Abstract
Various studies have described the biological properties of the Leucocyte- and Platelet Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) such as the antimicrobial effect against wound bacteria, but less is known about the effect against periodontal pathogens. The aim of this study was to evaluate the antibacterial properties of the L-PRF membrane and L-PRF exudate against the main periopathogens cultured on agar plates and in planktonic solution. This study demonstrated the antibacterial effect of the L-PRF membrane against P. intermedia, F. nucleatum, and A. actinomycetemcomitans, but especially against P. gingivalis. The L-PRF exudate also showed a strong inhibition against P. gingivalis on agar plates. No inhibition could be observed for the other bacterial strains. Moreover, L-PRF exudate decreased the number of viable P.gingivalis in a planktonic solution in a dose-dependent way. However, A. actinomycetemcomitans showed an increased growth in planktonic solution when in contact with the L-PRF exudate.
Subject terms: Applied microbiology, Periodontitis
Introduction
The classic experimental gingivitis studies in the 60 s1,2 demonstrated the direct relation between the accumulation of dental plaque and gingival inflammation. Dental plaque or dental biofilms are defined as a matrix-embedded microbial population, adherent to each other and/or to surfaces or interfaces3. Studies on biofilm development in deep periodontal pockets showed that the deepest sites are colonized predominantly by motile species (e.g. spirochetes) and gram-negative bacteria, located adjacent to the epithelial lining of the pocket. Some of these bacteria are part of the red complex (Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, Tannerella forsythia) and the orange complex (e.g. Fusobacterium nucleatum)4. On the other hand, gram-positive rods and cocci are more dominant in shallow sites, forming a firmly adherent band of microorganisms on the enamel or root surface4–6. One of the most solid associations between a periodontal pathogen and destructive periodontal disease is provided by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans JP2, a potential etiologic agent of localized aggressive periodontitis7–9.
Traditionally, the goal of non-surgical periodontal therapy is to eliminate the microbial and/or inflammatory etiology and to reduce the initial pockets to ≤5 mm. Antimicrobial agents are often used as adjuncts to initial therapy10. If the desired pocket depths are not achieved, surgical treatment is required11,12.
Recently, new tissue-engineering techniques have been proposed for regenerative procedures after non-surgical periodontal therapy13 or for bone augmentation14,15. Leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF), a second-generation platelet concentrate, was introduced as an autologous biomaterial that serves as a scaffold for regenerating cells. L-PRF is prepared from the patient’s own blood, without adding any additives, and concentrates >90% of the platelets and >75% of the leucocytes from the initial blood composition16. It offers a continuous release of growth factors and other bioactive substances that stimulate and protect the surgical site17,18. Different forms of L-PRF can be prepared, the membrane most commonly used.
Two recent systematic reviews19,20 have shown the various applications of L-PRF, concluding that favourable effects on hard and soft tissue healing and a decrease of postoperative discomfort could be obtained when L-PRF was used. Several studies have described other biological properties of L-PRF such as the antimicrobial effect against wound bacteria21,22. Given the cellular composition of L-PRF16 and its bioactive nature17, the aim of this study was to evaluate the antimicrobial capacity of an L-PRF membrane and L-PRF exudate against key periodontal pathogens (Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, Fusobacterium nucleatum, and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans). The null-hypothesis was postulated as (1) an L-PRF membrane and its exudate do not inhibit the four tested bacterial strains when applied directly on a cultured Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) agar plate, and (2), L-PRF exudate does not inhibit bacterial growth of the tested bacterial strains in planktonic form.
Results
Demographic data
Nine systemically healthy adult volunteers (6 women, 3 men) participated in this study. Their mean age was 37.7 ± 15.3 years (range 25–60 years). No complications were reported during blood collection.
Agar plate test
L-PRF membrane
The mean area of inhibition was 11.8 ± 5.0 mm2, 2.7 ± 5.2 mm2, 2.6 ± 3.0 mm2, and 0.6 ± 1.7 mm2 for P. gingivalis, P. intermedia, F. nucleatum, and A. actinomycetemcomitans, respectively (Table 1). More inhibition was found for P. gingivalis when compared to P. intermedia (p < 0.05), F. nucleatum (p < 0.05), and A. actinomycetemcomitans (p < 0.05).
Table 1.
Dimensions of L-PRF membranes at baseline and after 72 h of incubation as well as the difference between both observations (▲), and bacteria-free area (mm2) for nine participants (mean and standard deviation). *p < 0.05.
| L-PRF membrane | P. gingivalis | P.intermedia | F. nucleatum | A. actinomycetemcomitans | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | sd | mean | sd | mean | sd | mean | sd | ||
| Length and Width (mm) | |||||||||
| Baseline | length | 39.4 | 3.3 | 35.9 | 3.5 | 35.8 | 4.7 | 35.1 | 7.0 |
| width | 10.5 | 1.2 | 11.3 | 1.0 | 11.1 | 2.3 | 10.4 | 1.3 | |
| 72 h | length | 39.0 | 3.3 | 34.2 | 3.2 | 35.1 | 4.6 | 34.3 | 6.4 |
| width | 8.8 | 4.1 | 9.7 | 3.8 | 9.5 | 3.9 | 8.9 | 3.8 | |
| ▲ | length mm | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| width mm | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | |
| length % | 1.1 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 1.7 | |
| width % | 6.7 | 4.9 | 3.7 | 2.9 | 5.5 | 7.6 | 4.1 | 3.5 | |
| Surface (mm2) | |||||||||
| Baseline | membrane surface | 37.0 | 4.6 | 33.3 | 6.0 | 35.4 | 5.1 | 32.2 | 7.9 |
| 72 h | membrane surface | 34.4 | 4.4 | 31.1 | 11.1 | 33.6 | 5.0 | 30.5 | 7.0 |
| ▲ | shrinkage mm2 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 2.0 |
| shrinkage % | 7.2 | 2.9 | 5.5 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 2.5 | 4.8 | 5.1 | |
| Area of bacterial growth inhibition (mm 2 ) | |||||||||
| 72 h | full area | 11.8* | 5.0 | 2.7 | 5.2 | 2.6 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 1.8 |
| area without shrinkage | 9.1* | 3.2 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.7 | |
Over the 72-hour time incubation period, a shrinkage of the membranes was observed. The mean shrinkage of the L-PRF membrane was 5.7 ± 3.7% after 72 h of incubation at 37 °C in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The mean reduction in length and width was 1.0 ± 0.5 mm and 0.5 ± 0.1 mm, respectively. None of these changes (Table 1) were statistically significant (p > 0.05).
However, since membrane shrinkage could have influenced the mean area of inhibition, it was subtracted from the area of inhibition. After subtracting membrane shrinkage, P. gingivalis showed an area of inhibition of 9.1 ± 3.2 mm2 (p < 0.05). For P. intermedia, F. nucleatum and A. actinomycetemcomitans no statistically significant inhibition could be measured (p > 0.05).
L-PRF exudate
For the L-PRF exudate, only inhibition against P. gingivalis could be observed, with a mean area of inhibition of 17 ± 2.6 mm2 (Table 2). For the positive control (CHX 0.12%), the mean area of inhibition was statistically significantly larger (48.8 ± 4.2 mm2, p < 0.005).
Table 2.
Mean bacteria-free area (mm2) and standard deviation for the L-PRF exudate and chlorhexidine 0.12% (positive control). Data for nine participants. *p < 0.05.
| L-PRF exudate (mm2) | P. gingivalis | P. intermedia | F. nucleatum | A. actinomycetemcomitans | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | sd | mean | sd | mean | sd | mean | sd | ||
| 72 h | L-PRF exudate | 17.5* | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| chlorhexidine 0.12% | 48.0* | 4.2 | 79.4* | 7.0 | 28.8* | 4.0 | 27.4* | 3.0 | |
Planktonic bacteria
Vitality qPCR
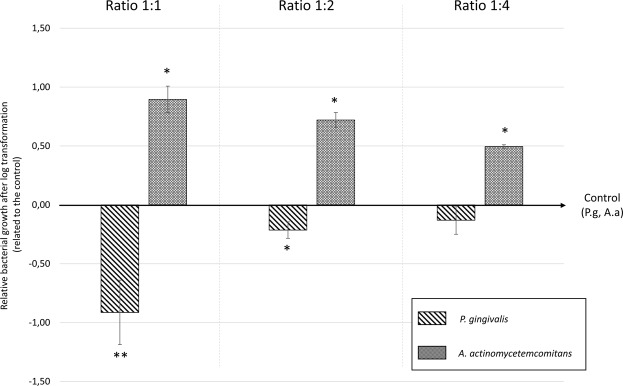
P. gingivalis and A. actinomycetemcomitans were considered for this analysis since they showed the highest and the lowest amount of inhibition induced by the membranes, respectively. The vitality qPCR analysis showed a mean reduction of 0.9 log (86%, p < 0.001), 0.2 log (38%, p < 0.05), and 0.1 log (24%, p > 0.05) in the growth of P. gingivalis when exposed to the L-PRF exudate with the ratios 1:1, 1:2, and 1:4, respectively. For the A. actinomycetemcomitans, a mean increase of 0.9 log (p < 0.05), 0.7 log (p < 0.05), and 0.5 log (p < 0.05) was observed for the respective ratios (Fig. 1).
Figure 1.
Effect of L-PRF exudate (1:1, 1:2, and 1:4 ratios) on P. gingivalis and A. actinomycetemcomitans in planktonic form. Results of the vitality qPCR shown after log transformation related to the control (P.g and A.a, respectively). Positive values represent bacterial growth. Negative values indicate bacterial inhibition. **p < 0.001; *p < 0.05.
Colonies counting (CFU/ml)
For P. gingivalis, the standard culture test showed a mean of 2.4 × 1012 CFU/ml in the control condition and of 9.4 × 109, 3.8 × 1010, and 2.0 × 1011 for the ratios 1:1, 1:2, and 1:4, respectively. For A. actinomycetemcomitans, the mean CFU/ml for the control was 3.1 × 107, whereas the counting was 3.0 × 1011, 1.8 × 1011, and 5.5 × 1010 for the respective ratios 1:1, 1:2, and 1:4 (Table 3).
Table 3.
Mean (±standard deviation, SD) qPCR and CFU counting (log values) for P. gingivalis and A. actinomycetemcomitans.
| Vitality qPCR (Log10 Geq/ml) | Culturing (Log10 CFU/ml) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | mean | sd | Mean | sd | |
| P. g | Control | 9.6 | 0.08 | 12.4 | 0.6 |
| 1:1 | 8.6 | 0.4 | 9.7 | 0.4 | |
| 1:2 | 9.4 | 0.2 | 10.4 | 0.4 | |
| 1:4 | 9.5 | 0.2 | 11.0 | 0.5 | |
| A. a | Control | 10.4 | 0.2 | 7.5 | 0.2 |
| 1:1 | 11.3 | 0.3 | 11.2 | 0.6 | |
| 1:2 | 11.1 | 0.3 | 11.2 | 0.3 | |
| 1:4 | 10.9 | 0.2 | 10.7 | 0.3 | |
Control: 150 µl bacteria + 150 µl saline. Ratio 1:1: 150 µl bacteria + 150 µl L-PRF exudate, ratio 1:2: 150 µl bacteria + 75 µl L-PRF exudate + 75 µl saline, and ratio 1:4: 150 µl bacteria + 37.5 µl L-PRF exudate + 112.5 µl saline. Data for nine volunteers.
Gram negative staining
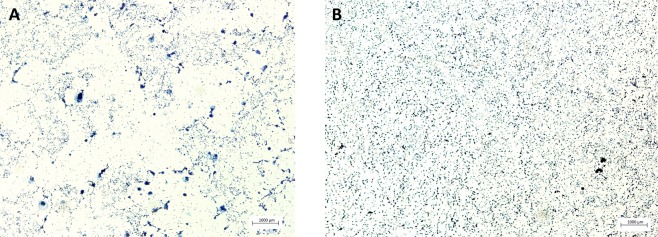
In order to find an explanation for the differences observed between the vitality qPCR data and the culture data for A. actinomycetemcomitans, gram staining was performed. As shown in Fig. 2, in the control group (Fig. 2A) A. actinomycetemcomitans formed aggregated clusters known as auto-aggregation. In the ratio 1:1, the bacteria appeared looser than those in the control group and no auto-aggregation was observed (Fig. 2B). Since clusters of bacteria were counted as one colony in the culturing method, and, all bacteria were counted as independent bacteria in the qPCR analysis, the discrepancy between culturing and vitality qPCR could be explained via inhibition of auto-aggregation.
Figure 2.
Gram negative staining of A. actinomycetemcomitans. (A) Control, bacteria in aggregated clusters; (B) ratio 1:1, bacteria in separate colonies.
Discussion
The results in this study demonstrated antimicrobial activity of the L-PRF membrane against P. gingivalis. No statistically significant inhibition could be observed for P. intermedia, F. nucleatum, and A. actinomycetemcomitans. The L-PRF exudate also showed a clear inhibition against P. gingivalis on agar plates. In planktonic form, a dose-dependent inhibition against P. gingivalis was observed for the L-PRF exudate, whereas for A. actinomycetemcomitans an increase in bacterial growth was detected.
Several studies showed an antimicrobial effect of platelet concentrates against wound bacteria. Burnouf and co-workers21 described bacterial inhibition by platelet-rich plasma (PRP) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli in planktonic form, after 3 h of aerobic incubation. Similar results were reported by Edelblute and co-workers22 on using a clotted form of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), after having added bovine thrombin. They concluded that the human platelet gel supernatant inactivated opportunistic pathogens on the skin, such as S. aureus and Acinetobacter baumannii, but not P. aeruginosa. However, controversial results were shown by Chen and co-workers23 stating that PRP had an antibacterial effect against S. aureus but not against E. coli or against P. aeruginosa in patients with diabetes.
Only few articles examined oral microorganisms. For instance, Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans isolated from the oral cavity were inhibited by pure-platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP), a type of PRP without leucocytes24,25. Yang and co-workers26 showed inhibition on P. gingivalis and A. actinomycetemcomitans by PRP whereas no inhibition could be observed for F. nucleatum. In this study, the effect of PRP and PRF was compared, concluding that PRP showed superior activity. It should be noted that PRF was prepared by adding calcium chloride to PRP in order to activate the platelets and convert fibrinogen into fibrin, which is not in line with the protocol to prepare PRF. Moreover, the authors affirmed that in their study PRF had neither platelets nor leucocytes. However, by definition, platelet concentrates are blood-derived products with an increased concentration in platelets, with or without the presence of leucocytes25,27. Therefore, these results must be interpreted with caution. More recently, Kour and co-workers (2018)28 compared the antibacterial capacity of PRP, PRF, and injectable-PRF (I-PRF) on P. gingivalis and A. actinomycetemcomitans. They concluded that all three platelet concentrates showed some antibacterial activity against both bacteria. However, PRP and I-PRF presented significantly greater inhibition against P. gingivalis compared to PRF. In the present study, limited inhibition could be observed on A. actinomycetemcomitans, which differs from their results. The bacterial strain used and the fact that they incubated A. actinomycetemcomitans anaerobically might have influenced the effect of PRF.
P. gingivalis was the most inhibited bacteria strain in this study. However, there is no evidence in the literature showing a direct effect of blood components on P. gingivalis. Proteinase inhibitors constitute 10% of the protein content of human plasma and they can affect the gingipain activity, known as the primary virulence factor of those bacteria. These proteinases also play an important role in the survival of the bacterium within host cells, due to their implication in the cellular invasion and in overcoming the protective defence mechanisms of epithelial cells29,30. An example of proteinase inhibitors is the human alpha-2-macroglobulin, a large plasma protein found in blood, that inhibited RgpA and RgpB, but not Kgp in an in-vitro study31. The alpha-granules from the platelets are also an important intracellular storage of biologically active proteins32,33. Seven antimicrobial peptides have been identified from human platelets, suggesting a direct antimicrobial role34. However, the direct relation between those peptides and the antimicrobial capacity of the L-PRF has not been proved yet. For the L-PRF membrane, two theories could be advocated: (1) the living cells inside the fibrin matrix constantly released antimicrobial peptides against the targeted bacteria, or (2) the antimicrobial peptides were entrapped in the fibrin matrix and they were gently released as the fibrin matrix was being disintegrated. Concerning the L-PRF exudate, no specific pathways are known between blood-derived products and P. gingivalis. Therefore, further research should investigate this association.
Two effects on A. actinomycetemcomitans could be observed in this present study. First, there was an effect on the auto-aggregation of these bacteria. One possible explanation is that the L-PRF exudate might impair the aggregation of those bacteria35. Given that most bacteria exist in environments with fluctuating conditions (e.g. shear forces, nutrient availability or physiological conditions), the bacteria within co-aggregated communities will survive and proliferate under conditions that reduce the prevalence of single non-aggregated cells. For these reasons, co-aggregation processes are likely to have an important ecological role in the development and maintenance of multiple-species biofilm36,37. Regarding the second effect, bacterial growth stimulation of A. actinomycetemcomitans was detected when it was in contact with the L-PRF exudate. Fresh human serum is known for enhancing leukotoxic activity of these bacteria38,39. Johansson and co-workers40 indicated that the increased leukotoxicity of A. actinomycetemcomitans observed in the presence of human serum is caused by the serum protease inhibitors, which counteract the proteolytic degradation of the leukotoxin.
To the best of our knowledge, this was the first time that the shrinkage of the L-PRF membrane was considered, in surface as well as in length and width. A mean surface shrinkage of 5% in vitro after 3 days was reported. These results cannot be straightforwardly extrapolated to the clinical situation. However, they provide insight into the dimensional changes that might occur when used in the oral cavity. It must be noted that the shrinkage of the L-PRF membrane probably occurred progressively. The area of shrinkage was thus gradually exposed, but not colonised by the surrounding bacteria. The explanation for the absence of microbial growth in the area that became exposed after membrane shrinkage is more complex, including factors such as antimicrobial activity at distance, antimicrobial activity due to direct contact or growth inhibition due to mechanical coverage.
Within the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that an L-PRF membrane has antimicrobial properties against P. gingivalis, whereas the inhibition against P. intermedia, F. nucleatum, and A. actinomycetemcomitans was not statistically significant on agar plates. The L-PRF exudate showed a strong inhibition against P. gingivalis on agar plates, but no inhibition could be observed for the rest of the bacterial strains. Therefore, we cannot reject the first null-hypothesis. For the L-PRF exudate, the second hypothesis cannot be rejected because A. actinomycetemcomitans even showed increased growth. However, the L-PRF exudate has an antimicrobial effect against P. gingivalis in a dose-dependent way.
Methods
Bacterial strains
All bacterial species (P. gingivalis ATCC 33277, P. intermedia ATCC 25611, F. nucleatum ATCC 20482, A. actinomycetemcomitans ATCC 43718) were maintained on blood agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) supplemented with 5 mg/ml hemin (Sigma, St. Louis, USA), 1 mg/ml menadione (Calbiochem-Novabiochem, La Jolla, CA, USA), and 5% sterile horse blood (E&O Laboratories, Bonnybridge, Scotland). Overnight liquid cultures were prepared in BHI broth (Difco, Detroit, MI, USA). The bacteria were cultured under anaerobic conditions (80% N2, 10% H2 and 10% CO2) for P. gingivalis, P. intermedia, and F. nucleatum or aerobic conditions (5% CO2) for A. actinomycetemcomitans.
Leucocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) preparation
The participants in this study (n = 9) were systemically healthy, non-smokers, without a history of periodontal disease and who had not taken any antibiotics for at least 6 months before the study. Four blood samples were collected from each volunteer (n = 9) in a 9 mL glass-coated plastic tube and immediately centrifuged at 408 g for 12 minutes (Intraspin™, Intra-Lock, Boca Raton, FL, USA). The L-PRF clot was compressed and transformed into a standardized membrane of 1 mm in thickness (Xpression® box, Intra-Lock, Boca Raton, FL, USA). During this process, the released exudate was also kept for further use at −80 °C. Due to the low cellular content of L-PRF exudate (<2.5% of platelets and <0.9% of leucocytes for the initial blood composition)41, we could freeze it without damaging the possible active molecules.
Agar plate test
L-PRF membrane
BHI agar plates (Difco, Sparks, MD, USA) were seeded with an overnight culture 2 h before the application of an L-PRF membrane and incubated in anaerobic (80% N2, 10% H2 and 10% CO2) or aerobic (5% CO2) conditions, depending on the bacteria. The L-PRF membranes on the surface of a BHI agar plate were in direct contact with P. gingivalis, P. intermedia, F. nucleatum or A. actinomycetemcomitans. The incubation time was 72 h.
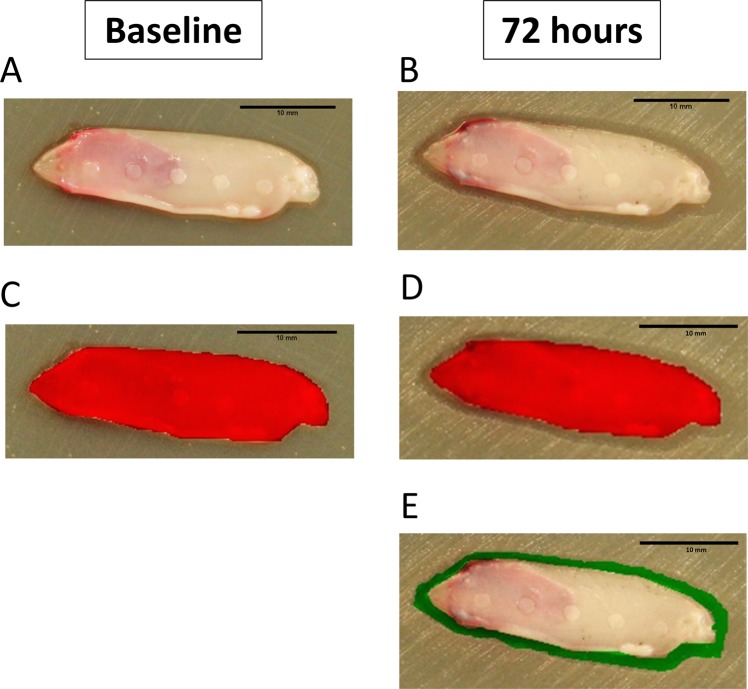
Standardized pictures (constant distance between agar plate and camera) were taken at baseline and after 72 h. In order to verify the shrinkage, the difference in surface area of the membrane between pictures at baseline and those after 72 h was computed with PictZar® Pro 7.1 (Digital Planimetry Software). Each image was calibrated based on the ruler that was attached to the agar plate. First, the area of the L-PRF membrane at baseline was coloured (red) and its area was calculated. The same was done for the L-PRF membrane after 72 h of incubation. The area free of bacterial growth around each membrane was coloured (green) and calculated. To evaluate the shrinkage, the area of the L-PRF membrane at baseline was subtracted from the area after 72 h (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
(A) L-PRF membrane on BHI agar plate previously inoculated with an overnight culture of P. gingivalis. (B) Calculation of initial membrane surface area using PictZar® software (red area). (C) After 72 hours of anaerobic incubation, bacterial growth became visible (white colonies). (D) Calculation of the membrane’s new surface area (red area), in order to detect membrane shrinkage. (E) Calculation of area without bacterial growth (green area).
The length and width of each membrane were measured at baseline and after 72 h with the software ImageJ® (Image Processing and Analysis in Java, 1.8.0_77). All images were individually calibrated based on the ruler that was fixed to each agar plate. A horizontal (length) and a vertical (width) line were drawn from the middle point of the membrane with an angle of 90°.
L-PRF exudate
Twenty-five microliters of L-PRF exudate, 25 µl of pure chlorhexidine (CHX) 0.12% (positive control) and 25 µl of BHI broth (negative control) were applied directly to the surface of each BHI agar plate, prepared and inoculated in the same way as in the previous experiment. The incubation time was 72 h.
Standardized pictures were taken at baseline and after 72 h. The area free of bacterial growth around each drop of L-PRF exudate was measured with the software PictZar® Pro 7.1.
L-PRF exudate dilution test
If inhibition with L-PRF exudate was detected, bacteria were cultured in BHI broth and optical densities were adjusted using spectrophotometry (OD600, GeneQuant Spectrophotometer, Buckinghamshire, UK) to an OD of 0.5–0.7 (OD600 = 0.5 ≈ 1 × 108 colony forming unit/ml (CFU/ml). Three dilutions of L-PRF exudate were prepared in a 96-well plate, for a total volume of 300 µl/well: ratio 1:1 (150 µl of bacteria + 150 µl of L-PRF exudate), ratio 1:2 (150 µl of bacteria + 75 µl of L-PRF exudate + 75 µl of saline), and ratio 1:4 (150 µl of bacteria + 37.5 µl of L-PRF exudate + 112.5 µl of saline). The positive control consisted of 150 µl of bacteria + 150 µl of saline. The incubation time was 24 h. One bacterial strain that was not inhibited during the agar plate test was also cultured.
After 24 h, 90 µl of the mixtures mentioned above was taken for vitality quantitative PCR (qPCR). Another 50 µl was used for microbial culturing and colony counting (CFU/ml). This experiment was performed in triplicate.
Vitality qPCR
The vitality-DNA extraction was performed with a QIAamp DNA Mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany)42. Briefly, 90 μl aliquots of the samples were immediately incubated with 10 μl of propidium monoazide (PMA) (Biotium, Hayward, CA, USA) at a final concentration of 100 μg/ml42. Samples were incubated in the dark for 5 min, following photo-induced cross-linking of PMA by 10-min light exposure using a 400 W (500 lm) light source, placed 20 cm above the sample, while samples were kept on ice. The PMA treated bacteria were pelleted by centrifugation at 20,000 × g for 10 min and DNA extraction was performed using the QIAamp DNA Mini kit following the manufacturer’s instruction, extending the incubation step of the bacteria in the lytic enzyme solution at 37 °C to 2 h.
A qPCR assay was performed with a CFX96 Real-Time System (Biorad, Hercules, CA, USA) using the Taqman 5′ nuclease assay PCR method for detection and quantification of bacterial DNA. Primers and probes were targeted against the 16 S rRNA gene for the test group and for the negative control. Taqman reactions contained 12.5 µl Mastermix (Eurogentec, Seraing, Belgium), 4.5 µl sterile H2O, 1 ml of each primer and probe, and 5 ml template DNA. Assay conditions for all primer/probe sets consisted of an initial 2 min at 50 °C, followed by a denaturation step at 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 45 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 60 seconds. Quantification was based on a plasmid standard curve (Table 4).
Table 4.
Primers and probes used for the detection and qualification by vitality qPCR.
| STRAIN | Primer/Probe (5′-3′) | Fragment length | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. gingivalis | Forward | GCG CTC AAC GTT CAG CC | 68 bp |
| Reverse | CAC GAA TTC CGC CTG C | ||
| Probe | CAC TGA ACT CAA GCC CGG CAG TTT CAA | ||
| P. intermedia | Forward | CGG TCT GTT AAG CGT GTT GTG | 99 bp |
| Reverse | CAC CAT GAA TTC CGC ATA CG | ||
| Probe | TGG CGG ACT TGA GTG CAC GC | ||
| F. nucleatum | Forward | GGA TTT ATT GGG CGT AAA GC | 162 bp |
| Reverse | GGC ATT CCT ACA AAT ATC TAC GAA | ||
| Probe | CTC TAC ACT TGT AGT TCC G | ||
| A. actinomycetemcomitans | Forward | GAA CCT TAC CTA CTC TTG ACA TCC GAA | 80 bp |
| Reverse | TGC AGC ACC TGT CTC AAA GC | ||
| Probe | AGA ACT CAG AGA TGG GTT TGT GCC TTA GGG |
Colony counting (CFU/ml)
All samples were also diluted from 10−1 to 10−9 in PBS and plated by means of a spiral plater on blood agar plates supplemented with 5 mg/ml hemin (Sigma, St. Louis, USA), 1 mg/ml menadione, and 5% sterile horse blood. After 7 days of anaerobic (80% N2, 10% H2 and 10% CO2) or aerobic (5% CO2) incubation (depending on the bacteria), the total number of CFU/ml was counted by means of Fiji software (Image Processing and Analysis in Java, 1.8.0_77). Briefly, all images were transformed into a 16-bit-image and a region of interest (ROI) with all colonies was selected. The image was then converted into a binary image. The latter was modified (watershed) to improve the separation of each colony when the colonies were too close. Finally, the count was performed based on the size and the circularity43 (Fig. S1). If the number of colonies on an agar plate was above 300, this plate was considered not countable. CFU/ml were calculated according to the dilution point.
Gram negative staining
Given the differences in values between the qPCR and the CFU reported in Table 3, a gram negative staining was performed for A. actinomycetemcomitans (control and ratio 1:1). The samples were analysed with the Axio Imager 2 Microscope (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging GmbH, Germany) with a 40x magnification.
Ethical Statement
The use of human blood was approved by the ethical committee of the KU Leuven and registered with identifier B322201628215. The procedures were executed according to the Helsinki Declaration and the regulations of the University Hospital, approved by the ethical committee. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects after the purpose of the study had been explained. The subjects were aware that the results would be used in a scientific study.
Statistical analysis
For all variables, mean values and standard deviations were calculated. The normality of the data was tested with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The normally distributed data were then analysed with Student’s T-test (parametric test) and the 95% confidence interval was computed. For non-parametric data, the Wilcoxon test was used. A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Martine Pauwels for her support in performing the vitality qPCRs and colony counting. Furthermore, we would like to thank Dr. Wim Coucke for his help in the statistical analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.B.C., N.P., W.T. and M.Q.; Methodology: A.B.C., E.R.H, V.S. and W.T.; Analysis: A.B.C., E.R.H., W.T. and M.Q., Writing-Original Draft: A.B.C.; Writing-Review and Editing: N.P., W.T. and M.Q.; Founding acquisition: M.Q.; Resources: W.T. and M.Q.; Supervision: W.T., and M.Q.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41598-019-44755-6.
References
- 1.Loe H, Theilade E, Jensen SB. Experimental Gingivitis in Man. J Periodontol. 1965;36:177–187. doi: 10.1902/jop.1965.36.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Loe H, Theilade E, Jensen SB, Schiott CR. Experimental gingivitis in man. 3. Influence of antibiotics on gingival plaque development. J Periodontal Res. 1967;2:282–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1967.tb01901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Costerton JW, Lewandowski Z, Caldwell DE, Korber DR, Lappin-Scott HM. Microbial biofilms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995;49:711–745. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.49.100195.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Socransky SS, Haffajee AD, Cugini MA, Smith C, Kent RL., Jr. Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J Clin Periodontol. 1998;25:134–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.1998.tb02419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wecke J, et al. A novel technique for monitoring the development of bacterial biofilms in human periodontal pockets. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000;191:95–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Marsh PD. Dental plaque: biological significance of a biofilm and community life-style. J Clin Periodontol. 2005;32(Suppl 6):7–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Socransky SS, Haffajee AD. The bacterial etiology of destructive periodontal disease: current concepts. J Periodontol. 1992;63:322–331. doi: 10.1902/jop.1992.63.4s.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kornman KS, Loe H. The role of local factors in the etiology of periodontal diseases. Periodontol 2000. 1993;2:83–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.1993.tb00222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Haffajee AD, Socransky SS. Microbial etiological agents of destructive periodontal diseases. Periodontol 2000. 1994;5:78–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.1994.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.da Costa L, Amaral C, Barbirato DDS, Leao ATT, Fogacci MF. Chlorhexidine mouthwash as an adjunct to mechanical therapy in chronic periodontitis: A meta-analysis. J Am Dent Assoc. 2017;148:308–318. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2017.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hung HC, Douglass CW. Meta-analysis of the effect of scaling and root planing, surgical treatment and antibiotic therapies on periodontal probing depth and attachment loss. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29:975–986. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051X.2002.291102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. American Academy of, P. Comprehensive periodontal therapy: a statement by the American Academy of Periodontology *. J. Periodontol 82, 943–949, 10.1902/jop.2011.117001 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Wikesjo UM, et al. Periodontal repair in dogs: rhBMP-2 significantly enhances bone formation under provisions for guided tissue regeneration. J Clin Periodontol. 2003;30:705–714. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051X.2003.00363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jung RE, et al. Effect of rhBMP-2 on guided bone regeneration in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003;14:556–568. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.2003.00921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jung RE, et al. A randomized-controlled clinical trial evaluating clinical and radiological outcomes after 3 and 5 years of dental implants placed in bone regenerated by means of GBR techniques with or without the addition of BMP-2. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20:660–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2008.01648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Del Corso M, Diss A, Mouhyi J, Charrier JB. Three-dimensional architecture and cell composition of a Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin clot and membrane. J Periodontol. 2010;81:546–555. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schar MO, Diaz-Romero J, Kohl S, Zumstein MA, Nesic D. Platelet-rich concentrates differentially release growth factors and induce cell migration in vitro. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473:1635–1643. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4192-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dohan Ehrenfest DM, de Peppo GM, Doglioli P, Sammartino G. Slow release of growth factors and thrombospondin-1 in Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a gold standard to achieve for all surgical platelet concentrates technologies. Growth Factors. 2009;27:63–69. doi: 10.1080/08977190802636713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Castro AB, et al. Regenerative potential of leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin. Part A: intra-bony defects, furcation defects and periodontal plastic surgery. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology. 2017;44:67–82. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Castro AB, et al. Regenerative potential of leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin. Part B: sinus floor elevation, alveolar ridge preservation and implant therapy. A systematic review. Journal of Clinical Periodontology. 2017;44:225–234. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Burnouf T, Chou ML, Wu YW, Su CY, Lee LW. Antimicrobial activity of platelet (PLT)-poor plasma, PLT-rich plasma, PLT gel, and solvent/detergent-treated PLT lysate biomaterials against wound bacteria. Transfusion. 2013;53:138–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2012.03668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Edelblute CM, Donate AL, Hargrave BY, Heller LC. Human platelet gel supernatant inactivates opportunistic wound pathogens on skin. Platelets. 2015;26:13–16. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2013.863859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen L, Wang C, Liu H, Liu G, Ran X. Antibacterial effect of autologous platelet-rich gel derived from subjects with diabetic dermal ulcers in vitro. J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:269527. doi: 10.1155/2013/269527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Drago L, Bortolin M, Vassena C, Taschieri S, Del Fabbro M. Antimicrobial activity of pure platelet-rich plasma against microorganisms isolated from oral cavity. BMC Microbiol. 2013;13:47. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dohan Ehrenfest DM, et al. Classification of platelet concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF) for topical and infiltrative use in orthopedic and sports medicine: current consensus, clinical implications and perspectives. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014;4:3–9. doi: 10.32098/mltj.01.2014.02. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yang LC, et al. Antimicrobial activity of platelet-rich plasma and other plasma preparations against periodontal pathogens. J Periodontol. 2015;86:310–318. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.140373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dohan DM, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: Technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology. Oral Radiology, and Endodontics. 2006;101:E37–E44. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kour P, Pudakalkatti PS, Vas AM, Das S, Padmanabhan S. Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Platelet-rich Plasma, Platelet-rich Fibrin, and Injectable Platelet-rich Fibrin on the Standard Strains of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Contemp Clin Dent. 2018;9:S325–S330. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_367_18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Andrian E, Grenier D, Rouabhia M. Porphyromonas gingivalis-epithelial cell interactions in periodontitis. J Dent Res. 2006;85:392–403. doi: 10.1177/154405910608500502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kadowaki T, et al. A role for gingipains in cellular responses and bacterial survival in Porphyromonas gingivalis-infected cells. Front Biosci. 2007;12:4800–4809. doi: 10.2741/2428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gron H, et al. The potential role of alpha 2-macroglobulin in the control of cysteine proteinases (gingipains) from Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Periodontal Res. 1997;32:61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1997.tb01383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Blair P, Flaumenhaft R. Platelet alpha-granules: basic biology and clinical correlates. Blood Rev. 2009;23:177–189. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2009.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cieslik-Bielecka A, Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Lubkowska A, Bielecki T. Microbicidal properties of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Plasma/Fibrin (L-PRP/L-PRF): new perspectives. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2012;26:43S–52S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tang YQ, Yeaman MR, Selsted ME. Antimicrobial peptides from human platelets. Infect Immun. 2002;70:6524–6533. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.12.6524-6533.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sreenivasan PK, Meyer DH, Fives-Taylor PM. Factors influencing the growth and viability of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1993;8:361–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.1993.tb00612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Karched M, Bhardwaj RG, Asikainen SE. Coaggregation and biofilm growth of Granulicatella spp. with Fusobacterium nucleatum and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. BMC Microbiol. 2015;15:114. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0439-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rickard AH, Gilbert P, High NJ, Kolenbrander PE, Handley PS. Bacterial coaggregation: an integral process in the development of multi-species biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11:94–100. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(02)00034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.McArthur WP, Tsai CC, Baehni PC, Genco RJ, Taichman NS. Leukotoxic effects of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Modulation by serum components. J Periodontal Res. 1981;16:159–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1981.tb00962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tsai CC, et al. Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actimycetemcomitans leukotoxin and human periodontitis - A historic review with emphasis on JP2. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2018;34:186–193. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2018.01.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Johansson A, et al. Protease inhibitors, the responsible components for the serum-dependent enhancement of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxicity. Eur J Oral Sci. 2001;109:335–341. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0722.2001.00055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Castro, A. B. et al. Characterization of the Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Block: Release of Growth Factors, Cellular Content, and Structure. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 10.11607/jomi.7275 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Loozen G, Boon N, Pauwels M, Quirynen M, Teughels W. Live/dead real-time polymerase chain reaction to assess new therapies against dental plaque-related pathologies. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2011;26:253–261. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2011.00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schindelin J, et al. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012;9:676–682. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.