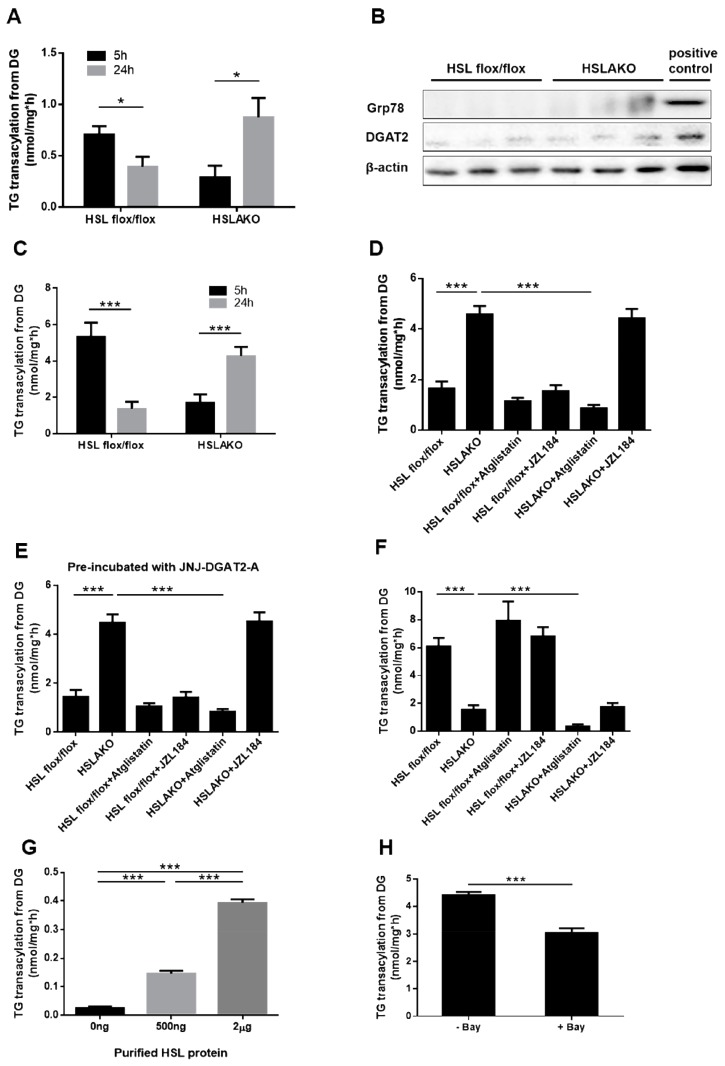
Figure 2.
Levels of 3H-TG transacylation from 3H-DGs. (A) Levels of 3H-TG transacylation from 3H-DGs in WAT cytosol from 5-h and 24-h fasted mice. (B) Levels of DGAT2 and ER marker Grp78 protein in the isolated lipid droplet (LD) fraction of HSL flox/flox and HSLAKO mice were measured by Western blotting. Positive control means cytosolic protein from HSL flox/flox mice. (C) Levels of 3H-TG transacylation from 3H-DGs in WAT lipid droplet extracts from 5-h and 24-h fasted mice. (D) Levels of 3H-TG transacylation from 3H-DGs in WAT lipid droplet extracts from 24-h fasted mice in the presence or absence of ATGL inhibitor and MGL inhibitor. (E) Levels of 3H-TG transacylation from 3H-DGs in WAT lipid droplet extracts, which were pre-incubated with DGAT2 inhibitor, from 24-h fasted mice in the presence or absence of ATGL inhibitor and MGL inhibitor. (F) Levels of 3H-TG transacylation from 3H-DGs in WAT lipid droplet extracts from 5-h fasted mice in the presence or absence of ATGL inhibitor and MGL inhibitor. (G) Levels of 3H-TG transacylation from 3H-DGs in the presence of the indicated amounts of purified HSL protein. (H) Levels of 3H-TG transacylation from 3H-DGs in WAT lipid droplet extracts in the presence or absence of the HSL inhibitor, Bay. HSLAKO: adipose specific HSL deficient mice. Atglistatin (40 μM), ATGL inhibitor; Bay (50 nM), HSL inhibitor; JZL184 (1 μM), MGL inhibitor; JNJ-DGAT2-A (50 µM), DGAT2 inhibitor. (n = 6 mice under each condition.). Values are mean ± S.E.M. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.