Abstract
Objective:
To measure the impact of staged implementation of full versus partial ABCDE bundle on mechanical ventilation (MV) duration, intensive care unit (ICU) and hospital lengths of stay (LOS), and cost.
Design:
Prospective cohort study
Setting:
Two medical ICUs within Montefiore Healthcare Center (Bronx, New York)
Patients:
1855 mechanically ventilated patients admitted to ICUs between July 2011 - July 2014.
Interventions:
At baseline, spontaneous (B)reathing trials (B) were ongoing in both ICUs; in period 1, (A)wakening and (D)elirium (AD) were implemented in both full and partial bundle ICU’s; in period 2, (E)arly mobilization and structured bundle (C)oordination (EC) were implemented in the full bundle (B-AD-EC) but not the partial bundle ICU (B-AD).
Measurements and Main Results
In the full bundle ICU, 95% patient days were spent in bed before EC (period 1). After EC was implemented (period 2), 65% of patients stood, 54% walked at least once during their ICU stay, and ICU-acquired pressure ulcers and physical restraint use decreased (period 1 vs 2: 39% vs 23% of patients; 30% vs 26% patient days, respectively, p<0.001 for both). After adjustment for patient-level covariates, implementation of the full (B-AD-EC) vs partial (B-AD) bundle was associated with reduced MV duration (−22.3%, 95% CI −22.5% to −22.0%, p <0.001), ICU LOS (−10.3%, 95% CI −15.6% to −4.7%, p=0.028), and hospital LOS (−7.8%, 95% CI −8.7% to −6.9%, p=0.006). Total ICU and hospital cost were also reduced by 24.2% (95% CI −41.4% to −2.0%, p=0.03) and 30.2% (95% −46.1% to −9.5%, p=0.007), respectively.
Conclusions
In a clinical practice setting, the addition of (E)arly mobilization and structured (C)oordination of ABCDE bundle components to a spontaneous (B)reathing, (A)wakening, and (D)elirium management background led to substantial reductions in the duration of mechanical ventilation, LOS, and cost.
Keywords: critical care, mechanical ventilation, delirium, early mobilization, implementation
Introduction
Intensive care unit (ICU)-acquired delirium and weakness can lead to devastating cognitive and physical impairments and psychiatric symptoms in ICU survivors, also known as post-intensive care syndrome.(1–6) The (A)wakening and (B)reathing, (C)oordination, (D)elirium monitoring and management, and (E)arly mobilization (ABCDE) bundle (7, 8) is an interdisciplinary patient-centered evidence-based strategy endorsed by critical care societies and national quality improvement agencies to prevent and reduce ICU delirium and weakness, and operationalize the Society of Critical Care Medicine’s Pain, Agitation, and Delirium clinical practice guidelines. (9–13)
Individual components of the ABCDE bundle are associated with substantial benefits in research settings (14–20). While studies in clinical practice settings suggest that implementation of the full ABCDE bundle is associated with clinical benefits, its uptake has been limited and implementation often incomplete.(21–28) Sequential implementation of bundle components may improve overall execution by allowing providers to: 1) maximize efficacy of implementation by focusing on individual components, 2) assess process improvement by performing step-wise evaluation of components, and 3) make practice adjustments before moving to the next component. In addition, studies suggest that the efficacy of early mobilization can be maximized if programs to reduce unnecessary sedation and delirium are already in place.(25, 29)
Accordingly, we sought to determine the impact of adding EC to B-AD in the context of staged implementation of the ABCDE bundle in mechanically ventilated (MV) patients. We hypothesized that implementation of early mobilization on a foundation of targeted sedation practices and routine delirium monitoring would improve clinical outcomes and reduce hospital cost. Preliminary results have been presented in abstract form. (30, 31)
Materials and Methods
See Supplemental Digital Content for a more detailed description of study procedures.
Study Design and Setting
This prospective study took place in two academic medical ICUs at Montefiore Medical Center (Bronx, New York). ICUs had the same size (14 beds) and staffing (2 patients per nurse, 24 hour onsite intensivist coverage), except the full bundle ICU was staffed by medical residents and the partial bundle ICU by physician assistants. The Institutional Review Board approved a waiver of informed consent (IRB number 2014–3466).
Cohort
Our primary cohort consisted of all MV adults (≥18 years) admitted to the ICUs for ≥24 hours between July 1, 2011-June 30, 2014 (Figure 1). This cohort was used for analyses of clinical outcomes; alternative cohorts were used for process of care and cost outcomes (Figure S1 and text in Supplemental Digital Content).
Figure 1. Timeline of staged implementation of ABCDE in partial (B-AD only) vs full (B-AD-EC) bundle ICU’s and data measurement periods.
Definition of abbreviations: A = awakening from sedation; B = spontaneous breathing trial; C = structured coordination of bundle components; D = delirium monitoring and management; E = early mobilization
(A) Periods of component implementation in the full and partial bundle ICU’s. At baseline, spontaneous (B)reathing trials were ongoing in both full and partial bundle ICU’s; on July 1, 2012, (A)wakening and (D)elirium monitoring/management were implemented in both ICU’s; on July 1, 2013, (E)arly mobilization and structured bundle (C)oordination were implemented in only the full bundle ICU.
(B) Periods in which process of care, clinical outcomes, and cost data were collected relative to bundle implementation.
a Process of care measurements (sedative use, delirium prevalence, maximum level of mobility) were compared across time in the full bundle ICU (B-AD-EC) only.
b ICU quality indicators, clinical outcomes, and cost were compared across time in both the full (B-AD-EC) and partial (B-AD) bundle ICU’s.
c Cost periods were truncated because cost data are calculated based on a cost-to-charge ratio which varies between calendar years. The following periods were compared for the cost analysis: 1) Baseline vs Period 1 (i vs ii); and 2) Period 1 vs Period 2 (iii vs iv)
Implementation Stages
Interdisciplinary teams of critical care nursing, physician, pharmacy, respiratory therapy, and rehabilitation leadership and champions developed and implemented bundle components.
(A)wakening and (D)elirium Monitoring/Management (AD) (both ICU’s):
At baseline, both ICUs used MV order sets that included daily sedation vacations and spontaneous (B)reathing trials (B) (Figure 1); however, no guidance was given on performance or coordination of these bundles. Beginning in January 2012, the (A)wakening from sedation and (D)elirium monitoring/management (AD) bundles were implemented in both ICUs; this included physician-directed targeted sedation using the Richmond Agitation and Sedation Scale (RASS) (32, 33), twice-daily delirium assessments using the Confusion Assessment Method-ICU (CAM-ICU) by nurses (32, 34), and suggestions for non-pharmacologic delirium reduction methods. To account for time to adopt these changes, AD bundles were considered fully implemented by July 1, 2012.
(E)arly Mobilization and (C)oordination of components (EC): (full bundle ICU only)
(E)arly mobilization (E) consisted of evaluation by physical (PT) and occupational therapy (OT) at ICU admission, and daily rehabilitation by PT and/or OT according to a staged protocol in which patients advanced from passive range of motion to independent ambulation with respiratory therapy and nursing assistance as needed (17, 35) (Figure S3, Supplemental Digital Content). As part of this bundle, daily structured interdisciplinary rounds were established for ICU nurses, respiratory therapists, and rehabilitation staff to (C)oordinate bundle components (C), diagnostic tests and procedures. On July 1, 2013, EC were implemented in the full bundle ICU only because of resource and staffing limitations.
Data Collection:
Clinical data were extracted from electronic medical records using health care surveillance software (Clinical Looking GlassTM (36)). To determine if practices changed after ICU-wide implementation of bundle components, we also examined process of care data (Figure 1, Figure S1 and text in Supplemental Digital Content).
Outcomes
Clinical outcomes
The primary outcome of interest was the hospital LOS after the index ICU admission (i.e., ICU LOS + post-ICU LOS). Secondary outcomes included ICU LOS, duration of MV, hospital mortality, discharge location.
Cost outcomes
Total hospital and ICU cost and average daily ICU cost (i.e., total cost divided by ICU LOS) were determined using cost-to-charge ratios at Montefiore Medical Center. Because cost-to-charge ratios differ by calendar year, the cohort in the cost analyses was limited to patients with hospitalizations that ended between January 1, 2012 and December 31, 2013. Costs were calculated as the sum of daily direct variable costs from cost centers related to inpatient, non-operative care (e.g., respiratory support, room and board, laboratory, medications) as previously described.(37)
Clinical quality outcomes
Clinical quality metrics that may be affected by implementation of the ABCDE bundle (e.g., ICU restraint use, prevalence of ICU-acquired pressure ulcers) were obtained from aggregate hospital-reported data for Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) quality indicators in both full and partial bundle ICU’s. Data were only available for periods 1 and 2.
Statistical Analysis
Patient characteristics and unadjusted clinical outcomes were compared across ICUs and time periods using standard descriptive statistics. Nonparametric tests were used for skewed continuous measures.
To evaluate the impact of EC on clinical and cost outcomes, we compared trends in these outcomes in the full vs partial bundle ICU’s before and after EC implementation using a multivariable difference-in-differences (DiD) approach.(38, 39) This methodology uses a multivariable regression model that includes an interaction term for “time period” (e.g., Period 1 vs 2) and “ICU” (full vs partial bundle) that measures the magnitude of the effect of EC. (Figure 1). In contrast to standard before-after studies, DiD controls for temporal trends in patient characteristics (e.g., increasing severity of illness) that might impact outcomes. DiD analyses are based on 4 assumptions to ensure validity of the model, the most important of which is the parallel trend assumption (i.e., prior to interventions, temporal changes in outcomes for both ICUs are similar).(38) To test this assumption, separate regression models were constructed for each outcome in the baseline period (for B vs B-AD analysis) and period 1 (for B-AD vs B-AD-EC analysis); models included interaction terms for ICU admission date and ICU. We also performed sensitivity analyses to determine if including patients with hospital LOS > 90 would alter our estimates. Although AD was implemented in both units, we used DiD (Baseline vs Period 1) to evaluate for differential impact of AD implementation on clinical outcomes between ICUs. All models were adjusted for patient-level characteristics that differed between ICUs (univariable p≤0.2). Because APACHE IV scores were missing in 10% of patients, we used dummy variable adjustment.(40)
All tests were 2-tailed and p<0.05 defined statistical significance. Analyses were performed with STATA/MP 13 (Statacorp, College Station, TX).
Results
Patient characteristics
Between July 1, 2011 and June 30, 2014, 1855 MV patients were admitted to the full (1036, 56%) and partial bundle (819, 44%) ICUs. The full bundle ICU had younger patients and more minorities (Table 1). Patients in the full bundle ICU also had more comorbidities, higher severity of illness, and fewer lived at home prior to hospitalization. Severity of illness (APACHE IV) increased across periods in both ICUs (p ≤ 0.001).
Table 1.
Patient characteristics in partial (B-AD) vs full bundle (B-AD-EC) ICU’s across implementation periods
| Patient characteristic |
BASELINE B ongoing in both ICU’s |
PERIOD 1 B-AD in both ICU’s |
PERIOD 2 B-AD in partial bundle ICU B-AD-EC in full bundle ICU |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Partial bundle ICU (n=267) |
Full bundle ICU (n=356) |
Partial bundle ICU (n=271) |
Full bundle ICU (n=314) |
Partial bundle ICU (n=281) |
Full bundle ICU (n=366) |
|
| Age, mean (SD)a | 64 (54,74) | 64 (53,75) | 66 (53,77) | 64 (51,75) | 67 (56,78)c | 61 (51,73)c |
| Male | 49% | 46% | 48% | 46% | 45% | 51% |
| Race | c | c | c | c | ||
| White | 22% | 18% | 33% | 21% | 33% | 17% |
| Black | 37% | 35% | 27% | 33% | 30% | 35% |
| Multiracial | 30% | 32% | 30% | 34% | 28% | 37% |
| Other | 11% | 15% | 10% | 11% | 10% | 11% |
| Hispanic ethnicity | 33%c | 42%c | 37% | 39% | 29%c | 42%c |
| Resided at home | 79%c | 70%c | 82%c | 74%c | 80% | 76% |
| Admit from EDa | 66% | 67% | 79%c | 68%c | 78%c | 69%c |
| CCI, median (IQR) | 0 (0,1) | 0 (0,2) | 0 (0,2) | 0 (0,2) | 0 (0,1)c | 0 (0,2)c |
| APACHE IVd | 59 (43,76) | 59 (43,77) | 61 (47,77) | 62 (47,77) | 66 (52,86) | 72 (56,90) |
| Primary admitting diagnosis | ||||||
| Sepsis | 52% | 48% | 54% | 49% | 55% | 49% |
| Respiratory | 18% | 19% | 17% | 22% | 15% | 17% |
| Cardiovascular | 4% | 4% | 4% | 3% | 4% | 5% |
| GI | 3% | 5% | 5% | 8% | 7% | 7% |
| Endocrine/renal | 3% | 4% | 1% | 3% | 4% | 4% |
| Other | 21% | 19% | 18% | 16% | 15% | 18% |
Definitions: A = awakening from sedation; B = spontaneous breathing trial; C = coordination of bundle components; D = delirium monitoring and management; E = early mobilization; APACHE IV = Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation IV; CCI=Charlson Comorbidity Index
Partial bundle ICU between 3 periods, p≤0.04
Full bundle ICU between 3 periods, p<0.001
Partial vs Full bundle ICU within period, p<0.01
Test for trend across 3 periods within partial and full bundle ICU, p≤0.001
Results are listed as frequency (%) or median (IQR). Multiple comparisons are being made in this table. Interpretive example: (1) Patients were younger in full bundle ICU vs partial bundle ICU; (2) Severity of illness increased over time in both partial and full bundle ICU’s
Process of Care Evaluation (full bundle ICU only)
Sedative use and delirium prevalence (Figure S2, Supplemental Digital Content)
In the full bundle ICU, the proportion of patients receiving continuous sedation decreased across all three periods (p<0.001 for midazolam and fentanyl, p=0.06 for propofol) (Figure S3A). Proportion of patients with ICU delirium and/or coma also decreased across all 3 periods (p≤0.02) and similar to sedative use, the largest decrease occurred after AD was implemented (Figure S3B).
ICU Mobility
After EC was implemented in the full bundle ICU (period 1 vs 2), the proportion of patients evaluated by the rehabilitation team (i.e., either PT and/or OT) increased from 19% to 90% and the proportion of patient days spent passively lying or sitting in bed decreased from 95% to 37%. Patients received rehabilitation therapy within 1 day of ICU admission (median ICU day 1, interquartile range (IQR) 0–1) for a median of 60% of all ICU days (IQR 50–80%); 77% of patients dangled at the bed’s edge, 65% stood, and 54% walked at least once during their ICU stay. No serious complications occurred during the 1345 rehabilitation treatments. The main reasons why patients did not receive rehabilitation therapy were lack of staff and clinical instability (61% and 29% of patient days with no rehabilitation, respectively).
Outcomes
Clinical quality outcomes
The proportion of patients with ICU-acquired pressure ulcers decreased (39% to 23%, p<0.001) and the proportion of ICU patient-days in restraints decreased (30% to 26%, <0.001) after implementation of EC in the full bundle ICU (period 1 vs 2, Figure 2A). In contrast, the prevalence of ICU-acquired pressure ulcers increased (18% to 23% of patients, p=0.04) and proportion of ICU days in restraints increased (50% to 54%, p=0.001) in the partial bundle ICU during the same periods of time (Figure 2B).
Figure 2. Clinical quality outcomes in full and partial bundle ICU’s (Periods 1 vs 2).
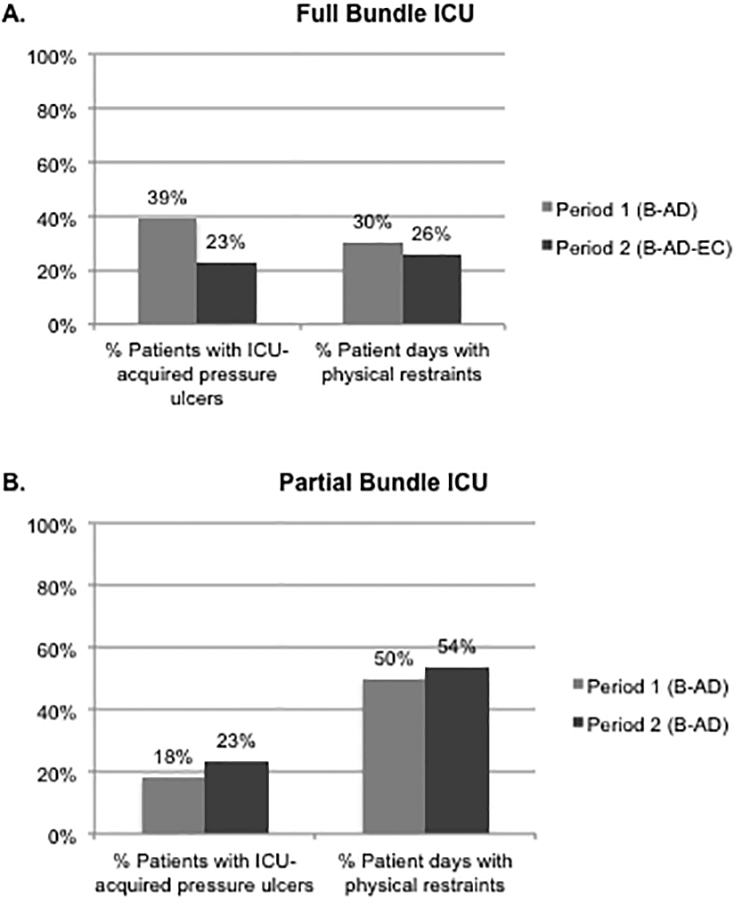
Definition of abbreviations: A = awakening from sedation; B = spontaneous breathing trial; C = structured coordination of bundle components; D = delirium monitoring and management; E = early mobilization
Quality metrics from aggregate hospital-reported data Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services quality indicators were compared between Periods 1 vs 2 in both full and partial bundle ICU’s
(A) In the full bundle ICU (B-AD vs B-AD-EC), pressure ulcer incidence and physical restraint use decreased (p<0.001 for both)
(B) In the partial bundle ICU (B-AD vs B-AD), pressure ulcer incidence and physical restraint use increased (p=0.04, p=0.001, respectively)
Clinical outcomes
Duration of MV and ICU LOS significantly changed in the full bundle ICU but not in the partial bundle ICU across 3 periods (Table 2). The duration of MV was significantly shorter in period 2 in full vs partial bundle ICU, and ICU LOS was significantly shorter across all three periods in the full vs partial bundle ICU (p<0.001). Hospital LOS and hospital mortality did not differ across all periods in both ICUs.
Table 2.
Clinical outcomes in partial (B-AD) vs full bundle (B-AD-EC) ICU’s across implementation periods
|
BASELINE B ongoing in both ICU’s |
PERIOD 1 B-AD in both ICU’s |
PERIOD 2 B-AD in partial bundle ICU B-AD-EC in full bundle ICU |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Outcome | Partial bundle ICU (n=267) |
Full bundle ICU (n=356) |
Partial bundle ICU (n=271) |
Full bundle ICU (n=314) |
Partial bundle ICU (n=281) |
Full bundle ICU (n=366) |
| Duration of mechanical ventilation (days)a | 5 (3,11) | 4 (3,9) | 5 (3,10) | 5 (3,10) | 6 (3,11)b | 4 (2,7)b |
| ICU LOS (days)a | 6.9 (3.4,12.7)b |
5.0 (3.0,10.3)b |
7.6 (4.7,13.0)b |
6.2 (3.9,11.7)b |
6.9 (3.8,13.3)b |
5.0 (3.0,9.3)b |
| Hospital LOS (days)c | 13.2 (6.6,22.9) |
12.2 (7.0,21.5) |
13.4 (8.9,21.9) |
13.9 (8.0,24.4) |
14.0 (7.7,24.2) |
13.3 (7.1,23.3) |
| Hospital mortality | 22% | 25% | 30% | 26% | 28% | 30% |
| Discharge Location | b | b | ||||
| Home | 46% | 45% | 46% | 48% | 43% | 48% |
| Rehabilitation | 6% | 3% | 4% | 2% | 5% | 3% |
| Skilled nursing facility | 42% | 46% | 41% | 46% | 44% | 41% |
| Acute care hospital | 1% | 3% | 4% | 0% | 4% | 4% |
| Hospice | 1% | 1% | 4% | 0% | 2% | 1% |
| Left against medical advice | 3% | 2% | 2% | 3% | 1% | 3% |
Definition of abbreviations: A = awakening from sedation; B = spontaneous breathing trial; C = coordination of bundle components; D = delirium monitoring and management; E = early mobilization; APACHE IV = Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation IV; CCI=Charlson Comorbidity Index
Full bundle ICU across 3 periods, p<0.001; Partial bundle ICU did not significantly differ across 3 periods
Partial vs Full bundle ICU within period, p≤0.01
Hospital LOS defined as index ICU LOS + post-ICU LOS
Results are listed as frequency (%) or median (IQR). Multiple comparisons are being made in this table. Interpretive example: (1) Duration of mechanical ventilation in period 2 was shorter in the full vs partial bundle ICU; (2) Duration of mechanical ventilation significantly differed across 3 periods in the full bundle ICU
In our DiD analyses, implementation of AD in both full bundle and partial bundle ICUs was associated with no significant changes in clinical outcomes, except for increased hospital LOS in the full vs partial bundle ICU (5.9%, 95% CI 4.6 to 7.2%, p=0.011). (Table 3) Implementation of EC in the full bundle ICU after AD was associated with a 22.3% decrease in duration of MV (95% confidence interval (CI) −22.5 to −22.0%, p<0.001), a 10.3% decrease in ICU LOS (95% CI −15.6 to −4.7%, p=0.028), and a 7.8% decrease in hospital LOS (95% CI −8.7 to −6.9%, p=0.006) compared to the partial bundle ICU (Table 3). The parallel trend assumption was met for all outcomes except for hospital LOS in period 1, where hospital LOS increased more in the full vs partial bundle ICU (0.17% change per calendar day (95% CI: 0.10–0.24%), p=0.022) (Table S2, Supplemental Digital Content). Sensitivity analyses including patients with hospital LOS ≥90 days (n=28, who had been excluded from our primary cohort) revealed similar results (Table S3, Supplemental Digital Content).
Table 3.
Difference-in-differences estimates of change in clinical and cost outcomes after AD implementation (Baseline vs Period 1) and EC implementation (Period 1 vs Period 2) in mechanically ventilated patientsa
| Full bundle ICU minus Partial bundle ICU | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Measure | Baseline vs Period 1 % change (95% CI) (B minus B-AD) |
p-value | Period 1 vs Period 2 % change (95% CI) (B-AD minus B-AD-EC) |
p-value |
| Clinical outcomes | ||||
| Duration of mechanical ventilation | 7.2% (−3.3%, 18.9%) | 0.07 | −22.3% (−22.5%, −22.0%) | <0.001 |
| ICU length of stay | 3.0% (−6.5%, 13.5%) | 0.16 | −10.3% (−15.6%, −4.7%) | 0.03 |
| Hospital length of stayb | 5.9% (4.6%, 7.2%) | 0.01 | −7.8% (−8.7%, −6.9%) | 0.006 |
| Cost outcomes | ||||
| Average daily ICU cost | 2.69% (−4.9%, 10.9%) | 0.50 | 4.4% (−4.5%,14.1%) | 0.34 |
| Total ICU cost | −0.47% (−22.3%, 27.4%) | 0.97 | −24.2% (−41.4%, −2.0%) | 0.03 |
| Total Hospital cost | −0.06% (−21.4%, 27.0%) | 0.10 | −30.2% (−46.1%, −9.5%) | 0.007 |
Definition of abbreviations: A = awakening from sedation; B = spontaneous breathing trial; C = coordination of bundle components; D = delirium monitoring and management; E = early mobilization
Both models are adjusted for age, race, ethnicity, pre-hospital residence, admission location, Charlson Comorbidity Index, primary admitting diagnosis, APACHE IV
Hospital length of stay (LOS) defined as index ICU LOS + post ICU LOS
Baseline vs Period 1 compares clinical and cost outcomes after AD was implemented in both full and partial bundle ICU’s. Period 1 vs Period 2 compares clinical and cost outcomes in full bundle vs partial bundle ICU’s after EC was implemented in full bundle ICU only. Interpretive example: 1) Implementation of AD in both ICU’s was associated with no differential change in total hospital cost; 2) Implementation of EC in full bundle ICU only was associated with a 7.8% reduction in hospital length of stay.
Cost outcomes
In DiD analyses, implementation of AD in both full and partial bundle ICUs was associated with no significant changes in cost between the two units (Table 3). Implementation of EC in only the full bundle ICU was associated with a 24.2% reduction in total ICU cost (95% CI −41.4% to −2.0%, p=0.034, Table 3) and a 30.2% reduction in total hospital cost (95% CI −46.1% to −9.5%, p=0.007) in the full vs partial bundle ICU; there was no reduction in average daily ICU cost (4.4%, 95% CI −4.5 to 14.1%, p=0.342). The parallel trend assumption was met for all cost outcomes (Table S2, Supplemental Digital Content).
Discussion
This is the first large-scale prospective quality improvement study demonstrating the value of staged implementation of a bundle of evidence-based interventions aimed at reducing ICU associated weakness and delirium. We showed that the addition of (E)arly mobilization and structured interdisciplinary (C)oordination of bundle components to a spontaneous (B)reathing trial, (A)wakening from sedation, and (D)elirium monitoring/management program (B-AD + EC), is feasible, associated with improvements in quality of care, and is independently associated with substantial reductions in MV duration, ICU LOS, hospital LOS, and cost savings after adjusting for secular trends and patient level confounders.
Our findings complement the growing literature demonstrating the clinical benefit of ABCDE bundle.(25, 41) Simultaneous implementation of ABCDE/F bundle components has been associated with increased hospital survival and delirium and coma free days, and reduced duration of MV.(21–23)
Studies suggest that ABCDE, and early mobilization in particular, can be challenging to implement in routine practice.(24–26, 42) Over 100 unique barriers have been identified in recent literature reviews.(43) Dubb et al. (44) classified these barriers into 4 categories: patient-related (e.g., deep sedation, delirium, new immobility/weakness), structural (e.g., lack of mobility protocol, limited staff and equipment, inadequate training), process related (e.g., lack of coordination), and cultural (e.g., lack of ICU mobility culture, staff buy in, expertise). The positive outcomes in our study may be explained by our use of strategies specifically targeting these barriers, including: 1) reducing sedative use and delirium (B-AD, period 1) before implementation of EC (period 2) so patients were more awake and could actively engage in mobilization 2) mobilization of patients within 1 day of ICU admission to prevent the development of new immobility/weakness; 3) developing an interdisciplinary mobility protocol with pre-specified roles and responsibilities before EC implementation; 4) obtaining administrative buy-in to finance dedicated rehabilitation staff and rehabilitation equipment; 5) interdisciplinary simulation training of mobilization scenarios to enhance skills, improve inter-disciplinary communication, and increase buy-in; 6) daily interdisciplinary coordination of staff and bundle components; 7) including local nursing, respiratory, rehabilitation champions in protocol development, training, and dissemination.
Our large effect size may also be explained by our use of DiD analysis which mitigates against secular trends that can confound pre-post study designs.(21, 23) In addition, prior studies implemented bundle components all at once, which may reduce overall bundle compliance and offset clinical benefit if components are not fully adopted.(25, 45) Barnes-Daly et al. showed that for every 10% increase in ABCDEF bundle compliance, odds for hospital survival increased by 7%.(22) Finally, our study excluded non-MV patients from analysis since only a fraction of the bundle (i.e., D, E) applies to them. Their inclusion in prior studies may have diminished any effect seen.(21, 23)
This is the first report on the financial impact of the entire ABCDE bundle. Prior analyses on the Awakening/Delirium bundle components suggested cost savings, but studies on Early Mobilization have reported conflicting results.(35, 46, 47) Using patient-level data, we found that adding EC to B-AD led to substantial cost savings which appear to be primarily explained by reductions in LOS (as indicated by decreased overall costs but unchanged average daily ICU cost before and after EC implementation).
Our finding that EC implementation was associated with shorter ICU and hospital LOS is consistent with prior randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and quality improvement studies.(17, 35, 48) However, two recent RCTs on early mobilization found no effect on hospital LOS. In Morris et al., a sedation protocol was not used, which may have limited the efficacy of spontaneous breathing trials and early mobilization.(49) In Moss et al., mobilization was initiated 8 days after ICU admission (vs 1 day in this study).(50) Given the rapid degradation of muscle of critically ill patients, mobilization may be less effective if initiated after muscle loss has occurred.(4)
Our study highlights several areas for future research. These include: assessment of patient-centered outcomes such as short and long-term disability and readmission rate, determination of return on investment, cost analyses accounting for payer status, and evaluation of bundle dissemination and sustainability. The ABCDE bundle has been reframed since our 2014 study to include assessment, management and prevention of pain, and (F)amily empowerment and engagement (“F” in ABCDEF).(28) Future studies will need to reconcile our findings with the updated components.
This study has several strengths. Our DiD approach allowed us to adjust for secular trends which could have confounded prior historically-controlled studies. We also fulfilled a majority of the rigorous assumptions required for internal validity of the DiD estimates. Our cost data were generated from costs attributed to individual patients rather than assumptions based on average published costs. Finally, our study evaluated one of the largest cohorts to date.
This study has some limitations. Despite adjusting for patient characteristics, unmeasured differences and/or changes in cohort composition could have impacted our results. We also did not include discharge location in our model. Our study was conducted in a single medical center, which may limit generalizability. For example, the bundle’s impact on quality metrics (e.g., pressure ulcers) may be greater in ICUs with higher rates at baseline than sites that have already achieved low rates. There was potential for cross-contamination of practices between the two ICUs. However, cross-contamination would have biased the estimates towards the null. Because cost-to-charge ratios change across calendar years, we were unable to compare costs between the same seasonal periods and needed to use a smaller cohort for the cost analyses. Although changes in processes of care were demonstrated in the full bundle ICU, data were not collected in the partial bundle ICU for comparison. Finally, we were unable to fulfill the parallel trend assumption for hospital LOS as it increased in the full bundle ICU relative to the partial bundle ICU in period 1. However, this would bias our findings towards the null making it more difficult to demonstrate subsequent decreased hospital LOS after EC implementation in period 2. Because hospital LOS decreased despite this bias, our results may underestimate the full impact of ABCDE bundle implementation.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that the complex ABCDE bundle can be successfully implemented into routine care. We showed that the addition of early mobilization and bundle coordination to an established targeted sedation and delirium management program led to substantial reductions in MV duration, LOS, and hospital cost, liberated patients from restraints, and reduced iatrogenic complications. These data underscore the value of the ABCDE bundle, and support the concept that the entire bundle is truly greater than the individual parts.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge the data collection contributions of Stephanie Coehlo PT, Glenmore Wiggan OT, and the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine staff for this project.
Supported by: 8KL2TR0000088–05 from the AECOM-MMC ICTR (SJ Hsieh), R03AG050927 (AA Hope), NHLBI HL084060 and HL086667 (MN Gong); 1 UL1 TR001073–01, 1 TL1 TR001072–01, 1 KL2 TR001071–01 (Einstein-Montefiore CTSA)
Copyright form disclosure: Drs. Hsieh, Hope, and Gong received support for article research from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Dr. Hsieh’s institution received funding from Einstein-Montefiore Institute for Clinical and Translational Research and La Jolla Pharmaceutical. Dr. Gong’s institution received funding from NIH grants and Philips Healthcare. The remaining authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Footnotes
This article has an online data supplement.
All work was performed at Montefiore Healthcare Center
REFERENCES
- 1.Hopkins RO, Weaver LK, Collingridge D, et al. : Two-year cognitive, emotional, and quality-of-life outcomes in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171: 340–347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brummel NE, Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, et al. : Delirium in the ICU and subsequent long-term disability among survivors of mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med 2014; 42: 369–377 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, Jackson JC, et al. : Long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 1306–1316 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Puthucheary ZA, Rawal J, McPhail M, et al. : Acute skeletal muscle wasting in critical illness. JAMA 2013; 310: 1591–1600 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, et al. : Depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and functional disability in survivors of critical illness in the BRAIN-ICU study: a longitudinal cohort study. The Lancet Respiratory medicine 2014; 2: 369–379 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Needham DM, Davidson J, Cohen H, et al. : Improving long-term outcomes after discharge from intensive care unit: report from a stakeholders’ conference. Crit Care Med 2012; 40: 502–509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vasilevskis EE, Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, et al. : A screening, prevention, and restoration model for saving the injured brain in intensive care unit survivors. Crit Care Med 2010; 38: S683–691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Morandi A, Brummel NE, Ely EW. Sedation, delirium and mechanical ventilation: the ‘ABCDE’ approach. Curr Opin Crit Care 2011; 17: 43–49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bassett R, Adams KM, Danesh V, et al. : Rethinking critical care: decreasing sedation, increasing delirium monitoring, and increasing patient mobility. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 2015; 41: 62–74 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barr J, Fraser GL, Puntillo K, et al. : Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain, agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 2013; 41: 278–280 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Implementing the ABCDE bundle at the bedside. Available at: https://innovations.ahrq.gov/qualitytools/implementing-abcde-bundle-bedside. Accessed August 20, 2018
- 12.Institute for Healthcare Improvement: Sedation, Delirium, and Mobility in ICU Patients. Available from: http://www.ihi.org/Topics/SedationDeliriumMobility/Pages/default.aspx. Accessed August 20, 2018
- 13.Society of Critical Care Medicine: ICU Liberation. Available from: http://www.sccm.org/Research/Quality/ICU-Liberation. Accessed August 20, 2018
- 14.Ely EW, Baker AM, Dunagan DP, et al. : Effect on the duration of mechanical ventilation of identifying patients capable of breathing spontaneously. N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 1864–1869 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kress JP, Pohlman AS, O’Connor MF, et al. : Daily interruption of sedative infusions in critically ill patients undergoing mechanical ventilation. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 1471–1477 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Girard TD, Kress JP, Fuchs BD, et al. : Efficacy and safety of a paired sedation and ventilator weaning protocol for mechanically ventilated patients in intensive care (Awakening and Breathing Controlled trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008; 371: 126–134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schweickert WD, Pohlman MC, Pohlman AS, et al. Early physical and occupational therapy in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009; 373: 1874–1882 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Needham DM, Korupolu R. Rehabilitation quality improvement in an intensive care unit setting: implementation of a quality improvement model. Top Stroke Rehabil 2010; 17: 271–281 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Strom T, Martinussen T, Toft P. A protocol of no sedation for critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation: a randomised trial. Lancet 2010; 375: 475–480 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Klompas M, Anderson D, Trick W, et al. : The preventability of ventilator-associated events. The CDC Prevention Epicenters Wake Up and Breathe Collaborative. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015; 191: 292–301 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Balas MC, Vasilevskis EE, Olsen KM, et al. : Effectiveness and safety of the Awakening and Breathing Coordination, Delirium monitoring/management, and Early exercise/mobility bundle. Crit Care Med 2014; 42: 1024–1036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Barnes-Daly MA, Phillips G, Ely EW. Improving hospital survival and reducing brain dysfunction at seven California community hospitals: Implementing PAD Guidelines via the ABCDEF bundle in 6,064 Patients. Crit Care Med 2017; 45: 171–178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kram SL, DiBartolo MC, Hinderer K, et al. : Implementation of the ABCDE Bundle to improve patient outcomes in the intensive care unit in a rural community hospital. Dimens Crit Care Nurs 2015; 34: 250–258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Carrothers KM, Barr J, Spurlock B, et al. : Contextual issues influencing implementation and outcomes associated with an integrated approach to managing pain, agitation, and delirium in adult ICUs. Crit Care Med 2013; 41: S128–135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Miller MA, Govindan S, Watson SR, et al. : ABCDE, but in that order? A cross-sectional survey of Michigan intensive care unit sedation, delirium, and early mobility practices. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2015; 12: 1066–1071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Boehm LM, Dietrich MS, Vasilevskis EE, et al. : Perceptions of workload burden and adherence to ABCDE bundle among intensive care providers. Am J Crit Care 2017; 26: e38–e47 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Morandi A, Piva S, Ely EW, et al. : Worldwide survey of the “Assessing Pain, Both Spontaneous Awakening and Breathing Trials, Choice of Drugs, Delirium Monitoring/Management, Early Exercise/Mobility, and Family Empowerment” (ABCDEF) Bundle. Crit Care Med 2017; 45: e1111–e1122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Balas MC, Devlin JW, Verceles AC, et al. : Adapting the ABCDEF bundle to meet the needs of patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation in the long-term acute care hospital setting: historical perspectives and practical implications. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2016; 37: 119–135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jolley SE, Regan-Baggs J, Dickson RP, et al. : Medical intensive care unit clinician attitudes and perceived barriers towards early mobilization of critically ill patients: a cross-sectional survey study. BMC Anesthesiol 2014; 14: 84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hsieh SJ, Levi D, Prince D, et al. : Staged implementation of the ABCDE Bundle improves ICU patient outcomes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014; 189:A2540 [Google Scholar]
- 31.Otusanya O, Hsieh SJ, Gong MN, et al. : Awakening and Breathing Coordination, Delirium Monitoring/Management and Early Mobilization (ABCDE) bundle reduces hospital Costs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016; 193: A4357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ely EW, Truman B, Shintani A, et al. : Monitoring sedation status over time in ICU patients: reliability and validity of the Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS). JAMA 2003; 289: 2983–2991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sessler CN, Gosnell MS, Grap MJ, et al. : The Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 166: 1338–1344 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ely EW, Inouye SK, Bernard GR, et al. : Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: validity and reliability of the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM-ICU). JAMA 2001; 286: 2703–2710 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Morris PE, Goad A, Thompson C, et al. : Early intensive care unit mobility therapy in the treatment of acute respiratory failure. Crit Care Med 2008; 36: 2238–2243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bellin E, Fletcher DD, Geberer N, et al. : Democratizing information creation from health care data for quality improvement, research, and education -- the Montefiore Medical Center Experience. Acad Med 2010; 85: 1362–1368 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gershengorn HB, Garland A, Gong MN. Patterns of daily costs differ for medical and surgical intensive care unit patients. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2015; 12:1831–1836 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Abadie A Semiparametric difference-in-differences estimators. Review of Economic Studies 2005; 72: 1–19 [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dimick JB, Ryan AM. Methods for evaluating changes in health care policy: the difference-in-differences approach. JAMA 2014; 312: 2401–2402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Puma MJ, Olsen RP, Bell SH, et al. : What to do when data are missing in group randomized controlled trials (NCEE 2009–0049): National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ely EW. The ABCDEF bundle: science and philosophy of how ICU Liberation serves patients and families. Crit Care Med 2017; 45: 321–330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Honiden S, Connors GR. Barriers and challenges to the successful implementation of an intensive care unit mobility program: understanding systems and human factors in search for practical solutions. Clin Chest Med 2015; 36: 431–440 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Costa DK, White MR, Ginier E, et al. : Identifying barriers to delivering the Awakening and Breathing Coordination, Delirium, and Early Exercise/Mobility bundle to minimize adverse outcomes for mechanically ventilated patients: a systematic review. Chest 2017; 152: 304–311 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dubb R, Nydahl P, Hermes C, et al. : Barriers and strategies for early mobilization of patients in intensive care units. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2016; 13: 724–730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Trogrlic Z, van der Jagt M, Bakker J, et al. : A systematic review of implementation strategies for assessment, prevention, and management of ICU delirium and their effect on clinical outcomes. Crit Care 2015; 19: 157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lord RK, Mayhew CR, Korupolu R, et al. : ICU early physical rehabilitation programs: financial modeling of cost savings. Crit Care Med 2013; 41: 717–724 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Awissi DK, Begin C, Moisan J, et al. : I-SAVE study: impact of sedation, analgesia, and delirium protocols evaluated in the intensive care unit: an economic evaluation. Ann Pharmacother 2012; 46: 21–28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Needham DM, Korupolu R, Zanni JM, et al. : Early physical medicine and rehabilitation for patients with acute respiratory failure: a quality improvement project. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2010; 91: 536–542 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Morris PE, Berry MJ, Files DC, et al. : Standardized rehabilitation and hospital length of stay among patients with acute respiratory failure: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016; 315: 2694–2702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Moss M, Nordon-Craft A, Malone D, et al. : A randomized trial of an intensive physical therapy program for patients with acute respiratory failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016; 193: 1101–1110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.



