Abstract
Background
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique, which has yielded promising results in treating major depressive disorder. However, its effect on treatment-resistant depression remains to be determined. Meanwhile, as an emerging treatment option, patients’ acceptability of tDCS is worthy of attention.
Methods
This pilot study enrolled 18 patients (women = 13) with treatment-resistant unipolar (n = 13) or bipolar (n = 5) depression. Twelve sessions of tDCS were administered with anode over F3 and cathode over F4. Each session delivered a current of 2 mA for 30 min per ten working days, and at the 4th and 6th week. Severity of depression was determined by Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS); cognitive performance was assessed by a computerized battery.
Results
Scores of MADRS at baseline (29.6, SD = 9.7) decreased significantly to 22.9 (11.7) (p = 0.03) at 6 weeks and 21.5 (10.3) (p = 0.01) at 8 weeks. Six (33.3%) participants were therapeutically responsive to tDCS. MADRS scores of responders were significantly lower than those of non-responders at the 6th and 8th week. Regarding change of cognitive performance, improved accuracy of paired association (p = 0.017) and social cognition (p = 0.047) was observed at the 8th week. Overall, tDCS was perceived as safe and tolerable. For the majority of patients, it is preferred than pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy.
Conclusions
TDCS can be a desirable option for treatment-resistant depression, however, its efficacy may be delayed; identifying predictors of therapeutic response may achieve a more targeted application. Larger controlled studies with optimized montages and sufficient periods of observation are warranted.
Trial registration
This trial has been registered at the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR-INR-16008179).
Keywords: Transcranial direct-current stimulation, Treatment-resistant depression, Cognitive ability
Background
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a highly prevalent mental illness associated with substantial personal impairments and societal costs [1]. Although progress has been made in the pharmacological and psychotherapeutic intervention of MDD, there are still up to 50% of patients with poor response to multiple trials of antidepressants, defined as treatment-resistant depression (TRD) [2–5]. Patients with TRD have lower quality of life. They account for more frequent medical visits and higher health care costs [6].
Empirical pharmacotherapy of TRD includes augmentation with lithium or second generation antipsychotics, often with suboptimal efficacy and poor tolerance [7]. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) remains as an efficient treatment for TRD, however, its application is limited due to risk of anesthesia and cognitive side effects [7–9]. Indeed, current treatment for TRD is still far from satisfactory; there is an urgent need for novel therapeutics. Recently, non-invasive brain stimulation has emerged as a promising candidate. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treating TRD [10]; interests in transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is growing following its demonstrated efficacy on MDD.
TDCS, a non-convulsive brain stimulation technique involves injecting a low-amplitude (generally 1-2 mA), direct electric current flows from the anode to the cathode in cerebral cortex by using two surface scalp electrodes [11, 12], which alters the membrane potentials of neurons and changes the rate of spontaneous depolarization [13–15]. The anode area becomes hypo-polarized and the cathode area becomes hyper-polarized. One well-known hypothesis of depression is hypoactivity in left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) leading to psychomotor retardation and executive dysfunction [16, 17]. Researchers suppose that tDCS anodal stimulation over left DLPFC increases its cortical activity, which would lead to improvement of depression. In recent years, multiple randomized studies have confirmed the antidepressant effect of tDCS among patients with MDD [18–23]. Rigonatti et al. published that tDCS had equal but faster antidepressant effects in comparison with fluoxetine [24]. Brunoni and colleagues demonstrated that effects of tDCS plus antidepressants can be synergistic [25].
Given the encouraging findings of tDCS in MDD, several pilot studies have explored its effect in TRD patients, with mixed results. In a randomized controlled study applying 10 sessions of tDCS, there were no significant differences of depressive symptoms between active and sham groups after 4 weeks [26]. Blumberger and his team extended that a 15-session tDCS was not efficacious in TRD [27]. In another controlled study, tDCS efficacy on psychomotor and neuropsychological functioning in TRD is limited [28]. On the contrary, the promising result from Dell’Osso el al. revealed that tDCS administered twice a day for 5 consecutive days help reduce depressive symptoms, particularly melancholic features [29]. Another encouraging study conducted by Ferrucci applied the identical tDCS protocol among hospitalized patients with severe MDD; improvement was observed on day 5 after ten tDCS sessions and persisted to the end of 5 weeks [30].
It has been observed that the effect of brain stimulation can be delayed [31], with its effect manifesting beyond treatment periods. However, existing research often completed follow-up at the end of treatment. The majority of studies examined the effect of tDCS on depressive symptomatology, few have comprehensively assessed cognitive performance, a crucial determinant of functional recovery. Moreover, as a novel treatment modality, the acceptability of tDCS needs to be further established. Thus, in the present study, we examined, at the 8th week, the antidepressant and cognitive effects of a 6-week tDCS treatment for TRD, identified potential predictors for treatment responsiveness, and elaborated the subjective experiences receiving tDCS.
Methods
Study participants
This pilot study recruited 18 patients (women = 13) meeting Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5 (DSM-5) criteria for unipolar (n = 13) or bipolar (n = 5) depression at Taipei City Psychiatric Center, Taipei City Hospital. In unipolar depression patients, current depressive episode needed to be treatment-resistant, which was defined as failure to respond to 2 adequate trials of pharmacotherapy. The definition of treatment-resistant bipolar depression has not been established yet [32]. We followed Sachs’s definition of treatment-resistant bipolar depression: non-remission despite two adequate trials of standard antidepressant agents, with or without augmentation strategies [33]. Regimen of psychotropic needed to be fixed at least 4 weeks prior to enrollment, and maintain unchanged throughout the study. Participants must score over 20 on the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS). Those with metal implants, intracranial lesions, cerebrovascular or cardiovascular diseases and pregnancy were excluded. Additionally, participants receiving DSM-5 diagnosis of schizophrenia and substance use disorder were excluded, as well as those failing to respond to previous ECT. This study conformed with the Declaration of Helsinki and received proper Institutional Review Board approval (TCHIRB-10409114). Written informed consent was obtained from each participant prior to study initiation. This trial has been registered at the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR-INR-16008179).
Transcranial direct-current stimulation
Direct current was generated by a constant-current stimulator (Starstim tCS, manufactured by Neuroelectrics, Barcelona). tDCS were administered with anode over F3 (International 10/20 System for EEG Electrodes) and cathode over F4. The size of conductive electrodes was about 35cm2. Each session delivered a direct current of 2 mA for 30 min. A total of 12 sessions were administrated, patients received daily tDCS administration for 10 days of the first 2 weeks and followed by a single tDCS administration on the 4th and 6th week [25]. The single booster stimulation on the 4th and 6th week was implemented due to our previous experiences that effects of tDCS may diminish after a 2-week stimulation protocol. After 12 sessions of tDCS administration, the patients received an intervention-free follow-up observation at the 8th week.
Psychiatric assessment
Severity of depression was measured by the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), a 10-item instrument tapping into the symptomatology of depression. MADRS was measured at baseline, the 2nd, 4th, 6th, and 8th week. To ensure the reliability, all the assessments were carried out by one senior psychiatrist (G.C.H). Response to tDCS was defined by a > 50% decrease of MADRS scores. For each assessment, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) was self-administered as a complimentary outcome.
Cognitive assessment
Cognitive performance was assessed by a computerized battery, COGSTATE, which included 11 tasks examining domains of attention, working memory, verbal and visual memory, social cognition and executive function. Performance was evaluated either by accuracy rate, number of errors or reaction time.
Subjective experiences of tDCS
Structured interview was conducted to elicit: 1) participants’ understanding of tDCS; 2) adverse effects of tDCS; 3) perceived benefits of tDCS on mood and cognition, and 4) preference of tDCS in comparison with pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy. A research assistant (L.Y.Y.) uninvolved in the study procedure conducted the interview independently.
Statistical analysis
Paired t-test was used to examine changes of MADRS and BDI over 8 weeks, as compared to scores at baseline. As for cognitive outcomes, paired t-test was used to compare the reaction time and accuracy of a given task at baseline and at 8 weeks. With an intention to identify predictors for tDCS response, we used Fisher’s exact test (for categorical variables) and unpaired t-test (for continuous variables) to compare the demographic and clinical characteristics of tDCS responders and non-responders. Compared to baseline, differences between responders and non-responders on change of MADRS, BDI and cognitive scores at 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks were examined by paired t-tests. Effect size (Cohen’s d) was then calculated.
Results
Participants
We enrolled 18 patients (women = 13) with treatment-resistant unipolar (n = 13) or bipolar (n = 5) depression. Average age was 44.6 (SD = 14.2) years, with onset of depression at 29.8 (15.6) years. Twelve (66.7%) participants had visited psychiatric ER, and 10 (55.6%) had attempted suicide, indicating a more severe course of depression. Eight (44.4%) participants reported family history of psychiatric disorders. The majority of participants received antidepressants and benzodiazepines. Notably, half of them were prescribed with antipsychotics (Table 1).
Table 1.
Comparison of clinical characteristics and severity of depression in all participants, responders and non-responders
| All participants | Responders N = 6 |
Non-responders N = 12 |
P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 44.6 | 14.2 | 47.7 | 12.5 | 43 | 15.3 | .527 |
| Sex | 1.00 | ||||||
| Male | 5 | 27.8% | 2 | 33.3% | 3 | 25% | |
| Female | 13 | 72.2% | 4 | 66.7% | 9 | 75% | |
| Diagnosis | 1.00 | ||||||
| MDD | 13 | 72% | 4 | 66.7% | 9 | 75% | |
| Bipolar | 5 | 28% | 2 | 33.3% | 3 | 25% | |
| Onset age (years) | 29.8 | 15.6 | 29 | 14.6 | 30.2 | 16.8 | .887 |
| Ever received ECT | 1.00 | ||||||
| No | 16 | 88.9% | 5 | 83.3% | 11 | 91.7% | |
| Yes | 2 | 11.1% | 1 | 16.7% | 1 | 8.3% | |
| Every visited ER for psychiatric emergency | .344 | ||||||
| No | 6 | 33.3% | 3 | 50% | 3 | 33.3% | |
| Yes | 12 | 66.7% | 3 | 50% | 9 | 66.7% | |
| History of suicide attempt | .321 | ||||||
| No | 8 | 44.4% | 4 | 66.7% | 4 | 33.3% | |
| Yes | 10 | 55.6% | 2 | 33.3% | 8 | 66.7% | |
| Family history of psychiatric disorders | .638 | ||||||
| No | 10 | 55.6% | 4 | 66.7% | 6 | 50% | |
| Yes | 8 | 44.4% | 2 | 33.3% | 6 | 50% | |
| With antidepressants | 1.00 | ||||||
| No | 2 | 11.1% | 1 | 16.7% | 1 | 8.3% | |
| Yes | 16 | 88.9% | 5 | 83.3% | 11 | 91.7% | |
| With antipsychotics | 1.00 | ||||||
| No | 9 | 50% | 3 | 50% | 6 | 50% | |
| Yes | 9 | 50% | 3 | 50% | 6 | 50% | |
| With mood stabilizers | 1.00 | ||||||
| No | 14 | 77.8% | 5 | 83.3% | 9 | 75% | |
| Yes | 4 | 22.2% | 1 | 16.7% | 3 | 25% | |
| With benzodiazepines | 1.00 | ||||||
| No | 1 | 5.6% | 0 | 0% | 1 | 83.3% | |
| Yes | 17 | 94.4% | 6 | 100% | 11 | 91.7% | |
| MADRS at baseline | 29.61 | 9.71 | 30.83 | 15.09 | 29 | 6.41 | .718 |
| BDI at baseline | 34.56 | 13.05 | 31.83 | 15.74 | 35.92 | 12.02 | .548 |
MADRS Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, BDI Beck Depression Inventory; numbers in the table are either means with standard deviation or counts with percentage
Depressive symptoms
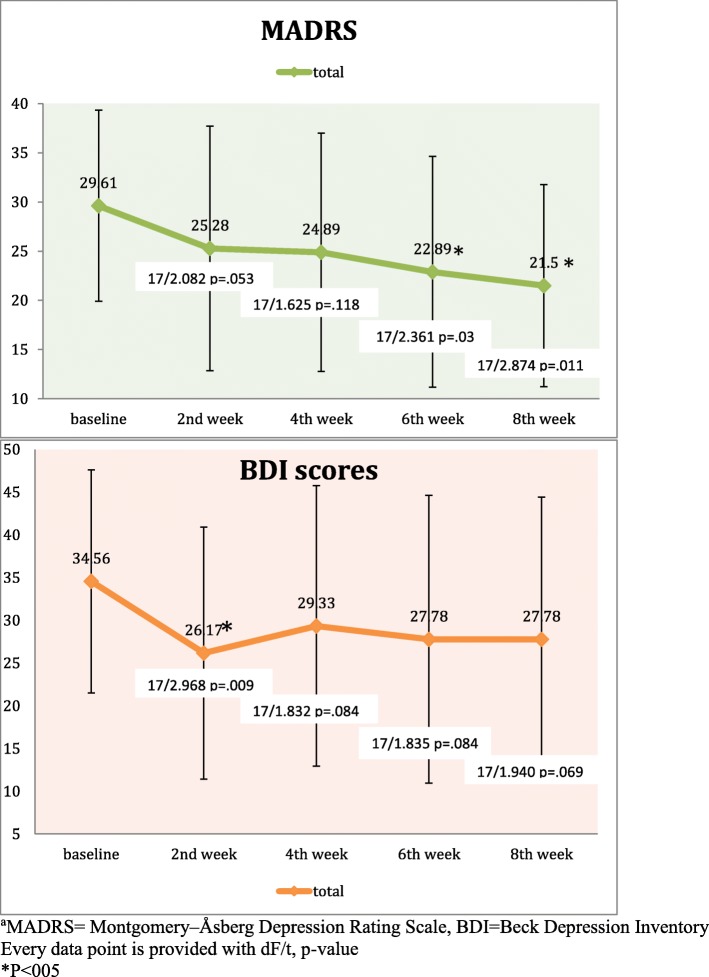
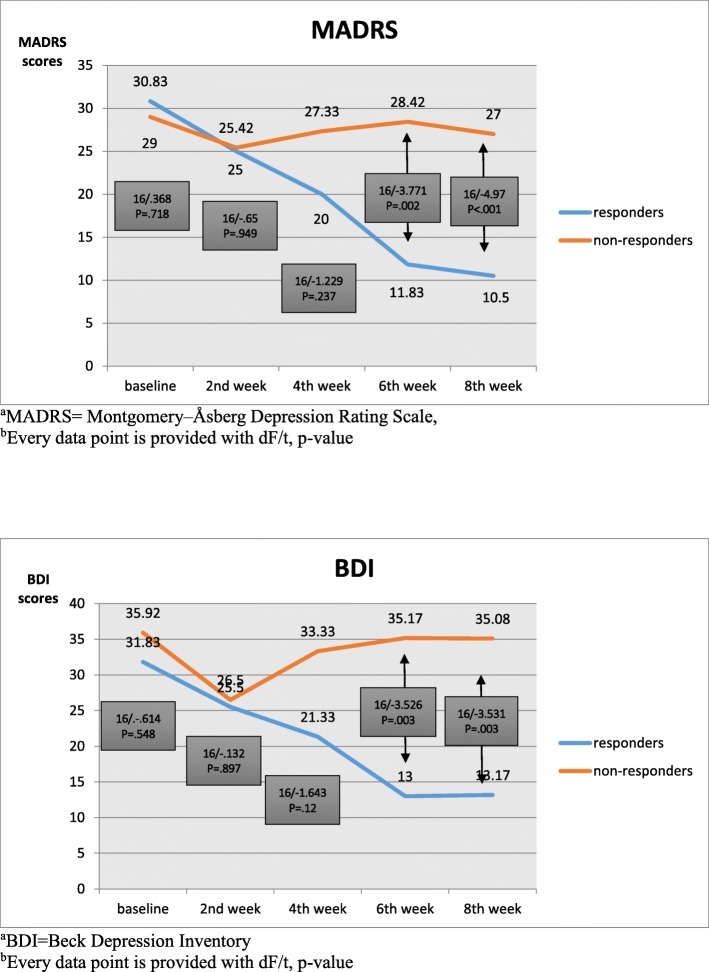
In the current sample, scores of MADRS at baseline (29.6, SD = 9.7) showed a significant decrease at week 6 (t = − 2.361; p = .03) and week 8 (t = 2.874; p = 0.011). As for BDI, a significant change from baseline was observed only at week 2 (t = 2.968; p = .009) (Fig. 1). Six (33.3%) participants were therapeutically responsive to tDCS. Paired t-tests revealed a more pronounced decrease in MADRS scores of responders than non-responders at weeks 6 (t = − 3.771, p = .002, Cohen’s d = 1.71) and 8 (t = − 4.97, p < .001, Cohen’s d = 2.44). Similarly, paired t-tests revealed a more pronounced decrease in BDI scores of responders than non-responders at weeks 6 (t = − 3.526, p = .003, Cohen’s d = 1.92) and 8 (t = − 3.531, p = .003, Cohen’s d = 1.92) (Fig. 2). Treatment responsiveness was not predicted by any demographic or clinical characteristics and cognitive performance at baseline (Table 1).
Fig. 1.
Change of depressive symptoms over 8 weeks
Fig. 2.
Comparison of change of depressive symptoms in responders and non-responders
Cognitive performance
Among 11 cognitive tasks administered, improved accuracy of one task regarding visual learning (p = 0.017) and another regarding social cognition (p = 0.047) was observed at the 8th week (Table 2). Change of cognitive performances was similar in responders and non-responders (data not shown).
Table 2.
Comparison of performances regarding tasks in Cogstate at baseline and at 8 weeks
| Test item | baseline | 8 weeks | t/dF | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shopping list | ||||
| Time Spent (sec) | 216,301 | 227,146.36 | −8.35/13 | .419 |
| Accuracy (sin−1) | .920322 | .884031 | 1.033/13 | .321 |
| Detection Task | ||||
| Reaction Time (log) | 2.664721 | 2.694657 | −1.332/13 | .206 |
| Accuracy (sin−1) | 1.492700 | 1.490980 | .039/13 | .969 |
| Identification Task | ||||
| Reaction Time (log) | 2.784243 | 2.792496 | −.302/13 | .767 |
| Accuracy (sin− 1) | 1.336756 | 1.356455 | −.376/13 | .713 |
| One Card Learning Task | ||||
| Reaction Time (log) | 3.035103 | 3.052699 | −.601/13 | .558 |
| Accuracy (sin−1) | .921514 | .899249 | .937/13 | .366 |
| One Back Working Memory Task | ||||
| Reaction Time (log) | 2.954759 | 2.973666 | −.454/13 | .657 |
| Accuracy (sin−1) | 1.276753 | 1.255471 | .504/13 | .622 |
| Two Back Working Memory Task | ||||
| Reaction Time (log) | 3.079240 | 3.067496 | .408/13 | .690 |
| Accuracy (sin−1) | 1,146,574 | 1.148721 | −.050/13 | .961 |
| Social-Emotional Cognition Task | ||||
| Reaction Time (log) | 3.426776 | 3.526582 | −1.786/13 | .097 |
| Accuracy (sin−1) | .881219 | 1.029940 | −2.196/13 | .047 |
| Continuous Paired Associate Learning Task | ||||
| Time Spent (sec) | 268,342.43 | 245,706.86 | 1.711/13 | .111 |
| Reaction Time (log) | 3.426164 | 3.370106 | 1.784/13 | .098 |
| Accuracy (sin−1) | .747632 | .851417 | −2.749/13 | .017 |
| Shopping List Task-Delayed Recall | ||||
| Time Spent (sec) | 50,757.79 | 58,700.93 | −1.327/13 | .207 |
| Accuracy (sin−1) | .829577 | .866724 | −.509/13 | .619 |
Subjective experiences with tDCS
In general, tDCS was regarded as ‘an electrical treatment to stimulate the brain’, with the purpose to ‘reset your emotion center’ and ‘achieve a balance of the left and right brain’. Regarding adverse effects, participants reported headache (n = 3), fatigue (2), dizziness (2), increased emotional reactivity (2), nausea (1), insomnia (1), and pain over scalp contacting electrodes (1). Most adverse effects were tolerable, with reduced intensity after the first 3 sessions.
For depressive symptoms, tDCS responders described universally that depressed mood was ‘much better’, ‘with reduced duration and intensity’. Positive affect was experienced that participants were ‘feeling relaxed’, and ‘able to smile again’. Their motivation increased, energy restored, and the ability to complete tasks resumed. Interestingly, in non-responders, 6 out of 12 participants still reported some improvement in depressed mood; 2 with less anxiety; 2 with attenuated suicide idea, 2 with restored executive function, and 1 with improved appetite. No participants suffered from a deterioration of depressive symptoms. Moreover, we used YMRS to measure manic symptoms in bipolar patients; none of them exceeded a score of 7.
Regarding perceived cognitive effects, 5 participants had increased attention. Memory improved in 4 patients but worsened in 2. Processing speed improved in 1 but deteriorated in 2. The majority of responses were that domains of cognitive ability were unchanged after tDCS treatment.
As for treatment preference, 11 participants listed tDCS as their first choice, reasoning that ‘effects of tDCS were faster and more natural than drugs, with fewer adverse events’. Two participants identified medications as their first choice because of its convenience and immediate effect. Three participants preferred psychotherapy because it helped ‘develop coping skills’ and ‘deal with underlying causes’. Notably, 5 participants had never received psychotherapy.
Overall, tDCS was perceived as safe and tolerable, with substantial effects on depression and equivocal benefits on cognitive ability. It is preferred than pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy in the majority of patients.
Discussion
The present study demonstrated that tDCS could be advantageous to patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD) in improving depressive symptoms and cognitive performance. Its effect may be delayed, with marked discrepancy between responders and non-responders. TDCS is well accepted and preferred than other treatment modalities.
The findings here need to be interpreted with a number of limitations considered, including a relatively small sample size, an open-label design, lacking of a controlled group, and less stringent definition of TRD. It is likely that response rates may increase in open-label studies due to positive expectations from both un-blinded patients and un-blinded raters. With the multiple tests for cognitive performance, the 2 significant outcomes may be prone to type-I errors. Also, the inclusion of bipolar patients is likely to increase heterogeneity. Prior studies examining the efficacy of tDCS on TRD were universally small (i.e. sample size < 25), yielding conflictual results. Our positive findings are in agreement with those of Dell’Osso et al. and Ferrucci et al., both applying augmented, F3-F4 tDCS with a five-days, twice-daily protocol [29, 30]. In contrast, in three controlled studies, reduction of depressive symptoms was similar in active and sham groups [26–28]. Results from another open-label study also showed no benefit of tDCS in patients with TRD [34]. The montages of tDCS in these negative studies are mostly different from the established F3-F4 positioning, and their period of observation is, at most, 4 weeks. Comparatively, our tDCS application spans for 6 weeks, with the lengthiest follow-up of 8 weeks, which is more likely to capture its full effect.
Due to the differential antidepressant effect of tDCS, it raises the need to investigate predictors of treatment response. It has been shown that pre-treatment verbal fluency predicts the response of tDCS on depression [35]. In a recent report pooled from 3 tDCS trials with 171 depressed patients, pre-treatment cognitive disturbance, retardation, anxiety and somatization played a role in prediction of response to tDCS [36]. Nonetheless, in our study, no demographic, clinical or cognitive characteristics at baseline could predict response to tDCS, potentially owing to limited sample size, higher severity of depression and unmeasured covariates.
We observed an improvement of visual learning and social cognition at the end of 8 weeks. The result is in accordance with a report by Boggio et al., that, in depressed patients, tDCS stimulation of left DLPFC had a significant effect on improving the accuracy of identifying figures with positive emotional content [37]. Wolkenstein et al. [38] and Brunoni et al. [39] reasoned that tDCS may improve cognition via modifying the emotional inhibitory control and negative attentional bias. Effects of tDCS may extent to cortico-subcortical regions, which can modify the cognitive dysfunction and emotion processing. In contrast, several studies found no effect of tDCS on cognition in patients with TRD [26, 28, 30]. One recent systematic review could not conclude the cognitive benefits of tDCS in depressed patients [40]. Future research is needed to clarify the equivocal findings.
We observed a delayed effect of tDCS over depressive symptoms. In an animal study, cathodal stimulation combined with task assignment showed effects 3 weeks later [41]. In another controlled study examining effects of tDCS in MDD, antidepressant effect in the 3-week masked face was only modest, but the number of responders in the following 3-week, open-label phase was much more encouraging [22]. The after-effects of tDCS have been linked to non-synaptic mechanisms involving neurogenesis [42–44]. TDCS may also induce long-term cortical plastic change via metabolic pathways, for example, increasing BDNF release [41, 45, 46].
Conclusions
Given that available treatments of TRD had unsatisfactory efficacy or tolerability [9], the high acceptance, perceived benefits, and preference of tDCS demonstrated here have important clinical implications. TDCS is inexpensive and easily administered, which has a potential to serve as a scalable treatment. Our preliminary findings suggest that tDCS can be a desirable option for TRD, however, its efficacy may be delayed; identifying predictors of therapeutic response may achieve more targeted application. Larger controlled studies with optimized montages and sufficient periods of observation are warranted.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the staffs of ward 7D, Taipei City Hospital, for their assistance in the recruitment and management of study participants. We would also like to express our gratitude for the technical support of Vanguard Trade Co., LTD and Sooma Oy.
Funding
This work was supported by Department of Health, Taipei City Government (10501-62-051), Jiangsu Commission of health-Planned technology projects (H2017069) and Suzhou Key Medical Center for Psychiatric Diseases (Szzx201509). The funding organizations did not participate in the design, implementation, analysis and reporting of this study.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to ethical restrictions and personal data protection, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- BDI
Beck Depression Inventory
- DSM-5
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5
- ECT
Electroconvulsive Therapy
- MADRS
Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale; MDD: Major Depressive Disorder
- RTMS
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
- TDCS
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
- TRD
Treatment-Resistant Depression
Authors’ contributions
MSL drafted the manuscript. XDD and WP provided statisitical consultation. YYL interviewed the patients and managed the study. HCC carried out data analysis. ZL revised the manuscript. GCH assessed the patients, supervised the study and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol and informed consent procedure were approved by the Institutional Review Board of Taipei city hospital (TCHIRB-10409114). The investigation was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant prior to study initiation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Min-Shan Li, Email: minshanli728@gmail.com.
Xiang-Dong Du, Email: minshanli728@gmail.com.
Hsiao-Chi Chu, Email: pennychi118@gmail.com.
Yen-Ying Liao, Email: awonder4ying@gmail.com.
Wen Pan, Email: minshanli728@gmail.com.
Zhe Li, Email: hilizhe@hotmail.com.
Galen Chin-Lun Hung, Phone: +886-2-55963919, Email: galenhung@blossomclinic.org.
References
- 1.Pincus HA, Pettit AR. The societal costs of chronic major depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62(Suppl 6):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sackeim HA. The definition and meaning of treatment-resistant depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62(Suppl 16):10–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fava M. Diagnosis and definition of treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;53:649–659. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(03)00231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Stewart JW, Warden D, Niederehe G, Thase ME, Lavori PW, Lebowitz BD, et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1905–1917. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2006.163.11.1905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Berlim MT, Turecki G. Definition, assessment, and staging of treatment-resistant refractory major depression: a review of current concepts and methods. Can J Psychiatr. 2007;52:46–54. doi: 10.1177/070674370705200108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mrazek DA, Hornberger JC, Altar CA, Degtiar I. A review of the clinical, economic, and societal burden of treatment-resistant depression: 1996-2013. Psychiatric Serv. 2014;65:977–987. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.201300059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.de Sousa RT, Zanetti MV, Brunoni AR, Machado-Vieira R. Challenging treatment-resistant major depressive disorder: a roadmap for improved therapeutics. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015;13:616–635. doi: 10.2174/1570159X13666150630173522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Group UER Efficacy and safety of electroconvulsive therapy in depressive disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2003;361:799–808. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12705-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lucas N, Hubain P, Loas G, Jurysta F. Treatment resistant depression: actuality and perspectives in 2017. Rev Med Brux. 2017;38:16–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff-Class II Special Controls Guidance Document: Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Systems. In.: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2011.
- 11.Fregni F, Pascual-Leone A. Technology insight: noninvasive brain stimulation in neurology-perspectives on the therapeutic potential of rTMS and tDCS. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2007;3:383–393. doi: 10.1038/ncpneuro0530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brunoni AR, Amadera J, Berbel B, Volz MS, Rizzerio BG, Fregni F. A systematic review on reporting and assessment of adverse effects associated with transcranial direct current stimulation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011;14:1133–1145. doi: 10.1017/S1461145710001690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nitsche MA, Paulus W. Sustained excitability elevations induced by transcranial DC motor cortex stimulation in humans. Neurol. 2001;57:1899–1901. doi: 10.1212/WNL.57.10.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brunoni AR, Nitsche MA, Bolognini N, Bikson M, Wagner T, Merabet L, Edwards DJ, Valero-Cabre A, Rotenberg A, Pascual-Leone A, et al. Clinical research with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): challenges and future directions. Brain Stimul. 2012;5:175–195. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2011.03.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Berlim MT, Van den Eynde F, Daskalakis ZJ. Clinical utility of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for treating major depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind and sham-controlled trials. J Psychiatr Res. 2013;47:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.09.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brunoni AR, Teng CT, Correa C, Imamura M, Brasil-Neto JP, Boechat R, Rosa M, Caramelli P, Cohen R, Del Porto JA, et al. Neuromodulation approaches for the treatment of major depression: challenges and recommendations from a working group meeting. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2010;68:433–451. doi: 10.1590/S0004-282X2010000300021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Campbell S, Marriott M, Nahmias C, MacQueen GM. Lower hippocampal volume in patients suffering from depression: a meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161:598–607. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.4.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Boggio PS, Rigonatti SP, Ribeiro RB, Myczkowski ML, Nitsche MA, Pascual-Leone A, Fregni F. A randomized, double-blind clinical trial on the efficacy of cortical direct current stimulation for the treatment of major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:249–254. doi: 10.1017/S1461145707007833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Loo CK, Sachdev P, Martin D, Pigot M, Alonzo A, Malhi GS, Lagopoulos J, Mitchell P. A double-blind, sham-controlled trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13:61–69. doi: 10.1017/S1461145709990411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Brunoni AR, Ferrucci R, Bortolomasi M, Vergari M, Tadini L, Boggio PS, Giacopuzzi M, Barbieri S, Priori A. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in unipolar vs. bipolar depressive disorder. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011;35:96–101. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kalu UG, Sexton CE, Loo CK, Ebmeier KP. Transcranial direct current stimulation in the treatment of major depression: a meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2012;42:1791–1800. doi: 10.1017/S0033291711003059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Loo CK, Alonzo A, Martin D, Mitchell PB, Galvez V, Sachdev P. Transcranial direct current stimulation for depression: 3-week, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Br J Psychiatry. 2012;200:52–59. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.111.097634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shiozawa P, Fregni F, Bensenor IM, Lotufo PA, Berlim MT, Daskalakis JZ, Cordeiro Q, Brunoni AR. Transcranial direct current stimulation for major depression: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014;17:1443–1452. doi: 10.1017/S1461145714000418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rigonatti SP, Boggio PS, Myczkowski ML, Otta E, Fiquer JT, Ribeiro RB, Nitsche MA, Pascual-Leone A, Fregni F. Transcranial direct stimulation and fluoxetine for the treatment of depression. Eur Psychiatry. 2008;23:74–76. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Brunoni AR, Valiengo L, Baccaro A, Zanao TA, de Oliveira JF, Goulart A, Boggio PS, Lotufo PA, Bensenor IM, Fregni F. The sertraline vs. electrical current therapy for treating depression clinical study: results from a factorial, randomized, controlled trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70:383–391. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamapsychiatry.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Palm U, Schiller C, Fintescu Z, Obermeier M, Keeser D, Reisinger E, Pogarell O, Nitsche MA, Moller HJ, Padberg F. Transcranial direct current stimulation in treatment resistant depression: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Brain Stimul. 2012;5:242–251. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2011.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Blumberger DM, Tran LC, Fitzgerald PB, Hoy KE, Daskalakis ZJ. A randomized double-blind sham-controlled study of transcranial direct current stimulation for treatment-resistant major depression. Front Psychiatry. 2012;3:74. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2012.00074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bennabi D, Nicolier M, Monnin J, Tio G, Pazart L, Vandel P, Haffen E. Pilot study of feasibility of the effect of treatment with tDCS in patients suffering from treatment-resistant depression treated with escitalopram. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;126:1185–1189. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.09.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dell'Osso B, Zanoni S, Ferrucci R, Vergari M, Castellano F, D'Urso N, Dobrea C, Benatti B, Arici C, Priori A, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation for the outpatient treatment of poor-responder depressed patients. Eur Psychiatry. 2012;27:513–517. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2011.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ferrucci R, Bortolomasi M, Vergari M, Tadini L, Salvoro B, Giacopuzzi M, Barbieri S, Priori A. Transcranial direct current stimulation in severe, drug-resistant major depression. J Affect Disord. 2009;118:215–219. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2009.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li Z, Yin M, Lyu XL, Zhang LL, Du XD, Hung GC. Delayed effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) on negative symptoms of schizophrenia: findings from a randomized controlled trial. Psychiatry Res. 2016;240:333–335. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.04.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sienaert P, Lambrichts L, Dols A, De Fruyt J. Evidence-based treatment strategies for treatment-resistant bipolar depression: a systematic review. Bipolar Disord. 2013;15:61–69. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sachs GS. Treatment-resistant bipolar depression. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1996;19:215–236. doi: 10.1016/S0193-953X(05)70285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Martin DM, Alonzo A, Mitchell PB, Sachdev P, Galvez V, Loo CK. Fronto-extracephalic transcranial direct current stimulation as a treatment for major depression: an open-label pilot study. J Affect Disord. 2011;134:459–463. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.05.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Martin DM, Yeung K, Loo CK. Pre-treatment letter fluency performance predicts antidepressant response to transcranial direct current stimulation. J Affect Disord. 2016;203:130–135. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.05.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.D'Urso G, Dell’Osso B, Rossi R, Brunoni AR, Bortolomasi M, Ferrucci R, Priori A, de Bartolomeis A, Altamura AC. Clinical predictors of acute response to transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in major depression. J Affect Disord. 2017;219:25–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Boggio PS, Bermpohl F, Vergara AO, Muniz AL, Nahas FH, Leme PB, Rigonatti SP, Fregni F. Go-no-go task performance improvement after anodal transcranial DC stimulation of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in major depression. J Affect Disord. 2007;101:91–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2006.10.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wolkenstein L, Plewnia C. Amelioration of cognitive control in depression by transcranial direct current stimulation. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;73:646–651. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Brunoni AR, Zanao TA, Vanderhasselt MA, Valiengo L, de Oliveira JF, Boggio PS, Lotufo PA, Bensenor IM, Fregni F. Enhancement of affective processing induced by bifrontal transcranial direct current stimulation in patients with major depression. Neuromodulation. 2014;17:138–142. doi: 10.1111/ner.12080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tortella G, Selingardi PM, Moreno ML, Veronezi BP, Brunoni AR. Does non-invasive brain stimulation improve cognition in major depressive disorder? A systematic review. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014;13:1759–1769. doi: 10.2174/1871527313666141130224431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dockery CA, Liebetanz D, Birbaumer N, Malinowska M, Wesierska MJ. Cumulative benefits of frontal transcranial direct current stimulation on visuospatial working memory training and skill learning in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2011;96:452–460. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2011.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ardolino G, Bossi B, Barbieri S, Priori A. Non-synaptic mechanisms underlie the after-effects of cathodal transcutaneous direct current stimulation of the human brain. J Physiol. 2005;568:653–663. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.088310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Deng W, Aimone JB, Gage FH. New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11:339–350. doi: 10.1038/nrn2822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nitsche MA, Fricke K, Henschke U, Schlitterlau A, Liebetanz D, Lang N, Henning S, Tergau F, Paulus W. Pharmacological modulation of cortical excitability shifts induced by transcranial direct current stimulation in humans. J Physiol. 2003;553:293–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.049916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fritsch B, Reis J, Martinowich K, Schambra HM, Ji Y, Cohen LG, Lu B. Direct current stimulation promotes BDNF-dependent synaptic plasticity: potential implications for motor learning. Neuron. 2010;66:198–204. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.03.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tanaka T, Takano Y, Tanaka S, Hironaka N, Kobayashi K, Hanakawa T, Watanabe K, Honda M. Transcranial direct-current stimulation increases extracellular dopamine levels in the rat striatum. Front Syst Neurosci. 2013;7:6. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2013.00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to ethical restrictions and personal data protection, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.