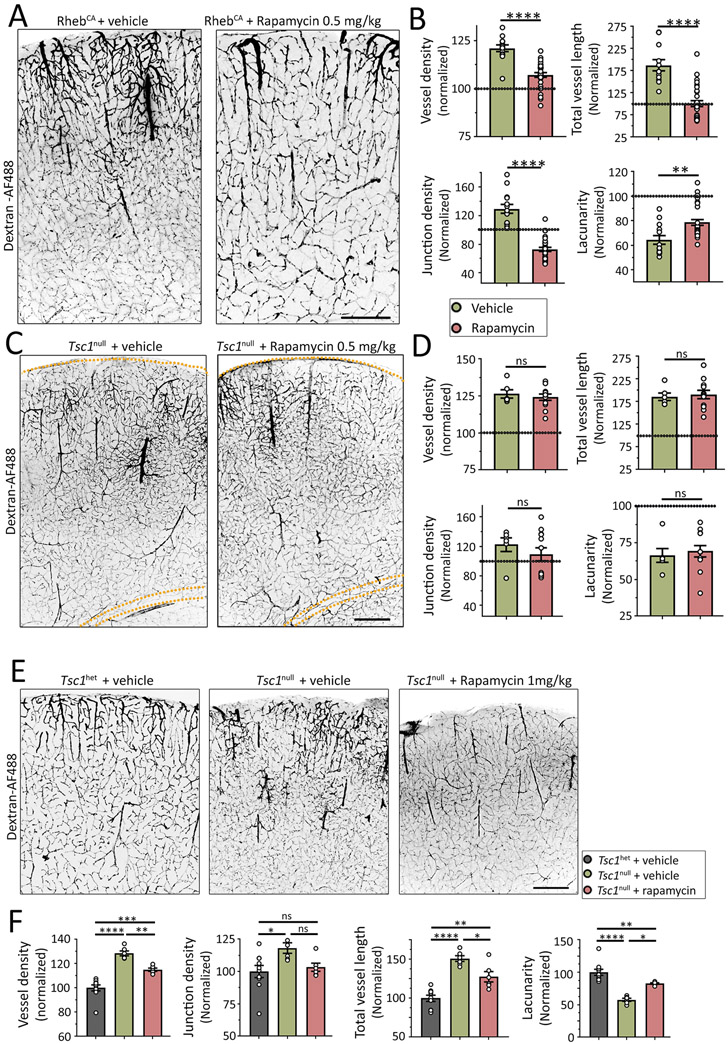
Figure 5: Rapamycin differentially reduces hypervascularization in focal and global MCDs.
(A and C) Images of Dextran-AF488-filled blood vessels in coronal sections containing RhebCA neurons (A) or Tsc1null cells (C) in the somatosensory cortex of mice treated with vehicle (left) or 0.5 mg/kg rapamycin (right). Mice with RhebCA neurons had a focal MCD and transgenic mice with Tsc1null cells had a global MCD. Scale bars: 300 μm (A) and 500 μm (C). (B and D) Bar graphs of the different vessel parameters in both sets of mice with focal (B) or global MCD (D). Values were normalized to their respective control shown in Figure 1 and 2. (E) Images of Dextran-AF488-filled blood vessels in coronal sections containing Tsc1het or Tsc1null cells in the somatosensory cortex of mice treated with vehicle (left) or 1 mg/kg rapamycin. Scale bar: 200 μm. (F) Bar graphs of the different vessel parameters in mice with global MCD. N≥2 sections from 3-5 mice. Student’s t-test in B and D or one-way ANOVA in F, ****: p<0.0001, **:P<0.01, *:P<0.05, and ns: not significant.