Abstract
This study uses data from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services to investigate the association between Medicare copayment policies and discharge rates of vulnerable patients from skilled nursing facilities.
Medicare pays for 100% of postacute care provided by skilled nursing facilities (SNFs) during the first 20 days within a benefit period. However, on the 21st day, most patients become responsible for a daily copayment of more than $150.1 This copayment may present a significant financial burden for some patients—particularly those with limited economic means—and motivate them to discharge from SNFs on the 20th day of care based on their financial resources rather than their recovery status. Skilled nursing facilities may also prematurely discharge some patients to avoid the risk of accruing bad debt from partially uncompensated postacute care. However, it is not known whether patterns of SNF discharge are associated with this change in Medicare payment responsibility on day 20.
Methods
We used data from the Medicare Provider Analysis and Review files and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services’ Minimum Data Set 3.0 to identify Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries discharged from an acute care hospital to an SNF between January 1, 2012, and November 1, 2016 (N = 8 969 940). We excluded discharges for beneficiaries who were dually enrolled in Medicare and Medicaid and were therefore not responsible for the SNF copayment (n = 2 789 578), appeared to have supplemental insurance (ie, did not pay the inpatient deductible) and were therefore more likely to have coverage for the SNF copayment (n = 823 423), received hospice care (n = 323 604), had a life expectancy of less than 6 months reported in the Minimum Data Set (n = 112 060), or had a long-term care nursing home stay within the 100 days before hospital admission (n = 355 113). This study was approved by the institutional review board of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, with a Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act waiver of informed consent.
For each of the remaining SNF discharges (n = 4 566 162), we computed the SNF benefit day at the time of SNF discharge based on the number of SNF benefit days used in that benefit period (which may have included a previous SNF stay).2 We compared patient characteristics across benefit days used at SNF discharge, including age, sex, race/ethnicity (as reported in the claims data), and 31 comorbidities identified in the Elixhauser Comorbidity Index. We also used data from the US Census Bureau’s American Community Survey from 2012 to 2016 to compare zip code–level socioeconomic characteristics across groups, including median household income, poverty rate, and unemployment rate. Differences in patient characteristics between discharges on benefit days 19 and 20 and benefit days 20 and 21 were assessed using bivariate linear regression analysis, regressing each characteristic on an indicator of day. Analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc). Significance testing was 2-sided, with the significance threshold set at P < .05.
Results
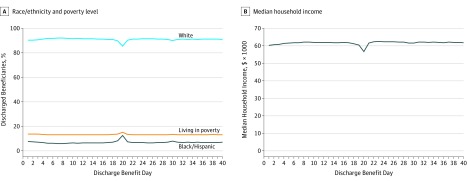
More patients were discharged from the SNF on benefit day 20 (220 037) than on benefit days 19 or 21 (131 558 and 121 339, respectively; Table). Patients discharged on benefit day 20 were more likely to be racial or ethnic minorities and to live in lower socioeconomic status zip codes compared with patients discharged on days 19 or 21. More black and Hispanic patients were discharged on day 20 (12.5%) than on days 19 or 21 (8.2% and 7.5%, respectively; P < .001). Patients discharged on day 20 were more likely to live in high-poverty areas (15.2% vs 13.8% on day 19 and 13.4% on day 21; P < .001) and to have lower median household incomes ($56 680 vs $60 480 on day 19 and $61 564 on day 21; P < .001) and higher unemployment rates (7.7% vs 7.2% on day 19 and 7.1% on day 21; P < .001). The differences in patient characteristics across benefit days by race/ethnicity and socioeconomic status were greatest on day 20 when measured across the first 40 days of the benefit period (Figure). Patients discharged on benefit day 20 were also more likely to have 5 or more comorbidities (42.2%) than patients discharged on days 19 and 21 (39.9% and 40.6%, respectively; P < .001).
Table. Characteristics of Medicare Beneficiaries Discharged From Skilled Nursing Facilities (SNFs) by Benefit Day on SNF Discharge.
| Characteristic | Day | Difference (95% CI) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | Days 19 vs 20 |
Days 20 vs 21 |
|
| Discharges, No. | 113 343 | 109 700 | 117 186 | 131 558 | 220 037 | 121 339 | 103 062 | 85 377 | 79 305 | ||
| Age, mean (SD), y | 80.5 (9.3) |
80.5 (9.3) |
80.4 (9.4) |
80.0 (9.6) |
79.0 (10.1) |
81.2 (9.2) |
81.6 (9.1) |
81.8 (9.1) |
81.9 (9.0) |
−1.0 (−1.1 to −0.9) |
2.2 (2.1 to 2.2) |
| Male, % | 37.5 | 37.9 | 37.2 | 37.6 | 40.2 | 36.7 | 36.2 | 36.0 | 36.4 | 2.6 (2.3 to 2.9) |
−3.5 (−3.8 to −3.1) |
| Not married, % | 60.5 | 60.7 | 61.2 | 61.9 | 64.1 | 62.9 | 62.9 | 63.4 | 63.5 | 2.2 (1.8 to 2.5) |
−1.2 (−1.5 to −1.0) |
| Race/ethnicity, % | |||||||||||
| White | 91.4 | 91.1 | 91.0 | 89.9 | 85.5 | 90.5 | 91.3 | 91.4 | 91.4 | −4.3 (−4.6 to −4.1) |
5.0 (4.8 to 5.2) |
| Black/Hispanic | 6.6 | 6.9 | 7.1 | 8.2 | 12.5 | 7.5 | 6.9 | 6.9 | 6.8 | 4.3 (4.1 to 4.6) |
−5.0 (−5.1 to −4.7) |
| Other | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 0.0 (−0.1 to 0.1) |
−0.1 (−0.2 to 0) |
| Socioeconomic status, mean (SD), %a | |||||||||||
| Median household income | 61 960 (24 670) | 61 683 (24 694) | 61 204 (24 492) | 60 480 (24 377) | 56 680 (23 184) | 61 564 (24 749) | 62 240 (24 873) | 62 504 (25 045) | 62 412 (24 695) | −3780 (−3961 to −3638) |
4884 (4717 to 5051) |
| Living in poverty | 13.2 (8.2) |
13.3 (8.2) |
13.4 (8.2) |
13.8 (8.4) |
15.2 (8.9) |
13.4 (8.3) |
13.1 (8.2) |
13.1 (8.2) |
13.1 (8.1) |
1.5 (1.4 to 1.5) |
−1.8 (−1.9 to −1.8) |
| Unemployed | 7.1 (3.5) |
7.1 (3.5) |
7.1 (3.5) |
7.2 (3.6) |
7.7 (3.9) |
7.1 (3.5) |
7.0 (3.5) |
7.1 (3.5) |
7.1 (3.4) |
0.5 (0.5 to 0.5) |
−0.6 (−0.6 to −0.6) |
| No. of comorbidities, % | |||||||||||
| 0 | 9.8 | 9.3 | 9.5 | 9.7 | 8.8 | 9.3 | 9.0 | 8.6 | 8.4 | −0.8 (−1.1 to −0.7) |
0.5 (0.3 to 0.7) |
| 1 | 18.0 | 17.7 | 17.8 | 17.9 | 17.0 | 17.5 | 17.1 | 16.6 | 16.2 | −0.9 (−1.2 to −0.6) |
0.4 (0.2 to 0.7) |
| 2 | 15.8 | 15.9 | 16.2 | 15.8 | 15.5 | 15.7 | 15.5 | 15.0 | 14.8 | −0.3 (−0.5 to 0) |
0.2 (−0.1 to 0.4) |
| 3 | 10.2 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 9.9 | 10.1 | 10.1 | 10.0 | 9.9 | −0.1 (−0.3 to 0.1) |
0.2 (0 to 0.4) |
| 4 | 6.9 | 6.7 | 6.7 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 7.0 | 7.2 | −0.1 (−0.3 to 0) |
0.2 (0.1 to 0.4) |
| ≥5 | 39.3 | 40.1 | 39.6 | 39.9 | 42.2 | 40.6 | 41.4 | 42.9 | 43.6 | 2.3 (2.0 to 2.6) |
−1.5 (−1.9 to −1.2) |
Measured at the zip code level.
Figure. Markers of Socioeconomic Status of Medicare Beneficiaries Discharged From Skilled Nursing Facilities (SNFs) by Benefit Day on SNF Discharge.
A, Percentage of beneficiaries living in poverty was measured at the zip code level. B, Median household income was measured at the zip code level.
Discussion
Medicare beneficiaries were more often discharged from SNFs on benefit day 20 than on benefit days 19 or 21. Those discharged on day 20 were more likely to be racial/ethnic minorities and to live in areas of lower socioeconomic status compared with those discharged before or after day 20. Our study was limited to fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries who did not have other sources of insurance; thus, the findings may not be generalizable to the broader Medicare population. In addition, we measured socioeconomic status at the zip code and not the individual level. Nonetheless, these findings suggest an association between disproportionately high SNF discharge rates of vulnerable patients and existing Medicare payment policies. Although the clinical implications of these discharge patterns are unknown, payment policies should be designed with consideration of the potential for such unintended consequences, and any potential consequences should be mitigated by balancing existing payment structures with incentives to provide optimal patient care.
References
- 1.Medicare Payment Advisory Commission Skilled nursing facility services. In: Report to the Congress: Medicare Payment Policy Washington, DC: Medicare Payment Advisory Commission; 2017:197-227. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/mar17_medpac_ch8.pdf2017. Accessed April 17, 2019.
- 2.Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Medicare coverage of skilled nursing facility care. Baltimore, MD: Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services; 2015. https://www.medicare.gov/pubs/pdf/10153.pdf. Accessed April 17, 2019.