential centrifugation Ultracentrifugation Density gradient ultracentrifugation 0.45-μm pore membrane filtration |
In vivo (female MC57BL/6 mice/hindlimb ischemia model) | miR-210-3p | / | VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and VEGF↑ | Gangadaran et al. [125] |
| ADSCs | Exosomes | ExoQuick-TC reagent | In vivo (male C57BL/6 J mice/skin flap model) | IL-6 | phosphorylation of STAT3 | Exosomes treatments led to significantly increased flap survival and capillary density compared with I/R on postoperative day 5 | Pu et al. [126] |
| ADSCs | Exosomes |
Differential centrifugation 0.22-μm pore membrane filtration Ultracentrifugation |
In vitro (HUVECs) In vivo (male Sprague-Dawley rats/skin flap model) |
/ | / | ADSC-exos can enhance skin flap survival, promote neovascularization | Bai et al. [127] |
Abbreviation: iMSCs human iPSC differentiate into mesenchymal stem cells, PMSCs placenta tissue mesenchymal stem cells, EPCs endothelial progenitor cells, BM-MSCs bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells, ADSCs adipose-derived stem cells, HUVECs human umbilical vein endothelial cells, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, IL-6 interleukin-6, HIF-1a hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha, TGF-β transforming growth factor beta, VEGF-A1 vascular endothelial growth factor A1, VEGF-A2 vascular endothelial growth factor A2, bFGF basic fibroblast growth factor, bFGFR basic fibroblast growth factor receptor, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, MMP-9 matrix metallopeptidase 9
Therapeutic effect of EVs in peripheral arterial disease
Peripheral arterial obstructive disease, caused by atherosclerotic occlusion of the leg arteries, is often accompanied by moderate to severe ischemic pain in limbs, which directly affects the quality of life of patients and imposes a huge economic burden on society and families [128]. Many researches have shown that stem cells such as MSCs and EPCs contribute to angiogenesis after hindlimb ischemia and EVs have been emerging as an important paracrine regulator for stem cells to exert positive therapeutic effects. iPSC-derived mesenchymal stem cells (iMSCs) own powerful therapeutic effects through a paracrine mechanism. Hu et al. reported that exosomes derived from iMSCs (iMSCs-Exo) have the ability to promote angiogenesis after transplantation into ischemic limbs of mice [121]. In another study, exosomes were isolated from human PMSCs cultured with a nitric oxide releasing polymer and revealed superior angiogenic effects on hind limb ischemia in a murine model. Further analysis indicated that enhanced VEGF and miR-126 expressions in exosomes were responsible for exosome promoting angiogenic processes [122]. MVs derived from EPC also contained miR-126 and miR-296 which are known to be angiogenetic, suggesting a role of RNAs transferred by MVs in EPC-derived MVs treatment of severe hindlimb ischemia of mice [123]. CD34+ stem cells have been demonstrated to improve perfusion and function of the ischemic limb of patients. CD34+-Exo can directly transfer miR-126-3p and mimic the angiogenic activity of their parent cells. MiR-126-3p suppresses the expression of SPRED1 and simultaneously regulates the expression of genes which are involved in angiogenic pathways to promote angiogenesis [124]. In addition, administration of BM-MSC-EVs enhanced the formation of new blood vessels in the ischemic limb. The research on mechanisms revealed the enriched presence of miR-210-3p and VEGF protein in BM-MSC-EV and the high levels of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 in endothelial cells [125]. The miR-210-3p induces expression of several proangiogenic mRNAs (VEGF and VEGFR2) [129]. Therefore, all above researches indicate that angiogenesis-related miRNAs and proteins are the main components in EVs to exert their proangiogenesis function.
Therapeutic effect of EVs in flap graft
Skin flap transplantation is the most widely used treatment in orthopedic surgery and the most effective treatment for ischemic tissue damage. Adequate blood supply is the basis for improving the survival rate of transplanted flaps. Skin flap transplantation has certain limitations in specific clinical applications, as ischemic necrosis occurs at the distal end of the flap [130]. How to safely and effectively improve the survival rate of transplant flaps and ensure their blood supply has always been a difficult problem for burn orthopedics. Therefore, promoting the angiogenesis of flap grafts is key to solving this problem. With a flap ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) model, the capability of ADSCs to protect tissue against IRI were examined. Treatment with ADSCs remarkably increased flap survival when compared with the control group and enhanced expression of proangiogenic genes [131]. Further study demonstrated that ADSC-CM and ADSC-Exo increased tube formation after injection into the flaps and interleukin 6 (IL-6) contained in ADSC-Exo stimulated angiogenesis and led to recovery after IRI [126]. A specific micro-environment can be used for in vitro ADSC culture to develop the customized EVs. Compared with ADSC-Exo and control groups, exosomes isolated from ADSC exposed to low concentration of H2O2 generated more cord-like structures on Matrigel in vitro and increased blood perfusion and microvascular density in the flap in vivo [127]. These results suggest that low H2O2 micro-environment facilitates the customized exosome development for cell-free therapeutic applications during skin flap transplantation.
Future directions and potential limitations (Table 6)
Table 6.
The advantages and potential limitations of EV therapy
| Advantages |
Lipid bilayer shell can avert proteolytic degradation; EVs contain many potential regulatory components; EVs can be applied to personalized medicine. |
[129, 132–134] |
| Potential limitations |
Short-term effects because of short half-life; Rapid clearance by the innate immune system; Efficiency of EV uptake needs to be improved; Administration routes of EVs must be appropriately selected. |
[135–138] |
EVs have opened a new promising avenue for the treatment of ischemic diseases. Angiogenesis-related miRNAs and proteins in EVs derived from MSCs (Fig. 2) and other stem cells (Fig. 3) have shown potential to treat ischemic diseases by directly or indirectly activating angiogenesis-related signaling pathways in target cells. Based on recent researches, many miRNAs including miRNA-21-5p, miRNA-31, miRNA-125a, miRNA-126, miRNA-130a, miRNA-132, miRNA-146a, miRNA-181-5p, miRNA-210, and miRNA-296 are found to promote angiogenesis in ischemic disease [57, 93, 95, 101, 102, 106, 119, 122–125, 135, 139]. VEGF, as a major mediator of angiogenesis, is the most common functional protein component in EVs [125]. In view of the complex components in EVs, other specific functional proteins and miRNAs that play an important role in angiogenesis need to be further identified.
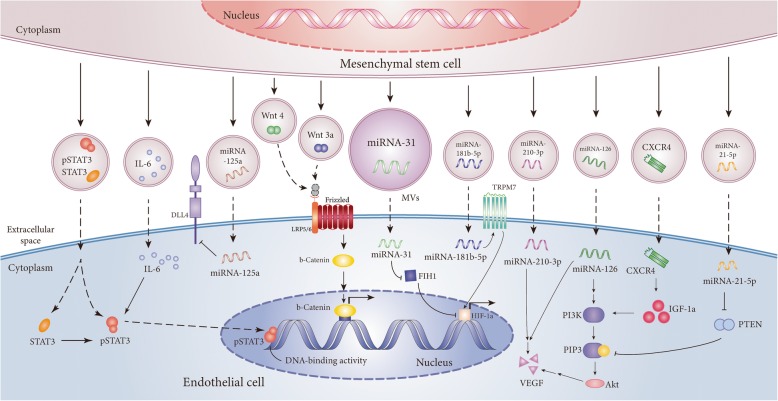
Fig. 2.
The mechanisms of angiogenesis induced by MSC-derived EVs in ischemic diseases. EVs from BM-MSCs, ADSCs, UC-MSCs, and PMSCs play an important role in neovascularization of ischemic diseases. MSC-derived EVs are enriched with specific cargo molecules including proteins (pSTAT3, IL-6, Wnt 3a, Wnt 4, and CXCR4) and miRNAs (miRNA-31, miRNA-125a, miRNA-181b, miRNA-210, miRNA-126, and miRNA-21). These proteins and miRNAs activate their related signal pathway to regulate the expression of angiogenic factors in endothelial cells. Abbreviation: IL-6, interleukin-6; FIH1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha inhibitor; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog
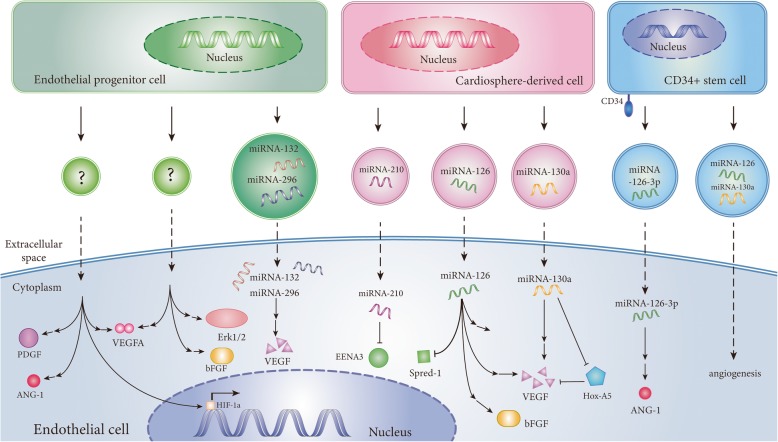
Fig. 3.
The mechanisms of angiogenesis induced by EVs derived from EPCs, CDCs, and CD34+ stem cells in ischemic diseases. EPC-derived EVs promote angiogenesis through upregulating the expression of related transcription factors. CDC-derived EVs are enriched with miR-210, miR-126, and miR-130a, which promote the expression of angiogenic proteins in endothelial cells. EVs derived from CD34+ stem cells transfer miR-126 and miR-130 into endothelial cells to stimulate angiogenesis. “?” represents uncertained functional cargo molecules in EVs. Abbreviation: PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor subunit; ANG-1, angiopoietin-1; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
EVs produced by stem cells would be expected to have many advantages in the ischemic environment. First of all, EVs could transfer signals more effectively to target cells because their lipid bilayer shell can avert proteolytic degradation. Scientists are trying to harness the natural ability of EVs to transfer therapeutic payloads into the desired cells. For example, siRNA was effectively delivered by plasma exosomes into the target cells, leading to selective gene silencing of MAPK-1 [132]. Secondly, EVs contain many potential regulatory components such as miRNAs, mRNAs, and proteins. These informational molecules could function simultaneously to generate a strong effect on the characteristics of recipient cells. MiR-210-3p and VEGF protein, as the effective components of BM-MSC-EV, have the same function to promote new blood vessel formation of endothelial cells [125]. Finally, EVs can be applied to personalized medicine [133, 134]. Gene editing in stem cells can produce the desired EVs with specific cell-surface molecules. EVs from gene-edited patient-specific stem cells will hold potential for treatment of ischemic diseases of each individual patient. Furthermore, EVs from iPSC-derivatives can be used for an autologous therapy by activating endogenous repair. We believe that EVs generated from patient-specific iPSC-derivatives probably have a higher angiogenic effect and provide a safer way than stem cell transplantation because EVs used as cell-free therapy are not affected by the ischemic and hypoxic micro-environment and have no tumorigenic risk.
Numerous attempts to treat ischemic diseases with EVs have been made and the results are quite encouraging. However, there are many limitations remaining to be solved. Firstly, EVs transplanted into the damaged tissues may have only short-term effects owing to their short half-life and rapid clearance by the innate immune system. Takahashi et al. showed exosomes from murine melanoma cells disappeared very quickly with a half-time of approximately 2 min from the blood circulation [136]. So how to maintain the retention and stability of EVs over time in vivo is a main challenge in clinical application. Zhang et al. demonstrated that chitosan hydrogel remarkably increased the retention of exosomes in vivo and enhanced the stability of miRNAs and proteins in exosomes, enhancing angiogenesis in ischemic site [135]. Secondly, the efficiency of EV uptake needs to be improved. Cellular uptake of large number of EVs by target cells may improve the effects of angiogenesis. The efficiency of EVs uptake has been found to be related to intracellular and micro-environmental acidity [137]. Finally, the administration routes of EVs must be appropriately selected. Some studies explored whether the angiogenesis effects of EVs are influenced by intravascular injection or local injection of ischemic tissue. Results showed that topical injection of EVs made a better therapeutic effect, while intravascular injection caused EVs to degrade rapidly [138]. In conclusion, we believe that through continued and collaborative efforts, EV-based therapy will yield satisfactory responses in patients with ischemic diseases.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported in part by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81830064, 81721092, 81571905), the National Key Research Development Plan (2017YFC1103300), and the Military Logistics Research Key Project (AWS17J005).
Availability of data and materials
All data and material are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- ADSC-Exo
Adipose-derived stem cells -derived exosomes
- ADSC-MVs
Adipose-derived stem cells derived microvesicles
- ADSCs
Adipose-derived stem cells
- AMI
Acute myocardial ischemia
- ApoBDs
Apoptotic bodies
- bFGF
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- BMECs
Brain microvascular endothelial cells
- BM-MSC-EVs
Bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells- derived extracellular vesicles
- BM-MSCs
Bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells
- CD34+-Exo
Exosomes from CD34+ cells
- CDC-EVs
Extracellular vesicles derived from cardiosphere-derived cells
- CDC-Exo
Cardiosphere-derived cells–derived exosomes
- CDCs
Cardiosphere-derived cells
- CECs
Murine cardiac endothelial cells
- EMMPRIN
Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer
- EnMSC
Human endometrium-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- EPC-EVs
Extracellular vesicles derived from endothelial progenitor cells
- EPCs
Endothelial progenitor cells
- ESC-Exo
Embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes
- ESCRT-3
Endosomal sorting complex required for transport
- ESCs
Embryonic stem cells
- EVs
Extracellular vesicles
- FIH1
Factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor 1
- HIF-1α
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- HUVECs
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- IL-6
Interleukin 6
- ILVs
Intraluminal vesicles
- iMSCs
Induced pluripotent stem cells-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- iMSCs-Exo
Exosomes-derived from induced pluripotent stem cells-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- iPSC-EVs
Extracellular vesicles derived from induced pluripotent stem cells
- iPSC-Exo
Exosomes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells
- iPSCs
Induced pluripotent stem cells
- IRI
Ischemia-reperfusion injury
- LncRNAs
Long nc-RNAs
- MiRNAs
MicroRNAs
- MVEs
Multi-vesicular endosomes
- MVs
Microvesicles
- Nc-RNAs
Non-coding RNAs
- PDGFA
Platelet-derived growth factor subunit A
- PDGFR
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor
- Pi-RNAs
Piwi-RNA
- PMSC-Exo
PMSCs derived exosomes
- PMSCs
Placenta tissue mesenchymal stem cells
- Shh
Sonic hedgehog
- SiRNA
Small interfering RNA
- SncRNAs
Small nc-RNAs
- SnoRNA
Small nucleolar RNA
- TGF-β
Transforming growth factor beta
- TRPM7
Transient receptor potential melastatin 7
- UCB-Exo
Umbilical cord blood-derived exosomes
- UCB-MSCs
Umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells
- UC-MSCs
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
- VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFA
Vascular endothelial growth factor A
- VEGFR2
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2
Authors’ contributions
BX and ZC conceived the manuscript. BX and MK wrote the manuscript and designed the figures. FX and ZC revised and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Xiaowei Bian, Email: celineeeee@163.com.
Kui Ma, Email: kingmk.ok@163.com.
Cuiping Zhang, Phone: 0086 10 66867391, Email: zcp666666@sohu.com.
Xiaobing Fu, Phone: 0086 10 66867391, Email: fuxiaobing@vip.sina.com.
References
- 1.Pande RL, et al. A pooled analysis of the durability and predictors of treatment response of cilostazol in patients with intermittent claudication. Vasc Med. 2010;15:181–188. doi: 10.1177/1358863X10361545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mellière D, et al. The underestimated advantages of iliofemoral endarterectomy. Ann Vasc Surg. 2000;14:343–349. doi: 10.1007/s100169910068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Trams EG, et al. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645:63–70. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wu R, et al. Drug-eluting balloon versus standard percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in infrapopliteal arterial disease: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Int J Surg. 2016;35:88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Li S, et al. Advances in the treatment of ischemic diseases by mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:5896061. doi: 10.1155/2016/5896061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Choi M, et al. Proangiogenic features of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells and their ability to form functional vessels. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45:560–570. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fouraschen SM, et al. Secreted factors of human liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote liver regeneration early after partial hepatectomy. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21:2410–2419. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ionescu L, et al. Stem cell conditioned medium improves acute lung injury in mice: in vivo evidence for stem cell paracrine action. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;303:L967–L977. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00144.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Panfoli I, et al. Microvesicles as promising biological tools for diagnosis and therapy. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018;15:801–808. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2018.1528149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Muralidharan-Chari V, et al. Microvesicles: mediators of extracellular communication during cancer progression. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:1603–1611. doi: 10.1242/jcs.064386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Amini A, et al. Stereological and molecular studies on the combined effects of T photobiomodulation and human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium on wound healing in diabetic rats. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018;182:42–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Doeppner TR, et al. Extracellular vesicles improve post-stroke neuroregeneration and prevent postischemic immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4:1131–1143. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Riazifar M, et al. Stem cell extracellular vesicles: extended messages of regeneration. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017;6:125–154. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-061616-030146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Johnstone RM, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes) J Biol Chem. 1987;262:9412–9420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Théry C, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;30:3.22–3.29. doi: 10.1002/0471143030.cb0322s30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Qin J, Xu Q. Functions and application of exosomes. Acta Pol Pharm. 2014;71:537–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200:373–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Akers JC, et al. Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles (EV): exosomes, microvesicles, retrovirus-like vesicles, and apoptotic bodies. J Neuro-Oncol. 2013;113:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s11060-013-1084-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Atkin-Smith GK, et al. A novel mechanism of generating extracellular vesicles during apoptosis via a beads-on-a-string membrane structure. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7439. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ferguson TA, et al. Uptake of apoptotic antigen-coupled cells by lymphoid dendritic cells and cross-priming of CD8(+) T cells produce active immune unresponsiveness. J Immunol. 2002;168:5589–5595. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.11.5589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Poon IK, et al. Apoptotic cell clearance: basic biology and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:166–180. doi: 10.1038/nri3607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hochreiter-Hufford A, Ravichandran K. Clearing the dead: apoptotic cell sensing, recognition, engulfment, and digestion. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5:a008748. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Choi DS, et al. Proteomics, transcriptomics and lipidomics of exosomes and ectosomes. Proteomics. 2013;13:1554–1571. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201200329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Choi DS, et al. Proteomics of extracellular vesicles: exosomes and ectosomes. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2015;34:474–490. doi: 10.1002/mas.21420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tauro BJ, et al. Two distinct populations of exosomes are released from LIM1863 colon carcinoma cell-derived organoids. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013;12:587–598. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.021303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Choi DS, et al. Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human colorectal cancer cells. J Proteome Res. 2007;6:4646–4655. doi: 10.1021/pr070192y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Safdar A, et al. The potential of endurance exercise-derived exosomes to treat metabolic diseases. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12:504–517. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Record M, et al. Exosomes as new vesicular lipid transporters involved in cell-cell communication and various pathophysiologies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1841:108–120. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shahabipour F, et al. Exosomes as nanocarriers for siRNA delivery: paradigms and challenges. Arch Med Sci. 2016;12:1324–1326. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2016.62911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hannafon BN, Ding WQ. Intercellular communication by exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:14240–14269. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ratajczak J, et al. Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia. 2006;20:1487–1495. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Guescini M, et al. Astrocytes and glioblastoma cells release exosomes carrying mtDNA. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2010;117:1–4. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0288-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Valadi H, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–659. doi: 10.1038/ncb1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Xiong XD, et al. Long non-coding RNAs: an emerging powerhouse in the battle between life and death of tumor cells. Drug Resist Updat. 2016;26:28–42. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2016.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ha M, Kim V. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:509–524. doi: 10.1038/nrm3838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bellingham SA, et al. Small RNA deep sequencing reveals a distinct miRNA signature released in exosomes from prion-infected neuronal cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:10937–10949. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nolte-'t Hoen EN, et al. Deep sequencing of RNA from immune cell-derived vesicles uncovers the selective incorporation of small non-coding RNA biotypes with potential regulatory functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:9272–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ogawa Y, et al. Small RNA transcriptomes of two types of exosomes in human whole saliva determined by next generation sequencing. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36:66–75. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b12-00607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gandellini P, et al. microRNAs as players and signals in the metastatic cascade: implications for the development of novel anti-metastatic therapies. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017;44:132–140. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tosar J. P., Gambaro F., Sanguinetti J., Bonilla B., Witwer K. W., Cayota A. Assessment of small RNA sorting into different extracellular fractions revealed by high-throughput sequencing of breast cell lines. Nucleic Acids Research. 2015;43(11):5601–5616. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li B, et al. piRNA-823 delivered by multiple myeloma-derived extracellular vesicles promoted tumorigenesis through re-educating endothelial cells in the tumor environment. Oncogene. 2019. 10.1038/s41388-019-0788-4. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Rimer JM, et al. Long-range function of secreted small nucleolar RNAs that direct 2′-O-methylation. J Biol Chem. 2018;293:13284–13296. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pi F, et al. Nanoparticle orientation to control RNA loading and ligand display on extracellular vesicles for cancer regression. Nat Nanotechnol. 2018;13:82–89. doi: 10.1038/s41565-017-0012-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Clinton A, Carter T. Chronic wound biofilms: pathogenesis and potential therapies. Lab Med. 2015;46:277–284. doi: 10.1309/LMBNSWKUI4JPN7SO. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bhate K, Williams HC. What's new in acne? An analysis of systematic reviews published in 2011-2012. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:273–277. doi: 10.1111/ced.12270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lefrancois T, et al. Evidence based review of literature on detriments to healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;23:215–224. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2016.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Crawford JM, et al. Pathophysiology of venous ulceration. 9J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017;5:596–605. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2017.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis. Nature. 2000;407:233–241. doi: 10.1038/35025203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Uccioli L, et al. Critical limb ischemia: current challenges and future prospects. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2018;26:63–74. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S125065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Veeravagu A, et al. National trends in burn and inhalation injury in burn patients: results of analysis of the nationwide inpatient sample database. J Burn Care Res. 2015;36:258–265. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0000000000000064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zafren K. Frostbite: prevention and initial management. High Alt Med Biol. 2013;14:9–12. doi: 10.1089/ham.2012.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pazyar N, et al. Skin wound healing and phytomedicine: a review. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27:303–310. doi: 10.1159/000357477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tonnesen MG, et al. Angiogenesis in wound healing. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2000;5:40–46. doi: 10.1046/j.1087-0024.2000.00014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Shabbir A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes induce proliferation and migration of normal and chronic wound fibroblasts, and enhance angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cell Dev. 2015;24:1635–1647. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.McBride JD, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived CD63+ exosomes transport Wnt3a exteriorly and enhance dermal fibroblast proliferation, migration and angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2017;26:1384–1398. doi: 10.1089/scd.2017.0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ren S, et al. Microvesicles from human adipose stem cells promote wound healing by optimizing cellular functions via AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:47. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1152-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Liang X, et al. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci. 2016;129:2182–2189. doi: 10.1242/jcs.170373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Xue C, et al. Exosomes derived from hypoxia-treated human adipose mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis through the PKA signaling pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27:456–465. doi: 10.1089/scd.2017.0296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hu Y, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord blood accelerate cutaneous wound healing through miR-21-3p-mediated promotion of angiogenesis and fibroblast function. Theranostics. 2018;8:169–184. doi: 10.7150/thno.21234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang B, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance angiogenesis through the Wnt4/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4:513–522. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Komaki M, et al. Exosomes of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells stimulate angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8:219. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0660-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kobayashi H, et al. Effects of exosomes derived from the induced pluripotent stem cells on skin wound healing. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2018;80:141–153. doi: 10.18999/nagjms.80.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zhang JY, et al. Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J Transl Med. 2015;13:49. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0417-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Li X, et al. Exosomes derived from endothelial progenitor cells attenuate vascular repair and accelerate reendothelialization by enhancing endothelial function. Cytotherapy. 2016;18:253–262. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2015.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Li X, et al. Human endothelial progenitor cells-derived exosomes accelerate cutaneous wound healing in diabetic rats by promoting endothelial function. J Diabetes Complicat. 2016;30:986–992. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.O'Loughlin A, et al. Topical administration of allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells seeded in a collagen scaffold augments wound healing and increases angiogenesis in the diabetic rabbit ulcer. Diabetes. 2013;62:2588–2594. doi: 10.2337/db12-1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Vojtassák J, et al. Autologous biograft and mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of the diabetic foot. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2006;27:134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Shen L, et al. Neurotrophin-3 accelerates wound healing in diabetic mice by promoting a paracrine response in mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2013;22:1011–1021. doi: 10.3727/096368912X657495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kim CH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells improve wound healing in vivo via early activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and vascular endothelial growth factor. J Korean Med Sci. 2011;26:726–733. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.6.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Chen L, et al. Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS One. 2008;3:e1886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Choudhery MS, et al. Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp, bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue by gene expression. Cytotherapy. 2013;15:330–343. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2012.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kim SM, et al. The effect of diabetes on the wound healing potential of adipose-tissue derived stem cells. Int Wound J. 2016;13:33–41. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Cramer C, et al. Persistent high glucose concentrations alter the regenerative potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19:1875–1884. doi: 10.1089/scd.2010.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kim EK, et al. The effect of human adipose-derived stem cells on healing of ischemic wounds in a diabetic nude mouse model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128:387–394. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31821e6de2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kensler TW, et al. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:89–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.46.120604.141046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Spirli C, et al. ERK1/2-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor signaling sustains cyst growth in polycystin-2 defective mice. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:360–371. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ballen KK, et al. Umbilical cord blood transplantation: the first 25 years and beyond. Blood. 2013;122:491–498. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-453175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Doi H, et al. Potency of umbilical cord blood- and Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells for scarless wound healing. Sci Rep. 2016;6:18844. doi: 10.1038/srep18844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lee C, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and small intestinal submucosa hydrogel composite promotes combined radiation-wound healing of mice. Cytotherapy. 2017;19:1048–1059. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2017.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kong P, et al. Placenta mesenchymal stem cell accelerates wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;438:410–419. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Liu L, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells transplantation promotes cutaneous wound healing of severe burned rats. PLoS One. 2014;9:e88348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wang S, et al. Wound dressing model of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-alginates complex promotes skin wound healing by paracrine signaling. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3269267. doi: 10.1155/2016/3269267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Liu Z, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve irradiation-induced skin ulcers healing of rat models. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;101:729–736. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kashpur O, et al. Differentiation of diabetic foot ulcer-derived induced pluripotent stem cells reveals distinct cellular and tissue phenotypes. FASEB J. 2018;33:1262–1277. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Martin PE, et al. The potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells for modelling diabetic wound healing in vitro. Clin Sci (Lond) 2018;132:1629–1643. doi: 10.1042/CS20171483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kanzler I, et al. Differential roles of angiogenic chemokines in endothelial progenitor cell-induced angiogenesis. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013;108:310. doi: 10.1007/s00395-012-0310-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Basile DP, Yoder MC. Circulating and tissue resident endothelial progenitor cells. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229:10–16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Zhang J, et al. Exosomes derived from human endothelial progenitor cells accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting angiogenesis through Erk1/2 signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12:1472–1487. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.15514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ertl G, Frantz S. Healing after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;66:22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kanashiro-Takeuchi RM, et al. Pharmacologic and genetic strategies to enhance cell therapy for cardiac regeneration. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;51:619–625. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.05.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Iglesias-García O, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells as a new strategy for cardiac regeneration and disease modeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013;62:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.04.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Makridakis M, et al. Stem cells: insights into the secretome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1834:2380–2384. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Ibrahim AG, et al. Exosomes as critical agents of cardiac regeneration triggered by cell therapy. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;2:606–619. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Lang JK, et al. Inhibiting extracellular vesicle release from human cardiosphere derived cells with lentiviral knockdown of nSMase2 differentially effects proliferation and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells in vitro. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0165926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Namazi H, et al. Exosomes secreted by hypoxic cardiosphere-derived cells enhance tube formation and increase pro-angiogenic miRNA. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:4150–4160. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Gallet R, et al. Exosomes secreted by cardiosphere-derived cells reduce scarring, attenuate adverse remodelling, and improve function in acute and chronic porcine myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2017;38. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 97.Teng XM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improve the microenvironment of infarcted myocardium contributing to angiogenesis and anti-inflammation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37:2415–2424. doi: 10.1159/000438594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kang K, et al. Exosomes secreted from CXCR4 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote cardioprotection via Akt signaling pathway following myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:659890. doi: 10.1155/2015/659890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Vrijsen KR, et al. Exosomes from cardiomyocyte progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells stimulate angiogenesis via EMMPRIN. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5:2555–2565. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201600308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Zhao YY, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells relieve acute myocardial ischemic injury. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:761643. doi: 10.1155/2015/761643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kang T, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells induce angiogenesis via microvesicle transport of miRNA-31. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5:440–450. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Wang K, et al. Enhanced cardioprotection by human endometrium mesenchymal stem cells driven by exosomal microRNA-21. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6:209–222. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Khan M, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes promote endogenous repair mechanisms and enhance cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2015;117:52–64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.305990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Adamiak M, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived extracellular vesiclesare safer and more effective for cardiac repair than iPSCs. Circ Res. 2018;122:296–309. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.El Harane N, et al. Acellular therapeutic approach for heart failure: in vitro production of extracellular vesicles from human cardiovascular progenitors. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:1835–1847. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Sahoo S, et al. Exosomes from human CD34(+) stem cells mediate their proangiogenic paracrine activity. Circ Res. 2011;109:724–728. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.253286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Marbán E. Breakthroughs in cell therapy for heart disease: focus on cardiosphere-derived cells. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89:850–858. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.02.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Smith Rachel Ruckdeschel, Barile Lucio, Cho Hee Cheol, Leppo Michelle K., Hare Joshua M., Messina Elisa, Giacomello Alessandro, Abraham M. Roselle, Marbán Eduardo. Regenerative Potential of Cardiosphere-Derived Cells Expanded From Percutaneous Endomyocardial Biopsy Specimens. Circulation. 2007;115(7):896–908. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.655209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kreke M, et al. Cardiospheres and cardiosphere-derived cells as therapeutic agents following myocardial infarction. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2012;10:1185–1194. doi: 10.1586/erc.12.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Mirotsou M, et al. Repeated doses of cardiosphere-derived cell extracellular vesicles are hypo-immunogenic. Proceedings of the Abstracts from the 4th International Meeting of ISEV (ISEV '15); April 2015; Washington, DC, USA.
- 111.Lai RC, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4:214–222. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2009.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Kawamoto A, et al. CD34-positive cells exhibit increased potency and safety for therapeutic neovascularization after myocardial infarction compared with total mononuclear cells. Circulation. 2006;114:2163–2169. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.644518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Mackie AR, et al. Sonic hedgehog - modified human CD34+ cells preserve cardiac function following acute myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2012;111:312–321. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.266015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Navaratna D, et al. Mechanisms and targets for angiogenic therapy after stroke. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009;3:216–223. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2009.n.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Sharp FR, et al. Multiple molecular penumbras after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:1011–1032. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200007000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Hack W, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1317–1329. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0804656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Xian X, et al. Exosomes with highly angiogenic potential for possible use in pulp regeneration. J Endod. 2018;44:751–758. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2017.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Xin H, et al. Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33:1711–1715. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Yang Y, et al. Exosomes secreted by adipose-derived stem cells contribute to angiogenesis of brain microvascular endothelial cells following oxygen–glucose deprivation in vitro through microRNA-181b/TRPM7 axis. J Mol Neurosci. 2018;65:74–83. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Li Y, Chopp M. Marrow stromal cell transplantation in stroke and traumatic brain injury. Neurosci Lett. 2009;456:120–123. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.03.096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Hu GW, et al. Exosomes secreted by human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate limb ischemia by promoting angiogenesis in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:10. doi: 10.1186/scrt546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Du W, et al. Enhanced proangiogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulated by a nitric oxide releasing polymer. Biomaterials. 2017;133:70–81. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.04.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ranghino A, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell-derived microvesicles improve neovascularization in a murine model of hindlimb ischemia. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012;25:75–85. doi: 10.1177/039463201202500110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Mathiyalagan P, et al. Angiogenic mechanisms of human CD34+ stem cell exosomes in the repair of Iischemic hindlimb. Circ Res. 2017;120:1466–1476. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.310557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Gangadaran P, et al. Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells activates VEGF receptors and accelerates recovery of hindlimb ischemia. J Control Release. 2017;264:112–126. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Pu CM, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells protect skin flaps against ischemia/reperfusion injury via interleukin-6 expression. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:1353–1362. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.12.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Bai Y, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulated by hydrogen peroxide enhanced skin flap recovery in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500:310–317. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Chen JC, et al. Risks of peripheral arterial occlusive disease in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea: a population-based case-control study. Clin Otolaryngol. 2015;40:437–442. doi: 10.1111/coa.12393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Liu F, et al. Upregulation of microRNA-210 regulates renal angiogenesis mediated by activation of VEGF signaling pathway under ischemia/perfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012;35:182–191. doi: 10.1159/000331054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Akhavani MA, et al. Angiogenesis and plastic surgery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008;61:1425–1437. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2008.05.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Reichenberger MA, et al. Adipose derived stem cells protect skin flaps against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8:854–862. doi: 10.1007/s12015-012-9368-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Wahlgren J, et al. Plasma exosomes can deliver exogenous short interfering RNA to monocytes and lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:e130. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Contreras-Naranjo JC, et al. Microfluidics for exosome isolation and analysis: enabling liquid biopsy for personalized medicine. Lab Chip. 2017;17:3558–3577. doi: 10.1039/c7lc00592j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Srivastava A, et al. Exploitation of exosomes as nanocarriers for gene-, chemo-, and immune-therapy of cancer. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2016;12:1159–1173. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2016.2205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Zhang K, et al. Enhanced therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes with an injectable hydrogel for hindlimb ischemia treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:30081–30091. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b08449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Takahashi Y, et al. Visualization and in vivo tracking of the exosomes of murine melanoma B16-BL6 cells in mice after intravenous injection. J Biotechnol. 2013;165:77–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Tian T, et al. Visualizing of the cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of exosomes by live-cell microscopy. J Cell Biochem. 2010;111:488–496. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Arderiu G, et al. Tissue factor regulates microvessel formation and stabilization by induction of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31:2607–2615. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.233536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Barile L., Lionetti V., Cervio E., Matteucci M., Gherghiceanu M., Popescu L. M., Torre T., Siclari F., Moccetti T., Vassalli G. Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac progenitor cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovascular Research. 2014;103(4):530–541. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data and material are included in this published article.