Abstract
Objectives
Previous studies showed reductions in recurrence and mortality rate of several cancer types in patients receiving perioperative epidural analgesia. This study aimed to investigate the effects of thoracic epidural analgesia on oncological outcomes after resection for lung cancer.
Design
Retrospective study using propensity score matching methodology.
Setting
Single medical centre in Taiwan.
Participants
Patients with stages I–III non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing primary tumour resection between January 2005 and December 2015 and had either epidural analgesia, placed preoperatively and used intra- and postoperatively, or intravenous analgesia were evaluated through May 2017.
Primary and secondary outcome measures
Primary endpoint was postoperative recurrence-free survival and secondary endpoint was overall survival.
Results
The 3-year recurrence-free and overall survival rates were 69.8% (95% CI 67.4% to 72.2%) and 92.4% (95% CI 91% to 93.8%) in the epidural group and 67.4% (95% CI 62.3% to 72.5%) and 89.6% (95% CI 86.3% to 92.9%) in the non-epidural group, respectively. Multivariable Cox regression analysis before matching demonstrated no significant difference in recurrence or mortality between groups (adjusted HR: 0.93, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.14 for recurrence; 0.81, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.13 for mortality), similar to the results after matching (HR: 0.97, 95% CI 0.71 to 1.31; 0.94, 95% CI 0.57 to 1.54). Independent risk factors for both recurrence and mortality were male, higher pretreatment carcinoembryonic antigen level, advanced cancer stage, poor differentiation, lymphovascular invasion, microscopic necrosis and postoperative radiotherapy.
Conclusions
Thoracic epidural analgesia was not associated with better recurrence-free or overall survival in patients receiving surgical resection for stages I–III non-small-cell lung cancer.
Keywords: epidural analgesia, cancer, recurrence, mortality, non-small-cell lung carcinoma, propensity score
Strengths and limitations of this study.
Large sample size and long follow-up time were employed to evaluate the impacts of epidural analgesia on long-term outcomes after lung cancer surgery.
Propensity score matching was used to deal with possible imbalances in collected variables.
Epidural assignment was not randomised, clinical care was not standardised and potential selection bias cannot be ruled out.
Effects of unmeasured confounders on outcomes after lung cancer surgery cannot be further evaluated.
Introduction
Lung cancer is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy worldwide, and its incidence continues to grow.1 An estimated 2.1 million new cases of lung cancer were diagnosed and 1.76 million lung cancer deaths occurred globally in 2018.1 Surgical removal of the primary tumour is the mainstay of treatment for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer staged I through IIIA.2 However, surgical dissection and manipulation are associated with unintentional dispersal of cancer cells into the blood and lymphatic systems.3 Whether the residual neoplastic cell would develop into a metastasis depends on the perioperative immune competence of the patient. Surgically induced stress hormone, as well as inhaled volatile anaesthetics and systemic opioids, can diminish natural killer cell function, the primary defense against cancer cells.4
Opioids inhibit components of both cell-mediated and humoral immunity.5 Morphine also has proangiogenic properties that may promote dissemination of angiogenesis-dependent tumours.6 Inflammatory cytokines have been shown to regulate the expression of the mu-opioid receptor (MOR) gene, highlighting an interaction between the opioid and immune systems.7 It is noted that the MOR is over-expressed in several types of lung cancer and it promotes opioid- and growth factor-induced proliferation and migration in human lung cancer cells.8 Furthermore, silencing the MOR greatly reduced opioid-induced tumour growth and metastasis in vitro.9
Anaesthetic management in primary cancer surgery has been proposed to impact recurrence or metastases, including blood transfusion,10 narcotics consumption11–13 and analgesic techniques.14 Thoracic epidural analgesia, commonly used for the management of postoperative pain, has been shown to reduce mortality, respiratory complications and opioid consumption and improved time to ambulation in thoracic surgeries.15 However, the effect of epidural analgesia on oncological outcomes after lung cancer resection remains unclear. It is hypothesised that epidural analgesia may reduce tumour growth and spread through its opioid and general anaesthetic sparing and surgical stress alleviating properties, but only one retrospective study with limited sample size is available for this issue.16 Therefore, we conducted this retrospective cohort study to investigate the relationship between perioperative thoracic epidural analgesia and cancer recurrence or overall survival in patients following surgical resection for non-small-cell lung cancer. The effects of other major prognostic factors were assessed as well to determine the significant predictors of oncological outcomes after lung cancer resection.
Methods
Setting and patient selection
Patients undergoing surgical resection of pulmonary neoplasms between January 2005 and December 2015 at our hospital were retrospectively identified from the institutional electronic medical database. Patients with secondary lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, stage IV disease determined at the time of surgery or missing data about demographics, pathological details or postoperative analgesic were excluded from the study (figure 1). Patients were analysed in two groups: those receiving general anaesthesia with perioperative epidural analgesia and their counterparts receiving general anaesthesia without epidural analgesia.
Figure 1.
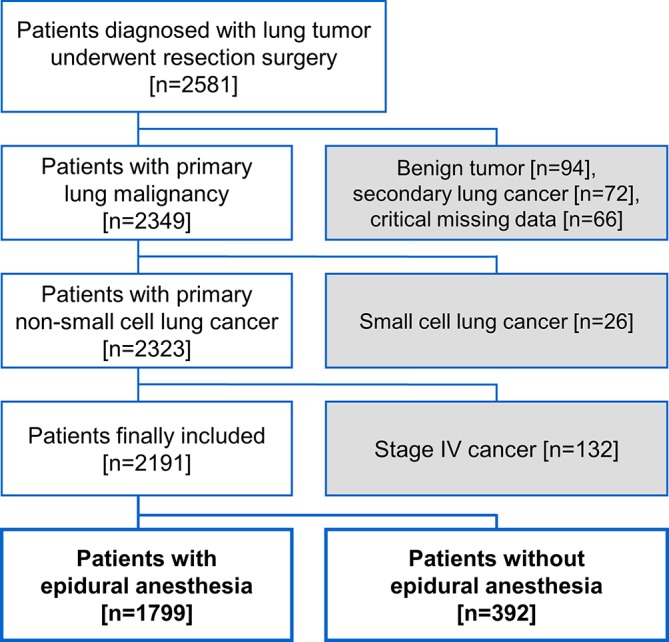
Flow diagram for patient inclusion.
Analgesia management
All patients undergoing open thoracotomy or video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery at our hospital were offered the choice of epidurals with preoperative catheter placement or intravenous analgesia with a demand pump. If epidural analgesia was selected, an epidural catheter was typically placed at a middle thoracic region (eg, T6–T8) and assessed its function with a test dose of local anaesthetic preoperatively. Epidural analgesia was started intraoperatively with local anaesthetic (bupivacaine 0.25% or 0.5%) with or without fentanyl 1–2 µg/mL at an infusion rate of 5–10 mL/hour, continued postoperatively for 48–72 hours, and switched to oral acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs thereafter. Typically, patients undergoing lung cancer surgery received intravenous fentanyl 50–150 µg for anaesthetic induction. Patients with effective epidurals were rarely given additional opioids perioperatively. If patients refused epidurals or it was contraindicated, an intravenous patient-controlled analgesia was administered via an ambulatory infusion pump (Gemstar Yellow, Hospira, Illinois, USA) programmed to deliver morphine sulfate 1 mg/mL in normal saline, at a demand dose of 1 mg with a lockout time of 6 min.
Data retrieval
An electronic medical database was used to determine the baseline clinicopathological risk factors for cancer recurrence and mortality. The following data were obtained from medical records: demographic characteristics; the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance score17; coexisting diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease and so on); preoperative pulmonary function tests (forced vital capacity, forced expiratory volume in one second and their predicted percentages); pretreatment carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level18; anaesthesia time, perioperative packed red blood cell (pRBC) transfusion19; pathologic features (tumour differentiation, microscopic necrosis,20 lymphovascular invasion21 and perineural invasion)22; whether preoperative or postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy was used and each patient’s current status as determined by documentation of follow-up visits to the hospital’s outpatient clinic or subsequent admissions. Tumour nodes metastasis (TNM) staging was also obtained from the record and translated into stages I–III according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer criteria (AJCC-7 staging system).23 Adjuvant therapies given in the form of chemotherapy (cisplatin-gemcitabine, cisplatin-paclitaxel, cisplatin-docetaxel or carboplatin-paclitaxel) or radiotherapy were at the discretion of surgeons and patients, and was defined as any therapy given within 90 days of surgery. The radiologists and thoracic surgeons of our hospital determined whether cancer recurred or not, which was mainly based on imaging studies (CT, MRI, bone scan and so on) and defined by response evaluation criteria in solid tumours guidelines.24 Pathology-proven second primary lung cancer was not considered as a recurrent disease. At our hospital, close surveillance was performed for survivors of lung cancer following definitive surgical therapy, including chest CT every 6 months for at least the first 2 years, and annually thereafter. The follow-up rates of this cohort were 95.3%, 88.7% and 78.8% in the end of the postoperative first, third and fifth year, respectively (online supplementary table 1). The date of death was determined based on medical record or death certificate.
bmjopen-2018-027618supp001.pdf (286.7KB, pdf)
Medical records of all the patients included were extracted by specialist anaesthesiologists who were not involved in data analysis. The quality of the extracted data was verified through random sampling by the authors. Data were collected up to the end of May 2017.
The primary endpoint was recurrence-free survival, which was defined as time from the date of surgery to the date of cancer recurrence. The secondary endpoint was overall survival, defined as time from the date of surgery to the date of death. For those without the event of cancer recurrence or death, their survival times were regarded as the corresponding censored observations with the last visit date used as the censored date.
Statistical analysis
The comparisons of patient characteristics between the epidural and non-epidural groups were performed using Χ2 tests for categorical variables and either t tests or Wilcoxon rank sum tests for continuous variables, as appropriate. The Kaplan-Meier method and log rank test were used to compare recurrence-free and overall survival distributions between the two groups. Univariate Cox regression analysis was used to evaluate the effects of epidural analgesia and other variables collected in the study on recurrence-free or overall survival. Significant predictors of recurrence-free or overall survival in the univariate analysis were used as candidates for stepwise model selection processes in the following multivariable analysis. The entry and exit criteria of significance level were set at 0.05 and 0.1, respectively, to select factors associated with recurrence-free and overall survival in the multivariable analysis. Afterward the effects of epidural analgesia adjusted for the selected predictors in the multivariable analysis on recurrence-free and overall survival were further evaluated.
To account for the potential imbalance in measured confounders related to cancer recurrence or survival of lung cancer between epidural and non-epidural groups, propensity scores based on a collection of patient characteristics was developed to estimate the probability of receiving epidurals (online supplementary table 2). Propensity score matching was performed as the primary analysis using a calliper with width equal to 0.2 of the SD of the logit of the propensity score to ensure sufficient balance in collected variables between matching pairs.25 Imbalance of the distribution of baseline attributes between groups was measured by standardised difference, the difference in mean, proportion or rank divided by the pooled SE, expressed as percentage and was defined as absolute value greater than 20.26 For sensitivity analysis, all subjects were divided into five equal-size groups using the quintiles of the estimated propensity score and stratified Cox regression analysis was conducted to obtain a pooled HR across the five strata to ensure the consistency among different estimates of the effects of epidurals on cancer recurrence or overall survival. The significance level of all hypotheses was 0.05 for a two-sided test. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows V.22.0 (IBM Corp.) was used for all analyses.
Patient and public involvement
This study is a retrospective analysis using the institutional medical database. There was no patient involved in the recruitment to and conduct of the study.
Results
Total of 2191 patients were included in this study and 1799 (82.1%) of them received epidural analgesia. There were some differences in the distributions of baseline characteristics between groups, including less thoracoscopic surgery (standardised difference=36.1) and longer follow-up time (standardised difference=20.4) in epidural group (table 1). The rate of epidural placement declined because more resections of lung cancer were done with thoracoscopic technique at our hospital in recent years (online supplementary table 3). Those not receiving epidurals, as mentioned above, had intravenous patient-controlled opioid analgesia. Table 2 shows the details of cancer stages and pathological features of the two groups. The epidural group had higher rate of lymphocytic infiltration. After propensity score matching, the final sample of 372 matched pairs of patients was analysed and no significant difference was found in demographical or pathological characteristics between groups (table 1).
Table 1.
Patient demographics
| Before matching | After matching | |||||
| EA (n=1799) | Non-EA (n=392) | Standardised difference | EA (n=372) | Non-EA (n=372) | Standardised difference | |
| Age, year | 64±11 | 64±11 | 0.1 | 64±12 | 64±11 | 5.8 |
| Sex, male | 918 (51.0%) | 194 (49.5%) | 3.1 | 192 (51.6%) | 183 (49.2%) | 4.8 |
| ASA physical status≥3 | 424 (23.6%) | 109 (27.8%) | 9.7 | 104 (28.0%) | 100 (26.9%) | 2.4 |
| ECOG PS≥1 | 549 (30.5%) | 130 (33.2%) | 5.7 | 132 (35.5%) | 117 (31.5%) | 8.6 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| COPD | 474 (26.3%) | 107 (27.3%) | 2.1 | 102 (27.4%) | 100 (26.9%) | 1.2 |
| Diabetes | 297 (16.5%) | 56 (14.3%) | 6.2 | 56 (15.1%) | 52 (14.0%) | 3.1 |
| Coronary artery disease | 171 (9.5%) | 41 (10.5%) | 3.2 | 41 (11.0%) | 39 (10.5%) | 1.7 |
| Heart failure | 74 (4.1%) | 21 (5.4%) | 5.9 | 15 (4.0%) | 19 (5.1%) | 5.2 |
| Stroke | 60 (3.3%) | 18 (4.6%) | 6.4 | 25 (6.7%) | 17 (4.6%) | 9.3 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 141 (7.8%) | 35 (8.9%) | 3.9 | 25 (6.7%) | 31 (8.3%) | 6.1 |
| Pulmonary function test | ||||||
| FVC (L) | 2.88±0.76 | 2.81±0.73 | 9.5 | 2.83±0.76 | 2.82±0.73 | 1.9 |
| % Predicted | 87.6±15.7 | 85.9±15.6 | 10.8 | 87.1±16.3 | 86.1±15.6 | 6.4 |
| FEV1 (L) | 2.22±0.62 | 2.15±0.60 | 12.3 | 2.17±0.62 | 2.16±0.59 | 2.8 |
| % Predicted | 86.3±16.4 | 83.8±16.6 | 15.5 | 85.4±16.3 | 84.1±16.4 | 7.8 |
| Pretreatment CEA (μg/L) | 2.4 (1.8–3.7) | 2.6 (1.7–4.2) | 8.5 | 2.5 (1.7–4.0) | 2.6 (1.7–4.2) | 2.0 |
| Surgeon experience | 1.2 | 0.6 | ||||
| Specialist<20 years | 701 (39.0%) | 155 (39.5%) | 141 (37.9%) | 142 (38.2%) | ||
| Specialist≥20 years | 1098 (61.0%) | 237 (60.5%) | 231 (62.1%) | 230 (61.8%) | ||
| Thoracoscopic surgery | 1199 (66.6%) | 322 (82.1%) | 36.1 | 292 (78.5%) | 305 (82.0%) | 8.8 |
| Anaesthesiologist experience | 3.9 | 10.8 | ||||
| Specialist<15 years | 810 (45.0%) | 169 (43.1%) | 183 (49.2%) | 163 (43.8%) | ||
| Specialist≥15 years | 989 (55.0%) | 223 (56.9%) | 189 (50.8%) | 209 (56.2%) | ||
| Anaesthesia time (min) | 315 (265–360) | 300 (240–368) | 8.4 | 300 (240–360) | 300 (240–360) | 1.4 |
| pRBC transfusion | 203 (11.3%) | 52 (13.3%) | 6.0 | 51 (13.7%) | 49 (13.2%) | 1.6 |
| Year of procedure | 25.7 | 5.7 | ||||
| 2005–2009 | 627 (34.9%) | 69 (17.6%) | 74 (19.9%) | 67 (18.0%) | ||
| 2010–2012 | 517 (28.7%) | 157 (40.1%) | 148 (39.8%) | 145 (39.0%) | ||
| 2013–2015 | 655 (36.4%) | 166 (42.3%) | 150 (40.3%) | 160 (43.0%) | ||
| Preoperative C/T±R/T | 77 (4.3%) | 21 (5.4%) | 5.0 | 17 (4.6%) | 20 (5.4%) | 3.7 |
| Postoperative C/T | 834 (46.4%) | 163 (41.6%) | 9.6 | 151 (40.6%) | 158 (42.5%) | 3.8 |
| Postoperative R/T | 98 (5.4%) | 22 (5.6%) | 0.7 | 26 (7.0%) | 21 (5.6%) | 5.5 |
| Follow-up time, month | 43.5 (25.3–72.4) | 39.4 (21.9–59.9) | 20.4 | 40.3 (24.4–62.2) | 39.6 (21.9–59.8) | 8.8 |
Values were mean ±SD, counts (%) or median (IQR). Continuous variables are analysed with Wilcoxon rank-sum tests; categorical variables are analysed with Pearson Χ2 tests. Standardised difference is the difference in mean, proportion or rank divided by the pooled SE, expressed as percentage; imbalance is defined as absolute value greater than 20 (small effect size).
ASA, American Society of Anesthesiologists; C/T, chemotherapy; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in one second; FVC, forced vital capacity; pRBC, packed red blood cell; R/T, radiotherapy.
Table 2.
Cancer stages and pathological features
| Before matching | After matching | |||||
| EA (n=1799) | Non-EA (n=392) | Standardised difference | EA (n=372) | Non-EA (n=372) | Standardised difference | |
| AJCC stage | 2.0 | 1.8 | ||||
| Stage I | 1316 (73.2%) | 289 (73.7%) | 271 (72.8%) | 276 (74.2%) | ||
| IA | 546 (30.4%) | 116 (29.6%) | 114 (30.7%) | 110 (29.6%) | ||
| IB | 770 (42.8%) | 173 (44.1%) | 157 (42.2%) | 166 (44.6%) | ||
| Stage II | 205 (11.4%) | 52 (13.3%) | 55 (14.8%) | 48 (12.9%) | ||
| IIA | 106 (5.9%) | 26 (6.6%) | 32 (8.6%) | 24 (6.5%) | ||
| IIB | 99 (5.5%) | 26 (6.6%) | 23 (6.2%) | 24 (6.5%) | ||
| Stage III | 278 (15.5%) | 51 (13.0%) | 46 (12.4%) | 48 (12.9%) | ||
| IIIA | 253 (14.1%) | 46 (11.7%) | 42 (11.3%) | 44 (11.8%) | ||
| IIIB | 25 (1.4%) | 5 (1.3%) | 4 (1.1%) | 4 (1.1%) | ||
| Pathologic features | ||||||
| Subtype | 6.8 | 5.1 | ||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 1511 (84.0%) | 314 (80.1%) | 292 (78.5%) | 303 (81.5%) | ||
| SCC | 200 (11.1%) | 54 (13.8%) | 54 (14.5%) | 46 (12.4%) | ||
| Other | 88 (4.9%) | 24 (6.1%) | 26 (7.0%) | 23 (6.2%) | ||
| Tumour differentiation | 5.3 | 1.8 | ||||
| Good | 181 (10.1%) | 46 (11.7%) | 39 (10.5%) | 46 (12.4%) | ||
| Moderate | 1100 (61.2%) | 215 (54.8%) | 209 (56.2%) | 201 (54.0%) | ||
| Poor | 516 (28.7%) | 131 (33.4%) | 124 (33.3%) | 125 (33.6%) | ||
| Microscopic necrosis | 388 (21.6%) | 77 (19.6%) | 4.8 | 77 (20.7%) | 71 (19.1%) | 4.0 |
| Lymphocytic infiltration | 189 (10.5%) | 27 (6.9%) | 12.9 | 34 (9.1%) | 27 (7.3%) | 6.9 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | 497 (27.6%) | 127 (32.4%) | 10.4 | 115 (30.9%) | 118 (31.7%) | 1.7 |
| Perineural infiltration | 58 (3.2%) | 12 (3.1%) | 0.9 | 10 (2.7%) | 11 (3.0%) | 1.6 |
Values were counts (%). Categorical variables are analysed with Pearson Χ2 tests or Mann-Whitney U tests, as appropriate. Standardised difference is the difference in mean, proportion or rank divided by the pooled SE, expressed as percentage; imbalance is defined as absolute value greater than 20 (small effect size).
AJCC, American Joint Committee on Cancer; SCC, squamous cell carcinoma.
Association between thoracic epidural analgesia and recurrence-free survival
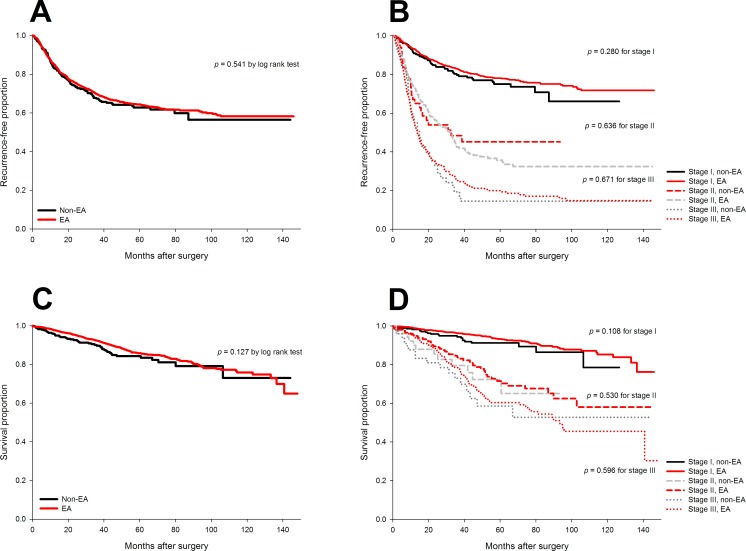
The 3-year and 5-year recurrence-free survival were 69.8% (95% CI 67.4% to 72.2%) and 64.4% (95% CI 61.9% to 66.9%) in the epidural group and 67.4% (95% CI 62.3% to 72.5%) and 62.8% (95% CI 57.1% to 68.5%) in the non-epidural group, respectively. No significant difference in the distribution of recurrence-free survival after lung cancer surgery was noted when comparing epidural with non-epidural group (p=0.54 by log rank test, figure 2A). Moreover, epidural analgesia was not associated with better recurrence-free survival in patients stratified by cancer stages (figure 2B).
Figure 2.
Unadjusted Kaplan-Meier curves for recurrence-free and overall survival of epidural and non-epidural groups. No significant difference in recurrence-free survival (A and B) or overall survival (C and D) after surgery for non-small-cell lung cancer was noted when comparing epidural with non-epidural group as a whole or stratified by cancer stage.
The multivariable regression model indicated eight independent prognostic factors, including male (HR: 1.30), pretreatment CEA level (HR: 1.26, on base-10 logarithmic scale), cancer stage (II vs I, HR: 1.93; III vs I, HR: 2.85), tumour differentiation (moderate vs good, HR: 3.75; poor vs good, HR: 5.20), microscopic tumour necrosis (HR: 1.44), pathological lymphovascular invasion (HR: 2.05), and postoperative chemotherapy (HR: 1.46) and radiotherapy (HR: 1.44) (table 3). Adjusting for other covariates, the effect of epidurals on recurrence-free survival after lung cancer surgery was non-significant (HR: 0.93, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.14, p=0.47) in the multivariable analysis, similar to the results after propensity-score matching (HR: 0.97, 95% CI 0.71 to 1.3, p=0.82) and the quintile-stratified analysis (pooled HR: 0.94, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.15, p=0.53).
Table 3.
Multivariable analysis for cancer recurrence and all-cause mortality after model selection
| Cancer recurrence | All-cause mortality | ||||||
| HR | 95% CI | P value | HR | 95% CI | P value | ||
| EA vs non-EA | 0.927 | 0.755 to 1.139 | 0.473 | EA vs non-EA | 0.811 | 0.582 to 1.129 | 0.214 |
| Sex (M vs F) | 1.297 | 1.026 to 1.642 | 0.030 | Sex (M vs F) | 1.969 | 1.344 to 2.882 | 0.001 |
| Pretreatment CEA* | 1.263 | 1.046 to 1.524 | 0.015 | ECOG PS≥1 | 1.494 | 1.105 to 2.019 | 0.009 |
| Postoperative C/T | 1.456 | 1.187 to 1.786 | <0.001 | Pretreatment CEA* | 1.672 | 1.221 to 2.290 | 0.001 |
| Postoperative R/T | 1.443 | 1.126 to 1.849 | 0.004 | pRBC transfusion | 1.402 | 1.008 to 1.948 | 0.045 |
| Stage | <0.001 | Postoperative R/T | 1.810 | 1.271 to 2.578 | 0.001 | ||
| II vs I | 1.927 | 1.521 to 2.440 | <0.001 | Stage | <0.001 | ||
| III vs I | 2.848 | 2.265 to 3.581 | <0.001 | II vs I | 2.059 | 1.388 to 3.054 | <0.001 |
| Tumour differentiation | <0.001 | III vs I | 2.964 | 2.032 to 4.323 | <0.001 | ||
| Moderate vs good | 3.752 | 1.919 to 7.338 | <0.001 | Tumour differentiation | 0.014 | ||
| Poor vs good | 5.198 | 2.632 to 10.265 | <0.001 | Moderate vs good | 4.718 | 1.153 to 19.310 | 0.031 |
| Microscopic necrosis | 1.444 | 1.203 to 1.733 | <0.001 | Poor vs good | 6.169 | 1.487 to 25.587 | 0.012 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | 2.053 | 1.717 to 2.456 | <0.001 | Microscopic necrosis | 1.378 | 1.037 to 1.831 | 0.027 |
*On base-10 logarithmic scale.
C/T, chemotherapy; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; EA, epidural analgesia; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score; M, male; F, female; pRBC, packed red blood cell; R/T, radiotherapy.
Association between thoracic epidural analgesia and overall survival
The 3-year and 5-year overall survival were 92.4% (95% CI 91% to 93.8%) and 85.8% (95% CI 83.8% to 87.8%) in the epidural group and 89.6% (95% CI 86.3% to 92.9%) and 84.3% (95% CI 80% to 88.6%) in the non-epidural group.
No significant difference in the distribution of long-term mortality after lung cancer surgery was found between the epidural and non-epidural groups (figure 2C, p=0.13 by log rank test). In addition, no significant difference in overall survival was noted between the two groups in the subgroup analysis for distinct cancer stages (figure 2D).
Nine independent prognostic factors were identified after the multivariable analysis (table 3), including male (HR: 1.97), ECOG performance score ≥1 (HR: 1.49), pretreatment CEA level (HR: 1.67), cancer stage (II vs I HR: 2.06; III vs I, HR: 2.96), perioperative pRBC transfusion (HR: 1.40), tumour differentiation (moderate vs good, HR: 4.72; poor vs good, HR: 6.17), microscopic necrosis (HR: 1.38), pathological lymphovascular invasion (HR: 2.13) and postoperative radiotherapy (HR: 1.81). Multivariable analysis indicated no association between epidural analgesia and mortality in non-small-cell lung cancer after surgery (HR: 0.81, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.13, p=0.21). Propensity score matching generated similar results to the multivariable regression analysis (HR: 0.94, 95% CI 0.57 to 1.54, p=0.8) as well as the quintile-stratified (HR: 0.8, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.1, p=0.17) propensity score analyses.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the largest retrospective study applying propensity scoring methods to evaluate the impacts of epidural analgesia on oncological outcomes after lung cancer surgery. We found no evidence that epidural analgesia was associated with improved recurrence-free survival or overall survival in patients following surgical resection of non-small-cell lung cancer. Major clinicopathological prognostic factors were also taken into account in this study to estimate the adjusted effects of epidurals and avoid potential confounding effects from unbalanced distributions of important risk factors between the epidural group and its counterpart. From the perspective of methodology, we used propensity score matching to cancel out the potential imbalances in baseline characteristics and obtained similar results with those from traditional multivariable model. The combination of both analytical methods provided more persuasive proof than either of them did. Our study provided valuable information to reject the hypothesis of beneficial effect of epidurals on cancer recurrence or long-term survival after surgical resection of non-small-cell lung cancer with large sample size and considerable prognostic factors which were lacked in the previous survey.16
Perioperative immune function is an important determinant for metastases after cancer resection surgery. Anaesthetic management of cancer patients could impact long-term outcome, and potentially beneficial interventions include minimising the use of volatile anaesthetics and blood transfusion, administration of cyclooxygenase antagonists and statin, and hypothermia therapy.27 However, whether regional analgesia reduces cancer recurrence after resection surgery remains inconclusive. The Cochrane review included four post-hoc analyses of previous controlled trials and indicated that current evidence for the benefit of regional anaesthesia on cancer outcome is inadequate due to limitations of study design and incomplete consideration of confounders.28
Although Cata and colleagues reported null results of epidural analgesia on recurrence-free and overall survival after lung cancer surgery,16 they found an association between the intraoperative opioid consumption and recurrence-free survival or overall survival later only for stage I disease.11 Our results did not support beneficial effects of epidural analgesia on oncological outcomes in patients stratified by cancer stages. This may be attributed to the difference in distributions of patient attributes or treatment modality. Maher and co-workers reported an association between increased opioid doses during initial 96 hours postoperative period and higher recurrence rate of non-small-cell lung cancer within 5 years.12 However, they found no difference in intraoperative opioid administration among those with or without recurrence of lung cancer at the 5-year follow-up. The effects of regional block and opioid doses on long-term cancer outcomes in early-stage lung cancer await further investigation.
Our results showed perioperative blood transfusion is a risk factor for all-cause mortality, in line with previous literature.19 In addition to mortality, allogenic blood transfusion may be associated with increased risk of cancer recurrence.29 Transfused leucocytes can lead to immunomodulation, including changes in circulating lymphocytes, helper T-cell, suppressor T-cell ratios and B-cell function.29 The meta-analysis by Churchhouse and colleagues examined the effect of blood transfusion on cancer recurrence and overall survival in patients undergoing surgical resection of lung cancer in 5378 patients. Though no definitive conclusions could be drawn, there appeared to be a relationship between transfusion and reduction of disease-free survival.30 In our analysis, the association between blood transfusion and recurrence was non-significant after adjustment for covariates. This finding may imply that the potential impacts of other important confounders (eg, disease severity, presence of postoperative complications) may have a greater bearing on prognosis than the reception of blood itself.
As a sided observation, in the study period, the use of epidurals gradually decreased with concomitant increasing uses of thoracoscopic surgery. Thoracoscopic pulmonary resection for primary lung cancer has been demonstrated to achieve less postoperative pain, faster recovery, shorter hospitalisationand long-term survival comparable to that of open thoracotomy.31 32 In our analysis, the distributions of thoracoscopic surgery and year of surgery between groups have been balanced after propensity score matching and are therefore unlikely to affect the results.
Several limitations are inherent in this retrospective observational study. First, patients were not randomised and clinical care was not standardised, so that potential selection bias and effects from unmeasured confounders cannot be excluded. Second, relatively small percentage (17.9%) of the patients was cared for without epidural analgesia. Third, the rate of epidural placement was lower in the latter years and this may result in longer follow-up period of epidural group. However, these imbalances have been cancelled out after propensity score matching. Fourth, it is difficult to determine the total narcotic consumptions for each patient due to the incompleteness of our electronic medical records.
In conclusion, our study rejected the association between epidural analgesia and cancer recurrence or long-term mortality in patients after surgery for stage I through III non-small-cell lung cancer. Prospective randomised trials are warranted to confirm or refute causal relationships between epidural analgesia and the long-term outcomes after lung cancer surgery.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Contributors: The author contributions were as follows: H.L.W. and Y.H.T. contributed to data acquisition and manuscript drafting. M.Y.C. helped in data verification. M.Y.T. helped revise the manuscript. H.H.C. contributed to study design and statistical analysis. K.Y.C. contributed to statistical review, manuscript revision and final approval of the version to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding: This work was supported by the grants from Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan (V105C-050) and Ministry of Science and Technology, Taipei, Taiwan (MOST 104-2314-B-075-015).
Competing interests: None declared.
Ethics approval: The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan (IRB-TPEVGH No. 2015-11-010CC).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: No additional data are available.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
References
- 1. World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer. GLOBOCAN: Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide in 2018. http://gco.iarc.fr/today/fact-sheets-cancers (accessed 15 Mar 2019).
- 2. Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, et al. . Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc 2008;83:584–94. 10.1016/S0025-6196(11)60735-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Lloyd JM, McIver CM, Stephenson SA, et al. . Identification of early-stage colorectal cancer patients at risk of relapse post-resection by immunobead reverse transcription-PCR analysis of peritoneal lavage fluid for malignant cells. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:417–23. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1473 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Gupta K, Kshirsagar S, Chang L, et al. . Morphine stimulates angiogenesis by activating proangiogenic and survival-promoting signaling and promotes breast tumor growth. Cancer Res 2002;62:4491–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Boland JW, Pockley AG. Influence of opioids on immune function in patients with cancer pain: from bench to bedside. Br J Pharmacol 2018;175:2726–36. 10.1111/bph.13903 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Colvin LA, Fallon MT, Buggy DJ. Cancer biology, analgesics, and anaesthetics: is there a link? Br J Anaesth 2012;109:140–3. 10.1093/bja/aes255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Yeager MP, Colacchio TA, Yu CT, et al. . Morphine inhibits spontaneous and cytokine-enhanced natural killer cell cytotoxicity in volunteers. Anesthesiology 1995;83:500–8. 10.1097/00000542-199509000-00008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lennon FE, Mirzapoiazova T, Mambetsariev B, et al. . The Mu opioid receptor promotes opioid and growth factor-induced proliferation, migration and Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in human lung cancer. PLoS One 2014;9:e91577 10.1371/journal.pone.0091577 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Mathew B, Lennon FE, Siegler J, et al. . The novel role of the mu opioid receptor in lung cancer progression: a laboratory investigation. Anesth Analg 2011;112:558–67. 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31820568af [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Wu HL, Tai YH, Lin SP, et al. . The Impact of Blood Transfusion on Recurrence and Mortality Following Colorectal Cancer Resection: A Propensity Score Analysis of 4,030 Patients. Sci Rep 2018;8:13345 10.1038/s41598-018-31662-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Cata JP, Keerty V, Keerty D, et al. . A retrospective analysis of the effect of intraoperative opioid dose on cancer recurrence after non-small cell lung cancer resection. Cancer Med 2014;3:900–8. 10.1002/cam4.236 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Maher DP, Wong W, White PF, et al. . Association of increased postoperative opioid administration with non-small-cell lung cancer recurrence: a retrospective analysis. Br J Anaesth 2014;113(Suppl 1):i88–i94. 10.1093/bja/aeu192 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Tai YH, Wu HL, Chang WK, et al. . Intraoperative Fentanyl Consumption Does Not Impact Cancer Recurrence or Overall Survival after Curative Colorectal Cancer Resection. Sci Rep 2017;7:10816 10.1038/s41598-017-11460-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Tai YH, Chang WK, Wu HL, et al. . The effect of epidural analgesia on cancer progression in patients with stage IV colorectal cancer after primary tumor resection: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS One 2018;13:e0200893 10.1371/journal.pone.0200893 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Pöpping DM, Elia N, Marret E, et al. . Protective effects of epidural analgesia on pulmonary complications after abdominal and thoracic surgery: a meta-analysis. Arch Surg 2008;143:990–9. 10.1001/archsurg.143.10.990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Cata JP, Gottumukkala V, Thakar D, et al. . Effects of postoperative epidural analgesia on recurrence-free and overall survival in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer. J Clin Anesth 2014;26:3–17. 10.1016/j.jclinane.2013.06.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Hoang T, Xu R, Schiller JH, et al. . Clinical model to predict survival in chemonaive patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with third-generation chemotherapy regimens based on eastern cooperative oncology group data. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:175–83. 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Grunnet M, Sorensen JB. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as tumor marker in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2012;76:138–43. 10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.11.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Glance LG, Dick AW, Mukamel DB, et al. . Association between intraoperative blood transfusion and mortality and morbidity in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 2011;114:283–92. 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182054d06 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Park SY, Lee HS, Jang HJ, et al. . Tumor necrosis as a prognostic factor for stage IA non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;91:1668–73. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2010.12.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Higgins KA, Chino JP, Ready N, et al. . Lymphovascular invasion in non-small-cell lung cancer: implications for staging and adjuvant therapy. J Thorac Oncol 2012;7:1141–7. 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182519a42 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Yilmaz A, Duyar SS, Cakir E, et al. . Clinical impact of visceral pleural, lymphovascular and perineural invasion in completely resected non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2011;40:664–70. 10.1016/j.ejcts.2010.12.059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Edge SB, Byrd SR, Compton CC, et al. ; AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed New York, NY: Springer-Verlag,, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 24. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. . New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 2009;45:228–47. 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Austin PC. An Introduction to Propensity Score Methods for Reducing the Effects of Confounding in Observational Studies. Multivariate Behav Res 2011;46:399–424. 10.1080/00273171.2011.568786 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Austin PC. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat Med 2009;28:3083–107. 10.1002/sim.3697 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Heaney A, Buggy DJ. Can anaesthetic and analgesic techniques affect cancer recurrence or metastasis? Br J Anaesth 2012;109(Suppl 1):i17–i28. 10.1093/bja/aes421 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Cakmakkaya OS, Kolodzie K, Apfel CC, et al. . Anaesthetic techniques for risk of malignant tumour recurrence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014:CD008877 10.1002/14651858.CD008877.pub2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Weber RS, Jabbour N, Martin RC. Anemia and transfusions in patients undergoing surgery for cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2008;15:34–45. 10.1245/s10434-007-9502-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Churchhouse AM, Mathews TJ, McBride OM, et al. . Does blood transfusion increase the chance of recurrence in patients undergoing surgery for lung cancer? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2012;14:85–90. 10.1093/icvts/ivr025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Bendixen M, Jørgensen OD, Kronborg C, et al. . Postoperative pain and quality of life after lobectomy via video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery or anterolateral thoracotomy for early stage lung cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:836–44. 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)00173-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Yamamoto K, Ohsumi A, Kojima F, et al. . Long-term survival after video-assisted thoracic surgery lobectomy for primary lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 2010;89:353–9. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.10.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2018-027618supp001.pdf (286.7KB, pdf)