Figure 1.
HNF4A Mutation (p.Ile271fs) Causes Impaired Foregut/Early Hepatopancreatic Progenitor (HPP) Development
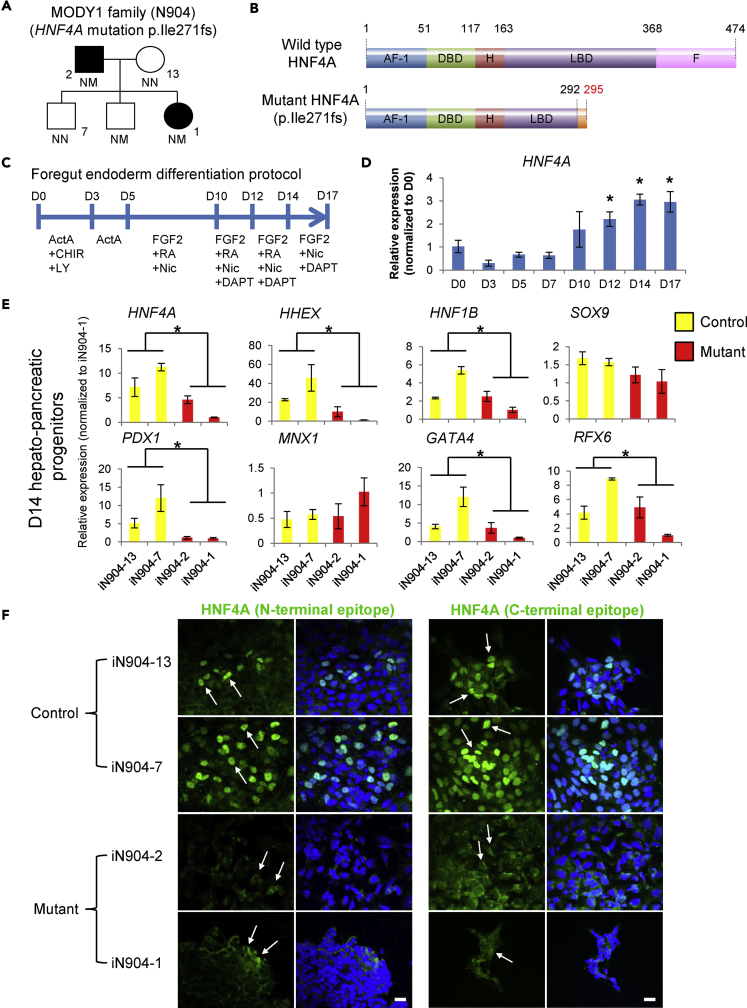
(A) MODY1 family node showing non-diabetic control-hiPSCs (iN904-13 and iN904-7) and MODY1-hiPSCs (iN904-2 and iN904-1).
(B) p.Ile271fs mutation results in C-terminally truncated HNF4A that lacks part of the ligand-binding domain (LBD) and the entire F repressor domain (not drawn to scale).
(C) The 17-day differentiation protocol for generating foregut endoderm and HPPs.
(D) qPCR analysis of HNF4A expression during HPP differentiation.
(E) qPCR analyses of HNF4A transcripts and foregut endoderm markers such as HHEX, HNF1B, PDX1, GATA4, and RFX6 in control and MODY1-HPPs.
(F) Immunofluorescent confocal images showing the localization of HNF4A protein in control and MODY1-HPPs, based on antibodies targeting the N- or C-terminal regions of HNF4A. Blue, DAPI; green, HNF4A; scale bars, 50 μm. White arrows point to the nuclear or cytoplasmic localization signal of HNF4A. Confocal images were acquired using similar scan settings across samples.
Data are represented as mean ± SD of n = 3; representative of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 versus D0 or control samples by Student's t test. See also Figures S1 and S2.