Abstract
The most useful strategies for the alkylation of allylic systems are related to the Tsuji–Trost reaction or the use of different Lewis acids. Herein we report a photocatalytic approach for the allylation reaction of a variety of nucleophiles, such as heteroarenes, amines and alcohols. This method is compatible with a large variety of pyrroles and indoles, containing different substituents such as electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups, unprotected nitrogen atoms and bromo derivatives. Moreover, this methodology enables the chromoselective synthesis of Z- or E-allylated compounds. While the use of UV-light irradiation has allowed the synthesis of the previously inaccessible Z-allylated products, E-isomers are prepared simply by changing both the light source to the visible region, and the catalytic system. Based on mechanistic and photochemical proofs, laser flash photolysis studies and DFT calculations, a rational mechanism is presented.
Subject terms: Homogeneous catalysis, Synthetic chemistry methodology, Reaction mechanisms, Photocatalysis
Tsuji–Trost allylation is a traditional method for selective C-C bond formation that involves the use of palladium-based catalysts. Here, the authors report a metal-free, photocatalytic allylation of several heterocycles, amines and alcohols, which can be easily tuned towards the Z- or E- allylated product.
Introduction
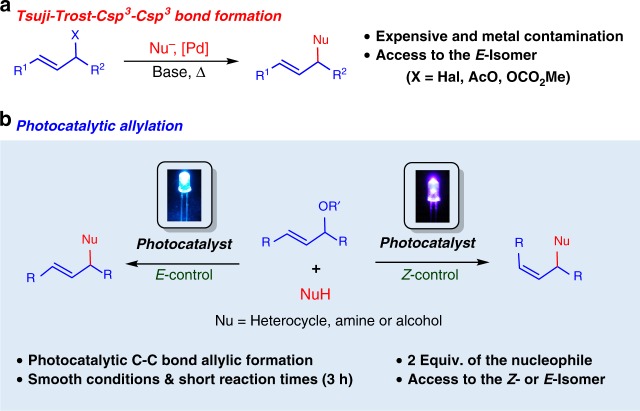
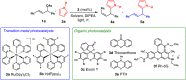
The preparation of allyl-substituted compounds has attracted a special interest due to their utility as building blocks in organic synthesis1–3. The Tsuji–Trost reaction4 is one of the most powerful methodologies for the alkylation of allylic systems, which is commonly catalyzed by palladium, and the allylic position is usually activated by a halide, an acetate, or a carbonate (eq. a, Fig. 1) and affords exclusively the E-isomer. The high selectivity and the general scope of this reaction makes it one of the most prominent Csp3–Csp3 bond formation methodologies5. Indoles and pyrroles are versatile and useful heterocycles for the synthesis of a large variety of biologically active compounds and natural products6. Different authors have reported the allylation of indoles at the C-3 position via the Tsuji–Trost reaction in a racemic manner7–12. However, although this methodology is very important, to the best of our knowledge, no photocatalytic approaches for the allylation of heterocycles have been reported so far.
Fig. 1.
The photocatalytic allylation reaction. a Precedents in the Tsuji–Trost allylation and b this work
Over the past decade, photocatalysis has emerged as a powerful tool for the construction of new bonds that are difficult to obtain using other established procedures13–31. A large number of photocatalytic methodologies have been described for the formation of new Csp2–Csp2 bonds. In particular, the arylation of (hetero)-aromatic rings, usually pyrroles, under different photocatalytic systems has been recently reported32–40. However, one of the major problems related to this photocatalytic arylation is the large excess of the heterocycle required in this reaction (24–40 equiv.). Although the photocatalytic heteroatomatic ring arylation has been extensively studied, the photoallylation of heterocycles remains an elusive process.
We hypothesize that the reduction of the allylic derivative by a photocatalyst with the adequate redox potential would result in the appropriate intermediate, which will allow the functionalization of the allylic position. There are two prerequisites to achieve this goal: (i) the development of a photocatalytic system able to activate the C–O bond; (ii) since an unsaturation is present, it is necessary to control the isomerization of the double bond (Z or E).
In this work, we present a chromoselective photocatalytic allylation of heteroaromatic rings, using smooth conditions and short reaction times to access the Z- or E-double bonds, depending on the reaction conditions (eq. b, Fig. 1). In addition, mechanistic and photochemical proofs, DFT calculations, and laser flash photolysis studies enabled us to postulate a plausible mechanistic pathway.
Results
Optimization of the model reaction
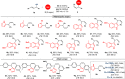
Based on the previous photocatalytic arylation reactions32–40, we started the screening of the reaction using the acetate allylic derivative 1a and pyrrole 2a (18 equiv.) in the presence of different photocatalysts 3 under light irradiation (Table 1). Transition-metal-based photocatalysts (3a–3b) failed to promote the formation of the allylated heterocycle (entries 1 and 2). Several photoorganocatalysts with different reductive power (3c–3f) were tested, but only the 10-phenyl-10H-phenothiazine (PTH) (3e) gave the Z-allylated pyrrole 4a with low conversion under 420-nm LED irradiation (entries 3–6). Encouraged by these results, we used an irradiation source with a wavelength closer to the maximum absorption of PTH (entry 7). Pleasantly, using a 365-nm LED, 4a was obtained with a 65% conversion. In the absence of a photocatalyst, light, and both, the allylation did not proceed (entries 8–10), confirming the photocatalytic nature of this transformation. Different solvents were then evaluated, and the best result was obtained using CH3CN (entries 7 and 11–14). In order to decrease the amount of heterocycle, the reaction was carried out using 10 and 2 equivalents of 2a (entries 15 and 16) and 4a was obtained with a good yield of 58% in only 3 h, using just two equivalents of the heterocycle. The use of inorganic bases (Na2CO3, LiOAc) afforded the final product, although with moderate yield, due to the lower solubility of such bases in acetonitrile (entries 17 and 18).
Table 1.
Optimization of the photocatalytic allylation reactiona
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | 3 (mol%) | Light (nm) | Solvent | Pyrrole (equiv.) | t (h) | 4a:5ab |
| 1 | 3a (5) | 420 | MeCN | 18 | 1 | n.r. |
| 2 | 3b (5) | 420 | MeCN | 18 | 1 | n.r. |
| 3 | 3c (5) | 530 | MeCN | 18 | 1 | n.r. |
| 4 | 3d (5) | 420 | MeCN | 18 | 1 | n.r. |
| 5 | 3e (5) | 420 | MeCN | 18 | 1 | 100:0 (5%)c |
| 6 | 3f (10) | 455 | MeCN | 18 | 41 | n.r. |
| 7 | 3e (5) | 365 | MeCN | 18 | 1 | 100:0 (65%)c |
| 8 | 3e (5) | – | MeCN | 18 | 1 | n.r. |
| 9 | – | 365 | MeCN | 18 | 1 | n.r. |
| 10 | – | – | MeCN | 18 | 1 | n.r. |
| 11 | 3e (5) | 365 | DMSO | 18 | 1 | 100:0 (61%)c |
| 12 | 3e (5) | 365 | DMF | 18 | 1 | 100:0 (49%)c |
| 13 | 3e (5) | 365 | Toluene | 18 | 1 | 100:0 (21%)c |
| 14 | 3e (5) | 365 | DCM | 18 | 1 | 100:0 (10%)c |
| 15 | 3e (5) | 365 | MeCN | 10 | 3 | 94:6 (86%)c |
| 16 | 3e (5) | 365 | MeCN | 2 | 3 | 94:6 (91%) c,d |
| 17e | 3e (5) | 365 | MeCN | 2 | 3 | 80:20 (33%)c |
| 18f | 3e (5) | 365 | MeCN | 2 | 3 | 78:22 (28%)c |
aConditions: 1a (0.1 mmol), 2a (see table), DIPEA (0.5 mmol), and catalyst (mol%) in the solvent indicated (1.0 mL)
bMeasured by 1H-NMR
cConversion in the crude mixture
dOptimized conditions highlighted in bold
eReaction carried out under standard conditions but using Na2CO3 (0.5 mmol) instead of DIPEA
fReaction carried out under standard conditions but using LiOAc (0.5 mmol) instead of DIPEA
Substrate scope
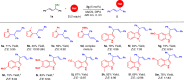
Having established the best conditions (Table 1, entry 16), we performed the scope of the reaction (Table 2). With N-methyl pyrrole, the allylic derivative 4b was obtained with a better yield than 4a and with a similar selectivity for the Z-isomer. Other substituents were tolerated at the N-atom of the pyrrole (4c and 4d) with excellent Z/E selectivity (up to 96:4) and with a slight decrease for the phenyl derivative 4c. Indoles without protecting groups at the nitrogen were also employed, keeping the high selectivity for the Z-isomers, and with better yields than with the pyrroles (compare 4e and 4f with 4a and 4b). Electron-donating groups (EDGs) were well tolerated at different positions of the indole ring (4g, 4h, and 4i) as well as electron-withdrawing groups (EWG) at the aromatic ring (4j). A methyl substituent next to the indolinic nitrogen (4k) or the reactive C-3 center (4l) did not have a negative influence on the reactivity, obtaining both in very good yields and high selectivity. Remarkably, the presence of Br at the 5-position (4m) was also well tolerated under the presence of the high-reducing photocatalyst 3e. The scope of the allylic derivative was also evaluated. Electron-rich (4n, 4o, and 4p) as well as electron-poor aromatic rings (4q) worked with excellent selectivities (up to > 98:2). We then studied the influence of the leaving group at the allylic position (R group in 1a). The reaction worked with other leaving groups such as benzoate, carbamate, or carbonate, which were suitable for this process. However, the reaction with the hydroxyl group did not proceed, because of its higher reduction potential (−2.52 V vs. SCE) compared with the other activated allylic alcohols (E = −2.06 to −2.35 V vs. SCE, see Suplementary Note 4 for cyclic voltammetry).
Table 2.
Scope of the allylation reaction for the synthesis of Z-isomers with pyrroles and indoles under catalyst 3ea,b
|
aConditions: 1 (0.1 mmol), 2 (0.2 mmol), DIPEA (0.5 mmol), and 3e (5 mol%) in MeCN (1.0 mL)
bIsolated yields after flash chromatography
cCombined isolated yield along with the C2-allylated compound
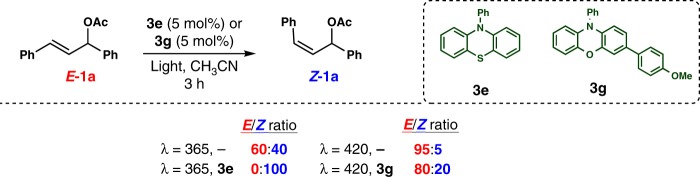
After obtaining these good results with the Z-isomer, our next objective was the development of a photocatalytic variant to obtain the corresponding E-isomers. To achieve this goal, we analyzed the conditions that avoided the isomerization of the reagent 1a. A sample containing E-1a in MeCN was irradiated for 3 h under different reaction conditions (Fig. 2). Without the use of the photocatalyst under 365-nm irradiation, we found a mixture of 60/40 E/Z-1a, while in the presence of 3e, this isomerization to Z-1a was complete (Fig. 2). According to theoretical calculations, photosensitization and subsequent isomerization of E-1a by the photocatalyst is feasible, while photosensitization and subsequent isomerization of Z-1a cannot take place (see Supplementary Information Fig. 25). The absorption spectra of E-1a at the reaction conditions revealed a significant absorption at 365 nm (see Supplementary Information Fig. 8), while at 420 nm, it was negligible, suggesting that the reaction must be carried out in the visible-light region to avoid isomerization. Under 420-nm irradiation, only 5% of the E-1a was isomerized to the Z-isomer after 3 h. Therefore, a photocatalyst with high reduction potential (≥2.35 V vs. SCE) and absorption in the visible-light region is required. The phenoxazine 3g, that meets all these criteria41, resulted in only a small amount of Z-1a at 420-nm irradiation after 3 h (Fig. 2). Therefore, under these conditions (using photocatalyst 3g and 420-nm irradiation), it should be possible to avoid the isomerization step and selectively form E-allylated products 5.
Fig. 2.
Isomerization studies. Isomerization proofs of E-1a under different catalysts (3e and 3g) and different irradiation wavelengths
To our delight, when carrying out the reaction between the allylic derivative 1a and pyrrole (2a) in the presence of the photocatalyst 3g under 420-nm irradiation, the allylated product E-5a was obtained with a good yield as the major isomer (Table 3). Other N-substituted pyrroles were also employed and maintained the same selectivity (5b–5c). Only compound 5d was obtained as a complex mixture. The reaction with indoles afforded even better yield and selectivity than pyrroles (5e and 5f). Unprotected indolinic nitrogen as well as different substituents were tolerated, from EDGs (5g–i) to EWGs (5j), methyl (5k–l), or bromo derivatives (5m), obtaining in all cases good yields (67–92%) and excellent selectivities (up to > 98:2). The isomerization of the final product 5e under 420-nm irradiation was also studied, obtaining a Z/E mixture 30/70 after 3 h of irradiation, without the photocatalyst, while in the presence of the photocatalyst 3g, a Z/E mixture 20/80 was obtained. The final product is present in the reaction in higher concentrations only after 2 h of reaction. Therefore, the irradiation time is not enough to produce its isomerization, which explains the obtention of the E-isomer as the major one.
Table 3.
Scope of the allylation reaction for the synthesis of E-isomers with pyrroles and indoles under catalyst 3ga,b
|
a Conditions: 1a (0.1 mmol), 2 (0.2 mmol), DIPA (0.5 mmol), and 3g (5 mol%) in MeCN (1.0 mL)
bIsolated yields after flash chromatography
cCombined isolated yield along with the C2-allylated compound
Mechanistic studies
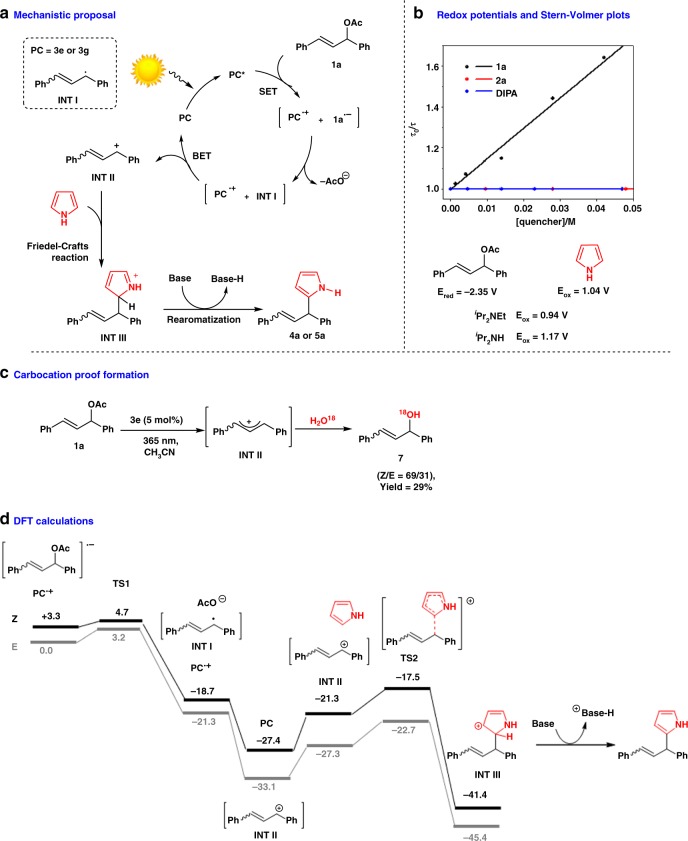
The proposed reaction mechanism is outlined in Fig. 3a. After light absorption by the photocatalyst under LED irradiation (λ = 365 or 420 nm), single-electron transfer (SET) takes place from its S1 excited state (ES1 = 3.2 eV, see Supplementary Information Figs. 11 and 12) to 1a. Steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence quenching studies in the presence of 1a afforded a quenching rate constant of kq(S1) = 4.7 × 109 M−1 s−1 (see Supplementary Information Fig. 9a), indicating that the radical ion pair (PC•+ + 1a•−) formation occurs at nearly diffusion rate. In addition, SET from the excited singlet state would be an exergonic process, taking into account the free energy change (ΔGET = −4.0 kcal mol−1) associated with the electron transfer (see Supplementary Note 4 for Rehm–Weller equation).
Fig. 3.
Mechanistic studies. a Mechanistic proposal for the photoallylation. b Redox potentials and Stern–Volmer plots of the time-resolved fluorescence quenching of 3g with 1a, pyrrole, and DIPA (DIPA = diisopropylamine). c Reaction of 1a with H2O18 under standard reaction conditions. d For DFT calculations, geometry optimizations were performed using the M06-2X functional in combination with the 6-311G** basis set
Importantly, photooxidation of DIPEA (Eox = 0.94 V vs. SCE)42, DIPA (Eox = 1.17 V vs. SCE)43, or pyrrole (Eox = 1.04 V vs. SCE)44 by PC S1 excited state could not occur, taking into account the oxidation power of 3e and 3g (E (Pc*/Pc·−) = −0.3 V vs. SCE for 3e and 3g, see Supplementary Note 4), and was further confirmed by fluorescent-quenching studies (see Fig. 3b). The fate of such reduced species has been investigated by DFT calculations, considering both Z- and E-isomers (Fig. 3d). Initial single-electron transfer process from the photocatalyst (PC) to 1a generates the radical cation PC·+ and the radical anion 1a·−, that evolves through the C–O bond scission to afford acetate anion and the radical intermediate I (INT I). This step is a very exergonic process (−22 or −21.3 kcal mol−1) and proceeds through a very shallow kinetic barrier (Ea = 1.4 or 3.2 kcal mol−1). Then, the oxidation of INT I by the oxidized photocatalyst (PC·+), results in the regeneration of the photocatalyst (PC) and formation of a carbocationic intermediate II (INT II) (Fig. 3d). Such electron transfer is calculated as a thermodynamically favorable process (−8.7 or −11.8 kcal mol−1). The calculated energetic barriers for E to Z isomerizations for radical or carbocation intermediates I and II rule out this process from such transient species (see Supplementary Information Fig. 28). Formation of this carbocation INT II was experimentally confirmed, carrying out the reaction in the presence of H2O18 as the nucleophile obtaining the isotopically labeled compound 7 (Fig. 3c). In addition, when two nonsymmetric allylic derivatives bearing different aryl groups were studied, an equimolecular mixture of products was obtained (see Supplementary Fig. 30, compounds 6 and 6′), indicating that the reaction takes places through a common intermediate. Then, a Friedel–Crafts reaction between the carbocation INT II and pyrrole takes place, generating the protonated intermediate III (INT III). This step is also theoretically found exergonic (−14 or −26.3 kcal mol−1) and kinetically favorable (Ea = 3.8 kcal mol−1). A final rearomatization by deprotonation of INT III gives the final product (Fig. 3d). For such deprotonation, both DIPEA and the anion acetate (formed during the reaction) would act as a base through very exergonic processes (see entries 16 and 17 from Table 1 for reactions in the presence of Na2CO3 and LiOAc).
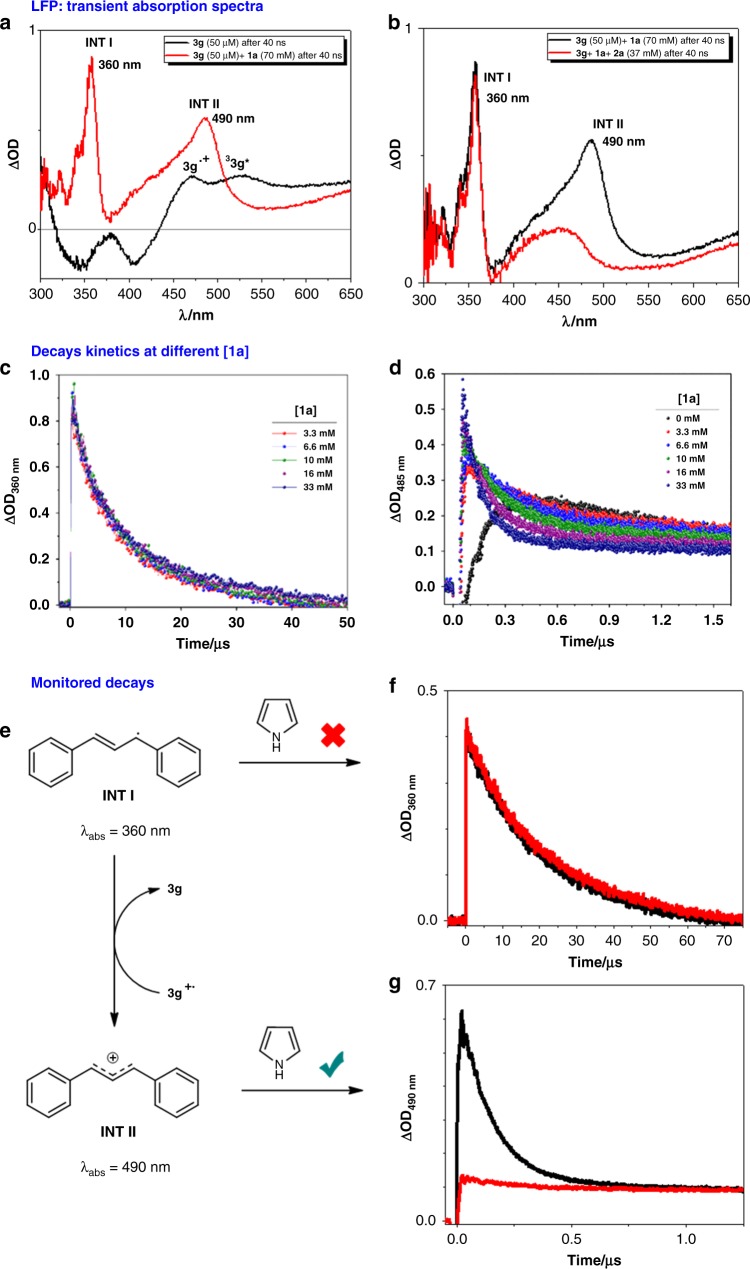
In order to gain a better understanding of the reaction mechanism, laser flash photolysis (LFP) measurements have been carried out. Excitation of 3g at 355 nm results in two peaks at 468 and 530 nm at 40 ns after the laser pulse, which are assigned to the 3g radical cation (3 g•+) and the excited triplet state of 3g (33g*), respectively (Fig. 4a, black line, for further details, see also Supplementary Note 2). This experiment was performed in the presence of 1a to identify the possible transient reaction intermediates (Fig. 4a, red line). Two new absorption bands at 360 and 490 nm are clearly observed, which correspond to intermediates I and II, respectively, based on literature data45. The lifetime of the carbocation INT II also depends on the nucleophilicity of the anionic leaving group (see Supplementary Information Fig. 4). In order to check whether formation of INT II and INT I is instantaneous with the laser pulse, additional LFP experiments of 3g in the presence of increasing amounts of 1a were performed (Fig. 4c and d). Generation of INT II is practically instantaneous even at lower concentration of 1a (Fig. 4d), whereas lifetimes of INT I are not affected by higher amounts of 1a (Fig. 4c). This result suggests that SET from 3g* to 1a at diffusion control rate (see Supplementary Information Fig. 9) gives rise to the contact radical ion pair at this singlet stage (Fig. 3a). All processes in the contact radical ion pairs undergo in the sub-nanosecond scale46. Fast acetate release from 1a·− led to INT I, which is still in close contact with 3g•+. At this point, INT I undergoes an ultrafast back electron transfer with 3g•+ restoring 3g and generating INT II, whose amount is slightly dependent on the concentration of 1a in the sample (Fig. 4d). In addition, 3g•+ and INT I can split up, forming the corresponding free 3g•+ and free INT I, that are detected in the LFP experiments with lifetimes in the microsecond scale (Fig. 4a, red line). Once the detection of both intermediates I and II by LFP has been established, the question arises whether INT I or INT II (radical or carbocation) would react with a trapping agent (Fig. 4e and transient absorption spectrum in Fig. 4b). Addition of pyrrole to a 3g/1a mixture results only in a marked decrease of the INT II lifetime (Fig. 4g), while the band corresponding to INT I (360 nm) is not affected (Fig. 4f). Therefore, this experiment clearly corroborated with the previous data (Fig. 3) that the carbocation INT II is the reactive intermediate in our reaction. A quantum yield of 1.5% was found, suggesting a photocatalytic process without a significant radical chain propagation47.
Fig. 4.
Laser flash photolysis (λexc = 355 nm, MeCN/Ar) experiments. a Transient absorption spectra recorded at 40 ns after the laser pulse of 3g (50 mM) without 1a (black), with 70 mM of 1a (red). b Transient absorption spectra recorded at 40 ns after the laser pulse of 3g (50 mM) with 70 mM of 1a (black) and with 35 mM of 2a (red). c Decay kinetics at 360 nm after 355-nm LFP of 3g (50 µM) in the presence of increasing amounts of 1a. d Decay kinetics at 485 nm after 355-nm LFP of 3g (50 µM) in the presence of increasing amounts of 1a. e Scheme of the formation of intermediate II from intermediate I and their reaction with 2a. f Lifetime of INT I: decays monitored at 360 nm of 3g (50 mM) and 1a (70 mM) (black line) and in the presence of 2a (37 mM) (red line). g Lifetime of INT II: decays monitored at 490 nm of 3g (50 mM) and 1a (70 mM) (black line) and in the presence of 2a (37 mM) (red line)
Scope with alcohols and amines
Once that we proved that the reaction takes place through a carbocation intermediate formation, we decided to study other nucleophiles to prove the generality of our protocol. Allylic amines are very useful compounds that can be employed as building blocks for the synthesis of amino acids, alkaloids, and carbohydrate derivatives48–50. Moreover, this structure is present in numerous natural products and drugs with antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory action51–53. Different amines were tried under UV irradiation in order to obtain the Z-allylated amines which are not accessible by other methodologies (Table 4). Aniline gave the corresponding Z-allylated amine 9a with high selectivity. Aromatic amines with EDGs were well tolerated (9b–d) with moderate selectivity, whereas anilines with EWGs gave significant better yield (9e) and Z/E ratio. In addition, the presence of Br at the aromatic ring was tolerated without detecting the corresponding reduced product (9f). Aliphatic primary and secondary amines were also suitable for the reaction conditions (9g–h). Cyclic allylated amine 9i was obtained in good selectivity (Z:E = 91:9) and good yield. Moreover, the use of morpholine as a nucleophile can be employed for the synthesis of 9j with excellent selectivity. The preparation of allylic ethers has a great interest, as they are also present in numerous pharmaceuticals and natural products54–57. For this reason, alcohols were employed as nucleophiles, obtaining Z-allylated ethers with good yields and good selectivities (9k–m)58.
Table 4.
Scope of the allylation reaction with amines and alcohols for the synthesis of Z-isomers under photocatalyst 3ea,b

|
a Conditions: 1a (0.1 mmol), 2 (0.2 mmol), DIPEA (0.5 mmol), and 3g (5 mol%) in MeCN (1.0 mL)
bIsolated yields after flash chromatography
Using the visible-light irradiation conditions and photocatalyst 3g with amines and alcohols is possible to obtain the corresponding E-isomers (Table 5). Aromatic amines gave the corresponding allylated compounds with high selectivities and good yields with EDGs (10b–d) and EWGs (10e), or ortho-bromo substituents (10f). Aliphatic primary (10g) and secondary amines (10h–j) were employed, keeping in all the cases high Z/E selectivity. Moreover, allylated ethers can also be obtained under visible-light irradiation with excellent selectivities (10k–m). A similar mechanistic scenario was found for amines and alcohols, using p-toluidine 8b as a nucleophile in the LFP and photochemical mechanistic probes (see Supplementary Fig. 9).
Table 5.
Scope of the allylation reaction with amines and alcohols for the synthesis of E-isomers under photocatalyst 3ga,b
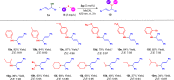
|
a Conditions: 1a (0.1 mmol), 8 (0.2 mmol), and 3g (5 mol%) in MeCN (1.0 mL)
bIsolated yields after flash chromatography
cReaction performed by adding DIPEA (0.5 mmol)
Discussion
In summary, a chromoselective photocatalytic approach for the allylation of indoles, pyrroles, amines, and alcohols has been developed. This approach represents a photocatalytic allylation reaction for the synthesis of demand of Z- or E-isomers, with only two equivalents of the desired nucleophile. Therefore, under UV-light irradiation Z-allylated products are obtained, while the E-isomer is simply prepared by changing both the light source to the visible region, and the catalytic system. DFT calculations, photochemical proofs, and mechanistic experiments indicate that the most plausible mechanism involves a nucleophilic attack to an allyl-cation intermediate.
Methods
Procedure for the preparation of Z-allylic compounds
A vial equipped with a magnetic stir bar and fitted with a Teflon screw cap septum was charged with the corresponding allylic compound 1 (0.1 mmol), the corresponding heterocycle, amine, or alcohol (0.2 mmol), N-phenyl phenothiazine (1.4 mg, 5 mol%), DIPEA (86 μL, 0.5 mmol), and acetonitrile (1 mL). The reaction was degassed with three freeze–pump–thaw cycles. The vial was then backfilled with N2 and stirred under 365-nm LED irradiation (8.2460 W m−2 intensity; approximate distance was 2 cm from the vial) at 20 °C. After 3 h, the vial was opened, the solvent evaporated, and the crude product was purified by column chromatography to give the corresponding products 4 or 9.
Procedure for the preparation of E-allylic compounds
A vial equipped with a magnetic stir bar and fitted with a Teflon screw cap septum was charged with the corresponding allylic compound 1 (0.1 mmol), the corresponding heterocycle, amine, or alcohol (0.2 mmol), 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-10-phenyl-10H-phenoxazine (1.7 mg, 5 mol%), DIPA (70 μL, 0.5 mmol, only base is needed for reactions with heterocycles as nucleophile), and acetonitrile (1 mL). The reaction was degassed with three freeze–pump–thaw cycles. The vial was then backfilled with N2 and stirred under 420-nm LED irradiation (18.3396 W m−2 intensity; approximate distance was 2 cm from the vial) at room temperature. After 3 h, the vial was opened, the solvent evaporated, and the crude product was purified by column chromatography to give the corresponding products 5 or 10.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the Spanish Government (CTQ2015-64561-R), CCC-UAM (computing time), and ERC (ERC-CG, 647550, 648319) is acknowledged. L.M., R.P-R, and R.C. thank CAM for the “Atracción de Talento” fellowship. The authors thank “Comunidad de Madrid” and European Structural Funds for their financial support to FotoArt-CM project (S2018/NMT-4367). We thank Miguel Ángel Miranda for helpful discussions about photochemical mechanisms.
Author contributions
A.M.M-G and A.F. carried out the optimization and scope of the reaction. R.C. and J.L-B. carried out the scope of the reaction. L.M. performed the photocatalytic studies for mechanism elucidation. R.P-R. and V.A.P. performed the Laser Flash Photolysis studies. R.M-B. carried out the DFT-computational studies. J.A. conceived the project and prepared the paper, which was edited by all other authors.
Data availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and Supplementary Information files, and also are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Journal peer review information: Nature Communications thanks anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41467-019-10441-4.
References
- 1.Trost BM, Strege PE. Asymmetric induction in catalytic allylic alkylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977;99:1649–1651. doi: 10.1021/ja00447a064. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Trost BM. New rules of selectivity: allylic alkylations catalyzed by palladium. Acc. Chem. Res. 1980;13:385–393. doi: 10.1021/ar50155a001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tsuji, J., Minami, I. & Shimizu, I. Palladium-catalyzed allylation of ketones and aldehydes with allylic carbonates via silyl enol ethers under neutral conditions. Chem. Lett. 12, 1325–1326 (1983).
- 4.Trost BM, Van Vranken DL. Asymmetric transition metal-catalyzed allylic alkylations. Chem. Rev. 1996;96:395–422. doi: 10.1021/cr9409804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.De Meijere, A., Diederich, F. (eds) Metal-Catalyzed Cross-coupling Reactions, 2nd edn (Wiley, Weinheim, 2008).
- 6.D’Ischia, A., Napolitano, A. & Pezella, A. Pyrroles and their Benzo Derivatives: Application. in Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III (eds Katritzky, A. R., Ramsden, C. A., Scriven, E. F. V. & Taylor, R. J. K.) 353–386 (Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 2008).
- 7.Malkov AV, Davis SL, Baxendale IR, Mitchell WL, Kočovsky P. Molybdenum(II)-catalyzed allylation of electron-rich aromatics and heteroaromatics. J. Org. Chem. 1999;64:2751–2764. doi: 10.1021/jo982178y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bandini M, Melloni A, Umani-Ronchi A. New versatile Pd-catalyzed alkylation of indoles via nucleophilic allylic substitution: controlling the regioselectivity. Org. Lett. 2004;6:3199–3202. doi: 10.1021/ol048663z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kimura M, Futamata M, Mukai R, Tamaru Y. Pd.catalyzed C3-selective allylation of indoles with allyl alcohols promoted by triethylborane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:4592–4593. doi: 10.1021/ja0501161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stanley LM, Hartwig JF. Iridium-catalyzed regio- and enantioselective N-allylation of indoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009;48:7841–7844. doi: 10.1002/anie.200904338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Xu K, Gilles T, Breit B. Asymmetric synthesis of N-allylic indoles via regio- and enantioselective allylation of aryl hydrazines. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:7616. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee JY, Ha H, Bae S, Han I, Joo JM. Catalytic C-2 allylation of indoles by electronic modulation of the indole ring and its application to the synthesis of functionalized carbazoles. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016;358:3458–3470. doi: 10.1002/adsc.201600568. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Narayanam JMR, Stephenson CRJ. Visible light photoredox catalysis: applications in organic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011;40:102–113. doi: 10.1039/B913880N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Prier CK, Rankic DA, MacMillan DWC. Visible light photoredox catalysis with transition metal complexes: applications in organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2013;113:5322–5363. doi: 10.1021/cr300503r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Meggers E. Asymmetric catalysis activated by visible light. Chem. Commun. 2015;51:3290–3301. doi: 10.1039/C4CC09268F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ravelli D, Protti S, Fagnoni M. Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions via photogenerated intermediates. Chem. Rev. 2016;116:9850–9913. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Skubi KL, Blum TR, Yoon TP. Dual catalysis strategies in photochemical synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2016;116:10035–10074. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pitre SP, McTiernan CD, Scaiano JC. Understanding the kinetics and spectroscopy of photoredox catalysis and transition-metal-free alternatives. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:1320–1330. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tellis JC, et al. Single-electron transmetalation via photoredox/nickel dual catalysis: unlocking a new paradigm for sp3-sp2 cross-coupling. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:1429–1439. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gentry EC, Knowles RR. Synthetic applications of proton-coupled electron transfer. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:1546–1556. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hernandez-Perez AC, Collins S. Heteroleptic Cu-based sensitizers in photoredox catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:1557–1565. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Goddard J-P, Ollivier C, Fensterbank L. Photoredox catalysis for the generation of carbon centered radicals. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:1924–1936. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Morris SA, Wang J, Zheng N. The prowess of photogenerated amine radical cations in cascade reactions: from carbocycles to heterocycles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:1957–1968. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fabry DC, Rueping M. Merging visible light photoredox catalysis with metal catalyzed C-H activations: on the role of oxygen and superoxide ions as oxidants. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:1969–1979. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Majek M, von Wangelin AJ. Mechanistic perspectives on organic photoredox catalysis for aromatic substitutions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:2316–2327. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shaw MH, Twilton J, MacMillan DWC. Photoredox catalysis in organic chemistry. J. Org. Chem. 2016;81:6898–6926. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b01449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhou W-J, Zhang Y-H, Gui Y-Y, Sun L, Yu D-G. Merging transition-metal catalysis with photoredox catalysis: an environmentally friendly strategy for C-H functionalization. Synthesis. 2018;50:3359–3378. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1610222. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Garrido-Castro AF, Carmen Maestro M, Alemán J. Asymmetric induction in photocatalysis—discovering a new side to light-driven chemistry. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018;59:1286–1294. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2018.02.040. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Marzo L, Pagire SK, Reiser O, König B. Visible-light photocatalysis: does it make a difference in organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018;57:10034–10072. doi: 10.1002/anie.201709766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang C-S, Dixneuf PH, Soule J-F. Photoredox catalysis for building C-C bonds from C(sp2)-H bonds. Chem. Rev. 2018;118:7532–7585. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hari DP, König B. The photocatalyzed Meerwein arylation: classic reaction of aryl diazonium salts in a new light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013;52:4734–4743. doi: 10.1002/anie.201210276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ghosh I, Marzo L, Das A, Shaikh R, König B. Visible-light mediated photoredox catalytic arylation reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:1566–1577. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hari DP, Schroll P, König B. Metal-free, visible-light-mediated direct C-H arylation of heteroarenes with aryl diazonium salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:2958–2961. doi: 10.1021/ja212099r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ghosh I, Ghosh T, Bardagi JI, König B. Reduction of aryl halides by consecutive visible light-induced electron transfer processes. Science. 2014;346:725–728. doi: 10.1126/science.1258232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Meyer AU, Slanina T, Yao C-J, König B. Metal-free perfluoroarylation by visible light photoredox catalysis. ACS Catal. 2016;6:369–375. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b02410. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ghosh I, König B. Chromoselective photocatalysis: controlled bond activation through light-color regulation of redox potentials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016;55:7676–7679. doi: 10.1002/anie.201602349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Marzo L, Ghosh I, Esteban F, König B. Metal-free photocatalyzed cross coupling of bromoheteroarenes with pyrroles. ACS Catal. 2016;6:6780–6784. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01452. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kalyani D, McMurtrey KB, Neufeldt SR, Sanford MS. Room-temperature C-H arylation: merger of Pd-catalyzed C-H functionalization and visible-light photocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:18566–18569. doi: 10.1021/ja208068w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zoller J, Fabry DC, Rueping M. Unexpected dual role of titanium dioxide in the visible light heterogeneous catalysed C-H arylation of heteroarenes. ACS Catal. 2015;5:3900–3904. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b00668. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Maity, P., Kundu, D. & Ranu, B. C. Multigram four-step synthesis of 1,4,7-triazacyclononanes with 2Ra/RbN-functionalization pattern by starting from diethylenetriamine. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 1727–1734 (2015).
- 41.McCarthy BG, et al. Structure-property relationships for tailoring phenoxazines as reducing photoredox catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018;140:5088–5101. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b12074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Roth HG, Romero NA, Nicewicz DA. Experimental and calculated electrochemical potentials of common organic molecules for applications to single-electron redox chemistry. Synlett. 2016;27:714–723. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Adenier A, Chehimi MM, Gallardo I, Pinson J, Vila N. Electrochemical oxidation of aliphatic amines and their attachment to carbon and metal surfaces. Langmuir. 2004;20:8243–8253. doi: 10.1021/la049194c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Garrido-Castro AF, Choubane H, Daaou M, Maestro MC, Alemán J. Asymmetric radical alkylation of N-sulfinimines under visible light photocatalytic conditions. Chem. Commun. 2017;53:7764–7767. doi: 10.1039/C7CC03724D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Miranda MA, Perez-Prieto J, Font-Sanchis E, Kónya K, Scaiano JC. Flash photolysis of 1,3-dichloro-1,3-diphenylpropane in polar solvents: generation of a stabilized γ-chloropropyl cation, subsequent formation of a propenyl cation, and nucleophilic trapping of both cations. J. Phys. Chem. A. 1998;102:5724–5727. doi: 10.1021/jp9814449. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mattay, J. & Vondenhof, M. Contact and solvent-separated radical ion pairs in organic. In Photoinduced electron transfer III. Topics in Current Chemistry (Ed. Mattay, J.) 219–255 (Springer, Heidelberg, 1991).
- 47.Kuhn HJ, Braslavsky SE, Schmidt R. Chemical actinometry (IUPAC technical report) Pure Appl. Chem. 2004;76:2105–2146. doi: 10.1351/pac200476122105. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cheikh, R. B., Chaabouni, R., Laurent, A., Mison, P. & Nafti, A. Synthesis of primary allylic amines. Synthesis 685−700 (1983).
- 49.Johannsen M, Jørgensen KA. Allylic amination. Chem. Rev. 1998;98:1689–1708. doi: 10.1021/cr970343o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Trost BM, Crawley ML. Asymmetric transition-metal-catalyzed allylic alkylations: applications in total synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2003;103:2921–2943. doi: 10.1021/cr020027w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Petranyi G, Ryder NS, Stutz A. Allylamine derivatives: new class of synthetic antifungal agents inhibiting fungal squalene epoxidase. Science. 1984;224:1239–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.6547247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Stutz A. Allylamine derivatives—a new class of active substances in antifungal chemotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1987;26:320–328. doi: 10.1002/anie.198703201. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Nanavati SM, Silverman RB. Mechanisms of inactivation of gamma-aminobutyric acid aminotransferase by the antiepilepsy drug gamma-vinyl GABA (vigabatrin) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991;113:9341–9349. doi: 10.1021/ja00024a043. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mizuguchi E, Achiwa K. Chiral palladium complex-catalyzed synthesis of optically active vinylchroman. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997;45:1209–1211. doi: 10.1248/cpb.45.1209. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Nicolaou KC, et al. Natural product-like combinatorial libraries based on privileged structures. 1. General principles and solid-phase synthesis of benzopyrans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:9939–9953. doi: 10.1021/ja002033k. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cao B, Park H, Joullié MM. Total synthesis of Ustiloxin D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:520–521. doi: 10.1021/ja017277z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ishibashi H, Ishihara K, Yamamoto H. A new artificial cyclase for polyprenoids: enantioselective total synthesis of (−)-chromazonarol, (+)-8-epi-puupehedione, and (−)-11′-deoxytaondiol methyl ether. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:11122–11123. doi: 10.1021/ja0472026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Pochetti G, et al. Structural insight into peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ binding of two ureidofibrate-like enantiomers by molecular dynamics, cofactor interaction analysis, and site-directed mutagenesis. J. Med. Chem. 2010;53:4354–4366. doi: 10.1021/jm9013899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and Supplementary Information files, and also are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.