Figure 1.
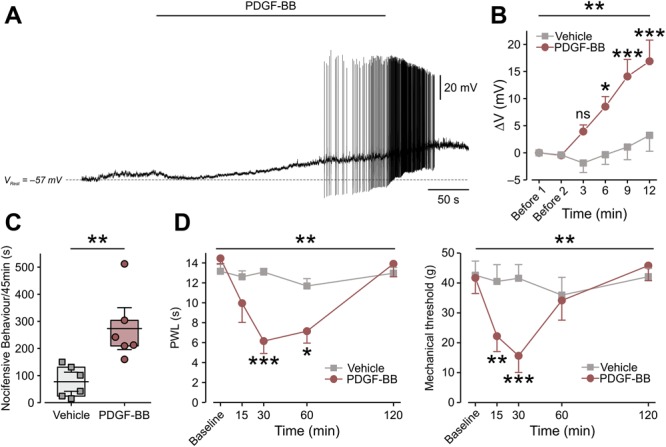
Platelet-derived growth factor-BB activates nociceptor-like cultured DRG neurons and induces nocifensive behavior and pain hypersensitivity. (A) Representative trace (12 of 18 neurons) of current-clamp perforated patch recordings from nociceptor-like cultured DRG neurons showing membrane voltage response to continuous focal application (marked by horizontal bar) of 125 ng/mL of PDGF-BB. Dashed lines indicate resting potentials before drug application (−57 mV). (B) Mean ± SEM of changes in resting membrane potential ΔV (Vt − V0) after focal application of PDGF-BB alone (red) or vehicle (5 μM HCl, light gray). Time point “Before 1” indicates the time where V0 values were measured (3 minutes before application of either PDGF-BB or vehicle). Time point “Before 2” indicates the time just before application of either PDGF-BB or vehicle. ns, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; Repeated-measures (RM) 2-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni. In the “PDGF-BB,” only neurons that showed depolarization without firing (n = 6 neurons) were used for the analysis; n = 5 cells for the “Vehicle” group. (C) Graph comparing box plots and individual values of the total time (in seconds) spent by rats licking, biting, flinching, and guarding the hind paw (nocifensive behavior) during 45 minutes after intraplantar injection of 50 μg/mL of PDGF-BB or its vehicle (2 mM of HCl). **P < 0.01; Student t-test; n = 6 rats per group. Box plots depict mean, 25th, 75th percentile, and SD. (D) The decrease in thermal (radiant heat) paw withdrawal latency (PWL, left) and mechanical threshold (electronic von Frey, right) after intraplantar injection of 12 μg/mL of PDGF-BB as compared to injection of vehicle (500 μM HCl, n = 6 rats per group, ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; RM 2-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni). ANOVA, analysis of variance; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor.
