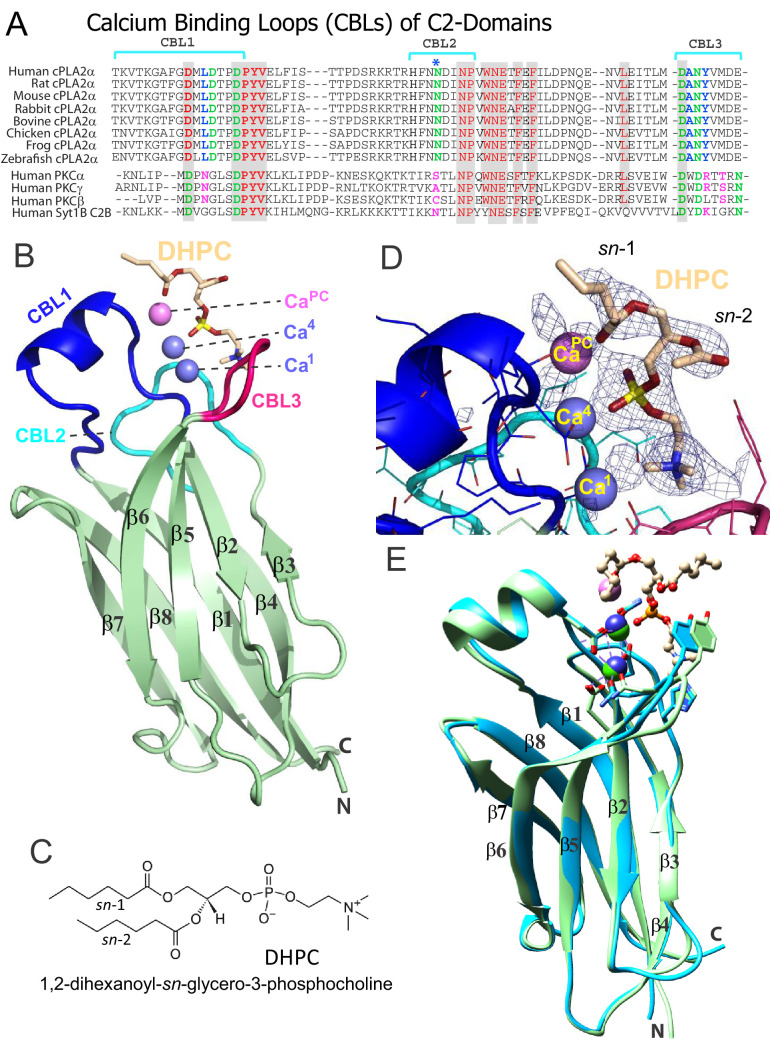
Figure 1. Structure of cPLA2α C2‒domain containing bound DHPC and calcium.
(A) Sequence alignment of C2-domain calcium-binding loop (CBL) regions in cPLA2α from different eukaryotes compared to human PKCs and Syt1. Residues that bind Ca2+ are green. Residues interacting directly with PC in our structural complex (blue or blue asterisk) are absolutely conserved among eukaryotic cPLA2α proteins but not in PKCs and Syt1. Conversely, residues that interact with PS in the PKCα-PS structure (magenta) are highly conserved in PKCs and Syt1, but not in cPLA2α. Shaded residues are identical. The human and chicken cPLA2α CBL sequences are 92% identical and 94.5% highly conserved (see Figure 1—figure supplement 1 for full-length sequence alignment). (B) Ribbon structure representation of the cPLA2α C2-domain bound to 1,2-dihexanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DHPC). The DHPC molecule (beige stick) straddles the β1–β2 loop (CBL1, blue), β3–β4 loop (CBL2, cyan) and β5–β6 loop (CBL3, red). Ca1 and Ca4 (blue spheres) are in a similar position in the apo-form structure; whereas CaPC (magenta sphere) is unique to the DHPC-bound form. (C) DHPC structural formula. (D) Fo-Fc omit electron density map for the bound DHPC molecule at the 2.5σ contour level. (E) Superimposition of the chicken cPLA2α C2-domain with bound DHPC (colored as in Figure 1B) on the human lipid-free structure (PDB: 1RLW, cyan). Root mean square deviation = 0.7 Å after superimposition of Cα atoms.